Abstract
Background: Obesity is a pressing public health issue in Malaysia, involving not only excess weight but also complex metabolic and physiological changes. Addressing these complexities requires comprehensive strategies, including understanding the population-level differences in obesity susceptibility. This review aims to compile the genetic variants studied among Malaysians and emphasize their implications for obesity risk. Methods: Relevant articles published up to March 2024 were extracted from the Scopus, PubMed, and ScienceDirect databases. The review process was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA-ScR guidelines. From an initial pool of 579 articles, 35 of these were selected for the final review. Results: The identified gene variants, including LEPR (K656N), LEP (G2548A—Indian only), ADIPOQ (rs17366568), UCP2 (45bp-I/D), ADRB3 (rs4994), MC3R (rs3827103), PPARγ (pro12Ala—Malay only), IL1RA (intron 2 VNTR), NFKB1 (rs28362491), and FADS1 (rs174547—Indian only), showed significant associations with obesity as measured by the respective studies. Conclusions: Overall, more intensive genetic research is needed, starting with population-based profiling of genetic data on obesity, including among children. Sociocultural contexts and environmental factors influence variations in genetic elements, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to mitigate the impacts of obesity in the population.
1. Introduction
The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies overweight and obesity as the fifth leading risk for global mortality, with elevated BMI contributing to diseases like cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain types of cancer [1,2]. Obesity, once considered a problem predominantly in high-income countries, has now become an increasing public health issue worldwide.
In Malaysia, the trends in overweight, obesity, and abdominal obesity have continued to rise, as evidenced by the National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS) in 2011 (29.4%, 15.1%, and 45.4%) and 2015 (30%, 17.7%, and 48.6%) [3,4]. Currently, obesity remains a major health challenge in the country, with no sign of abating. The latest NHMS report reveals that over half of the adult population is affected by weight issues, with 54.4% being overweight or obese and 54.5% having abdominal obesity [5].
Recently, the Health Research Priorities for the 12th Malaysia Plan (12MP-HRP) 2021–2025 have identified 15 priority research areas related to overweight and obesity, with one of them being the need to investigate the role of genetic factors in the development of overweight and obesity [6]. This shows that studies in this area and scientific data on this topic are still scarce in Malaysia.
Obesity is widely recognized as a polygenetic disease influenced by interactions between genes and the environment, including factors such as diet, lack of physical exercise, microbiome, and chemical contaminants, all of which can alter gene expression [7]. In addition to environmental, social, and economic factors, phenotypic heterogeneity exists among overweight and obese individuals due to interactions at the molecular, genetic, and cellular levels [8]. Another form of obesity also exists, known as monogenic obesity, in which mutations in specific genes cause early-onset of obesity, often from infancy or early childhood. Recently, gene discovery studies have found common fundamental biology between polygenic and monogenic obesity, with central nervous system (CNS) and neuronal pathways that control food intake being major drivers of body weight in both forms [9]. Early evidence also shows that individuals’ polygenic susceptibility to obesity may partly influence the expression of mutations that cause monogenic obesity [10]. Therefore, it is crucial to identify population-based genetic variants associated with obesity to enhance understanding of their predisposition for improved diagnosis and management.
Given these considerations, this scoping review aims to compile and present genetic research on obesity conducted in Malaysia up to March 2024. To date, no review has specifically focused on this aspect within Malaysia. This review consolidates the studied genetic variants and their associations with obesity and offers recommendations for future research based on the limitations of current studies. Ultimately, this review seeks to effectively guide future obesity research in Malaysia and address the gaps highlighted in the 12th Malaysia Plan.
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol
The framework for analyzing this scoping review was conducted following the methodology outlined by Arksey and O’Malley [11]. The scoping review protocol was prospectively registered with the Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/qyzka, accessed on 11 July 2024). Guidelines for conducting a scoping review were adhered to [12], along with the PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analyses extension for Scoping Reviews) guidelines for reporting [13].
2.2. Identification of Relevant Studies
A systematic literature search was performed using a predefined search strategy across Scopus, PubMed, and ScienceDirect databases. This search was conducted by at least two independent researchers. The search included articles published from the earliest available date to March 2024, as research on this topic was limited in Malaysia. English language terms were used and review articles including scoping, systematic, narrative, meta-synthesis, and meta-analysis were omitted. Boolean operators (AND, OR) were utilized to combine words. The identified records were exported to EndNote and independently screened for inclusion by four reviewers. Disagreements were addressed through discussion until a consensus was achieved.
