Unraveling the Mitogenomic Characteristics and Phylogenetic Implications of Leuciscus merzbacheri (Zugmayer, 1912), an Endangered Fish in the Junggar Basin of Xinjiang, Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
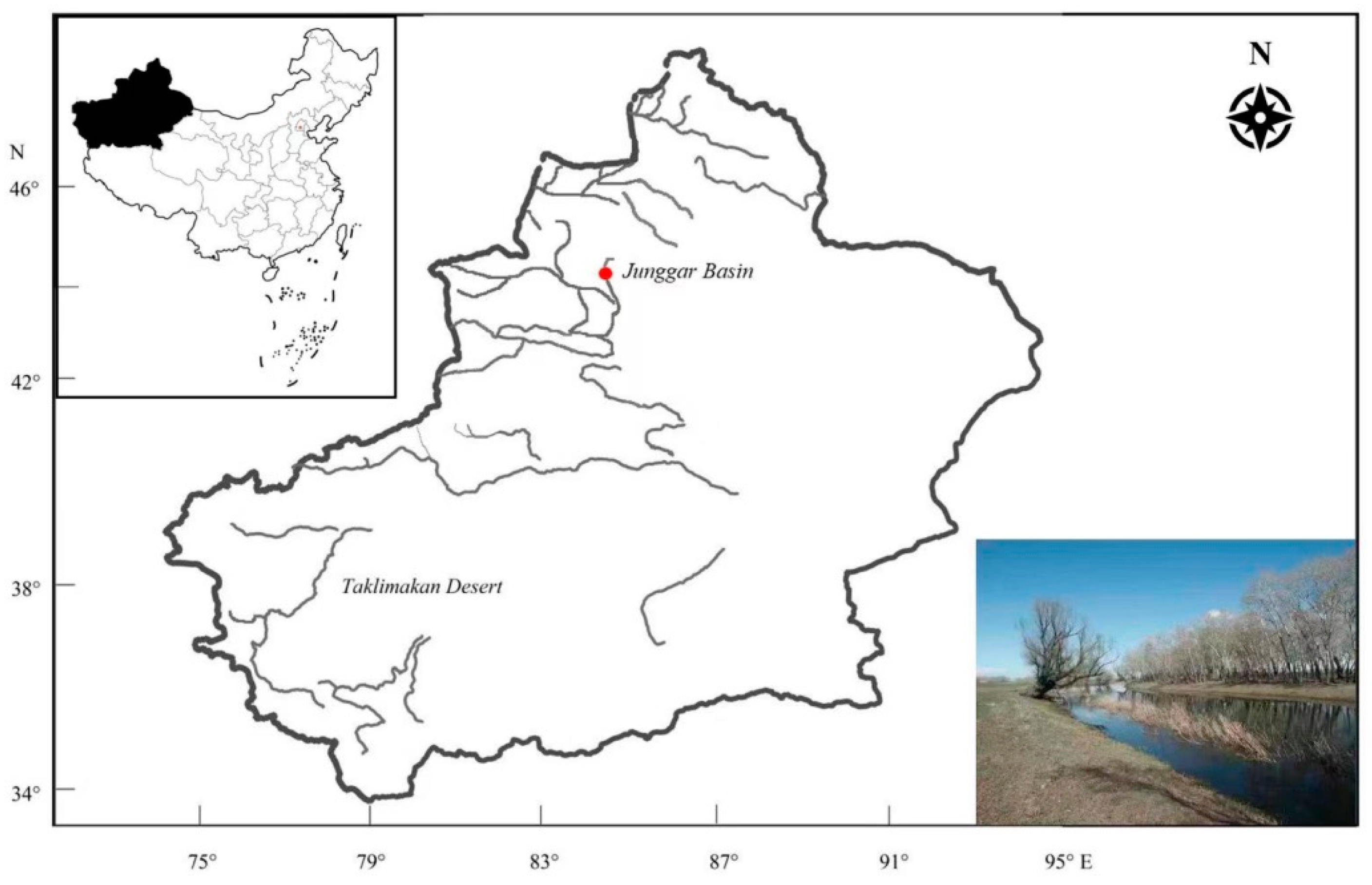
2.1. Sampling, DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.2. Mitochondrial Genome Assembly and Annotation
2.3. Mitogenome Sequence Analysis
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mitogenome Structure and Nucleotide Composition
