Sequence Analysis of the Malaysian Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus Strain H5N2 from Duck
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
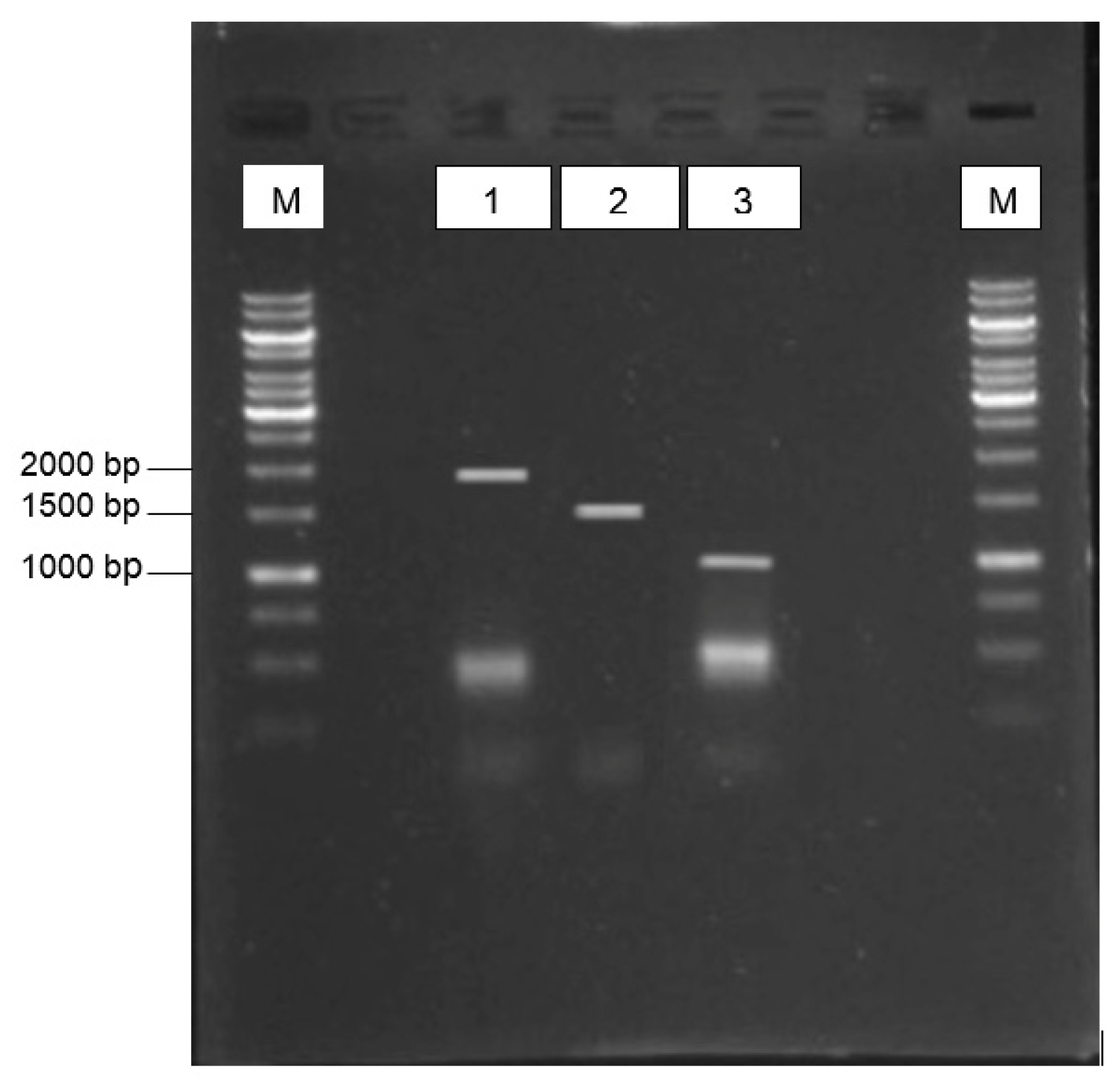
3.1. Virus Isolation and Gene Amplications
3.2. Nucleotide Sequence Analysis
3.3. Amino acid Sequence Analysis
3.3.1. HA Protein
3.3.2. NA Protein
3.3.3. M Protein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutchinson, E.C.; Charles, P.D.; Hester, S.S.; Thomas, B.; Trudgian, D.; Martínez-Alonso, M.; Fodor, E. Conserved and host-specific features of influenza virion architecture. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosik, I.; Yewdell, J.W. Influenza hemagglutinin and neuraminidase: Yin-yang proteins coevolving to thwart immunity. Viruses 2019, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, D.L.; Perdue, M.L.; Cox, N.; Rowe, T.; Bender, C.; Huang, J.; Swayne, D.E. Comparisons of highly virulent H5N1 influenza A viruses isolated from humans and chickens from Hong Kong. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 6678–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwhab, E.-S.M.; Veits, J.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Genetic changes that accompanied shifts of low pathogenic avian influenza viruses toward higher pathogenicity in poultry. Virulence 2013, 4, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, M.S.; Artois, J.; Dellicour, S.; Lemey, P.; Dauphin, G.; Von Dobschuetz, S.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Castellan, D.M.; Morzaria, S.; Gilbert, M. Geographical and historical patterns in the emergences of novel highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5 and H7 viruses in Poultry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, N.J.; Bishop, M.A.; Trovão, N.S.; Ineson, K.M.; Schaefer, A.L.; Puryear, W.B.; Zhou, K.; Foss, A.D.; Clark, D.E.; MacKenzie, K.G.; et al. Ecological divergence of wild birds drives avian influenza spillover and global spread. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchipudi, S.V.; Nelli, R.; White, G.A.; Bain, M.; Chang, K.C.; Dunham, S. Differences in influenza virus receptors in chickens and ducks: Implications for interspecies transmission. J. Mol. Genet. Med. 2009, 3, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, J.B.; Vervelde, L.; Post, J.; Rebel, J.M. Differences in highly pathogenic avian influenza viral pathogenesis and associated early inflammatory response in chickens and ducks. Avian Pathol. 2013, 42, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Adibah, M.; Zailina, H.; Arshad, S.S. Avian influenza outbreaks in Malaysia, 1980–2017. APEOHJ 2017, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Rasoli, M.; Omar, A.R.; Aini, I.; Jalilian, B.; Syed Hassan, S.H.; Mohamed, M. Fusion of HSP70 gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to hemagglutinin (H5) gene of avian influenza virus in DNA vaccine enhances its potency. Acta Virol. 