Hypercholesterolemia in the Malaysian Cohort Participants: Genetic and Non-Genetic Risk Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, Data Collection, and Study Design
2.2. DNA Isolation and WES
2.3. Bioinformatics Data Analysis
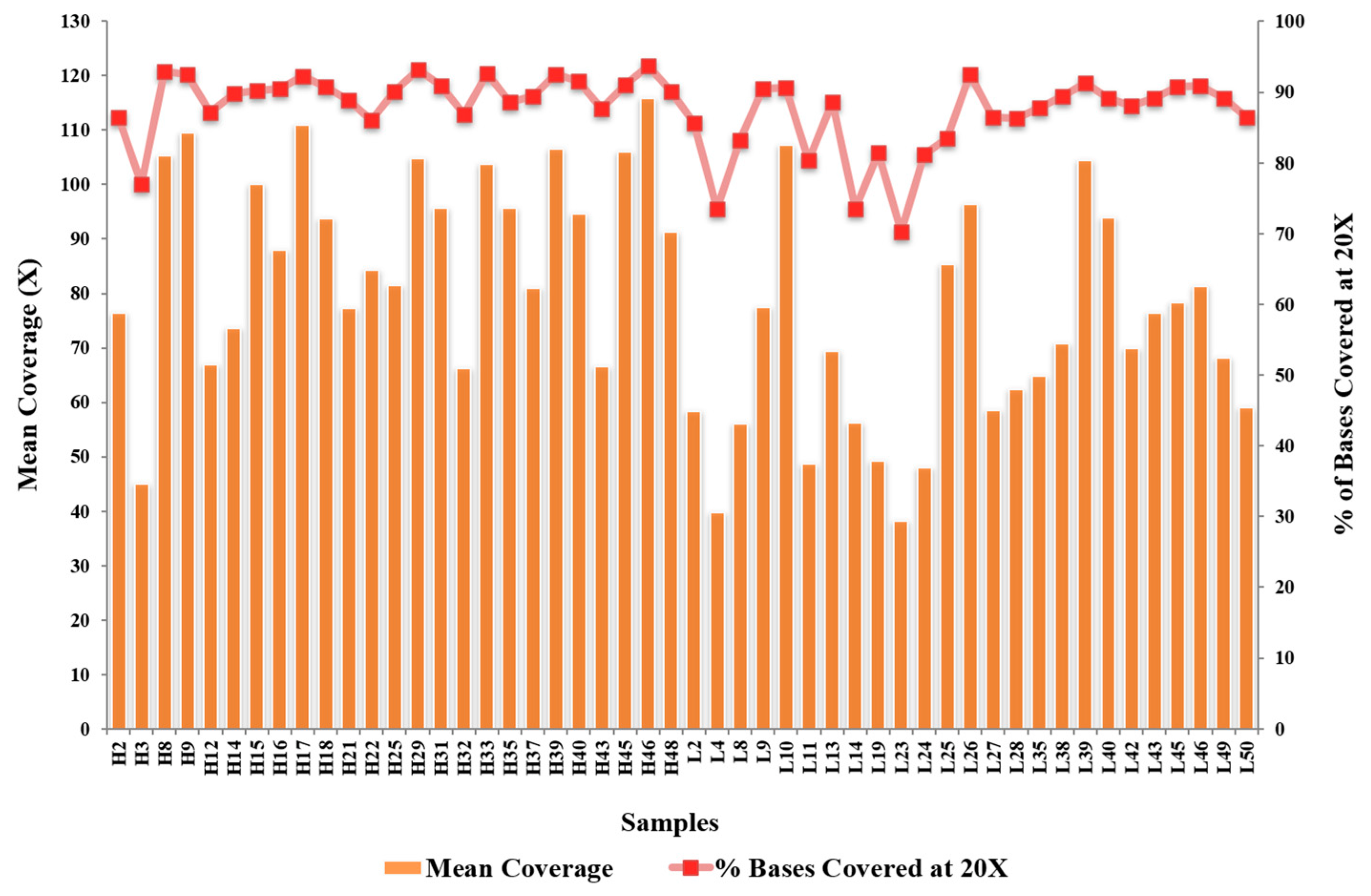
2.4. Internal Validation of 45 Variants
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data and Non-Genetic Risk Factors Associated with Hypercholesterolemia
3.2. WES Identification of Risk-Increasing and -Reducing Variants
3.3. Variants and Association with Hypercholesterolemia Risk in Malaysian Malays
3.4. Hypercholesterolemia Predictive Models Combining Genetic and Non-Genetic Risk Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, B.; Kruse, G.; Kutikova, L.; Ray, K.K.; Mata, P.; Bruckert, E. Cardiovascular Disease Risk Associated with Familial Hypercholesterolemia: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 1696–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Institute for Public Health. National Health & Morbidity Survey 2015 (NHMS 2015); Institute for Public Health: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jamal, R.; Syed Zakaria, S.Z.; Kamaruddin, M.A.; Abd Jalal, N.; Ismail, N.; Mohd Kamil, N.; Abdullah, N.; Baharudin, N.; Hussin, N.H.; Othman, H.; et al. Cohort Profile: The Malaysian Cohort (TMC) Project: A Prospective Study of Non-Communicable Diseases in a Multi-Ethnic Population. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karr, S. Epidemiology and Management of Hyperlipidemia. Am. J. Manag. Care 2017, 23, S139–S148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, M.; Futema, M.; Nair, D.; Humphries, S.E. Genetic Architecture of Familial Hypercholesterolaemia. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2017, 19, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, C.K.; Wilund, K.; Arca, M.; Zuliani, G.; Fellin, R.; Maioli, M.; Calandra, S.; Bertolini, S.; Cossu, F.; Grishin, N.; et al. Autosomal Recessive Hypercholesterolemia Caused by Mutations in a Putative LDL Receptor Adaptor Protein. Science 2001, 292, 1394–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teslovich, T.M.; Musunuru, K.; Smith, A.v.; Edmondson, A.C.; Stylianou, I.M.; Koseki, M.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Ripatti, S.; Chasman, D.I.; Willer, C.J.; et al. Biological, Clinical and Population Relevance of 95 Loci for Blood Lipids. Nature 2010, 466, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willer, C.J.; Schmidt, E.M.; Sengupta, S.; Peloso, G.M.; Gustafsson, S.; Kanoni, S.; Ganna, A.; Chen, J.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Mora, S.; et al. Discovery and Refinement of Loci Associated with Lipid Levels. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soutar, A.K. Rare Genetic Causes of Autosomal Dominant or Recessive Hypercholesterolaemia. IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, S.; Futema, M.; Whittall, R.; Taylor-Beadling, A.; Williams, M.; den Dunnen, J.T.; Humphries, S.E. The UCL Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor Gene Variant Database: Pathogenicity Update. