Association of XPC Gene Polymorphisms with Colorectal Cancer Risk in a Southern Chinese Population: A Case-Control Study and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of Study Subjects
2.2. Stratification Analysis
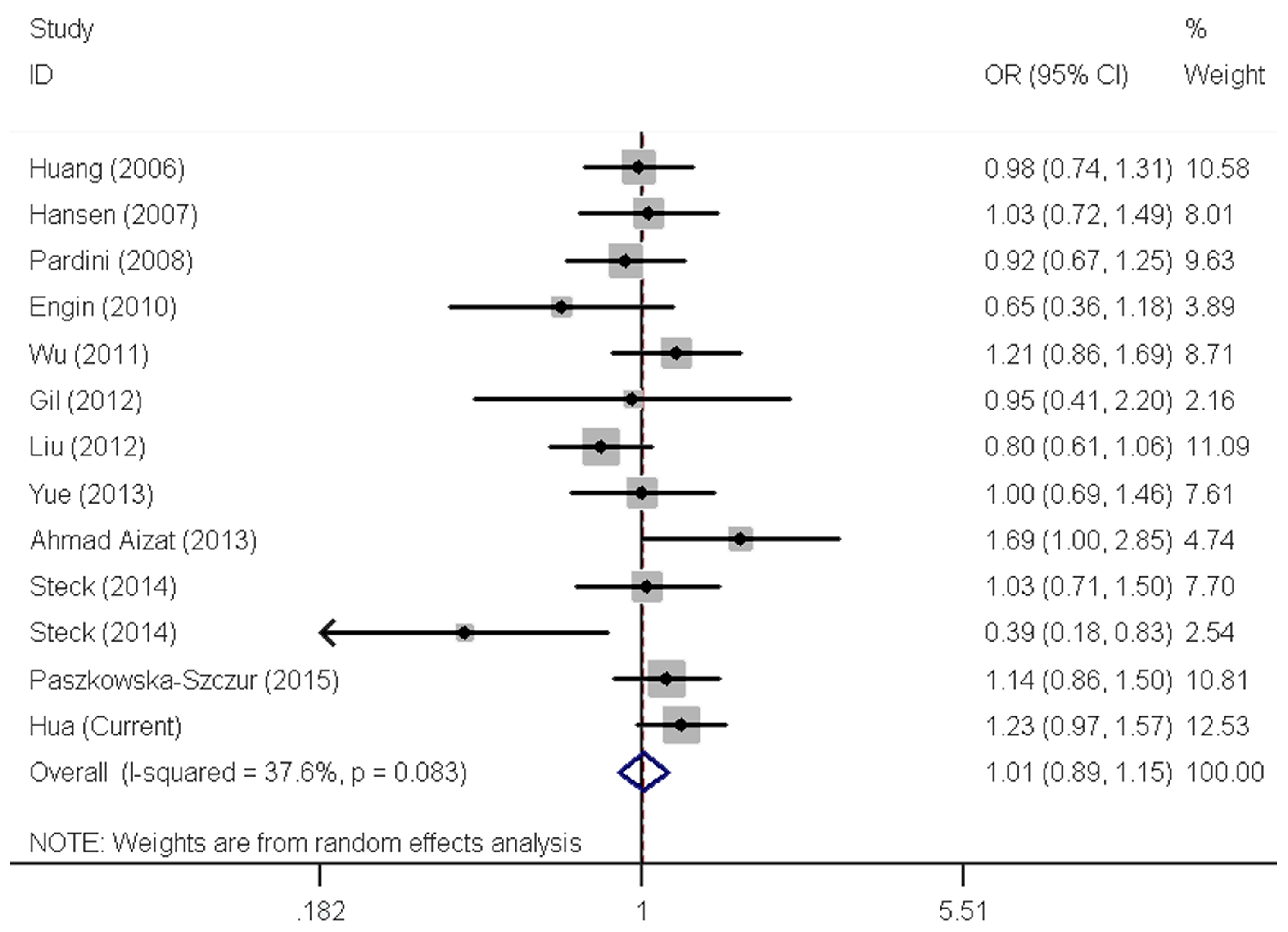
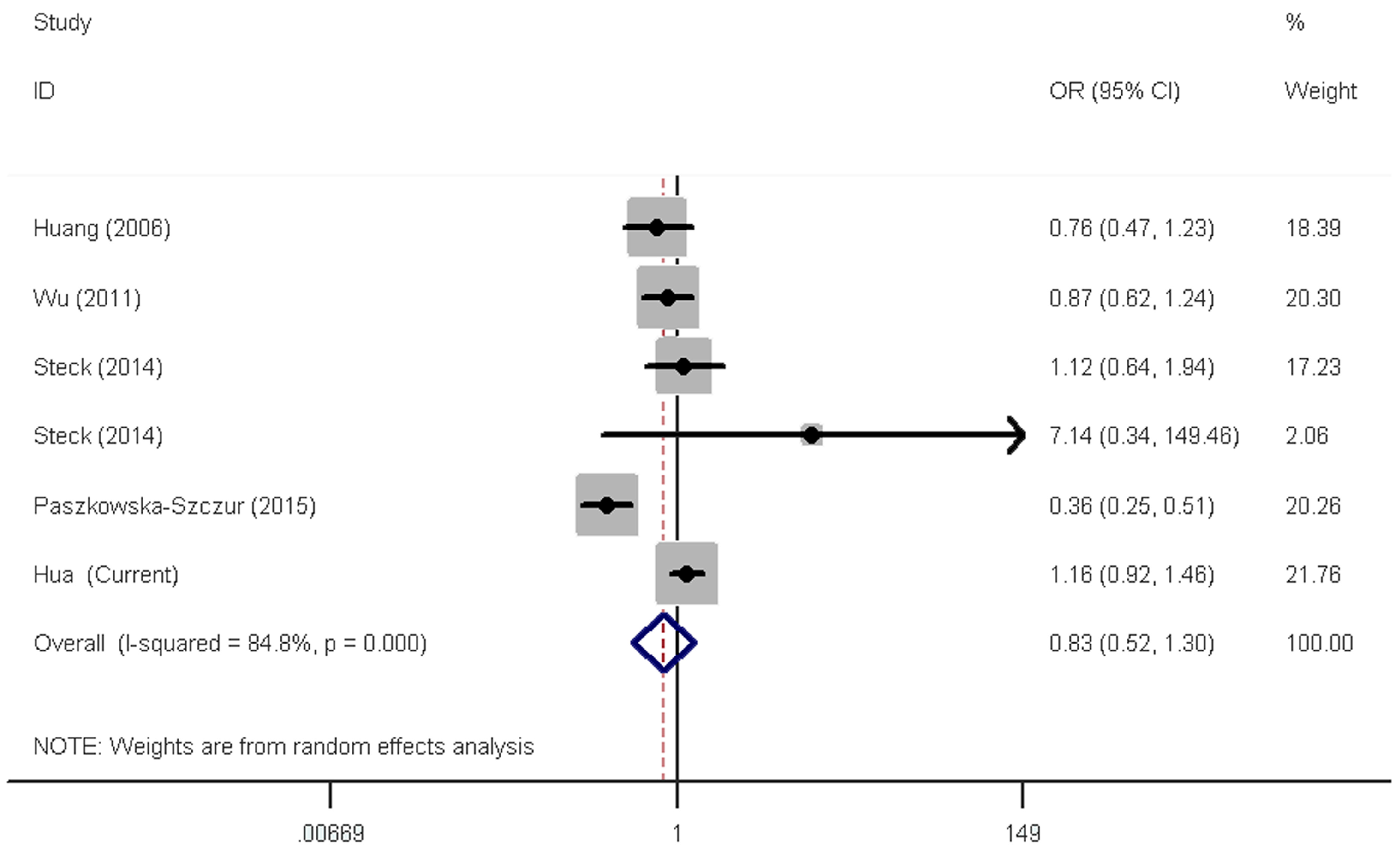
2.3. Meta-Analysis Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Genotyping
4.3. Statistical Analysis
4.4. Meta-Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Silva, I.U.; McHugh, P.J.; Clingen, P.H.; Hartley, J.A. Defining the roles of nucleotide excision repair and recombination in the repair of DNA interstrand cross-links in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 7980–7990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedberg, E.C. How nucleotide excision repair protects against cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christmann, M.; Tomicic, M.T.; Roos, W.P.; Kaina, B. Mechanisms of human DNA repair: An update. Toxicology 2003, 193, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugasawa, K.; Ng, J.M.; Masutani, C.; Iwai, S.; van der Spek, P.J.; Eker, A.P.; Hanaoka, F.; Bootsma, D.; Hoeijmakers, J.H. Xeroderma pigmentosum group C protein complex is the initiator of global genome nucleotide excision repair. Mol. Cell 1998, 2, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, B.S.; Vasquez, K.M. Critical DNA damage recognition functions of XPC-hHR23B and XPA-RPA in nucleotide excision repair. Mol. Carcinog. 2003, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, R.D. DNA damage recognition during nucleotide excision repair in mammalian cells. Biochimie 1999, 81, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCBI. dbSNP: Short Genetic Variations. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/SNP (accessed on 26 August 2016).
