Identification and Expression Analysis of PIN-Like (PILS) Gene Family of Rice Treated with Auxin and Cytokinin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.3. qRT-PCR Analysis for Gene Expression
| Gene Name | Locus ID | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| OsPILS1 | LOC_Os09g31478.1 | AGCAAGCGTCCAGCCTTCAG | CTCTCCCCCACGCCGAACAG |
| OsPILS2 | LOC_Os08g09190.1 | CTCCAGCCACCAACCATCG | CGGGAGAATCAGGAGCCTTGC |
| OsPILS5 | LOC_Os07g20510.1 | GTCGTCCTCGCCTCCATCCA | CGCACCTTCCAAAGCAGAGC |
| OsPILS6a | LOC_Os01g60230.1 | GATGGAGAGGTCGCTGATGGAG | GCGAGAACACAAGCCCATTG |
| OsPILS6b | LOC_Os05g40330.1 | GAGGTCGGTGCTGGAGATGGTG | GGCAAGGAAGGAGCAGAGAGAACAC |
| OsPILS7a | LOC_Os09g38130.1 | CCGCTCTCGTGGGCTCTCCT | GCCGCCTCCTCATCAGCGTA |
| OsPILS7b | LOC_Os09g38210.1 | GAAGATGGCAACCCGTTCGG | CCTCCTCATCGGCGTAAGCA |
3. Results
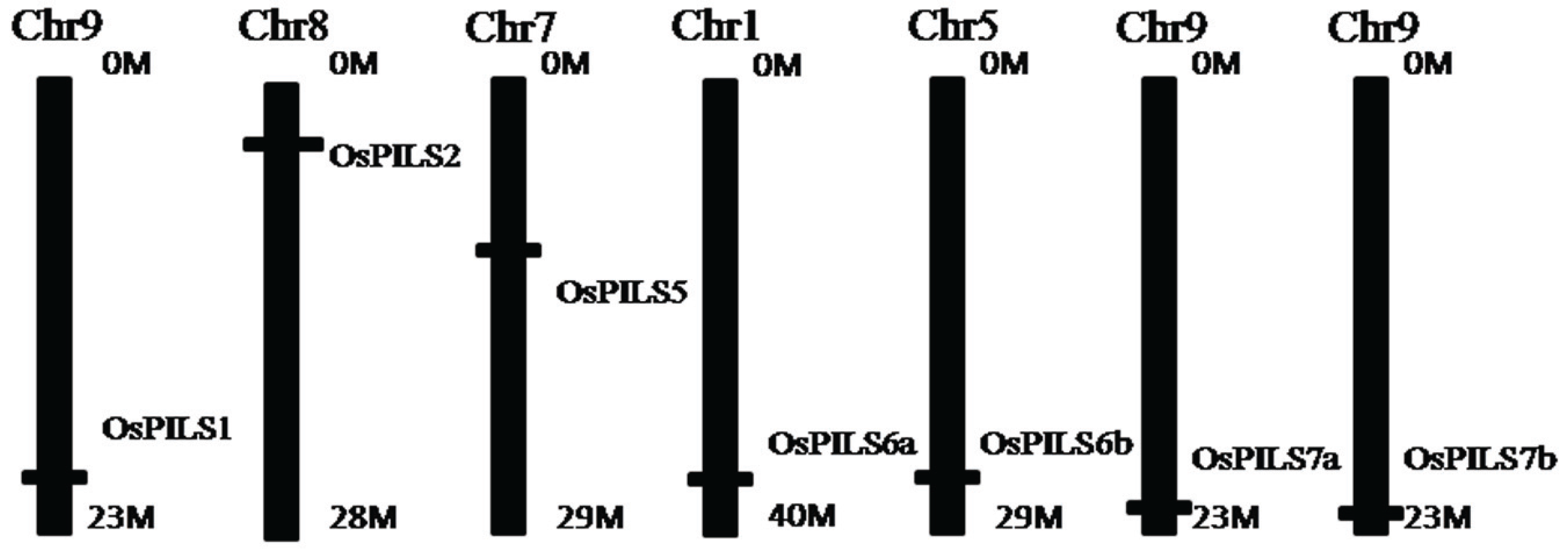
3.1. Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of OsPILS Genes
| Gene Name | Locus ID | ORF | No. of Amino Acids | No. of Introns | 5'–3' Coordinates | pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsPILS1 | LOC_Os09g31478.1 | 1242 | 414 | 10 | Chr9: 18983481–18978136 | 8.38 |
| OsPILS2 | LOC_Os08g09190.1 | 1368 | 456 | 1 | Chr8: 5322709–5325262 | 6.93 |
| OsPILS5 | LOC_Os07g20510.1 | 3840 | 1280 | 7 | Chr7: 11845862–11851637 | 6.91 |
| OsPILS6a | LOC_Os01g60230.1 | 1299 | 433 | 10 | Chr1: 34834581–34838747 | 8.02 |
| OsPILS6b | LOC_Os05g40330.1 | 1314 | 438 | 10 | Chr5: 23700670–23697738 | 8.20 |
| OsPILS7a | LOC_Os09g38130.1 | 1287 | 429 | 10 | Chr9: 21963498–21968222 | 7.02 |
| OsPILS7b | LOC_Os09g38210.1 | 1272 | 424 | 9 | Chr9: 22007511–22010336 | 7.23 |


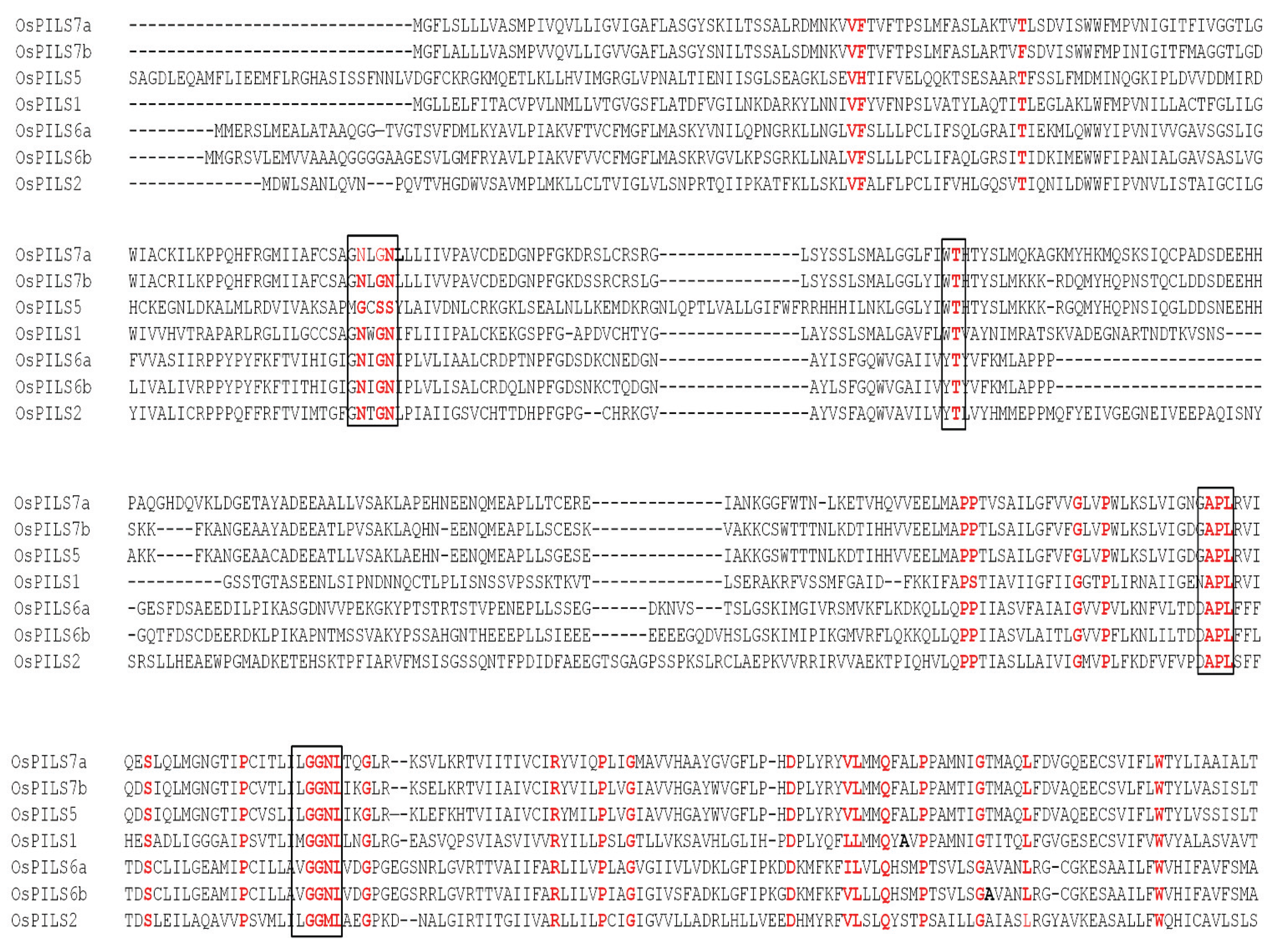

3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of OsPILS

3.3. Expression of OsPILS Genes in Leaf Tissue Treated with IAA
3.4. Expression of OsPILS Genes in Root Tissue Treated with IAA
3.5. Expression of OsPILS Genes in Leaf Tissue Treated with Cytokinin
3.6. Expression of OsPILS Genes in Root Tissue Treated with Cytokinin


4. Discussion
| Gene | Protein domains | Putative Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|
| OsPILS1 | Integral membrane protein | Vacuolar |
| OsPILS2 | Integral membrane protein | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| OsPILS5 | Integral membrane protein | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| OsPILS6a | Integral membrane protein | Vacuolar |