3.2. Protein-Coding Genes, Amino Acids and Codon Usage Pattern
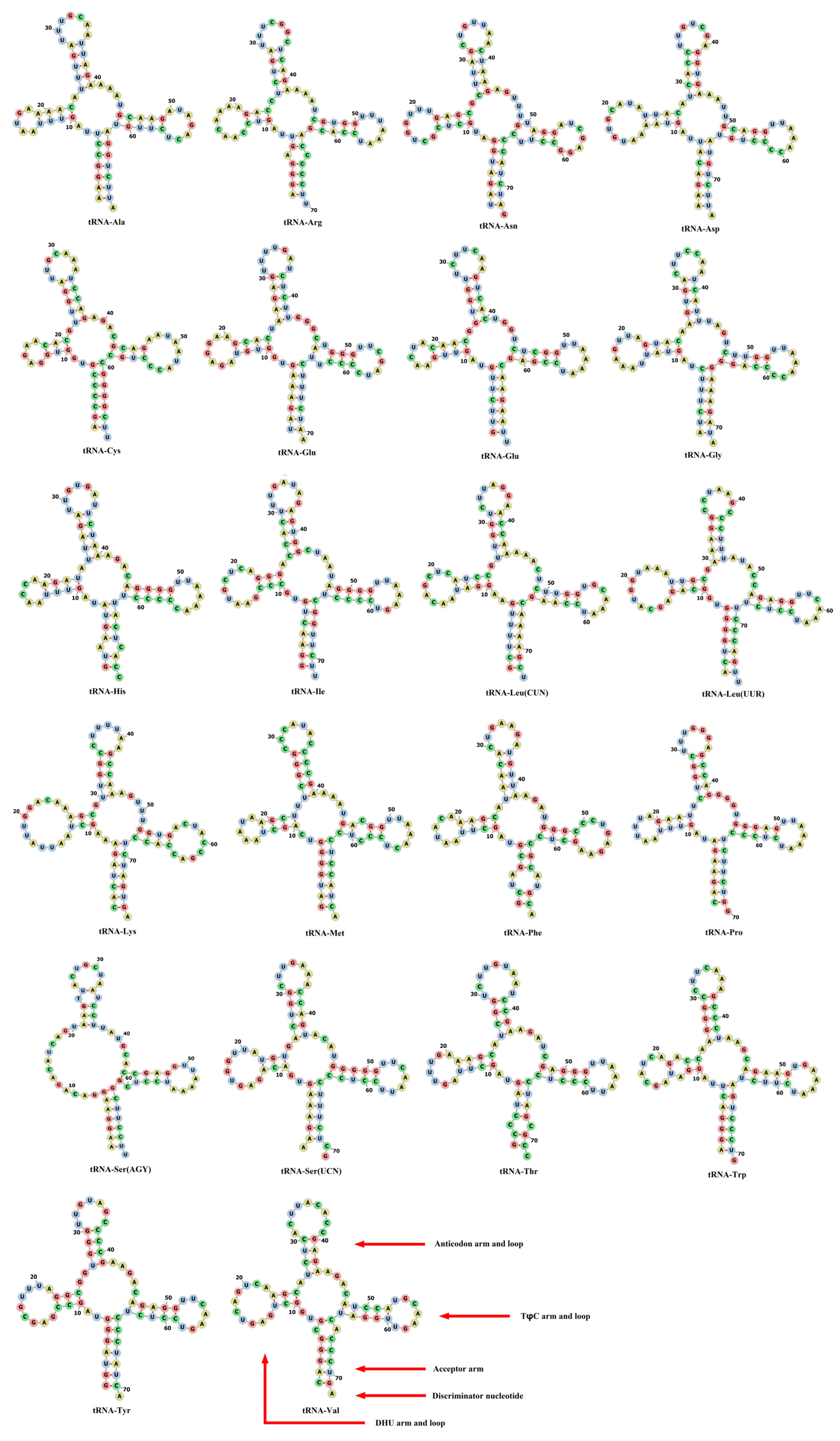
3.3. Characterization and Structural Prediction of tRNAs and rRNAs
3.4. Non-Coding Regions
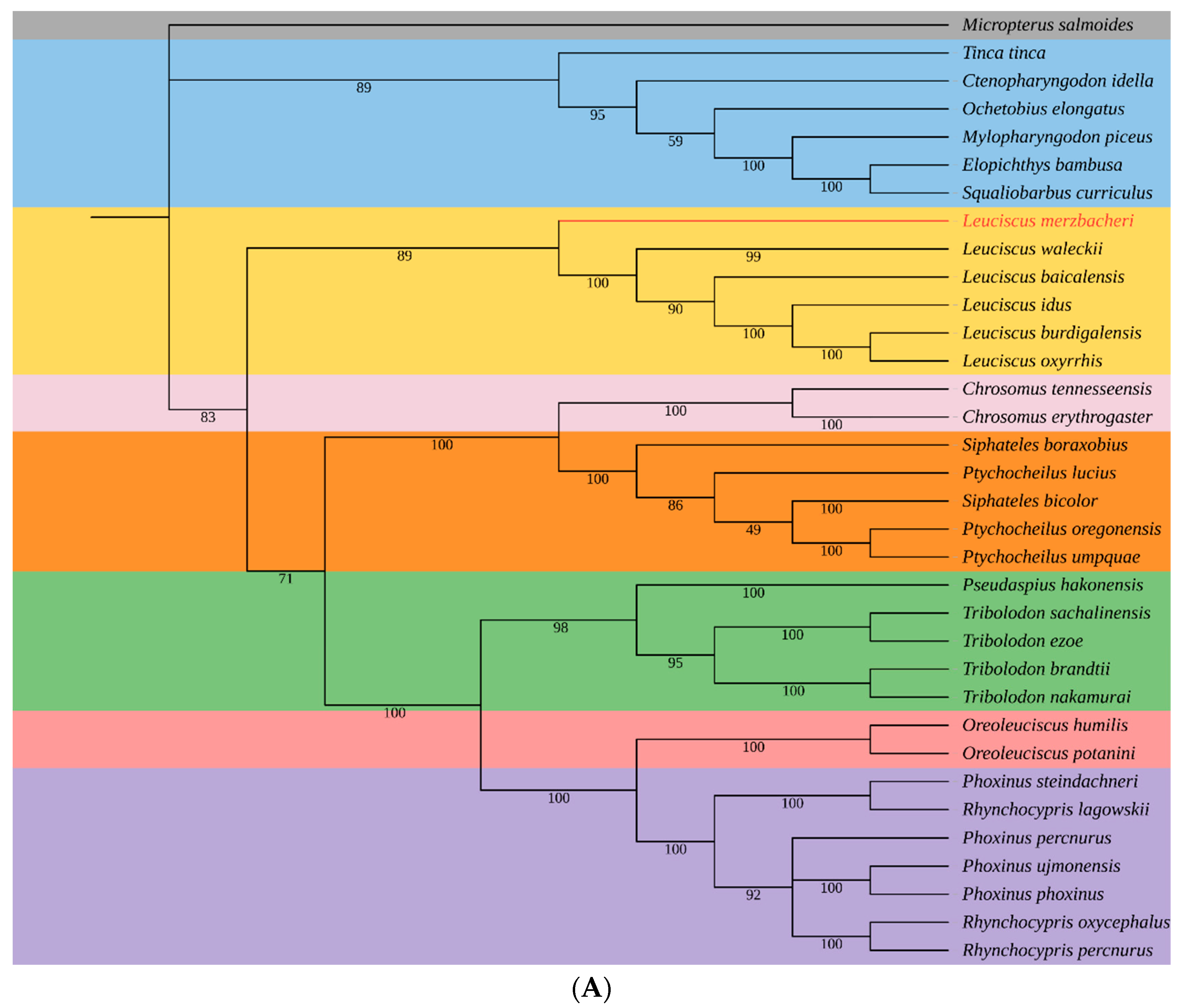
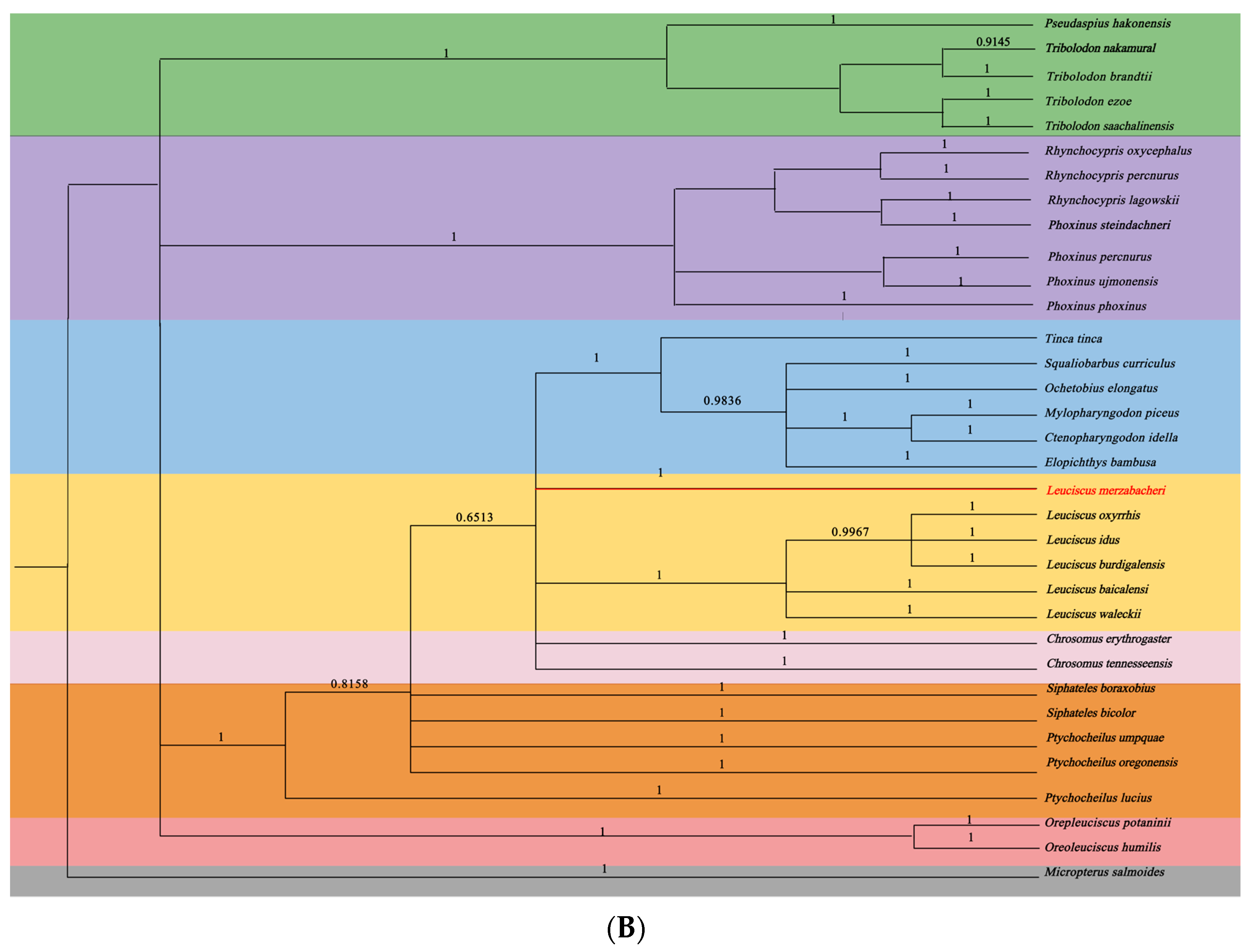
3.5. Phylogenetic Relationships of L. merzbacheri
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nelson, J.C.; Grande, T.C.; Wilson, M.V.H. Fishes of the World, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Y. Fauna Sinica, Osteichthyes, Cyprinformes II; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, R.M.; Cai, L.G. Fishes of Xinjiang; Xinjiang Science and Technology Press: Urumqi, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Z.C. Study on Genetic Diversity of Endangered Fish: Leueiscus merzbacheri (Zugmayer l912) and Introgression among the Three Leuciscus subspecies in Sailimu Lake of Xinjiang, China Using ISSR Markers. Master’s Thesis, Shihezi University, Shihezi, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, P.Q.; Chen, Y.U. China Red Data Book of Endangered Animals (Pisces); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Zhao, Y. Leuciscus merzbacheri. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2023. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/212785578/212785580 (accessed on 7 January 2024).