- He, J.; Shi, T.Y.; Zhu, M.L.; Wang, M.Y.; Li, Q.X.; Wei, Q.Y. Associations of Lys939Gln and Ala499Val polymorphisms of the XPC gene with cancer susceptibility: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 1765–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yin, Q.; Ying, M.; Lin, J.; Li, L.; Jiao, G.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y. XPC Lys939Gln and Ala499Val polymorphisms in colorectal cancer susceptibility: A meta-analysis of case-control studies. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Lao, X.; Tang, W.; Chen, Z.; Li, R.; Qin, X.; Li, S. XPC Lys939Gln polymorphism contributes to colorectal cancer susceptibility: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad Aizat, A.A.; Siti Nurfatimah, M.S.; Aminudin, M.M.; Ankathil, R. XPC Lys939Gln polymorphism, smoking and risk of sporadic colorectal cancer among Malaysians. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 3623–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wu, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.N.; Kang, H.; Sun, M.J.; Wang, E.H.; Yang, X.L.; Lian, M.Q.; Yu, Z.J.; Zhao, L.; et al. DNA repair genes XPC, XPG polymorphisms: Relation to the risk of colorectal carcinoma and therapeutic outcome with oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. Mol. Carcinog. 2012, 51 (Suppl. 1), E83–E93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Gu, J.; Grossman, H.B.; Amos, C.I.; Etzel, C.; Huang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Millikan, R.E.; Lerner, S.; Dinney, C.P.; et al. Bladder cancer predisposition: A multigenic approach to DNA-repair and cell-cycle-control genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saladi, R.N.; Persaud, A.N. The causes of skin cancer: A comprehensive review. Drugs Today 2005, 41, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugasawa, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Iwai, S.; Hanaoka, F. A molecular mechanism for DNA damage recognition by the xeroderma pigmentosum group C protein complex. DNA Repair 2002, 1, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.M.; Chigancas, V.; Galhardo Rda, S.; Carvalho, H.; Menck, C.F. The eukaryotic nucleotide excision repair pathway. Biochimie 2003, 85, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.S.; Hua, R.X.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Y.S.; Hua, Z.M.; Yun, C.T.; Zeng, R.F.; Long, J.T. Poly (AT) deletion/insertion polymorphism of the XPC gene contributes to urinary system cancer susceptibility: A meta-analysis. Gene 2013, 528, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, G.; Menezes, P.R.; Eluf-Neto, J.; Chammas, R. XPC polymorphisms play a role in tissue-specific carcinogenesis: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 16, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Spitz, M.R.; Shen, H.; Guo, Z.; Shete, S.; Hedayati, M.; Grossman, L.; Mohrenweiser, H.; Wei, Q. Modulation of repair of ultraviolet damage in the host-cell reactivation assay by polymorphic XPC and XPD/ERCC2 genotypes. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naccarati, A.; Soucek, P.; Stetina, R.; Haufroid, V.; Kumar, R.; Vodickova, L.; Trtkova, K.; Dusinska, M.; Hemminki, K.; Vodicka, P. Genetic polymorphisms and possible gene-gene interactions in metabolic and DNA repair genes: Effects on DNA damage. Mutat. Res. 2006, 593, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavanello, S.; Pulliero, A.; Siwinska, E.; Mielzynska, D.; Clonfero, E. Reduced nucleotide excision repair and GSTM1-null genotypes influence anti-B[a]pde-DNA adduct levels in mononuclear white blood cells of highly PAH-exposed coke oven workers. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engin, A.B.; Karahalil, B.; Engin, A.; Karakaya, A.E. Oxidative stress, Helicobacter pylori, and OGG1 Ser326Cys, XPC Lys939Gln, and XPD Lys751Gln polymorphisms in a Turkish population with colorectal carcinoma. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2010, 14, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, J.; Ramsey, D.; Stembalska, A.; Karpinski, P.; Pesz, K.A.; Laczmanska, I.; Leszczynski, P.; Grzebieniak, Z.; Sasiadek, M.M. The C/A polymorphism in intron 11 of the XPC gene plays a crucial role in the modulation of an individual’s susceptibility to sporadic colorectal cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, R.D.; Sorensen, M.; Tjonneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Wallin, H.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Vogel, U. XPA A23G, XPC Lys939Gln, XPD Lys751Gln and XPD Asp312Asn polymorphisms, interactions with smoking, alcohol and dietary factors, and risk of colorectal cancer. Mutat. Res. 2007, 619, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.Y.; Berndt, S.I.; Kang, D.; Chatterjee, N.; Chanock, S.J.; Yeager, M.; Welch, R.; Bresalier, R.S.; Weissfeld, J.L.; Hayes, R.B. Nucleotide excision repair gene polymorphisms and risk of advanced colorectal adenoma: XPC polymorphisms modify smoking-related risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardini, B.; Naccarati, A.; Novotny, J.; Smerhovsky, Z.; Vodickova, L.; Polakova, V.; Hanova, M.; Slyskova, J.; Tulupova, E.; Kumar, R.; et al. DNA repair genetic polymorphisms and risk of colorectal cancer in the Czech Republic. Mutat. Res. 2008, 638, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszkowska-Szczur, K.; Scott, R.J.; Gorski, B.; Cybulski, C.; Kurzawski, G.; Dymerska, D.; Gupta, S.; van de Wetering, T.; Masojc, B.; Kashyap, A.; et al. Polymorphisms in nucleotide excision repair genes and susceptibility to colorectal cancer in the Polish population. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 42, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steck, S.E.; Butler, L.M.; Keku, T.; Antwi, S.; Galanko, J.; Sandler, R.S.; Hu, J.J. Nucleotide excision repair gene polymorphisms, meat intake and colon cancer risk. Mutat. Res. 2014, 762, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Jin, M.; Liu, B.; Liang, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, Q.; Ma, X.; Yao, K.; Chen, K. The association of XPC polymorphisms and tea drinking with colorectal cancer risk in a Chinese population. Mol. Carcinog. 2011, 50, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, A.M.; Xie, Z.B.; Zhao, H.F.; Guo, S.P.; Shen, Y.H.; Wang, H.P. Associations of ABCD1 and XPC genetic polymorphisms with susceptibility to colorectal cancer and therapeutic prognosis in a Chinese population. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 3085–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Sun, H.; Liu, Z.; Huang, R.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Q.; Yu, L.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X. Lack of associations between XPC polymorphisms and colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. J. BUON 2015, 20, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ke, J.; Lou, J.