Inherited Dyslipidemic Splenomegaly: A Genetic Macrophage Storage Disorder Caused by Disruptive Apolipoprotein E (APOE) Variants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.1.1. Brief Description of the ZOEMBA Study
2.1.2. Ethics Approval
2.1.3. Beacon Protocol
2.1.4. Genomic Analysis
2.1.5. Nomenclature of APOE Isoforms
2.2. Functional Assays in Monocytes of the Index Patient and Three Healthy Control Subjects
2.2.1. Nomenclature of Monocyte Fractions
2.2.2. Intracellular Lipid Droplet Accumulation
2.2.3. Flow Cytometry
2.3. Literature Search
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
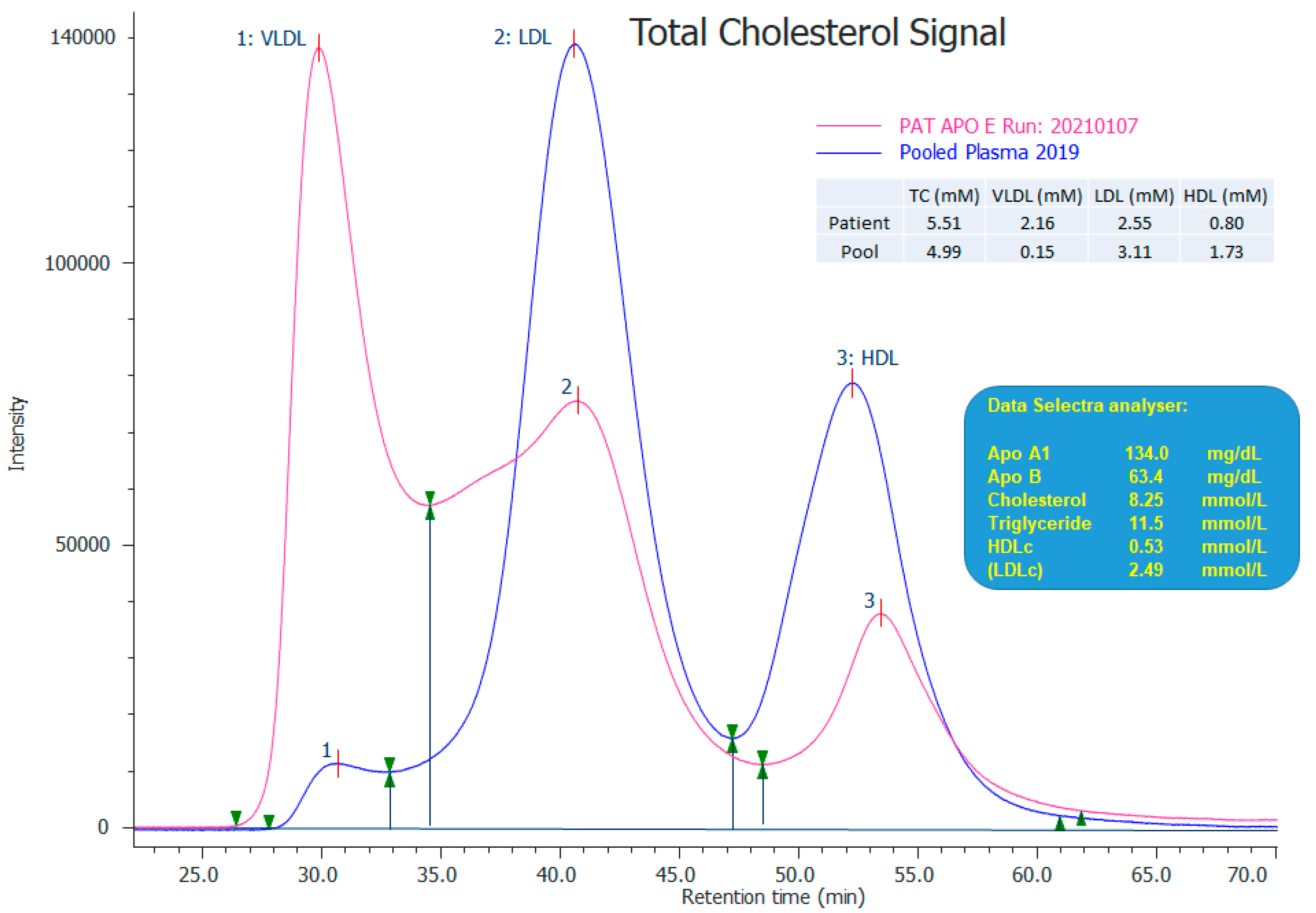
3.1. Case Report
| Patient ID (Reference) | Case Type | Age (Years), Sex | APOE Allele 1 (Isoform) * | APOE Allele 2 (Isoform) * | BMI > 25 kg/m2 | Cardiovascular Involvement | Splenomegaly | Plasma Lipid Spectrum (mmol/L) # | Foam Cells (Location of Infiltration) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG | TC | |||||||||
| Index (current study) | Index patient | 37, M | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | Y | N | Y | 11.7 | 7.2 | Y (Bone marrow and spleen) |
| Brother (current study) | Brother of index patient | 26, M | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | Y | N | Y | 3.2 | 9.2 | NM |
| A [1] | Proband | 76, M | p.(Leu167del) (ε3) | p.(Arg202Cys) (ε2) | Y | Severe ischemic heart disease; essential hypertension; systolic ejection murmer (grade 2/6) | Y | 16.2 | 6.2 | N |
| B [12] | Proband | 49, M | p.(Leu167del) (ε3) | p.(Arg202Cys) (ε2) | Y | N | Y | <2.0 | Normal | Y (Spleen) |
| C [21] | Proband | 47, M | p.(Leu167del) (ε3) | p.(Arg202Cys) (ε2) | Y | N | Y | 13.6 | 4.8 | Y (Bone marrow and spleen) |
| D [21] | Brother of C | NR, M | p.(Leu167del) (ε3) | WT (ε3) | NR | Ischemic heart disease | Y | 1.9 | 5.7 | NR |
| E [8] | Proband | 29, M | p.(Leu167del) (ε3) | WT (ε3) | Y | Ischemic heart disease | Y | 2.1 | 2.3 | Y (Spleen) |
| F [8] | Mother of E | NR, F | p.(Leu167del) (ε3) | p.(Arg202Cys) (ε2) | NR | Ischemic heart disease | Y | 1.7 | 4.6 | NR |
| G [8] | Proband | 49, M | p.(Leu167del) (ε3) | WT (ε3) | Y | Ischemic heart disease | Y | 4.3 | 3.8 | Y (Spleen) |
| Patient ID (Reference) | Case Type | Age (Years), Sex | APOE Allele 1 (Isoform) * | APOE Allele 2 (Isoform) * | BMI > 25 kg/m2 | Cardiovascular Involvement | Splenomegaly | Plasma Lipid Spectrum (mmol/L # | Foam Cells (Location of Infiltration) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG | TC | |||||||||
| Index (current study) | Index patient | 37, M | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | Y | N | Y | 11.7 | 7.2 | Y (Bone marrow and spleen) |
| Brother (current study) | Brother of index patient | 26, M | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | Y | N | Y | 3.2 | 9.2 | NM |
| H [9] | Proband | 49, M | WT (ε3) | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | Y | Inverted T-waves on ECG | NR | 12.0 | 5.3 | NR |
| I [16] | Proband | 31, M | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | N | N | NR | 4.6 | 19.5 | NR |
| J [16] | Sister of I | 16, F | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | N | N | NR | 1.8 | 4.2 | NR |
| K [17] | Proband | 42, F | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | p.(Arg202Cys) (ε2) | Y | N | NR | 5.7 | 9.4 | NR |
| L [17] | Son of K | 15, M | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | p.(Arg202Cys) (ε2) | Absence significant obesity reported | NR | NR | 4.2 | 7.7 | NR |
| M [17] | Son of K | 13, M | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | WT (ε3) | NR | NR | NR | 0.5 | 4.8 | NR |