| OsPILS6b | Integral membrane protein | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| OsPILS7a | Integral membrane protein | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| OsPILS7b | Integral membrane protein | Plasmamembrane & ER |
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgment
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sabatini, S.; Beis, D.; Wolkenfelt, H.; Murfett, J.; Guilfoyle, T.; Malamy, J.; Benfey, P.; Leyser, O.; Bechtold, N.; Weisbeek, P.; et al. An auxin-dependent distal organizer of pattern and polarity in the Arabidopsis root. Cell 1999, 99, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friml, J.; Palme, K. Polar auxin transport—Old questions and new concepts? Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 49, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benková, E.; Michniewicz, M.; Sauer, M.; Teichmann, T.; Seifertová, D.; Jürgens, G.; Friml, J. Local, efflux-dependent auxin gradients as a common module for plant organ formation. Cell 2003, 115, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feraru, E.; Feraru, M.I.; Kleine-Vehn, J.; Martinière, A.; Mouille, G.; Vanneste, S.; Vernhettes, S.; Runions, J.; Friml, J. PIN polarity maintenance by the cell wall in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Mohanta, T.K.; Sinha, A.K. Unraveling the intricate nexus of molecular mechanisms governing rice root development: OsMPK3/6 and auxin-cytokinin interplay. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peer, W.A.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Blakeslee, J.J.; Makam, S.N.; Chen, R.J.; Masson, P.H.; Murphy, A.S. Variation in expression and protein localization of the PIN family of auxin efflux facilitator proteins in flavonoid mutants with altered auxin transport in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2010, 16, 1898–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forestan, C.; Varotto, S. The role of PIN auxin efflux carriers in polar auxin transport and accumulation and their effect on shaping maize development. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zazímalová, E.; Murphy, A.S.; Yang, H.; Hoyerová, K.; Hosek, P. Auxin transporters––why so many? Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abas, L.; Benjamins, R.; Malenica, N.; Paciorek, T.; Wiśniewska, J.; Wirniewska, J.; Moulinier-Anzola, J.C.; Sieberer, T.; Friml, J.; Luschnig, C. Intracellular trafficking and proteolysis of the Arabidopsis auxin-efflux facilitator PIN2 are involved in root gravitropism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbez, E.; Kubeš, M.; Rolčík, J.; Béziat, C.; Pěnčík, A.; Wang, B.; Rosquete, M.R.; Zhu, J.; Dobrev, P.I.; Lee, Y.; et al. A novel putative auxin carrier family regulates intracellular auxin homeostasis in plants. Nature 2012, 485, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gälweiler, L.; Guan, C.; Müller, A.; Wisman, E.; Mendgen, K.; Yephremov, A.; Palme, K. Regulation of polar auxin transport by AtPIN1 in Arabidopsis vascular tissue. Science 1998, 282, 2226–2230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blilou, I.; Xu, J.; Wildwater, M.; Willemsen, V.; Paponov, I.; Friml, J.; Heidstra, R.; Aida, M.; Palme, K.; Scheres, B. The PIN auxin efflux facilitator network controls growth and patterning in Arabidopsis roots. Nature 2005, 433, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-R.; Hu, H.; Wang, G.-H.; Li, J.; Chen, J.-Y.; Wu, P. Expression of PIN genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Tissue specificity and regulation by hormones. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friml, J.; Wiśniewska, J.; Benková, E.; Mendgen, K.; Palme, K. Lateral relocation of auxin efflux regulator PIN3 mediates tropism in Arabidopsis. Nature 2002, 415, 806–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paponov, I.A.; Teale, W.D.; Trebar, M.; Blilou, I.; Palme, K. The PIN auxin efflux facilitators: Evolutionary and functional perspectives. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estelle, M. Polar auxin transport. New support for an old model. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1775–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Men, S.; Fischer, U.; Stepanova, A.N.; Alonso, J.M.; Ljung, K.; Grebe, M. Local auxin biosynthesis modulates gradient-directed planar polarity in Arabidopsis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrásek, J.; Mravec, J.; Bouchard, R.; Blakeslee, J.J.; Abas, M.; Seifertová, D.; Wisniewska, J.; Tadele, Z.; Kubes, M.; Covanová, M.; et al. PIN proteins perform a rate-limiting function in cellular auxin efflux. Science 2006, 312, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Křeček, P.; Skůpa, P.; Libus, J.; Naramoto, S.; Tejos, R.; Friml, J.; Zažímalová, E. Protein family review the PIN-FORMED ( PIN ) protein family of auxin transporters. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mravec, J.; Skůpa, P.; Bailly, A.; Hoyerová, K.; Krecek, P.; Bielach, A.; Petrásek, J.; Zhang, J.; Gaykova, V.; Stierhof, Y.-D.; et al. Subcellular homeostasis of phytohormone auxin is mediated by the ER-localized PIN5 transporter. Nature 2009, 459, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanta, T.K.; Mohanta, N. Genome wide identification of auxin efflux carrier gene family in Solanum tuberosum L. J. Nat. Sci. 2013, 1, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanta, T.K.; Mohanta, N. Genome wide identification of auxin efflux carrier gene family in physcomitrella patens. J. Biotechnol. Sci. 2013, 1, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, E.M.; Bennett, M.J. Auxin transport: A field in flux. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, S.; Zhu, W.; Hamilton, J.; Lin, H.; Campbell, M.; Childs, K.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Malek, R.L.; Lee, Y.; Zheng, L.; et al. The TIGR rice genome annotation resource: Improvements and new features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D883–D887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, L.-P.; Nicole, M.-C.; Sritubtim, S.; Morency, M.-J.; Ellis, M.; Ehlting, J.; Beaudoin, N.; Barbazuk, B.; Klessig, D.; Lee, J.; et al. Ancient signals: Comparative genomics of plant MAPK and MAPKK gene families. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C.; Hwang, J. Prediction of protein subcellular localization. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2006, 64, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhardt, D.; Mandel, T.; Kuhlemeier, C. Auxin regulates the initiation and radial position of plant lateral organs. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Xie, Q.; Fei, J.; Chua, N. MicroRNA directs mRNA cleavage of the transcription factor NAC1 to downregulate auxin signals for Arabidopsislateral root development. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorteau, M.; Ferguson, B.J.; Guinel, C. Effects of cytokinin on ethylene production and nodulation in pea ( Pisumsativum ) cv. Sparkle. Physiol. Plant. 2001, 112, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanta, T.K.; Mohanta, N. Understanding the role of Oryza sativa OsPILS (PIN Like) genes in auxin signaling. Available online: https://peerj.com/preprints/586v1.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2014).