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows:
- Peer-reviewed articles, including original research and clinical studies;
- Human-based research;
- Study conducted among Malaysian (Malay, Chinese, Indian, indigenous people, bumiputra Sabah and Sarawak);
- English and Malay language;
- Any articles published until March 2024.
The exclusion criteria were as follows:
- Books, book chapters, and book reviews;
- Review articles (systematic, meta-analysis, meta-synthesis, scoping, narrative);
- Animal studies;
- Non-Malaysian population;
- Perspective, opinion, and commentary in peer-reviewed journal;
- Non-genetics or obesity studies.
2.4. Data Extraction
Data extraction from the included studies was conducted using a standardized data extraction sheet in Microsoft Excel 2021 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA). The extraction process included recording the year of publication, scientific study title, authors, objectives, sex distribution, sample size, ethnicity, comparison group details, and findings.
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
Based on the keyword searches, 579 potentially eligible records were identified, out of which 153 articles were excluded due to redundancy. Following abstract screening, 378 articles were further excluded, leaving 47 articles for full-text screening. Subsequently, 13 studies were excluded during the full-text review, resulting in the inclusion of 34 studies for data extraction and analysis. In total, 391 articles were removed during screening for following reasons: 9 studies involved animal subjects, 306 were unrelated to genetics or obesity, 60 articles were conducted among non-Malaysians and 16 were review papers (Figure 1).
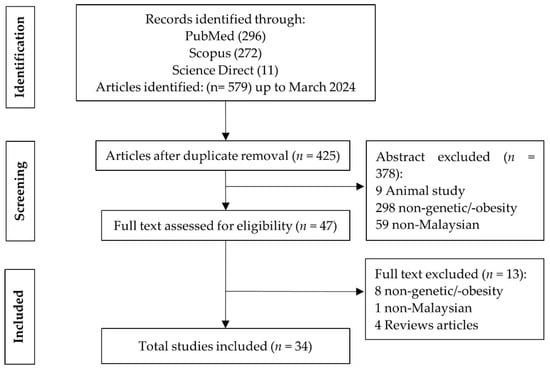
Figure 1.
PRISMA flowchart outlining selection process for including studies in the review.
The characteristics of the included studies are summarized in Table 1. The first genetic study on obesity in Malaysia was published in 2009 by Liew et al. followed by an increasing trend in research on gene polymorphisms and their association with obesity starting from 2018 until the present. Most studies focused on university students and local community members attending health clinics, with objectives primarily centered around the relationship between specific gene variants and obesity or health parameters associated with obesity. Only three studies were conducted among children. The majority of studies involved three or more ethnic groups (n = 19), while others focused exclusively on Malay participants or had more than 75% Malay participants (n = 11), Chinese participants (n = 2), or combined Chinese and Indian participants (n = 2). However, 99% of the studies did not stratify outcomes by ethnic group (except for the study by Kok et al.) but rather compared obese and non-obese individuals. It is noteworthy that all included studies had relatively small sample sizes, ranging from 150 to 1200 participants, which may impact the validity and generalizability of their research findings.

Table 1.
Participants characteristics.
3.2. Genetic Variants of Interest and Risk of Obesity
Forty-two variants of genes directly or indirectly involved in susceptibility to obesity were identified (Table 2). Each study examined the association between these gene variants and obesity, typically reporting results in terms of Minor Allele Frequency (MAF) and/or Odds Ratio (OR). Among these, the genetic variants of LEPR (K656N), LEP (G2548A- Indian only), ADIPOQ (rs17366568), UCP2 (45bp-I/D), ADRB3 (rs4994), MC3R (Rs3827103), PPARγ (pro12Ala—Malay only), IL1RA (intron 2 VNTR), NFKB1 (rs28362491), and FADS1 (rs174547—Indian only) have been significantly associated with obesity risk in Malaysians.

Table 2.
List of studied genetic variants associated with monogenic and polygenic obesity. The Minor Allele Frequency (MAF), Odds Ratio (OR), and findings on the association with obesity for each variant presented were taken directly from the respective studies.
