Altered Intracellular Milieu of ADAR2-Deficient Motor Neurons in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
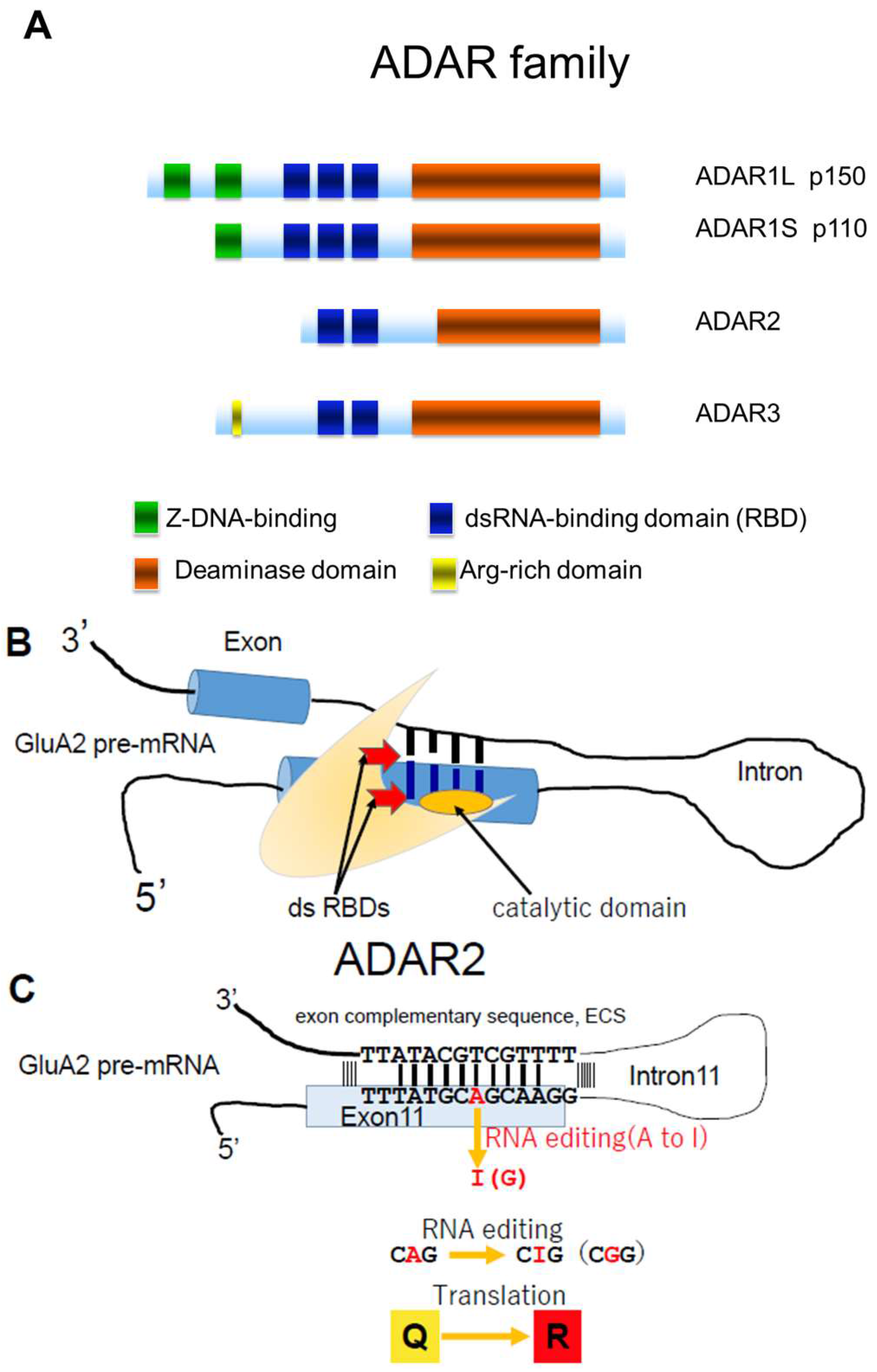
2. ADAR2 in Sporadic ALS
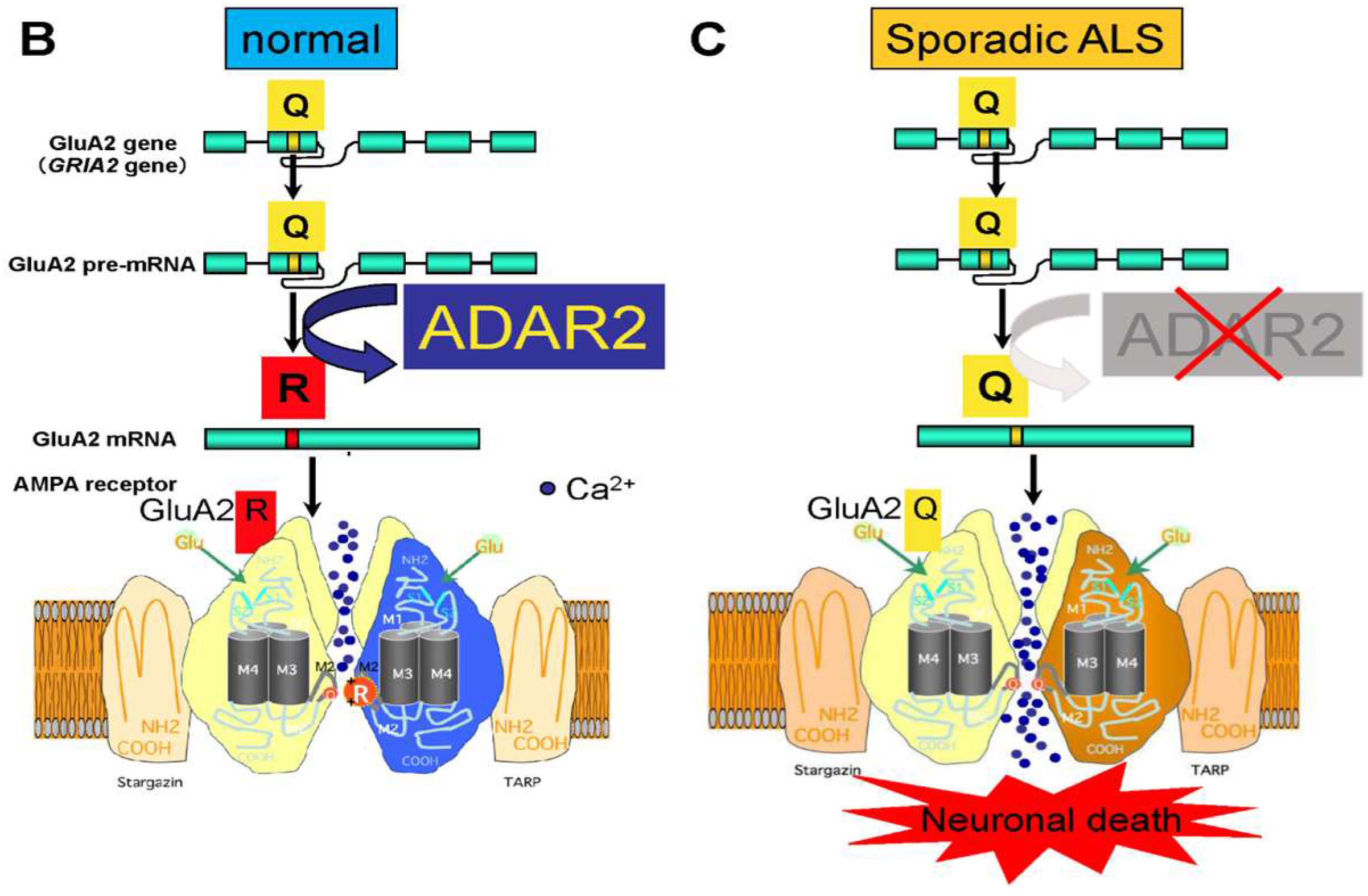
3. Q/R Site-Editing of AMPA Receptor Subunit GluA2 and Ca2+-Permeability of the AMPA Receptors in Sporadic ALS
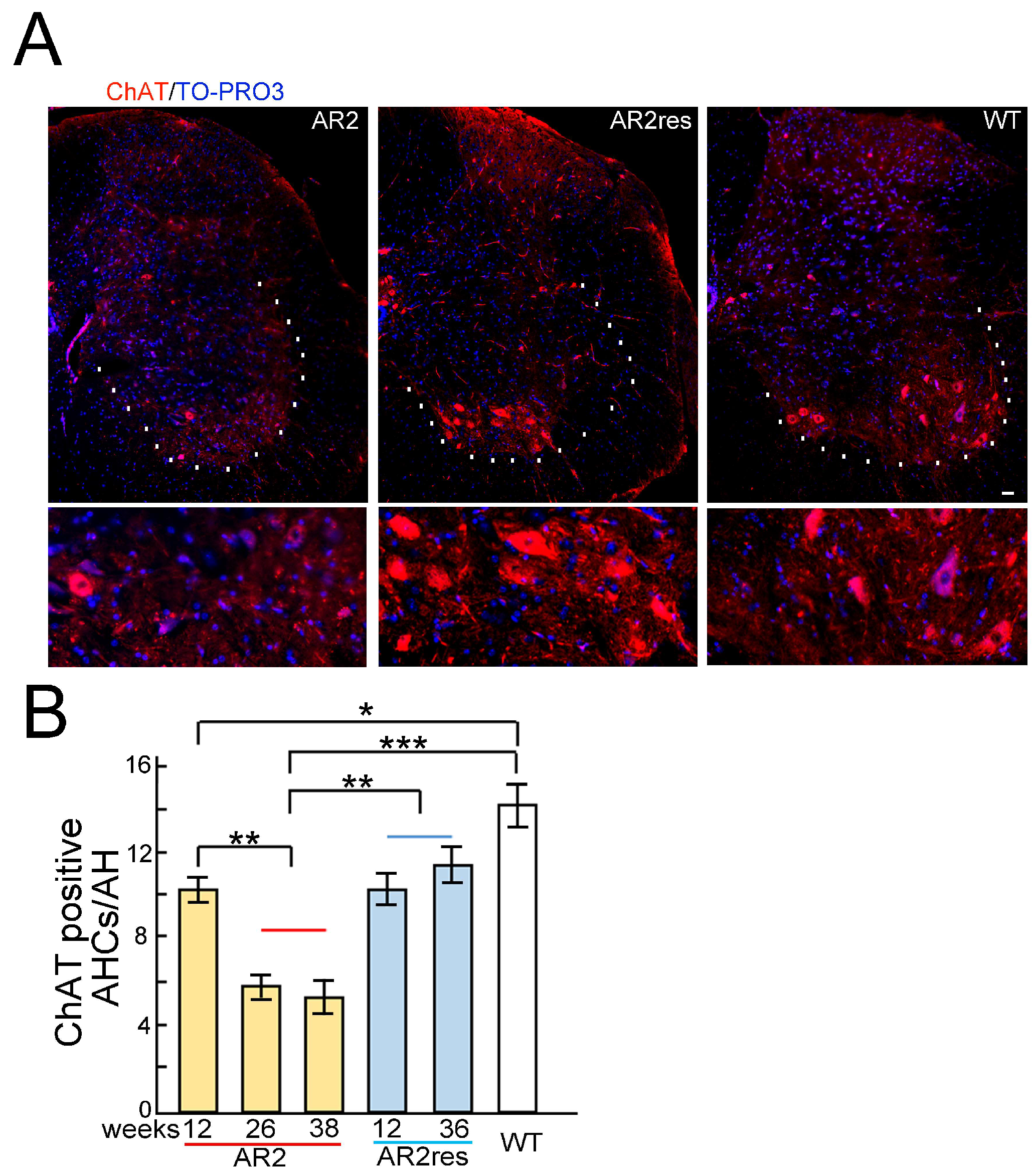
4. ADAR2 Downregulation Results in Motor Neuron Death in AR2 Mice
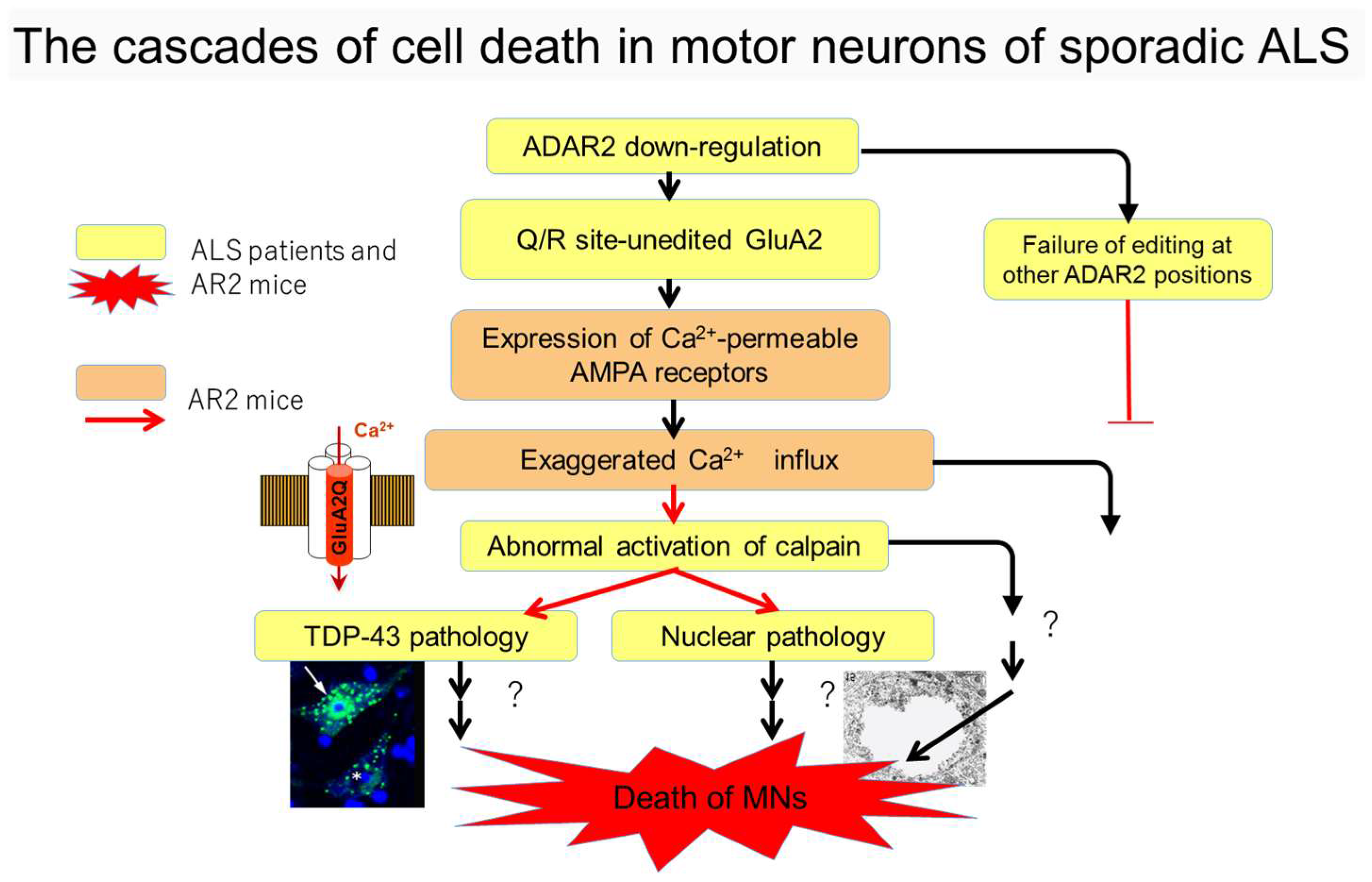
5. Cell Death Cascades in ALS
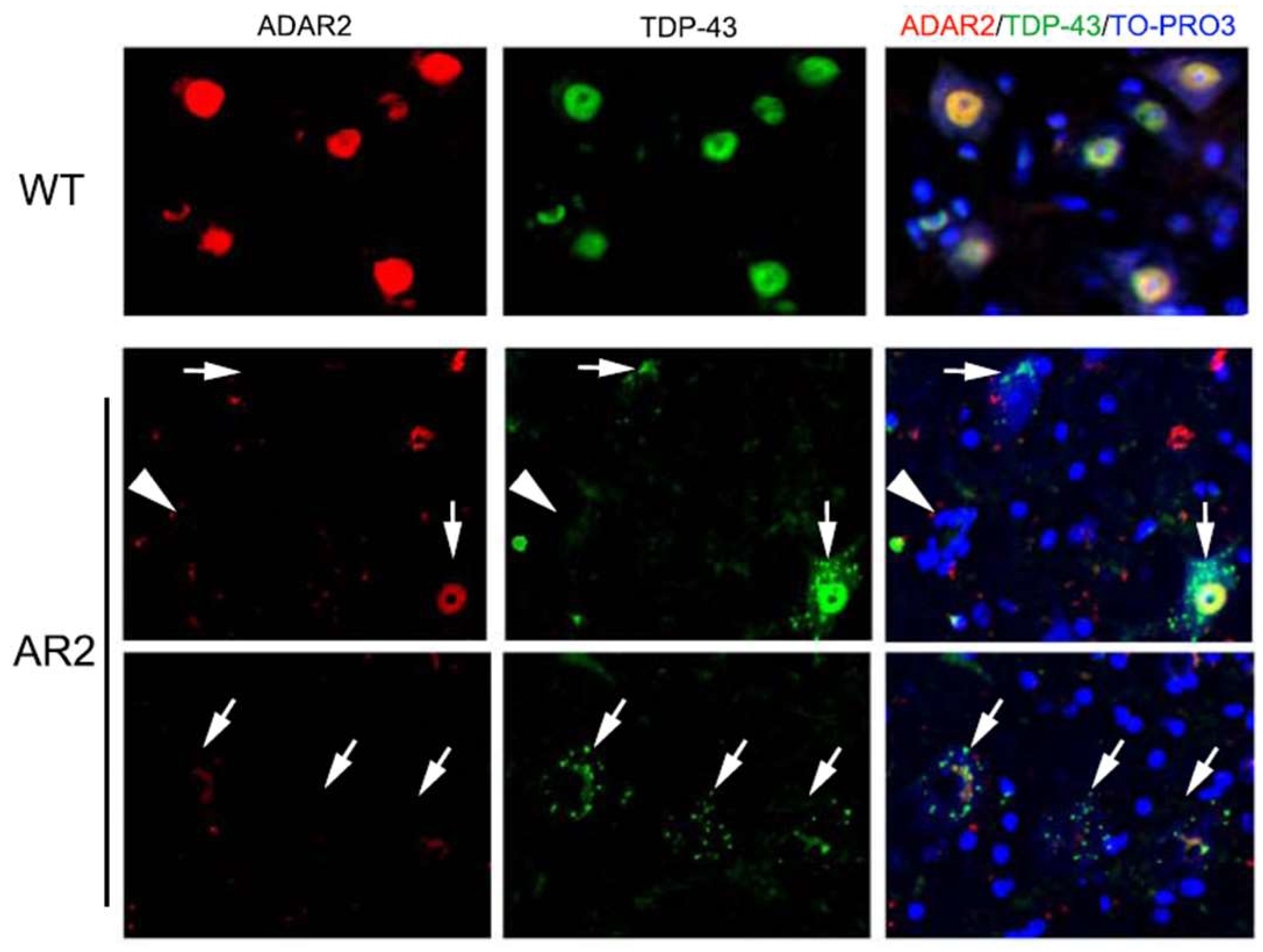
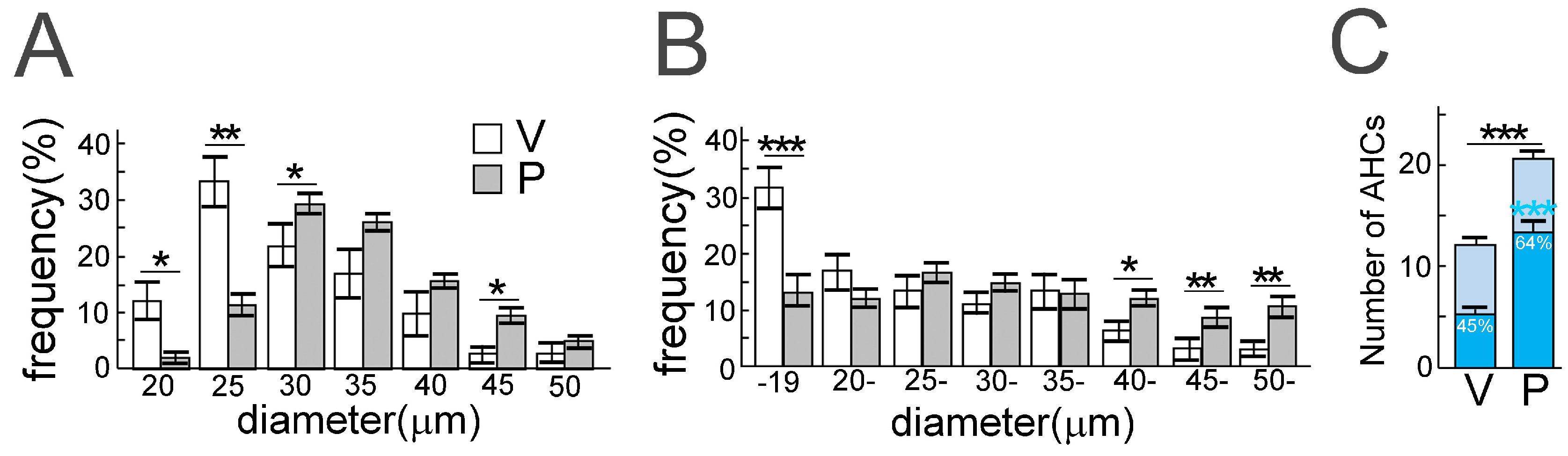
6. Subcellular Localization of TDP-43 in the ChAT Positive Anterior Horn Cells (AHCs) as Biomarkers of ALS Pathology
7. Mechanisms of TDP-43 Mislocalization in Relation to the Motor Neuron Death Cascade
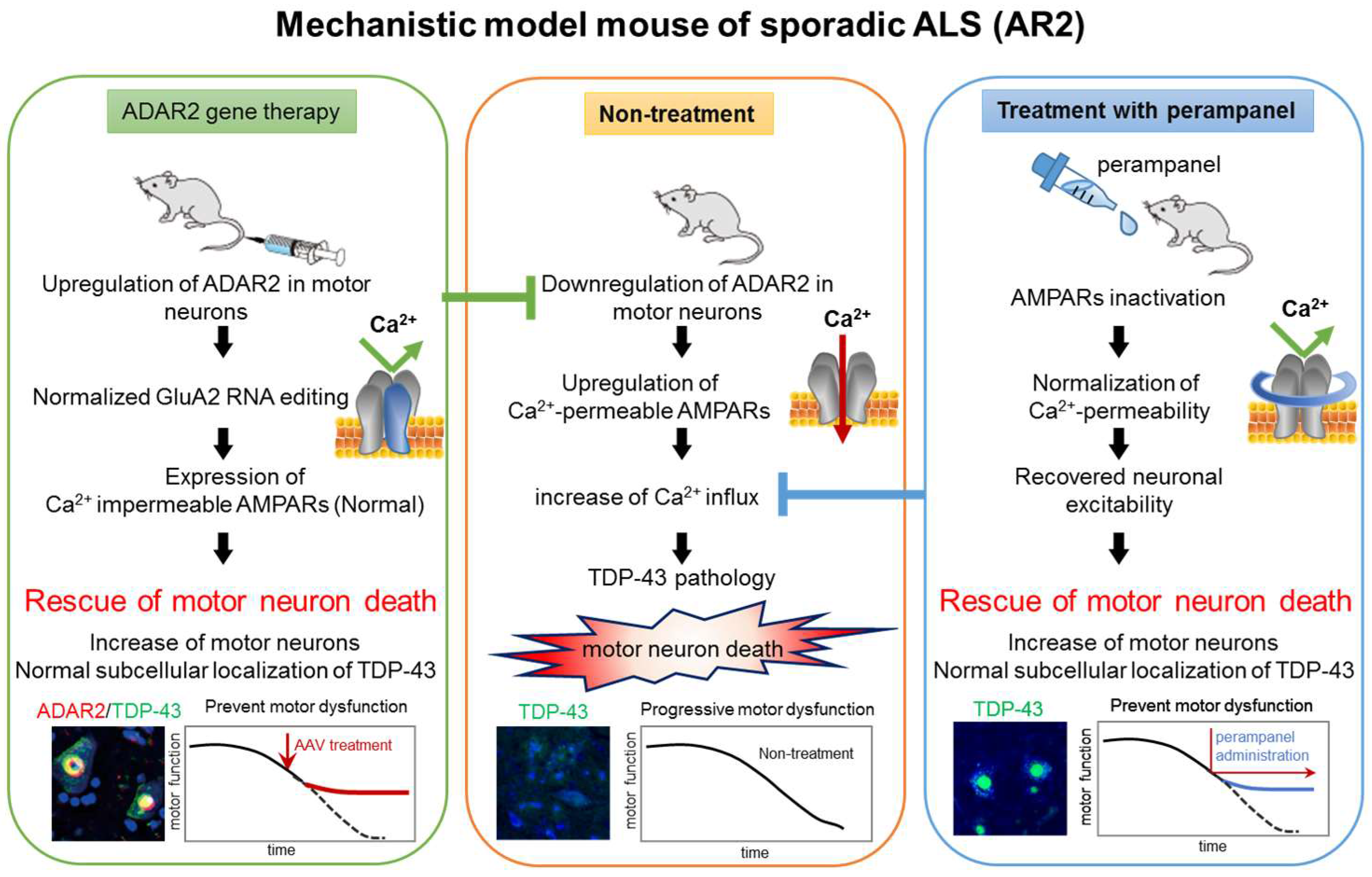
8. Conclusions and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paez-Colasante, X.; Figueroa-Romero, C.; Sakowski, S.A.; Goutman, S.A.; Feldman, E.L. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Mechanisms and therapeutics in the epigenomic era. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.P.; Brown, R.H., Jr.; Cleveland, D.W. Decoding als: From genes to mechanism. Nature 2016, 539, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravits, J.; Appel, S.; Baloh, R.H.; Barohn, R.; Brooks, B.R.; Elman, L.; Floeter, M.K.; Henderson, C.; Lomen-Hoerth, C.; Macklis, J.D.; et al. Deciphering amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: What phenotype, neuropathology and genetics are telling us about pathogenesis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Frontotemporal Degener. 2013, 14 (Suppl 1), 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arai, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Akiyama, H.; Ikeda, K.; Nonaka, T.; Mori, H.; Mann, D.; Tsuchiya, K.; Yoshida, M.; Hashizume, Y.; et al. Tdp-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, M.; Sampathu, D.M.; Kwong, L.K.; Truax, A.C.; Micsenyi, M.C.; Chou, T.T.; Bruce, J.; Schuck, T.; Grossman, M.; Clark, C.M.; et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2006, 314, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, M. Molecular neuropathology of TDP-43 proteinopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buratti, E.; Baralle, F.E. The multiple roles of TDP-43 in pre-mRNA processing and gene expression regulation. RNA Biol. 2010, 7, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, S.H.; Wu, F.; Harrich, D.; Garcia-Martinez, L.F.; Gaynor, R.B. Cloning and characterization of a novel cellular protein, TDP-43, that binds to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TAR DNA sequence motifs. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3584–3596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.; Wang, I.F.; Bose, J.; Shen, C.K. Structural diversity and functional implications of the eukaryotic TDP gene family. Genomics 2004, 83, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmada, S.J. Linking RNA dysfunction and neurodegeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabashi, E.; Valdmanis, P.N.; Dion, P.; Spiegelman, D.; McConkey, B.J.; Vande Velde, C.; Bouchard, J.P.; Lacomblez, L.; Pochigaeva, K.; Salachas, F.; et al. Tardbp mutations in individuals with sporadic and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, S.; Kawahara, Y. Deficient RNA editing of GluR2 and neuronal death in amyotropic lateral sclerosis. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 83, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hideyama, T.; Yamashita, T.; Aizawa, H.; Tsuji, S.; Kakita, A.; Takahashi, H.; Kwak, S. Profound downregulation of the RNA editing enzyme ADAR2 in ALS spinal motor neurons. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, Y.; Ito, K.; Sun, H.; Aizawa, H.; Kanazawa, I.; Kwak, S. Glutamate receptors: RNA editing and death of motor neurons. Nature 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takuma, H.; Kwak, S.; Yoshizawa, T.; Kanazawa, I. Reduction of GluR2 RNA editing, a molecular change that increases calcium influx through AMPA receptors, selective in the spinal ventral gray of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M.; Single, F.N.; Kohler, M.; Sommer, B.; Sprengel, R.; Seeburg, P.H. Rna editing of AMPA receptor subunit GluR-b: A base-paired intron-exon structure determines position and efficiency. Cell 1993, 75, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M.; Maas, S.; Single, F.N.; Hartner, J.; Rozov, A.; Burnashev, N.; Feldmeyer, D.; Sprengel, R.; Seeburg, P.H. Point mutation in an AMPA receptor gene rescues lethality in mice deficient in the RNA-editing enzyme ADAR2. Nature 2000, 406, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa, H.; Sawada, J.; Hideyama, T.; Yamashita, T.; Katayama, T.; Hasebe, N.; Kimura, T.; Yahara, O.; Kwak, S. TDP-43 pathology in sporadic ALS occurs in motor neurons lacking the RNA editing enzyme ADAR2. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hideyama, T.; Yamashita, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tsuji, S.; Higuchi, M.; Seeburg, P.H.; Takahashi, R.; Misawa, H.; Kwak, S. Induced loss of ADAR2 engenders slow death of motor neurons from Q/R site-unedited GluR2. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 11917–11925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Hideyama, T.; Hachiga, K.; Teramoto, S.; Takano, J.; Iwata, N.; Saido, T.C.; Kwak, S. A role for calpain-dependent cleavage of TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathology. Nat. Commun. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hideyama, T.; Kwak, S. When does als start? ADAR2-GluA2 hypothesis for the etiology of sporadic ALS. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Kwak, S. The molecular link between inefficient GluA2 Q/R site-RNA editing and TDP-43 pathology in motor neurons of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Brain Res. 2014, 1584, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, M.; Paro, S.; Keegan, L.P.; O’Connell, M.A. RNA editing by mammalian ADARs. Adv. Genet. 2011, 73, 87–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slotkin, W.; Nishikura, K. Adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing and human disease. Genome Med. 2013, 5, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melcher, T.; Maas, S.; Herb, A.; Sprengel, R.; Seeburg, P.H.; Higuchi, M. A mammalian RNA editing enzyme. Nature 1996, 379, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.X.; Cho, D.S.; Wang, Q.; Lai, F.; Carter, K.C.; Nishikura, K. A third member of the RNA-specific adenosine deaminase gene family, ADAR3, contains both single- and double-stranded RNA binding domains. RNA 2000, 6, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikura, K. A-to-I editing of coding and non-coding RNAs by ADARs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behm, M.; Ohman, M. RNA editing: A contributor to neuronal dynamics in the mammalian brain. Trends Genet. 