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 54, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoo, K.L. Hereditary Hyperlipidemia in Malaysia: A Historical Perspective of Six Decade of Research and Treatment. Med. J. Malays. 2014, 69, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khateeb, A.R.; Sapawi Mohd, M.; Yusof, Z.; Zilfalil, B.A. Molecular Description of Familial Defective APOB-100 in Malaysia. Biochem. Genet. 2013, 51, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khateeb, A.; Zahri, M.K.; Mohamed, M.S.; Sasongko, T.H.; Ibrahim, S.; Yusof, Z.; Zilfalil, B.A. Analysis of Sequence Variations in Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor Gene among Malaysian Patients with Familial Hypercholesterolemia. BMC Med. Genet. 2011, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azian, M.; Hapizah, M.N.; Khalid, B.A.K.; Khalid, Y.; Rosli, A.; Jamal, R. Use of the Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis (DGGE) Method for Mutational Screening of Patients with Familial Hypercholesterolaemia (FH) and Familial Defective Apolipoprotein B100 (FDB). Malays. J. Pathol. 2006, 28, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Khoo, K.L.; van Acker, P.; Tan, H.; Deslypere, J.P. Genetic Causes of Familial Hypercholesterolaemia in a Malaysian Population. Med. J. Malays. 2000, 55, 409–418. [Google Scholar]
- Lye, S.-H.; Chahil, J.K.; Bagali, P.; Alex, L.; Vadivelu, J.; Ahmad, W.A.W.; Chan, S.-P.; Thong, M.-K.; Zain, S.M.; Mohamed, R. Genetic Polymorphisms in LDLR, APOB, PCSK9 and Other Lipid Related Genes Associated with Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Malaysia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Institues of Health. ATP III At-A-Glance: Quick Desk Reference; National Cholesterol Education Program; NIH Publication: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Do, R.; Kathiresan, S.; Abecasis, G.R. Exome Sequencing and Complex Disease: Practical Aspects of Rare Variant Association Studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, R1–R9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional Annotation of Genetic Variants from High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting Functional Effect of Human Missense Mutations Using PolyPhen-2. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2013, 76, 7.20.1–7.20.41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.; Henikoff, S.; Ng, P.C. Predicting the Effects of Coding Non-Synonymous Variants on Protein Function Using the SIFT Algorithm. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Rödelsperger, C.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster Evaluates Disease-Causing Potential of Sequence Alterations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihab, H.A.; Gough, J.; Cooper, D.N.; Stenson, P.D.; Barker, G.L.A.; Edwards, K.J.; Day, I.N.M.; Gaunt, T.R. Predicting the Functional, Molecular, and Phenotypic Consequences of Amino Acid Substitutions Using Hidden Markov Models. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uranga, R.M.; Keller, J.N. Diet and Age Interactions with Regards to Cholesterol Regulation and Brain Pathogenesis. Curr. Gerontol. Geriatr. Res. 2010, 2010, 219683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohamed-Yassin, M.