Highlights
What are the main findings?
- Our findings established the expressed profiles of UFMylation in multiple tissues of mice mimicking MASLD.
- We found that the expression of UFMylation components, especially the UFM1-specific ligase UFL1, was decreased in multiple metabolic tissues of the mouse models.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- Our findings suggest novel physiological functions for UFMylation in MASLD development and progression.
- Our study clarifies that PTM regulation of UFMylation family proteins themselves is also important in understanding the biological functions and regulation of UFMylation.
- Our findings imply promising therapeutic strategies in the treatment of MASLD and other metabolic diseases by targeting UFMylation.
Abstract
Background/Objectives: UFMylation, a newly identified ubiquitin-like modification, modulates a variety of physiological processes, including endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis maintenance, DNA damage response, embryonic development, and tumor progression. Recent reports showed that UFMylation plays a protective role in preventing liver steatosis and fibrosis, serving as a defender of liver homeostasis in the development of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). However, the regulation of UFMylation in MASLD remains unclear. This study aimed to determine the expressed patterns of UFMylation components in multiple tissues of leptin-deficient ob/ob mice and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice, which are mimicking the conditions of MASLD. Methods: The ob/ob mice and HFD-fed mice were sacrificed to collect tissues indicated in this study. Total RNA and proteins were extracted from tissues to examine the expressed patterns of UFMylation components, including UBA5, UFC1, UFL1, DDRGK1, UFSP1, UFSP2 and UFM1, by real-time PCR and western blot analysis. Results: The protein levels of UBA5, UFC1 and UFL1 were down-regulated in liver, brown adipose tissue (BAT) and inguinal white adipose tissue (iWAT), whereas the messenger RNA (mRNA) levels of Ufl1 and Ufsp1 were both decreased in skeletal muscle, BAT, iWAT and epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT) of ob/ob mice. In contrast, the mRNA levels of Ufsp1 in skeletal muscle, BAT, iWAT and heart, and the protein levels of UFL1 were decreased in BAT, iWAT, heart and cerebellum of HFD-fed mice. Conclusions: Our findings established the expressed profiles of UFMylaiton in multiple tissues of mice mimicking MASLD, indicating an important regulation for UFMylation in these tissues’ homeostasis maintenance.
1. Introduction
The global epidemic of obesity has been accompanied by a rising burden of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), formerly known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which is a prevalent chronic liver disease worldwide that is characterized by hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and liver damage [1,2]. Both obesity and MASLD pathogenesis are multifactorial, and the genetic and environmental factors and metabolic factors are responsible for their development [2]. Accumulating evidence suggests that the dynamic post-translational modifications (PTMs) exerting diverse cellular outcomes also contribute to the pathogenesis of obesity and MASLD. For example, a very detailed portrait of the dynamic changes in protein phosphorylation was obtained in ob/ob mice, implicating that the kinase glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3) is hyperactivated via phosphorylation, thereby regulating the insulin secretion in mice islets [3]. Ubiquitin was identified as a marker of cell injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is now replaced with the term metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) [1,4], and ubiquitylation also plays a vital role in the progression of MASLD via modulating different targets, such as tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6), which can promote poly-ubiquitination and the subsequent activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) in hepatocytes, thereby aggravating hepatic inflammation and fibrosis during MASH development [5]. Additionally, the global NEDDylated proteome in patients and mouse models with liver fibrosis demonstrated that NEDDylation inhibition downregulates the inflammatory response, consequently reducing cell damage and subsequent liver fibrosis [6]. Although much attention has focused on obesity and MASLD, the pathogenesis is not completely understood.
