A TFAIII-Type Transcription Factor OsZFPH Regulating a Signaling Pathway Confers Resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material
2.2. Rice Plants and Methods of Pathogen Inoculation and Investigation
2.3. Henotypic Verification of OsZFPH Transgenic Plants via PXO99 Inoculation
2.4. DNA Extraction and Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR
2.5. Determination of H2O2 Content and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in OsZFPH Transgenic Plants
2.6. Analysis of the Relationship Between Exogenous Hormones and OsZFPH Gene Expression
2.7. Transient Expression and Subcellular Localization of OsZFPH Gene in Tobacco Leaves
2.8. Screening Proteins Interacting with OsZFPH
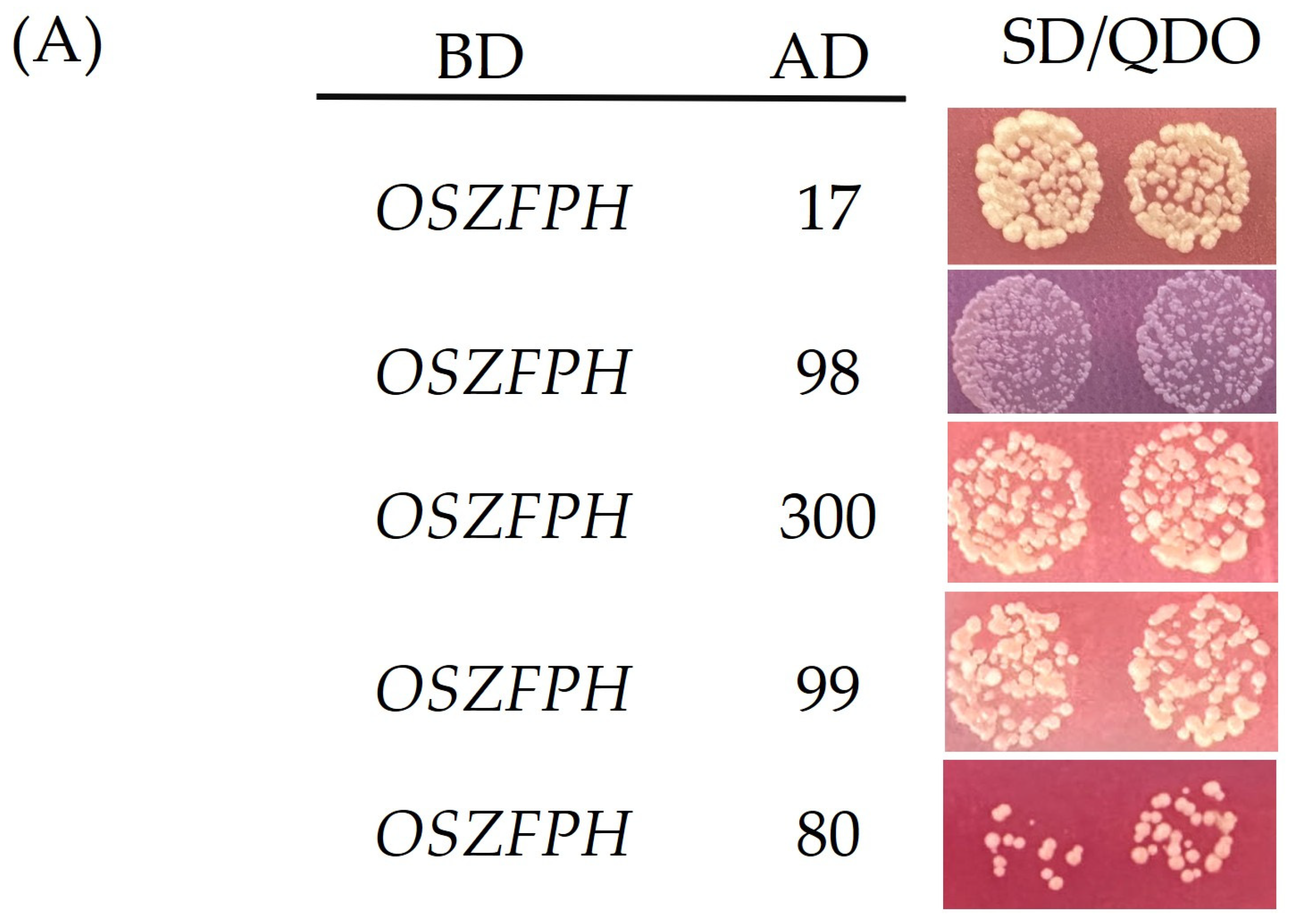
2.8.1. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay
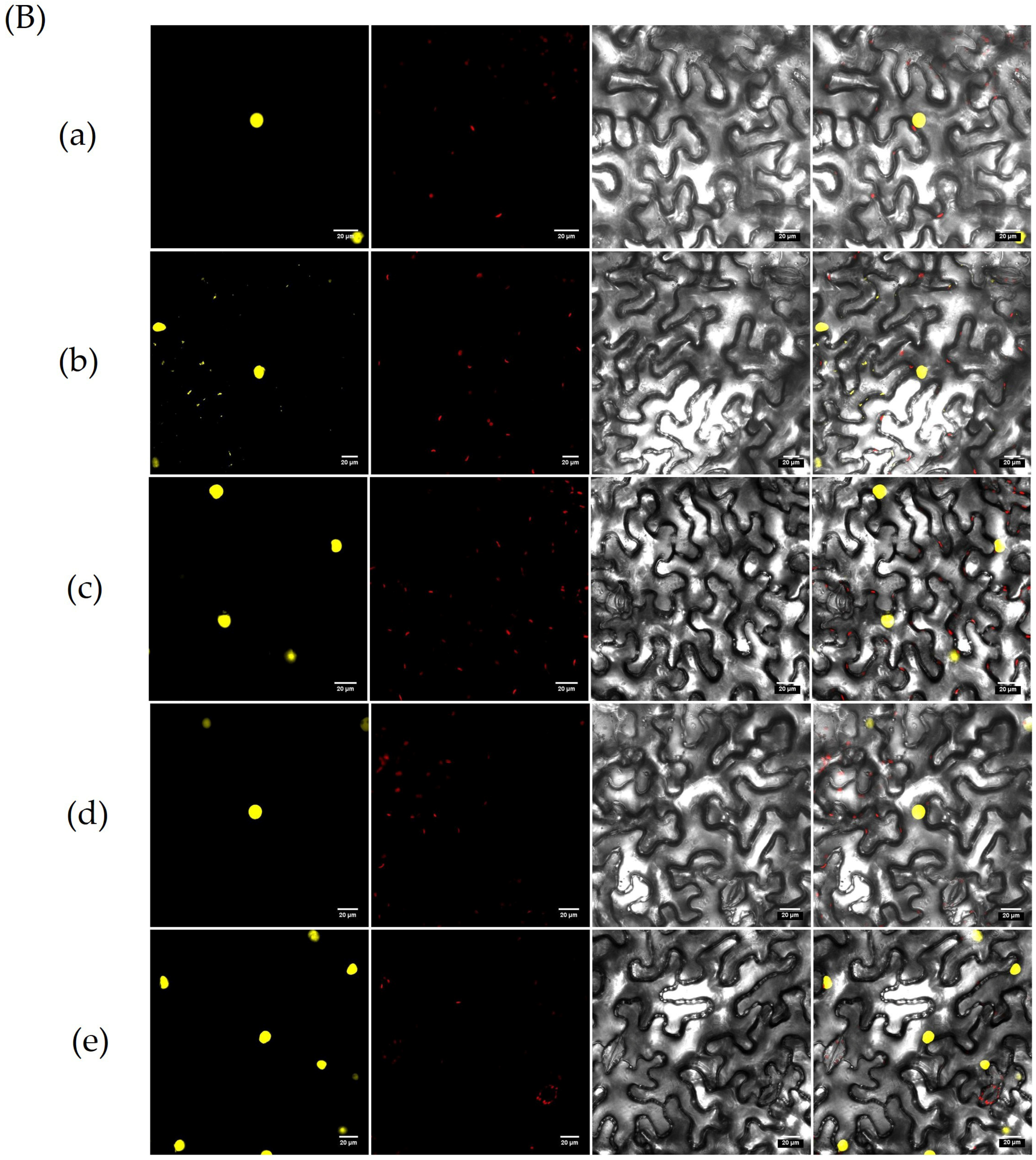
2.8.2. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) Technique
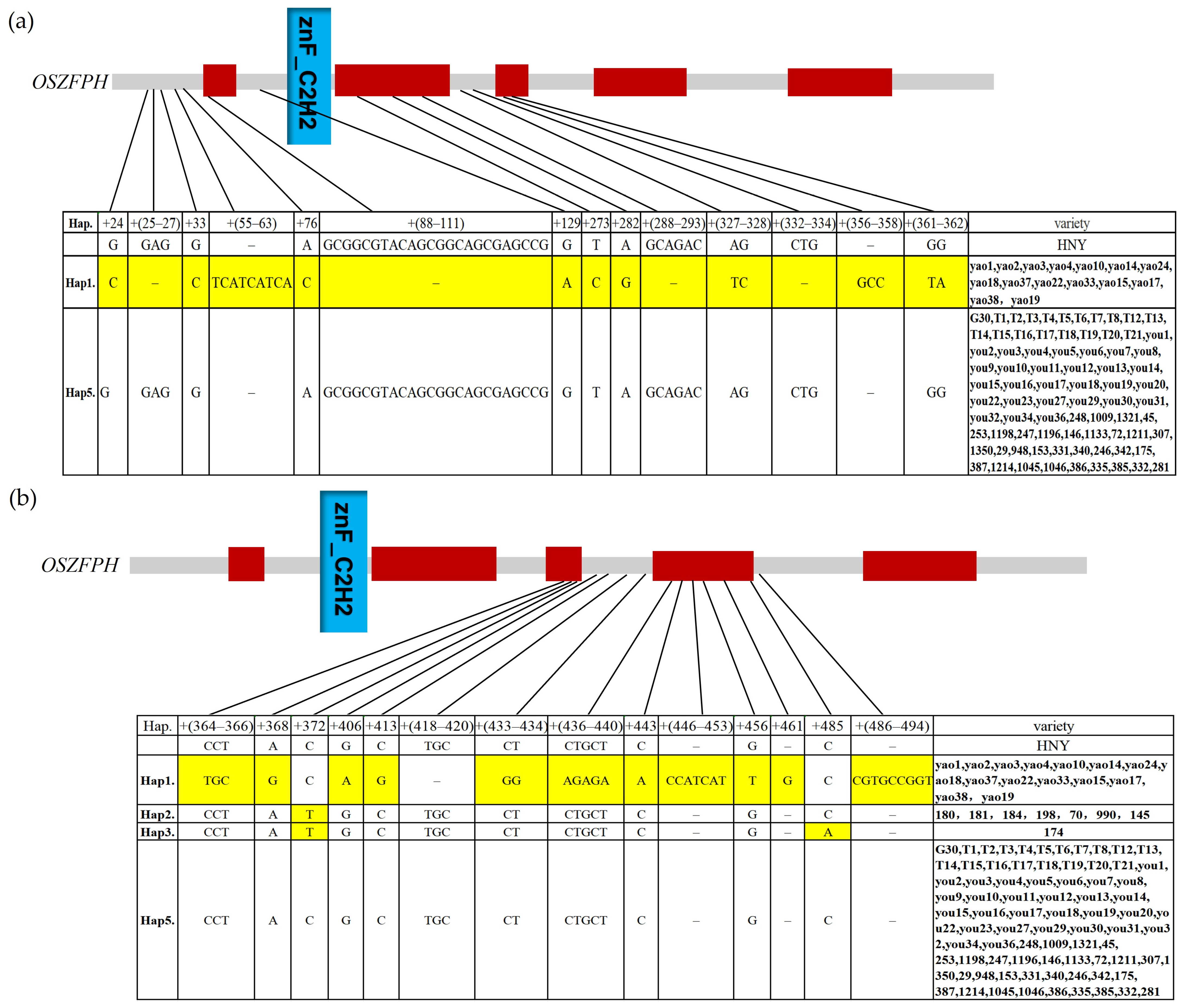
2.9. Haplotype Analysis of the Transcription Factor OsZFPH
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
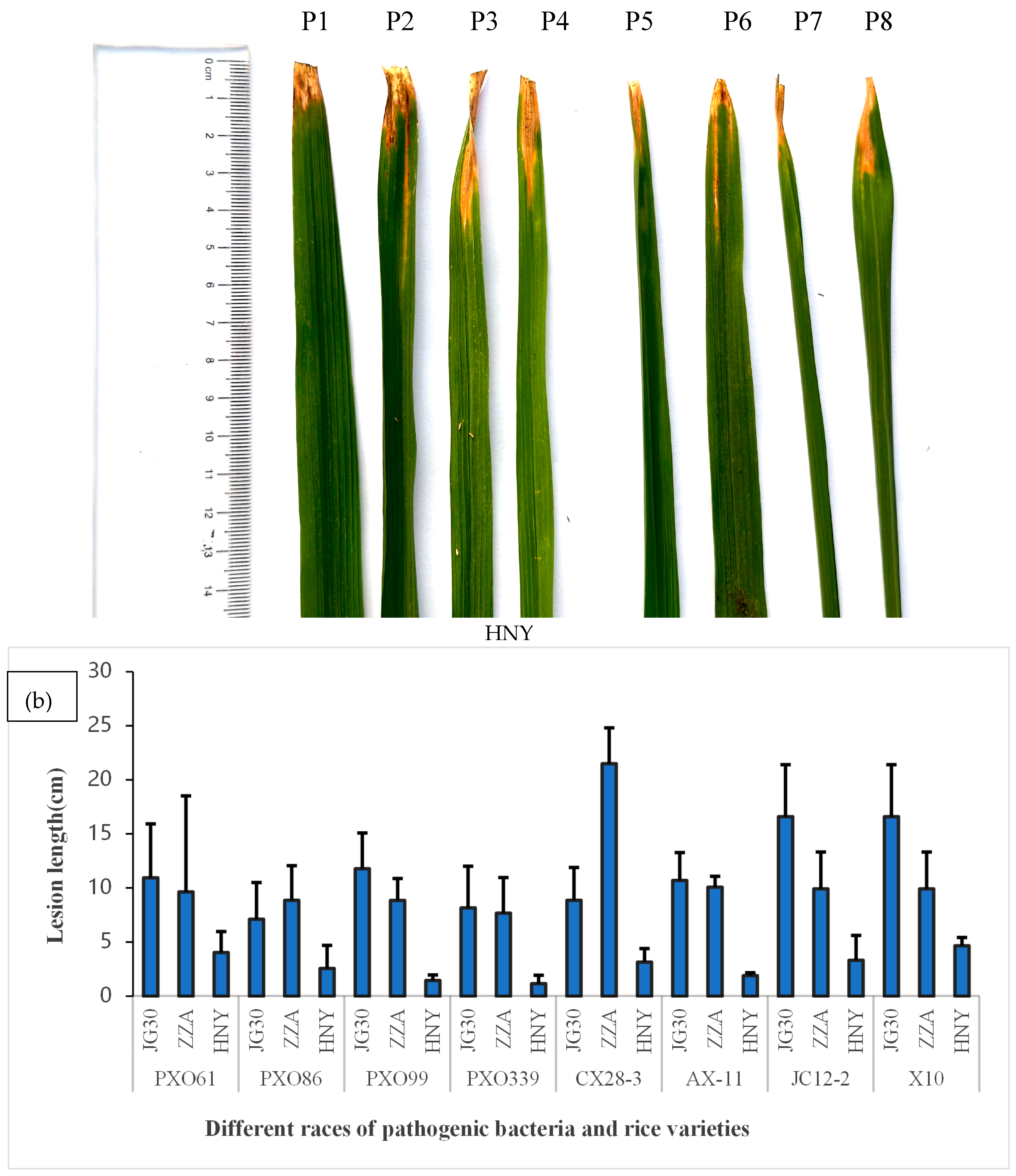
3.1. Characterization of Yunnan Local Rice HNY for High Resistance to Bacterial Leaf Blight
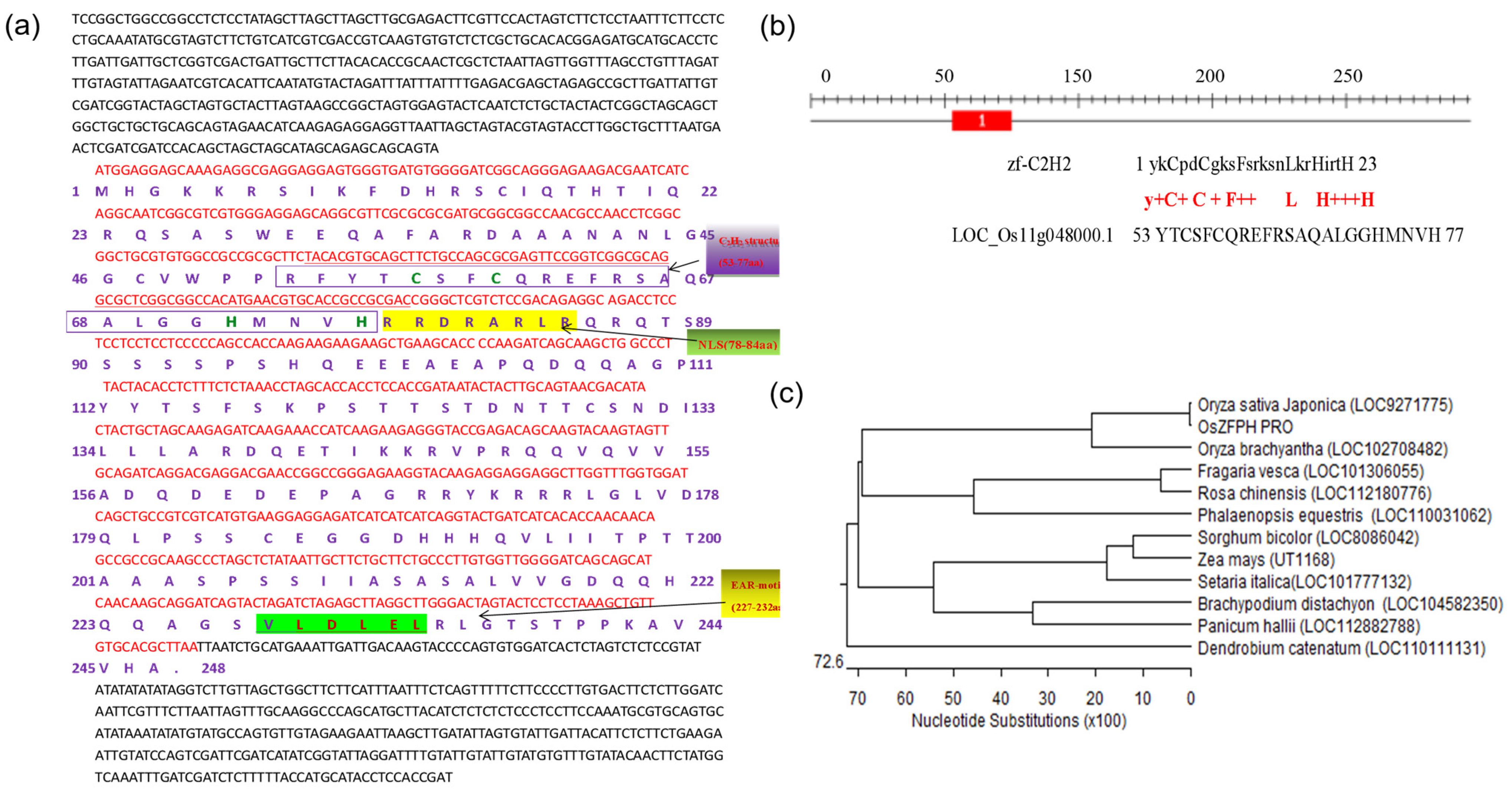
3.2. Acquisition of OsZFPH: A TFAIII Transcription Factor Gene of Yunnan Local Rice HNY
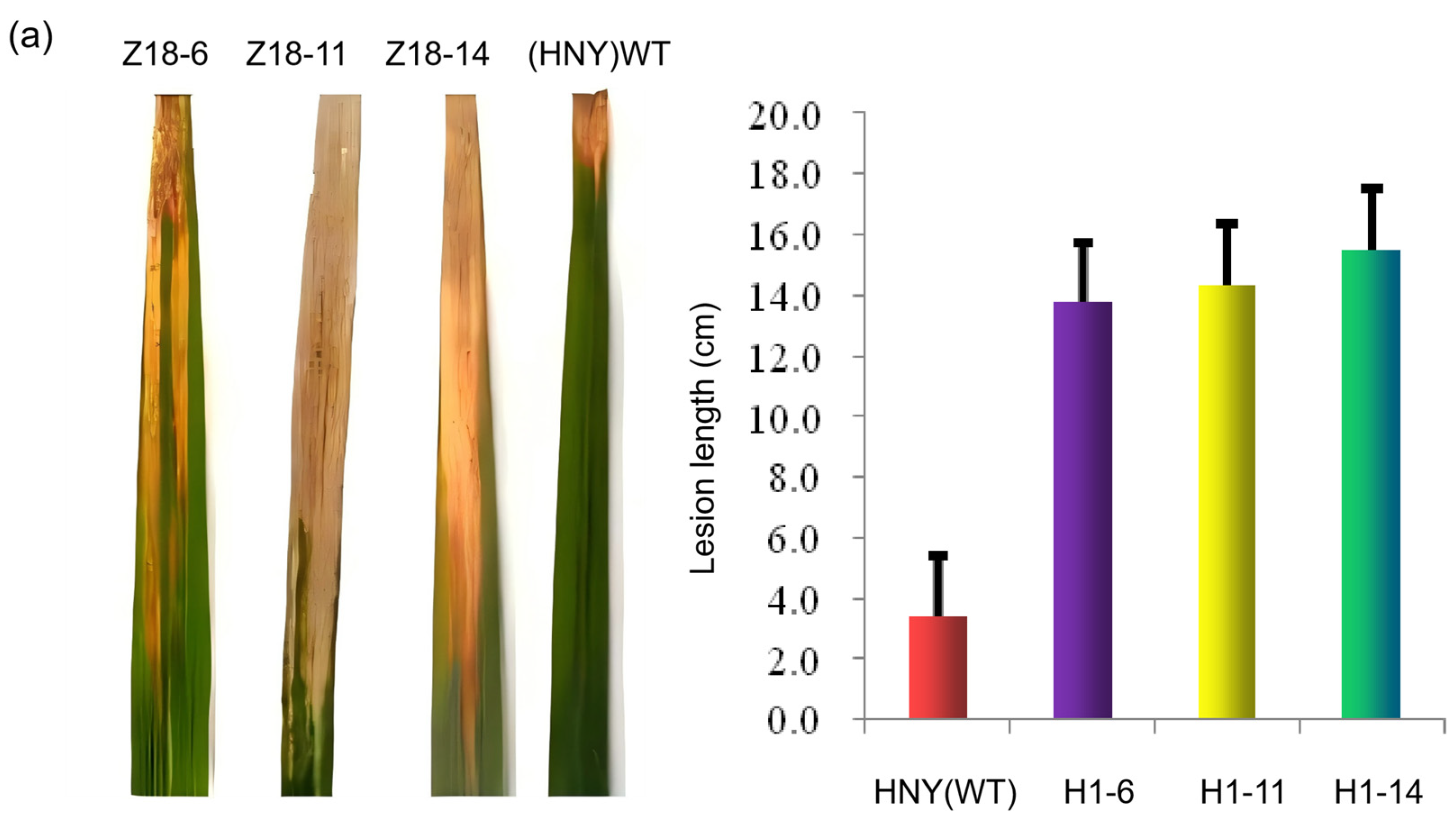
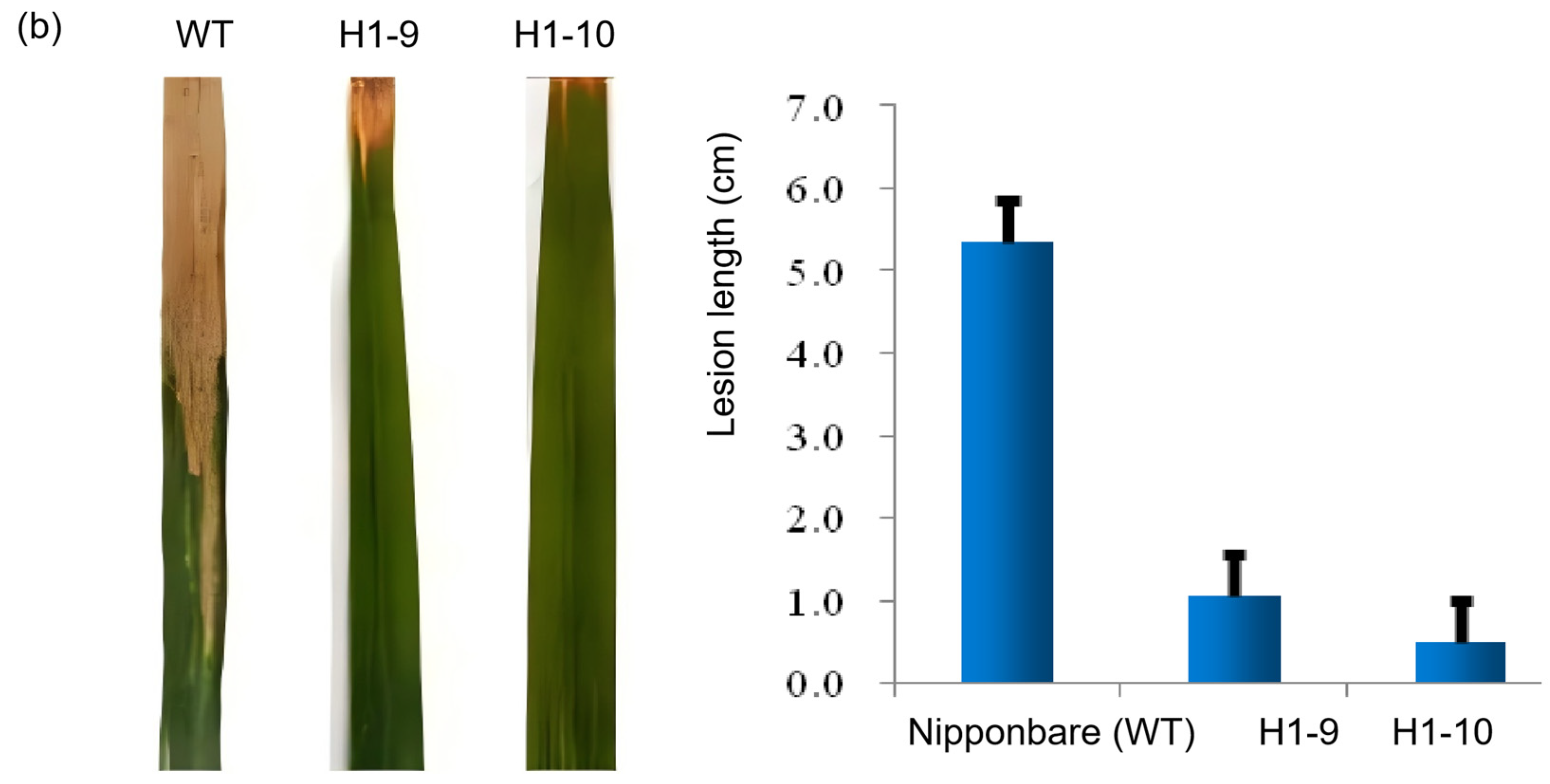
3.3. Phenotypic Verification via Inoculating OsZFPH Transgenic Plants with PXO99
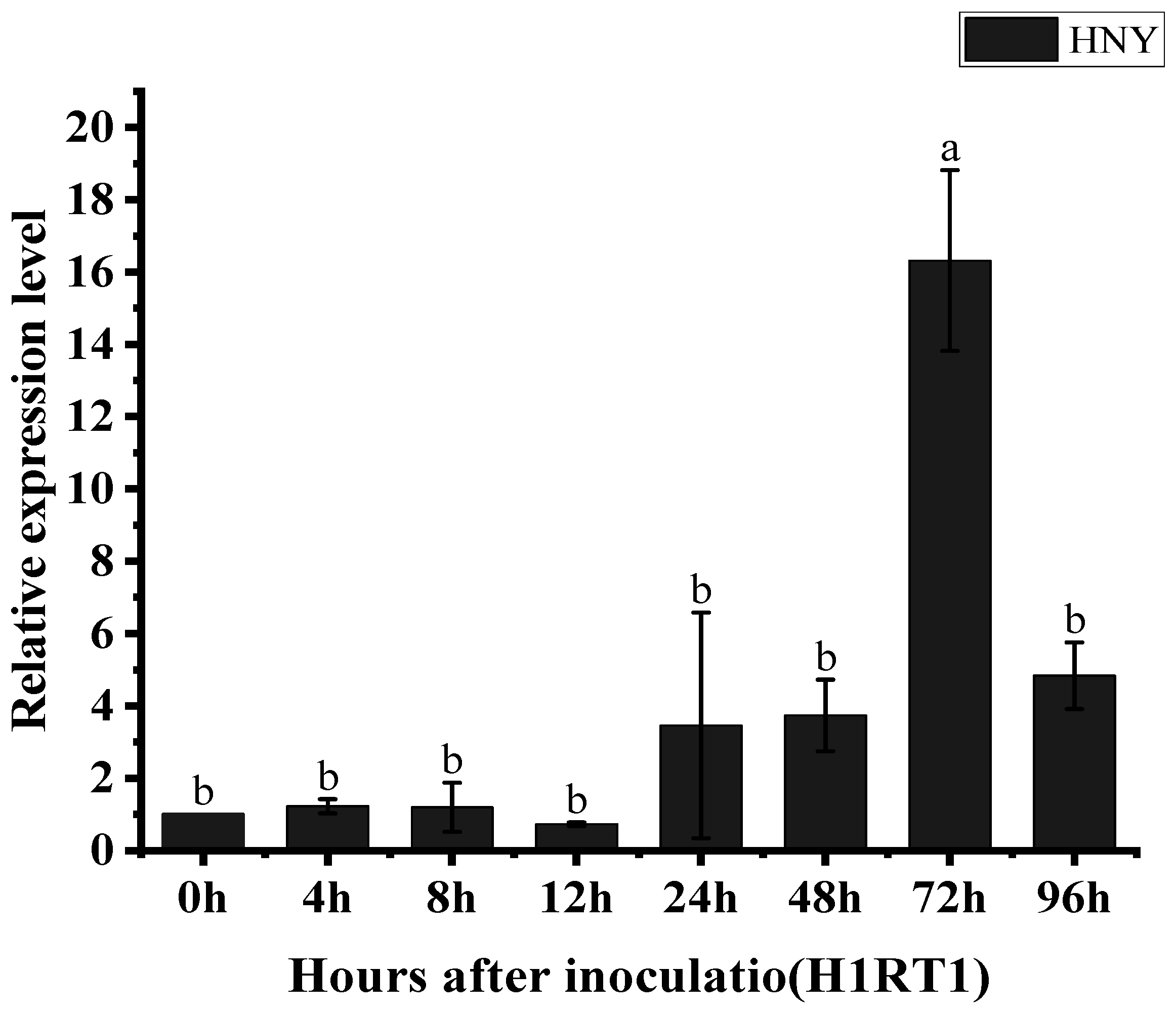
3.4. The Expression of the OsZFPH Gene Is Triggered in Response to PXO99
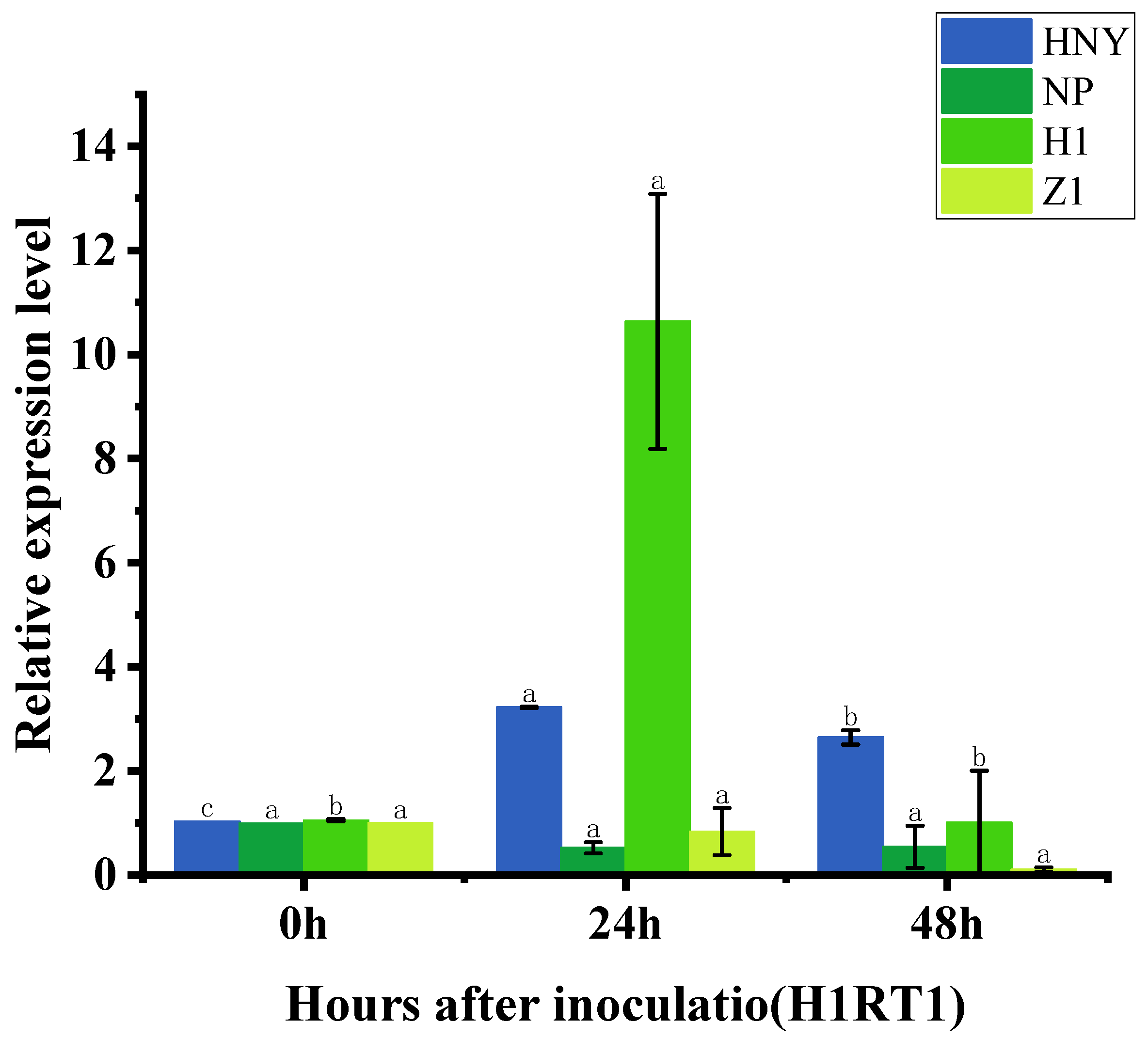
3.5. Expression of OsZFPH Gene in Different Rice Materials After Infestation by PXO99
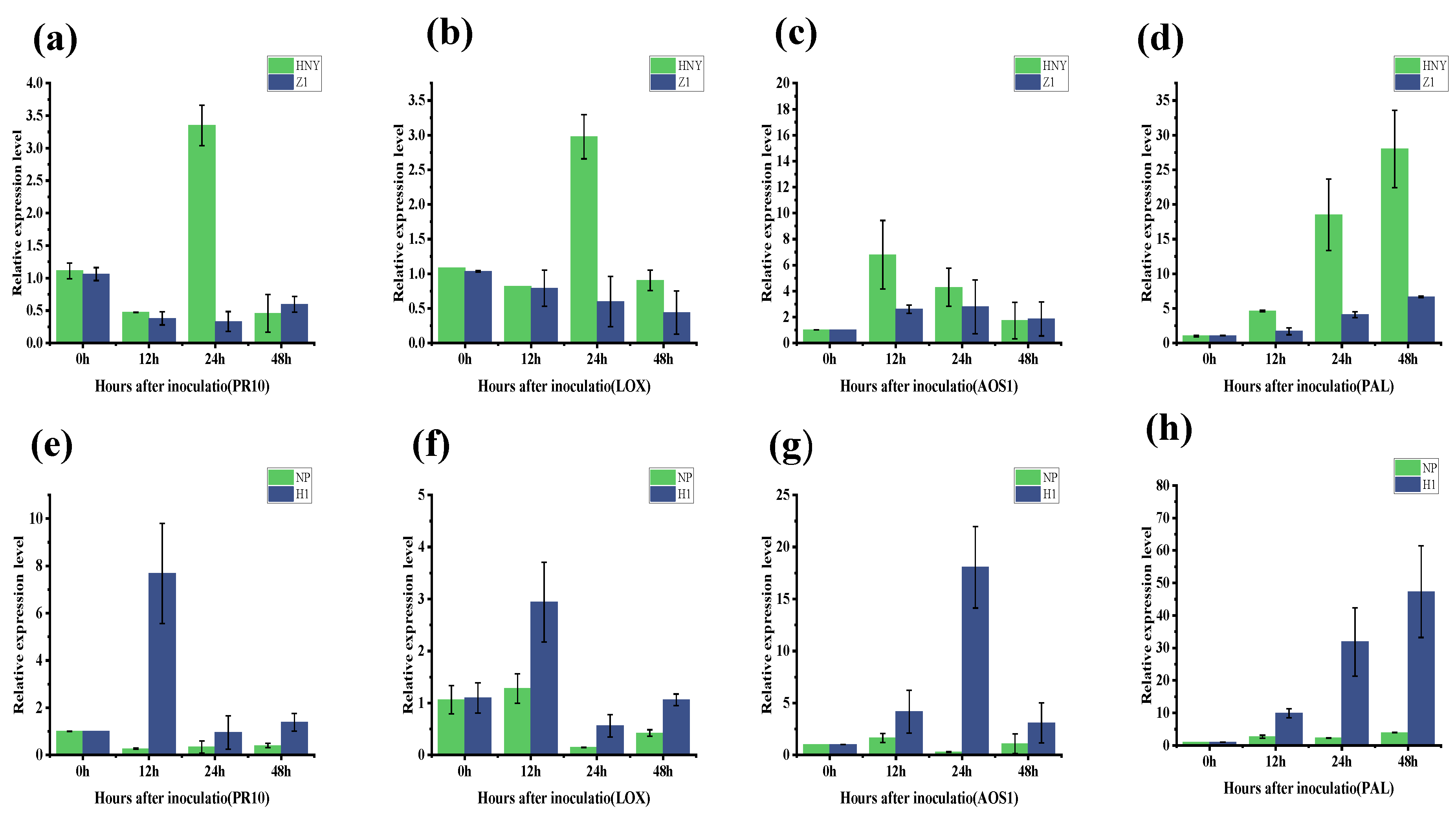
3.6. OsZFPH Resistance Levels Analyzed in Relation to Hormone Signaling Levels
3.7. Determination and Analysis of H2O2 Content and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Different OsZFPH-Harboring Plants Infected by PXO99
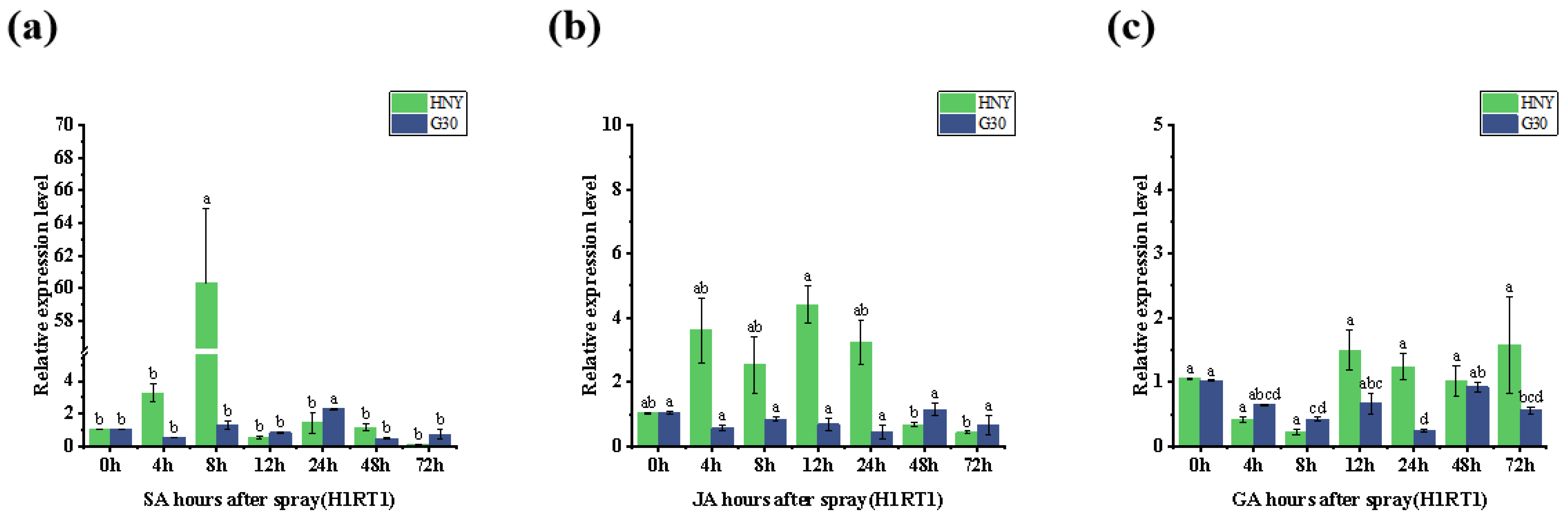