- Chen, X.Y. Studies on the skeleton of Leuciscine fishes of China, with particular reference to its significance in taxonomy. Acta Zootax. Sin. 1987, 12, 311–322. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Cai, L.G.; Zhang, R.M.; Tu, E.X.; Zhang, B.P. Preliminary study on the biological properties of Leuciscus merzbacheri Zugmayer in the Sayram Lake, Xinjiang. Arid Zone Res. 2005, 22, 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, T.B.; Ma, B.; Tang, F.J.; Jiang, Z.F.; Cai, L.G.; Adakbek, K.J.; Liu, L.Z. The growth models of three kind of leuciscusin from Xinjiang. China J. Fish. 2008, 21, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.N.; Li, S.Z.; Liu, C.L. Multivariate analysis on the morphological among three species of Leuciscus in Xinjiang. J. Fish Sci. China 2019, 26, 636–645. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Z. Studies on Zoogeographical Divisions for Fresh Water Fishes of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.B.; He, J.T.; Xie, C.G.; Cai, L.G.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Shi, C.M. Evaluate status of marked release of Leuciscus merzbacheri. Tianjin Agr. Sci. 2021, 27, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.B.; Hu, J.W.; Li, X.D.; Wang, X.; He, J.T.; Shi, C.M.; Wang, S.; Niu, J.G. Experimental starvation on Leuciscus merzbacheri larvae and determination of the point of no return. J. Fish Res. 2021, 43, 472–479. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.J.; Hu, W.G.; Kong, L. Karyotype and banding pattern of Leuciscus merzbacheri. China J. Zool. 2010, 45, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.P.; Dong, Y.Y.; Hu, W.G.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, D.W.; Wang, X. The specific expression of isozymes in Leuciscus merzbacheri tissues. China J. Zool. 2012, 47, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.G.; Duan, Z.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Sheng, J.L.; Ma, R.L. Divergence and systematical evolution of three Leuciscus species in Xinjiang based on mitochondrial DNA control region sequences. Acta Genet. Sin. 2004, 31, 970–975. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.G.; Duan, Z.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Sheng, J.L. Divergence and systematical evolution of three Leuciscus species in Xinjiang: Mitochondrial DNA cytochrome b sequences. China J. Zool. 2005, 40, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.G.; Ma, S.W.; Chen, C.F.; Wang, Y.Z.; Ren, Y.; Cao, X.D.; Sheng, J.L. Characterization of β-actin promoter of Leuciscus merzbacheri. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2012, 11, 3849–3854. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, W.; Li, L.; Yuan, X.Q.; Zhou, Y.D. The complete mitochondrial genome of Leuciscus merzbacheri (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2023, 8, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingenberg, M. The ADP, ATP shuttle of the mitochondrion. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1979, 4, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taanman, J.W. The mitochondrial genome: Structure, transcription, translation and replication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 1999, 1410, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkenberg, M.; Larsson, N.G.; Gustafsson, C.M. DNA replication and transcription in mammalian mitochondria. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 679–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadel, G.S.; Clayton, D.A. Mitochondrial DNA maintenance in vertebrates. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 66, 409–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avise, J.C.; Arnold, J.; Ball, R.M.; Bermingham, E.; Lamb, T.; Neigel, J.E.; Reeb, C.A.; Saunders, N.C. Intraspecific phylogeography: The mitochondrial DNA bridge between population genetics and systematics. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1987, 18, 489–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.R.; Stoneking, M.; Holland, M.M.; DiZinno, J.A.; Budowle, B. Guidelines for the use of mitochondrial DNA sequencing in forensic science. Crime Lab Digest. 1993, 20, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Unajak, S.; Meesawat, P.; Anyamaneeratch, K.; Anuwareepong, D.; Srikulnath, K.; Choowongkomon, K. Identification of species (meat and blood samples) using nested-PCR analysis of mitochondrial DNA. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 5670–5676. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, S.; Cai, L.G.; Meng, W.; Yang, T.Y.; Ma, X.F. Divergence time estimation of fishes in Leuciscinae in Xinjiang. China J. Fish. 2014, 27, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Z.; Liu, H.Z.; He, S.P.; Chen, Y.Y. Sequence analysis of cytochrome b gene indicates that East Asian group of cyprinid subfamily Leuciscinae (Teleostei: Cyprinidae) evolved independently. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2004, 14, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoto, J.M.; Saitoh, K.; Sasaki, T.; Yonezawa, T.; Adachi, J.; Kartavtsev, Y.P.; Miya, M.; Nishida, M.; Hanzawa, N. Phylogeny and biogeography of highly diverged freshwater fish species (Leuciscinae, Cyprinidae, Teleostei) inferred from mitochondrial genome analysis. Gene 2013, 514, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.S.A.; Aboim, M.A.; Ráb, P.; Collares-Pereira, M.J. Introgressive hybridization as a promoter of genome reshuffling in natural homoploid fish hybrids (Cyprinidae, Leuciscinae). Heredity 2014, 112, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D. Molecular Cloning—A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2001, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, C.; Bachmann, L.; Chevreux, B. Reconstructing mitochondrial genomes directly from genomic next-generation sequencing reads—A baiting and iterative mapping approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, M.; Drechsel, O.; Kahlau, S.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW—A suite of tools for generating physical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes and visualizing expression data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kück, P.; Longo, G.C. FASconCAT-G: Extensive functions for multiple sequence alignment preparations concerning phylogenetic studies. Front. Zool. 2014, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. Modeltest: Testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Mark, P.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; et al. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickson, R.E.; Simon, C.; Cooper, A.; Spicer, G.S.; Sullivan, J.; Penny, D. Conserved sequence motifs, alignment, and secondary structure for the third domain of animal 12S rRNA. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1996, 13, 150–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shioiri, C.; Takahata, N. Skew of mononucleotide frequencies, relative abundance of dinucleotides, and DNA strand asymmetry. J. Mol. Evol. 2001, 53, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, T.P.; Miya, M.; Mabuchi, K.; Nishida, M. Structure and variation of the mitochondrial genome of fishes. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA procession in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behura, S.K.; Severson, D.W. Codon usage bias: Causative factors, quantification methods and genome-wide patterns: With emphasis on insect genomes. Biol. Rev. 2012, 88, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, P.G.; Jameson, D.; Jow, H.; Rattray, M. The evolution of tRNA-Leu genes in animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 57, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M.; Takeshima, H.; Endo, H.; Ishiguro, N.B.; Inoue, J.G.; Mukai, T.; Satoh, T.P.