UFMylation, a newly identified ubiquitin-like modification, also requires a series of enzymatic cascades [7,8]. Mature ubiquitin-fold modifier 1 (UFM1) is generated from a UFM1 precursor cleaved by UFM1-specific eptidases 1 and 2 (UFSP1 and UFSP2) [9]. Subsequently, UFM1 is transferred to substrates via ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 5 (UBA5, E1), ubiquitin-fold modifier-conjugating enzyme 1 (UFC1, E2), and UFM1-specific ligase 1 (UFL1, E3) [7,8]. DDRGK domain-containing 1 (DDRGK1, also known as UFM1-binding protein 1 (UFBP1)) is associated with UFL1 to form an obligate heterodimer required for UFL1 E3 ligase activity [10]. To date, an array of UFMylation substrates are identified and well characterized, such as activating signal cointegrator 1 (ASC1) [10], meiotic recombination 11 homolog 1 (MRE11) [11], Histone H4 [12], p53 [13], retinoic acid-inducible gene 1 (RIG-1) [14], cytochrome b5 reductase 3 (CYB5R3) [15], and programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) [16], which led to a range of cellular processes and connected UFMylation to a variety of diseases, including hip dysplasia [17], kidney atrophy [18], heart failure [19], cancer, and neurodevelopmental disease [20,21,22,23,24]. Previous reports showed that UFMylation components are downregulated in MASH patients’ biopsies and disease mouse models [25,26]. Recently, a new study revealed that UFMylation of DDRGK1 can ameliorate obesity, hepatic lipogenesis, and insulin resistance in mice with MASLD, indicating an involvement of the UFMylation pathway in MASLD progression [27].
MASLD is a complex multisystem disease, and interactions between different organs contribute to MASLD pathogenesis and development [28]. To better understand the UFMylation pathway in MASLD regulatory networks, the messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein expression levels of UFMylation components were determined on more tissues of ob/ob mice and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice in this study. Our results showed that the expression levels of UFM1 and UFL1 are downregulated in the liver, skeletal muscle, brown adipose tissue (BAT), inguinal white adipose tissue (iWAT), epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT), heart, and cerebrum of ob/ob mice, whereas the expression levels of UFL1 are decreased in BAT, iWAT, and the heart of HFD-fed mice. Together, our results suggest a new discovery for UFMylation in regulating the homeostasis of these metabolic organs, implying novel insights for understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms of metabolic diseases in mammals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies
Antibodies used in this study were as follows: rabbit anti-UFL1 (HPA030559, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), rabbit anti-DDRGK1 (HPA013373, Sigma), rabbit anti-UFM1 (ab109305, Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA), rabbit anti-UFSP2 (ab185965, Abcam), rabbit anti-UFC1 (ab189252, Abcam), rabbit anti-UBA5 (ab177478, Abcam), rabbit anti-α-Tubulin (11224-1-AP, Proteintech, Chicago, IL, USA), mouse anti-GAPDH (M1310-2, HuaAn Biotechnology, Hangzhou, China), HRP-Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (A25012, Abbkine, Wuhan, China), and HRP-Mouse Anti-Rabbit IgG (A25022, Abbkine).
2.2. Animals
The ob/ob mice have been widely used as animal models in obesity and MASLD research, with the genetic background caused by leptin deficiency. For the analysis of the UFMylation family genes in ob/ob mice, five eight-week-old ob/ob male mice with the corresponding control C57BL/6J male mice were purchased from GemPharmatech (Nanjing, China). The C57BL/6J and ob/ob mice were allowed free access to water and a normal chow diet (NCD, 1010085, Synergy Biology, Jiangsu, China). The mice were sacrificed at ten weeks old, followed by the collection of tissue samples.
The HFD-fed mice mimic physiological conditions in humans and also are commonly used in obesity and MASLD research. For the analysis of the UFMylation family genes in HFD-fed mice, ten eight-week-old C57BL/6J male mice were purchased from GemPharmatech. The C57BL/6J male mice were randomized and separated into two groups matched by body weight, and the mice were fed an HFD (D12492, Research Diets, New Brunswick, NJ, USA) with 60% kcal or NCD for 8 weeks. The mice were sacrificed at sixteen weeks old, followed by the collection of tissue samples.
A comparison was performed in ob/ob mice vs. WT mice and HFD-fed mice vs. NCD-fed mice groups. The WT and NCD mice are different animals. All the mice were housed in an environment with a temperature of 22 ± 1 °C, a relative humidity of 50 ± 1%, and a light/dark cycle of 12/12 h. All animal studies (including the mouse euthanasia procedure) were approved and performed in compliance with the regulations and guidelines of the Animal Care and Use Committee of Hangzhou Normal University.