| N [17] | Son of K | 9, M | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | p.(Arg202Cys) (ε2) | NR | NR | NR | 1.6 | 4.5 | NR |
| O [17] | Uncle of K | 78, M | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | p.(Arg202Cys) (ε2) | NR | N | NR | 2.9 | 9.6 | NR |
| P [15] | Proband | 60, F | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | p.(Gly171Asp)/p.(Arg202Cys) (ε1) | Y | Hypertension (up to 240/150 mmHg) | NR | 2.9 | 8.2 | NR |
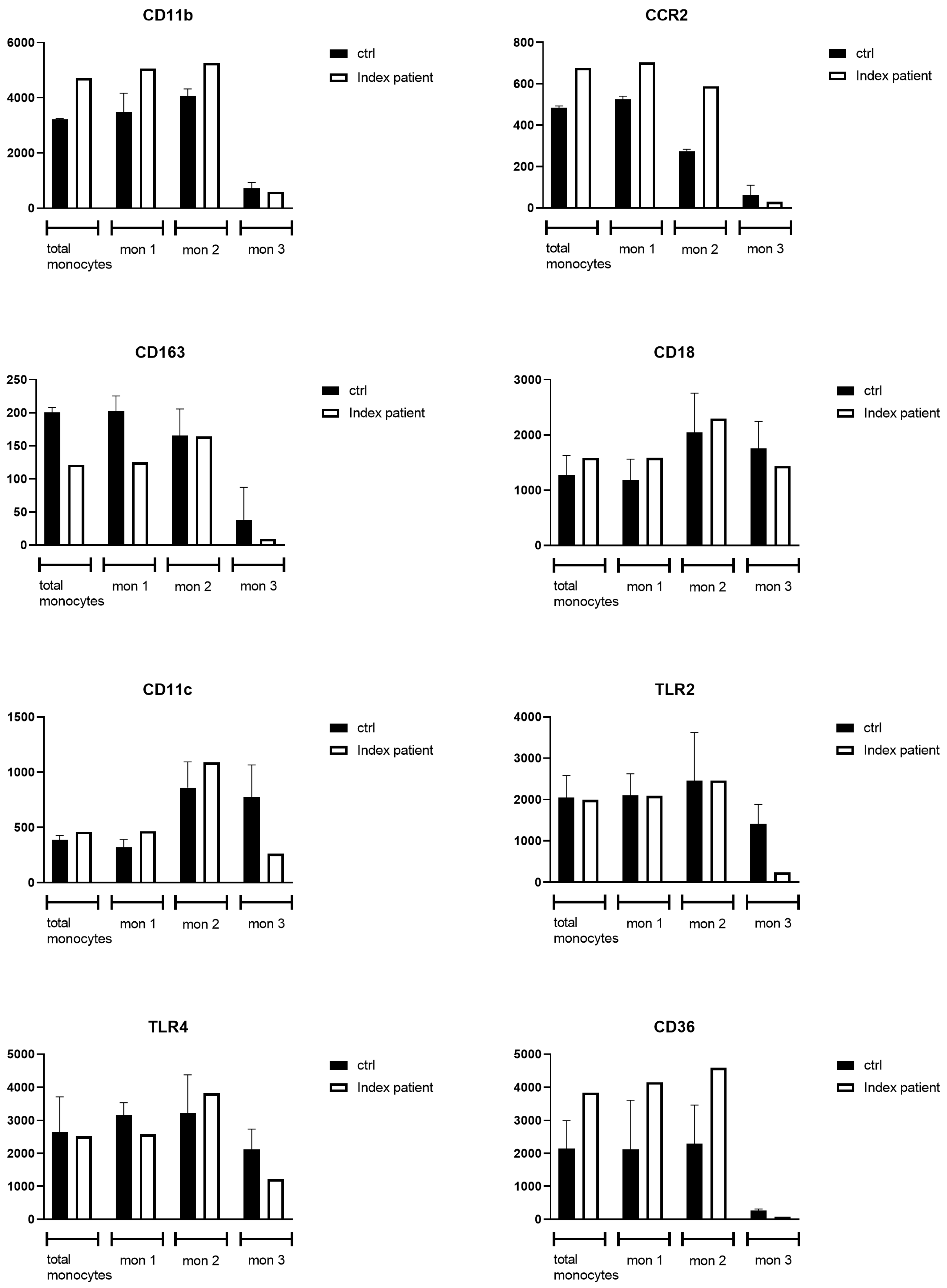
3.2. Functional Studies in Monocytes of Index Patient
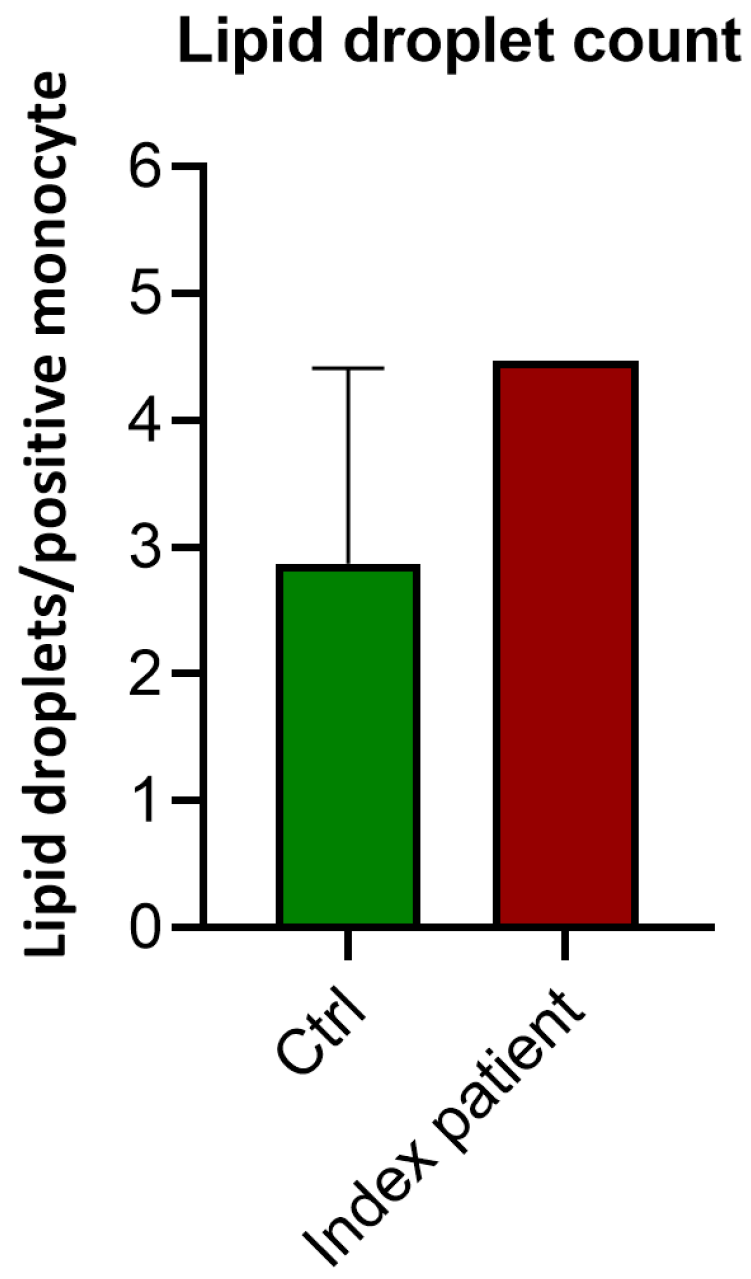
3.2.1. Lipid Droplet Count
3.2.2. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Monocytes
3.3. Meta-Analysis of Literature
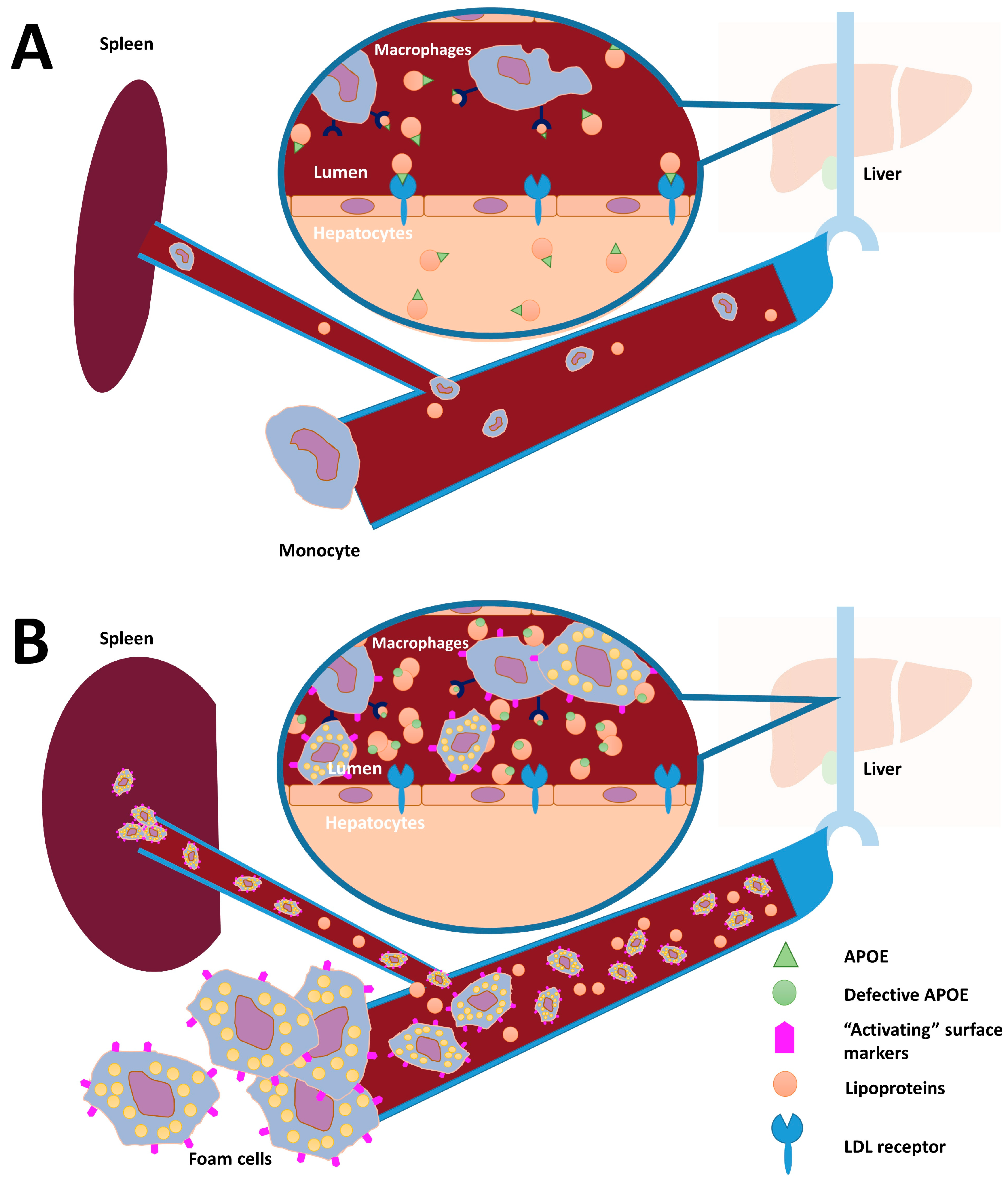
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PPCS | N-palmitoyl-O-phosphocholine-serine |
| APOE | Apolipoprotein E |
| IMD | Inherited metabolic disorder |
| LSD | lysosomal storage disease |
| NPB/NPC | Niemann–Pick type B/Niemann–Pick type C |
| FACS | Flow cytometry |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| VLDL | Very-low-density lipoprotein |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| CAD | Coronary artery disease |
| LDLR | Low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| CD | Cluster of differentiation |
| CCR | Chemokine receptor |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| Mon | Monocytes |
Appendix A
| Defect | Disorder | Symptoms in adult Phenotype | Dyslipidemia | Main Biomarker | Gene | Prevalence * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucocerebrosidase deficiency/Saposin C deficiency | Gaucher disease | Hepatosplenomegaly, skeletal symptoms, cytopenia, neurological symptoms (type II/III only) | Y (subtle) | Chitotriosidase, glucosylsphingosine | GBA or PSAP | 1–9/100,000 |
| Acid sphingomyelinase deficiency | Niemann–Pick type B | Hepatosplenomegaly, interstitial lung disease | Y | Lyso-sphingomyelin (lyso-SM), N-palmitoyl-O-phosphocholineserine (PPCS) | SMPD1 | 1–9/100,000 |
| Cholesterol trafficking disorder | Niemann–Pick type C | Hepatosplenomegaly, ataxia, hypotonia, vertical supranuclear gaze palsy, dysphagia, dysarthria, respiratory infections/failure, liver failure | Y | N-palmitoyl-O-phosphocholineserine (PPCS), Cholestane-3β,5α,6β-triol | NPC1 or NPC2 | 1–9/100,000 |
| Lysosomal β-mannosidase deficiency | β-Mannosidosis | Mild cognitive impairement, psychiatric symptoms, hearing loss, recurrent respiratory infections, coarse facial features, skeletal abnormalities hepatosplenomegaly | N | Oligosaccharides | MANBA | 1/1,000,000 |
| α-neuraminidase deficiency | Sialidosis | Seizures, hyperreflexia, ataxia, myoclonus, cherry-red maculas, hepatosplenomegaly, dysostosis multiplex | N | Oligosaccharides | NEU1 | <1/1,000,000 |
| Lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) deficiency | Cholesterol ester storage disease (CESD) | Hepatosplenomegaly, dyslipidemia, liver dysfunction, premature atherosclerosis | Y (marked) | Transaminases, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol and triglycerides | LIPA | 1/40,000–300,000 |
| High-density lipoprotein (HDL) deficiency | Tangier disease | Enlarged orange/yellow tonsils, premature atherosclerosis, hepatosplenomegaly, neuropathy, cytopenia, corneal clouding, dyslipidemia | Y (marked) | HDL-cholesterol/apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA1) | ABCA1 | <1/1,000,000 |
| LPL deficiency | Chylomicronemia syndrome | Acute pancreatitis, hepatosplenomegaly, xanthoma | Y (marked) | Triglycerides | LPL, APOC2, GPIHBP1, LMF1, APOA5 | 1–9/1,000,000 |