-S.; Baharudin, N.; Daher, A.M.; Abu Bakar, N.; Ramli, A.S.; Abdul-Razak, S.; Mohamed Noor Khan, N.-A.; Mohamad, M.; Yusoff, K. High Prevalence of Dyslipidaemia Subtypes and Their Associated Personal and Clinical Attributes in Malaysian Adults: The REDISCOVER Study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangiah, N.; Su, T.T.; Chinna, K.; Jalaludin, M.Y.; Mohamed, M.N.A.; Majid, H.A. Longitudinal Assessment between Lifestyle-Related Risk Factors and a Composite Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Risk Index among Adolescents in Malaysia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, Y.-A.; Razman, A.Z.; Ramli, A.S.; Mohd Kasim, N.A.; Nawawi, H. Familial Hypercholesterolaemia in the Malaysian Community: Prevalence, Under-Detection and Under-Treatment. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2021, 28, 57026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.W. Advances in Understanding of the Role of Lipid Metabolism in Aging. Cells 2021, 10, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitler, K.M.; Davies, B.S.J. Aging and Plasma Triglyceride Metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, M.; Tchernof, A. Lipid Metabolism in the Elderly. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 54, S121–S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhla, A.; Blei, T.; Jaster, R.; Vollmar, B. Aging Is Associatedwith a Shift of Fatty Metabolism Toward Lipogenesis. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2011, 66A, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mc Auley, M.T.; Mooney, K.M. LDL-C Levels in Older People: Cholesterol Homeostasis and the Free Radical Theory of Ageing Converge. Med.. Hypotheses 2017, 104, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravnskov, U.; Diamond, D.M.; Hama, R.; Hamazaki, T.; Hammarskjöld, B.; Hynes, N.; Kendrick, M.; Langsjoen, P.H.; Malhotra, A.; Mascitelli, L.; et al. Lack of an Association or an Inverse Association between Low-Density-Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Mortality in the Elderly: A Systematic Review. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergès, B. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Dyslipidaemia: Where Are We? Diabetologia 2015, 58, 886–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, T.; Brandmaier, S.; Messias, A.C.; Herder, C.; Draisma, H.H.M.; Demirkan, A.; Yu, Z.; Ried, J.S.; Haller, T.; Heier, M.; et al. Effects of Metformin on Metabolite Profiles and LDL Cholesterol in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakshmi, S.A. Effect of Intensity of Cigarette Smoking on Haematological and Lipid Parameters. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, BC11–BC13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, R.E.K.; Gan, A.H.W.; Fenwick, E.K.; Gan, A.T.L.; Gupta, P.; Sabanayagam, C.; Tan, N.; Wong, K.H.; Wong, T.Y.; Cheng, C.