Management of MET-Driven Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms of Resistance to Osimertinib (Third-Generation EGFR TKI)
3. MET Gene Amplification vs. Protein Overexpression vs. Exon 14 Skipping
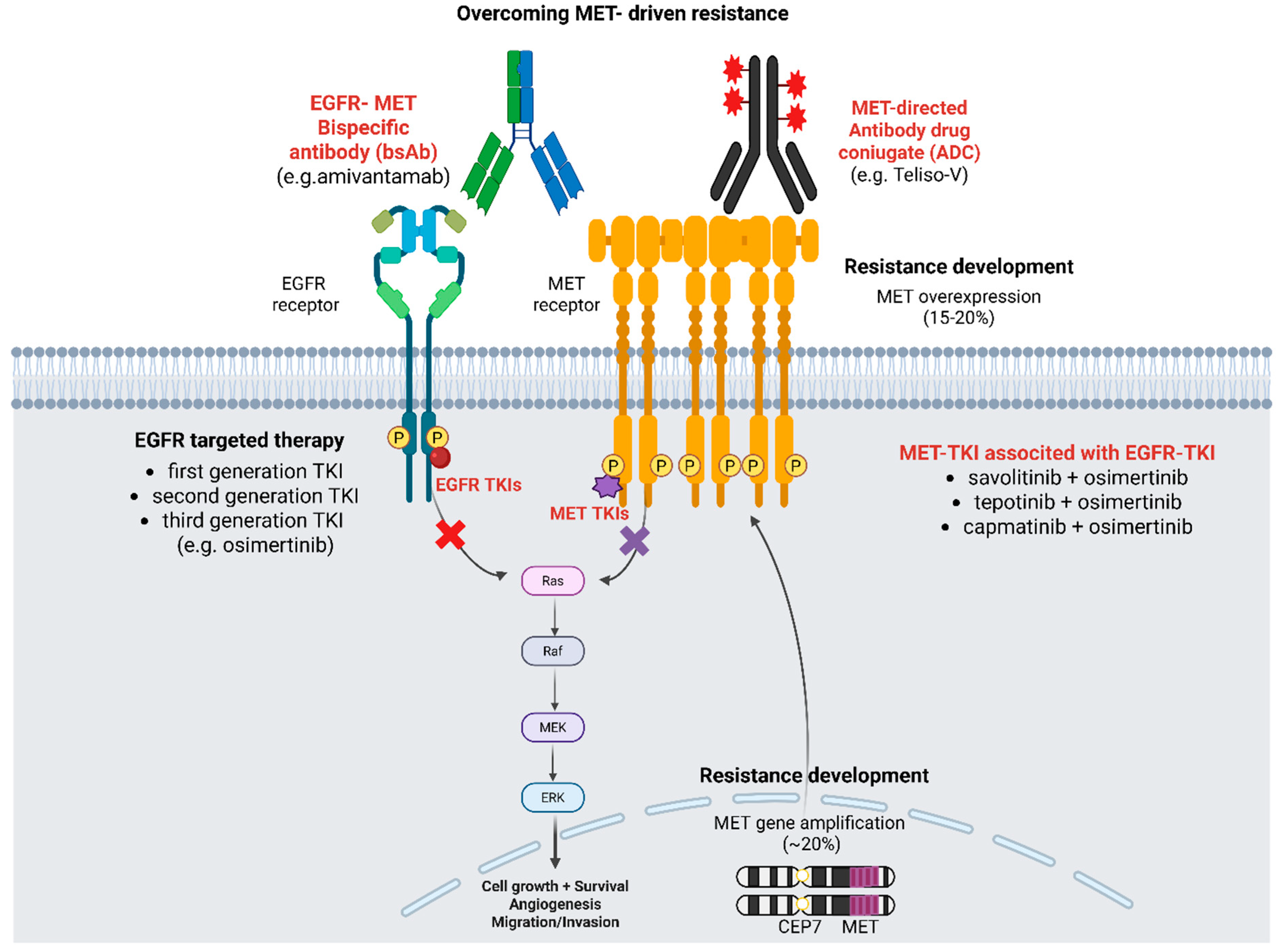
4. EGFR-MET Crosstalk
5. Strategies for Overcoming MET-Driven Resistance to Osimertinib
5.1. MET-TKIs
5.2. Bispecific Antibody Amivantamab (Anti-EGFR/c-MET)
5.3. Ongoing Clinical Trials and New Drugs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Bunn, P.A., Jr. EGFR testing in lung cancer is ready for prime time. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 432–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Ahn, M.J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, W.S.; et al. Osimertinib or Platinum-Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, M.; Herbst, R.S.; John, T.; Kato, T.; Majem, M.; Grohé, C.; Wang, J.; Goldman, J.W.; Lu, S.; Su, W.C.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Resected EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Mok, T.S.K.; Attili, I.; Wu, Y.-L.; Tsuboi, M.; de Marinis, F.; Peters, S. Adjuvant Treatments for Surgically Resected Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring EGFR Mutations: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 75ra26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Thress, K.S.; Mooradian, M.; Heist, R.S.; Azzoli, C.G.; Temel, J.S.; Rizzo, C.; Nagy, R.J.; Lanman, R.B.; Gettinger, S.N.; et al. MET amplification (amp) as a resistance mechanism to osimertinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35 (Suppl. 15), 9020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attili, I.; Del Re, M.; Guerini-Rocco, E.; Crucitta, S.; Pisapia, P.; Pepe, F.; Barberis, M.; Troncone, G.; Danesi, R.; de Marinis, F.; et al. The role of molecular heterogeneity targeting resistance mechanisms to lung cancer therapies. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 21, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucitta, S.; Cucchiara, F.; Mathijssen, R.; Mateo, J.; Jager, A.; Joosse, A.; Passaro, A.; Attili, I.; Petrini, I.; van Schaik, R.; et al. Treatment-driven tumour heterogeneity and drug resistance: Lessons from solid tumours. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2022, 104, 102340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attili, I.; Corvaja, C.; Spitaleri, G.; Del Signore, E.; Trillo Aliaga, P.; Passaro, A.; de Marinis, F. New Generations of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Treating NSCLC with Oncogene Addiction: Strengths and Limitations. Cancers 2023, 15, 5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attili, I.; Corvaja, C.; Spitaleri, G.; Trillo Aliaga, P.; Del Signore, E.; Passaro, A.; de Marinis, F. Post-Progression Analysis of EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Following Osimertinib Therapy in Real-World Settings. Cancers 2024, 16, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvaja, C.; Passaro, A.; Attili, I.; Aliaga, P.T.; Spitaleri, G.; Signore, E.D.; de Marinis, F. Advancements in fourth-generation EGFR TKIs in EGFR-mutant NSCLC: Bridging biological insights and therapeutic development. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2024, 130, 102824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attili, I.; Passaro, A.; Corvaja, C.; Trillo Aliaga, P.; Del Signore, E.; Spitaleri, G.; de Marinis, F. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2023, 119, 102602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attili, I.; Karachaliou, N.; Conte, P.; Bonanno, L.; Rosell, R. Therapeutic approaches for T790M mutation positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Therapeutic approaches for T790M mutation positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2018, 18, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabari, J.K.; Yu, H.A.; Mahadevia, P.J.; Liu, Y.; Demirdjian, L.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Passaro, A. Overall Survival in EGFR-mutant Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with First-line Osimertinib: A Cohort Study Integrating Clinical and Biomarker Data in the United States. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.S.; Park, M.; Blair, D.G.; Tainsky, M.A.; Huebner, K.; Croce, C.M.; Vande Woude, G.F. Molecular cloning of a new transforming gene from a chemically transformed human cell line. Nature 1984, 311, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Nawa, K.; Ichihara, A. Partial purification and characterization of hepatocyte growth factor from serum of hepatectomized rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1984, 122, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Cappuzzo, F.; Ou, S.I.; Camidge, D.R. Targeting MET in Lung Cancer: Will Expectations Finally Be MET? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiering, N.; Knapp, S.; Marconi, M.; Flocco, M.M.; Cui, J.; Perego, R.; Rusconi, L.; Cristiani, C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12654–12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trusolino, L.; Bertotti, A.; Comoglio, P.M. MET signalling: Principles and functions in development, organ regeneration and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, M.; Deakin, J.A.; Mizuno, K.; Nakamura, T.; Gallagher, J.T. Interaction of hepatocyte growth factor with heparan sulfate. Elucidation of the major heparan sulfate structural determinants. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 11216–11223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organ, S.L.; Tsao, M.S. An overview of the c-MET signaling pathway. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2011, 3 (Suppl. 1), S7–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccaccio, C.; Andò, M.; Tamagnone, L.; Bardelli, A.; Michieli, P.; Battistini, C.; Comoglio, P.M. Induction of epithelial tubules by growth factor HGF depends on the STAT pathway. Nature 1998, 391, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, R.; Alidousty, C.; Holz, B.; Wagener, S.; Baar, T.; Heydt, C.; Binot, E.; Zupp, S.; Kron, A.; Wolf, J.; et al. Comparison of the genomic background of MET-altered carcinomas of the lung: Biological differences and analogies. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazieres, J.; Vioix, H.; Pfeiffer, B.M.; Campden, R.I.; Chen, Z.; Heeg, B.; Cortot, A.B. MET Exon 14 Skipping in NSCLC: A Systematic Literature Review of Epidemiology, Clinical Characteristics, and Outcomes. Clin. Lung Cancer 2023, 24, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.H.; Yeung, S.F.; Chan, A.W.; Chung, L.Y.; Chau, S.L.; Lung, R.W.; Tong, C.Y.; Chow, C.; Tin, E.K.; Yu, Y.H.; et al. MET Amplification and Exon 14 Splice Site Mutation Define Unique Molecular Subgroups of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma with Poor Prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3048–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Jänne, P.A.; Mok, T.; Peters, S. Overcoming therapy resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volta, F.; La Monica, S.; Leonetti, A.; Gnetti, L.; Bonelli, M.; Cavazzoni, A.; Fumarola, C.; Galetti, M.; Eltayeb, K.; Minari, R.; et al. Intrinsic Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR Mutated NSCLC Cell Lines Induced by Alteration in Cell-Cycle Regulators. Target. Oncol. 2023, 18, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, A.; Attili, I.; Rappa, A.; Vacirca, D.; Ranghiero, A.; Fumagalli, C.; Guarize, J.; Spaggiari, L.; de Marinis, F.; Barberis, M.; et al. Genomic Characterization of Concurrent Alterations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Harboring Actionable Mutations. Cancers 2021, 13, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attili, I.; Asnaghi, R.; Vacirca, D.; Adorisio, R.; Rappa, A.; Ranghiero, A.; Lombardi, M.; Corvaja, C.; Fuorivia, V.; Carnevale Schianca, A.; et al. Co-Occurring Driver Genomic Alterations in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Retrospective Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Malapelle, U.; Del Re, M.; Attili, I.; Russo, A.; Guerini-Rocco, E.; Fumagalli, C.; Pisapia, P.; Pepe, F.; De Luca, C.; et al. Understanding EGFR heterogeneity in lung cancer. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e000919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, C.; Ohe, Y.; Imamura, F.; Cho, B.C.; Lin, M.C.; Majem, M.; Shah, R.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. LBA50-Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib: Preliminary data from the phase III FLAURA study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, viii740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Wu, Y.L.; Han, J.Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; John, T.; Okamoto, I.; Yang, J.C.H.; Bulusu, K.C.; Laus, G.; et al. LBA51-Analysis of resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in patients with EGFR T790M advanced NSCLC from the AURA3 study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, viii741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Yang, S.D.; Lim, S.; Heo, S.G.; Daniel, S.; Markovets, A.; Minoo, R.; Pyo, K.H.; Yun, M.R.; Hong, M.H.; et al. Molecular landscape of osimertinib resistance in patients and patient-derived preclinical models. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2022, 14, 17588359221079125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Chan, J.M.; Kubota, D.; Sato, H.; Rizvi, H.; Daneshbod, Y.; Chang, J.C.; Paik, P.K.; Offin, M.; Arcila, M.E.; et al. Tumor Analyses Reveal Squamous Transformation and Off-Target Alterations as Early Resistance Mechanisms to First-line Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2654–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oser, M.G.; Niederst, M.J.; Sequist, L.V. Transformation from non-small-cell lung cancer to small-cell lung cancer: Molecular drivers and cells of origin. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e165–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Han, J.Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Delmonte, A.; Hsia, T.C.; Laskin, J.; Kim, S.W.; He, Y.; Tsai, C.M.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation analysis in tissue and plasma from the AURA3 trial: Osimertinib versus platinum-pemetrexed for T790M mutation-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2020, 126, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabon, J.J.; Simmons, A.D.; Lovejoy, A.F.; Esfahani, M.S.; Newman, A.M.; Haringsma, H.J.; Kurtz, D.M.; Stehr, H.; Scherer, F.; Karlovich, C.A.; et al. Circulating tumour DNA profiling reveals heterogeneity of EGFR inhibitor resistance mechanisms in lung cancer patients. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitaleri, G.; Trillo Aliaga, P.; Attili, I.; Del Signore, E.; Corvaja, C.; Corti, C.; Uliano, J.; Passaro, A.; de Marinis, F. MET in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Cross ‘a Long and Winding Road’ Looking for a Target. Cancers 2023, 15, 4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attili, I.; Bonanno, L.; Karachaliou, N.; Bracht, J.W.P.; Berenguer, J.; Codony-Servat, C.; Codony-Servat, J.; Aldeguer, E.; Gimenez-Capitan, A.; Dal Maso, A.; et al. SRC and PIM1 as potential co-targets to overcome resistance in MET deregulated non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 1810–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turke, A.B.; Zejnullahu, K.; Wu, Y.L.; Song, Y.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Lifshits, E.; Toschi, L.; Rogers, A.; Mok, T.; Sequist, L.; et al. Preexistence and clonal selection of MET amplification in EGFR mutant NSCLC. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.N.; Selinger, C.I.; Kohonen-Corish, M.R.; McCaughan, B.; Kennedy, C.; O’Toole, S.A.; Cooper, W.A. Alterations of MET Gene Copy Number and Protein Expression in Primary Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Corresponding Nodal Metastases. Clin. Lung Cancer 2016, 17, 30–38.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wei, W.; Gao, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X. Clinicopathological characteristics of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) patients with c-MET exon 14 skipping mutation, MET overexpression and amplification. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gulik, A.L.; Sluydts, E.; Vervoort, L.; Kockx, M.; Kortman, P.; Ylstra, B.; Finn, S.P.; Bubendorf, L.; Bahce, I.; Sie, D.; et al. False positivity in break apart fluorescence in-situ hybridization due to polyploidy. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, S.; Li, J.; Cheng, B.; Li, C.; Feng, Y.; Fan, L.; Xiong, S.; Zeng, W.; Cai, Q.; Xiang, Y.; et al. Landscape of C-MET overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer: A large-scale study of clinicomolecular features and prognosis based on Chinese data. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2024, 16, 17588359241279715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, Y.L.; Sung, C.O.; An, J.; Seo, J.; Ahn, M.J.; Ahn, J.S.; Park, K.; Shin, Y.K.; Erkin, O.C.; et al. High MET copy number and MET overexpression: Poor outcome in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Histol. Histopathol. 2012, 27, 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Kong-Beltran, M.; Seshagiri, S.; Zha, J.; Zhu, W.; Bhawe, K.; Mendoza, N.; Holcomb, T.; Pujara, K.; Stinson, J.; Fu, L.; et al. Somatic mutations lead to an oncogenic deletion of met in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M.; Oxnard, G.R.; Jackman, D.M.; Savukoski, D.O.; Hall, D.; Shivdasani, P.; Heng, J.C.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Jänne, P.A.; Verma, S.; et al. MET Exon 14 Mutations in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Are Associated with Advanced Age and Stage-Dependent MET Genomic Amplification and c-Met Overexpression. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Mandal, E.; Liu, F.X.; O’Hara, R.M.; Lesher, B.; Sanborn, R.E. Non-small cell lung cancer with MET amplification: Review of epidemiology, associated disease characteristics, testing procedures, burden, and treatments. Front. Oncol. 2024, 13, 1241402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attili, I.; Karachaliou, N.; Bonanno, L.; Berenguer, J.; Bracht, J.; Codony-Servat, J.; Codony-Servat, C.; Ito, M.; Rosell, R. STAT3 as a potential immunotherapy biomarker in oncogene-addicted non-small cell lung cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1758835918763744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Nishioka, Y.; Sekido, Y.; Sone, S.; Yano, S. Hepatocyte growth factor reduces susceptibility to an irreversible epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor in EGFR-T790M mutant lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielecki, J.; Mok, T.; Wu, Y.L.; Han, J.Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; John, T.; Okamoto, I.; Yang, J.C.; Shepherd, F.A.; et al. Analysis of acquired resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer from the AURA3 trial. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Hu, Y.; Mileham, K.F.; Husain, H.; Costa, D.B.; Tracy, P.; Feeney, N.; Sholl, L.M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Redig, A.J.; et al. Assessment of Resistance Mechanisms and Clinical Implications in Patients with EGFR T790M-Positive Lung Cancer and Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motwani, M.; Panchabhai, S.; Bar, J.; Girard, N.; Bradbury, P.; Lu, S.; Jin, J.; Hotson, A.; Maag, D.; Planchard, D.; et al. P60.12 Prevalence of c-Met overexpression (c-Met+) and Impact of Prior Lines of Treatment on c-Met Protein Expression in NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16 (Suppl. S10), S1169–S1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Kim, D.W.; Soo, R.A.; Kim, S.W.; Pan, H.; et al. Tepotinib plus gefitinib in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer with MET overexpression or MET amplification and acquired resistance to previous EGFR inhibitor (INSIGHT study): An open-label, phase 1b/2, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, N.; Ou, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wu, X.; Bao, H.; Tong, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, Y.W.; et al. Investigating Novel Resistance Mechanisms to Third-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Osimertinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3097–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, S.; Pecci, F.; Ricciuti, B.; Gottlieb, F.H.; Facchinetti, F.; Harada, G.; Chen, M.F.; Repetto, M.; Giacomini, F.; Jiang, J.; et al. Activating Mutations in the MET Kinase Domain Co-Occur With Other Driver Oncogenes and Mediate Resistance to Targeted Therapy in NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzawa, K.; Offin, M.; Schoenfeld, A.J.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Odintsov, I.; Lu, D.; Lockwood, W.W.; Arcila, M.E.; Rudin, C.M.; Drilon, A.; et al. Acquired MET Exon 14 Alteration Drives Secondary Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Zeng, L.; Xiang, M.; Zhang, Y. Presence of MET exon 14 skipping and fusion as mechanism of osimertinb resistance in a lung adenocarcinoma with an EGFR exon 19 deletion that responds to combination of capmatinib and osimertinb: A case report. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, L.; Tang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Guo, L.; He, Q.; He, T.; Feng, W. Case Report: Durable partial response to icotinib plus crizotinib in a lung adenocarcinoma patient with double uncommon EGFR G719D/L861Q mutations and an acquired novel CUX1-MET fusion. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 911362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Zejnullahu, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Song, Y.; Hyland, C.; Park, J.O.; Lindeman, N.; Gale, C.M.; Zhao, X.; Christensen, J.; et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 2007, 316, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Oh, Y.T.; Zhang, G.; Yao, W.; Yue, P.; Li, Y.; Kanteti, R.; Riehm, J.; Salgia, R.; Owonikoko, T.K.; et al. Met gene amplification and protein hyperactivation is a mechanism of resistance to both first and third generation EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer treatment. Cancer Lett. 2016, 380, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Puri, S.; Negrao, M.V.; Nilsson, M.B.; Robichaux, J.; Boyle, T.; Hicks, J.K.; Lovinger, K.L.; Roarty, E.; Rinsurongkawong, W.; et