Modeling of the SV40 DNA Replication Machine
Abstract
:Abbreviations
| OBD | origin binding domain |
| DH | double hexamer |
| pol/prim | polymerase alpha/primase |
| RPA | replication protein A |
| ssDNA | single-stranded DNA |
| dsDNA | double-stranded DNA |
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
3. Results and Discussion
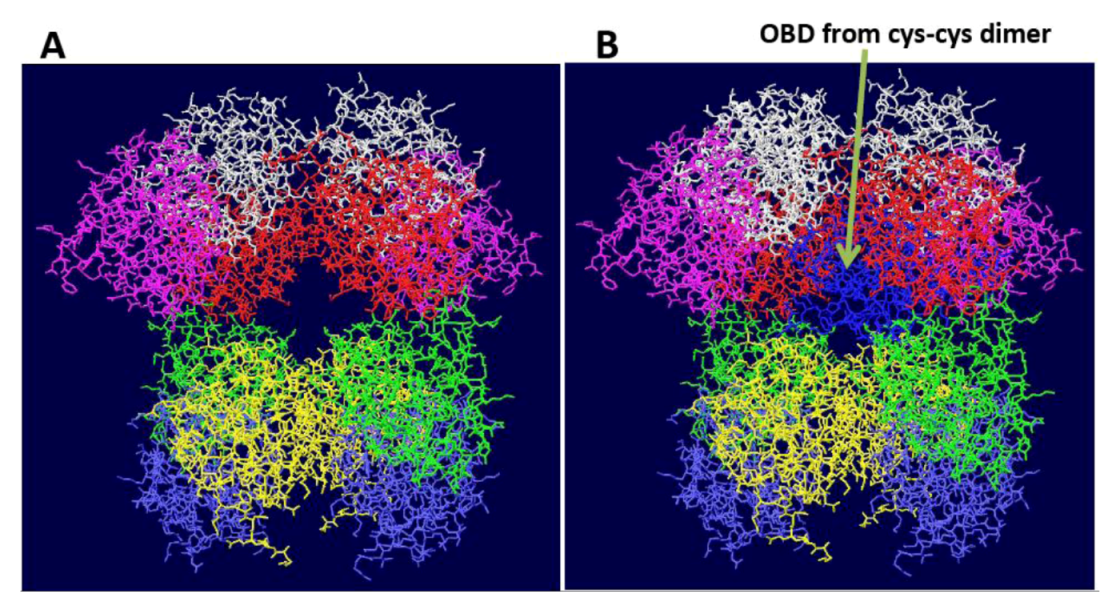
3.1. The Origin Binding Domain Double Hexamer
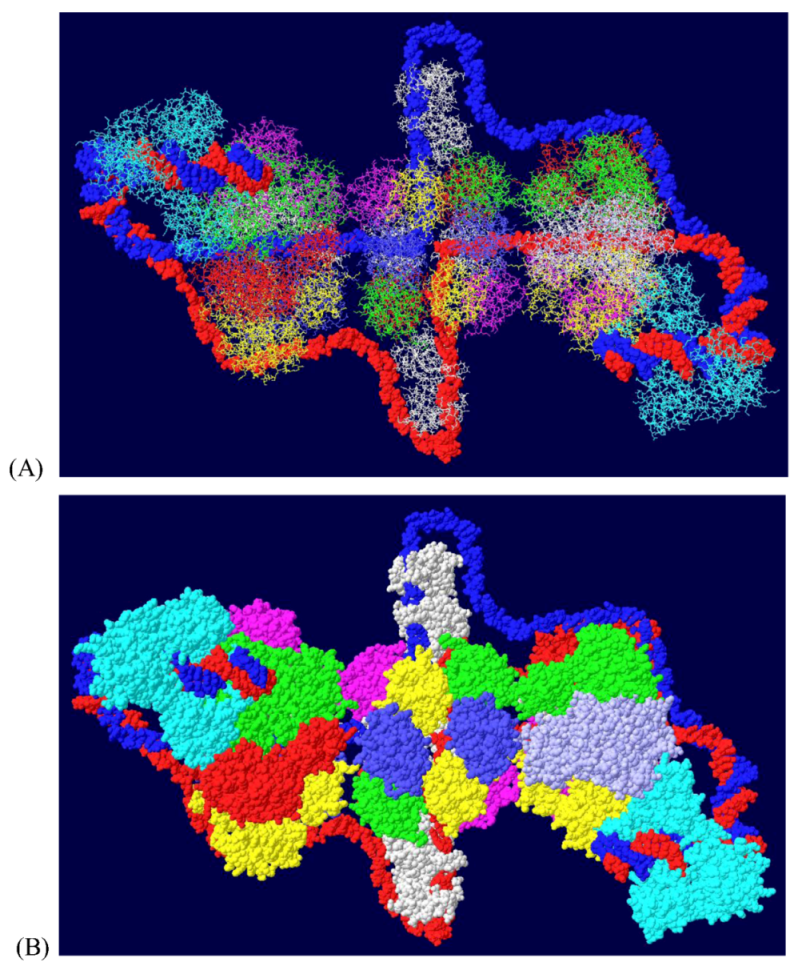
3.2. Structure of theDouble Hexamer
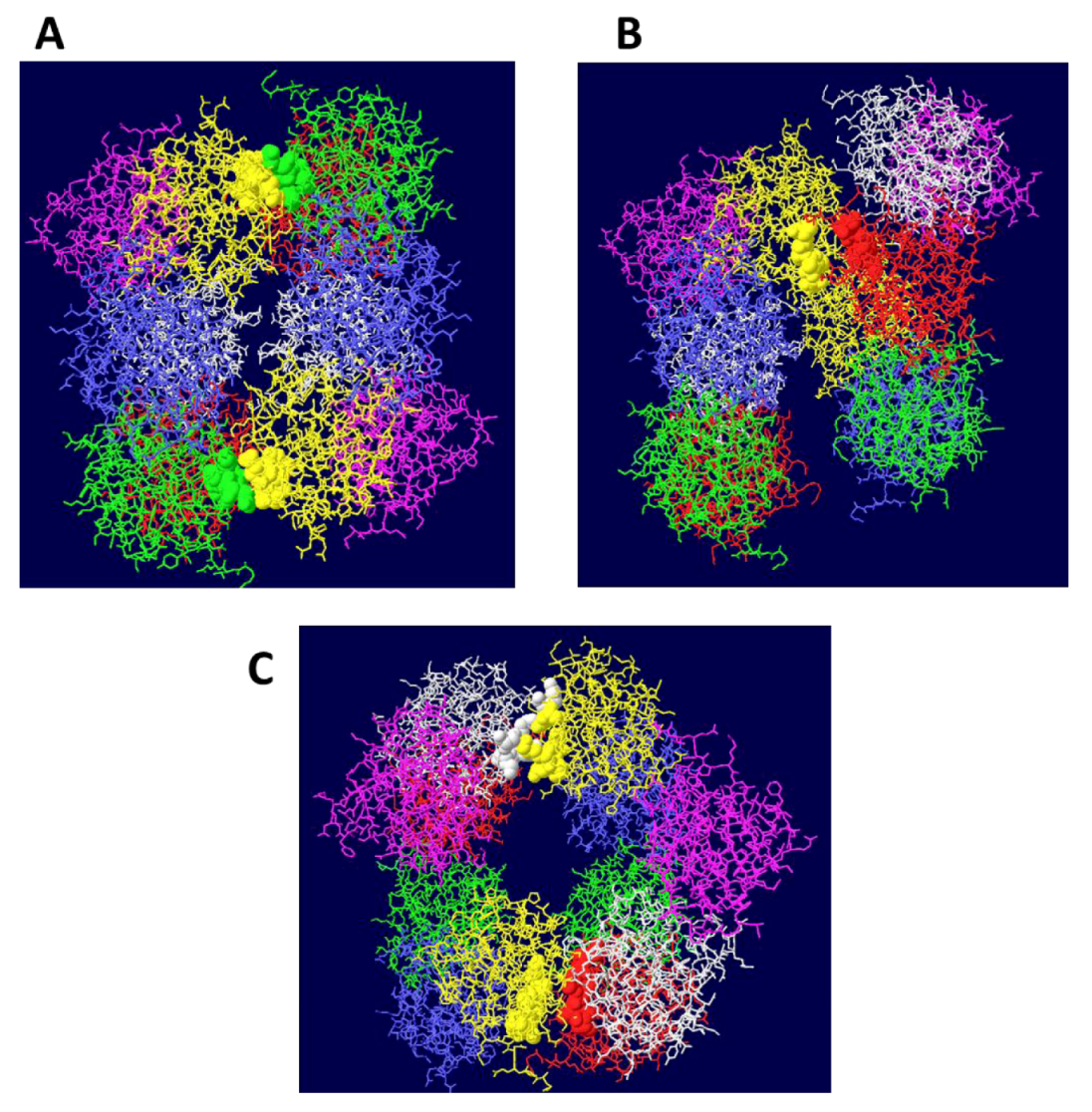
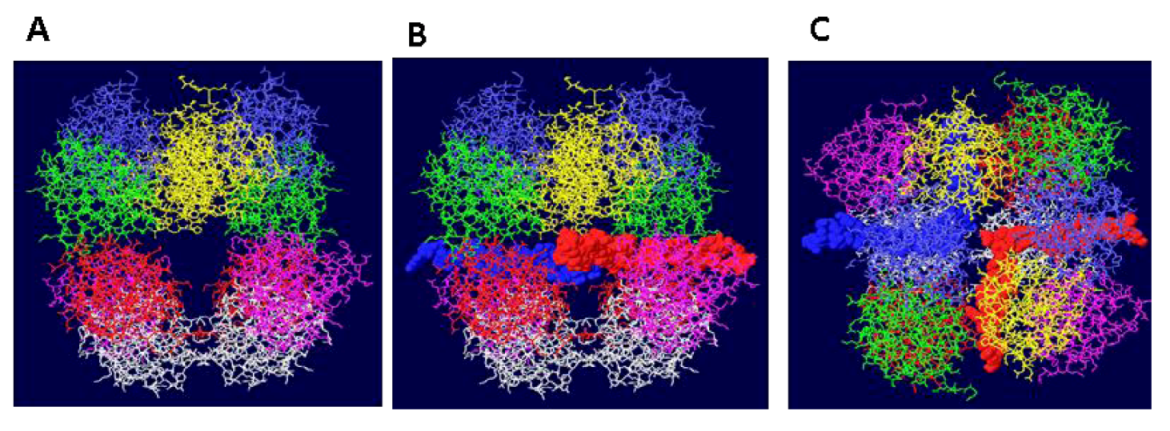

3.3. Mechanism of DNA Unwinding
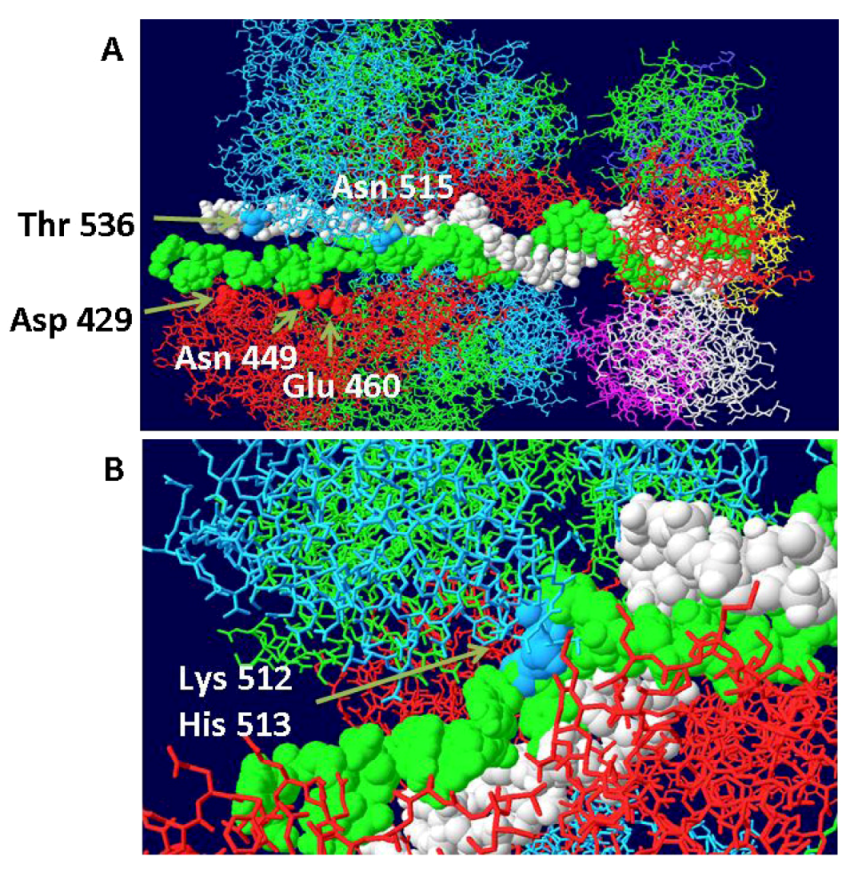
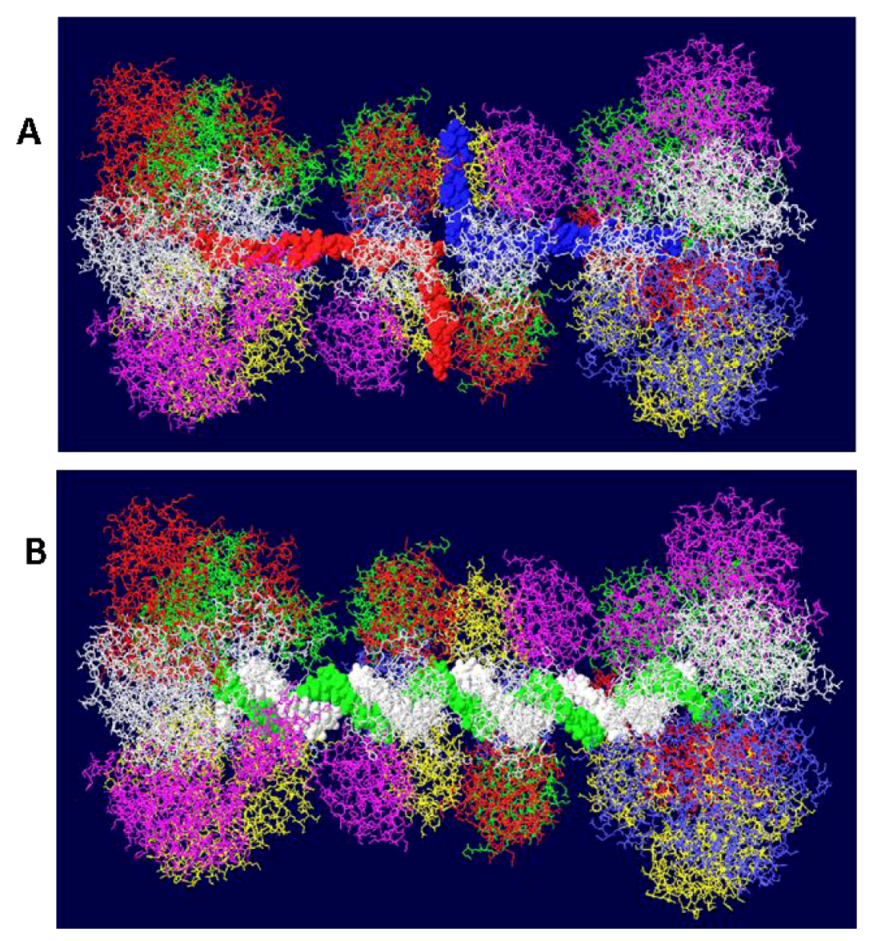
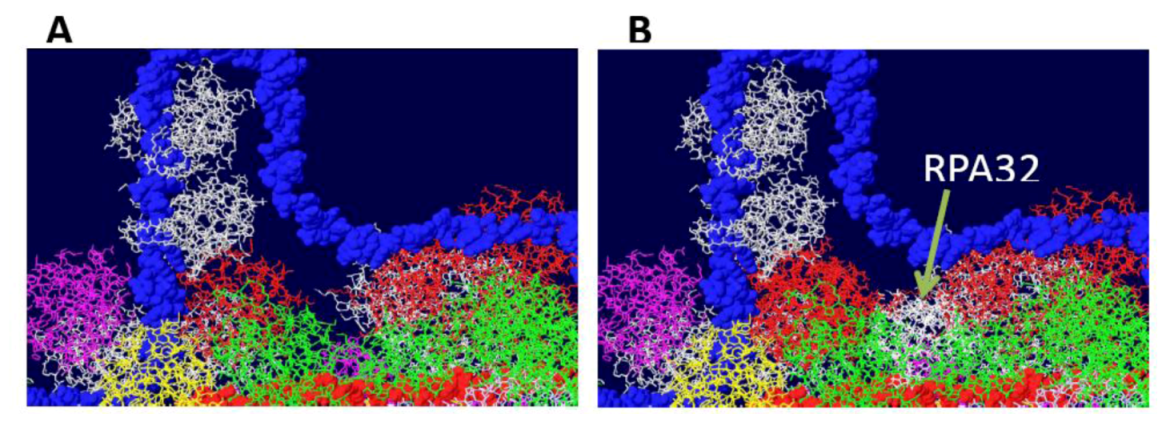
3.4. RPA-DH Structure

3.5. Placement of Topoisomerase I at the C Terminal Regions
3.6. Placement of Part of pol/prim on the RPA/Topo I/T DH
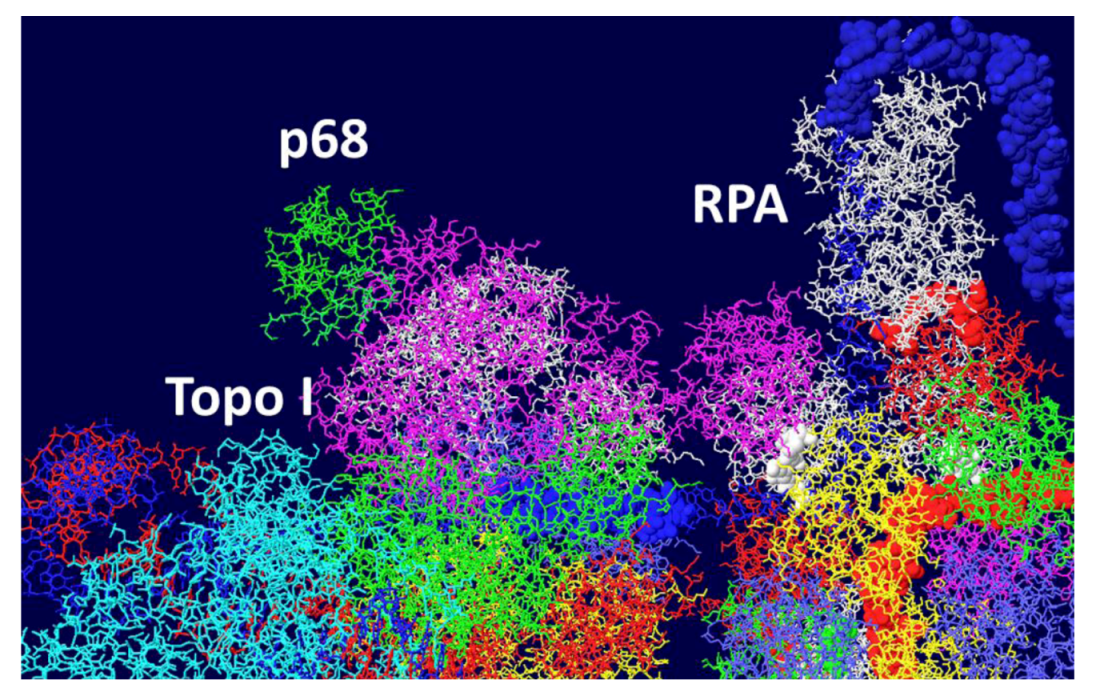
3.7. Position of the J Domain and Topo I at N Terminal Regions
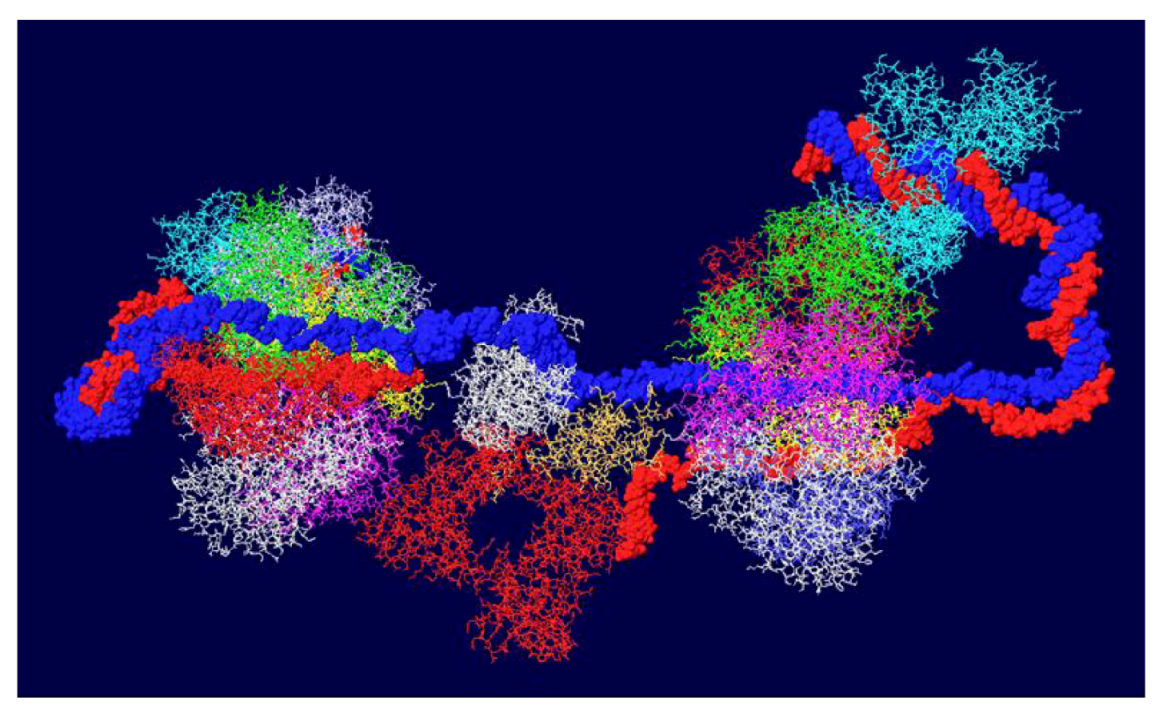
3.8. What Doesn’t Work

4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgements
References
- Simmons, D.T. Initiation of DNA Replication from Closed Circular DNA. In Fundamental Aspects of DNA Replication; Kusic-Tisma, J., Ed.; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 161–186. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, D.T. SV40 large T antigen: Functions in DNA replication and transformation [In Process Citation]. Adv. Virus Res. 2000, 55, 75–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, E.; Zhao, K. SV40 DNA replication: from the A gene to a