2016, 32, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, S.; Nishimoto, Y.; Yamashita, T. Newly identified ADAR-mediated A-to-I editing positions as a tool for ALS research. RNA Biol. 2008, 5, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.D.; McFarland, K.N.; Darnell, S.B.; Huizenga, M.N.; Sangrey, G.R.; Cha, J.H.; Pierce, R.C.; Sadri-Vakili, G. ADAR2-dependent GluA2 editing regulates cocaine seeking. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollmann, M.; Hartley, M.; Heinemann, S. Ca2+ permeability of KA-AMPA—Gated glutamate receptor channels depends on subunit composition. Science 1991, 252, 851–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.; Vissel, B. The essential role of AMPA receptor GluR2 subunit RNA editing in the normal and diseased brain. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, B.; Kohler, M.; Sprengel, R.; Seeburg, P.H. RNA editing in brain controls a determinant of ion flow in glutamate-gated channels. Cell 1991, 67, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeburg, P.H. A-to-I editing: New and old sites, functions and speculations. Neuron 2002, 35, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Hideyama, T.; Teramoto, S.; Kwak, S. The abnormal processing of TDP-43 is not an upstream event of reduced ADAR2 activity in ALS motor neurons. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 73, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Arai, T.; Nonaka, T.; Kametani, F.; Yoshida, M.; Hashizume, Y.; Beach, T.G.; Buratti, E.; Baralle, F.; Morita, M.; et al. Phosphorylated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen-Plotkin, A.S.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. TAR DNA-binding protein 43 in neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.C.; Dugger, B.N.; Dickson, D.W.; Wang, D.S. TDP-43 in aging and Alzheimer′s disease—A review. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2011, 4, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McKee, A.C.; Gavett, B.E.; Stern, R.A.; Nowinski, C.J.; Cantu, R.C.; Kowall, N.W.; Perl, D.P.; Hedley-Whyte, E.T.; Price, B.; Sullivan, C.; et al. TDP-43 proteinopathy and motor neuron disease in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 69, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, S.H.; Spires-Jones, T.; Hyman, B.T.; Growdon, J.H.; Frosch, M.P. TAR-DNA binding protein 43 in pick disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 67, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujishiro, H.; Uchikado, H.; Arai, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Akiyama, H.; Yokota, O.; Tsuchiya, K.; Togo, T.; Iseki, E.; Hirayasu, Y. Accumulation of phosphorylated TDP-43 in brains of patients with argyrophilic grain disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 117, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, C.; Arai, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Yu, S.; McGeer, P.L. Colocalization of transactivation-responsive DNA-binding protein 43 and huntingtin in inclusions of huntington disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 67, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uryu, K.; Nakashima-Yasuda, H.; Forman, M.S.; Kwong, L.K.; Clark, C.M.; Grossman, M.; Miller, B.L.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Concomitant TAR-DNA-binding protein 43 pathology is present in alzheimer disease and corticobasal degeneration but not in other tauopathies. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 67, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima-Yasuda, H.; Uryu, K.; Robinson, J.; Xie, S.X.; Hurtig, H.; Duda, J.E.; Arnold, S.E.; Siderowf, A.; Grossman, M.; Leverenz, J.B.; et al. Co-morbidity of TDP-43 proteinopathy in lewy body related diseases. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amador-Ortiz, C.; Lin, W.L.; Ahmed, Z.; Personett, D.; Davies, P.; Duara, R.