Isolation and Genetic Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from a Patas Monkey (Erythrocebus patas) in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Clinical Case Report
2.2. T. gondii Antibody and T. gondii DNA Were Detected in Monkey Tissues
2.3. Histopathological Analysis
2.4. Isolation of Viable T. gondii from Monkey Tissues Using Mice Bioassay
2.5. In Vitro Cultivation and Genotyping
2.6. Evaluation of the Virulence of the T. gondii Strain Isolated from Monkeys
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
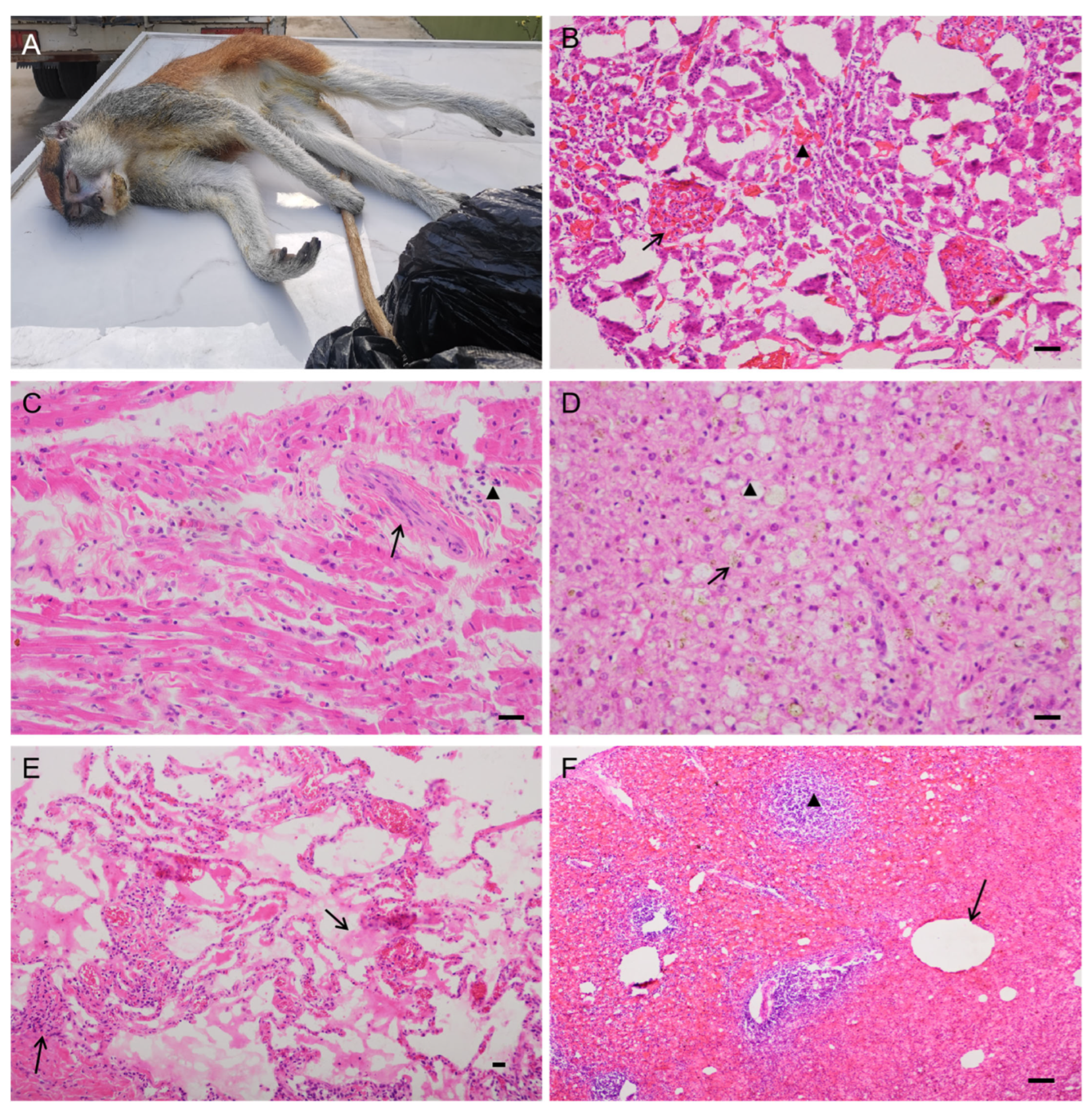
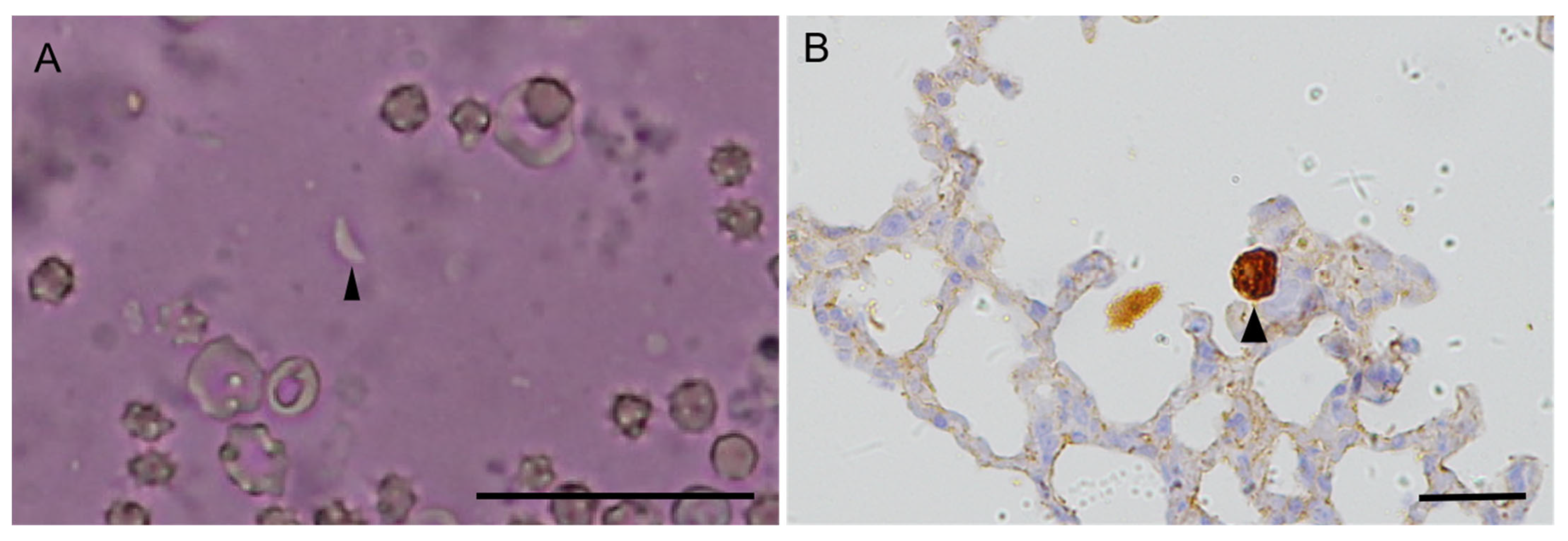
3.1. Clinical Signs, Pathological Evaluation, and Immunohistochemistry
3.2. T. gondii Examination by MAT and PCR
3.3. Viable T. gondii Was Isolated from Monkey Tissue Samples Using Mouse Bioassays and Genetic Characterization
3.4. Virulence Evaluation of TgMonkeyCHn2 by Mice
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 1–313. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 1–542. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, W.; Venturini, M.C.; Moré, G.; Quiroga, A.; Bacigalupe, D.; Unzaga, J.M.; Larsen, A.; Laplace, R.; Venturini, L. Toxoplasmosis in captive Bennett’s wallabies (Macropus rufogriseus) in Argentina. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 144, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermúdez, R.; Faílde, L.D.; Losada, A.P.; Nieto, J.M.; Quiroga, M.I. Toxoplasmosis in Bennett’s wallabies (Macropus rufogriseus) in Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 160, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouer, A.; Werther, K.; Catão-Dias, J.L.; Nunes, A.L. Outbreak of toxoplasmosis in Lagothrix lagotricha. Folia Primatol. 1999, 70, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Kramer, L.W.; Weisbrode, S.E. Acute death associated with Toxoplasma gondii in ring-tailed lemurs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1985, 187, 1272–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Epiphanio, S.; Guimarães, M.A.; Fedullo, D.L.; Correa, S.H.; Catão-Dias, J.L. Toxoplasmosis in golden-headed lion tamarins (Leontopithecus chrysomelas) and emperor marmosets (Saguinus imperator) in captivity. J. Zoo Wildl. 2000, 31, 231–235. [Google Scholar]
- Dietz, H.H.; Henriksen, P.; Bille-Hansen, V.; Henriksen, S.A. Toxoplasmosis in a colony of New World monkeys. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 68, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carme, B.; Ajzenberg, D.; Demar, M.; Simon, S.; Dardé, M.L.; Maubert, B.; de Thoisy, B. Outbreaks of toxoplasmosis in a captive breeding colony of squirrel monkeys. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 163, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Eo, K.Y.; Gumber, S.; Hong, J.J.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, H.H.; Jung, Y.M.; Kim, J.; Whang, G.W.; Lee, J.M.; et al. An outbreak of toxoplasmosis in squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus) in South Korea. J. Med. Primatol. 2018, 47, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Yang, Y.; Su, C. Recent epidemiologic, clinical, and genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii infections in non-human primates. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 136, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Li, G.F.; Zhi, G.L.; Zhao, C.Y.; Liu, K.X.; Zuo, K.J.; Lan, H.; Chen, X.J.; Yuan, Z.G. Isolation and identification of Toxoplasma gondii from black-crown squirrel monkey (Saimiri vanzolinii) of South China. Chin. Vet. Sci. 2018, 48, 316–322. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Reis Amendoeira, M.R.; Arruda, I.F.; Moreira, S.B.; Ubiali, D.G.; da Silva Barbosa, A.; Jesus Pena, H.F.; Barbosa Pereira, A.H.; Nascimento da Silveira, C.; Bonifácio, T.F.; Clemes, Y.S.; et al. Isolation and genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from a captive black-and-gold howler monkey (Alouatta caraya Humboldt, 1812) in Brazil. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 19, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, K.X.; Xu, C.Z.; Shan, F.; Chen, W.; Peng, S.M.; Li, W.P.; Li, G.Q. Multi-locus genotyping of the Toxoplasma gondii isolated from captive ring-tailed lemur (Lemur catta) in China. Chin. J. Wildl. 2017, 38, 187–193. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Desmonts, G. Serological responses of equids fed Toxoplasma gondii oocysts. Equine Vet. J. 1987, 19, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schares, G.; Herrmann, D.C.; Beckert, A.; Schares, S.; Hosseininejad, M.; Pantchev, N.; Vrhovec, M.G.; Conraths, F.J. Characterization of a repetitive DNA fragment in Hammondia hammondi and its utility for the specific differentiation of H. hammondi from Toxoplasma gondii by PCR. Mol. Cell. Probes 2008, 22, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.; Dong, H.; Li, T.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Su, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y. Toxoplasma gondii in four captive kangaroos (Macropus spp.) in China: Isolation of a strain of a new genotype from an eastern grey kangaroo (Macropus giganteus). Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 8, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.M.; Raine, L.; Fanger, H. Use of avidin–biotin–peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: A comparison between ABC and unlabelled antibody (PAP) procedures. J. Histochem. Cytochemi. 1981, 29, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Ferreira, L.R.; Martins, J.; McLeod, R. Oral oocyst-induced mouse model of toxoplasmosis: Effect of infection with Toxoplasma gondii strains of different genotypes, dose, and mouse strains (transgenic, out-bred, in-bred) on pathogenesis and mortality. Parasitology 2012, 139, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, T.C.; Bienz, K.A.; Erb, P. In vitro cultivation of Toxoplasma gondii cysts in astrocytes in the presence of gamma interferon. Infect. Immun. 1986, 51, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, Q.; Ochiai, E.; Tiwari, A.; Perkins, S.; Mullins, J.; Gehman, M.; Huckle, W.; Eyestone, W.H.; Saunders, T.L.; Shelton, B.J.; et al. Cutting edge: IFN-γ produced by brain-resident cells is crucial to control cerebral infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, A.; Mun, H.S.; Chin, M.; Norose, K.; Hata, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Aosai, F.; Iwakura, Y. Roles of IFN-gamma on stage conversion of an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite, Toxoplasma gondii. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 21, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Shwab, E.K.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Dubey, J.P. Moving towards an integrated approach to molecular detection and identification of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology 2010, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwab, E.K.; Jiang, T.; Pena, H.F.