Comparative Analysis of Complete Chloroplast Genomes and Phylogenetic Relationships of 21 Sect. Camellia (Camellia L.) Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and DNA Extraction
2.2. DNA Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
2.3. Repetitive Sequence Analysis
2.4. Chloroplast Genome Boundary Regions, Genome Comparison, and Identification of Differential Hotspots
2.5. Crypton Bias Analysis
2.6. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
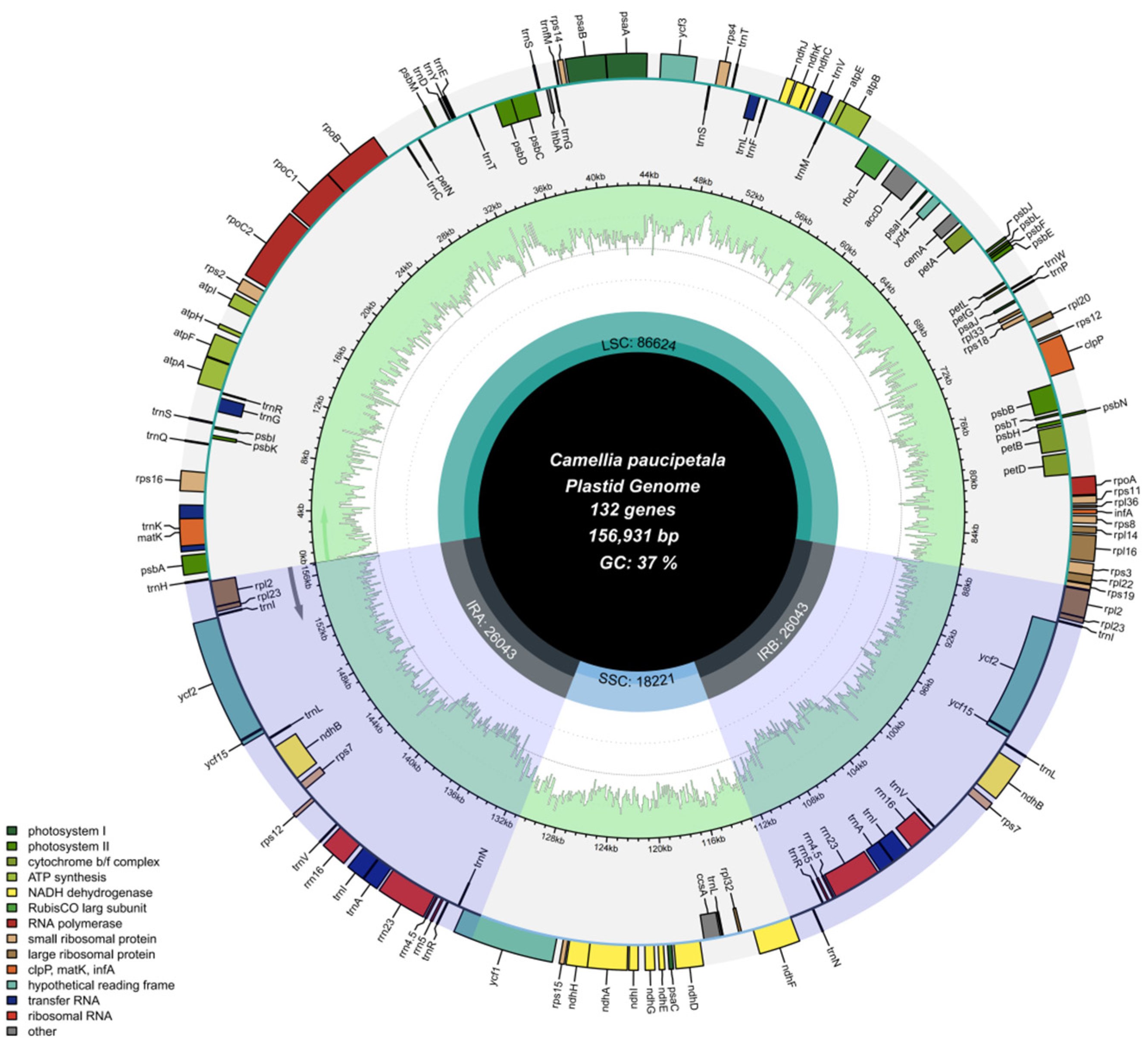
3.1. Basic Structure of the Chloroplast Genome
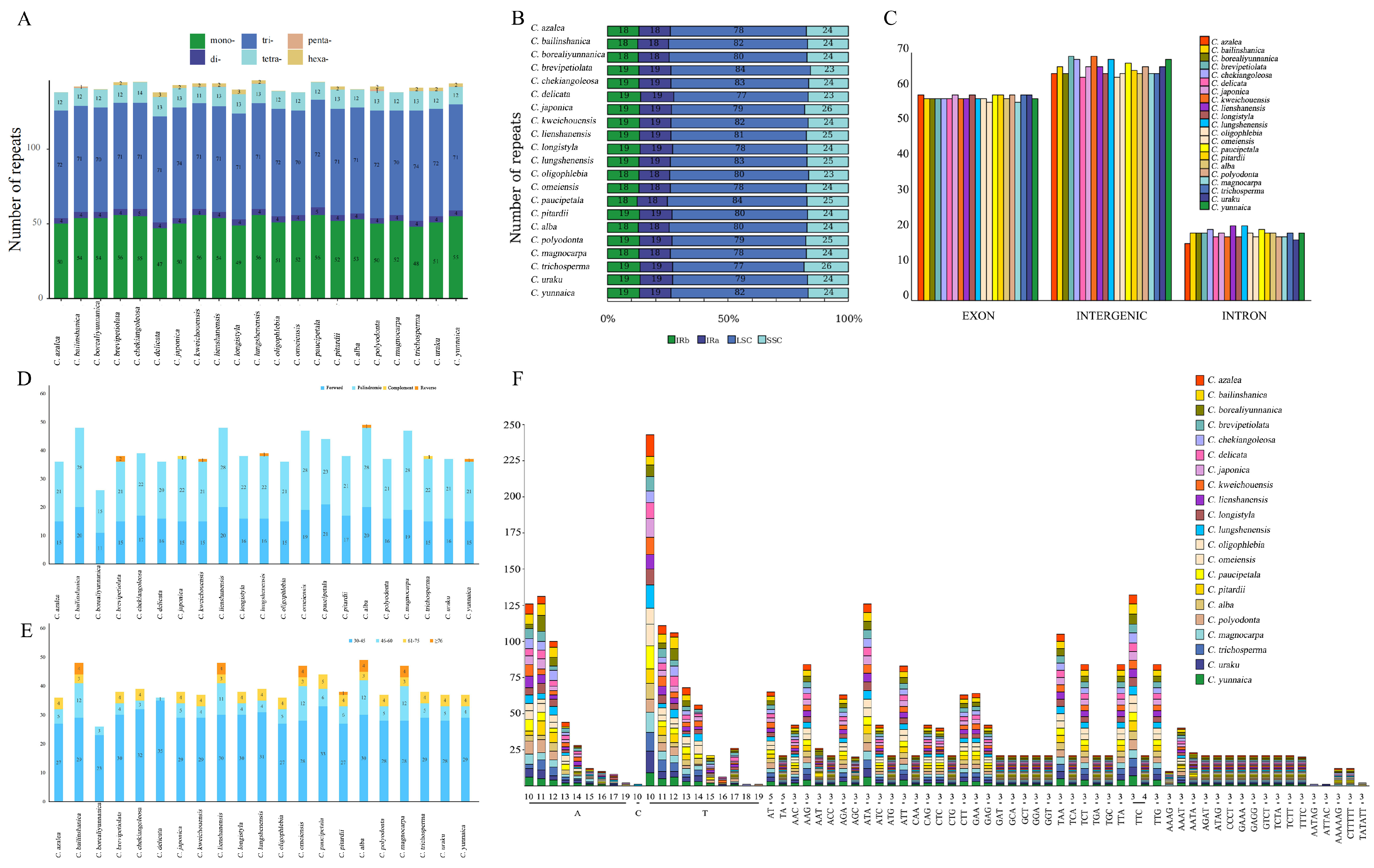
3.2. Repeat Sequence Analysis
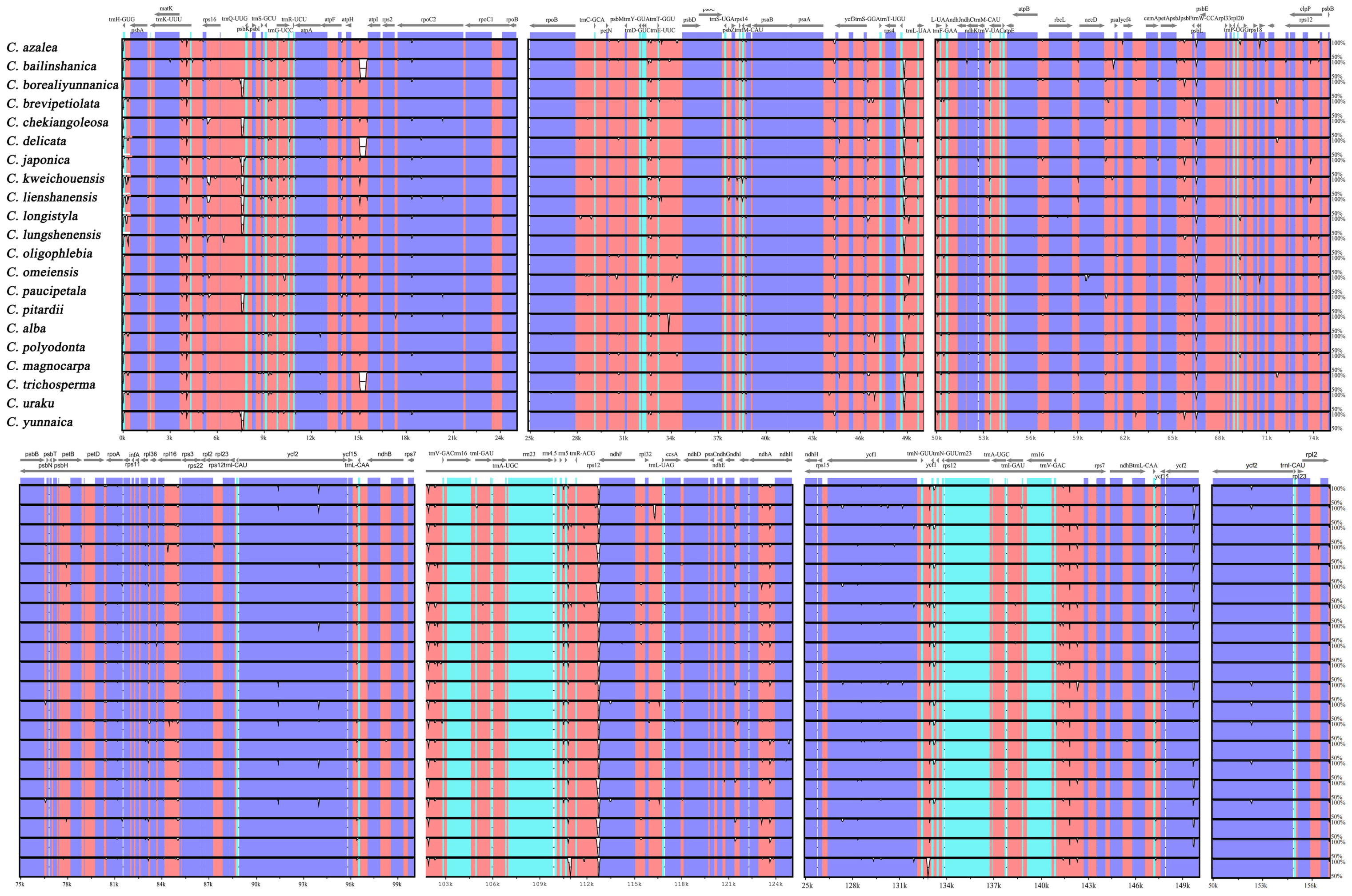
3.3. Contraction and Expansion of the IR Boundary
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Chloroplast Genomes
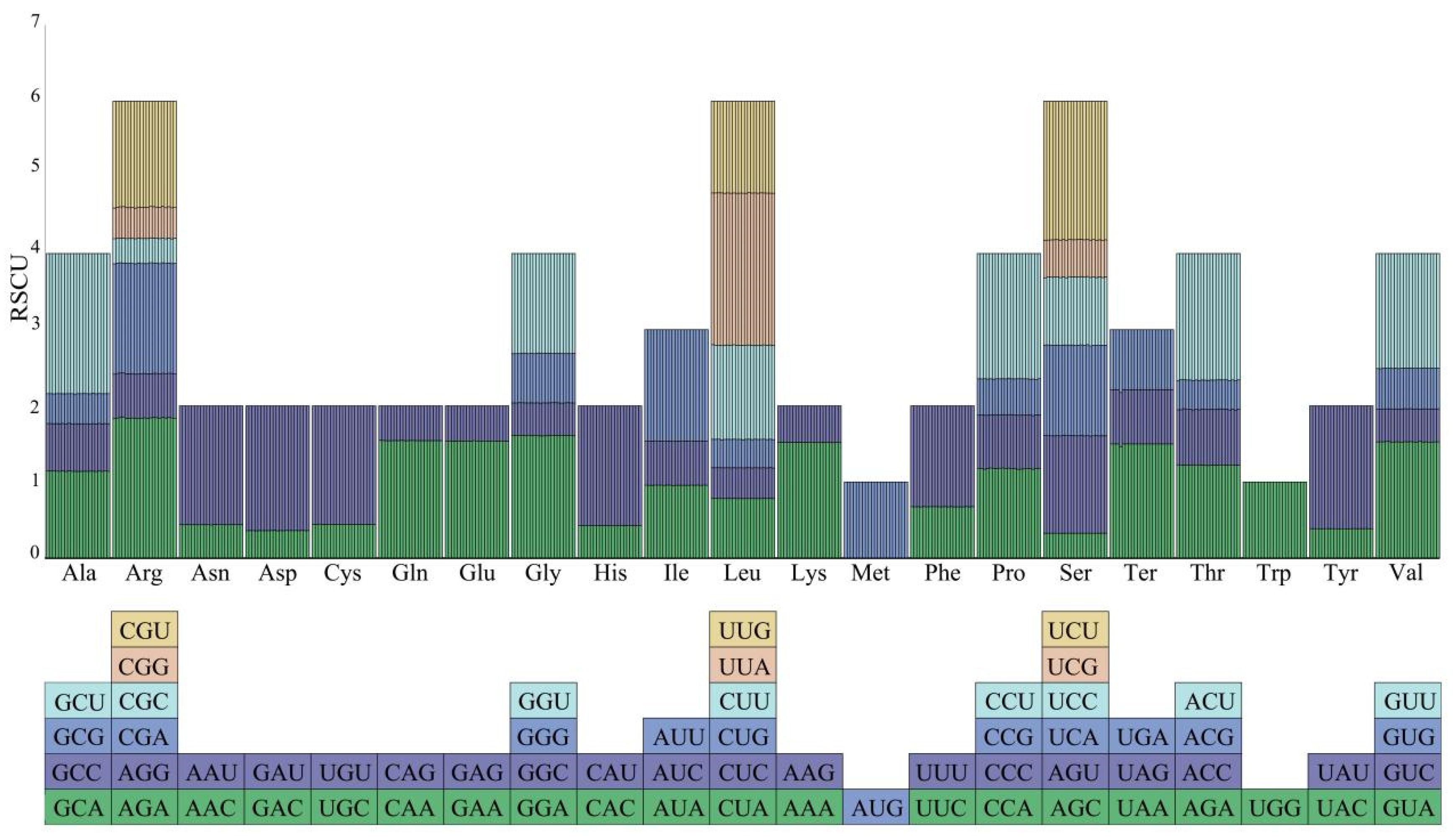
3.5. Codon Preference Analysis
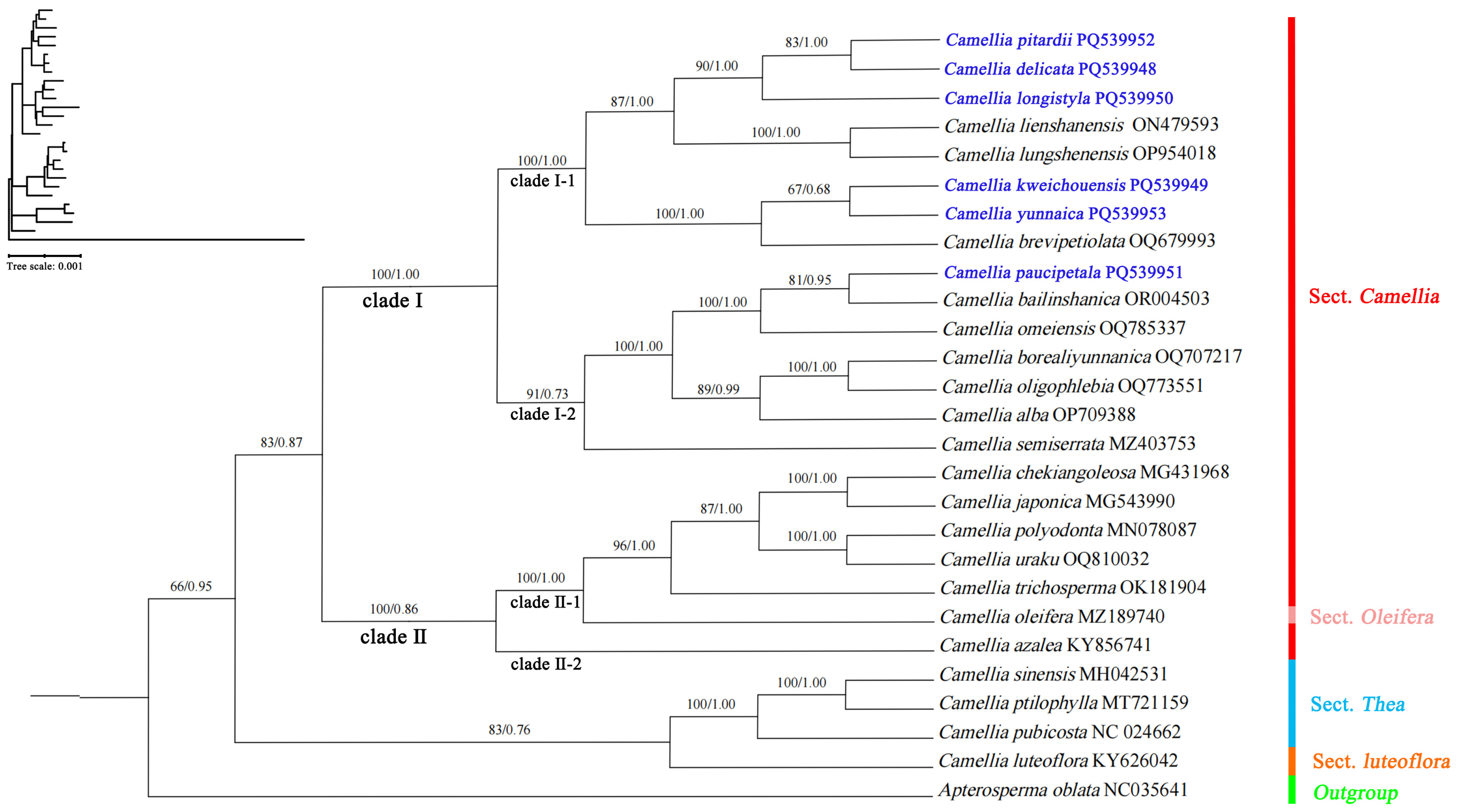
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, H.; Ren, S. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H. Camellia. In Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H. Systematic study of the genus Camellia. J. Sun Yatsen Univ. Forum 1981, 108–125. [Google Scholar]
- Min, T.; Zhong, Y. A revision of genus Camellia sect. Tuberculata. Acta Bot. Yunnanica 1993, 15, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Min, T.; Zhang, W. The evolution and distribution of genus Camellia. Acta Bot. Yunnanica 1996, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Min, T. A systematic synopsis of genus Camellia. Acta Bot. Yunnanica 1999, 21, 149–159. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, B.; Tan, X.; Qi, L. RAPD Analysis and Taxonomy of Sect. Camellia Species in Camellia. For. Sci. 2006, 42, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Yang, S.; Li, D. Phylogenetic Relationships of Theaceae Inferred from Mitochondrial matR Gene