Alterations of miRNAs and Their Potential Roles in Arsenite-Induced Transformation of Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Establishment of the Arsenite-Induced Neoplastic Transformation Cells
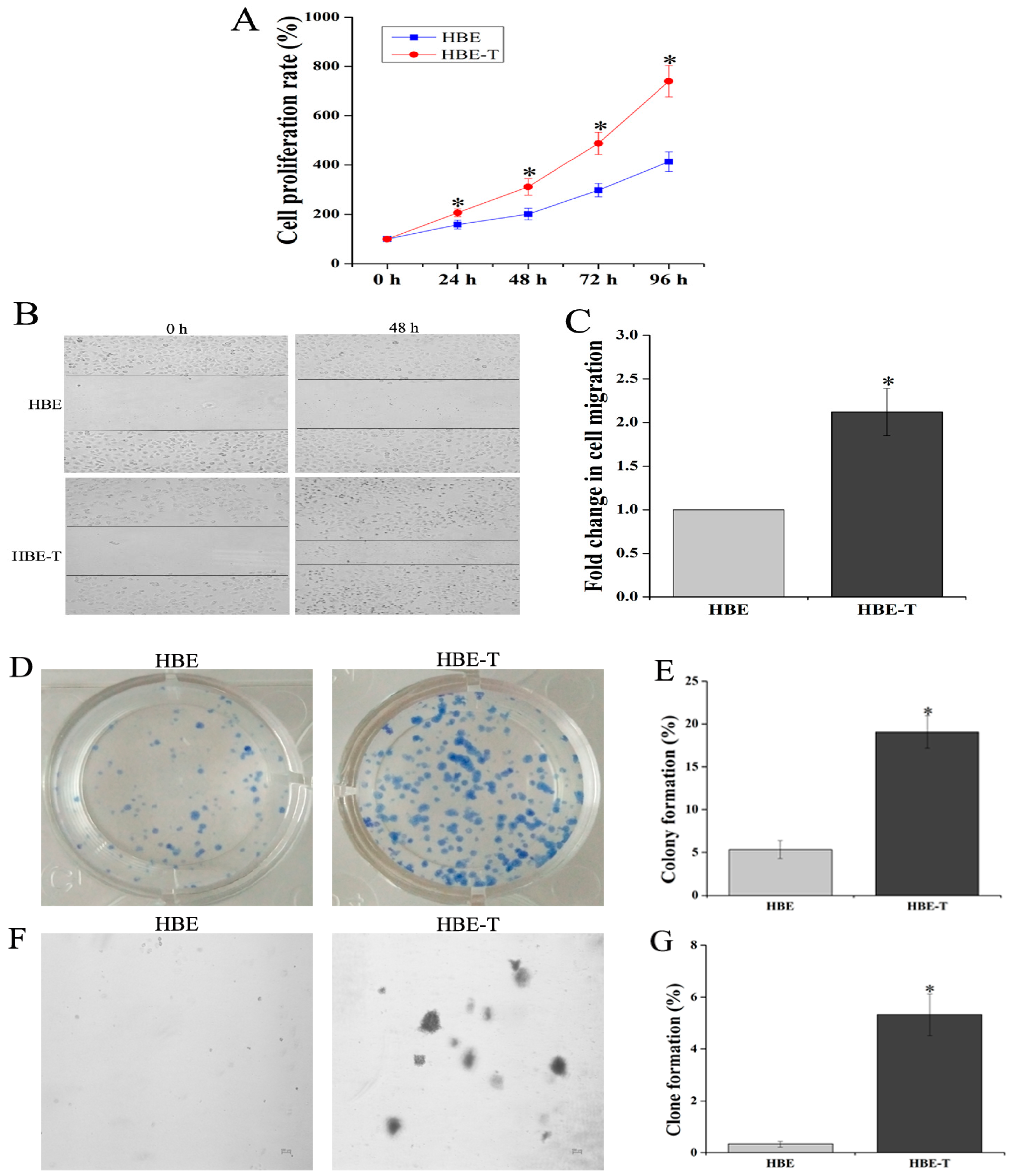
2.3. MTT Assay
2.4. Plate Colony Formation Assay
2.5. Soft Agar Clone Formation Assay
2.6. Wound-Healing Cell Migration Assay
2.7. RNA Isolation
2.8. miRNA Array and Data Analysis
2.9. Fluorescence Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.10. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.11. Detection of Cell Cycle Distribution
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Neoplastic Phenotype
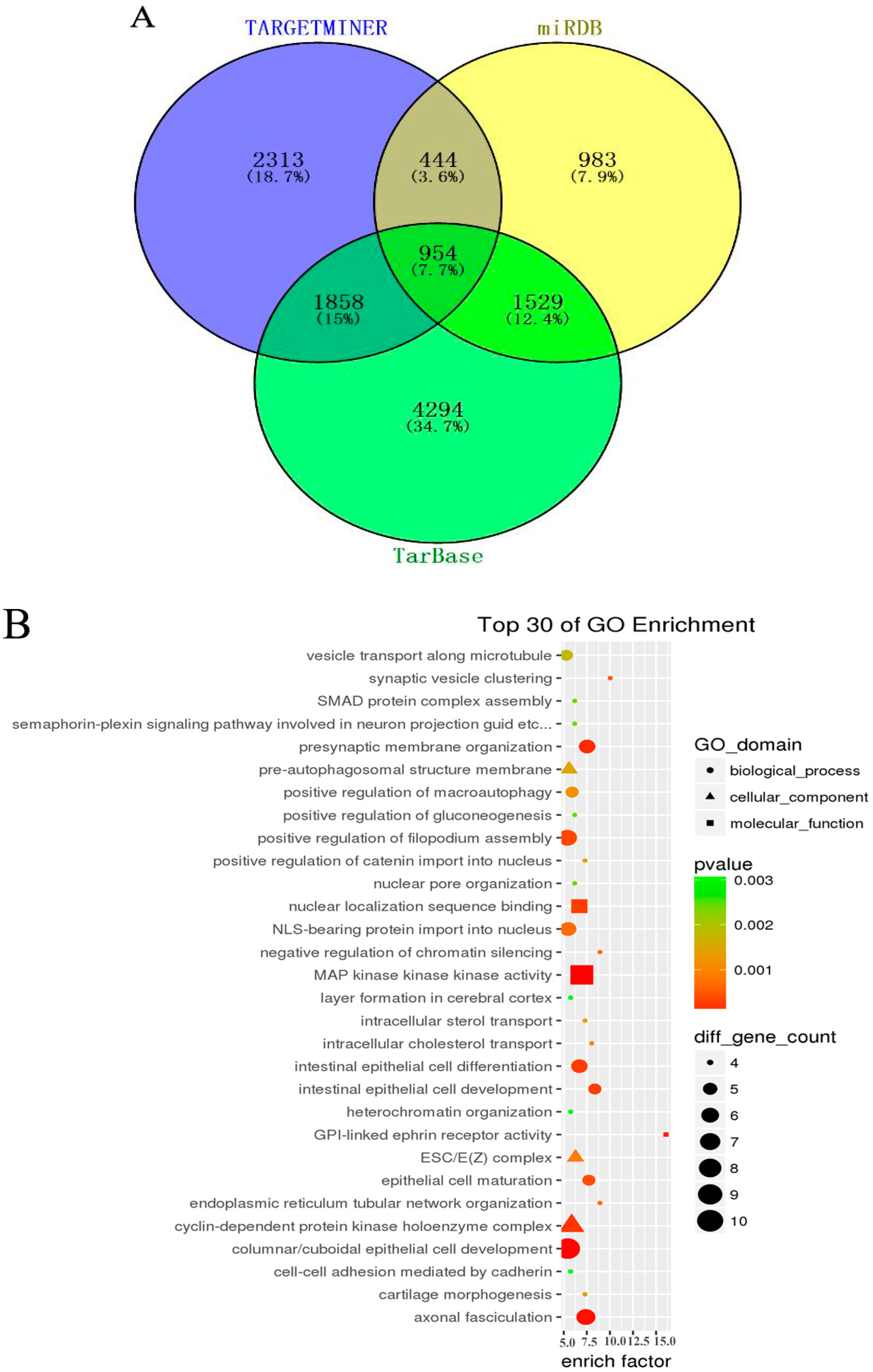
3.2. The Identification of Aberrant miRNAs in Arsenite-Transformed Cells
3.3. The Results of qPCR Validation
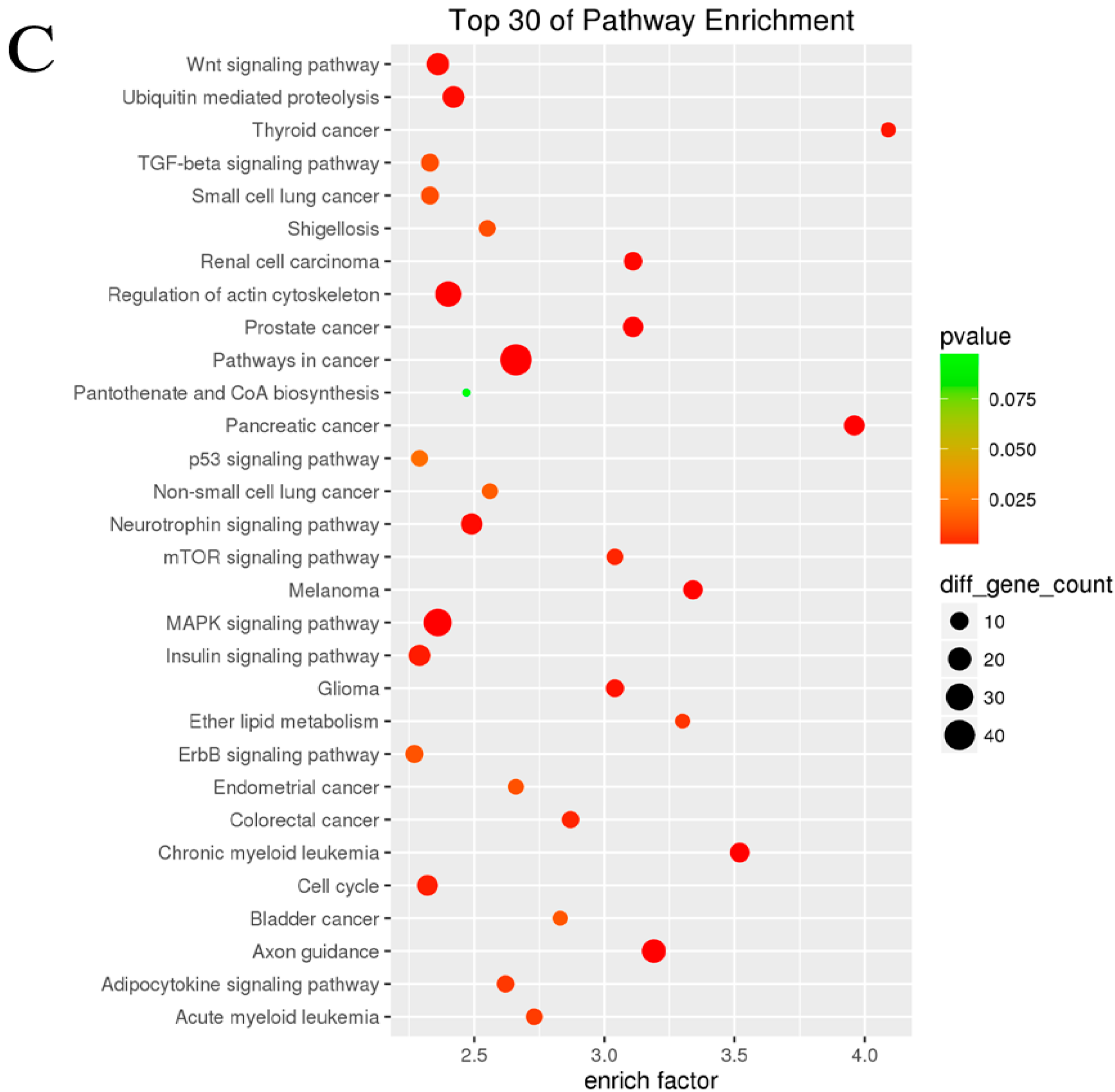
3.4. GO and KEGG Pathway Analysis
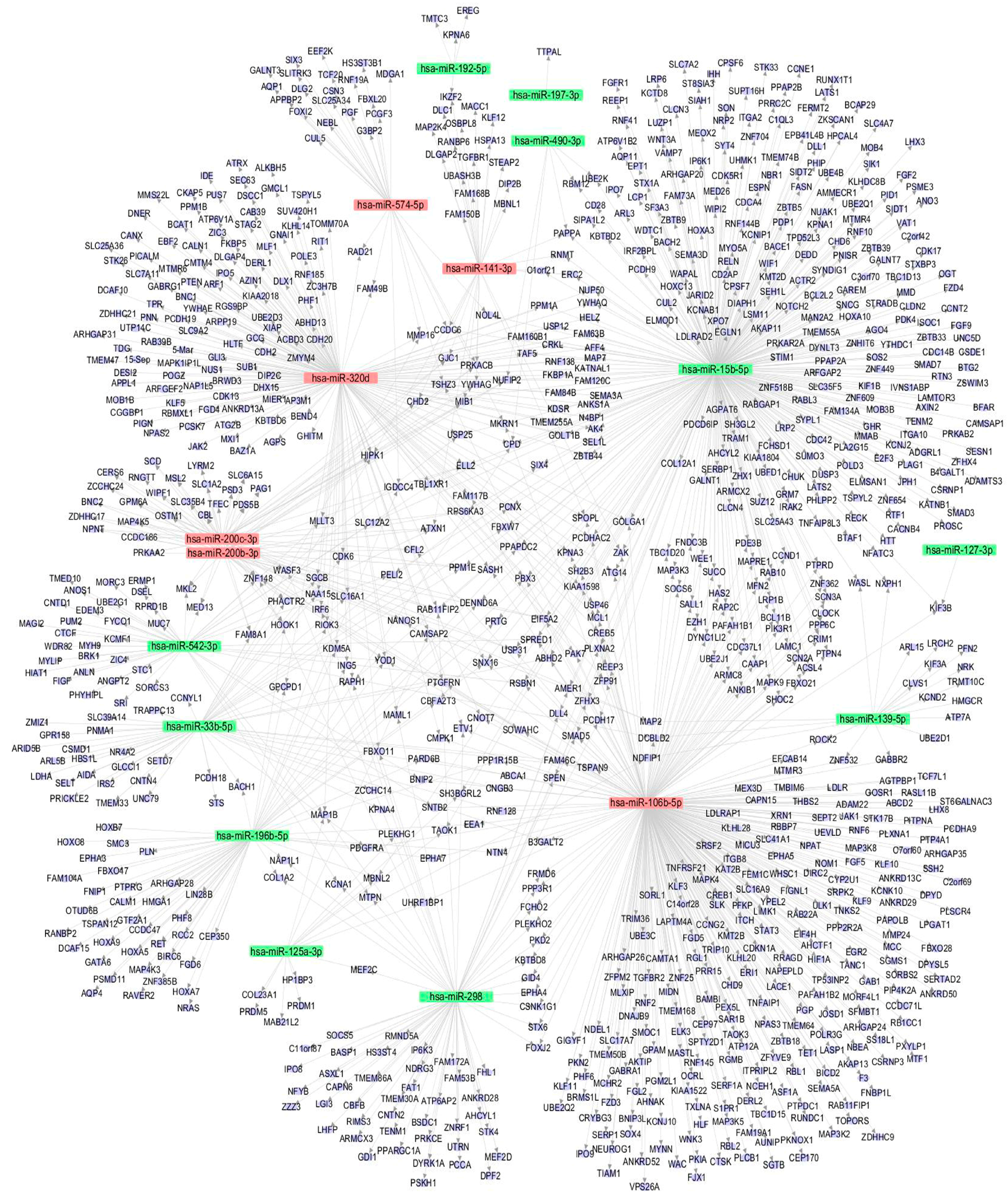
3.5. The miRNA-Gene Regulatory Network
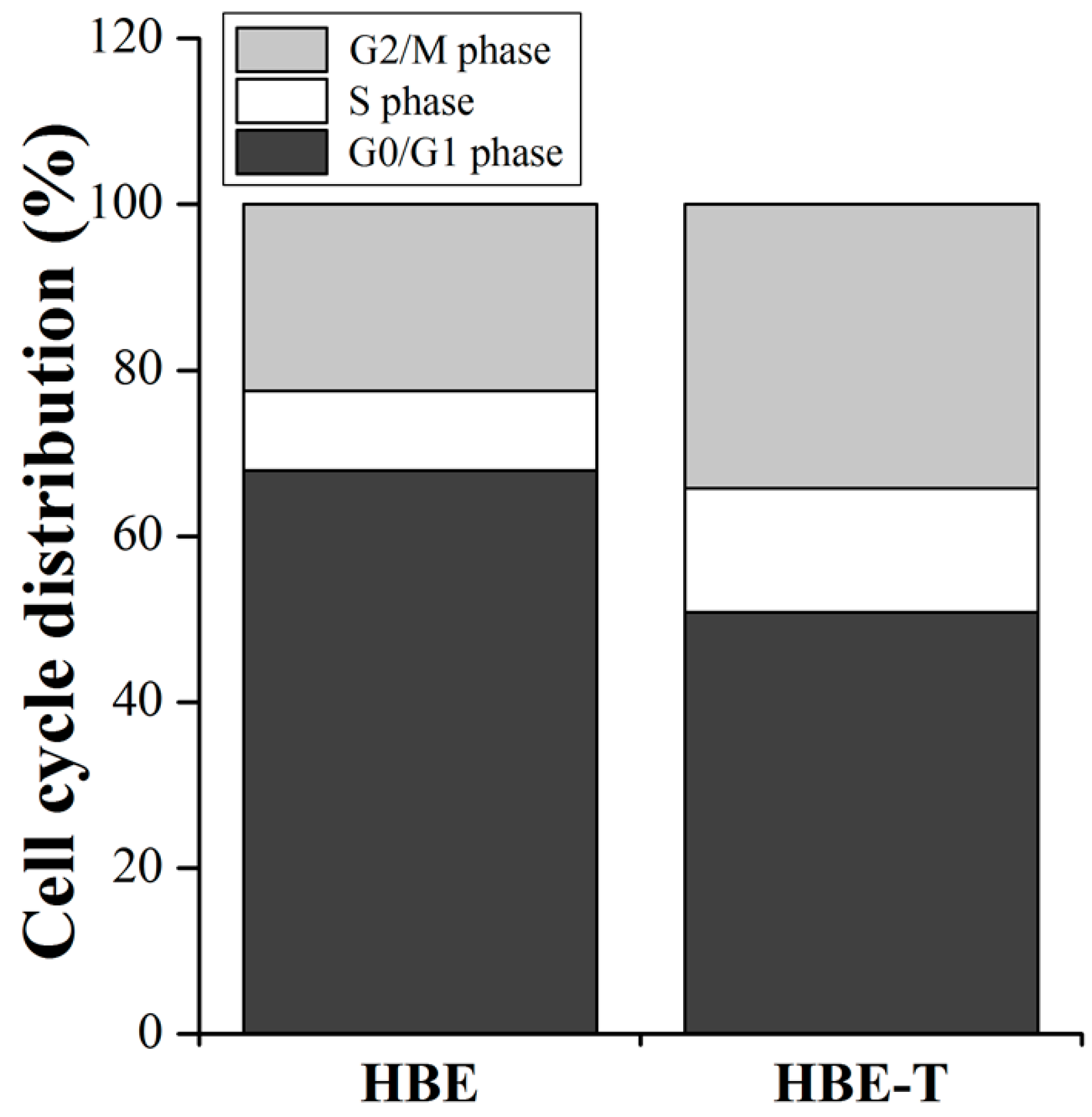
3.6. The Cell Cycle Distribution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez-Lado, L.; Sun, G.; Berg, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, H.; Zheng, Q.; Johnson, C.A. Groundwater arsenic contamination throughout China. Science 2013, 341, 866–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberoi, S.; Barchowsky, A.; Wu, F. The global burden of disease for skin, lung, and bladder cancer caused by arsenic in food. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Pang, Y.; Shen, L.; Jiang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J. Regulation of miRNA-21 by reactive oxygen species-activated ERK/NF-kappaB in arsenite-induced cell transformation. Free Radic Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1508–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.; Xu, Y.; Ling, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, W.; Liang, X.; Jiang, R.; Wang, B.; Bian, Q.; Liu, Q. Arsenite evokes IL-6 secretion, autocrine regulation of STAT3 signaling, and miR-21 expression, processes involved in the EMT and malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 273, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Fisher, T.; Xiao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, C. Akt activation is responsible for enhanced migratory and invasive behavior of arsenic-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Sowinska, A.; Huang, X.; Klein, C.B.; Pelle, E.; Frenkel, K. Impairment of antioxidant defenses as a contributor to arsenite-induced cell transformation. Biometals 2012, 25, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ling, M.; Pang, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Opposed arsenite-mediated regulation of p53-survivin is involved in neoplastic transformation, DNA damage, or apoptosis in human keratinocytes. Toxicology 2012, 300, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.H.; Kim, D.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Z. Human bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells, an appropriate in vitro model to study heavy metals induced carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 287, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Qi, Y.; Liao, M.; Xu, M.; Bower, K.A.; Frank, J.A.; Shen, H.M.; Luo, J.; Shi, X.; Chen, G. Autophagy is a cell self-protective mechanism against arsenic-induced cell transformation. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 130, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngalame, N.N.; Tokar, E.J.; Person, R.J.; Xu, Y.; Waalkes, M.P. Aberrant microRNA expression likely controls RAS oncogene activation during malignant transformation of human prostate epithelial and stem cells by arsenic. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 138, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, P.; Chakraborty, A.; Sarkar, D.; Langthasa, M.; Rahman, M.; Bari, M.; Singha, R.S.; Malakar, A.K.; Chakraborty, S. Interplay between miRNAs and human diseases: A review. J. Cell Physiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wightman, B.; Ha, I.; Ruvkun, G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 1993, 75, 855–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- miRBase. Available online: http://microrna.sanger.ac.uk (accessed on 30 September 2017).