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. The ROP18 and ROP5 gene allele types are highly predictive of virulence in mice across globally distributed strains of Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwab, E.K.; Jiang, T.; Pena, H.F.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. Corrigendum to "The ROP18 and ROP5 gene allele types are highly predictive of virulence in mice across globally distributed strains of Toxoplasma gondii" (Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 141–146). Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rêgo, W.; Costa, J.; Baraviera, R.; Pinto, L.V.; Bessa, G.L.; Lopes, R.; Vitor, R. Association of ROP18 and ROP5 was efficient as a marker of virulence in atypical isolates of Toxoplasma gondii obtained from pigs and goats in Piauí, Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 247, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, P.; Shwab, E.K.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. On the determination of Toxoplasma gondii virulence in mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2017, 174, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedillo-Peláez, C.; Rico-Torres, C.P.; Salas-Garrido, C.G.; Correa, D. Acute toxoplasmosis in squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus) in Mexico. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 180, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Hodgin, E.C.; Hamir, A.N. Acute fatal toxoplasmosis in squirrels (Sciurus carolensis) with bradyzoites in visceral tissues. J. Parasitol. 2006, 92, 658–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, N.F.; Dutra, K.S.; Oliveira, A.R.; Santos, D.O.D.; Rocha, C.E.V.; Vitor, R.W.A.; Tinoco, H.P.; Costa, M.E.L.T.D.; Paixão, T.A.D.; Santos, R.L. Host range and susceptibility to Toxoplasma gondii infection in captive neotropical and Old-world primates. J. Med. Primatol. 2020, 49, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salant, H.; Weingram, T.; Spira, D.T.; Eizenberg, T. An outbreak of toxoplasmosis amongst squirrel monkeys in an Israeli monkey colony. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 159, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.A.; Joiner, K.S.; Hilton, C.D.; Dubey, J.P.; Toivio-Kinnucan, M.; Minc, J.K.; Blagburn, B.L. Disseminated toxoplasmosis in a captive ring-tailed lemur (Lemur catta). J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 904–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, S.B.; Pereira, A.H.B.; Pissinatti, T.A.; Arruda, I.F.; de Azevedo, R.R.M.; Schiffler, F.B.; Workgroup Outbreak; Amendoeira, M.R.R.; Dos Santos, A.F.A.; Pissinatti, A.; et al. Subacute multisystemic toxoplasmosis in a captive black-and-gold howler monkey (Alouatta caraya) indicates therapy challenging. J. Med. Primatol. 2022, 51, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Thulliez, P.; Weigel, R.M.; Andrews, C.D.; Lind, P.; Powell, E.C. Sensitivity and specificity of various serologic tests for detection of Toxoplasma gondii infection in naturally infected sows. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 56, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Sundar, N.; Hill, D.; Velmurugan, G.V.; Bandini, L.A.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Majumdar, D.; Su, C. High prevalence and abundant atypical genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from lambs destined for human consumption in the USA. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Laurin, E.; Kwowk, O.C. Validation of the modified agglutination test for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii in free range chickens by using cat and mouse bioassay. Parasitology 2016, 143, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Jiang, N.; Yang, L.; Zhu, N.