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Hutton, M.L.; Dickson, D.W. TDP-43 immunoreactivity in hippocampal sclerosis and Alzheimer′s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, S.; Iseki, E.; Yamamoto, R.; Minegishi, M.; Hino, H.; Fujisawa, K.; Togo, T.; Katsuse, O.; Uchikado, H.; Furukawa, Y.; et al. Concurrence of TDP-43, tau and alpha-synuclein pathology in brains of Alzheimer′s disease and dementia with lewy bodies. Brain Res. 2007, 1184, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Chai, H.L.; Teramoto, S.; Tsuji, S.; Shimazaki, K.; Muramatsu, S.; Kwak, S. Rescue of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis phenotype in a mouse model by intravenous AAV9-ADAR2 delivery to motor neurons. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akamatsu, M.; Yamashita, T.; Hirose, N.; Teramoto, S.; Kwak, S. The AMPA receptor antagonist perampanel robustly rescues amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) pathology in sporadic ALS model mice. Sci. Rep. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirulli, E.T.; Lasseigne, B.N.; Petrovski, S.; Sapp, P.C.; Dion, P.A.; Leblond, C.S.; Couthouis, J.; Lu, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Krueger, B.J.; et al. Exome sequencing in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis identifies risk genes and pathways. Science 2015, 347, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philips, T.; Rothstein, J.D. Rodent models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.F.; Eguchi, H.; Tagawa, A.; Onodera, O.; Iwasaki, T.; Tsujino, A.; Nishizawa, M.; Kakita, A.; Takahashi, H. TDP-43 immunoreactivity in neuronal inclusions in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with or without SOD1 gene mutation. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 113, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, I.R.; Bigio, E.H.; Ince, P.G.; Geser, F.; Neumann, M.; Cairns, N.J.; Kwong, L.K.; Forman, M.S.; Ravits, J.; Stewart, H.; et al. Pathological TDP-43 distinguishes sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with SOD1 mutations. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, A.; Takino, N.; Miyauchi, H.; Shimazaki, K.; Muramatsu, S. Systemic delivery of tyrosine-mutant AAV vectors results in robust transduction of neurons in adult mice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarzi, D.; Colotta, V.; Varano, F. Competitive AMPA receptor antagonists. Med. Res. Rev. 2007, 27, 