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Gong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; et al. Identification of a functional variant for colorectal cancer risk mapping to chromosome 5q31.1. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35199–35207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Qiu, L.X.; Wang, M.Y.; Hua, R.X.; Zhang, R.X.; Yu, H.P.; Wang, Y.N.; Sun, M.H.; Zhou, X.Y.; Yang, Y.J.; et al. Polymorphisms in the XPG gene and risk of gastric cancer in Chinese populations. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhu, M.; He, J.; Wang, J.C.; Jin, L.; Wang, X.F.; Xiang, J.Q.; Wei, Q. Associations of PI3KR1 and mTOR polymorphisms with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk and gene-environment interactions in Eastern Chinese populations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; He, J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J.C.; Jin, L.; Wang, X.F.; Yang, Y.J.; Xiang, J.Q.; Wei, Q. Polymorphisms in the AKT1 and AKT2 genes and oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk in an Eastern Chinese population. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Hua, R.X.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, L.Q.; Sun, X.; Luan, J.; Lang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shang, K.; Peng, S.; et al. Association studies of ERCC1 polymorphisms with lung cancer susceptibility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Liao, X.Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Xue, W.Q.; Shen, G.P.; Huang, S.Y.; Chen, W.; Jia, W.H. Association of mTHFRC677T and A1298C polymorphisms with non-Hodgkin lymphoma susceptibility: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Shan, X.F.; Shang, K.; Xu, H.; He, J.; Cai, Z.G. Relevance of LIG4 gene polymorphisms with cancer susceptibility: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, R.X.; Li, H.P.; Liang, Y.B.; Zhu, J.H.; Zhang, B.; Ye, S.; Dai, Q.S.; Xiong, S.Q.; Gu, Y.; Sun, X.Z. Association between the PARP1 Val762Ala polymorphism and cancer risk: Evidence from 43 studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Cases No. (%) | Controls No. (%) | p a |
|---|---|---|---|
| All subjects | 1141 (100.0) | 1173 (100.0) | |
| Gender | |||
| Males | 753 (66.0) | 789 (67.3) | 0.518 |
| Females | 388 (34.0) | 384 (32.7) | |
| Age, year | 13–89 | 16–80 | |
| Mean b | 55.7 ± 13.7 | 45.2 ± 11.6 | <0.0001 |
| ≤50 | 367 (32.2) | 789 (67.3) | |
| 51–60 | 342 (30.0) | 285 (24.3) | |
| 61–70 | 273 (23.9) | 73 (6.2) | |
| >70 | 159 (13.9) | 26 (2.2) | |
| Smoking status | |||
| Never | 830 (72.7) | 662 (56.4) | <0.0001 |
| Ever | 311 (27.3) | 511 (43.6) | |
| Drinking status | |||
| No | 968 (84.8) | 600 (51.2) | <0.0001 |
| Yes | 173 (15.2) | 573 (48.8) | |
| Pack-years | |||
| 0 | 830 (72.7) | 662 (56.4) | <0.0001 |
| ≤30 | 207 (18.1) | 383 (32.7) | |
| >30 | 104 (9.1) | 128 (10.9) | |
| Sites | |||
| Colon | 505 (44.3) | - | |
| Rectal | 636 (55.7) | - | |
| Duke Stages | |||
| A | 130 (11.4) | - | |
| B | 363 (31.8) | - | |
| C | 359 (31.5) | - | |
| D | 289 (25.3) | - |
| Genotypes | Cases | Controls | p a | OR (95% CI) | p | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs2228001 A > C | |||||||
| AA | 476 (41.7) | 472 (40.2) | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
| AC | 497 (43.6) | 557 (47.5) | 0.89 (0.74–1.06) | 0.172 | 0.92 (0.76–1.13) | 0.667 | |
