Mechanisms and Physiological Roles of the CBL-CIPK Networking System in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
:1. Introduction
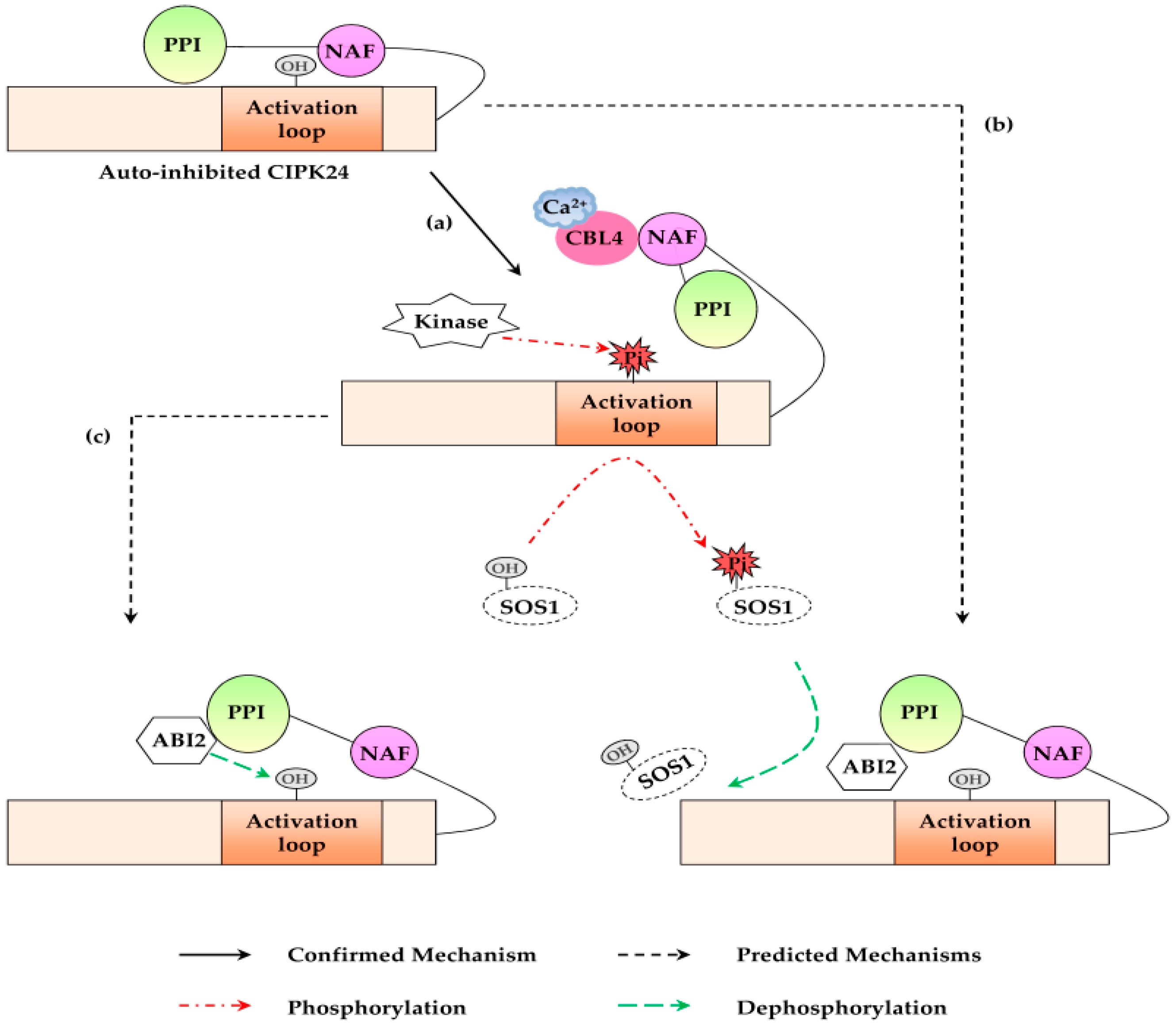
2. Mechanisms of CBL-CIPK Pathway
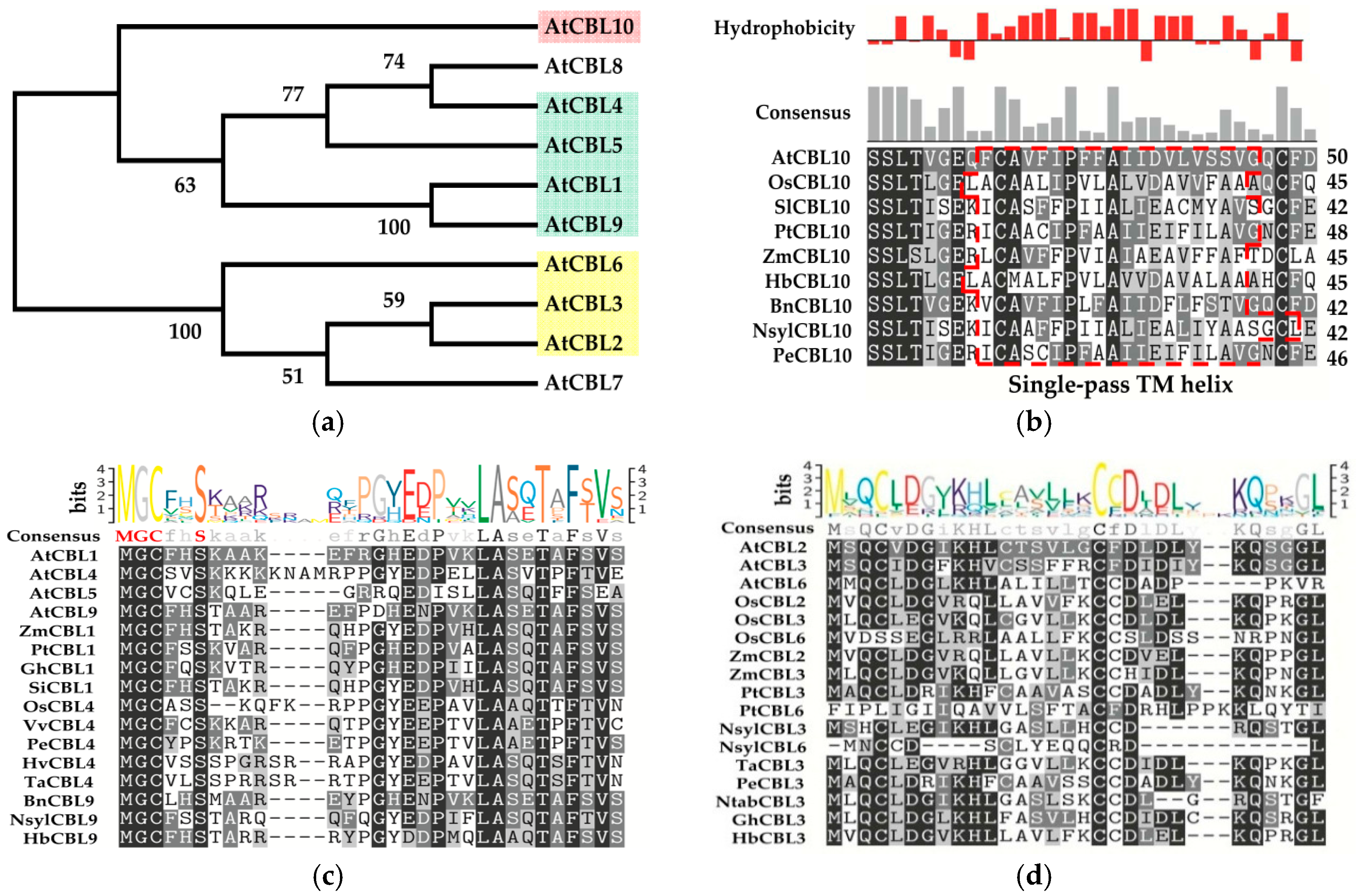
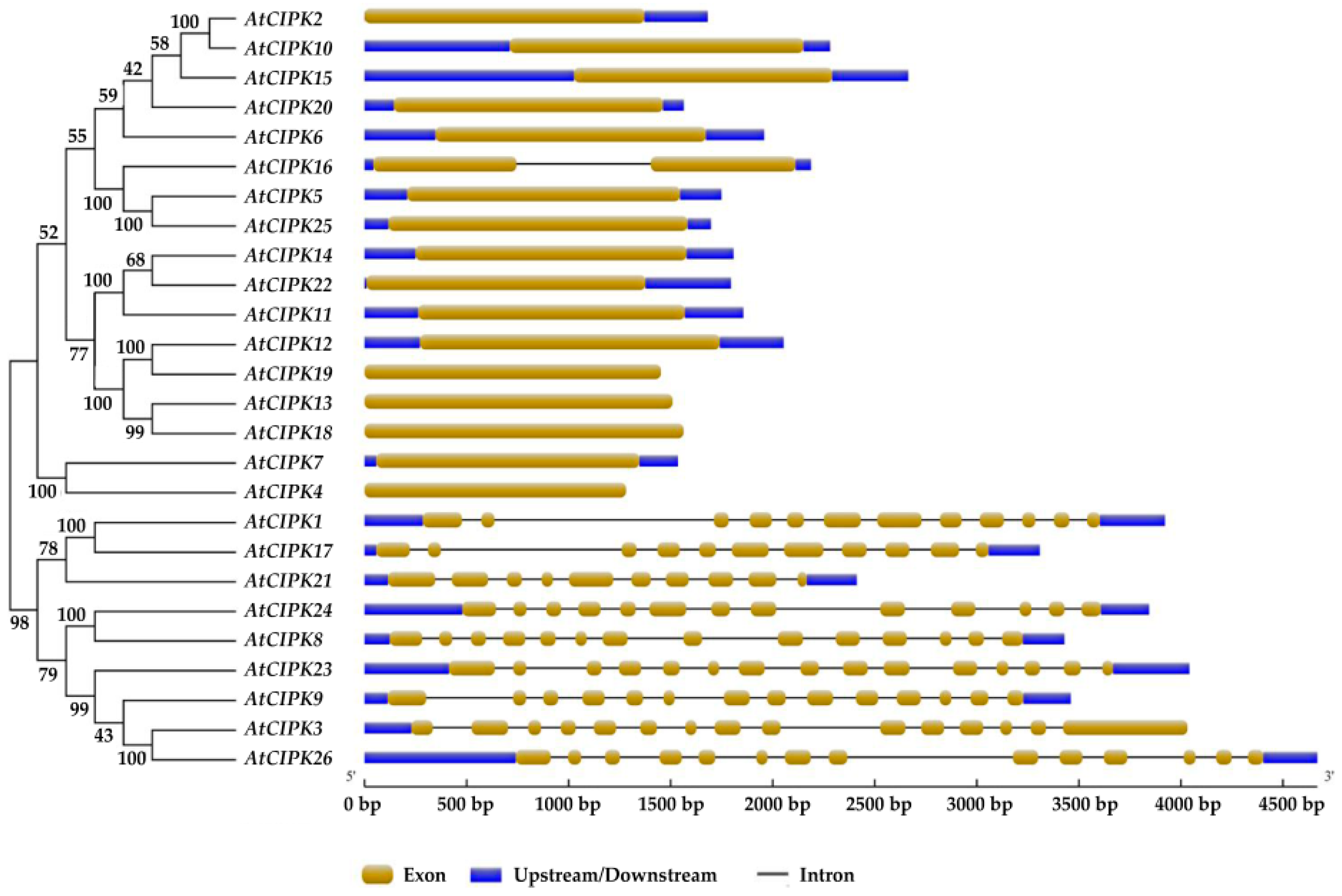
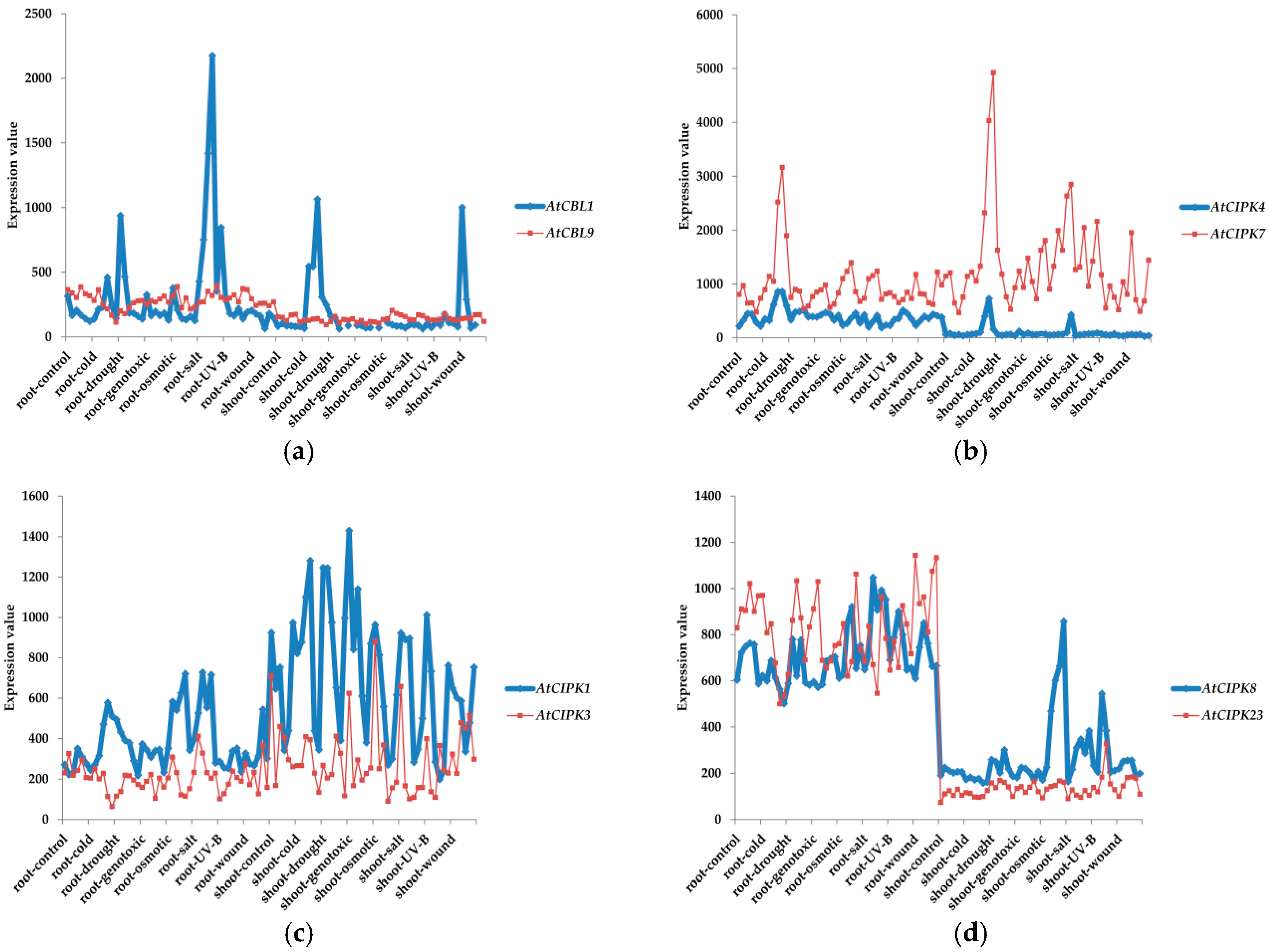
3. Classifications and Expression Patterns of CBLs and CIPKs
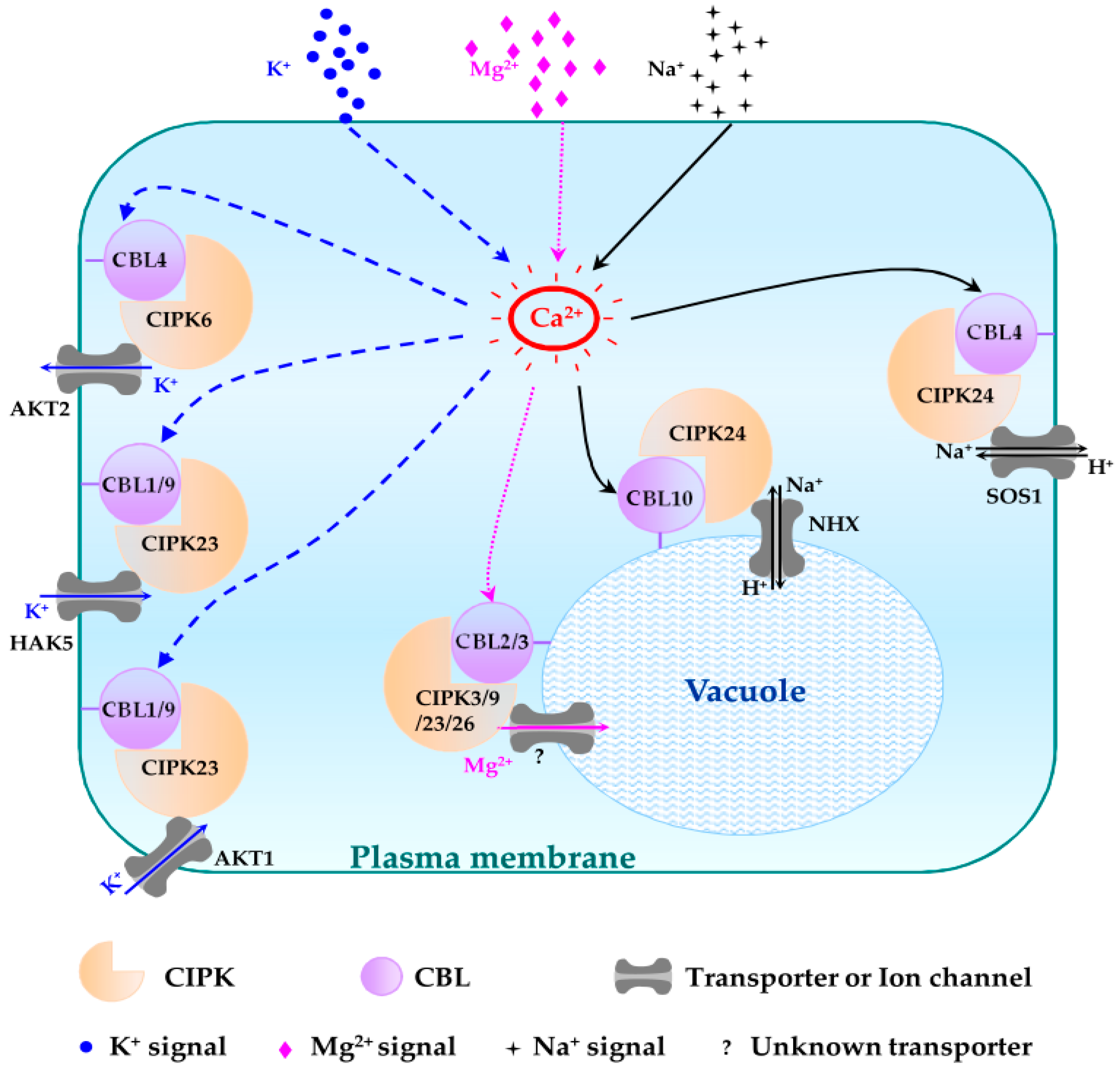
4. Physiological Roles of CBL-CIPK Signaling Pathways in Arabidopsis
4.1. Plasma Membrane Targeting CBL-CIPK Pathways
4.1.1. CBL1/CBL9-CIPK23 Pathways
4.1.2. CBL1/9-CIPK26 Pathways
4.1.3. CBL9-CIPK3 Pathway
4.1.4. CBL2-CIPK11 Pathway
4.1.5. CBL4-CIPK6 Pathway
4.1.6. CBL4-CIPK24 Pathway
4.2. Tonoplast Targeting CBL-CIPK Pathways
4.2.1. CBL2/3-CIPK3/9/23/26 Pathways
4.2.2. CBL2/3-CIPK12 Pathways
4.2.3. CBL2/3-CIPK21 Pathways
4.2.4. CBL10-CIPK24 Pathway
5. Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix
| Substrates | CBL-CIPK Complexes Upstream | Functions of the Substrate Proteins | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ion channels | AKT1 | CBL1/9-CIPK23 | An inward K+ channel uptaking K+ at K+ concentrations higher than 10 μM [15]. |
| AKT2 | CBL4-CIPK6 | An outward K+ channel exporting K+ for the K+ unloading [35,61]. | |
| SLAC1 | CBL1/9-CIPK23 | An anion channel involved in the ABA-regulation of stomata aperture, leading to the closure of stomata [46,47]. | |
| SLAC3 | CBL1/9-CIPK23 | An anion channel involved in the ABA-regulation of stomata aperture, leading to the closure of stomata [48]. | |
| Ion transporters | CHL1 | CBL1/9-CIPK23 | A nitrate transporter uptaking or secreting NO3− [18,19]. |
| HAK5 | CBL1/9-CIPK23 | A K+ transporter uptaking K+ at K+ concentrations below 200 μM [45]. | |
| SOS1 | CBL4-CIPK24 | A Na+/H+ exchanger exporting Na+ back into soil [11,29]. | |
| Vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter | CBL10-CIPK24 | A Na+/H+ antiporter sequestrating Na+ into vacuole [32]. | |
| Other | PM H+-ATPase | CBL2-CIPK11 | A proton pump localized in the PM, driving ion and metabolite to transport across the PM [59,60]. |
| Vacuolar H+-ATPase | CBL2/3-CIPK3/9/23/26 | A proton pump localized in the tonoplast, driving ion and metabolite to transport across the tonoplast [17,36]. | |
| RBOHF | CBL1/9-CIPK26 | A member of respiratory burst oxidase homologues which are the indispensable components of the enzymatic complexes generating ROS [54,55]. | |
References