239–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, J.A.; Krauss, G.L.; Wechsler, R.T.; Wang, X.F.; DiVentura, B.; Brandt, C.; Trinka, E.; O’Brien, T.J.; Laurenza, A.; Patten, A.; et al. Perampanel for tonic-clonic seizures in idiopathic generalized epilepsy a randomized trial. Neurology 2015, 85, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, S.; Yamashita, T.; Hideyama, T.; Kwak, S. Unique nuclear vacuoles in the motor neurons of conditional ADAR2-knockout mice. Brain Res. 2014, 1550, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, T.J.; Hartmann, H.A. RNA content and volume of motor neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. II. The lumbar intumescence and nucleus dorsalis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1981, 40, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Chalabi, A.; Hardiman, O. The epidemiology of ALS: A conspiracy of genes, environment and time. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Lammich, S.; Mackenzie, I.R.; Forne, I.; Zilow, S.; Kretzschmar, H.; Edbauer, D.; Janssens, J.; Kleinberger, G.; Cruts, M.; et al. HnRNP A3 binds to GGGGCC repeats and is a constituent of p62-positive/TDP43-negative inclusions in the hippocampus of patients with C9ORF72 mutations. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woerner, A.C.; Frottin, F.; Hornburg, D.; Feng, L.R.; Meissner, F.; Patra, M.; Tatzelt, J.; Mann, M.; Winklhofer, K.F.; Hartl, F.U.; et al. Cytoplasmic protein aggregates interfere with nucleocytoplasmic transport of protein and RNA. Science 2016, 351, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freibaum, B.D.; Lu, Y.; Lopez-Gonzalez, R.; Kim, N.C.; Almeida, S.; Lee, K.H.; Badders, N.; Valentine, M.; Miller, B.L.; Wong, P.C.; et al. GGGGCC repeat expansion in C9ORF72 compromises nucleocytoplasmic transport. Nature 2015, 525, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovicic, A.; Mertens, J.; Boeynaems, S.; Bogaert, E.; Chai, N.; Yamada, S.B.; Paul, J.W., 3rd; Sun, S.; Herdy, J.R.; Bieri, G.; et al. Modifiers of C9ORF72 dipeptide repeat toxicity connect nucleocytoplasmic transport defects to FTD/ALS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1226–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Donnelly, C.J.; Haeusler, A.R.; Grima, J.C.; Machamer, J.B.; Steinwald, P.; Daley, E.L.; Miller, S.J.; Cunningham, K.M.; Vidensky, S.; et