However, no significant association with obesity was reported for the genetic variants of LEP (A19G), LEPR (K109R, Q223R), PYY (R72T), NPY (rs16147T, rs161139C), PPAR (L162V), PPAR2 (C161T), PPARδ (T294C), UCP1 (-3826 A/G), UCP3 (-55C/T), CARTPT (rs2239670), POMC (Rsal), MC4R (V1031), FTO (rs9930506, rs9939609, rs17817288, rs9930501, rs9932754), ADIPOQ (rs3774261), INSIG2 (rs7566605), RETN, DRD2 (Taq1A, Taq1B, Taq1C), VDR (bsml), IRX (rs3751723), FASN (rs4246445, rs2229425, rs2228305,rs2229422), and ADRB2 (rs1042713).
3.3. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
Out of the thirty-three genes for which selected genetic variants were reported as significantly associated with obesity, only four genes (LEP, LEPR, POMC, and MC4R) are known to be linked with monogenic obesity. Mutations in these genes can cause early-onset obesity which is not easily influenced by environmental factors alone, unlike polygenic obesity. Since the majority of the reviewed articles are highly heterogenous, biased in terms of selecting candidate genes, and the studies were mostly underpowered, only the genes associated with monogenic obesity were selected for protein—protein interaction analysis. The STRING database shows that interactions between LEP, LEPR, POMC, and MC4R have been reported from various experimental data, curated databases, and co-expression studies (Figure 2). Nodes in these networks represent proteins, and the edges denote their interactions. The roles of these genes in many biological processes and important molecular pathways are also well established. Examples of Gene Ontology (GO) biological processes involving some or all of the genes include response to a melanocyte-stimulating hormone, leptin-mediated signaling pathway, regulation of appetite, and regulation of feeding behavior. In terms of KEGG pathways, examples include adipocytokine signaling pathway and AMPK signaling pathway (Table 3).
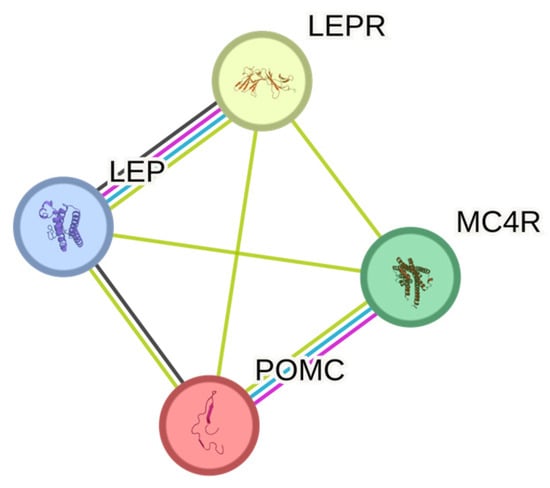
Figure 2.
STRING protein networks of genes associated with monogenic obesity.

Table 3.
GO Biological Process and KEGG pathways of genes associated with monogenic obesity (POMC, MC4R, LEP, and LEPR).
4. Discussion
Review findings suggest that there was a growing focus on genetic variants associated with obesity in Malaysians. This trend may be attributed to substantial evidence indicating that specific genetic variants may affect populations differently, influenced by factors such as sociocultural contexts, dietary habits, and patterns of body fat distribution [48]. It was noted that the majority of the included studies (94%) were conducted among adults in universities and local health clinics. However, defining early predictors of obesity is crucial, as the National Health Morbidity Survey 2022 (NHMS 2022) reported that childhood obesity is currently a major health problem in Malaysia, with one in three teens aged 13–17 being overweight or obese [49]. Therefore, while it is more convenient to recruit adults, there is also a need for more biomarker studies involving children and adolescents. This would simultaneously address the scarcity of scientific data on the genetics of childhood obesity, as identified in the Health Research Priorities for the 12th Malaysia Plan (12MP-HRP) [6].
The present review also found that a considerable number of genetic variants have been explored. Out of 42 gene polymorphisms investigated, fewer than half were reported to have a significant association with obesity by the authors, and several studies investigated overlapping targets. For example, variants like LEPR Q223R [14,23,25,46] LEP Q2548A [23,25,37,46], LEP A19G [14,37], PPAR L162V and PPAR2 C161T [24,38], FTO rs9930506 [38,45], UCP2 45-bp I/D [15,27], DRD2 Taq1A, Taq1B and Taq1D [39,44]. Notably, the findings across these studies were consistent, showing that none of the genetic variants were linked to obesity, except for LEP G2548A [23], which may be associated with overweight/obesity among Indian males; UCP2 45 bp I/D [27] with overall adiposity among Malaysian women; and DRD2 polymorphisms with eating behavior but not with obesity [39,44]. It is worth noting that these findings may, in part, reflect the small sample sizes used in the studies and the fact that the claimed significance level may not be entirely reliable due to the insufficient statistical power. To address this issue more effectively, studies with larger sample sizes and adequate power are needed to produce more reliable and valid findings that contribute more effectively to scientific knowledge.