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Su, C.; Yang, Y. Isolation, genotyping and virulence determination of a Toxoplasma gondii strain from non-human primate from China. Transboundary Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Esquivel, C.; Gayosso-Dominguez, E.A.; Villena, I.; Dubey, J.P. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in captive mammals in three zoos in Mexico City, Mexico. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2013, 44, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Terriza, D.; Almería, S.; Caballero-G´omez, J.; Díaz-Cao, J.M.; Jim´enez-Ruiz, S.; Dubey, J.P.; García-Bocanegra, I. Serological survey of Toxoplasma gondii in captive nonhuman primates in zoos in Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 65, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.F.; Tang, Y.; Wang, S.K.; Chen, X.L.; Hu, L.Y.; Chen, M.Z.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.Q. Serological investigation of chlamydia and Toxoplasma gondii infection in wild animals from Fuzhou Zoo. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2015, 47, 77–80. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Marujo, R.B.; Langoni, H.; Ullmann, L.S.; Pellizzaro, M.; Neto, R.N.D.; Camossi, L.G.; Teixeira, R.F.; Nunes, A.V.; da Silva, R.C.; Menozzi, B.D. Toxoplasma gondii antibodies and related risk factors in mammals at Sorocaba zoo, Sao Paulo, Brazil. Semin. Cienc. Agrar. 2017, 38, 2845–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Esquivel, C.; Rajendran, C.; Ferreira, L.R.; Kwok, O.C.; Choudhary, S.; Alvarado-Esquivel, D.; Rodríguez-Peña, S.; Villena, I.; Dubey, J.P. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in wild birds in Durango, Mexico. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Velmurugan, G.V.; Alvarado-Esquivel, C.; Alvarado-Esquivel, D.; Rodríguez-Peña, S.; Martínez-García, S.; González-Herrera, A.; Ferreira, L.R.; Kwok, O.C.; Su, C. Isolation of Toxoplasma gondii from animals in Durango, Mexico. J. Parasitol. 2009, 95, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichan, P.; Mercier, A.; Galal, L.; Mahittikorn, A.; Ariey, F.; Morand, S.; Boumediene, F.; Udonsom, R.; Hamidovic, A.; Murat, J.B.; et al. Geographical distribution of Toxoplasma gondii genotypes in Asia: A link with neighboring continents. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 53, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Cortés-Vecino, J.A.; Vargas-Duarte, J.J.; Sundar, N.; Velmurugan, G.V.; Bandini, L.M.; Polo, L.J.; Zambrano, L.; Mora, L.E.; Kwok, O.C.; et al. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in dogs from Colombia, South America and genetic characterization of T. gondii isolates. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 145, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Huong, L.T.; Sundar, N.; Su, C. Genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii isolates in dogs from Vietnam suggests their South American origin. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 146, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Rajapakse, R.P.V.J.; Wijesundera, R.R.M.K.K.; Sundar, N.; Velmurugan, G.V.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Su, C. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in dogs from Sri Lanka and genetic characterization of the parasite isolates. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 146, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olinda, R.G.; Pena, H.F.; Frade, M.T.; Ferreira, J.S.; Maia, L.Â.; Gennari, S.M.; Oliveira, S.; Dantas, A.F.; Riet-Correa, F. Acute toxoplasmosis in pigs in Brazil caused by Toxoplasma gondii genotype Chinese 1. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2561–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shwab, E.K.; Zhu, X.Q.; Majumdar, D.; Pena, H.F.J.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. Geographical patterns of Toxoplasma gondii genetic diversity revealed by multilocus PCR-RFLP genotyping. Parasitology 2014, 141, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.R.; Feng, Y.J.; Lu, Y.Y.; Dong, H.; Li, T.Y.; Jiang, Y.B.; Zhu, X.Q.; Zhang, L.X. Antibody detection, isolation, genotyping, and virulence of Toxoplasma gondii in captive felids from China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zhang, H.; Lin, R.Q.; Zhang, D.L.; Song, H.Q.; Su, C.; Zhu, X.Q. Genetic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from China. Parasitol. Int. 2009, 58, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.L.; Zheng, H.; He, S.; Lin, R.Q.; Zhu, X.Q. Toxoplasma gondii infection in humans in China. Parasit. Vectors 2011, 4, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dong, H.; Su, R.; Jiang, N.; Li, T.; Su, C.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, L. Direct evidence of an extra-intestinal cycle of Toxoplasma gondii in tigers (Panthera tigris) by isolation of viable strains. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Sundar, N.; Zhang, H.; Kwok, O.C.; Su, C. Genetic and biologic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii isolates of cats from China. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 145, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, G.; Yuan, G.; He, J.; Su, C.; Yang, N. Seroprevalence and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from pigs intended for human consumption in Liaoning province, northeastern China. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L. Seroprevalence, isolation, genotyping, and pathogenicity of Toxoplasma gondii strains from sheep in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwab, E.K.; Saraf, P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Zhou, D.H.; McFerrin, B.M.; Ajzenberg, D.; Schares, G.; Hammond-Aryee, K.; van Helden, P.; Higgins, S.A.; et al. Human impact on the diversity and virulence of the ubiquitous zoonotic parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6956–E6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan-Sallés, C.; Mainez, M.; Marco, A.; Sanchís, A.M. Localized toxoplasmosis in a ring-tailed lemur (Lemur catta) causing placentitis, stillbirths, and disseminated fetal infection. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2011, 23, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ying, Y.; Verma, S.K.; Cassinelli, A.B.; Kwok, O.C.; Liang, H.; Pradhan, A.K.; Zhu, X.Q.; Su, C.; Dubey, J.P. Isolation and genetic characterization of viable Toxoplasma gondii from tissues and feces of cats from the central region of China. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 211, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Su, R.; Li, T.; Su, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y. Isolation, genotyping and pathogenicity of a Toxoplasma gondii strain isolated from a Serval (Leptailurus serval) in China. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Xin, S.