| CC | 168 (14.7) | 144 (12.3) | 1.16 (0.90–1.50) | 0.266 | 1.15 (0.86–1.54) | 0.426 | |
| AC/CC | 665 (58.3) | 701 (59.8) | 0.470 d | 0.94 (0.80–1.11) | 0.470 | 0.97 (0.80–1.17) | 0.752 |
| Additive model | 0.089 c | 1.02 (0.91–1.15) | 0.734 | 1.06 (0.86–1.31) | 0.568 | ||
| AA/AC | 973 (85.3) | 1029 (87.7) | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
| CC | 168 (14.7) | 144 (12.3) | 0.085 e | 1.23 (0.97–1.57) | 0.086 | 1.20 (0.92–1.58) | 0.188 |
| rs2228000 C > T | |||||||
| CC | 432 (37.9) | 429 (36.6) | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
| CT | 531 (46.5) | 583 (49.7) | 0.91 (0.76–1.08) | 0.269 | 0.95 (0.78–1.16) | 0.621 | |
| TT | 178 (15.6) | 161 (13.7) | 1.10 (0.85–1.41) | 0.467 | 1.11 (0.83–1.47) | 0.485 | |
| CT/TT | 709 (62.1) | 744 (63.4) | 0.521 d | 0.95 (0.80–1.12) | 0.521 | 0.99 (0.81–1.19) | 0.878 |
| Additive model | 0.241 c | 1.01 (0.90–1.14) | 0.837 | 1.03 (0.90–1.18) | 0.688 | ||
| CC/CT | 963 (84.4) | 1012 (86.3) | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
| TT | 178 (15.6) | 161 (13.7) | 0.202 e | 1.16 (0.92–1.46) | 0.203 | 1.14 (0.88–1.48) | 0.327 |
| Combined effect of XPC risk genotypes | |||||||
| 0 | 71 (6.2) | 77 (6.6) | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
| 1 | 766 (67.1) | 747 (63.7) | 1.11 (0.79–1.56) | 0.538 | 1.13 (0.77–1.66) | 0.524 | |
| 2 | 304 (26.6) | 349 (29.8) | 0.208 | 0.95 (0.66–1.35) | 0.756 | 1.03 (0.69–1.54) | 0.884 |
| Variables | rs2228001 A > C (Cases/Controls) | OR (95% CI) | p | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p a | rs2228000 C > T (Cases/Controls) | OR (95% CI) | p | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA/AC | CC | CC/CT | TT | |||||||||
| Median age, years | ||||||||||||
| ≤57 | 501/874 | 97/125 | 1.35 (1.02–1.80) | 0.039 | 1.37 (1.004–1.86) | 0.047 | 500/865 | 98/134 | 1.27 (0.95–1.68) | 0.103 | 1.20 (0.89–1.62) | 0.236 |
| >57 | 472/155 | 71/19 | 1.23 (0.72–2.10) | 0.456 | 1.09 (0.63–1.89) | 0.749 | 463/147 | 80/27 | 0.94 (0.59–1.51) | 0.801 | 0.93 (0.57–1.50) | 0.755 |
| Gender | ||||||||||||
| Males | 643/689 | 110/100 | 1.18 (0.88–1.58) | 0.269 | 1.14 (0.81–1.60) | 0.445 | 628/685 | 125/104 | 1.31 (0.99–1.74) | 0.060 | 1.28 (0.92–1.77) | 0.140 |
| Females | 330/340 | 58/44 | 1.36 (0.89–2.07) | 0.153 | 1.47 (0.91–2.39) | 0.116 | 335/327 | 53/57 | 0.91 (0.61–1.36) | 0.638 | 0.90 (0.58–1.42) | 0.661 |
| Smoking status | ||||||||||||
| Never | 701/586 | 129/76 | 1.42 (1.05–1.92) | 0.024 | 1.37 (0.96–1.95) | 0.084 | 705/569 | 125/93 | 1.08 (0.81–1.45) | 0.584 | 1.15 (0.82–1.61) | 0.433 |
| Ever | 272/443 | 39/68 | 0.93 (0.61–1.43) | 0.753 | 1.03 (0.65–1.64) | 0.898 | 258/443 | 53/68 | 1.34 (0.91–1.98) | 0.144 | 1.16 (0.75–1.81) | 0.501 |
| Pack-year | ||||||||||||
| 0 | 701/586 | 129/76 | 1.42 (1.05–1.92) | 0.024 | 1.37 (0.96–1.95) | 0.084 | 705/569 | 125/93 | 1.08 (0.81–1.45) | 0.584 | 1.15 (0.82–1.61) | 0.433 |
| ≤30 | 175/328 | 32/55 | 1.09 (0.68–1.75) | 0.720 | 1.00 (0.59–1.71) | 0.991 | 170/330 | 37/53 | 1.36 (0.86–2.14) | 0.194 | 1.13 (0.66–1.93) | 0.656 |
| >30 | 97/115 | 7/13 | 0.64 (0.25–1.66) | 0.358 | 0.87 (0.32–2.38) | 0.791 | 88/113 | 16/15 | 1.37 (0.64–2.92) | 0.416 | 1.18 (0.53–2.62) | 0.681 |
| Drinking status | ||||||||||||
| Never | 813/533 | 155/67 | 1.52 (1.12–2.06) | 0.008 | 1.53 (1.10–2.12) | 0.011 | 818/512 | 150/88 | 1.07 (0.80–1.42) | 0.658 | 1.09 (0.81–1.48) | 0.575 |