-Y.; et al. Prevalence, Determinants and Association of Unawareness of Diabetes, Hypertension and Hypercholesterolemia with Poor Disease Control in a Multi-Ethnic Asian Population without Cardiovascular Disease. Popul. Health Metr. 2019, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aekplakorn, W.; Taneepanichskul, S.; Kessomboon, P.; Chongsuvivatwong, V.; Putwatana, P.; Sritara, P.; Sangwatanaroj, S.; Chariyalertsak, S. Prevalence of Dyslipidemia and Management in the Thai Population, National Health Examination Survey IV, 2009. J. Lipids 2014, 2014, 249584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, D.; Garcia, A.; Lohsoonthorn, V.; Williams, M.A. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Hypercholesterolemia among Thai Men and Women Receiving Health Examinations. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2006, 37, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Febriani, D.; Febriani, B. The Effect of Lifestyle on Hypercholesterolemia. Open Public Health J. 2018, 11, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Riley, G.R.; Jang, W.; Rubinstein, W.S.; Church, D.M.; Maglott, D.R. ClinVar: Public Archive of Relationships among Sequence Variation and Human Phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D980–D985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koivisto, U.M.; Viikari, J.S.; Kontula, K. Molecular Characterization of Minor Gene Rearrangements in Finnish Patients with Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Identification of Two Common Missense Mutations (Gly823-->Asp and Leu380-->His) and Eight Rare Mutations of the LDL Receptor Gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1995, 57, 789–797. [Google Scholar]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Amode, M.R.; Barrell, D.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Cummins, C.; Gall, A.; Girón, C.G.; et al. Ensembl 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D754–D761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Lehto, M.; Rasilainen, L.; Metso, J.; Ehnholm, C.; Ylaä-Herttuala, S.; Jauhiainen, M.; Olkkonen, V.M. Oxysterol Binding Protein Induces Upregulation of SREBP-1c and Enhances Hepatic Lipogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.S.; Zhang, H.; Cheung, C.Y.Y.; Xu, M.; Ho, J.C.Y.; Zhou, W.; Cherny, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Holmen, O.; Au, K.-W.; et al. Exome-Wide Association Analysis Reveals Novel Coding Sequence Variants Associated with Lipid Traits in Chinese. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.R.; Altshuler, D.M.; Durbin, R.M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Bentley, D.R.; Chakravarti, A.; Clark, A.G.; Donnelly, P.; Eichler, E.E.; et al. A Global Reference for Human Genetic Variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schulz, R.; Schlüter, K.-D.; Laufs, U. Molecular and Cellular Function of the Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9). Basic Res. Cardiol. 2015, 110, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Clinical Factor | High LDL | Low LDL | cOR (95% CI) | χ2 (df) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | |||||
| Age at baseline | 53.36 (6.36) | 51.63 (6.45) | 1.04 (1.02, 1.07) | 11.94 (1) | 0.001 * | |
| Fasting blood glucose (mg/L) | 7.15 (3.62) | 6.51 (2.79) | 1.07 (1.01, 1.12) | 6.30 (1) | 0.012 * | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.71 (4.15) | 26.65 (5.19) | 1.00 (0.97, 1.04) | 0.03 (1) | 0.854 | |
