Hsa-miR-874-3p Reduces Endogenous Expression of RGS4-1 Isoform In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Recombinants Constructed with the 3′ Regulatory Region of the RGS4 Gene
2.2. Cell Culture and Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.3. Bioinformatic Platform Prediction
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
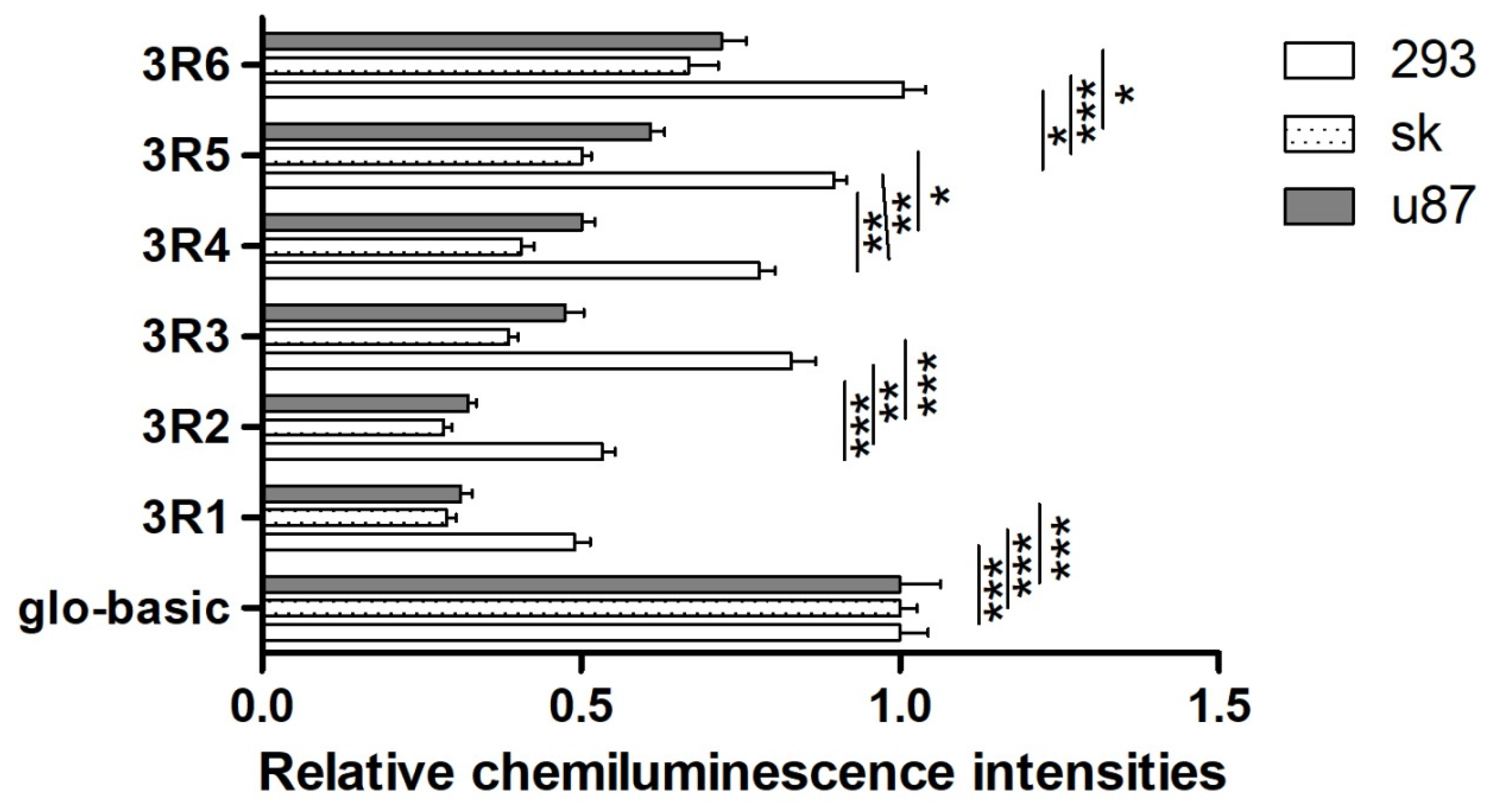
3.1. Comparison and Analysis of Relative Fluorescence Intensities of Recombined Vectors
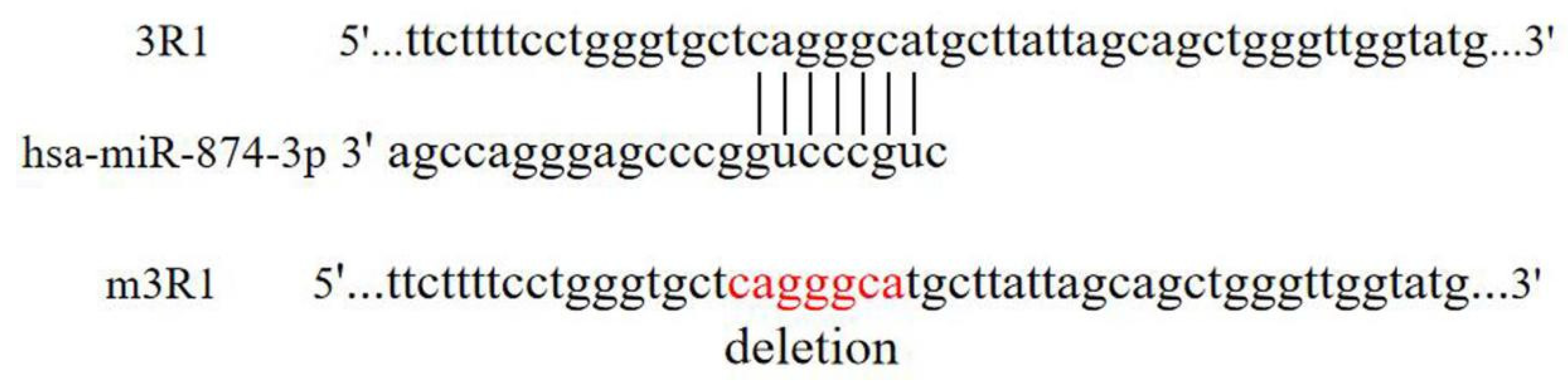
3.2. Results of Bioinformatic Platform Prediction
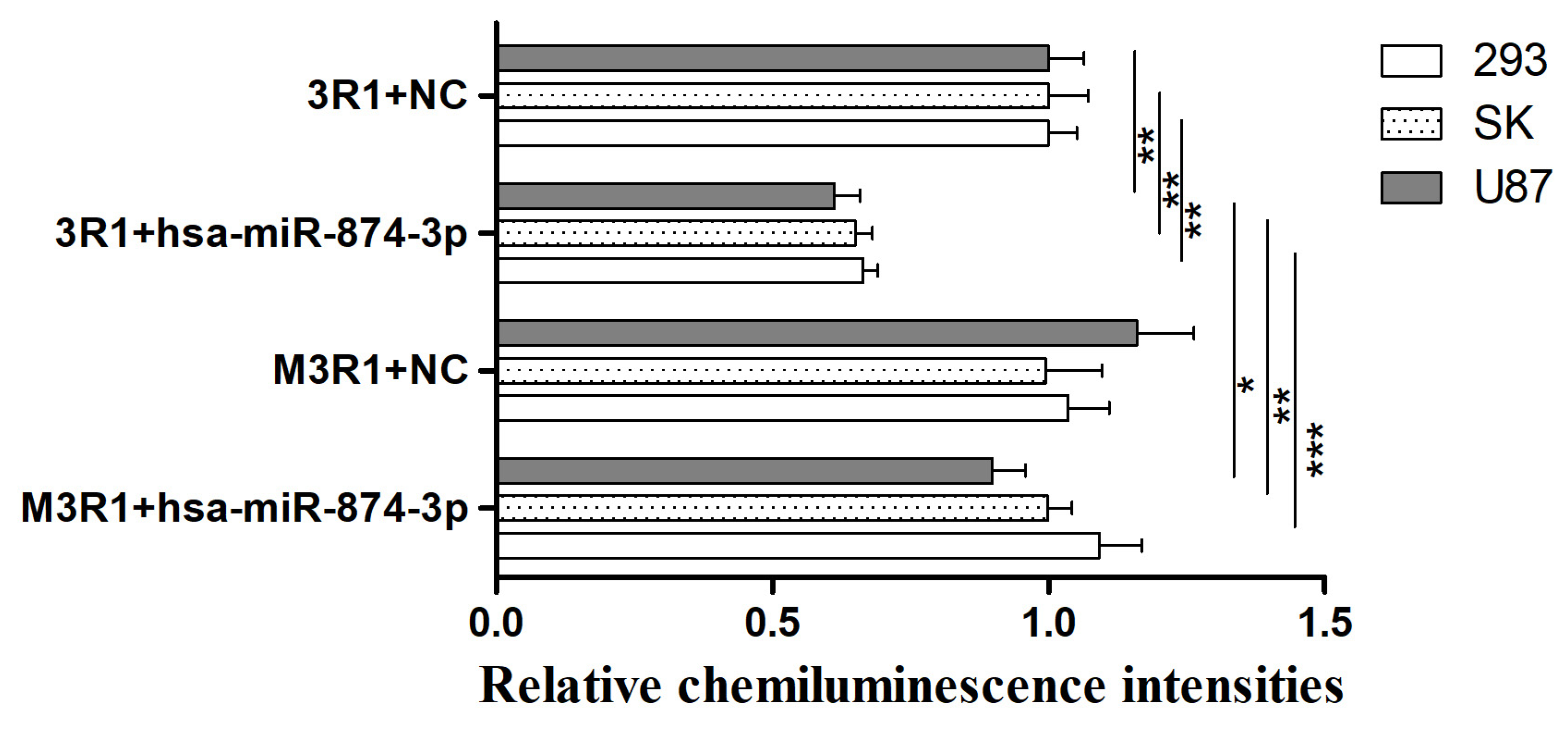
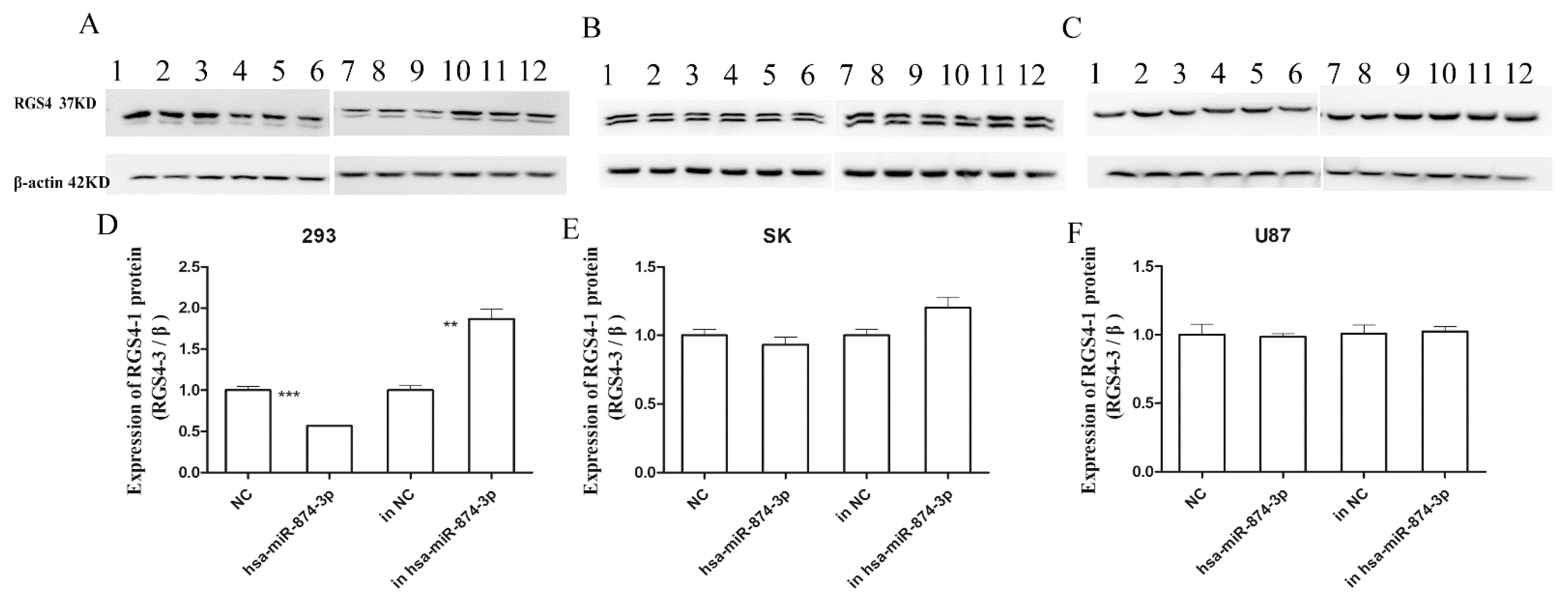
3.3. Hsa-miR-874-3p Mimic Inhibited Expression Relative Fluorescence Intensity of 3R1 and Endogenous RGS4-1 Isoform
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Zhang, P.; Kofron, C.M.; Mende, U. Heterotrimeric G protein-mediated signaling and its non-canonical regulation in the heart. Life Sci. 2015, 129, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddle, E.L.; Schwartzman, R.A.; Bond, M.; Insel, P.A. Multi-tasking RGS proteins in the heart: The next therapeutic target? Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Z.; Ran, Z. MiR-21-3p modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and apoptosis via targeting TGS4 in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 46, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelides, M.; Miller, M.L.; Egervari, G.; Primeaux, S.D.; Gomez, J.L.; Ellis, R.J.; Landry, J.A.; Szutorisz, H.; Hoffman, A.F.; Lupica, C.R.; et al. Striatal Rgs4 regulates feeding and susceptibility to diet-induced obesity. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 2058–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.S.; Redes, J.L.; Balenga, N.; McCullough, M.; Fuentes, N.; Gokhale, A.; Koziol-White, C.; Jude, J.A.; Madigan, L.A.; Chan, E.C.; et al. RGS4 promotes allergen- and aspirin-associated airway hyperresponsiveness by inhibiting PGE2 biosynthesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1152–1164.