- Ameres, S.L.; Zamore, P.D. Diversifying microRNA sequence and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichmüller, S.B.; Osen, W.; Mandelboim, O.; Seliger, B. Immune modulatory microRNAs involved in tumor attack and tumor immune escape. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, A.; Kashima, R. Dysregulation of microRNA biogenesis machinery in cancer. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 51, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, S.R.; Yang, C.H.; Pfeffer, L.M. The role of miR-21 in Cancer. Drug Dev. Res. 2015, 76, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.; Ji, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, G.; Jing, J.; Wang, B.; Xu, W.; Shi, L.; Lu, X.; et al. MicroRNA-21, up-regulated by arsenite, directs the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances the invasive potential of transformed human bronchial epithelial cells by targeting PDCD4. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 232, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Wang, B.; Xu, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, F.; Liu, Q. The acquisition of cancer stem cell-like properties and neoplastic transformation of human keratinocytes induced by arsenite involves epigenetic silencing of let-7c via Ras/NF-κB. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 227, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beezhold, K.; Liu, J.; Kan, H.; Meighan, T.; Castranova, V.; Shi, X.; Chen, F. miR-190-mediated downregulation of PHLPP contributes to arsenic-induced Akt activation and carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 123, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Ji, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, F.; Wang, B.; et al. MicroRNA-191, by promoting the EMT and increasing CSC-like properties, is involved in neoplastic and metastatic properties of transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, E148–E161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Fujino, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Wu, K.; Xia, Y.; Yoshimura, T. Arsenic contamination of groundwater and prevalence of arsenical dermatosis in the Hetao plain area, Inner Mongolia, China. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2001, 222, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Wen, D.; Liu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Guo, Q. A review of high arsenic groundwater in Mainland and Taiwan, China: Distribution, characteristics and geochemical processes. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 41, 196–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yao, Q.; Tao, Z. miR-15b regulates cisplatin resistance and metastasis by targeting PEBP4 in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinegaglia, N.C.; Andrade, S.C.; Tokar, T.; Pinheiro, M.; Severino, F.E.; Oliveira, R.A.; Hasimoto, E.N.; Cataneo, D.C.; Cataneo, A.J.; Defaveri, J.; et al. Integrative transcriptome analysis identifies deregulated microRNA-transcription factor networks in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 28920–28934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmonds, M.D.; Eischen, C.M. Differences in miRNA expression in early stage lung adenocarcinomas that did and did not relapse. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Li, M.; An, J.; Zhao, B.; Zhong, W.; Gu, Q.; Cao, L.; Yang, H.; Hu, C. MicroRNA-33b inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell growth, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by suppressing Wnt/â-catenin/ZEB1 signaling. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 2141–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Qiao, F.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Shang, Y. Curcumin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of human non-small cell lung cancer cells through the upregulation of miR-192-5p and suppression of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2782–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, L.; Han, M.; Li, X.; Zhao, C. MicroRNA signature of lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR exon 19 deletion. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TargetMiner. Available online: http://www.biomedsearch.com/nih/TargetMinermicroRNA-target-prediction-with/19692556.html (accessed on 30 September 2017).