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
Tissues isolated from mice were lysed in a lysis buffer (150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.4], 1 mM EDTA, 1% NP40, and 0.1% SDS) with protease inhibitors. Whole protein samples were loaded and separated on a 12.5% (to determine UFC1 and UFM1) or 7.5% (to determine the rest of the proteins) sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) followed by transferring the proteins onto polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. The membranes were blocked with a solution of 0.1% Tween 20/PBS (PBS-T) containing 5% fat-free milk (BS102, Biosharp, Hefei, China) for 1 h and were then incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C, followed by washing for 3 × 6 min with PBS-T buffer. The blots were re-blocked with PBS-T containing 5% fat-free milk, followed by incubation with HRP-Goat Anti-Mouse IgG or HRP-Mouse Anti-Rabbit IgG for 1 h at room temperature. After washing 3 × 6 min with PBS-T, the membranes were incubated with Western blot chemiluminescence reagents (FD8020, FDbio science, Hangzhou, China) for 1 min and then exposed to scanning with an automatic luminescence imaging system (5200, Tanon, Shanghai, China).
2.4. Real-Time PCR Assays
Total RNA was extracted from tissues using the Total RNApure Reagent (ZP401, Zoman Biotechnology, Beijing, China); complementary DNA was then prepared using the 5 × HiScript Q RT SuperMix (R122-01, Vazyme, Nanjing, China) for qPCR. Real-time PCR assays were performed using the AceQ qPCR SYBR Green Master Mix (Q111-02, Vazyme) with a CFX96 Real-time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad, Los Angeles, CA, USA). The sequences of the primers used for real-time PCR are described in Table 1. The expression of UFMylation component mRNA in tissues was normalized to the corresponding β-actin mRNA. Student’s t-tests were applied to compare the two groups.

Table 1.
Primer sequences used in real-time PCR.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All values are shown as mean standard deviations (SDs), and all experiments were repeated at least three times. Student’s t-tests were applied to compare the two groups. Differences with p-values < 0.05 were deemed statistically significant.
3. Results
Previous studies showed that the expression of UFM1 is substantially decreased in MASH and alcoholic hepatitis (AH) patients’ biopsies [25,26], indicating a fundamental role of UFMylation in liver homeostasis. As expected, the expression levels of hepatic Uba5, Ufc1, Ufl1, and Ufm1 are significantly reduced in patients with obesity, MASLD, and MASH by analyzing the public data sets (Figure 1A–C). To further understand the regulation of UFMylation in MASLD progression, the mRNA and protein-expressed patterns of UFMylation components were determined by real-time PCR and Western blotting analysis in ob/ob mice and HFD-fed mice. Except for UFSP2, the protein expression level was unchanged, and our results showed that the protein expression levels of UBA5, UFC1, UFL1, UFM1, and DDRGK1 were significantly decreased in the livers of ob/ob mice compared with those of wild-type mice (Figure 1D), whereas there was only a minor decrease in the UFL1 protein level in the livers of HFD-fed mice compared with those of NCD-fed mice, accompanied with the unchanged expression levels of rest proteins (Figure 1E). Interestingly, there were no differences in Uba5, Ufc1, Ufl1, Ufm1, Ddrgk1, Ufsp1, and Ufsp2 expression in the livers of ob/ob mice and HFD-fed mice compared with those of control mice (Figure S1A,B). Together, these observations indicated a context-dependent role of UFMylation in liver diseases, increasing the complexity of UFMylation regulation in liver homeostasis.