| Ever | 160/496 | 13/77 | 0.52 (0.28–0.97) | 0.039 | 0.63 (0.32–1.23) | 0.178 | 145/500 | 28/73 | 1.32 (0.82–2.12) | 0.247 | 1.48 (0.84–2.61) | 0.175 |
| Tumor sites | ||||||||||||
| Colon | 431/1209 | 74/144 | 1.23 (0.91–1.66) | 0.185 | 1.31 (0.93–1.85) | 0.124 | 429/1012 | 76/161 | 1.11 (0.83–1.50) | 0.475 | 1.12 (0.80–1.57) | 0.497 |
| Rectal | 542/1209 | 94/144 | 1.24 (0.94–1.64) | 0.133 | 1.15 (0.84–1.58) | 0.377 | 534/1012 | 102/161 | 1.20 (0.92–1.57) | 0.183 | 1.14 (0.84–1.54) | 0.394 |
| Duke stages | ||||||||||||
| A + B | 425/1209 | 68/144 | 1.14 (0.84–1.56) | 0.397 | 1.10 (0.77–1.58) | 0.593 | 421/1012 | 72/161 | 1.08 (0.80–1.45) | 0.637 | 1.09 (0.77–1.54) | 0.644 |
| C + D | 548/1209 | 100/144 | 1.30 (0.99–1.72) | 0.059 | 1.31 (0.97–1.79) | 0.083 | 542/1012 | 106/161 | 1.23 (0.94–1.61) | 0.129 | 1.18 (0.88–1.59) | 0.272 |
| Study | Year | Country | Ethnicity | Source | Genotyping | Number of Cases | Number of Controls | MAF | HWE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs2228001 A > C | All | AA | AC | CC | All | AA | AC | CC | |||||||
| Huang | 2006 | USA | Caucasian | PB | TaqMan | 665 | 253 | 300 | 112 | 667 | 241 | 312 | 114 | 0.40 | 0.450 |
| Hansen | 2007 | Denmark | Caucasian | PB | TaqMan | 395 | 141 | 204 | 50 | 797 | 307 | 392 | 98 | 0.37 | 0.112 |
| Pardini | 2008 | Czech | Caucasian | HB | PCR-RFLP | 532 | 171 | 268 | 93 | 532 | 189 | 243 | 100 | 0.42 | 0.165 |
| Engin | 2010 | Turkey | Caucasian | HB | PCR-RFLP | 110 | 22 | 63 | 25 | 116 | 25 | 55 | 36 | 0.55 | 0.642 |
| Wu | 2011 | China | Asian | PB | PCR-RFLP | 420 | 155 | 204 | 61 | 842 | 363 | 375 | 104 | 0.35 | 0.639 |
| Gil | 2012 | Poland | Caucasian | HB | PCR-RFLP | 133 | 48 | 71 | 14 | 100 | 43 | 46 | 11 | 0.34 | 0.803 |
| Liu | 2012 | China | Asian | PB | TaqMan | 1028 | 360 | 565 | 103 | 1085 | 453 | 500 | 132 | 0.35 | 0.740 |
| Yue | 2013 | China | Asian | HB | PCR-RFLP | 428 | 142 | 225 | 61 | 450 | 174 | 212 | 64 | 0.38 | 0.964 |
| Ahmad Aizat | 2013 | Malaysia | Asian | HB | PCR-RFLP | 255 | 108 | 106 | 41 | 255 | 129 | 100 | 26 | 0.30 | 0.316 |
| Steck | 2014 | USA | Caucasian | PB | MassARRAY | 303 | 103 | 148 | 52 | 532 | 191 | 252 | 89 | 0.40 | 0.704 |
| Steck | 2014 | USA | African | PB | MassARRAY | 226 | 126 | 91 | 9 | 322 | 149 | 142 | 31 | 0.32 | 0.736 |
| Paszkowska-Szczur | 2015 | Poland | Caucasian | PB | TaqMan | 471 | 187 | 202 | 82 | 1336 | 480 | 647 | 209 | 0.40 | 0.711 |
| Hua | Current | China | Asian | PB | TaqMan | 1141 | 476 | 497 | 168 | 1173 | 472 | 557 | 144 | 0.36 | 0.300 |
| rs2228000 C > T | All | CC | CT | TT | All | CC | CT | TT | |||||||
| Huang | 2006 | USA | Caucasian | PB | TaqMan | 689 | 397 | 261 | 31 | 703 | 403 | 259 | 41 | 0.24 | 0.942 |
| Wu | 2011 | China | Asian | PB | PCR-RFLP | 419 | 172 | 195 | 52 | 838 | 315 | 406 | 117 | 0.38 | 0.447 |
| Steck | 2014 | USA | Caucasian | PB | MassARRAY | 303 | 177 | 104 | 22 | 535 | 293 | 207 | 35 | 0.26 | 0.847 |
| Steck | 2014 | USA | African | PB | MassARRAY | 228 | 175 | 51 | 2 | 323 | 276 | 47 | 0 | 0.07 | 0.158 |
| Paszkowska-Szczur | 2015 | Poland | Caucasian | PB | TaqMan | 753 | 443 | 269 | 41 | 1288 | 548 | 563 | 177 | 0.36 | 0.094 |
| Hua | Current | China | Asian | PB | TaqMan | 1141 | 432 | 531 | 178 | 1173 | 429 | 583 | 161 | 0.39 | 0.095 |
| Variables | No. of Studies | Homozygous | Heterozygous | Recessive | Dominant | Allele Comparison | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p het | OR (95% CI) | p het | OR (95% CI) | p het | OR (95% CI) | p het | OR (95% CI) | p het | ||