Sequence Data. Acta Bot. Yunnanica 2006, 28, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.; Li, J.; Ni, S. Phylogenetic Study on Section Camellia Based on ITS Sequences Data. Hortic. Plant J. 2008, 35, 1685–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, S. Research on Phylogenesis of Sect Camellia in the Genus Camellia. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, Q. Phylogeny and Molecular Evolution of Chloroplast Genome in Camellia. Master’s Thesis, Sichuan Agricultural University, Ya’an, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z. Preliminary Study of Molecular Phylogenetics and Biogeography of the Genus Camellia L. Based on Chloroplast DNA. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Hu, Y.; He, M.; Zhang, B.; Wu, W.; Cai, P.; Huo, D.; Hong, Y. Comparative chloroplast genomes: Insights into the evolution of the chloroplast genome of Camellia sinensis and the phylogeny of Camellia. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Tong, W.; Zhao, H.; Ge, R.; Li, R.; Huang, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Mallano, A.I.; Deng, W.; et al. Comparative transcriptomic analysis unveils the deep phylogeny and secondary metabolite evolution of 116 Camellia plants. Plant J. 2022, 111, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.-F.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Guo, Z.-H.; Li, D.-Z. Evidence for horizontal transfer of mitochondrial DNA to the plastid genome in a bamboo genus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Cosner, M.; A Raubeson, L.; Jansen, R.K. Chloroplast DNA rearrangements in Campanulaceae: Phylogenetic utility of highly rearranged genomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2004, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kress, W.J.; Erickson, D.L. A two-locus global DNA barcode for land plants: The coding rbcL gene complements the non-coding trnH-psbA spacer region. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicke, S.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; de Pamphilis, C.W.; Müller, K.F.; Quandt, D. The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: Gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.J.; Soltis, P.S.; Bell, C.D.; Burleigh, J.G.; Soltis, D.E. Phylogenetic analysis of 83 plastid genes further resolves the early diversification of eudicots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4623–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, C.F.; Freudenstein, J.V.; Li, J.; Mayfield-Jones, D.R.; Perez, L.; Pires, J.C.; Santos, C. Investigating the path of PLASTID genome degradation in an early-transitional clade of heterotrophic orchids, and implications for heterotrophic angiosperms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 3095–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, J.-G.; Chen, X.-L.; Cui, Y.-X.; Xu, Z.-C.; Li, Y.-H.; Song, J.-Y.; Duan, B.-Z.; Yao, H. Gene losses and partial deletion of small single-copy regions of the chloroplast genomes of two hemiparasitic Taxillus species. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Xie, X.; Chen, A.; Li, F.; Tian, E.; Chao, Z. The chloroplast genomes of four Bupleurum (Apiaceae) species endemic to Southwestern China, a diversity center of the genus, as well as their evolutionary implications and phylogenetic inferences. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Nie, L.; Xu, Z.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; He, C.; Song, J.; Yao, H. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of three paeonia section moutan species (Paeoniaceae). Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Niu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, B.; Hai, L.; Wen, J.; Chen, Z. Taxonomy and biogeography of Diapensia (Diapensiaceae) based on chloroplast genome data. J. Syst. Evol. 2020, 58, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xia, X.; Peng, J.; Wang, D. Comparative analyses of six complete chloroplast genomes from the genus Cupressus and Juniperus (Cupressaceae). Gene 2022, 837, 146696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. GigaScience 2012, 1, 2047-2217X-1-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierckxsens, N.; Mardulyn, P.; Smits, G. NOVOPlasty: De novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq—Versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.P.; Lowe, T.M. tRNAscan-SE: Searching for tRNA Genes in Genomic Sequences. In Gene Prediction; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1962, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Munch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Guo, Q.; Xu, L.; Gao, H.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X. CPJSdraw: Analysis and visualization of junction sites of chloroplast genomes. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3030–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. A more accurate relationship between ‘effective number of codons’ and GC3s under assumptions of no selection. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2013, 42, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.-H. The codon adaptation index-a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, D.C.; Sharp, P.M. Synonymous codon usage in Bacillus subtilis reflects both translational selection and mutational biases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 8023–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Z.; Li, Z.; Xiao, X.; Tang, M. Camellia neriifolia and Camellia ilicifolia (Theaceae) as separate species: Evidence from Morphology, Anatomy, Palynology, Molecular Systematics. Bot. Stud. 2024, 65, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Yin, H.; Wang, K.; Gao, H.; Liu, L.; Yao, X. Comparative genomic analysis uncovers the chloroplast genome variation and phylogenetic relationships of Camellia species. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-B.; Yang, S.-X.; Li, H.-T.; Yang, J.; Li, D.-Z. Comparative chloroplast genomes of Camellia species. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, R.K.; Graner, A.; Sorrells, M.E. Genic microsatellite markers in plants: Features and applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, Z.; Li, Z.; Xiao, X.; An, M.; Yan, C. Complete chloroplast genomes of 13 species of sect. Tuberculata Chang (Camellia L.): Genomic features, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Tong, Y.H.; Kong, Q.B. Characterization of Complete Chloroplast Genome and Phylogenetic Analysis of Camellia trichosperma Chang. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 2022, 40, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, L.; Biradar, S.S.; Tan, X.; Wan, F.; Weining, S. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of a major invasive species, crofton weed (Ageratina adenophora). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.H.; Zheng, Q.; Du, X.M. Analysis on sequence characteristics of chloroplast genome of Camellia polyodonta. J. Plant Resour. Environ. 2022, 31, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.-F.; Su, T.; Cheng, G.-Q.; Wang, B.-X.; Li, X.; Deng, C.-L.; Gao, W.-J. Chromosome Evolution in Connection with Repetitive Sequences and Epigenetics in Plants. Genes 2017, 8, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-B.; Lim, C.E.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, H.-J.; Mun, J.-H. Comparative chloroplast genome analysis of Artemisia (Asteraceae) in East Asia: Insights into evolutionary divergence and phylogenomic implications. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nock, C.J.; Waters, D.L.; Edwards, M.A.; Bowen, S.G.; Rice, N.; Cordeiro, G.M.; Henry, R.J. Chloroplast genome sequences from total DNA for plant identification. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.; Ma, X.; Guo, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L. Comparative Analysis and Phylogeny of the Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Nine Cynanchum (Apocynaceae) Species. Genes 2024, 15, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Dong, S.; Gong, Q.; Xu, Q.; Ge, Y. Comparative chloroplast genome analysis of four Polygonatum species insights into DNA barcoding, evolution, and phylogeny. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dai, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, G.; Gao, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, S. Comparative analysis the chloroplast genomes of Celastrus (Celastraceae) species: Provide insights into molecular evolution, species identification and phylogenetic relationships. Phytomedicine 2024, 131, 155770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Guo, Q.Q.; Gao, C.; Li, H.E. Characterization of Complete Chloroplast Genome of Camellia weiningensis in Weining, Guizhou Province. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2020, 47, 779–787. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1924.S.20200413.1356.001.html (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Zhang, S.-D.; Ling, L.-Z.; Zhang, Q.-H. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of ten Pittosporum species from East Asia. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2024, 24, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firetti, F.; Zuntini, A.R.; Gaiarsa, J.W.; Oliveira, R.S.; Lohmann, L.G.; Van Sluys, M. Complete chloroplast genome sequences contribute to plant species delimitation: A case study of the Anemopaegma species complex. Am. J. Bot. 2017, 104, 1493–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingvarsson, P.K. Gene expression and protein length influence codon usage and rates of sequence evolution in populus tremula. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 24, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.-Q.; Drew, B.T.; Yang, J.-B.; Gao, L.-M.; Li, D.-Z. Comparative chloroplast genomes of eleven Schima (Theaceae) species: Insights into DNA barcoding and phylogeny. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Hodkinson, T.R.; Parnell, J.A. Phylogenetics of global Camellia (Theaceae) based on three nuclear regions and its implications for systematics and evolutionary history. J. Syst. Evol. 2023, 61, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, X.; Chen, J.; Ran, Z.; Huang, L.; Li, Z. Comparative Analysis of Complete Chloroplast Genomes and Phylogenetic Relationships of 21 Sect. Camellia (Camellia L.) Plants. Genes 2025, 16, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010049
Xiao X, Chen J, Ran Z, Huang L, Li Z. Comparative Analysis of Complete Chloroplast Genomes and Phylogenetic Relationships of 21 Sect. Camellia (Camellia L.) Plants. Genes. 2025; 16(1):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010049
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Xu, Juyan Chen, Zhaohui Ran, Lang Huang, and Zhi Li. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of Complete Chloroplast Genomes and Phylogenetic Relationships of 21 Sect. Camellia (Camellia L.) Plants" Genes 16, no. 1: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010049
APA StyleXiao, X., Chen, J., Ran, Z., Huang, L., & Li, Z. (2025). Comparative Analysis of Complete Chloroplast Genomes and Phylogenetic Relationships of 21 Sect. Camellia (Camellia L.) Plants. Genes, 16(1), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16010049