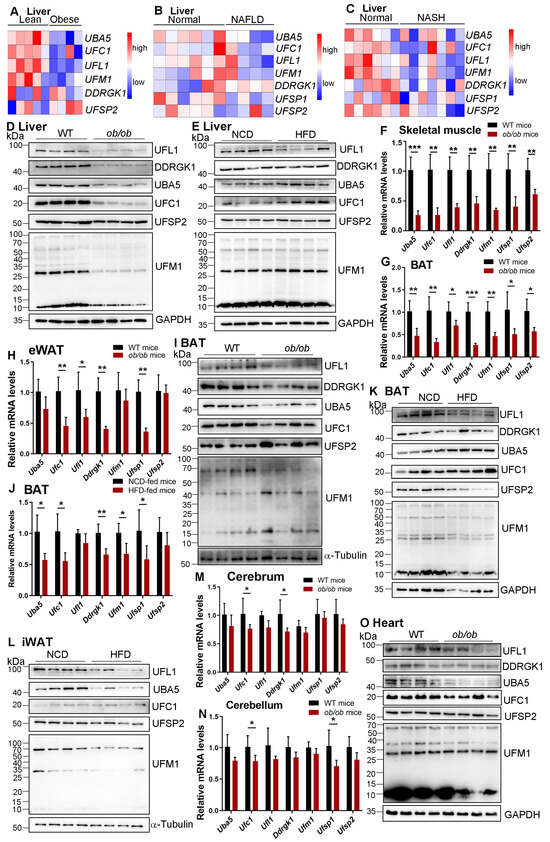
Figure 1.
Systematic analysis of UFMylation components in the liver of patients and tissues of mice with MASLD. (A) The level of UFMylation components expression in the human liver with or without obesity in the Gene Expression Omnibus database (GSE15653). (B) The level of UFMylation components expression in the human liver with or without MASLD in the Gene Expression Omnibus database (GSE59045). (C) The level of UFMylation components expression in the human liver with or without MASH in the Gene Expression Omnibus database (GSE159676). (D) Liver samples were collected from wild-type and ob/ob mice and used to determine the expression of indicated proteins by a Western blot. n = 4. (E) Liver samples were collected from mice fed with NCD or HFD and used to determine the expression of indicated proteins by a Western blot. n = 4. Skeletal muscle (F), BAT (G), and eWAT (H) samples were collected from wild-type and ob/ob mice and used to determine the mRNA expression of indicated genes by real-time PCR. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001 by Student’s t-test, n = 5. (I) BAT samples were collected from wild-type and ob/ob mice and used to determine the expression of indicated proteins by a Western blot. n = 4. (J) BAT samples were collected from mice fed with NCD or HFD and used to determine the mRNA expression of indicated genes by real-time PCR. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 by Student’s t-test, n = 5. BAT (K) and iWAT (L) samples were collected from mice fed with NCD or HFD and used to determine the expression of indicated proteins by a Western blot. n = 4. Cerebrum (M) and cerebellum (N) samples were collected from wild-type and ob/ob mice and used to determine the mRNA expression of indicated genes by real-time PCR. * p < 0.05 by Student’s t-test, n = 5. (O) Heart samples were collected from wild-type and ob/ob mice and used to determine the expression of indicated proteins by a Western blot. n = 4.
MASLD, as a common metabolic disease, is involved in multi-organ interaction [28]. Therefore, we examined the expression levels of UFMylation family genes in other metabolic organs in mice, including skeletal muscle, brown adipose tissue (BAT), inguinal white adipose tissue (iWAT), and epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT). In ob/ob mice, the mRNA levels of all the detected UFMylation components in the skeletal muscle and BAT were dramatically decreased (Figure 1F,G). Similarly, the mRNA expression levels of Ufc1, Ufl1, Ddrgk1, and Ufsp1 in eWAT, as well as Ufl1 and Ufsp1 in iWAT, were clearly reduced in ob/ob mice compared with those in wild-type mice (Figure 1H and Figure S2A). In addition, the protein expression levels of UBA5, UFC1, UFL1, and DDRGK1 in BAT, UBA5, UFC1, UFL1, and UFM1 in iWAT, and UFC1 and DDRGK1 in the skeletal muscle were significantly decreased in ob/ob mice (Figure 1I and Figure S2B,C). However, the protein expression levels of UFSP2 and UFM1 in BAT, DDRGK1 and UFSP2 in iWAT, and UFL1, UBA5, UFM1, and UFSP2 in the skeletal muscle were not significantly decreased in ob/ob mice (Figure 1I and Figure S2B,C). There were no significant differences in eWAT between ob/ob mice and wild-type mice in terms of the protein expression levels of UFMylation components (Figure S2D). Notably, the protein expression of UFSP1 was unable to be detected in all of these organs we described in this study, which is probably due to the bad quality of the antibody.