- Mohanta, T.; Malnoy, M.; Mohanta, N.; Kanchiswamy, C. In-silico identification and phylogenetic analysis of auxin efflux carrier gene family in Setaria italica L. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 211–225. [Google Scholar]
- Geldner, N.; Palme, K. Auxin transport inhibitors block PIN1 cycling and vesicle trafficking. Nature 2001, 413, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxmi, A.; Pan, J.; Morsy, M.; Chen, R. Light plays an essential role in intracellular distribution of auxin efflux carrier PIN2 in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrovsky, J.G.; Sauer, M.; Napsucialy-Mendivil, S.; Ivanchenko, M.G.; Friml, J.; Shishkova, S.; Celenza, J.; Benková, E. Auxin acts as a local morphogenetic trigger to specify lateral root founder cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8790–8794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliday, K.J.; Martínez-García, J.F.; Josse, E.-M. Integration of light and auxin signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupinski, P.; Jönsson, H. Modeling auxin-regulated development. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSteen, P. Auxin and monocot development. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, B.; Weijers, D. Auxin control of embryo patterning. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overvoorde, P.; Fukaki, H.; Beeckman, T. Auxin control of root development. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpella, E.; Barkoulas, M.; Tsiantis, M. Control of leaf and vein development by auxin. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friml, J. Auxin transport-shaping the plant. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, A.W.; Bartel, B. Auxin: Regulation, action, and interaction. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyser, O. Dynamic integration of auxin transport and signalling. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, R424–R433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muday, G.K.; Murphy, A.S. An emerging model of auxin transport regulation. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrásek, J.; Friml, J. Auxin transport routes in plant development. Development 2009, 136, 2675–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, A.K.; Jaggi, M.; Raghuram, B.; Tuteja, N. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plants under abiotic stress. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanta, T.K.; Arora, P.K.; Mohanta, N.; Parida, P.; Bae, H. Identification of new members of the MAPK gene family in plants shows diverse conserved domains and novel activation loop variants. BMC Genomics 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohanta, T.K.; Mohanta, N.; Bae, H. Identification and Expression Analysis of PIN-Like (PILS) Gene Family of Rice Treated with Auxin and Cytokinin. Genes 2015, 6, 622-640. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6030622
Mohanta TK, Mohanta N, Bae H. Identification and Expression Analysis of PIN-Like (PILS) Gene Family of Rice Treated with Auxin and Cytokinin. Genes. 2015; 6(3):622-640. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6030622
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohanta, Tapan Kumar, Nibedita Mohanta, and Hanhong Bae. 2015. "Identification and Expression Analysis of PIN-Like (PILS) Gene Family of Rice Treated with Auxin and Cytokinin" Genes 6, no. 3: 622-640. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6030622
APA StyleMohanta, T. K., Mohanta, N., & Bae, H. (2015). Identification and Expression Analysis of PIN-Like (PILS) Gene Family of Rice Treated with Auxin and Cytokinin. Genes, 6(3), 622-640. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6030622