nanomachine. Virology 2009, 384, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, I.A.; Hough, P.V. C.; Wall, J.S.; Dodson, M.; Dean, F.B.; Hurwitz, J. ATP-dependent assembly of double hexamers of SV40 T antigen at the viral origin of DNA replication. Nature 1989, 338, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, F.B.; Bullock, P.; Murakami, Y.; Wobbe, C.R.; Weissbach, L.; Hurwitz, J. Simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA replication: SV40 large T antigen unwinds DNA containing the SV40 origin of replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wessel, R.; Schweizer, J.; Stahl, H. Simian virus 40 T-antigen DNA helicase is a hexamer which forms a binary complex during bidirectional unwinding from the viral origin of DNA replication. Cell 1992, 66, 804–815. [Google Scholar]
- Eichman, B.F.; Fanning, E. The power of pumping together; deconstructing the engine of a DNA replication machine. Cell 2004, 119, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, D.K.; Sreekumar, K.R.; Bullock, P.A. Interactions required for binding of simian virus 40 T antigen to the viral origin and molecular modeling of initial assembly events. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 2921–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinke, G.; Bullock, P.A.; Bohm, A. Crystal structure of the simian virus 40 large T-antigen origin-binding domain. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4304–4312. [Google Scholar]
- Meinke, G.; Phelan, P.; Moine, S.; Bochkareva, E.; Bochkarev, A.; Bullock, P.A.; Bohm, A. The crystal structure of the SV40 T-antigen origin binding domain in complex with DNA. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinke, G.; Phelan, P.J.; Fradet-Turcotte, A.; Bohm, A.; Archambault, J.; Bullock, P.A. Structure-based analysis of the interaction between the simian virus 40 T-antigen origin binding domain and single-stranded DNA. J. Virol. 2010, 85, 818–827. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkareva, E.; Martynowski, D.; Seitova, A.; Bochkarev, A. Structure of the origin-binding domain of simian virus 40 large T antigen bound to DNA. Embo. J. 2006, 25, 5961–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.T.; Upson, R.; Wun-Kim, K.; Young, W. Biochemical analysis of mutants with changes in the origin-binding domain of simian virus 40 tumor antigen. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4227–4236. [Google Scholar]
- Weisshart, K.; Taneja, P.; Jenne, A.; Herbig, U.; Simmons, D.T.; Fanning, E. Two Regions of Simian Virus 40 T Antigen Determine Cooperativity of Double-Hexamer Assembly on the Viral Origin of DNA Replication and Promote Hexamer Interactions during Bidirectional Origin DNA Unwinding. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar]
- Reese, D.K.; Meinke, G.; Kumar, A.; Moine, S.; Chen, K.; Sudmeier, J.L.; Bachovchin, W.; Bohm, A.; Bullock, P.A. Analyses of the interaction between the origin binding domain from simian virus 40 T antigen and single-stranded DNA provide insights into DNA unwinding and initiation of DNA replication. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 12248–12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, E.C.; Simmons, D.T. The SV40 large T-antigen origin binding domain directly participates in DNA unwinding. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 2087–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, M.; Gruss, C.; Halmer, L.; Carazo, J.M.; Donate, L.E. Large T-antigen double hexamers imaged at the simian virus 40 origin of replication. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanLoock, M.S.; Alexandrov, A.; Yu, X.; Cozzarelli, N.R.; Egelman, E.H. SV40 large T antigen hexamer structure: domain organization and DNA-induced conformational changes. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Lorenzo, M.G.; Valle, M.; Frank, J.; Gruss, C.; Sorzano, C.O.; Chen, X.S.; Donate, L.E.; Carazo, J.M. Large T antigen on the simian virus 40 origin of replication: a 3D snapshot prior to DNA replication. Embo. J. 2003, 22, 6205–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, M.; Chen, X.S.; Donate, L.E.; Fanning, E.; Carazo, J.M. Structural basis for the cooperative assembly of large T antigen on the origin of replication. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 357, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, I.; Nunez-Ramirez, R.; Scheres, S.H.; Gai, D.; Chen, X.S.; Fanning, E.; Carazo, J.M. Conformational rearrangements of SV40 large T antigen during early replication events. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 397, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.T.; Loeber, G.; Tegtmeyer, P. Four major sequence elements of simian virus 40 large T antigen coordinate its specific and nonspecific DNA binding. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, D.T.; Wun-Kim, K.; Young, W. Identification of simian virus 40 T antigen residues important for specific and nonspecific binding to DNA and for helicase activity. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 4858–4865. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Zhao, R.; Lilyestrom, W.; Gai, D.; Zhang, R.; DeCaprio, J.A.; Fanning, E.; Jochimiak, A.; Szakonyi, G.; Chen, X.S. Structure of the replicative helicase of the oncoprotein SV40 large tumour antigen. Nature 2003, 423, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, D.; Zhao, R.; Li, D.; Finkielstein, C.V.; Chen, X.S. Mechanisms of conformational change for a replicative hexameric helicase of SV40 large tumor antigen. Cell 2004, 119, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, D.; Li, D.; Finkielstein, C.V.; Ott, R.D.; Taneja, P.; Fanning, E.; Chen, X.S. Insights into the oligomeric states, conformational changes, and helicase activities of SV40 large tumor antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 38952–38959. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Meinke, G.; Reese, D.K.; Moine, S.; Phelan, P.J.; Fradet-Turcotte, A.; Archambault, J.; Bohm, A.; Bullock, P.A. Model for T-antigen-dependent melting of the simian virus 40 core origin based on studies of the interaction of the beta-hairpin with DNA. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4808–4818. [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec, J.A.; Hurwitz, J. Localized melting and structural changes in the SV40 origin of replication induced by T-antigen. Embo. J. 1988, 7, 3149–3158. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Manna, D.; Simmons, D.T. Role of the hydrophilic channels of simian virus 40 T-antigen helicase in DNA replication. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4510–4519. [Google Scholar]