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, E. A gene-based review of RGS4 as a putative risk gene for psychiatric illness. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2018, 177, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, B.; Boer, S.; Gibbons, A.; Money, T.; Scarr, E. Recent advances in postmortem pathology and neurochemistry in schizophrenia. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2009, 22, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, N.A.; Scott, R.J.; Tooney, P.A. Altered expression of regulator of G-protein signalling 4 (RGS4) mRNA in the superior temporal gyrus in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2007, 89, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, S.; Glausier, J.R.; Fish, K.N.; Volk, D.W.; Bazmi, H.H.; Arion, D.; Datta, D.; Lewis, D.A. Reciprocal Alterations in Regulator of G Protein Signaling 4 and microRNA16 in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2016, 42, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnics, K.; Middleton, F.A.; Stanwood, G.D.; Lewis, D.A.; Levitt, P. Disease-specific changes in regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) expression in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2001, 6, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.W.; Lin, Y.J.; Chang, C.W.; Lei, F.J.; Ho, E.P.; Liu, R.S.; Shyu, W.C.; Hsieh, C.H. RGS4 deficit in prefrontal cortex contributes to the behaviors related to schizophrenia via system xc(-)-mediated glutamatergic dysfunction in mice. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4781–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; Hegde, A.N. Full length cloning and expression analysis of splice variants of regulator of G-protein signaling RGS4 in human and murine brain. Gene 2007, 401, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Hegde, A.N. Expression of RGS4 splice variants in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of schizophrenic and bipolar disorder patients. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Styblo, M.; Drobna, Z.; Hegde, A.N. Expression of the Longest RGS4 Splice Variant in the Prefrontal Cortex Is Associated with Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Schizophrenia Patients. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambor, H.; Surendranath, V.; Kalinka, A.T.; Mejstrik, P.; Saalfeld, S.; Tomancak, P. Systematic imaging reveals features and changing localization of mRNAs in Drosophila development. eLife 2015, 4, e05003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreassi, C.; Riccio, A. To localize or not to localize: mRNA fate is in 3′UTR ends. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutet, S.C.; Cheung, T.H.; Quach, N.L.; Liu, L.; Prescott, S.L.; Edalati, A.; Iori, K.; Rando, T.A. Alternative polyadenylation mediates microRNA regulation of muscle stem cell function. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wu, C.N.; Xu, J.; Feng, G.; Xing, Q.H.; Fu, W.; Li, C.; He, L.; Zhao, X.Z. Polymorphisms in microRNA target sites influence susceptibility to schizophrenia by altering the binding of miRNAs to their targets. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 23, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Gao, H.X. Mechanism of miR-107-targeting of regulator of G-protein signaling 4 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 5145–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Fan, X.; Zhou, F.; Gu, J.; Deng, X. lncRNA RPL34-AS1 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion while promoting apoptosis by competitively binding miR-3663-3p/RGS4 in papillary thyroid cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 3669–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrigal, A.; Tan, L.; Zhao, Y. Expression regulation and functional analysis of RGS2 and RGS4 in adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duricki, D.A.; Soleman, S.; Moon, L.D. Analysis of longitudinal data from animals with missing values using SPSS. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1112–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwalds-Gilbert, G.; Veraldi, K.L.; Milcarek, C. Alternative poly(A) site selection in complex transcription units: Means to an end? Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 2547–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yi, R. 3′UTRs take a long shot in the brain. Bioessays 2014, 36, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, C. What Are 3′ UTRs Doing? Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipowicz, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Sonenberg, N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, K.W.; Cheng, C.W.; Wong, C.M.; Ng, I.O.; Kwong, Y.L.; Tse, E. miR-874-3p is down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and negatively regulates PIN1 expression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 11343–11355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotto, C.; Biscontin, A.; Millino, C.; Mognato, M. Functional validation of miRNAs targeting genes of DNA double-strand break repair to radiosensitize non-small lung cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2018, 1861, 1102–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.G.; Zhuo, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ji, Y.X.; Guo, Q. miR-874-3p inhibits cell migration through targeting RGS4 in osteosarcoma. J. Gene Med. 2020, 22, e3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suento, W.J.; Kunisawa, K.; Wulaer, B.; Kosuge, A.; Iida, T.; Fujigaki, S.; Fujigaki, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tanra, A.J.; Saito, K.; et al. Prefrontal cortex miR-874-3p prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behavior through inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 expression in mice. J. Neurochem. 2020, 157, 1963–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, S.N.; Baker, L.C.; Mittelman, D.; Porteus, M.H. Lentiviral and targeted cellular barcoding reveals ongoing clonal dynamics of cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer | Sequences |
|---|---|
| 3RF | 5′ CTAGCTAGCTGCTTCCCTGGTCC 3′ |
| 3RR1 | 5′ CCCTCGAGATTTTTCTAAAGTCACC 3′ |
| 3RR2 | 5′ CCCTCGAGGACCTATTAGTAAGACAGC 3′ |
| 3RR3 | 5′ CCCTCGAGAGGTGATATCCTGTACC 3′ |
| 3RR4 | 5′ CCCTCGAGAGCCTCATCTGATGG 3′ |
| 3RR5 | 5′ CCCTCGAGAGCATGAAGTTCCTTG 3′ |
| 3RR6 | 5′ CCCTCGAGTCTGGAGAACGTGC 3′ |
| Primer | Sequences | |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-874-3p mimics | 5′-3′ | CUGCCCUGGCCCGAGGGACCGA |
| GGUCCCUCGGGCCAGGGCAGUU | ||
| hsa-miR-874-3p inhibitor | 5′-3′ | UCGGUCCCUCGGGCCAGGGCAG |
| NC | 5′-3′ | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT |
| TTAAGAGGCUUGCACAGUGCA | ||
| NC inhibitor | 5′-3′ | CAGUACUUUUGUGUAGUACAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.-L.; Wang, B.-J. Hsa-miR-874-3p Reduces Endogenous Expression of RGS4-1 Isoform In Vitro. Genes 2024, 15, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15081057
Xu F-L, Wang B-J. Hsa-miR-874-3p Reduces Endogenous Expression of RGS4-1 Isoform In Vitro. Genes. 2024; 15(8):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15081057
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Feng-Ling, and Bao-Jie Wang. 2024. "Hsa-miR-874-3p Reduces Endogenous Expression of RGS4-1 Isoform In Vitro" Genes 15, no. 8: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15081057
APA StyleXu, F.-L., & Wang, B.-J. (2024). Hsa-miR-874-3p Reduces Endogenous Expression of RGS4-1 Isoform In Vitro. Genes, 15(8), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15081057