| Partial LCAT deficiency (Fish-eye disease) | Lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) | Corneal opacities, progressive renal disease, hemolytic anemia, hepatosplenomegaly | Y (marked) | HDL-cholesterol/apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA1)/primary HDL proteins | LCAT | <1/1,000,000 |
Appendix B
| Target Antigen | Vendor or Source | Catalog # | Working Concentration | Lot # |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD91-FITC | BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA | 550,496 | 1:500 | 5,069,533 |
| CCR2-Alexa fluor 647 | BD Biosciences | 558,406 | 1:50 | 6,105,900 |
| CD11c-APC | BD Biosciences | 559,877 | 1:50 | 6,187,944 |
| CD36-APC | BD Biosciences | 550,956 | 1:100 | 5,240,938 |
| CD18-APC | BD Biosciences | 551,060 | 1:25 | 4,324,584 |
| TLR2-FITC | BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA | 121,806 | 1: 100 | B218,515 |
| TLR4-PE | BioLegend | 312,806 | 1:10 | B252,428 |
| CD11b-PE | BD Biosciences | 555,388 | 1:25 | 9,045,644 |
| CD163 | BD Biosciences | 556,018 | 1:25 | 36,295 |
| HLA-DR-PercpC5.5 | BD Biosciences | 560,652 | 1: 50 | 9,074,606 |
| CD14-PEcy7 | BD Biosciences | 557,742 | 1: 50 | 8,019,559 |
| CD16-APC-Cy7 | BD Biosciences | 560,195 | 1: 50 | 9,037,577 |
| Nanogram IVIG | Sanquin, Amsterdam, The Netherlands | 8,717,185,830,262 | 1:50 | 18625H462B |
| Gene name | phyloP | CADD | SpliceAI-G | OMIM_DISEASE | ClinVar | ClinVar Accession | Zygosity | gnomAD-G AF (%) | Hgvsg | Hgvsc | Hgvsp | Mutation Taster | PolyPhen2 | SIFT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APOE | 2.669 | 24.3 | 0 | Hyperlipoproteinemia, type III, 617347 (3); {Coronary artery disease, severe, susceptibility to}, 617347 (3); {?Alzheimer disease, protection against, due to APOE3-Christchurch}, 607822 (3), Autosomal dominant; Lipoprotein glomerulopathy, 611771 (3); Sea-blue histiocyte disease, 269600 (3), Autosomal recessive; {?Macular degeneration, age-related}, 603075 (3), Autosomal dominant; Alzheimer disease 2, 104310 (3), Autosomal dominant | VUS | VCV000478904.7 | Homozygous | 0.0128 | 19:g.45411987G>A | NM_001302688.2(APOE):c.512G>A | p.(Gly171Asp) | Tolerated | ||
| APOE | 0.344 | 25 | 0 | Hyperlipoproteinemia, type III, 617347 (3); {Coronary artery disease, severe, susceptibility to}, 617347 (3); {?Alzheimer disease, protection against, due to APOE3-Christchurch}, 607822 (3), Autosomal dominant; Lipoprotein glomerulopathy, 611771 (3); Sea-blue histiocyte disease, 269600 (3), Autosomal recessive; {?Macular degeneration, age-related}, 603075 (3), Autosomal dominant; Alzheimer disease 2, 104310 (3), Autosomal dominant | Inconsistent | VCV000017848.16 | Homozygous | 8.27 | 19:g.45412079C>T | NM_001302688.2(APOE):c.604C>T | p.(Arg202Cys) | Deleterious | ||
| BAG3 | 3.719 | 42 | 0 | Cardiomyopathy, dilated, 1HH, 613881 (3), Autosomal dominant; Myopathy, myofibrillar, 6, 612954 (3), Autosomal dominant | Homozygous | ND | 10:g.121436630C>T | NM_004281.4(BAG3):c.1564C>T | p.(Gln522*) | |||||
| MYH3 | 0.196 | 11.71 | 0 | Contractures, pterygia, and spondylocarpotarsal fusion syndrome 1B, 618469 (3), Autosomal recessive; Arthrogryposis, distal, type 2B3 (Sheldon-Hall), 618436 (3), Autosomal dominant; Arthrogryposis, distal, type 2A (Freeman-Sheldon), 193700 (3), Autosomal dominant; Contractures, pterygia, and spondylocarpostarsal fusion syndrome 1A, 178110 (3), Autosomal dominant | Heterozygous | ND | 17:g.10552930_10552931ins121 | NM_002470.4(MYH3):c.605_606ins121 | p.(Gly203Profs*78) | |||||
| NPC1 | 0.437 | 8.503 | 0 | Niemann-Pick disease, type D, 257220 (3), Autosomal recessive; Niemann-Pick disease, type C1, 257220 (3), Autosomal recessive | Benign | VCV000378276.8 | Heterozygous | 0.21 | 18:g.21148768T>C | NM_000271.5(NPC1):c.463+19A>G | p.? | |||