- Gilroy, S.; Trewavas, A. Signal processing and transduction in plant cells: The end of the beginning? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, D.; Pelloux, J.; Brownlee, C.; Harper, J.F. Calcium at the crossroads of signaling. Plant Cell 2002, 14, S401–S417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Batistič, O.; Kudla, J. Analysis of calcium signaling pathways in plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D.M.; Harmon, A.C. Calcium-modulated proteins: targets of intracellular calcium signals in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1992, 43, 375–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, S. The CBL-CIPK network in plant calcium signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinl, S.; Kudla, J. The CBL-CIPK Ca2+-decoding signaling network: function and perspectives. New Phytol. 2009, 184, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, S.; Kudla, J.; Rodriguez-Concepcion, M.; Yalovsky, S.; Gruissem, W. Calmodulins and calcineurin B-like proteins calcium sensors for specific signal response coupling in plants. Plant Cell 2002, 14, S389–S400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, J.K. A calcium sensor homolog required for plant salt tolerance. Science 1998, 280, 1943–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Kim, K.N.; Ritz, O.; Albrecht, V.; Gupta, R.; Harter, K.; Luan, S.; Kudla, J. Novel protein kinases associated with calcineurin B-like calcium sensors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 2393–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ishitani, M.; Halfter, U.; Kim, C.S.; Zhu, J.K. The Arabidopsis thaliana SOS2 gene encodes a protein kinase that is required for salt tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3730–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Q.S.; Guo, Y.; Dietrich, M.A.; Schumaker, K.S.; Zhu, J.K. Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8436–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.K.; Liu, J.; Xiong, L. Genetic analysis of salt tolerance in Arabidopsis: Evidence for a critical role of potassium nutrition. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Quintero, F.J.; Pardo, J.M.; Zhu, J.K. The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolukisaoglu, Ü.; Weinl, S.; Blazevic, D.; Batistic, O.; Kudla, J. Calcium sensors and their interacting protein kinases: Genomics of the Arabidopsis and Rice CBL-CIPK signaling networks. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Kim, B.G.; Cheong, Y.H.; Pandey, G.K.; Luan, S. A Ca2+ signaling pathway regulates a K+ channel for low-K response in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12625–12630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, H.D.; Chen, L.Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.L.; He, L.; Wu, W.H. A protein kinase, interacting with two calcineurin B-like proteins, regulates K+ transporter AKT1 in Arabidopsis. Cell 2006, 125, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.J.; Zhao, F.G.; Garcia, V.J.; Kleist, T.J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.X.; Luan, S. Tonoplast CBL-CIPK calcium signaling network regulates magnesium homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3134–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.H.; Lin, S.H.; Hu, H.C.; Tsay, Y.F. CHL1 functions as a nitrate sensor in plants. Cell 2009, 138, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leran, S.; Edel, K.H.; Pervent, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Corratge-Faillie, C.; Offenborn, J.N.; Tillard, P.; Gojon, A.; Kudla, J.; Lacombe, B. Nitrate sensing and uptake in Arabidopsis are enhanced by ABI2, a phosphatase inactivated by the stress hormone abscisic acid. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuglsang, A.T.; Guo, Y.; Cuin, T.A.; Qiu, Q.; Song, C.; Kristiansen, K.A.; Bych, K.; Schulz, A.; Shabala, S.; Schumaker, K.S.; et al. Arabidopsis protein kinase PKS5 inhibits the plasma membrane H+-ATPase by preventing interaction with 14-3-3 protein. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1617–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manik, S.M.N.; Shi, S.; Mao, J.; Dong, L.; Su, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H. The calcium sensor CBL-CIPK is involved in plant’s response to abiotic stresses. Int. J. Genom. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoday-Kennedy, E.L.; Jacobs, A.K.; Roy, S.J. The role of the CBL-CIPK calcium signaling network in regulating ion transport in response to abiotic stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 76, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Barrena, M.J.; Fujii, H.; Angulo, I.; Martínez-Ripoll, M.; Zhu, J.K.; Albert, A. The structure of the C-terminal domain of the protein kinase AtSOS2 bound to the calcium sensor AtSOS3. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Barrena, M.J.; Martínez-Ripoll, M.; Albert, A. Structural biology of a major signaling network that regulates plant abiotic stress: The CBL-CIPK mediated pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 5734–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagae, M.; Nozawa, A.; Koizumi, N.; Sano, H.; Hashimoto, H.; Sato, M.; Shimizu, T. The crystal structure of the novel calcium-binding protein AtCBL2 from Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 42240–42246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Barrena, M.J.; Martínez-Ripoll, M.; Zhu, J.K.; Albert, A. The structure of the Arabidopsis thaliana SOS3: Molecular mechanism of sensing calcium for salt stress response. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 345, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, R. Functions and mechanisms of the CBL-CIPK signaling system in plant response to abiotic stress. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2009, 19, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Halfter, U.; Ishitani, M.; Zhu, J.K. Molecular characterization of functional domains in the protein kinase SOS2 that is required for plant salt tolerance. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1383–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.K. Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, M.; Guo, Y.; Halfter, U.; Zhu, J.K. A novel domain in the protein kinase SOS2 mediates interaction with the protein phosphatase 2C ABI2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11771–11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batistič, O.; Waadt, R.; Steinhorst, L.; Held, K.; Kudla, J. CBL-mediated targeting of CIPKs facilitates the decoding of calcium signals emanating from distinct cellular stores. Plant J. 2010, 61, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.G.; Waadt, R.; Cheong, Y.H.; Pandey, G.K.; Dominguez-Solis, J.R.; Schültke, S.; Lee, S.C.; Kudla, J.; Luan, S. The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007, 52, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, R.; Lin, H.; Mendoza, I.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, W.; Yang, Y.; Shang, M.; Chen, S.; Pardo, J.M.; Guo, Y. SCABP8/CBL10, a putative calcium sensor, interacts with the protein kinase SOS2 to protect Arabidopsis shoots from salt stress. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batistič, O.; Sorek, N.; Schültke, S.; Yalovsky, S.; Kudla, J. Dual fatty acyl modification determines the localization and plasma membrane targeting of CBL/CIPK Ca2+ signaling complexes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1346–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Held, K.; Pascaud, F.; Eckert, C.; Gajdanowicz, P.; Hashimoto, K.; Corratgé-Faillie, C.; Offenborn, J.N.; Lacombe, B.; Dreyer, I.; Thibaud, J.B. Calcium-dependent modulation and plasma membrane targeting of the AKT2 potassium channel by the CBL4/CIPK6 calcium sensor/protein kinase complex. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.J.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Gao, X.S.; Garcia, V.J.; Luan, S.; Zhang, H.X. Tonoplast calcium sensors CBL2 and CBL3 control plant growth and ion homeostasis through regulating V-ATPase activity in Arabidopsis. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 1650–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleist, T.J.; Spencley, A.L.; Luan, S. Comparative phylogenomics of the CBL-CIPK calcium-decoding network in the moss Physcomitrella, Arabidopsis, and other green lineages. Front. Plant Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.Y.; Xia, X.; Yin, W. Evolutionary analysis of CBL-interacting protein kinase gene family in plants. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 71, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, C.; Weinl, S.; Batistic, O.; Pandey, G.K.; Cheong, Y.H.; Schültke, S.; Albrecht, V.; Ehlert, B.; Schulz, B.; Harter, K. Alternative complex formation of the Ca2+-regulated protein kinase CIPK1 controls abscisic acid-dependent and independent stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2006, 48, 857–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.K.; Cheong, Y.H.; Kim, K.N.; Grant, J.J.; Li, L.; Hung, W.; D’Angelo, C.; Weinl, S.; Kudla, J.; Luan, S. The calcium sensor calcineurin B-like 9 modulates abscisic acid sensitivity and biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1912–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilian, J.; Whitehead, D.; Horak, J.; Wanke, D.; Weinl, S.; Batistic, O.; D’Angelo, C.; Bornberg-Bauer, E.; Kudla, J.; Harter, K. The AtGenExpress global stress expression data set: protocols, evaluation and model data analysis of UV-B light, drought and cold stress responses. Plant J. 2007, 50, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, Y.H. CBL1, a calcium sensor that differentially regulates salt, drought, and cold responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1833–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, V.; Weinl, S.; Blazevic, D.; D’Angelo, C.; Batistic, O.; Kolukisaoglu, Ü.; Bock, R.; Schulz, B.; Harter, K.; Kudla, J. The calcium sensor CBL1 integrates plant responses to abiotic stresses. Plant J. 2003, 36, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, Y.H.; Pandey, G.K.; Grant, J.J.; Batistic, O.; Li, L.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, S.C.; Kudla, J.; Luan, S. Two calcineurin B-like calcium sensors, interacting with protein kinase CIPK23, regulate leaf transpiration and root potassium uptake in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007, 52, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragel, P.; Ródenas, R.; García-Martín, E.; Andrés, Z.; Villalta, I.; Nieves-Cordones, M.; Rivero, R.M.; Martínez, V.; Pardo, J.M.; Quintero, F.J. CIPK23 regulates HAK5-mediated high-affinity K+ uptake in Arabidopsis roots. Plant physiol. 2015, 169, 2863–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maierhofer, T.; Diekmann, M.; Offenborn, J.N.; Lind, C.; Bauer, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.; Luan, S.; Kudla, J.; Geiger, D. Site-and kinase-specific phosphorylation-mediated activation of SLAC1, a guard cell anion channel stimulated by abscisic acid. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, D.; Scherzer, S.; Mumm, P.; Stange, A.; Marten, I.; Bauer, H.; Ache, P.; Matschi, S.; Liese, A.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.; et al. Activity of guard cell anion channel SLAC1 is controlled by drought-stress signaling kinase-phosphatase pair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21425–21430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, D.; Maierhofer, T.