3.8. Analysis of the Relationship Between OsZFPH and Exogenous Hormones
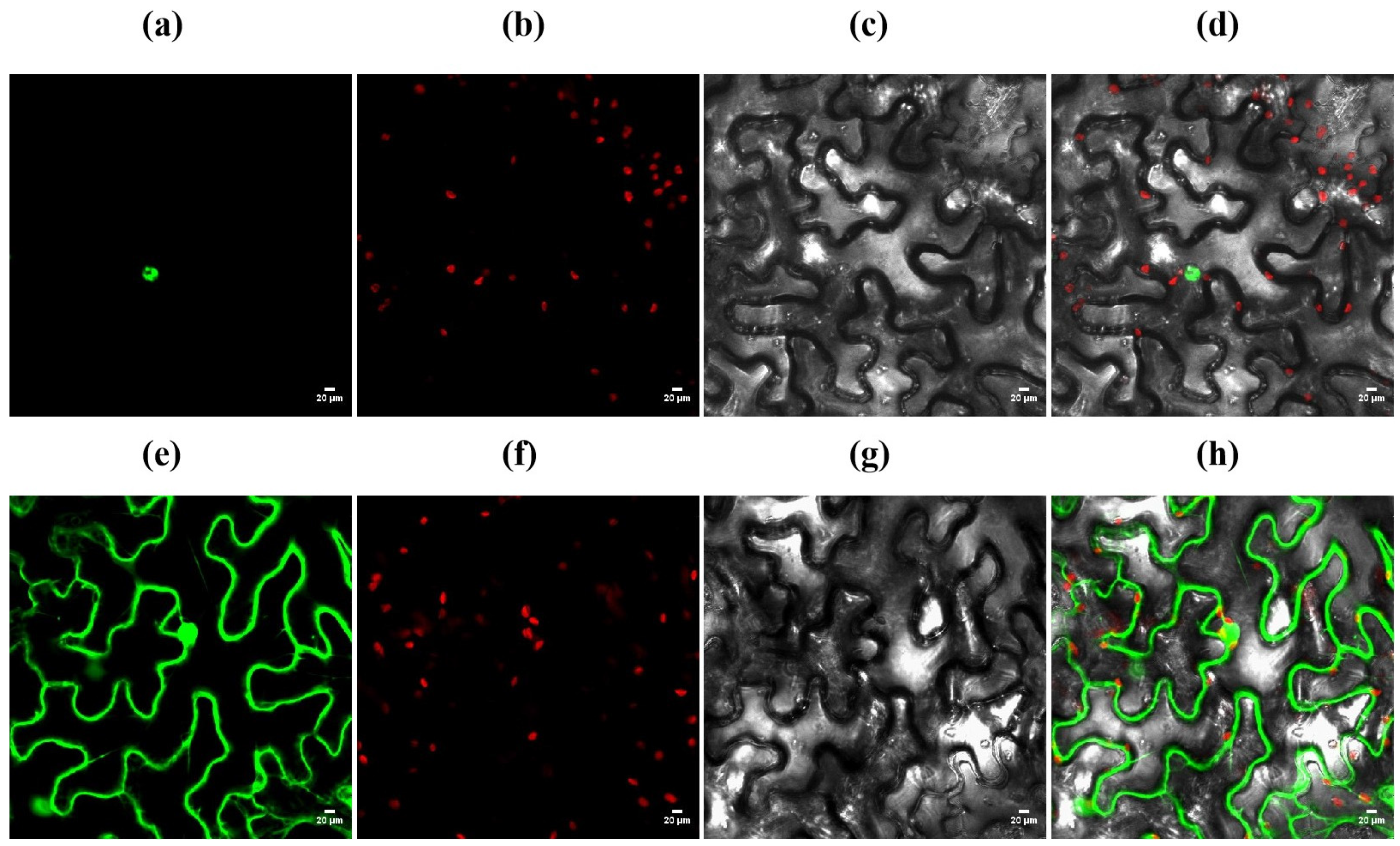
3.9. Subcellular Localization of OsZFPH
3.10. Screening for Proteins Interacting with OsZFPH Protein
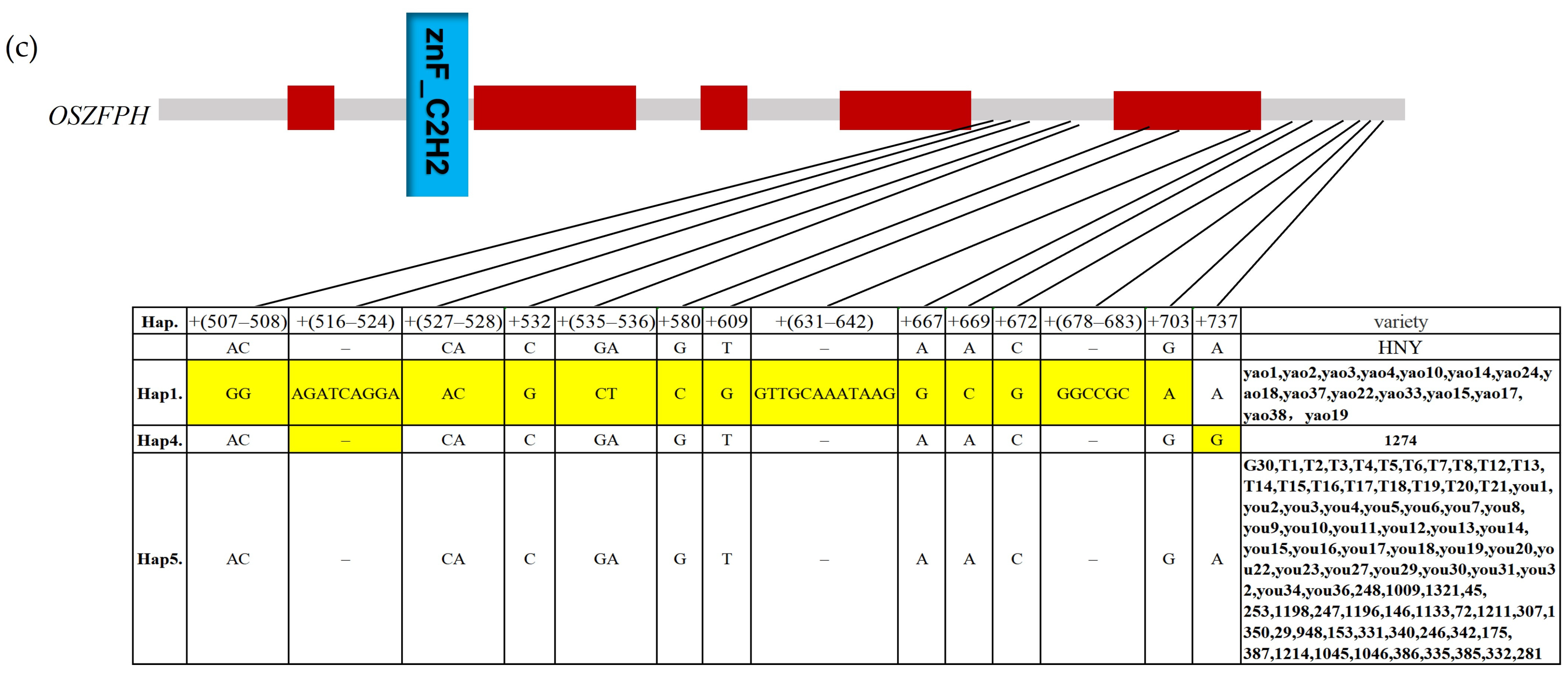
3.11. Haplotype Analysis Analysis of the Transcription Factor OsZFPH in Different Rice Species Materials
4. Discussion
4.1. OsZFPH Enhances Rice Resistance to Bacterial Blight via JA/SA/GA Signaling and Antioxidant Enzyme-Mediated ROS Homeostasis
4.2. OsZFPH Interacted with WRKY71, PTP1, and Metabolic Enzymes to Form a Multi-Layered Defense Network Against Bacterial Blight in Rice
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, H.; Qiu, J.; Ding, X.; Kou, Y. Recent Progress in Rice Broad-Spectrum Disease Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanya, D.R.A.; Syed-Ab-Rahman, S.F.; Jia, A.; Onésime, D.; Kim, K.M.; Ahohuendo, B.C.; Rohr, J.R. A review of approaches to control bacterial leaf blight in rice. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, R.; Sengupta, D.; Das, S.N.; Pandey, M.K.; Bohra, A.; Sharma, N.K.; Sinha, P.; SkM, H.; Ghazi, I.A.; et al. Deployment of genetic and genomic tools toward gaining a better understanding of rice-Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae interactions for development of durable bacterial blight resistant rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1152. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.; Ji, Z.; Liu, B.; Cheng, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Yang, B.; Chen, G. Xa1 Allelic R Genes Activate Rice Blight Resistance Suppressed by Interfering TAL Effectors. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Y.; Tian, D.; Ong, K.H.; Teo, J.C.Y.; Yin, Z. TAL effector-dependent Bax gene expression in transgenic rice confers disease resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Transgenic Res. 2022, 31, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhou, L.; Wu, B.; Li, S.; Zha, W.; Li, W.