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y. Isolation and characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from captive caracals (Caracal caracal). Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2020, 13, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Xin, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y. Low prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in sheep and isolation of a viable strain from edible mutton from central China. Pathogens 2023, 12, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W.; Gao, J.M.; Huo, X.X.; Wang, L.; Yu, L.; Halm-Lai, F.; Xu, Y.H.; Song, W.J.; Hide, G.; Shen, J.L.; et al. Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from cats in different geographic regions of China. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 183, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, D.; Su, S.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, J.; Tao, J. Genotyping and virulence analysis of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from a dead human fetus and dead pigs in Jiangsu province, Eastern China. Acta Parasitol. 2018, 63, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Su, R.; Jian, F.; Su, C.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y. Toxoplasma gondii in lambs of China: Heart juice serology, isolation and genotyping. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 322, 108563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Nie, X.; Peng, Q.Y.; Mu, X.Q.; Zhang, M.; Tian, M.Y.; Min, S.J. Seroprevalence and genotype of Toxoplasma gondii in pigs, dogs and cats from Guizhou province, Southwest China. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Meng, Y.; Zou, F.; Hu, J.; Esch, G.W. Occurrence and genetic characterization of GRA6 and SAG2 from Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in cat feces, Kunming, China. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2016, 47, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Wang, H.; Su, C.; Shan, D.; Cui, X.; Yang, N.; Lv, C.; Liu, Q. Isolation and characterization of Toxoplasma gondii strains from stray cats revealed a single genotype in Beijing, China. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 187, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Yang, L.; Zhu, N.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y. Additional evidence of tigers (Panthera tigris altaica) as intermediate hosts for Toxoplasma gondii through the isolation of viable strains. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2022, 19, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Huo, X.; Gao, J.; Song, X.; Xu, X.; Huang, K.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Genotypes and mouse virulence of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from animals and humans in China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, H.W.; Huang, K.Q.; Xu, Y.H.; Li, Y.N.; Du, J.; Yu, L.; Luo, Q.L.; Wei, W.; Jiang, L.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii prevalence in food animals and rodents in different regions of China: Isolation, genotyping and mouse pathogenicity. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Xin, S.; Zhu, N.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Yang, Y. Two viable Toxoplasma gondii isolates from red-necked wallaby (Macropus rufogriseus) and red kangaroo (M. rufus). Parasitol. Int. 2023, 92, 102687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ren, H.; Zhu, N.; Mao, G.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y. Epidemiology and isolation of viable Toxoplasma gondii strain from macropods. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Dong, H.; Su, R.; Li, T.; Jiang, N.; Su, C.; Zhang, L. Evidence of red panda as an intermediate host of Toxoplasma gondii and Sarcocystis species. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 8, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Xin, S.; Zhang, L. Toxoplasma gondii infection in white spoonbills (Platalea leucorodia) from Henan Province, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2619–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, J.; Gong, H.; Zhou, J. Isolation and genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii from domestic rabbits in China to reveal the prevalence of type III strains. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 193, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, J.S.; Ma, Y.W.; Lu, S. Toxoplasma gondii isolated from a dead deformed fetus. Chin. J. Zoonoses 1987, 3, 26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
| Case No. | Received Date | Species | Sex, Age | Pathology No. | Clinical Signs | Pathological Findings | T. gondii | Mice Bioassay | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAT a | PCR b | Swiss | IFN-γ−/− | |||||||
| New World Monkeys | ||||||||||
| Case#16 | 27 February 2020 | Red howler monkey (Alouatta seniculus) | F, adult | 3022 | Asymptomatic | Age-related atrophy, fatty degeneration of the liver, lipofuscin deposition in multiple organs. | 1:64 | H, Sk, P, I c | 0/5 e | nd |
| Case#17 | 15 April 2020 | Red howler monkey (Alouatta seniculus) | F, adult | 3024 | Weight loss, lost two teeth | Renal insufficiency, necrotic splenitis, hypoproteinemia. | <1:2 | Sp | nd | nd |
| Case#18 | 9 Novemebr 2020 | Squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus) | M, adult | 3080 | Malaise, poor appetite, emaciation. Foamy nasal and oral discharge, died 2 days after onset of symptoms | Necrotic glomerulonephritis, necrotic enteritis, pulmonary congestion, interstitial pneumonia. | <1:2 | - d | 0/4 | 0/1 |
| Case#19 | 13 March 2021 | Red howler monkey (Alouatta seniculus) | F, adult | 3130 | Malaise, poor appetite, emaciation | Suppurative pneumonia, glomerulonephritis, hypoproteinemia. | <1:2 | Sp, Lu, T, Ly | nd | nd |
| Case#20 | 31 July 2021 | White-faced saki monkey (Pithecia pithecia) | M, adult | 3203 | Malaise, poor appetite, emaciation | Cardiac insufficiency, hydropericardium, hydrothorax, ascites, glomerulonephritis, skeletal muscle atrophy. | <1:2 | - | nd | nd |
| Old World Monkeys | ||||||||||
| Case#21 | 25 December 2020 | Patas monkey (Erythrocebus patas) | M, adult | 3108 | Tail gangrene | Multiple organ gas gangrene, renal insufficiency, cardiac insufficiency, lipofuscin deposition in the liver, interstitial pneumonia. | 1:3200 | Sp, Lu, K, Ly | 2/2 | 2/2 |
| Case#22 | 9 January 2020 | Hamadryas baboon (Papio hamadryas) | F, adult | 3112 | One week after the delivery of the fetus | Necrotizing metritis, necrotizing myocarditis. | 1:64 | - | nd | 0/2 |
| Case#23 | 17 February 2021 | Hamadryas baboon (Papio hamadryas) | M, 24 years | 3121 | Leader, asymptomatic | Parenchymatous myocarditis, renal insufficiency, fatty degeneration of the liver. | <1:2 | - | 0/3 | nd |
| Case#24 | 15 April 2021 | Mona monkey (Cercopithecus mona) | F, adult | 3148 | Emaciation | Renal insufficiency, skeletal muscle atrophy. | 1:8 | Sp | 0/5 | nd |
| Case#25 | 15 April 2021 | Mona monkey (Cercopithecus mona) | F, adult | 3149 | Emaciation | Renal insufficiency, skeletal muscle atrophy, necrotizing hepatitis. | 1:4 | K, T, Ly | 0/3 | nd |