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.; Scherzer, S.; Mumm, P.; Liese, A.; Ache, P.; Wellmann, C.; Marten, I.; Grill, E.; et al. Stomatal closure by fast abscisic acid signaling is mediated by the guard cell anion channel SLAH3 and the receptor RCAR1. Plant Biol. 2011, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieves-Cordones, M.; Caballero, F.; Martinez, V.; Rubio, F. Disruption of the Arabidopsis thaliana inward-rectifier K+ channel AKT1 improves plant responses to water stress. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyman, B.; Geelen, D.; Quintero, F.J.; Blatt, M.R. A tobacco syntaxin with a role in hormonal control of guard cell ion channels. Science 1999, 283, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.H.; Tsay, Y.F. Switching between the two action modes of the dual-affinity nitrate transporter CHL1 by phosphorylation. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vert, G.; Chory, J. A toggle switch in plant nitrate uptake. Cell 2009, 138, 1064–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leran, S.; Munos, S.; Brachet, C.; Tillard, P.; Gojon, A.; Lacombe, B. Arabidopsis NRT1.1 is a bidirectional transporter involved in root-to-shoot nitrate translocation. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1984–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, D.; Dunand, C.; Puppo, A.; Pauly, N. A burst of plant NADPH oxidases. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drerup, M.M.; Schlücking, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Manishankar, P.; Steinhorst, L.; Kuchitsu, K.; Kudla, J. The calcineurin B-like calcium sensors CBL1 and CBL9 together with their interacting protein kinase CIPK26 regulate the Arabidopsis NADPH oxidase RBOHF. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.K.; Grant, J.J.; Cheong, Y.H.; Kim, B.G.; Luan, S. Calcineurin-B-like protein CBL9 interacts with target kinase CIPK3 in the regulation of ABA response in seed germination. Mol. Plant 2008, 1, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.N.; Cheong, Y.H.; Grant, J.J.; Pandey, G.K.; Luan, S. CIPK3, a calcium sensor-associated protein kinase that regulates abscisic acid and cold signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Xiong, L.; Song, C.P.; Gong, D.; Halfter, U.; Zhu, J.K. A calcium sensor and its interacting protein kinase are global regulators of abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanczewska, J.; Marco, S.; Vandermeeren, C.; Maudoux, O.; Rigaud, J.L.; Boutry, M. Activation of the plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase by phosphorylation and binding of 14-3-3 proteins converts a dimer into a hexamer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11675–11680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuglsang, A.T.; Visconti, S.; Drumn, K.; Jahn, T.; Stensballe, A.; Mattei, B.; Jensen, O.N.; Aducci, P.; Palmgren, M.G. Binding of 14-3-3 protein to the plasma membrane H-ATPase AHA2 involves the three C-terminal residues Tyr946-Thr-Val and requires phosphorylation of Thr947. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 36774–36780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacombe, B.; Pilot, G.; Michard, E.; Gaymard, F.; Sentenac, H.; Thibaud, J.B. A shaker-like K+ channel with weak rectification is expressed in both source and sink phloem tissues of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.K.; Cheong, Y.H.; Kim, B.G.; Grant, J.J.; Li, L.; Luan, S. CIPK9: A calcium sensor-interacting protein kinase required for low-potassium tolerance in Arabidopsis. Cell Res. 2007, 17, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.L.; Ren, H.M.; Chen, L.Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.H. A protein kinase, calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase9, interacts with calcium sensor calcineurin B-like protein3 and regulates potassium homeostasis under low-potassium stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.K.; Kanwar, P.; Singh, A.; Steinhorst, L.; Pandey, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Tokas, I.; Sanyal, S.K.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, S.C. Calcineurin B-Like protein-interacting protein kinase CIPK21 regulates osmotic and salt stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhorst, L.; Mähs, A.; Ischebeck, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Arendt, S.; Schültke, S.; Heilmann, I.; Kudla, J. Vacuolar CBL-CIPK12 Ca2+-sensor-kinase complexes are required for polarized pollen tube growth. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, C.; Offenborn, J.N.; Heinz, T.; Armarego-Marriott, T.; Schültke, S.; Zhang, C.; Hillmer, S.; Heilmann, M.; Schumacher, K.; Bock, R. The vacuolar calcium sensors CBL2 and CBL3 affect seed size and embryonic development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2014, 78, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Lan, W.; Chen, B.; Fang, W.; Luan, S. A calcium sensor-regulated protein kinase, calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase 19, is required for pollen tube growth and polarity. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Q.S.; Guo, Y.; Quintero, F.J.; Pardo, J.M.; Schumaker, K.S.; Zhu, J.K. Regulation of vacuolar Na+/H+ exchange in Arabidopsis thaliana by the salt-overly-sensitive (SOS) pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaboshi, M.; Hashimoto, H.; Ishida, H.; Saijo, S.; Koizumi, N.; Sato, M.; Shimizu, T. The crystal structure of plant-specific calcium-binding protein AtCBL2 in complex with the regulatory domain of AtCIPK14. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 377, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tsay, Y.F. AtCIPK8, a CBL-interacting protein kinase, regulates the low-affinity phase of the primary nitrate response. Plant J. 2009, 57, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, N.H.; Pittman, J.K.; Zhu, J.K.; Hirschi, K.D. The protein kinase SOS2 activates the Arabidopsis H+/Ca2+ antiporter CAX1 to integrate calcium transport and salt tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 2922–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huibers, R.P.; De Jong, M.; Dekter, R.W.; Van den Ackerveken, G. Disease-specific expression of host genes during downy mildew infection of Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyndrickx, K.S.; Vandepoele, K. Systematic identification of functional plant modules through the integration of complementary data sources. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 884–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ok, S.H.; Cho, J.H.; Oh, S.I.; Choi, M.N.; Ma, J.Y.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, K.N. Calcineurin B-like 3 calcium sensor associates with and inhibits 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase 2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2015, 238, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.L.; Qi, G.N.; Feng, H.Q.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, S.S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.H. Calcineurin B-like protein CBL10 directly interacts with AKT1 and modulates K+ homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2013, 74, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, J.; Manik, S.M.N.; Shi, S.; Chao, J.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H. Mechanisms and Physiological Roles of the CBL-CIPK Networking System in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes 2016, 7, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7090062
Mao J, Manik SMN, Shi S, Chao J, Jin Y, Wang Q, Liu H. Mechanisms and Physiological Roles of the CBL-CIPK Networking System in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes. 2016; 7(9):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7090062
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Jingjing, S. M. Nuruzzaman Manik, Sujuan Shi, Jiangtao Chao, Yirong Jin, Qian Wang, and Haobao Liu. 2016. "Mechanisms and Physiological Roles of the CBL-CIPK Networking System in Arabidopsis thaliana" Genes 7, no. 9: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7090062
APA StyleMao, J., Manik, S. M. N., Shi, S., Chao, J., Jin, Y., Wang, Q., & Liu, H. (2016). Mechanisms and Physiological Roles of the CBL-CIPK Networking System in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes, 7(9), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7090062