In HFD-fed mice, the mRNA expression level of Ufsp1, but not other UFMylation components, was decreased in the skeletal muscle and iWAT (Figure S3A,B), and the expression levels of all UFMylation family genes, except Ufl1 and Ddrgk1, were reduced in BAT (Figure 1J). In contrast, no significant differences were detected in eWAT with regard to the expression of all UFMylation components between HFD-fed mice and NCD-fed mice (Figure S3C). Similar to our observation in ob/ob mice, the protein expression levels of UFL1, UFM1, and UFSP2 in BAT, as well as UBA5 and UFL1 in iWAT, were significantly decreased in HFD-fed mice (Figure 1K,L), whereas an increase in UFC1 expression was observed in eWAT in HFD-fed mice (Figure S3D). Furthermore, there were no differences in the UFMylation component expression in the skeletal muscle between HFD-fed mice and NCD-fed mice (Figure S3E). Together, our results revealed that UFMylation components play an essential role in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue homeostasis, contributing to MASLD development.
We further characterized the UFMylation-expressed patterns in the heart, cerebrum, and cerebellum in mouse models, and our results showed that the mRNA expression levels of all UFMylation family genes were not changed in the heart of ob/ob mice (Figure S4A). Additionally, the expression levels of Ufc1 and Ddrgk1 in the cerebrum and Ufc1 and Ufsp1 in the cerebellum were obviously downregulated in ob/ob mice compared to those of wild-type mice. However, the expression levels of the rest genes in the cerebrum or cerebellum were unchanged (Figure 1M,N). In contrast to the observations in the heart, we found that the protein expression levels of UBA5, UFC1, UFL1, and UFM1 were significantly decreased in ob/ob mice (Figure 1O). The protein expression levels of UFC1, UFL1, DDRGK1, and UFSP2 were also reduced in the cerebrum of ob/ob mice (Figure S4B). Interestingly, the UFC1 protein expression level was clearly upregulated in the cerebellum of ob/ob mice compared with those of control mice (Figure S4C), indicating that UFC1 might exert an independent role of UFMylation in brain homeostasis.
Next, we examined the expression levels of UFMylation components in the heart, cerebrum, and cerebellum in HFD-fed mice. Our results showed that the expression levels of Uba5, Ufl1, Ddrgk1, Ufsp1, and Ufsp2 in the heart were decreased compared to NCD-fed mice (Figure S5A). In the cerebrum and cerebellum, our findings did not show any significant expression differences of these UFMylation family genes between the NCD-fed mice and the HFD-fed mice (Figure S5B,C). Furthermore, the protein expression levels of UBA5, UFL1, and DDRGK1 were reduced in the heart of HFD-fed mice, accompanied by the unchanged expression levels of UFSP2, UFC1, and UFM1 proteins (Figure S5D). In the cerebrum, we did not find any differences between the NCD-fed mice and the HFD-fed mice with regard to the protein expression levels of UFMylation components (Figure S5E). In the cerebellum, the protein expression levels of UFL1 and DDRGK1 were observed with a minor decrease in HFD-fed mice compared to NCD-fed mice (Figure S5F). Collectively, these expressed patterns suggest potentially essential roles of UFMylation in heart and brain function.
4. Conclusions
MASLD is a complex disease that is involved with multi-organ interaction and modulated by numerous mechanisms in its pathogenesis. Although many features of MASLD pathogenesis are known, the regulation of post-translational modifications in MASLD is not well delineated. UFMylation is a newly identified ubiquitin-like modification, whose biological significance is largely unknown. In this study, we carried out a systematic analysis of UFMylation family gene expression in multiple tissues of the mice, mimicking MASLD, and our results reveal interesting findings that imply novel physiological functions for UFMylation in different organs in MASLD development and progression.