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, L.; Shi, L.; Lin, Y.; et al. Improvement of bacterial blight resistance in two conventionally cultivated rice varieties by editing the noncoding region. Cells 2022, 11, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, W.; Li, W.H.; Zhao, J.L.; Zhou, L.Y.; Yang, W. Advances in research and application of rice bacterial blight resistance genes. Crop J. 2024, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, W.; Schwessinger, B.; Wei, T.; Ruan, D.; Ronald, P. The Rice Xa3 Gene Confers Resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae in the Model Rice Kitaake Genetic Background. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quibod, I.L.; Atieza-Grande, G.; Oreiro, E.G.; Palmos, D.; Nguyen, M.H.; Coronejo, S.T.; Aung, E.E.; Nugroho, C.; Roman-Reyna, V.; Burgos, M.R.; et al. The Green Revolution shaped the population structure of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. ISME J. 2020, 14, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Xia, Z.; Liu, P.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Jiang, G.; Zhai, W. TALEN-based editing of TFIIAy5 changes rice response to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, P.; Mei, L.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Shen, S.; Ji, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Xa7, a new executor R gene that confers durable and broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight disease in rice. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, T.; Dong, J.; Fu, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome-wide association mapping and gene expression analysis reveal the negative role of OsMYB21 in regulating bacterial blight resistance in rice. Rice 2021, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Lan, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Dou, S.; Yang, M.; Li, L.; Liu, G. OsMKK1 is a novel element that positively regulates the Xa21-mediated resistance response to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, T.; Lan, J.; Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dou, S.; et al. Rice MPK17 plays a negative role in the Xa21-mediated resistance against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Rice 2022, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Lu, D.