- Sedman, J.; Stenlund, A. The initiator protein E1 binds to the bovine papillomavirus origin of replication as a trimeric ring-like structure. Embo. J. 1996, 15, 5085–5092. [Google Scholar]
- Enemark, E.J.; Joshua-Tor, L. Mechanism of DNA translocation in a replicative hexameric helicase. Nature 2006, 442, 270–275. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkarev, A.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Edwards, A.M.; Frappier, L. Structure of the single-stranded-DNA-binding domain of replication protein A bound to DNA. Nature 1997, 385, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkareva, E.; Korolev, S.; Lees-Miller, S.P.; Bochkarev, A. Structure of the RPA trimerization core and its role in the multistep DNA-binding mechanism of RPA. Embo. J. 2002, 21, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, A.I.; Klimovich, V.; Jiang, X.; Ott, R.D.; Mizoue, L.; Fanning, E.; Chazin, W.J. Insights into hRPA32 C-terminal domain--mediated assembly of the simian virus 40 replisome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisshart, K.; Taneja, P.; Fanning, E. The replication protein A binding site in simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen and its role in the initial steps of SV40 DNA replication. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 9771–9781. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, R.; Trowbridge, P.; Yang, Z.; Champoux, J.J.; Simmons, D.T. The Cap Region of Topoisomerase I Binds to Sites near Both Ends of Simian Virus 40 T Antigen. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 9809–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Simmons, D.T. Mapping the site of interaction between T antigen and topo I. University of Delaware, Newark, DE, USA, unpublished work, 2008.
- Khopde, S.; Simmons, D.T. Simian virus 40 DNA replication is dependent on an interaction between topoisomerase I and the C-terminal end of T antigen. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornreiter, I.; Hoss, A.; Arthur, A.K.; Fanning, E. SV40 T antigen binds directly to the large subunit of purified DNA polymerase alpha. Embo. J. 1990, 9, 3329–3336. [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter, I.; Erdile, L.F.; Gilbert, I.U.; von Winkler, D.; Kelly, T.J.; Fanning, E. Interaction of DNA polymerase alpha-primase with cellular replication protein A and SV40 T antigen. Embo. J. 1992, 11, 769–776. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.; Weisshart, K.; Guarino, L.A.; Dornreiter, I.; Fanning, E. Species-specific functional interactions of DNA polymerase alpha-primase with simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen require SV40 origin DNA. Mol. Cell Biol 1994, 14, 3176–3185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Arnett, D.R.; Yu, X.; Brewster, A.; Sowd, G.A.; Xie, C.L.; Vila, S.; Gai, D.; Fanning, E.; Chen, X.S. Structural Basis for the Interaction of a Hexameric Replicative Helicase with the Regulatory Subunit of Human DNA Polymerase α-Primase. J. Biol Chem 2012, 287, 26854–26866. [Google Scholar]