| SACS | 6.4 | 21.6 | 0 | Spastic ataxia, Charlevoix-Saguenay type, 270550 (3), Autosomal recessive | Likely benign/VUS | VCV000212109.41 | Homozygous | 0.175 | 13:g.23907033G>A | NM_014363.6(SACS):c.10982C>T | p.(Ala3661Val) | Benign | Probably damaging | Deleterious |
| SIPA1L3 | 1.963 | 20.2 | 0 | ?Cataract 45, 616851 (3), Autosomal recessive | Homozygous | 0.00319 | 19:g.38573424T>C | NM_015073.3(SIPA1L3):c.1219T>C | p.(Cys407Arg) | Benign | Benign | Tolerated | ||
| VHL | 0.256 | 20.9 | 0 | Pheochromocytoma, 171300 (3), Autosomal dominant; Erythrocytosis, familial, 2, 263400 (3), Autosomal recessive; von Hippel-Lindau syndrome, 193300 (3), Autosomal dominant; Renal cell carcinoma, somatic, 144700 (3); Hemangioblastoma, cerebellar, somatic (3) | VUS | VCV000132707.13 | ND | 3:g.10183635C>A | NM_000551.4(VHL):c.104C>A | p.(Ala35Asp) | Benign | Possibly damaging | Deleterious | |
| VHL | 0.125 | 21.6 | 0 | Pheochromocytoma, 171300 (3), Autosomal dominant; Erythrocytosis, familial, 2, 263400 (3), Autosomal recessive; von Hippel-Lindau syndrome, 193300 (3), Autosomal dominant; Renal cell carcinoma, somatic, 144700 (3); Hemangioblastoma, cerebellar, somatic (3) | VUS | VCV000216476.14 | ND | 3:g.10183545C>T | NM_000551.4(VHL):c.14C>T | p.(Ala5Val) | Benign | Possibly damaging | Tolerated | |
| BEX5 | 2.518 | 22.4 | 0 | Hemizygous | ND | X:g.101409056A>C | NM_001159560.2(BEX5):c.182T>G | p.(Ile61Arg) | Benign | Probably damaging | Deleterious | |||
| CAPN12 | 1.574 | 24.2 | 0 | Homozygous | 0.00637 | 19:g.39221807G>C | NM_144691.4(CAPN12):c.2014C>G | p.(Arg672Gly) | Benign | Probably damaging | Deleterious | |||
| DPY19L3 | 4.949 | 22.5 | 0 | Homozygous | 0.00956 | 19:g.32902201G>T | NM_207325.3(DPY19L3):c.160G>T | p.(Ala54Ser) | Benign | Benign | Tolerated | |||
| TAF5L | 6.292 | 24.7 | 0 | Homozygous | 0.0987 | 1:g.229730691T>C | NM_014409.4(TAF5L):c.1123A>G | p.(Thr375Ala) | Benign | Probably damaging | Tolerated | |||
| TNK2 | 5.948 | 25.9 | 0 | Heterozygous | 0.0128 | 3:g.195594795G>A | NM_001387707.1(TNK2):c.2470C>T | p.(Arg824Trp) | Deleterious | |||||
| TNK2 | 3.788 | 25.9 | 0 | Heterozygous | 0.0321 | 3:g.195594882G>A | NM_001387707.1(TNK2):c.2383C>T | p.(Arg795Trp) | Deleterious | |||||
| ZNF532 | 0.068 | 11.38 | 0 | Heterozygous | 0.271 | 18:g.56586091C>T | NM_018181.6(ZNF532):c.572C>T | p.(Thr191Met) | Benign | Benign | Tolerated | |||
| ZNF532 | 6.492 | 24.3 | 0 | Heterozygous | 0.0159 | 18:g.56651600G>A | NM_018181.6(ZNF532):c.3808G>A | p.(Ala1270Thr) | Benign | Possibly damaging | Tolerated | |||
Appendix C
| Total | Mon 1 | Mon 2 | Mon 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | |
| 3216.7 | 4718.4 | 3620 | 5059.1 | 4345 | 5262 | 642 | 595.9 | |
| 3247 | 4086 | 4006 | 554 | |||||
| 2700.9 | 2745.6 | 3845 | 960.1 | |||||
| 3216.7 | 3620 | 4006 | 642 | Median |
| Total | Mon 1 | Mon 2 | Mon 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | |
| 481 | 677 | 527 | 703 | 283.4 | 588 | 38 | 29 | |
| 477 | 540 | 274 | 117 | |||||
| 494.1 | 510.5 | 204 | 30 | |||||
| 481 | 527 | 274 | 38 | Median |
| Total | Mon 1 | Mon 2 | Mon 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | |
| 165.7 | 121.4 | 178 | 125.1 | 143 | 164 | −2 | 9.2 | |
| 208 | 223 | 212 | 92.9 | |||||
| 200.9 | 206.6 | 141 | 23 | |||||
| 200.9 | 206.6 | 143 | 23 | Median |
| Total | Mon 1 | Mon 2 | Mon 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | |
| 1271 | 1582 | 1210 | 1586 | 2094.4 | 2296 | 2081 | 1435 | |
| 1628 | 1550 | 2730 | 1993 | |||||
| 817.1 | 800.5 | 1311 | 1190 | |||||