| n (%) | n (%) | |||||
| Sex | Male | 134 (39.6) | 113 (33.3) | 1.31 (0.96, 1.80) | 2.90 (1) | 0.088 |
| Female (Ref.) | 204 (60.4) | 226 (66.7) | 1 | 0.09 | ||
| Tobacco product use | Yes | 102 (30.9) | 70 (21.2) | 1.66 (1.17, 2.36) | 7.98 (1) | 0.005 * |
| No (Ref.) | 228 (69.1) | 260 (78.8) | 1 | |||
| Stroke diagnosis history | Yes | 3 (0.9) | 7 (2.1) | 0.43 (0.11, 1.66) | 1.51 (1) | 0.219 |
| No (Ref.) | 334 (99.1) | 332 (97.9) | 1 | |||
| Angina or myocardial infarction diagnosis history | Yes | 11 (3.3) | 11 (3.2) | 1.00 (0.43, 2.35) | 0 | 0.989 |
| No (Ref.) | 326 (96.7) | 328 (96.8) | 1 | |||
| Heart failure diagnosis history | Yes | 7 (2.1) | 11 (3.2) | 0.63 (0.24, 1.65) | 0.88 (1) | 0.35 |
| No (Ref.) | 330 (97.9) | 328 (96.8) | 1 | |||
| Obesity with medication status | Yes | 26 (7.7) | 36 (10.6) | 0.70 (0.42, 1.19) | 1.70 (1) | 0.193 |
| No (Ref.) | 311 (92.3) | 303 (89.4) | 1 | |||
| Hypertension with medication status | Yes | 113 (33.5) | 127 (37.5) | 0.84 (0.61, 1.15) | 1.14 (1) | 0.286 |
| No (Ref.) | 224 (66.5) | 212 (62.5) | 1 | |||
| Diabetes mellitus with medication status | Yes | 55 (16.3) | 81 (23.9) | 0.62 (0.42, 0.91) | 5.97 (1) | 0.015 * |
| No (Ref.) | 282 (83.17) | 258 (76.1) | 1 | |||
| Family history of hypertension | Yes | 106 (31.5) | 118 (34.8) | 0.86 (0.62, 1.18) | 0.86 (1) | 0.354 |
| No (Ref.) | 231 (68.5) | 221 (65.2) | 1 | |||
| Family history of diabetes mellitus | Yes | 86 (25.5) | 92 (27.1) | 0.92 (0.65, 1.30) | 0.23 (1) | 0.633 |
| No (Ref.) | 251 (74.5) | 247 (72.9) | 1 | |||
| Family history of stroke | Yes | 29 (8.6) | 40 (11.8) | 0.70 (0.43, 1.17) | 1.87 (1) | 0.704 |
| No (Ref.) | 308 (91.4) | 299 (88.2) | 1 | |||
| Family history of angina | Yes | 18 (5.3) | 10 (2.9) | 1.86 (0.84, 4.08) | 2.37 (1) | 0.124 |
| No (Ref.) | 319 (94.7) | 329 (97.1) | 1 | |||
| Family history of hyperlipidemia | Yes | 21 (6.2) | 9 (2.7) | 2.44 (1.20, 5.40) | 4.81 (1) | 0.028 * |
| No (Ref.) | 316 (93.8) | 330 (97.3) | 1 | |||
| Family history of heart disease | Yes | 42 (12.5) | 31 (9.1) | 1.42 (0.87, 2.31) | 1.92 (1) | 0.166 |
| No (Ref.) | 295 (87.5) | 308 (90.9) | 1 | |||
| Family history of cardiovascular disease | Yes | 76 (22.6) | 71 (20.9) | 1.20 (0.76, 1.58) | 0.26 (1) | 0.612 |
| No (Ref.) | 261 (77.4) | 268 (79.1) | 1 |
| Chromosome | Gene | Nomenclature | Variant Type | snp138 | Clinical Significance (ClinVar) | Frequency in HLDL, n | Sample ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | APOB | NM_000384.3:c.C1400G;p.A467G | Non-synonymous SNV | rs376602710 | Uncertain significance | 1 | H39 |
| 2 | APOB | NM_000384.3:c.C3665T:p.T1222I | Non-synonymous SNV | rs1333175181 | - | 1 | H17 |
| 2 | APOB | NM_000384.3:c.G4796A:p.R1599H | Non-synonymous SNV | rs746414462 | Conflicting pathogenicity | 1 | H33 |
| 2 | APOB | NM_000384.3:c.A5768G:p.H1923R | Non-synonymous SNV | rs533617 | Benign/Likely benign | 1 | H48 |
| 19 | LDLR | NM_000527.5:c.1994_2010del:p.665_670del | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 1 | H14; H40 |
| 19 | LDLR | NM_000527.5:c.T2037A;p.Y679X | Stop-gain SNV | rs760436036 | Pathogenic | 1 | H15; H16 |