- Ott, R.D.; Rehfuess, C.; Podust, V.N.; Clark, J.E.; Fanning, E. Role of the p68 subunit of human DNA polymerase alpha-primase in simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol. Cell Biol 2002, 22, 5669–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khopde, S.; Roy, R.; Simmons, D.T. The Binding of Topoisomerase I to T Antigen Enhances the Synthesis of RNA-DNA Primers during Simian Virus 40 DNA Replication. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 9653–9660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Ahn, B.Y.; Cho, Y. Structural basis for the inactivation of retinoblastoma tumor suppressor by SV40 large T antigen. Embo. J. 2001, 20, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Simmons, D.T. Mapping the site of interaction between T antigen and RPA. University of Delaware, Newark, DE, USA, unpublished work, 2008.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Simmons, D.T. Modeling of the SV40 DNA Replication Machine. Genes 2012, 3, 742-758. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes3040742
Simmons DT. Modeling of the SV40 DNA Replication Machine. Genes. 2012; 3(4):742-758. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes3040742
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimmons, Daniel T. 2012. "Modeling of the SV40 DNA Replication Machine" Genes 3, no. 4: 742-758. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes3040742
APA StyleSimmons, D. T. (2012). Modeling of the SV40 DNA Replication Machine. Genes, 3(4), 742-758. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes3040742