Furthermore, this review has identified contradictory results regarding the association of well-established FTO gene variants with obesity risk among Malays, Chinese, and Indians. A research group in Singapore found that FTO variants, especially rs9939609, which are common in European populations, were significantly associated with obesity in Chinese and Malays but not in Asian Indians [50]. However, there was no evidence for this SNP or other FTO regions in obesity and obesity-related parameters in either Chinese, Malays, or Indians in Malaysia [21]. Nevertheless, these results further emphasize the variation in genetic elements among individuals that influence susceptibility to obesity. This is supported by Karra et al., who showed that people with two high-obesity-risk FTO variants have a 70% increased risk of becoming obese compared to those with low-obesity-risk variants [51]. Therefore, given that the targets examined in the included studies were based on evidence from various populations, it is essential for researchers in Malaysia to first conduct gene profiling among obese individuals. This preliminary step will help to identify specific biomarker targets for obesity, paving the way for more focused genetic investigations.
Due to the lack of homogeneity in the samples from most of the reviewed articles, only the protein interactions between studied genes related to monogenic obesity are analyzed using STRING. Monogenic obesity is relatively rare, follows a Mendelian pattern of inheritance, and is usually characterized by severe obesity, unlike the polygenic form of obesity, which often arises from the cumulative effect of multiple genetic variants, each contributing a small effect on obesity risk, as well as environmental factors. Genes such as LEP, LEPR, POMC, and MC4R are known to play crucial roles in various important biological processes and pathways. The most significant shared pathway relates to the adipocytokine signaling pathway. This pathway involves cytokines and adipokines produced by adipocytes and is interconnected with other pathways such as the AMPK signaling pathway, regulating processes such as the metabolism, inflammation, and energy balance. Some components of adipokines, including leptin, adiponectin, resistin, Interleukin-6 (IL-6), and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α), have been associated with the development of insulin resistance, obesity, and related health conditions [52,53,54,55]. Understanding the characteristics of genetic variants that cause each form of obesity is crucial for more precise disease management.
This scoping review has several limitations. Firstly, most of the included studies had small sample sizes and suboptimal study designs. Secondly, the majority of study participants were drawn from institutional and healthcare settings, which may limit the generalizability of the results. Thirdly, the studies encompassed a wide range of ages, and these variations should be considered when interpreting the results. Finally, the bibliographic search was conducted using only three databases, which might have led to the omission of some relevant articles.
For future obesity genetic research, it is crucial for researchers to adopt appropriate study designs and ensure the inclusion of larger sample sizes to strengthen the validity of the findings. Additionally, it is important to include participants from community settings to ensure the findings are applicable to a broader population. Given the significant role of gene–environment interactions in the onset of obesity, large-scale epigenetic studies are needed to identify novel genetic variants specific to the Malaysian population. Leveraging advanced technologies, such as long-read sequencing, can help overcome the limitations of genome-wide association studies (GWAS), which primarily capture common genetic variants.
5. Conclusions
In summary, genetic biomarker research on obesity among Malaysians remains limited in scope, primarily focusing on well-known genes or gene variants. While targeting established gene variants can be one research strategy, it is more compelling to establish comprehensive biomarker genetic profiles related to obesity across different age groups—from children to adults—in the local population.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S.H. and L.A.Z.; methodology, S.S.H., L.A.Z., N.A.S. and N.A.Z.A.; software, S.S.H.; formal analysis, S.S.H., L.A.Z., N.A.S. and N.A.Z.A.; data curation, S.S.H.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S.H.; writing—review and editing, S.S.H. and L.A.Z.; visualization, S.S.H. and L.A.Z.; supervision, S.S.H.; project administration, S.S.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research presented in this publication was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Malaysia, under registration number NMRR ID-23-01291-2ZC.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Director General of Health Malaysia for the permission to publish this paperThe content is the sole responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily reflect the official views of NIH Malaysia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Statistics. Available online: https://easo.org/media-portal/statistics/ (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Institute for Public Health. NHMS 2011. Available online: https://iku.gov.my/nhms-2011 (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Institute for Public Health. NHMS 2015. Available online: https://iku.gov.my/nhms-2015 (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- NHMS 2023. Available online: https://iku.gov.my/nhms-2023 (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Muhamad, N.A.; Lemna, F.N.; Mohd Dali, N.S.; Too, L.C.; Johari, M.Z.; Bakhtiar, F.; Ab. Ghani, R.M.; Mahjom, M.; Sapian, R.A.; Musa, N.S.E.; et al. Health Research Priorities for 12th Malaysia Plan (12MP-HRP) 2021–2025; National Institutes of Health, Ministry of Health Malaysia: Shah Alam, Malaysia, 2021.