In the present study, we found that the expression of UFMylation components, especially UFL1, was decreased in the livers of ob/ob mice and HFD-fed mice at the protein levels but not the mRNA levels, indicating that UFL1 should be regulated post-translationally in mice livers with MASLD conditions. Interestingly, UFL1 can be phosphorylated by AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which leads to the reduction in PD-1 UFMylation and the subsequent destabilization of PD-1, consequently enhancing CD8+ T cell activation and anti-tumor immunity. By contrast, the inhibition of AMPK activity elevated PD-1 UFMylation and stabilization to promote tumor growth [29]. Considering that AMPK negatively regulates mTOR signaling [30], it is not surprising that the hepatocyte-specific deletion of Ufl1 or Ddrgk1 in mice results in liver injury and increases susceptibility to HFD-induced fatty liver and diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-induced hepatocellular carcinoma by the activation of mTOR signaling [31]. Another interesting observation is that UFMylation components are involved in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue homeostasis in most cases of ob/ob mice and HFD-fed mice, indicating a comprehensive regulation of UFMylation and a complex crosstalk between these metabolic tissues, which may contribute to MASLD progression. We also found a significant decrease in UFL1 in the heart of both mouse models, which is consistent with a previous report that Ufl1 is downregulated in human failing hearts, and it can protect against heart failure [19]. Taken together, it is conceivable to conclude that UFMylation functions as a defender of multiple organ homeostasis maintenance, and disruption of the homeostasis may exacerbate MASLD.
Accumulating evidence showed that the UFMylation system is implicated in numerous cellular functions and human diseases [32], indicating that components of the UFMylation system are potential therapeutic targets. To date, several inhibitors of UFMylation have been discovered. Usenamine A, aUBA5-inhibiting compound, can effectively inhibit breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion [33]. Compound-8, a covalent inhibitor of UFSP2, has also been found to promote UFMylation activity and contribute to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy [16]. Therefore, chemicals targeting UFMylation present novel and promising therapeutic strategies in the treatment of MASLD and other metabolic diseases.
Limitations of This Study
Despite establishing the expressed profiles of UFMylaiton in multiple organs of mice mimicking MASLD, the mechanisms and functions of UFMylation in these organs’ homeostasis and their crosstalk remain unclear, largely because of the elusive identifications of bona fide UFMylation substrates in regulating these organs homeostasis. Moreover, most of the research articles in the literature about UFMylation research are focused on illustrating the substrates for UFMylation and their biological functions, whereas the PTMs of UFMylation family proteins are rarely reported, limiting our understanding of the PTMs’ regulation of themselves. Therefore, it will be important to clarify the regulation of UFMylation components themselves, as well as the regulation and functions of their targets. Nevertheless, our findings provide novel information that will guide multiple research directions to add to our knowledge concerning the physiological function of UFMylation in MASLD and other metabolic diseases.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/genes16010031/s1, Figure S1: The mRNA expression levels of UFMylation components in liver of mice with MASLD; Figure S2: The levels of UFMylation components in iWAT, skeletal muscle and eWAT of ob/ob mice; Figure S3: The levels of UFMylation components in skeletal muscle, iWAT and eWAT of HFD-fed mice; Figure S4: The levels of UFMylation components in heart, cerebrum and cerebellum of ob/ob mice; Figure S5: The levels of UFMylation components in heart, cerebrum and cerebellum of HFD-fed mice.
