MCD Inhibits Lipid Deposition in Goat Intramuscular Preadipocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Cell Isolation, and Culture
2.2. Induction of Cell Differentiation
2.3. Gene Cloning and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.4. Construction of pcDNA3.1-MCD Plasmid and Synthesis of siRNA
2.5. Cell Transfection
2.6. Extraction of RNA and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.7. Oil Red O Staining, Cellular TAG, and Malonyl-CoA Assay
2.8. Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis of the MCD Promoter
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
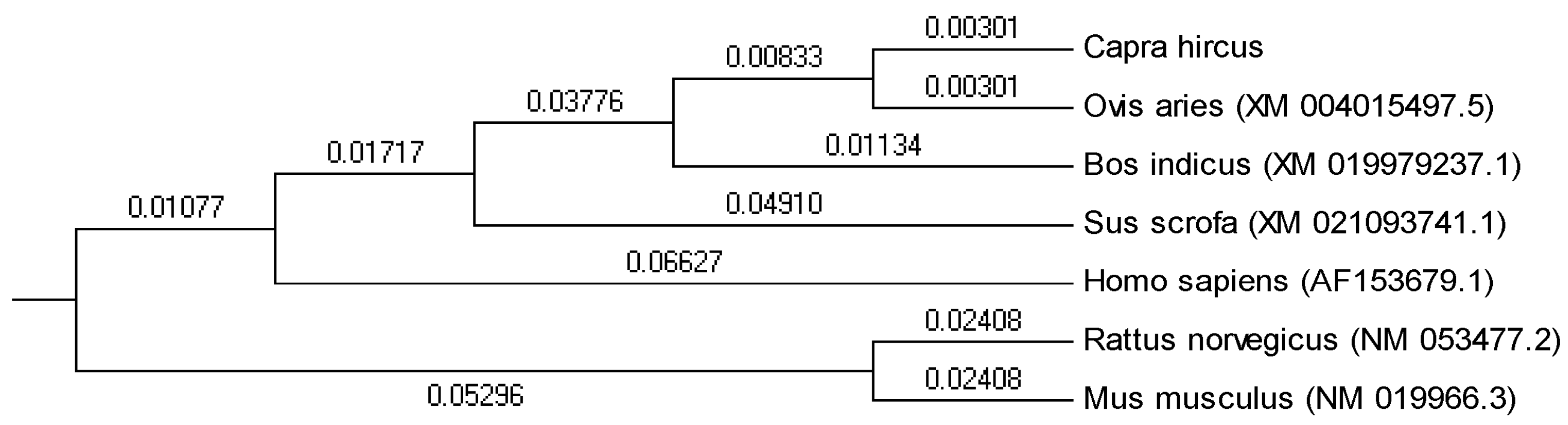
3.1. Characterization of MCD from Goat Liver
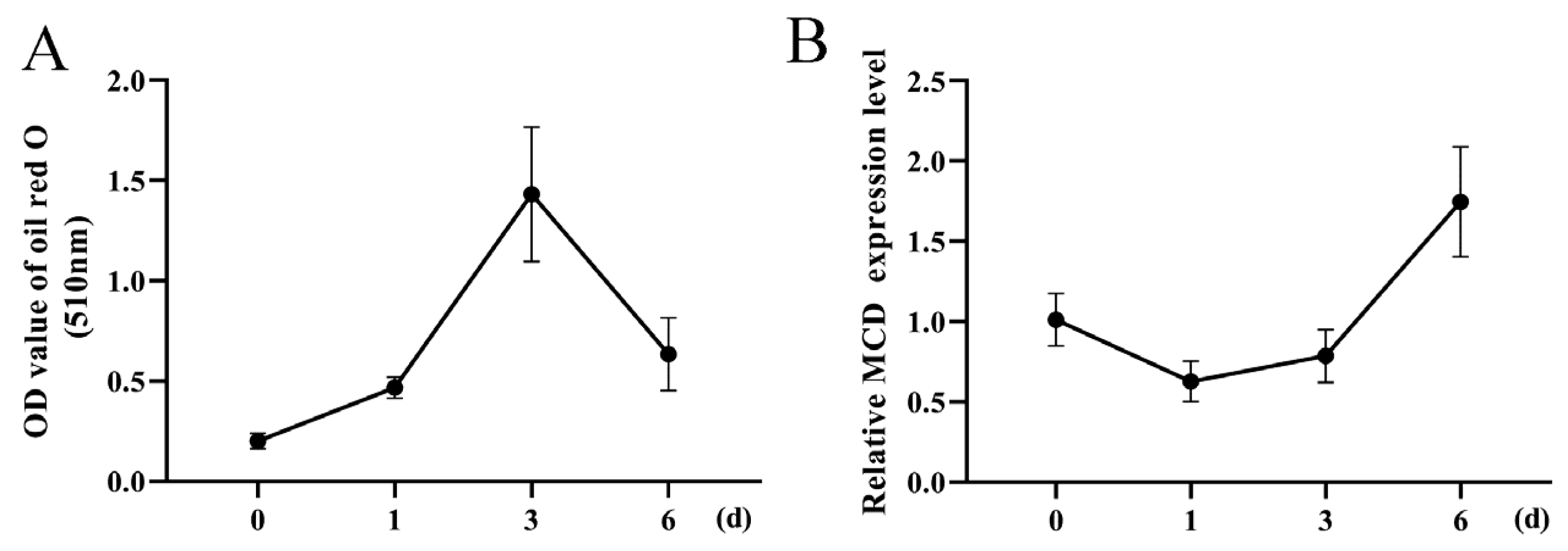
3.2. MCD Expression Is Negatively Correlated with Lipid Deposition
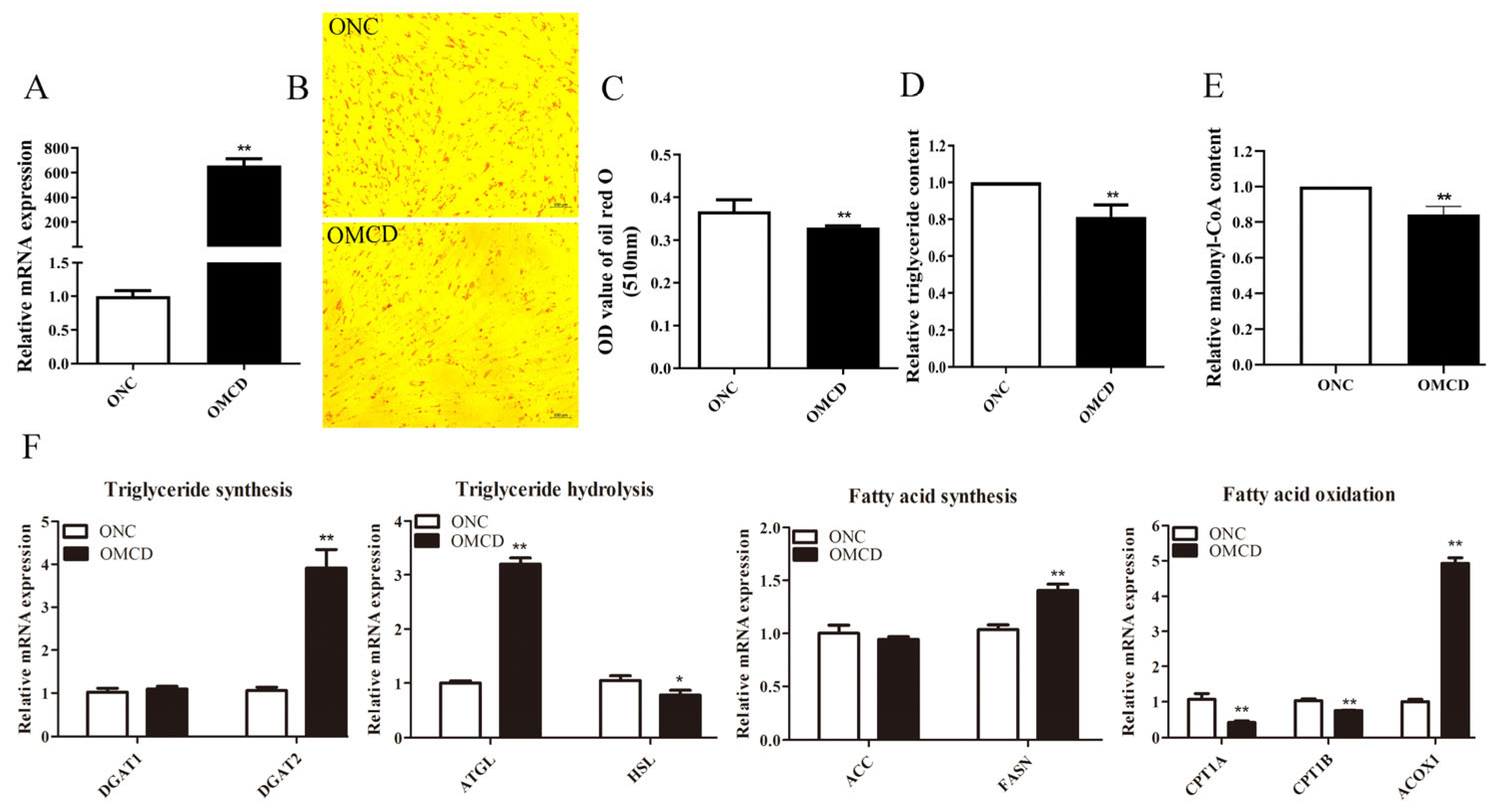
3.3. Overexpression of MCD Reduces Lipid Deposition
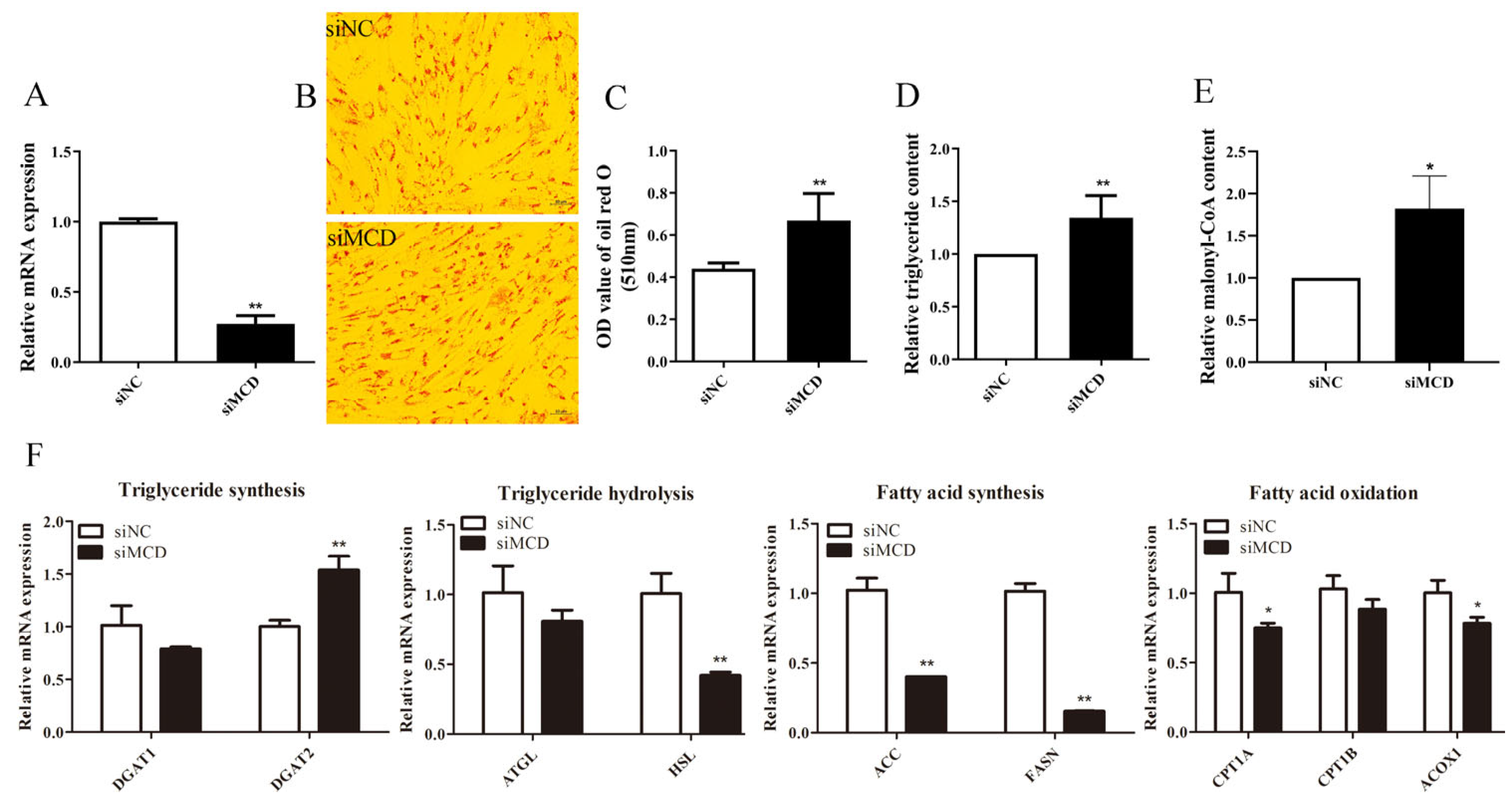
3.4. MCD Knockdown Increases Lipid Deposition
3.5. MCD Promoter Bioinformatics Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hocquette, J.F.; Gondret, F.; Baeza, E.; Medale, F.; Jurie, C.; Pethick, D.W. Intramuscular fat content in meat-producing animals: Development, genetic and nutritional control, and identification of putative markers. Animal 2010, 4, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausman, G.J.; Dodson, M.V.; Ajuwon, K.; Azain, M.; Barnes, K.M.; Guan, L.L.; Jiang, Z.; Poulos, S.P.; Sainz, R.D.; Smith, S.; et al. Board-invited review: The biology and regulation of preadipocytes and adipocytes in meat animals. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, 1218–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Kwon, E.G.; Im, S.K.; Seo, K.S.; Baik, M. Expression of fat deposition and fat removal genes is associated with intramuscular fat content in longissimus dorsi muscle of Korean cattle steers. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggerson, D. Malonyl-CoA, a key signaling molecule in mammalian cells. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2008, 28, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, L.A.; Heath, S.H.; Hagen, T.M. Acetyl-L-carnitine supplementation reverses the age-related decline in carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1) activity in interfibrillar mitochondria without changing the L-carnitine content in the rat heart. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2012, 133, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillmore, N.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Malonyl CoA: A promising target for the treatment of cardiac disease. IUBMB Life 2014, 66, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.K.; Kolattukudy, P.E. Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase from the uropygial gland of waterfowl: Purification, properties, immunological comparison, and role in regulating the synthesis of multimethyl-branched fatty acids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1978, 190, 585–597. [Google Scholar]
- Voilley, N.; Roduit, R.; Vicaretti, R.; Bonny, C.; Waeber, G.; Dyck, J.; Lopaschuk, G.D.; Prentki, M. Cloning and expression of rat pancreatic beta-cell malonyl-CoA decarboxylase. Biochem. J. 1999, 340 Pt 1, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, J.R.; Berthiaume, L.G.; Thomas, P.D.; Kantor, P.F.; Barr, A.J.; Barr, R.; Singh, D.; Hopkins, T.A.; Voilley, N.; Prentki, M.; et al. Characterization of rat liver malonyl-CoA decarboxylase and the study of its role in regulating fatty acid metabolism. Biochem. J. 2000, 350 Pt 2, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.; Saggerson, E. Malonyl-CoA and the regulation of fatty acid oxidation in soleus muscle. Biochem. J. 1998, 334 Pt 1, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, D.R.; Hill, A.; Tolmie, J.L.; Thorburn, D.R.; Christodoulou, J. The molecular basis of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 65, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polinati, P.P.; Valanne, L.; Tyni, T. Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency: Long-term follow-up of a patient new clinical features and novel mutations. Brain Dev. 2015, 37, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasapkara, C.S.; Civelek Urey, B.; Ceylan, A.C.; Unal Uzun, O.; Cetin, I.I. Malonyl coenzyme A decarboxylase deficiency with a novel mutation. Cardiol. Young 2021, 31, 1535–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Ko, J.M.; Song, M.K.; Song, J.; Park, K.S. A Korean child diagnosed with malonic aciduria harboring a novel start codon mutation following presentation with dilated cardiomyopathy. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Muoio, D.M.; Shiota, M.; Fujimoto, Y.; Cline, G.W.; Shulman, G.I.; Koves, T.R.; Stevens, R.; Millington, D.; Newgard, C.B. Hepatic expression of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase reverses muscle, liver and whole-animal insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, J.; Barr, R.L.; Kavanagh, K.M.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Contribution of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase to the high fatty acid oxidation rates seen in the diabetic heart. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbert, K.D.; Dyck, J. Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase is a major regulator of myocardial fatty acid oxidation. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2005, 7, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, R.; Tamm, C.; Papageorgiou, I.; Benzi, R.H. Myocardial fatty acid oxidation during ischemia and reperfusion. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1992, 116, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Tu, Y.; Simpson, P.J.; Kuhajda, F.P. Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase inhibition is selectively cytotoxic to human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2979–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yizhak, K.; Gaude, E.; Le Devedec, S.; Waldman, Y.Y.; Stein, G.Y.; van de Water, B.; Frezza, C.; Ruppin, E. Phenotype-based cell-specific metabolic modeling reveals metabolic liabilities of cancer. Elife 2014, 3, e03641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Du, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lin, Y. miR-10a-5p Inhibits the Differentiation of Goat Intramuscular Preadipocytes by Targeting KLF8 in Goats. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 700078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, S.; Sweetman, L.; Thorburn, D.R.; Mofidi, S.; Williams, J.C. A new case of malonyl coenzyme A decarboxylase deficiency presenting with cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1997, 156, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, N.D.; Handzlik, M.K.; Li, T.; Tian, R. The Role of Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase (DGAT) 1 and 2 in Cardiac Metabolism and Function. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, E.; Goldberg, E.B.; Makarova, K.S.; Lin, L.; Brown, W.J.; Jackson, C.L. ATGL has a key role in lipid droplet/adiposome degradation in mammalian cells. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brejchova, K.; Radner, F.P.W.; Balas, L.; Paluchova, V.; Cajka, T.; Chodounska, H.; Kudova, E.; Schratter, M.; Schreiber, R.; Durand, T.; et al. Distinct roles of adipose triglyceride lipase and hormone-sensitive lipase in the catabolism of triacylglycerol estolides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2020999118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xiong, Q.; Tao, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Li, X.F.; Suo, X.J.; Yang, Q.P.; Chen, M.X. ACOX1, regulated by C/EBPalpha and miR-25-3p, promotes bovine preadipocyte adipogenesis. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2021, 66, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Zhang, Y.T.; Tseng, Y.J.; Zhang, J. miR-222 targets ACOX1, promotes triglyceride accumulation in hepatocytes. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2019, 18, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadi, A.; Kersten, S. Mechanisms of gene regulation by fatty acids. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.J.; Luo, J.; Xu, H.F.; Wang, H.; Loor, J.J. Short communication: Altered expression of specificity protein 1 impairs milk fat synthesis in goat mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4893–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.F.; Luo, J.; Zhao, W.S.; Yang, Y.C.; Tian, H.B.; Shi, H.B.; Bionaz, M. Overexpression of SREBP1 (sterol regulatory element binding protein 1) promotes de novo fatty acid synthesis and triacylglycerol accumulation in goat mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.Y.; Kim, N.H.; Zhao, Z.S.; Cha, B.S.; Kim, Y.S. Peroxisomal-proliferator-activated receptor alpha activates transcription of the rat hepatic malonyl-CoA decarboxylase gene: A key regulation of malonyl-CoA level. Biochem. J. 2004, 378 Pt 3, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, S.J.; Myers, H.M.; Watkins, S.M.; Brown, B.E.; Feingold, K.R.; Elias, P.M.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Lipopenia and Skin Barrier Abnormalities in DGAT2-deficient Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11767–11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, W.C.; Morgan, E.E.; Huang, H.; McElfresh, T.A.; Sterk, J.P.; Okere, I.C.; Chandler, M.P.; Cheng, J.; Dyck, J.R.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase inhibition suppresses fatty acid oxidation and reduces lactate production during demand-induced ischemia. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H2304–H2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Name | Accession Numbers | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCD | OM937122 | Forward: AAGTGCTCCAGAGAATCAGCG Reverse: GGCTCAGCGAGTAGAAGATGG | 60 |