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xue, J.; He, X. Distribution of bacterial blight resistance genes in the main cultivars and application of Xa23 in rice breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 555228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Sun, H.; Wei, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Lei, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, K. Ectopic expression of executor gene Xa23 enhances resistance to both bacterial and fungal diseases in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.J.; Peng, W.Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, S.M.; Dai, L.Y.; Li, W. Advances of plant C2H2 zinc finger proteins in response to stresses. Plant Physiol. J. 2020, 56, 2356–2366. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.F.; Du, L.G.; Wang, M.X.; Ren, M.Y.; Yu, S.W.; Yang, Q.Y. Multifaceted roles of zinc finger proteins in regulating various agronomic traits in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 974396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; Ke, X.J.; Lan, H.X.; Yuan, X.; Huang, P.; Xu, E.S.; Gao, X.Y.; Wang, R.Q.; Tang, H.J.; Zhang, H.S.; et al. A Cys2/His2 zinc finger protein acts as a repressor of the green revolution gene SD1/OsGA20ox2 in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 2055–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, Y.; Kang, K.; An, G.; Paek, N.C. Rice DNA-Binding one zinc finger 24 (OsDOF24) delays leaf senescence in a Jasmonate-Mediated pathway. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 2065–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Qi, L.; Guo, Z.; Chen, X. Salicylic Acid Is Required for Broad-Spectrum Disease Resistance in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Su, S.; Yang, S.; Zhao, T.; Tang, P.; Luo, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, J. Effector MoSDT1 enhances Magnaporthe oryzae virulence and plays a dual role in regulating rice defense. Plant Physiol. 