al. Landscape of EGFR-Dependent and -Independent Resistance Mechanisms to Osimertinib and Continuation Therapy Beyond Progression in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6195–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tang, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y. Overcoming Resistance to AC0010, a Third Generation of EGFR Inhibitor, by Targeting c-MET and BCL-2. Neoplasia 2019, 21, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfoudhi, E.; Ricordel, C.; Lecuyer, G.; Mouric, C.; Lena, H.; Pedeux, R. Preclinical Models for Acquired Resistance to Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors in NSCLC: Functional Studies and Drug Combinations Used to Overcome Resistance. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 853501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, M.S.; Holland, W.S.; Chinn, D.; Burich, R.A.; Lara, P.N., Jr.; Gandara, D.R.; Kelly, K.; Mack, P.C. Preclinical Evaluation of MET Inhibitor INC-280 With or Without the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor Erlotinib in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmaier, R.J.; Markovets, A.A.; Ahn, M.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Han, J.Y.; Cho, B.C.; Yu, H.A.; Kim, S.W.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Osimertinib + Savolitinib to Overcome Acquired MET-Mediated Resistance in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated, MET-Amplified Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: TATTON. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.j.; De Marinis, F.; Bonanno, L.; Cho, B.C.; Kim, T.M.; Cheng, S.; Novello, S.; Proto, C.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.S.; et al. EP08.02-140 MET Biomarker-based Preliminary Efficacy Analysis in SAVANNAH: Savolitinib+osimertinib in EGFRm NSCLC Post-Osimertinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S469–S470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.J.; Kim, T.M.; Bonanno, L.; Cheng, S.; Kim, S.W.; Tiseo, M.; Chu, Q.S.C.; Proto, C.; Sacher, A.; Luo, Y.H.; et al. 2O: SAVANNAH: Savolitinib (savo) + osimertinib (osi) in patients (pts) with EGFRm advanced NSCLC and METoverexpression (OverExp) and/or amplification (Amp) following progressive disease (PD) on osi. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2025, 20, S4–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Guarneri, V.; Voon, P.J.; Lim, B.K.; Yang, J.-J.; Wislez, M.; Huang, C.; Liam, C.K.; Mazieres, J.; Tho, L.M.; et al. Tepotinib plus osimertinib in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer with MET amplification following progression on first-line osimertinib (INSIGHT 2): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Han, J.Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Cho, B.C.; Yu, H.; Kim, S.W.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, J.S.; Su, W.C.; Kowalski, D.; et al. Osimertinib plus savolitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, MET-amplified, non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Interim results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Yang, J.C.; Yu, H.; Kim, S.W.; Saka, H.; Horn, L.; Goto, K.; Ohe, Y.; Mann, H.; Thress, K.S.; et al. TATTON: A multi-arm, phase Ib trial of osimertinib combined with selumetinib, savolitinib, or durvalumab in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.; Han, J.; Sequist, L.; Cho, B.C.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.; Su, W.; Tsai, C.; Yang, J.C.; Yu, H.; et al. OA 09.03 TATTON Ph Ib Expansion Cohort: Osimertinib plus Savolitinib for Pts with EGFR-Mutant MET-Amplified NSCLC after Progression on Prior EGFR-TKI. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, S1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.; Cantarini, M.; Frewer, P.; Hawkins, G.; Peters, J.; Howarth, P.; Ahmed, G.; Sahota, T.; Hartmaier, R.; Li-Sucholeiki, X.; et al. P1.01-134 SAVANNAH: Phase II Trial of Osimertinib + Savolitinib in EGFR-Mutant, MET-Driven Advanced NSCLC, Following Prior Osimertinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S415–S416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Xu, W.; Telaranta-Keerie, A.; Jia, N.; Hartmaier, R. EP08.02-138 SAFFRON: Ph3 Savolitinib + Osimertinib vs Chemotherapy in EGFRm NSCLC with MET Overexpression/Amplification Post-Osimertinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S468–S469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liam, C.K.; Ahmad, A.R.; Hsia, T.C.; Zhou, J.; Kim, D.W.; Soo, R.A.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, S.; Shin, S.W.