| 1271 | 1210 | 2094.4 | 1993 | Median |
| Total | Mon 1 | Mon 2 | Mon 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | |
| 385 | 461 | 336 | 465 | 931.4 | 1087 | 1094 | 262 | |
| 428 | 379 | 1050 | 706 | |||||
| 248.1 | 237.5 | 601 | 523 | |||||
| 385 | 336 | 931.4 | 706 | Median |
| Total | Mon 1 | Mon 2 | Mon 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | |
| 2658 | 1996 | 2698 | 2093 | 3620 | 2462 | 1954 | 241 | |
| 1763 | 1855 | 2457 | 1140 | |||||
| 1735 | 1742 | 2361 | 1152 | |||||
| 1763 | 1855 | 2457 | 1152 | Median |
| Total | Mon 1 | Mon 2 | Mon 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | |
| 3128.7 | 2521.4 | 3161 | 2573.1 | 3779 | 3823 | 2519 | 1212.9 | |
| 3387 | 3541 | 3994 | 2427 | |||||
| 1416.9 | 1407.6 | 1896 | 1399.1 | |||||
| 3128.7 | 3161 | 3779 | 2427 | Median |
| Total | Mon 1 | Mon 2 | Mon 3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | Ctrl | Proband | |
| 3122 | 3835 | 3610 | 4151 | 3644.4 | 4594 | 296 | 72 | |
| 1716 | 2118 | 1636 | 287 | |||||
| 1593.1 | 1654.5 | 1612 | 194 | |||||
| 1716 | 2118 | 1636 | 287 | Median |
| Ctrl | Proband | |
|---|---|---|
| 2.87 | 4.47 | |
| 2.29 | ||
| 4.41 | ||
| 2.87 | Median | |
| 3.19 | Mean |
References
- Okorodudu, D.E.; Crowley, M.J.; Sebastian, S.; Rowell, J.V.; Guyton, J.R. Inherited lipemic splenomegaly and the spectrum of apolipoprotein E p.Leu167del mutation phenotypic variation. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2013, 7, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, V.; Dumpa, V. Lysosomal Storage Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Stirnemann, J.; Belmatoug, N.; Camou, F.; Serratrice, C.; Froissart, R.; Caillaud, C.; Levade, T.; Astudillo, L.; Serratrice, J.; Brassier, A.; et al. A Review of Gaucher Disease Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorink-Moret, M.; Goorden, S.M.I.; van Kuilenburg, A.B.P.; Wijburg, F.A.; Ghauharali-van der Vlugt, J.M.M.; Beers-Stet, F.S.; Zoetekouw, A.; Kulik, W.; Hollak, C.E.M.; Vaz, F.M. Rapid screening for lipid storage disorders using biochemical markers. Expert center data and review of the literature. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2018, 123, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang Do, A.N.; Chang, I.J.; Jiang, X.; Wolfe, L.A.; Ng, B.G.; Lam, C.; Schnur, R.E.; Allis, K.; Hansikova, H.; Ondruskova, N.; et al. Elevated oxysterol and N-palmitoyl-O-phosphocholineserine levels in congenital disorders of glycosylation. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2023, 46, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coene, K.L.M.; Kluijtmans, L.A.J.; van der Heeft, E.; Engelke, U.F.H.; de Boer, S.; Hoegen, B.; Kwast, H.J.T.; van de Vorst, M.; Huigen, M.; Keularts, I.; et al. Next-generation metabolic screening: Targeted and untargeted metabolomics for the diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism in individual patients. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haijes, H.A.; Willemsen, M.; Van der Ham, M.; Gerrits, J.; Pras-Raves, M.L.; Prinsen, H.; Van Hasselt, P.M.; De Sain-van der Velden, M.G.M.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M.; Jans, J.J.M. Direct Infusion Based Metabolomics Identifies Metabolic Disease in Patients’ Dried Blood Spots and Plasma. Metabolites 2019, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Kruckeberg, K.E.; O’Brien, J.F.; Ji, Z.S.; Karnes, P.S.; Crotty, T.B.; Hay, I.D.; Mahley, R.W.; O’Brien, T. Familial splenomegaly: Macrophage hypercatabolism of lipoproteins associated with apolipoprotein E mutation [apolipoprotein E (Δ149 Leu)]. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 4354–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisgraber, K.H.; Rall, S.C., Jr.; Innerarity, T.L.; Mahley, R.W.; Kuusi, T.; Ehnholm, C. A novel electrophoretic variant of human apolipoprotein E. Identification and characterization of apolipoprotein E1. J. Clin. Investig. 1984, 73, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.S.; Fazio, S.; Mahley, R.W. Variable heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding of apolipoprotein E variants may modulate the expression of type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 13421–13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahley, R.W.; Huang, Y.; Rall, S.C., Jr. Pathogenesis of type III hyperlipoproteinemia (dysbetalipoproteinemia). Questions, quandaries, and paradoxes. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 1933–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahalkar, A.R.; Wang, J.; Sirrs, S.; Dimmick, J.; Holmes, D.; Urquhart, N.; Hegele, R.A.; Mattman, A. An unusual case of severe hypertriglyceridemia and splenomegaly. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 606–610; discussion 610–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, C.B. Type III Hyperlipoproteinemia: Still Worth Considering? Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 59, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sienski, G.; Narayan, P.; Bonner, J.M.; Kory, N.; Boland, S.; Arczewska, A.A.; Ralvenius, W.T.; Akay, L.; Lockshin, E.; He, L.; et al. APOE4 disrupts intracellular lipid homeostasis in human iPSC-derived glia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaaz4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iron, A.; Richard, P.; de Zulueta, M.P.; Thomas, G.; Thomas, M. Genotyping of a patient homozygous for a rare apolipoprotein E1 [Gly127→Asp; Arg158→Cys] (Weisgraber allele). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1995, 18, 723–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, A.; Assefbarkhi, N.; Eltze, C.; Ehlenz, K.; Funke, H.; Pies, A.; Assmann, G.; Kaffarnik, H. Normolipemic dysbetalipoproteinemia and hyperlipoproteinemia type III in subjects homozygous for a rare genetic apolipoprotein E variant (apoE1). J. Lipid Res. 1990, 31, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenham, P.R.; McDowell, I.F.; Hodges, V.M.; McEneny, J.; O’Kane, M.J.; Jeremy, R.; Davies, H.; Nicholls, D.P.; Trimble, E.R.; Blundell, G. Rare apolipoprotein E variant identified in a patient with type III hyperlipidaemia. Atherosclerosis 1993, 99, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapellos, T.S.; Bonaguro, L.; Gemund, I.; Reusch, N.; Saglam, A.; Hinkley, E.R.; Schultze, J.L. Human Monocyte Subsets and Phenotypes in Major Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, B.; Moher, D.; Cameron, C. The PRISMA Extension Statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 163, 566–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Open Med. 2009, 3, e123–e130. [Google Scholar]
- Faivre, L.; Saugier-Veber, P.; Pais de Barros, J.P.; Verges, B.; Couret, B.; Lorcerie, B.; Thauvin, C.; Charbonnier, F.; Huet, F.; Gambert, P.; et al. Variable expressivity of the clinical and biochemical phenotype associated with the apolipoprotein E p.Leu149del mutation. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 13, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidemann, B.E.; Koopal, C.; Baass, A.; Defesche, J.C.; Zuurbier, L.; Mulder, M.T.; Roeters van Lennep, J.E.; Riksen, N.P.; Boot, C.; Marais, A.D.; et al. Establishing the relationship between familial dysbetalipoproteinemia and genetic variants in the APOE gene. Clin. Genet. 