2024, 196, 1042–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, H.; Araki, T.; Meshi, T.; Iwabuchi, M. Expression of a subset of the Arabidopsis Cys(2)/His(2)-type zinc-finger protein gene family under water stress. Gene 2000, 248, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Song, L.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Y.; Shen, X.; Guo, J.; Su, M.; Shi, G.; Wang, Z.; Lu, G.D. Rice ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme OsUBC26 is essential for immunity to the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. The C2H2-Type zinc finger transcription factor ZmDi19-7 regulates plant height and organ size by promoting cell size in maize. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.J.; Yi, X.Y.; Zeng, Y.L. Research progress on plant stress related C2H2 type zinc finger protein. Mol. Plant Breed. 2016, 14, 578–585. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.P.; Wen, F.; Yao, D.M.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Ni, L.; Zhang, A.Y.; Tan, M.P.; Jiang, M.Y. A novel rice C2H2-type zinc finger protein ZFP36 is a key player involved in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defence and oxidative stress tolerance in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 5803–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.L.; He, M.L.; Liu, C.X.; Liao, X.; Li, X.F.; Guan, Q.J. Zinc finger protein OsZFP6 expression features and functions in saline-alkali stress response. Bull. Bot. Res. 2020, 40, 424–432. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, Q.H.; Zhang, H.S. Identification of a rice zinc finger protein whose expression is transiently induced by drought, cold but not by salinity and abscisic acid. DNA Seq. 2005, 16, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Yu, G.