| rs2228001 A > C | CC vs. AA | AC vs. AA | CC vs. (AC + AA) | (AC + CC) vs. AA | C vs. A | ||||||
| All | 13 | 1.07 (0.96–1.19) | 0.175 | 1.09 (0.96–1.24) | 0.002 | 1.01 (0.89–1.15) | 0.083 | 1.08 (0.97–1.21) | 0.005 | 1.04 (0.97–1.12) | 0.050 |
| Ethnicity | |||||||||||
| Caucasian | 7 | 1.01 (0.87–1.18) | 0.984 | 1.04 (0.90–1.20) | 0.169 | 0.99 (0.87–1.14) | 0.789 | 1.02 (0.91–1.14) | 0.384 | 1.01 (0.94–1.08) | 0.851 |
| Asian | 5 | 1.18 (1.02–1.38) | 0.294 | 1.20 (0.98–1.48) | 0.004 | 1.11 (0.89–1.39) | 0.061 | 1.21 (1.03–1.43) | 0.030 | 1.12 (1.03–1.21) | 0.266 |
| African | 1 | 0.34 (0.16–0.75) | / | 0.76 (0.53–1.08) | / | 0.39 (0.18–0.84) | / | 0.68 (0.49–0.96) | / | 0.69 (0.52–0.90) | / |
| Source of control | |||||||||||
| PB | 8 | 1.04 (0.92–1.17) | 0.122 | 1.02 (0.87–1.20) | <0.001 | 1.01 (0.87–1.19) | 0.072 | 1.02 (0.88–1.18) | 0.002 | 1.02 (0.94–1.11) | 0.040 |
| HB | 5 | 1.16 (0.93–1.45) | 0.358 | 1.27 (1.08–1.49) | 0.995 | 1.00 (0.77–1.30) | 0.193 | 1.25 (1.07–1.45) | 0.924 | 1.11 (0.99–1.25) | 0.315 |
| rs2228000 C > T | TT vs. CC | CT vs. CC | TT vs. (CT + CC) | (CT + TT) vs. CC | T vs. C | ||||||
| All | 6 | 0.77 (0.46–1.31) | <0.001 | 0.91 (0.72–1.14) | <0.001 | 0.83 (0.52–1.30) | <0.001 | 0.90 (0.69–1.19) | <0.001 | 0.93(0.72–1.19) | <0.001 |
| Ethnicity | |||||||||||
| Caucasian | 3 | 0.60 (0.26–1.36) | <0.001 | 0.79 (0.56–1.13) | 0.001 | 0.66 (0.33–1.31) | 0.001 | 0.76 (0.49–1.17) | <0.001 | 0.78 (0.53–1.15) | <0.001 |
| Asian | 2 | 0.98 (0.74–1.30) | 0.195 | 0.90 (0.78–1.04) | 0.860 | 1.04 (0.79–1.37) | 0.182 | 0.92 (0.80–1.05) | 0.547 | 0.97 (0.87–1.09) | 0.261 |
| African | 1 | 7.88 (0.38–165.05) | / | 1.71 (1.10–2.66) | / | 7.14 (0.34–149.46) | / | 1.78 (1.15–2.75) | / | 1.75 (1.16–2.63) | / |
| Source of control | |||||||||||
| PB | 6 | 0.77 (0.46–1.31) | <0.001 | 0.91 (0.72–1.14) | <0.001 | 0.83 (0.52–1.30) | <0.001 | 0.90 (0.69–1.19) | <0.001 | 0.93(0.72–1.19) | <0.001 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, R.-X.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, D.-H.; Zhang, S.-D.; Zhang, J.-B.; Xue, W.-Q.; Li, X.-Z.; Zhang, P.-F.; He, J.; Jia, W.-H. Association of XPC Gene Polymorphisms with Colorectal Cancer Risk in a Southern Chinese Population: A Case-Control Study and Meta-Analysis. Genes 2016, 7, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7100073
Hua R-X, Zhu J, Jiang D-H, Zhang S-D, Zhang J-B, Xue W-Q, Li X-Z, Zhang P-F, He J, Jia W-H. Association of XPC Gene Polymorphisms with Colorectal Cancer Risk in a Southern Chinese Population: A Case-Control Study and Meta-Analysis. Genes. 2016; 7(10):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7100073
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Rui-Xi, Jinhong Zhu, Dan-Hua Jiang, Shao-Dan Zhang, Jiang-Bo Zhang, Wen-Qiong Xue, Xi-Zhao Li, Pei-Fen Zhang, Jing He, and Wei-Hua Jia. 2016. "Association of XPC Gene Polymorphisms with Colorectal Cancer Risk in a Southern Chinese Population: A Case-Control Study and Meta-Analysis" Genes 7, no. 10: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7100073
APA StyleHua, R.-X., Zhu, J., Jiang, D.-H., Zhang, S.-D., Zhang, J.-B., Xue, W.-Q., Li, X.-Z., Zhang, P.-F., He, J., & Jia, W.-H. (2016). Association of XPC Gene Polymorphisms with Colorectal Cancer Risk in a Southern Chinese Population: A Case-Control Study and Meta-Analysis. Genes, 7(10), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes7100073