| Case#26 | 4 August 2021 | White-cheeked Gibbon (Nomascus leucogenys) | M, adult | 3205 | Malaise, poor appetite, depression, fever, four limbs, neck and abdomen edema; died 35 days after treatment | Cachexia, age-related atrophy, necrotic enteritis, renal insufficiency, and acute hemorrhagic lymphadenitis. | <1:2 | H, Sp, K, T, Ly, Sk, D | 0/2 | nd |
| Case#27 | 10 August 2021 | Black-and-white colobus (Colobus polykomos) | M, adult | 3208 | Emaciation | Necrotic myocarditis, multiple organ atrophy. | <1:2 | T, P | nd | nd |
| Lemuriformes | ||||||||||
| Case#28 | 22 September 2021 | Ring-tailed lemur (Lemur catta) | F, adult | 3218 | White fluid comes out of the vulva | Suppurative hemorrhagic cystitis, urethral calculus. | <1:2 | - | 0/3 | nd |
| Isolated ID | SAG1 | (3′ + 5′) SAG2 | Alt SAG2 | SAG3 | BTUB | GRA6 | C22-8 | C29-2 | L358 | PK1 | Apico | ROP18 | ROP5 | ToxoDB Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT1, reference | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | 1 | 1 | #10 |
| PTG, reference | II/III | II | II | II | II | II | II | II | II | II | II | 2 | 2 | #1 |
| CTG, reference | II/III | III | III | III | III | III | III | III | III | III | III | 3 | 3 | #2 |
| TgCgCa1, reference | I | II | II | III | II | II | II | u-1 | I | u-2 | I | 2 | 5 | #66 |
| MAS, reference | u-1 | I | II | III | III | III | u-1 | I | I | III | I | 4 | 4 | #17 |
| TgCatBr5, reference | I | III | III | III | III | III | I | I | I | u-1 | I | 4 | 4 | #19 |
| TgCatBr64, reference | I | I | u-1 | III | III | III | u-1 | I | III | III | I | 3 | 3 | #111 |
| TgRsCr1, reference | u-1 | I | II | III | I | III | u-2 | I | I | III | I | 3 | 3 | #52 |
| TgMonkeyCHn2 | u-1 | II | II | III | III | II | II | III | II | II | II | 3 | 6 | #9, this study |
| No. of Tachyzoites | No. of Mice Infection/ No. of Mice Inoculation (%) | Days of Survival/Number of Mice | No. of Brain Cysts |
|---|---|---|---|
| 103 | 4/4 (100%) | ≥60 dpi/2, 46 dpi/1, 54 dpi/1 | 2.5 ± 2.5 |
| 102 | 2/4 (50%) | ≥60 dpi/4 | Not found |
| 101 | 2/4 (50%) | ≥60 dpi/4 | 35.0 ± 25.0 |
| 1 | 2/4 (50%) | ≥60 dpi/4 | Not found |
| <1 | 0/4 (-) | ≥60 dpi/4 | Not found |
| Blank control | 0 | ≥60 dpi/4 | Not found |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Ren, H.; Zhu, N.; Xin, S.; Mao, G.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, Q.; Yang, Y. Isolation and Genetic Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from a Patas Monkey (Erythrocebus patas) in China. Genes 2023, 14, 1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081606
Yang L, Ren H, Zhu N, Xin S, Mao G, Ma Y, Li J, Liang Q, Yang Y. Isolation and Genetic Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from a Patas Monkey (Erythrocebus patas) in China. Genes. 2023; 14(8):1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081606
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Liulu, Hongjie Ren, Niuping Zhu, Shilin Xin, Gaohui Mao, Yiheng Ma, Junbao Li, Qunchao Liang, and Yurong Yang. 2023. "Isolation and Genetic Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from a Patas Monkey (Erythrocebus patas) in China" Genes 14, no. 8: 1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081606
APA StyleYang, L., Ren, H., Zhu, N., Xin, S., Mao, G., Ma, Y., Li, J., Liang, Q., & Yang, Y. (2023). Isolation and Genetic Characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from a Patas Monkey (Erythrocebus patas) in China. Genes, 14(8), 1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081606