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z.; Yuan, L.; Liu, P. Importers drive leaf-to-leaf jasmonic acid transmission in wound-induced systemic immunity. Mol. Plant. 2020, 13, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. A CCCH-type zinc finger nucleic acid-binding protein quantitatively confers resistance against rice bacterial blight disease. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 876–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.H.; Kou, Y.J.; Shen, X.L.; Qiu, J.H. Functional analysis of rice jasmonic acid synthesis gene OsAOS1 in rice blast resistance. Mol. Plant Breed. 2022, 20, 6631–6637. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.M.; Zhao, H.W. OsWRKY13 mediates rice disease resistance by regulating defense-related genes in salicylic acid and jasmonic acid signaling pathways. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 279–291. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, Q.; Gao, S.; Yu, N.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Huang, P.; Yao, L.; Wang, M.; et al. Disruption of the primary salicylic acid hydroxylases in rice enhances broad-spectrum resistance against pathogens. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 2211–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.L.; Zhang, H.H.; Yang, Z.H.; Wang, C.; Li, S.S.; Cao, C.; Yao, T.S.; Wei, Z.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, J.P.; et al. Independently evolved viral effectors convergently suppress DELLA protein SLR1-mediated broad-spectrum antiviral immunity in rice. Nat. Com. 2022, 13, 6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Parvin, K.; Bardhan, K.; Nahar, K.; Anee, T.I.; Masud, A.A.C.; Fotopoulos, V. Biostimulants for the regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolism in plants under abiotic stress. Cells 2021, 10, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Bai, X.Q.; Wang, X.J.; Chu, C.C. OsWRKY71, a rice transcription factor, is involved in rice defense response. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 164, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.H.; Anand, S.; Singh, B.; Bohra, A.; Joshi, R. WRKY transcription factors and plant defense responses: Latest discoveries and future prospects. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y. Histone H2B monoubiquitination regulates salt stress-induced microtubule depolymerization in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 1512–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.W.; Mi, M.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Qian, M.; Chen, Y.H.; Zheng, L.Q.; Zhang, H.S.; Hu, Z.B.; Shen, Z.G.; Xia, Y. A methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase, OsMSRB5, is required for rice defense against copper toxicity. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 153, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, A.; Varshney, V.; Verma, P.; Kamble, N.U.; Ghosh, S.; Achary, R.K.; Gautam, S.; Majee, M. Methionine sulfoxide reductase B5 plays a key role in preserving seed vigor and longevity in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol. 2022, 236, 1042–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Chen, H.C.; Lu, Z.Q.; Diao, M.; Chen, K.; Dong, N.Q.; Shan, J.X.; Ye, W.W.; Huang, S.; Lin, H.X. A SAC phosphoinositide phosphatase controls rice development via hydrolyzing PI4P and PI(4,5)P2. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Yao, Q.; Hai, M.; Li, T.; Sun, J.; Liu, Z.; Ang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, X.; et al. Elite alleles of EPE1 identified via genome-wide association studies increase panicle elongation length in rice. Rice 2025, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Primer Name | Sequences | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| H1-RT-1F | AGCCACCAAGAAGAAGAAGC | qPCR |
| H1-RT-1R | TGGAGGTGGTGCTAGGTTTAG | qPCR |
| PR10-1F | CCCTGCCGAATACGCCTAA | qPCR |
| PR10-1R | CTCAAACGCCACGAGAATTTG | qPCR |
| PR1b-F | GGCAACTTCGTCGGACAGA | qPCR |
| PR1b-R | GGCAACTTCGTCGGACAGA | qPCR |
| OsActin2-F | GAGTATGATGAGTCGGGTCCAG | qPCR |