2022, 102, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tippett, E.; Cheng, W.J.; Westhorpe, C.; Cameron, P.U.; Brew, B.J.; Lewin, S.R.; Jaworowski, A.; Crowe, S.M. Differential expression of CD163 on monocyte subsets in healthy and HIV-1 infected individuals. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berberich, A.J.; Hegele, R.A. A Modern Approach to Dyslipidemia. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 611–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, S.; Brisson, D.; Gaudet, D. Influence of Abdominal Obesity on the Lipid-Lipoprotein Profile in Apoprotein E2/4 Carriers: The Effect of an Apparent Duality. J. Lipids 2015, 2015, 742408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidemann, B.E.; Wolters, F.J.; Kavousi, M.; Gruppen, E.G.; Dullaart, R.P.; Marais, A.D.; Visseren, F.L.; Koopal, C. Adiposity and the development of dyslipidemia in APOE ε2 homozygous subjects: A longitudinal analysis in two population-based cohorts. Atherosclerosis 2021, 325, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandor, N.; Lukacsi, S.; Ungai-Salanki, R.; Orgovan, N.; Szabo, B.; Horvath, R.; Erdei, A.; Bajtay, Z. CD11c/CD18 Dominates Adhesion of Human Monocytes, Macrophages and Dendritic Cells over CD11b/CD18. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, S.L.; Duivenvoorden, R.; Stiekema, L.C.A.; Nurmohamed, N.S.; van der Valk, F.M.; Versloot, M.; Verberne, H.J.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Nahrendorf, M.; Bekkering, S.; et al. CCR2 expression on circulating monocytes is associated with arterial wall inflammation assessed by 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients at risk for cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneshige, R.; Shimizu, N.; Motoki, Y.; Nojima, J. Antibody binding activity specific to monocyte scavenger receptor CD36 is frequently detectable in the plasma of patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus 2023, 32, 1353–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Xu, Y.; Sahebkar, A.; Xu, S. CD36 in Atherosclerosis: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2020, 22, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Munoz, C.; Mendez-Barbero, N.; Svendsen, P.; Sastre, C.; Fernandez-Laso, V.; Quesada, P.; Egido, J.; Escola-Gil, J.C.; Martin-Ventura, J.L.; Moestrup, S.K.; et al. CD163 deficiency increases foam cell formation and plaque progression in atherosclerotic mice. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 14960–14976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiuri, G.; Rudling, M.; Ollivier, V.; Jacob, M.P.; Michel, J.B.; Hansson, G.K.; Nicoletti, A. Interleukin-10 deficiency increases atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and low-density lipoproteins in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Mol. Med. 2003, 9, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leifer, C.A.; Medvedev, A.E. Molecular mechanisms of regulation of Toll-like receptor signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, P.; Bardoloi, A.; Parkash, A.A. Metabolic effects of obesity: A review. World J. Diabetes 2010, 1, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahik, V.D.; Frisdal, E.; Le Goff, W. Rewiring of Lipid Metabolism in Adipose Tissue Macrophages in Obesity: Impact on Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.; Despres, J.P.; Fullerton, H.J.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 133, e38–e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sijbrands, E.J.; Hoffer, M.J.; Meinders, A.E.; Havekes, L.M.; Frants, R.R.; Smelt, A.H.; De Knijff, P. Severe hyperlipidemia in apolipoprotein E2 homozygotes due to a combined effect of hyperinsulinemia and an SstI polymorphism. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 2722–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.M.; Ho, L.C.; Han, L.L.; Lu, J.J.; Yue, X.; Yang, N.Y. The role of splenectomy in lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis (AS). Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagral, A. Gaucher disease. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2014, 4, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranade, A.; Chintapatla, R.; Varma, M.; Sandhu, G. Hematologic manifestations and leukemia in Gaucher’s disease. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 11, 253–255. [Google Scholar]
- Fleshner, P.R.; Aufses, A.H., Jr.; Grabowski, G.A.; Elias, R. A 27-year experience with splenectomy for Gaucher’s disease. Am. J. Surg. 1991, 161, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, K.; Nagarajan, P.; Shankar, E.M.; Kamarul, T.; Kumar, J.M. High-fat diet- and angiotensin II-induced aneurysm concurrently elicits splenic hypertrophy. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 44, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wintjens, R.; Bozon, D.; Belabbas, K.; Mbou, F.; Girardet, J.P.; Tounian, P.; Jolly, M.; Boccara, F.; Cohen, A.; Karsenty, A.; et al. Global molecular analysis and APOE mutations in a cohort of autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia patients in France. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiewak, J.; Doykov, I.; Papandreou, A.; Hallqvist, J.; Mills, P.; Clayton, P.T.; Gissen, P.; Mills, K.; Heywood, W.E. New Perspectives in Dried Blood Spot Biomarkers for Lysosomal Storage Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, R.; Kell, P.; Dietzen, D.J.; Farhat, N.Y.; Do, A.N.D.; Porter, F.D.; Berry-Kravis, E.; Vite, C.H.; Reunert, J.; Marquardt, T.; et al. Application of N-palmitoyl-O-phosphocholineserine for diagnosis and assessment of response to treatment in Niemann-Pick type C disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2020, 129, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, E.A.; Oud, M.M.; van der Crabben, S.N.; Versloot, M.; Goorden, S.M.I.; van Karnebeek, C.D.M.; Kroon, J.; Langeveld, M. Inherited Dyslipidemic Splenomegaly: A Genetic Macrophage Storage Disorder Caused by Disruptive Apolipoprotein E (APOE) Variants. Genes 2025, 16, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030289
Ferreira EA, Oud MM, van der Crabben SN, Versloot M, Goorden SMI, van Karnebeek CDM, Kroon J, Langeveld M. Inherited Dyslipidemic Splenomegaly: A Genetic Macrophage Storage Disorder Caused by Disruptive Apolipoprotein E (APOE) Variants. Genes. 2025; 16(3):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030289
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Elise A., Machteld M. Oud, Saskia N. van der Crabben, Miranda Versloot, Susan M. I. Goorden, Clara D. M. van Karnebeek, Jeffrey Kroon, and Mirjam Langeveld. 2025. "Inherited Dyslipidemic Splenomegaly: A Genetic Macrophage Storage Disorder Caused by Disruptive Apolipoprotein E (APOE) Variants" Genes 16, no. 3: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030289
APA StyleFerreira, E. A., Oud, M. M., van der Crabben, S. N., Versloot, M., Goorden, S. M. I., van Karnebeek, C. D. M., Kroon, J., & Langeveld, M. (2025). Inherited Dyslipidemic Splenomegaly: A Genetic Macrophage Storage Disorder Caused by Disruptive Apolipoprotein E (APOE) Variants. Genes, 16(3), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030289