Author Contributions
M.J.: investigation, validation, and writing—original draft. C.Z.: investigation, validation, methodology, and writing—original draft. Z.Z.: investigation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft. Y.D.: investigation and validation. J.W.: investigation. J.Z.: investigation. S.Q.: investigation. Q.Z.: investigation. Y.J.: methodology. Y.W.: conceptualization, funding acquisition, and writing—review and editing. Y.C.: investigation, funding acquisition, and writing—original draft. J.L.: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32270751 to J.L., 82371571 to Y.W.), the health commission of Zhejiang Province of China (2024KY239 to J.L.), and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province of China (LQ24C070003 to Y.C., LY24H250002 to Y.W.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All animal studies in our investigation (including the mice euthanasia procedure) have been approved and were performed in compliance with the regulations and guidelines of the Animal Care and Use Committee of Hangzhou Normal University (study approval reference code 2022-1011, 3 March 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are included within the article and its Supplementary Information files or from the corresponding authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Rinella, M.E.; Sookoian, S. From NAFLD to MASLD: Updated naming and diagnosis criteria for fatty liver disease. J. Lipid Res. 2024, 65, 100485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Maurantonio, M.; Marrazzo, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Adinolfi, L.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Evolving paradigms. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6571–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, F.; Seelig, A.; Humphrey, S.J.; Krahmer, N.; Volta, F.; Reggio, A.; Marchetti, P.; Gerdes, J.; Mann, M. Phosphoproteomics Reveals the GSK3-PDX1 Axis as a Key Pathogenic Signaling Node in Diabetic Islets. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1422–1432.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banner, B.F.; Savas, L.; Zivny, J.; Tortorelli, K.; Bonkovsky, H.L. Ubiquitin as a marker of cell injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 114, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, H.; Fu, J.; Cai, L.; Li, P.L.; Zhao, C.L.; Dong, Z.F.; Ma, J.P.; Wang, X.; Tian, H.; et al. Hepatocyte TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 6 Aggravates Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis by Promoting Lysine 6-Linked Polyubiquitination of Apoptosis Signal-Regulating Kinase 1. Hepatology 2020, 71, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubiete-Franco, I.; Fernandez-Tussy, P.; Barbier-Torres, L.; Simon, J.; Fernandez-Ramos, D.; Lopitz-Otsoa, F.; Gutierrez-de Juan, V.; de Davalillo, S.L.; Duce, A.M.; Iruzubieta, P.; et al. Deregulated neddylation in liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2017, 65, 694–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, M.; Chiba, T.; Tatsumi, K.; Iemura, S.; Tanida, I.; Okazaki, N.; Ueno, T.; Kominami, E.; Natsume, T.; Tanaka, K. A novel protein-conjugating system for Ufm1, a ubiquitin-fold modifier. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, K.; Sou, Y.S.; Tada, N.; Nakamura, E.; Iemura, S.; Natsume, T.; Kang, S.H.; Chung, C.H.; Kasahara, M.; Kominami, E.; et al. A novel type of E3 ligase for the Ufm1 conjugation system. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5417–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millrine, D.; Cummings, T.; Matthews, S.P.; Peter, J.J.; Magnussen, H.M.; Lange, S.M.; Macartney, T.; Lamoliatte, F.; Knebel, A.; Kulathu, Y. Human UFSP1 is an active protease that regulates UFM1 maturation and UFMylation. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.M.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.E.; Seong, M.W.; Lee, S.W.; Ka, S.H.; Sou, Y.S.; Komatsu, M.; Tanaka, K.; et al. Modification of ASC1 by UFM1 is crucial for ERalpha transactivation and breast cancer development. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gong, Y.; Peng, B.; Shi, R.; Fan, D.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, H.; Lou, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. MRE11 UFMylation promotes ATM activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 4124–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.; Yu, J.; Nowsheen, S.; Wang, M.; Tu, X.; Liu, T.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Lou, Z. UFL1 promotes histone H4 ufmylation and ATM activation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guan, D.; Dong, M.; Yang, J.; Wei, H.; Liang, Q.; Song, L.; Xu, L.; Bai, J.; Liu, C.; et al. UFMylation maintains tumour suppressor p53 stability by antagonizing its ubiquitination. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snider, D.L.; Park, M.; Murphy, K.A.; Beachboard, D.C.; Horner, S.M. Signaling from the RNA sensor RIG-I is regulated by ufmylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119531119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimura, R.; El-Gowily, A.H.; Noshiro, D.; Komatsu-Hirota, S.; Ono, Y.; Shindo, M.; Hatta, T.; Abe, M.; Uemura, T.; Lee-Okada, H.C.; et al. The UFM1 system regulates ER-phagy through the ufmylation of CYB5R3. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ma, X.; He, X.; Chen, B.; Yuan, J.; Jin, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Cai, Y.; et al. Dysregulation of PD-L1 by UFMylation imparts tumor immune evasion and identified as a potential therapeutic target. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2215732120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egunsola, A.T.; Bae, Y.; Jiang, M.M.; Liu, D.S.; Chen-Evenson, Y.; Bertin, T.; Chen, S.; Lu, J.T.; Nevarez, L.; Magal, N.; et al. Loss of DDRGK1 modulates SOX9 ubiquitination in spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Guan, Z.; Yan, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, K.; Guan, D.; Liang, Q.; et al. Ufl1 deficiency causes kidney atrophy associated with disruption of endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis. J. Genet. Genom. 2021, 48, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yue, G.; Ma, W.; Zhang, A.; Zou, J.; Cai, Y.; Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; et al. Ufm1-Specific Ligase Ufl1 Regulates Endoplasmic Reticulum Homeostasis and Protects Against Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e004917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muona, M.; Ishimura, R.; Laari, A.; Ichimura, Y.; Linnankivi, T.; Keski-Filppula, R.; Herva, R.; Rantala, H.; Paetau, A.; Poyhonen, M.; et al. Biallelic Variants in UBA5 Link Dysfunctional UFM1 Ubiquitin-like Modifier Pathway to Severe Infantile-Onset Encephalopathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, E.; Daniel, J.; Ziegler, A.; Wakim, J.; Scrivo, A.; Haack, T.B.; Khiati, S.; Denomme, A.S.; Amati-Bonneau, P.; Charif, M.; et al. Biallelic Variants in UBA5 Reveal that Disruption of the UFM1 Cascade Can Result in Early-Onset Encephalopathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahorski, M.S.; Maddirevula, S.; Ishimura, R.; Alsahli, S.; Brady, A.F.; Begemann, A.; Mizushima, T.; Guzman-Vega, F.J.; Obata, M.; Ichimura, Y.; et al. Biallelic UFM1 and UFC1 mutations expand the essential role of ufmylation in brain development. Brain 2018, 141, 1934–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Shi, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Shen, L.; Jiang, H.; et al. UBA5 Mutations Cause a New Form of Autosomal Recessive Cerebellar Ataxia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; Mao, Z.; Chen, F. UFMylation System: An Emerging Player in Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2022, 14, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, J.; Tillman, B.; French, B.A.; French, S.W. Ufmylation and FATylation pathways are downregulated in human alcoholic and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and mice fed DDC, where Mallory-Denk bodies (MDBs) form. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2014, 97, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Gong, M.; French, B.A.; Li, J.; Tillman, B.; French, S.W. Mallory-Denk Body (MDB) formation modulates Ufmylation expression epigenetically in alcoholic hepatitis (AH) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2014, 97, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Ma, X.; Jing, Y.; Shen, M.; Ma, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Chen, F. Ufmylation on UFBP1 alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, H. Multiple organs involved in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Xing, X.; Chen, H.Y.; Gao, M.; Shi, J.; Xiang, B.; Xiao, X.; Sun, Y.; Yu, H.; Xu, G.; et al. UFL1 ablation in T cells suppresses PD-1 UFMylation to enhance anti-tumor immunity. Mol. Cell 2024, 84, 1120–1138.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwinn, D.M.; Shackelford, D.B.; Egan, D.F.; Mihaylova, M.M.; Mery, A.; Vasquez, D.S.; Turk, B.E.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Sheng, L.; Zhou, T.; Yan, L.; Loveless, R.; Li, H.; Teng, Y.; Cai, Y. Loss of Ufl1/Ufbp1 in hepatocytes promotes liver pathological damage and carcinogenesis through activating mTOR signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z. The Post-Translational Role of UFMylation in Physiology and Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, B.; Li, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Cho, N.; Yoo, H.M. Inhibition of UBA5 Expression and Induction of Autophagy in Breast Cancer Cells by Usenamine A. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).