| OsActin2-R | ACACCAACAATCCCAAACAGAG | qPCR |
| LOX-F | AAACGCTCGCTGGCATCAAC | qPCR |
| LOX-R | ATCGCCTCCTCCACCGTCAT | qPCR |
| AOS1-F | GGTGAAGAAGGACTACGACCGC | qPCR |
| AOS1-R | CCGAACGAGTTGAAGCAGAGC | qPCR |
| PAL-F | CACAAGCTGAAGCACCACCC | qPCR |
| PAL-R | GAGTTCACGTCCTGGTTGTG | qPCR |
| H1-1F | ATGGAGGAGCAAAGAGGCGA | PCR |
| H1-1R | TAAGCGTGCACAACAGCTT | PCR |
| 39425 | CAGTGGTCTCACAACATGGAGGAGCAAAGAGGCGAGG | Subcellular localization vector construction |
| 39425 | CAGTGGTCTCATACAAGCGTGCACAACAGCTTTAGGAGGAG | Subcellular localization vector construction |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; A, X.; Tang, C.; Dong, C.; Zhang, F.; He, C.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yan, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. A TFAIII-Type Transcription Factor OsZFPH Regulating a Signaling Pathway Confers Resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae in Rice. Genes 2025, 16, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030240
Yang C, A X, Tang C, Dong C, Zhang F, He C, Sun Y, Yang Y, Yan S, Liu Y, et al. A TFAIII-Type Transcription Factor OsZFPH Regulating a Signaling Pathway Confers Resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae in Rice. Genes. 2025; 16(3):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030240
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chunyun, Xinxiang A, Cuifeng Tang, Chao Dong, Feifei Zhang, Chunmei He, Yiding Sun, Yi Yang, Sandan Yan, Yanhong Liu, and et al. 2025. "A TFAIII-Type Transcription Factor OsZFPH Regulating a Signaling Pathway Confers Resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae in Rice" Genes 16, no. 3: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030240
APA StyleYang, C., A, X., Tang, C., Dong, C., Zhang, F., He, C., Sun, Y., Yang, Y., Yan, S., Liu, Y., Yang, Y., & Dai, L. (2025). A TFAIII-Type Transcription Factor OsZFPH Regulating a Signaling Pathway Confers Resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae in Rice. Genes, 16(3), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030240