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kawaguchi, A.; Mabuchi, K.; et al. Major patterns of higher teleostean phylogenies: A new perspective based on 100 complete mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozov, A.; Demeshkina, N.; Khusainov, I.; Westhof, E.; Yusupov, M.; Yusupova, G. Novel base-pairing interactions at the tRNA wobble position crucial for accurate reading of the genetic code. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, U.R.; Fitch, W.M. The biological significance of G-T/G-U mispairing in nucleic acid secondary structure. J. Theor. Biol. 1985, 117, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Shah, B.; Bondarenko, P.V. G/U and certain wobble position mismatches as possible main causes of amino acid misincorporations. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 8165–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumazawa, Y.; Nishida, M. Sequence evolution of mitochondrial tRNA genes and deep-branch animal phylogenetics. J. Mol. Evol. 1993, 37, 380–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, A. rRNA Structure; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Poulsen, J.Y.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H.; et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacek, N.; Mankin, A.S. The ribosomal peptidyl transferase center: Structure, function, evolution, inhibition. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 40, 285–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, S.; Böhme, M.; Zupančič, P.; Freyhof, J.; Šanda, R.; Özuluğ, M.; Abdoli, A.; Doadrio, I. Phylogenetic relationships and biogeographical patterns in Circum-Mediterranean subfamily Leuciscinae (Teleostei, Cyprinidae) inferred from both mitochondrial and nuclear data. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshabanan, A.; Yazdani-Moghaddam, F.; Ghassemzadeh, F.; Mousavi-Sabet, H.; Rossi, G.; Aliabadian, M. Morpho-species of the genus Leuciscus Cuvier, 1816 (Teleostei: Leuciscinae) from Iran revisited using molecular approaches. Zool. Middle East. 2021, 67, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradburd, G.; Ralph, P.; Coop, G. Disentangling the effects of geographic and ecological isolation on genetic differentiation. Evolution 2013, 67, 3258–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Li, Z.C.; Qin, X.G. Natural Environmental Evolution, Climate Change and Impact of Human Activities in Xinjiang Region; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]

| Genes | Strand | Initiation Site | Termination Site | Length | Spacer (+)/Overlap (−) | Initiation Codon | Termination Codon | Anti-Codon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tRNA-Phe | H | 1 | 69 | 69 | 0 | GAA | ||
| 12S rRNA | H | 70 | 1028 | 959 | 0 | |||
| tRNA-Val | H | 1029 | 1100 | 72 | 0 | UAC | ||
| 16S rRNA | H | 1101 | 2791 | 1691 | 0 | |||
| tRNA-Leu UUR | H | 2792 | 2867 | 76 | 0 | UAA | ||
| ND1 | H | 2868 | 3842 | 975 | −2 | ATG | TAG | |
| tRNA-Ile | H | 3847 | 3918 | 72 | 4 | GAU | ||
| tRNA-Gln | L | 3917 | 3987 | 71 | −2 | UUG | ||
| tRNA-Met | H | 3989 | 4057 | 69 | 1 | CAU | ||
| ND2 | H | 4058 | 5102 | 1045 | 0 | ATG | T | |
| tRNA-Trp | H | 5103 | 5173 | 71 | 0 | UCA | ||
| tRNA-Ala | L | 5175 | 5243 | 69 | 1 | UGC | ||
| tRNA-Asn | L | 5245 | 5317 | 73 | 1 | GUU | ||
| OL | H | 5318 | 5354 | 37 | 0 | |||
| tRNA-Cys | L | 5352 | 5418 | 67 | −3 | GCA | ||
| tRNA-Tyr | L | 5420 | 5490 | 71 | 1 | GUA | ||
| COI | H | 5492 | 7042 | 1551 | 1 | GTG | TAA | |
| tRNA-Ser UCN | L | 7043 | 7113 | 71 | 0 | UGA | ||
| tRNA-Asp | H | 7117 | 7190 | 74 | 3 | GUC | ||