| 19 | LDLR | NM_000527.5:c.G622A;p.E208K | Non-synonymous SNV | rs879254597 | Pathogenic/Likely pathogenic | 2 | H9 |
| 19 | LDLR | NM_000527.5:c.G1247T:p.R416L | Non-synonymous SNV | rs773658037 | Likely pathogenic | 1 | H39 |
| 19 | LDLR | NM_000527.5:c.A173G:p.E58G | Non-synonymous SNV | rs879254424 | Likely pathogenic | 2 | H45 |
| 19 | LDLR | NM_000527.5:c.G301A:p.E101K | Non-synonymous SNV | rs144172724 | Pathogenic/Likely pathogenic | 1 | H33 |
| 19 | LDLR | NM_000527.5:c.C1284G:p.N428K | Non-synonymous SNV | rs368708058 | Likely benign | 1 | H32 |
| 1 | LDLRAP1 | NM_015627.3:c.603_604del:p.201_202del | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 2 | H18; H48 |
| 1 | LDLRAP1 | NM_015627.3:c.584delC:p.A195fs | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 2 | H18 |
| 1 | PCSK9 | NM_174936.4:c79delG:p.G27fs | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 1 | H33 |
| 1 | PCSK9 | NM_174936.4:c.G644A:p.R215H | Non-synonymous SNV | rs794728683 | Conflicting pathogenicity | 1 | H32 |
| 1 | PCSK9 | NM_174936.4:c.77_79CGC | Non-frameshift substitution | - | - | 1 | H33 |
| Gene | Variants, n | Frequency in HLDL, n | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| NYNRIN | 12 | 13 | NYN domain and retroviral integrase containing protein. |
| CELSR2 | 11 | 12 | A member of the flamingo subfamily, part of the cadherin superfamily. It is postulated that these proteins are receptors involved in contact-mediated communication. |
| PARP10 | 6 | 9 | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs), such as PARP10, regulate gene transcription by altering chromatin organization by adding ADP-ribose to histones. PARPs can also function as transcriptional cofactors. |
| MAF1 | 1 | 7 | Repressor of RNA polymerase III transcription MAF1 homolog. |
| OSBPL7 | 3 | 6 | A member of the oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) family, a group of intracellular lipid receptors. |
| Chromosome | Gene | Nomenclature | Variant Type | snp138 | Clinical Significance (ClinVar) | Frequency in HLDL, n | Frequency in LLDL, n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | WDR74 | NM_018093.3:c.855delC:p.A285fs | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 19 | 0 |
| 20 | FRG1BP | NR_145491.1:n.509TTG | Nonframeshift insertion | rs112430454 | - | 18 | 0 |
| 3 | SEC13 | NM_183352.3:c.950delG:p.G317fs | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 18 | 0 |
| 19 | KEAP1 | NM_203500.2:c.966delC:p.P322fs | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 18 | 0 |
| 1 | C1orf85/ GLMP | NM_144580.3:c.35_36del:p.12_12del | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 17 | 0 |
| 7 | MUC12 | NM_001164462.2:c.A5251C:p.T1751P | Nonsynonymous SNV | rs71557212 | - | 17 | 0 |
| 15 | UBR1 | NM_174916.3:c.4519delC:p.P1507fs | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 17 | 0 |
| 1 | GBP7 | NM_207398.3:c.460delG:p.A154fs | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 16 | 0 |
| 4 | RNF212 | NM_001193318.3:c.A784G:p.I262V | Nonsynonymous SNV | rs1670534 | - | 16 | 0 |
| 6 | DPCR1/MUCL3 | NM_080870.4:c.2453delC:p.S818fs | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 16 | 0 |