| DGAT1 | NM_174693 | Forward: CCACTGGGACCTGAGGTGTC | 60 |
| Reverse: GCATCACCACACACCAATTCA | |||
| DGAT2 | BT030532.1 | Forward: CATGTACACATTCTGCACCGATT Reverse: TGACCTCCTGCCACCTTTCT | 60 |
| ATGL | GQ918145 | Forward: GGAGCTTATCCAGGCCAATG Reverse: TGCGGGCAGATGTCACTCT | 60 |
| HSL | EU273879 | Forward: GGGAGCACTACAAACGCAACG Reverse: TGAATGATCCGCTCAAACTCG | 60 |
| ACC | NM_174224.2 | Forward: CTCCAACCTCAACCACTACGG Reverse: GGGGAATCACAGAAGCAGCC | 60 |
| FASN | DQ915966.3 | Forward: GGGCTCCACCACCGTGTTCCA Reverse: GCTCTGCTGGGCCTGCAGCTG | 60 |
| CPT1A | XM_018043311.1 | Forward: TGACGGCTCTGGCACAAGAT Reverse: CGCGAAGTAGTTGCTATTCAC | 60 |
| CPTAB | MH340532 | Forward: ACGAGGAGTCTCACCACTACG Reverse: GTGTGAAGGACTTGTCGAACCA | 60 |
| ACOX1 | NM_00103528 | Forward: CGAGTTCATTCTCAACAGTCCT Reverse: GCATCTTCAAGTAGCCATTATCC | 60 |
| UXT | XP_005700899.1 | Forward: GCAAGTGGATTTGGGCTGTAAC Reverse: ATGGAGTCCTTGGTGAGGTTGT | 60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Li, Q.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, H.; Huang, L.; Zhao, W.; Xiang, H.; Zhu, J. MCD Inhibits Lipid Deposition in Goat Intramuscular Preadipocytes. Genes 2023, 14, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020440
Yang C, Li Q, Lin Y, Wang Y, Shi H, Huang L, Zhao W, Xiang H, Zhu J. MCD Inhibits Lipid Deposition in Goat Intramuscular Preadipocytes. Genes. 2023; 14(2):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020440
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Changheng, Qi Li, Yaqiu Lin, Yong Wang, Hengbo Shi, Lian Huang, Wangsheng Zhao, Hua Xiang, and Jiangjiang Zhu. 2023. "MCD Inhibits Lipid Deposition in Goat Intramuscular Preadipocytes" Genes 14, no. 2: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020440
APA StyleYang, C., Li, Q., Lin, Y., Wang, Y., Shi, H., Huang, L., Zhao, W., Xiang, H., & Zhu, J. (2023). MCD Inhibits Lipid Deposition in Goat Intramuscular Preadipocytes. Genes, 14(2), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020440