| COII | H | 7204 | 7894 | 691 | 13 | ATG | T | |
| tRNA-Lys | H | 7895 | 7970 | 76 | 0 | UUU | ||
| ATP8 | H | 7972 | 8136 | 165 | 1 | ATG | TAG | |
| ATP6 | H | 8130 | 8812 | 683 | −7 | ATG | TA | |
| COIII | H | 8813 | 9596 | 784 | 0 | ATG | T | |
| tRNA-Gly | H | 9597 | 9668 | 72 | 0 | UCC | ||
| ND3 | H | 9669 | 10,017 | 349 | 0 | ATG | T | |
| tRNA-Arg | H | 10,018 | 10,087 | 70 | 0 | UCG | ||
| ND4L | H | 10,088 | 10,384 | 297 | 0 | ATG | TAA | |
| ND4 | H | 10,378 | 11,759 | 1382 | −7 | ATG | TA | |
| tRNA-His | H | 11,760 | 11,828 | 69 | 0 | GUG | ||
| tRNA-Ser AGY | H | 11,829 | 11,897 | 69 | 0 | GCU | ||
| tRNA-Leu CUN | H | 11,899 | 11,971 | 73 | 1 | UAG | ||
| ND5 | H | 11,972 | 13,807 | 1836 | 0 | ATG | TAG | |
| ND6 | L | 13,804 | 14,325 | 522 | −4 | ATG | TAA | |
| tRNA-Glu | L | 14,326 | 14,394 | 69 | 0 | UUC | ||
| Cyt b | H | 14,399 | 15,539 | 1141 | 4 | ATG | T | |
| tRNA-Thr | H | 15,540 | 15,611 | 72 | 0 | UGU | ||
| tRNA-Pro | L | 15,611 | 15,680 | 70 | −1 | UGG | ||
| D-loop | H | 15,681 | 16,609 | 929 | 0 |
| Codon | Count | RSCU | Codon | Count | RSCU | Codon | Count | RSCU | Codon | Count | RSCU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UUU(F) | 95 | 0.84 | UCU(S) | 48 | 1.20 | UAU(Y) | 55 | 0.97 | UGU(C) | 14 | 1.08 |
| UUC(F) | 132 | 1.16 | UCC(S) | 59 | 1.47 | UAC(Y) | 58 | 1.03 | UGC(C) | 12 | 0.92 |
| UUA(L) | 103 | 0.99 | UCA(S) | 64 | 1.59 | UAA(*) | 0 | 0.00 | UGA(W) | 85 | 1.43 |
| UUG(L) | 45 | 0.43 | UCG(S) | 13 | 0.32 | UAG(*) | 0 | 0.00 | UGG(W) | 34 | 0.57 |
| CUU(L) | 118 | 1.13 | CCU(P) | 33 | 0.62 | CAU(H) | 27 | 0.52 | CGU(R) | 7 | 0.37 |
| CUC(L) | 107 | 1.03 | CCC(P) | 77 | 1.44 | CAC(H) | 76 | 1.48 | CGC(R) | 15 | 0.79 |
| CUA(L) | 191 | 1.84 | CCA(P) | 82 | 1.53 | CAA(Q) | 68 | 1.39 | CGA(R) | 36 | 1.89 |
| CUG(L) | 60 | 0.58 | CCG(P) | 22 | 0.41 | CAG(Q) | 30 | 0.61 | CGG(R) | 18 | 0.95 |
| AUU(I) | 161 | 1.22 | ACU(T) | 52 | 0.70 | AAU(N) | 45 | 0.79 | AGU(S) | 17 | 0.42 |
| AUC(I) | 102 | 0.78 | ACC(T) | 106 | 1.42 | AAC(N) | 69 | 1.21 | AGC(S) | 40 | 1.00 |
| AUA(M) | 88 | 1.02 | ACA(T) | 105 | 1.41 | AAA(K) | 48 | 1.23 | AGA(*) | 0 | 0.00 |
| AUG(M) | 85 | 0.98 | ACG(T) | 35 | 0.47 | AAG(K) | 30 | 0.77 | AGG(*) | 0 | 0.00 |
| GUU(V) | 59 | 0.90 | GCU(A) | 56 | 0.66 | GAU(D) | 32 | 0.82 | GGU(G) | 34 | 0.55 |
| GUC(V) | 63 | 0.96 | GCC(A) | 149 | 1.75 | GAC(D) | 46 | 1.18 | GGC(G) | 66 | 1.06 |
| GUA(V) | 98 | 1.49 | GCA(A) | 103 | 1.21 | GAA(E) | 63 | 1.24 | GGA(G) | 84 | 1.35 |
| GUG(V) | 43 | 0.65 | GCG(A) | 32 | 0.38 | GAG(E) | 39 | 0.76 | GGG(G) | 64 | 1.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Yang, T. Unraveling the Mitogenomic Characteristics and Phylogenetic Implications of Leuciscus merzbacheri (Zugmayer, 1912), an Endangered Fish in the Junggar Basin of Xinjiang, Northwest China. Genes 2024, 15, 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101284
Sun Y, Yang T. Unraveling the Mitogenomic Characteristics and Phylogenetic Implications of Leuciscus merzbacheri (Zugmayer, 1912), an Endangered Fish in the Junggar Basin of Xinjiang, Northwest China. Genes. 2024; 15(10):1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101284
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yan, and Tianyan Yang. 2024. "Unraveling the Mitogenomic Characteristics and Phylogenetic Implications of Leuciscus merzbacheri (Zugmayer, 1912), an Endangered Fish in the Junggar Basin of Xinjiang, Northwest China" Genes 15, no. 10: 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101284
APA StyleSun, Y., & Yang, T. (2024). Unraveling the Mitogenomic Characteristics and Phylogenetic Implications of Leuciscus merzbacheri (Zugmayer, 1912), an Endangered Fish in the Junggar Basin of Xinjiang, Northwest China. Genes, 15(10), 1284. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15101284