| 14 | HEATR5A | NM_015473.4:c.2656delG:p.V886fs | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 15 | 0 |
| 14 | HEATR5A | NM_015473.4:c.2656_2657AT | Non-frameshift substitution | - | - | 15 | 0 |
| 12 | TIMELESS | NM_003920.5:c.3280delG:p.A1094fs | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 15 | 0 |
| 16 | GTF3C1 | NM_001520.4:c.167delG:p.G56fs | Frameshift deletion | - | - | 15 | 0 |
| Gene | Changes/Type | rs# | Genotype | cOR (95% CI) | χ2 (df) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APOB | NM_000384.3:c.A5768G:p.H1923R | rs533617 | T (Ref) | 1 | ||
| Nonsynonymous SNV | TC | 2.37 (0.61, 9.24) | 1.54 (1) | 0.214 | ||
| APOB | NM_000384.3:c.G4796A:p.R1599H | rs746414462 | C (Ref) | 1 | ||
| Nonsynonymous SNV | CT | 3.04 (0.06, 15.15) | 3 (1) | 0.176 | ||
| APOB | NM_000384.3:c.C1400G:p.A467G | rs376602710 | G (Ref) | 1 | ||
| Nonsynonymous SNV | GC | 0.14 (0.02, 1.15) | 3.36 (1) | 0.067 | ||
| LDLRAP1 | NM_015627.3:c.603_604del:p.201-203del Frameshift deletion | Novel | T (Ref) | 1 | ||
| CT | 0.90 (0.65, 1,25) | 0.41 (1) | 0.521 | |||
| C | 1.11 (0.70, 1.77) | 0.21 (1) | 0.644 | |||
| CELSR2 | NM_001408.3:c.C6517T:p.R2173C | rs142780237 | C (Ref) | 1 | ||
| Nonsynonymous SNV | CT | 3.20 (0.64, 15.98) | 2.01 (1) | 0.156 | ||
| CELSR2 | NM_001408.3:c.6756delC:p.Y2252fs | Novel | C (Ref) | 1 | ||
| Frameshift deletion | G | 1.15 (0.07, 18.49) | 0.01 (1) | 0.921 | ||
| LPA | NM_005577.4:c.A4195C:p.T1399P | rs41272100 | T (Ref) | 1 | ||
| Nonsynonymous SNV | TG | 0.58 (0.17, 2.00) | 0.74 (1) | 0.389 | ||
| MAF1 | NM_032272.5:c.532delG: p.G178fs | Novel | G (Ref) | 1 | ||
| Frameshift deletion | GA | 0.57 (0.26, 1.26) | 1.94 (1) | 0.164 | ||
| NYNRIN | NM_025081.3:c.169_173GC | Novel | G (Ref) | 1 | ||
| Non-frameshift deletion | GC | 1.15 (0.07, 18.54) | 0.01 (1) | 0.919 | ||
| OSBPL7 | NM_145798.3:c.651_652del:p217_218del | Novel | C (Ref) | 1 | ||
| Frameshift deletion | CA | 16.89 (6.05, 47.12) | 29.15 (1) | <0.001 * | ||
| OSBPL7 | NM_145798.3:c.348_352ACCCT Non-frameshift substitution | Novel | C (Ref) | 1 | ||
| CT | 0.63 (0.36, 1.09) | 2.72 (1) | 0.099 | |||
| T | 0.96 (0.06, 15.39) | 0.01 (1) | 0.976 | |||
| SPATC1 | NM_198572.3:c.C1504A:p.Q502K | rs210925917 | C (Ref) | 1 | ||
| Nonsynonymous SNV | CA | 0.43 (0.17, 1.05) | 3.45 (1) | 0.063 | ||
| PARP10 | NM_032789.5:c.283delG | Novel | G (Ref) | 1 | ||
| Frameshift deletion | GDEL | 1.61 (0.73, 3.58) | 1.39 (1) | 0.238 | ||
| APOB | NM_000384.3:c.G4163A:p.R1388H Nonsynonymous SNV | rs13306187 | C (Ref) | 1 | ||
| CT | 1.40 (0.68, 2.89) | 0.81 (1) | 0.367 | |||
| T | ||||||
| PCSK9 | NM_174936.4:c.C277T:p.R93C Nonsynonymous SNV | rs151193009 | C (Ref) | |||
| CT | 0.12 (0.04, 0.41) | 11.72 (1) | 0.001 * | |||
| T | ||||||
| APOB | NM_000384.3:c.G7331A:p.R2444H | rs200143030 | C (Ref) | 1.14 (0.23, 5.67) | 0.02 (1) | 0.877 |
| Nonsynonymous SNV | CT | |||||
| LDLR | c.C4T:p.R2X Stop-gain SNV | rs2228671 | C (Ref) | 1 | ||
| CT | 0.67 (0.34, 1.33) | 1.32 (1) | 0.251 | |||
| T | ||||||
| LPA | NM_005577.4:c.C6046T:p.R2016C Nonsynonymous SNV | rs3124784 | G (Ref) | 1 | ||
| GA | 1.34 (0.90, 1.99) | 2.13 (1) | 0.145 | |||
| A | 0.40 (0.04, 3.87) | 0.63 (1) | 0.429 | |||