- miRDB. Available online: http://bioinfo.au.Tsinghua.edu.cn/micrornadb/index.php (accessed on 30 September 2017).
- TarBase. Available online: http://diana.imis.athena-innovation.gr/DianaTools/index.php?r=tarbase/index (accessed on 30 September 2017).
- Venny 2.1.0. Available online: http://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html (accessed on 30 September 2017).
- Calin, G.A.; Sevignani, C.; Dumitru, C.D.; Hyslop, T.; Noch, E.; Yendamuri, S.; Shimizu, M.; Rattan, S.; Bullrich, F.; Negrini, M.; et al. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2999–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturchio, E.; Colombo, T.; Boccia, P.; Carucci, N.; Meconi, C.; Minoia, C.; Macino, G. Arsenic exposure triggers a shift in microRNA expression. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, Z.S.; Khalili, S.; Forouzandeh Moghadam, M.; Sadroddiny, E. Lung cancer and miRNAs: A possible remedy for anti-metastatic, therapeutic and diagnostic applications. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2017, 11, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zheng, C.; Shen, H.; Zhou, Z.; Lei, Y. MicroRNAs-mRNAs expression profile and their potential role in malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells induced by cadmium. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 902025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.J.; Hao, S.; Wang, L.L.; Hu, C.Y.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L.J.; Zhang, G.; Gao, B.; Jiang, Y.; Tian, W.G.; et al. Long non-coding RNA ANRIL promotes the invasion and metastasis of thyroid cancer cells through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57903–57918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Fang, S.; Wang, Q.; Fang, R.; Chen, J. Fibulin-4 is associated with prognosis of endometrial cancer patients and inhibits cancer cell invasion and metastasis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 18991–19012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Kroemer, G. Defective autophagy initiates malignant transformation. Mol. Cell. 2016, 62, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, W.L.; Lam, C.S.; Ng, L.; Chow, A.K.; Chan, S.T.; Chan, J.Y.; Wo, J.Y.; Ng, K.T.; Man, K.; Poon, R.T.; et al. Over-expression of miR-106b promotes cell migration and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma by activating epithelial-mesenchymal transition process. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, S.; Sun, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Alterations of miRNAs and Their Potential Roles in Arsenite-Induced Transformation of Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Genes 2017, 8, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8100254
Gu S, Sun D, Li X, Zhang Z. Alterations of miRNAs and Their Potential Roles in Arsenite-Induced Transformation of Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Genes. 2017; 8(10):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8100254
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Shiyan, Donglei Sun, Xinyang Li, and Zunzhen Zhang. 2017. "Alterations of miRNAs and Their Potential Roles in Arsenite-Induced Transformation of Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells" Genes 8, no. 10: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8100254
APA StyleGu, S., Sun, D., Li, X., & Zhang, Z. (2017). Alterations of miRNAs and Their Potential Roles in Arsenite-Induced Transformation of Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Genes, 8(10), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8100254