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Randomized Trial of Tepotinib Plus Gefitinib versus Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC with EGFR Inhibitor Resistance Due to MET Amplification: INSIGHT Final Analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F Smit, E.; Dooms, C.; Raskin, J.; Nadal, E.; Tho, L.M.; Le, X.; Mazieres, J.; S Hin, H.; Morise, M.; W Zhu, V.; et al. INSIGHT 2: A phase II study of tepotinib plus osimertinib in MET-amplified NSCLC and first-line osimertinib resistance. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 1039–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Han, J.-Y.; Kato, T.; Barlesi, F.; Garon, E.B.; Cappuzzo, F.; Shibata, Y.; Smith, N.; Khanna, S.; Belli, R.; et al. Capmatinib plus osimertinib versus platinum-pemetrexed doublet chemotherapy as second-line therapy in patients with stage IIIb/IIIc or IV EGFR-mutant, T790M-negative NSCLC harboring MET amplification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S16), TPS9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Pyo, K.H.; Park, C.W.; Heo, S.G.; Yun, M.R.; Lim, S.; et al. Antitumor Activity of Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an EGFR-MET Bispecific Antibody, in Diverse Models of EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Driven NSCLC. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1194–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraghavan, S.; Lipfert, L.; Chevalier, K.; Bushey, B.S.; Henley, B.; Lenhart, R.; Sendecki, J.; Beqiri, M.; Millar, H.J.; Packman, K.; et al. Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an Fc Enhanced EGFR/cMet Bispecific Antibody, Induces Receptor Downmodulation and Antitumor Activity by Monocyte/Macrophage Trogocytosis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 2044–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.C.; Kim, D.W.; Spira, A.I.; Gomez, J.E.; Haura, E.B.; Kim, S.W.; Sanborn, R.E.; Cho, E.K.; Lee, K.H.; Minchom, A.; et al. Amivantamab plus lazertinib in osimertinib-relapsed EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2577–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, B.; Baik, C.S.; Marmarelis, M.E.; Sabari, J.K.; Goto, K.; Shu, C.A.; Lee, J.-S.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Cho, B.C.; Waqar, S.N.; et al. Predictive biomarkers for treatment with amivantamab plus lazertinib among EGFR-mutated NSCLC in the post-osimertinib setting: Analysis of tissue IHC and ctDNA NGS. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S16), 9013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Lu, S.; Felip, E.; Spira, A.I.; Girard, N.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.H.; Ostapenko, Y.; Danchaivijitr, P.; Liu, B.; et al. Amivantamab plus Lazertinib in Previously Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Melosky, B.; Shih, J.Y.; Wang, J.; Azuma, K.; Juan-Vidal, O.; Cobo, M.; et al. Amivantamab plus chemotherapy with and without lazertinib in EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC after disease progression on osimertinib: Primary results from the phase III MARIPOSA-2 study. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felip, E.; Cho, B.C.; Gutiérrez, V.; Alip, A.; Besse, B.; Lu, S.; Spira, A.I.; Girard, N.; Califano, R.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Amivantamab plus lazertinib versus osimertinib in first-line EGFR-mutant advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with biomarkers of high-risk disease: A secondary analysis from MARIPOSA. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spira, A.; Krebs, M.; Cho, B.C.; Besse, B.; Goldman, J.; Janne, P.; Lee, C.K.; Ma, Z.; Mansfield, A.; Minchom, A.; et al. OA15.03 Amivantamab in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with MET Exon 14 Skipping (METex14) Mutation: Initial Results from CHRYSALIS. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S874–S875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.; Spira, A.I.; Cho, B.C.; Besse, B.; Goldman, J.W.; Janne, P.A.; Ma, Z.; Mansfield, A.S.; Minchom, A.R.; Ou, S.-H.I.; et al. Amivantamab in patients with NSCLC with MET exon 14 skipping mutation: Updated results from the CHRYSALIS study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S16), 9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighl, N.; Cho, B.C.; Hiret, S.; Han, J.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Llacer Perez, C.; Krebs, M.G.; De Braud, F.; Haura, E.; Sanborn, R.E.; et al. OA21.04 Amivantamab in Patients with Advanced NSCLC and MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutation: Results from the CHRYSALIS Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, S93–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Jänne, P.A.; Peters, S. Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Lung Cancer: Recent Advances and Implementing Strategies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3747–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Morgensztern, D.; Heist, R.S.; Barve, M.; Vokes, E.; Goldman, J.W.; Hong, D.S.; Bauer, T.M.; Strickler, J.H.; Angevin, E.; et al. Phase I Study of 2- or 3-Week Dosing of Telisotuzumab Vedotin, an Antibody-Drug Conjugate Targeting c-Met, Monotherapy in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5781–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickler, J.H.; Weekes, C.D.; Nemunaitis, J.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Heist, R.S.; Morgensztern, D.; Angevin, E.; Bauer, T.M.; Yue, H.; Motwani, M.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I, Dose-Escalation and -Expansion Study of Telisotuzumab Vedotin, an Antibody–Drug Conjugate Targeting c-Met, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3298–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Bar, J.; Horinouchi, H.; Goldman, J.; Moiseenko, F.; Filippova, E.; Cicin, I.; Ciuleanu, T.; Daaboul, N.; Liu, C.; et al. Telisotuzumab Vedotin Monotherapy in Patients with Previously Treated c-Met Protein-Overexpressing Advanced Nonsquamous EGFR-Wildtype Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Phase II LUMINOSITY Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 3000–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Barlesi, F.; Goldman, J.W.; Morgensztern, D.; Heist, R.; Vokes, E.; Spira, A.; Angevin, E.; Su, W.C.; Hong, D.S.; et al. Phase Ib Study of Telisotuzumab Vedotin in Combination with Erlotinib in Patients With c-Met Protein-Expressing Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinouchi, H.; Cho, B.C.; Camidge, D.R.; Goto, K.; Tomasini, P.; Li, Y.; Vasilopoulos, A.; Brunsdon, P.; Hoffman, D.; Shi, W.; et al. Results from a phase Ib study of telisotuzumab vedotin in combination with osimertinib in patients with c-Met protein-overexpressing, EGFR-mutated locally advanced/metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after progression on prior osimertinib. Ann. Oncol. 2025, 36, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Phase Trial | Setting | MET Testing | Treatment | n | ORR (%) | mDoR (mos) | mPFS (mos) | mOS (mos) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hartmaier 2023 [70] TATTON | Ib-part B1 (dose exp.) | prior 3rd EGFR-TKI | MET GCN ≥ 5 or MET/CEP7 ratio ≥ 2 | osimertinib + savolitinib | 69 | 33 (22–46) | 9.5 (4.2–14.7) | 5.5 (4.1–7.7) | 30.3 (11.8–NC) |
| Ib-part B2 (dose exp.) | prior 1st, 2nd EGFR-TKI without T790M | MET GCN ≥ 5 or MET/CEP7 ratio ≥ 2 | osimertinib + savolitinib | 51 | 65 (50–78) | 10.7 (6.1–14.8) | 9.1 (5.5–12.8) | 18.8 (15.1–NC) | |
| Ib-part B3 (dose exp.) | prior 1st, 2nd EGFR-TKI with T790M | MET GCN ≥ 5 or MET/CEP7 ratio ≥ 2 | osimertinib + savolitinib | 18 | 67 (41–87) | 11.0 (2.8–NC) | 11.1 (4.1–22.1) | NC (24.4–NC) | |
| Ib-part D (dose exp.) | prior 1st, 2nd EGFR-TKI withoutT790M | MET GCN ≥ 5 or MET/CEP7 ratio ≥ 2 | osimertinib + savolitinib | 42 | 62 (46–76) | 9.7 (4.5–14.3) | 9.0 (5.6–12.7) | NC (13–NC) | |
| Ahn 2022 [71] SAVANNAH | II | ≥2 L (post-osimertinib) | all IHC50+ or FISH5+ | osimertinib + savolitinib | 193 | 32 (26–39) | 8.3 (6.9–9.7) | 5.3 (4.2–5.8) | na |
| with IHC90+ and/or FISH10+ | osimertinib + savolitinib | 108 | 49 (39–59) | 9.3 (7.6–10.6) | 7.1 (5.3–8.0) | na | |||
| without IHC90+ and/or FISH10+ | osimertinib + savolitinib | 77 | 9 (4–18) | 6.9 (4.1–16.9) | 2.8 (2.6–4.3) | na | |||
| Ahn 2025 [72] SAVANNAH | II | 2 L (post-osimertinib) | IHC 3+/90% and/or FISH10+ | osimertinib + savolitinib | 80 (inv) | 56 (45–67) | 7.1 (5.6–9.6) | 7.4 (5.5–7.6) | na |
| Wu 2024 [73] INSIGHT 2 | II | 2 L (post-osimertinib) | GCN ≥ 5 or MET: CEP7 ≥ 2 | osimertinib + tepotinib | 98 | 50 (39.7–60.3) | 8.5 (6.1–NE) | 5.6 (4.2–8.1) | 17.8 (11.1–NE) |
| NCT Number | Drug (s) | Phase | Description | Primary Outcomes | Secondary Outcomes | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monotherapies | ||||||
| Specific MET TKI | ||||||
| NCT03175224 (SPARTA) | Vebreltinib (also known as APL-101, PLB-1001, CBT-101, CBI-3103, bozitinib) | II | Study evaluating APL-101 in subjects with c-Met exon 14 skip mutations and c-Met dysregulation in advanced solid tumors (Cohort C2: EGFR-positive NSCLC harboring MET amplification as an acquired resistance to first-line EGFR inhibitors) | ORR by BIRC | ORR by inv; DoR, TTP, PFS, OS | Recruiting |
| Bispecific Antibodies (Anti-EGFR/c-MET) | ||||||