- Hinney, A.; Vogel, C.I.G.; Hebebrand, J. From Monogenic to Polygenic Obesity: Recent Advances. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2010, 19, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayoral, L.P.-C.; Andrade, G.M.; Mayoral, E.P.-C.; Huerta, T.H.; Canseco, S.P.; Rodal Canales, F.J.; Cabrera-Fuentes, H.A.; Cruz, M.M.; Pérez Santiago, A.D.; Alpuche, J.J.; et al. Obesity Subtypes, Related Biomarkers & Heterogeneity. Indian J. Med. Res 2020, 151, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.J.F.; Yeo, G.S.H. The Genetics of Obesity: From Discovery to Biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chami, N.; Preuss, M.; Walker, R.W.; Moscati, A.; Loos, R.J.F. The Role of Polygenic Susceptibility to Obesity among Carriers of Pathogenic Mutations in MC4R in the UK Biobank Population. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping Studies: Towards a Methodological Framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Marnie, C.; Tricco, A.C.; Pollock, D.; Munn, Z.; Alexander, L.; McInerney, P.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H. Updated Methodological Guidance for the Conduct of Scoping Reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Med. 2018, 169, 7. Available online: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M18-0850 (accessed on 14 July 2023). [CrossRef]
- Liew, S.F.; Chuah, H.S.; Lau, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Say, Y.H. Prevalence of the Leptin and Leptin Receptor Gene Variants and Obesity Risk Factors among Malaysian University Students of Setapak, Kuala Lumpur. Asian J. Epidemiol. 2009, 3, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiew, S.-K.; Khor, L.-Y.; Tan, M.-L.; Pang, C.-L.; Chai, V.-Y.; Kanachamy, S.S.; Say, Y.-H. No Association between Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor and Uncoupling Protein Gene Polymorphisms and Obesity in Malaysian University Students. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 4, e325–e331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.M.; Fan, S.H.; Say, Y.H. No Association of Peptide Tyrosine-Tyrosine (PYY) Gene R72T Variant with Obesity in the Kampar Health Clinic Cohort, Malaysia. Malays. J. Nutr. 2011, 17, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Lisa, Y.; Sook, H.F.; Yee, H.S. Association of the Cocaine- and Amphetamine-Regulated Transcript Prepropeptide Gene (CARTPT) Rs2239670 Variant with Obesity among Kampar Health Clinic Patrons, Malaysia. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 19, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.M.; Fan, S.H.; Say, Y.H. Prevalence of RsaI Polymorphism in the 5′ Untranslated Region (UTR) of Proopiomelanocortin (POMC) Gene and Its Association with Obesity in the Kampar Health Clinic Cohort, Malaysia. Malays. J. Med. Health Sci. 2012, 8, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, H.N.; Fan, S.H.; Say, Y.H. Prevalence of Melanocortin Receptor 4 (MC4R) V103I Gene Variant and Its Association with Obesity among the Kampar Health Clinic Cohort, Perak, Malaysia. Med. J. Malays. 2012, 67, 234–235. [Google Scholar]
- Apalasamy, Y.D.; Ming, M.F.; Rampal, S.; Bulgiba, A.; Mohamed, Z. Genetic Association of SNPs in the FTO Gene and Predisposition to Obesity in Malaysian Malays. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- WeiWei, C.; SookHa, F.; YeeHow, S. Association of Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated (FTO) Gene Rs9939609 Variant with Obesity among Multi-Ethnic Malaysians in Kampar, Perak. Sains Malays. 2013, 42, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Apalasamy, Y.D.; Ming, M.F.; Rampal, S.; Bulgiba, A.; Mohamed, Z. Association of Melanocortin-4 Receptor Gene Polymorphisms with Obesity-Related Parameters in Malaysian Malays. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2013, 40, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, Z.Y.; Veerapen, M.K.; Hon, W.M.; Lim, R.L.H. Association of Leptin/Receptor and TNF-α Gene Variants with Adolescent Obesity in Malaysia. Pediatr. Int. 2014, 56, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalasamy, Y.D.; Rampal, S.; Salim, A.; Moy, F.M.; Bulgiba, A.; Mohamed, Z. Association of ADIPOQ Gene with Obesity and Adiponectin Levels in Malaysian Malays. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 2917–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.-H.; Say, Y.-H. Leptin and Leptin Receptor Gene Polymorphisms and Their Association with Plasma Leptin Levels and Obesity in a Multi-Ethnic Malaysian Suburban Population. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2014, 33, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalasamy, Y.D.; Moy, F.M.; Rampal, S.; Bulgiba, A.; Mohamed, Z. Genetic Associations of the INSIG2 Rs7566605 Polymorphism with Obesity-Related Metabolic Traits in Malaysian Malays. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 4904–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Say, Y.-H.; Ban, Z.-L.; Arumugam, Y.; Kaur, T.; Tan, M.-L.; Chia, P.-P.; Fan, S.-H. Uncoupling Protein 2 Gene (UCP2) 45-Bp I/D Polymorphism Is Associated with Adiposity among Malaysian Women. J. Biosci. 2014, 39, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalasamy, Y.D.; Rampal, S.; Salim, A.; Moy, F.M.; Su, T.T.; Majid, H.A.; Bulgiba, A.; Mohamed, Z. Polymorphisms of the Resistin Gene and Their Association with Obesity and Resistin Levels in Malaysian Malays. Biochem Genet 2015, 53, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apalasamy, Y.D.; Ming, M.F.; Rampal, S.; Bulgiba, A.; Mohamed, Z. Gender-Dependent Association of a β(2)-Adrenergic Gene Variant with Obesity Parameters in Malaysian Malays. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2015, 27, NP154–NP165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, P.-P.; Fan, S.-H.; Say, Y.-H. Screening of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) α, γ and α Gene Polymorphisms for Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome Association in the Multi-Ethnic Malaysian Population. Ethn. Dis. 2015, 25, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, S.M.; Mohamed, Z.; Jalaludin, M.Y.; Fauzi, F.; Hamidi, A.; Zaharan, N.L. Comprehensive Evaluation of the Neuropeptide-Y Gene Variants in the Risk of Obesity: A Case–Control Study and Meta-Analysis. Pharmacogenetics Genom. 2015, 25, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharan, N.L.; Muhamad, N.H.; Jalaludin, M.Y.; Su, T.T.; Mohamed, Z.; Mohamed, M.N.A.; A Majid, H. Non-Synonymous Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Physical Activity Interactions on Adiposity Parameters in Malaysian Adolescents. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahri, M.K.; Emilia, A.; Rawi, R.I.M.; Taib, W.R.W.; Sani, A.I.; Baig, A.A. Contribution of the Pro12Ala Polymorphism of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Ɣ2 Gene in Relation to Obesity. Meta Gene 2016, 10, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunmugam, V.; Say, Y.-H. Evaluation of Association of ADRA2A Rs553668 and ACE I/D Gene Polymorphisms with Obesity Traits in the Setapak Population, Malaysia. Iran Red. Crescent. Med. J. 2016, 18, e22452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, Y.-Y.; Ong, H.-H.; Say, Y.-H. Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist and Interleukin-4 Genes Variable Number Tandem Repeats Are Associated with Adiposity in Malaysian Subjects. J. Obes. 2017, 2017, 4104137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmadhani, R.; Zaharan, N.L.; Mohamed, Z.; Moy, F.M.; Jalaludin, M.Y. The Associations between VDR BsmI Polymorphisms and Risk of Vitamin D Deficiency, Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Adolescents Residing in a Tropical Country. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohani, W.T.W.; Aryati, A.; Shamsuddin, A.A. Haplotype Analysis of Leptin Gene Polymorphisms in Obesity among Malays in Terengganu, Malaysia Population. Med. J. Malays. 2018, 73, 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, S.R.; Tan, P.Y.; Amini, F. Effect of FTO Rs9930506 on Obesity and Interaction of the Gene Variants with Dietary Protein and Vitamin E on C-Reactive Protein Levels in Multi-Ethnic Malaysian Adults. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 31, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lek, F.-Y.; Ong, H.-H.; Say, Y.