al. The C9ORF72 repeat expansion disrupts nucleocytoplasmic transport. Nature 2015, 525, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, C.J.; Zhang, P.W.; Pham, J.T.; Heusler, A.R.; Mistry, N.A.; Vidensky, S.; Daley, E.L.; Poth, E.M.; Hoover, B.; Fines, D.M.; et al. RNA toxicity from the ALS/FTD C9ORF72 expansion is mitigated by antisense intervention. Neuron 2013, 80, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizawa, H.; Hideyama, T.; Yamashita, T.; Kimura, T.; Suzuki, N.; Aoki, M.; Kwak, S. Deficient RNA-editing enzyme ADAR2 in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patient with a FUSP525L mutation. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 32, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, E.F.; Daley, E.L.; Tang, X.; Vidensky, S.; Sattler, R. Role of ADARB2 in GluA2 editing deficiency in C9ORF72 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Available online: http://www.abstractsonline.com/Plan/ViewAbstract.aspx?sKey=bbb8e674-1cb5-4e89-bd38-af620f401179&cKey=14f8813f-2a8b-4f99-bd0b-0f8379f73504&mKey=%7bD0FF4555-8574-4FBB-B9D4-04EEC8BA0C84%7d (accessed on 3 October 2016).


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamashita, T.; Akamatsu, M.; Kwak, S. Altered Intracellular Milieu of ADAR2-Deficient Motor Neurons in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Genes 2017, 8, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020060
Yamashita T, Akamatsu M, Kwak S. Altered Intracellular Milieu of ADAR2-Deficient Motor Neurons in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Genes. 2017; 8(2):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020060
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamashita, Takenari, Megumi Akamatsu, and Shin Kwak. 2017. "Altered Intracellular Milieu of ADAR2-Deficient Motor Neurons in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis" Genes 8, no. 2: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020060
APA StyleYamashita, T., Akamatsu, M., & Kwak, S. (2017). Altered Intracellular Milieu of ADAR2-Deficient Motor Neurons in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Genes, 8(2), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8020060