| NCT06885840 | Pamvatamig (MCLA-129) | II | Study of MCLA-129 as monotherapy in patients with advanced NSCLC with actionable gene alterations and MET amplification (Cohort 1: Patients with MET amplification after failure of treatment with EGFR-TKI). | ORR | CBR, DCR, PFS, DoR; TTR; OS, TEAEs, PK, ADA | Not yet recruiting |
| NCT04868877 | Pamvatamig (MCLA-129) | I/II | Dose escalation and expansion study evaluating MCLA-129 in patients with advanced NSCLC and other solid tumors (cohorts also evaluating post-osimertinib resistance). | MTD, RP2D, ORR | BOR, DCR, PFS, OS, safety | Recruiting |
| Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) | ||||||
| NCT06093503 | Telisotuzumab Vedotin (also known as Teliso-V or ABBV-399) | III | Study of Teliso-V (IgG1 monoclonal antibody anti-c-Met bound to the MMAE) combined with osimertinib vs. platinum-based chemotherapy in subjects with c-Met-overexpressing EGFR mutant, locally advanced/metastatic non-squamous NSCLC after a first progression to third-generation EGFR-TKI. | PFS with no CNS metastases at baseline | PFS, ORR, DoR, OS, QoL, safety | Withdrawn (for strategic consideration) |
| Combination Therapies | ||||||
| EGFR TKI + MET TKI | ||||||
| NCT06343064 | Vebreltinib + Andatinib (PLB1004) | Ib/II | Study of Vebreltinib in combination with Andatinib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC with MET overexpression or MET amplification following EGFR-TKI. | TEAEs, DLT, ORR | PK, safety | Recruiting |
| NCT04606771 | Osimertinib (Tagrisso) + Savolitinib (AZD6094 or HMPL-504) | II | Study of savolitinib in combination with osimertinib vs. savolitinib in combination with placebo in patients with EGFRm+ and MET-amplified locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who have progressed to osimertinib. | ORR by inv | PFS, DoR, OS, ctDNA clearance, PK | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT05261399 (SAFFRON) | Osimertinib + Savolitinib | III | Study evaluating savolitinib in combination with osimertinib versus platinum-based doublet chemotherapy in patients with EGFR-mutated, MET-overexpressed and/or amplified, locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC who have progressed on treatment with osimertinib. | PFS by BICR | OS, ORR, DCR, DoR, PK, safety | Recruiting |
| NCT05642572 (Lung-MAP) | Osimertinib + Capmatinib + Ramucirumab * | II | Study of capmatinib plus osimertinib with or without ramucirumab in participants with EGFR-mutant, MET-amplified stage IV or recurrent NSCLC. | PFS by inv | DoR, DLT | Recruiting |
| Bispecific Antibody (Anti-EGFR/c-MET) + TKI | ||||||
| NCT06015568 | MCLA-129 (Pamvatamig) + Befotertinib (D-0316) $ | I | Study evaluating MCLA-129 combined with befotertinib in patients with advanced NSCLC with EGFR-sensitive mutation (Cohort B patients with 3rd-generation EGFR-TKI resistance). | DLT, MTD, TEAEs | ORR, DoR, PFS, OS, ADA, PK | Not yet recruiting |
| NCT05488314 (METalmark) | Amivantamab (Rybrevant) + Capmatinib (Tabrecta) | I/II | Study evaluating amivantamab and capmatinib combination therapy in unresectable metastatic NSCLC (Cohort 1C MET amplification who have received prior therapy). | Aes, DLT, ORR | DoR, DCR, PFS, OS, TTST; QoL | Active, not recruiting |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angelopoulos, P.A.; Passaro, A.; Attili, I.; Trillo Aliaga, P.; Corvaja, C.; Spitaleri, G.; Battaiotto, E.; Del Signore, E.; Curigliano, G.; de Marinis, F. Management of MET-Driven Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Genes 2025, 16, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070772
Angelopoulos PA, Passaro A, Attili I, Trillo Aliaga P, Corvaja C, Spitaleri G, Battaiotto E, Del Signore E, Curigliano G, de Marinis F. Management of MET-Driven Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Genes. 2025; 16(7):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070772
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngelopoulos, Panagiotis Agisilaos, Antonio Passaro, Ilaria Attili, Pamela Trillo Aliaga, Carla Corvaja, Gianluca Spitaleri, Elena Battaiotto, Ester Del Signore, Giuseppe Curigliano, and Filippo de Marinis. 2025. "Management of MET-Driven Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" Genes 16, no. 7: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070772
APA StyleAngelopoulos, P. A., Passaro, A., Attili, I., Trillo Aliaga, P., Corvaja, C., Spitaleri, G., Battaiotto, E., Del Signore, E., Curigliano, G., & de Marinis, F. (2025). Management of MET-Driven Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Genes, 16(7), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070772