-H. Association of Dopamine Receptor D2 Gene (DRD2) Taq1 Polymorphisms with Eating Behaviors and Obesity among Chinese and Indian Malaysian University Students. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 27, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association of IRX3 Rs3751723 Polymorphism with the Risk of Overweight and Obesity: Case-Control Study and Meta-Analysis. Available online: https://colab.ws/articles/10.1016%2Fj.mgene.2018.01.007 (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Chong, E.T.J.; Kuok, S.S.E.; Lee, P.-C. Risk Association, Linkage Disequilibrium and Haplotype Analyses of FASN Rs4246445, Rs2229425, Rs2228305 and Rs2229422 Polymorphisms in Overweight and Obesity. Bioimpacts 2018, 8, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.R.; Tan, P.Y.; Amini, F. Association of ADRB2 Rs1042713 with Obesity and Obesity-Related Phenotypes and Its Interaction with Dietary Fat in Modulating Glycaemic Indices in Malaysian Adults. J. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 2019, 8718795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshajrawi, O.; Basit, E.; Baig, A. HIF1 (Rs11549465) and NFKB1 (Rs28362491) Variants Association with Obesity in Malaysia. Meta Gene 2020, 25, 100753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.-M.; Chie, Q.-T.; Teh, L.-K. Influence of Dopamine Receptor Gene on Eating Behaviour and Obesity in Malaysia. Meta Gene 2020, 25, 100736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.Y.; Mitra, S.R. The Combined Effect of Polygenic Risk from FTO and ADRB2 Gene Variants, Odds of Obesity, and Post-Hipcref Diet Differences. Lifestyle Genom 2020, 13, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, J.; D’Souza, U.J.A.; Fong, S.Y.; Karkada, I.R.; Jaiprakash, H. Association between Leptin (G2548A) and Leptin Receptor (Q223R) Polymorphisms with Plasma Leptin, BMI, Stress, Sleep and Eating Patterns among the Multiethnic Young Malaysian Adult Population from a Healthcare University. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, Y.K.; Chin, Y.S.; Appukutty, M.; Chan, Y.M.; Lim, P.Y.; Nasir, K.H. Interactions of Genetic and Macronutrient Intake with Abdominal Obesity among Middle-Aged Vegetarians in Malaysia. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 32, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprio, S.; Daniels, S.R.; Drewnowski, A.; Kaufman, F.R.; Palinkas, L.A.; Rosenbloom, A.L.; Schwimmer, J.B. Influence of Race, Ethnicity, and Culture on Childhood Obesity: Implications for Prevention and Treatment. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 2211–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health Malaysia. NHMS AHS 2022 States Report. Available online: https://iku.gov.my/nhms-ahs-2022-state-report (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Tan, J.T.; Dorajoo, R.; Seielstad, M.; Sim, X.L.; Ong, R.T.-H.; Chia, K.S.; Wong, T.Y.; Saw, S.M.; Chew, S.K.; Aung, T.; et al. FTO Variants Are Associated with Obesity in the Chinese and Malay Populations in Singapore. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2851–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karra, E.; O’Daly, O.G.; Choudhury, A.I.; Yousseif, A.; Millership, S.; Neary, M.T.; Scott, W.R.; Chandarana, K.; Manning, S.; Hess, M.E.; et al. A Link between FTO, Ghrelin, and Impaired Brain Food-Cue Responsivity. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3539–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangareddy, H.; Venkatapathappa, P.; Mandalaneni, K.; Srinivasaiah, A.; Bourne-Yearwood, K.; Rangareddy, H.; Venkatapathappa, P.; Mandalaneni, K.; Srinivasaiah, A.; Bourne-Yearwood, K. Leptin and Obesity: Understanding the Impact on Dyslipidemia. In Body Mass Index—Overweight, Normal Weight, Underweight; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-1-83768-335-2. [Google Scholar]
- Rachwalik, M.; Hurkacz, M.; Sienkiewicz-Oleszkiewicz, B.; Jasinski, M. Role of Resistin in Cardiovascular Diseases: Implications for Prevention and Treatment. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 30, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, J.K.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Metabolic Messengers: Tumour Necrosis Factor. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).