| LPA | NM_005577.4:c.A5673G:p.I1891M Nonsynonymous SNV | rs3798220 | T (Ref) | 1 | ||
| TC | 0.56 (0.34, 1.05) | 3.23 (1) | 0.072 | |||
| C | ||||||
| LDLR | c.G224A:p.G75D Nonsynonymous SNV | rs3826810 | G (Ref) | 1 | ||
| GA | 0.65 (0.42, 0.99) | 4.09 (1) | 0.043 | |||
| A | ||||||
| SPATC1 | NM_198572.3:c.T193C:p.S65P | rs60050811 | T (Ref) | 1 | ||
| Nonsynonymous SNV | TC | 0.89 (0.40, 1.99) | 0.09 (1) | 0.770 | ||
| NYNRIN | NM_025081.3c.A823G:p.S275G Nonsynonymous SNV | rs74036628 | A (Ref) | 1 | ||
| AG | 0.89 (0.62, 1.27) | 0.44 (1) | 0.505 | |||
| G | 0.68 (0.28, 1.68) | 0.69 (1) | 0.406 |
| Factor | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | aOR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 1.04 (1.02, 1.07) | 0.001 * | 1.04 (1.01, 1.07) | 0.004 * | 1.05 (1.02, 1.08) | 0.001 * |
| Fasting blood glucose (mmol/L) | 1.16 (1.09, 1.24) | <0.001 * | 1.17 (1.09, 1.25) | <0.001 * | 1.15 (1.07, 1.23) | <0.001 * |
| Ever-use of tobacco products (yes) | 1.60 (1.08, 2.38) | 0.019 | 1.52 (1.01, 2.28) | 0.045 | 1.69 (1.12, 2.55) | 0.013 |
| Diabetes with medication status (yes) | 0.27 (0.16, 0.45) | <0.001 * | 0.26 (0.15, 0.44) | <0.001 * | 0.29 (0.17, 0.50) | <0.001 * |
| Family history of hyperlipidemia (yes) | 2.94 (1.30, 6.68) | 0.010 | 3.30 (1.44, 7.56) | 0.010 | 2.19 (0.90, 5.35) | 0.084 |
| T2FH_OSBPL7_01 (novel) (CA vs. C) | 16.60 (5.82, 47.35) | <0.001 * | ||||
| rs151193009 (CT vs. C) | 0.12 (0.03, 0.42) | 0.001 * | ||||
| Nagelkerke’s R2 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.14 | |||
| AUC (95% CI) | 0.68 (0.64, 0.72) | 0.73 (0.69, 0.77) | 0.69 (0.65, 0.74) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdul Murad, N.A.; Mohammad Noor, Y.; Mohd. Rani, Z.Z.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Chow, Y.P.; Abdullah, N.; Ahmad, N.; Ismail, N.; Abdul Jalal, N.; Kamaruddin, M.A.; et al. Hypercholesterolemia in the Malaysian Cohort Participants: Genetic and Non-Genetic Risk Factors. Genes 2023, 14, 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030721
Abdul Murad NA, Mohammad Noor Y, Mohd. Rani ZZ, Sulaiman SA, Chow YP, Abdullah N, Ahmad N, Ismail N, Abdul Jalal N, Kamaruddin MA, et al. Hypercholesterolemia in the Malaysian Cohort Participants: Genetic and Non-Genetic Risk Factors. Genes. 2023; 14(3):721. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030721
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdul Murad, Nor Azian, Yusuf Mohammad Noor, Zam Zureena Mohd. Rani, Siti Aishah Sulaiman, Yock Ping Chow, Noraidatulakma Abdullah, Norfazilah Ahmad, Norliza Ismail, Nazihah Abdul Jalal, Mohd. Arman Kamaruddin, and et al. 2023. "Hypercholesterolemia in the Malaysian Cohort Participants: Genetic and Non-Genetic Risk Factors" Genes 14, no. 3: 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030721
APA StyleAbdul Murad, N. A., Mohammad Noor, Y., Mohd. Rani, Z. Z., Sulaiman, S. A., Chow, Y. P., Abdullah, N., Ahmad, N., Ismail, N., Abdul Jalal, N., Kamaruddin, M. A., Saperi, A. A., & Jamal, R. (2023). Hypercholesterolemia in the Malaysian Cohort Participants: Genetic and Non-Genetic Risk Factors. Genes, 14(3), 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030721