2010, 54, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariatulqabtiah, A.R.; Majid, N.N.; Giotis, E.S.; Omar, A.R.; Skinner, M.A. Inoculation of fowlpox viruses coexpressing avian influenza H5 and chicken IL-15 cytokine gene stimulates diverse host immune responses. As. Pac. J. Mol. Biol. Biotechnol. 2019, 27, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, N.N.; Omar, A.R.; Mariatulqabtiah, A.R. Negligible effect of chicken cytokine IL-12 integration into recombinant fowlpox viruses expressing avian influenza virus neuraminidase N1 on host cellular immune responses. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifah, S.H.; Suriani, M.N.; Maizan, M.; Ong, G.H.; Azizah, D.; Suzana, K.; Omar, A.R.; Aini, I. Potency and efficacy of a low pathogenic H5N2 inactivated vaccine against challenge with a Malaysian H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus. J. Vet. Malays. 2013, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, E.; Stech, J.; Guan, Y.; Webster, R.G.; Perez, D.R. Universal primer set for the full-length amplification of all influenza A viruses. Arch. Virol. 2001, 146, 2275–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fereidouni, S.R.; Starick, E.; Grund, C.; Globig, A.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Beer, M.; Harder, T. Rapid molecular subtyping by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction of the neuraminidase gene of avian influenza A viruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 135, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. Mega11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, D.S.-Y.; Ng, S.-H.; Liaw, C.-W.; Ng, L.-M.; Wee, E.J.-H.; Lim, E.A.-S.; Seah, S.L.-K.; Wong, W.-K.; Lim, C.-W.; Sugrue, R.J.; et al. Molecular characterization of low pathogenic avian influenza viruses, isolated from food products imported into Singapore. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 138, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Kamigaki, T.; Oshitani, H. Evolution of the M gene of the influenza A virus in different host species: Large-scale sequence analysis. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElHefnawi, M.; AlAidi, O.; Mohamed, N.; Kamar, M.; El-Azab, I.; Zada, S.; Siam, R. Identification of novel conserved functional motifs across most influenza a viral strains. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horimoto, T.; Nakayama, K.; Smeekens, S.P.; Kawaoka, Y. Proprotein-processing endoproteases PC6 and furin both activate hemagglutinin of virulent avian influenza viruses. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 6074–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, V.; Rinder, M.; Hafner-Marx, A.; Rabl, S.; Bogner, K.H.; Neubauer-Juric, A.; Büttner, M. Avian Influenza A virus monitoring in wild birds in bavaria: Occurrence and heterogeneity of H5 and N1 encoding genes. Zoonoses Public Health 2010, 57, e184–e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse, D.J.; Webster, R.G.; Russell, R.J.; Perez, D.R. Molecular determinants within the surface proteins involved in the pathogenicity of H5N1 influenza viruses in chickens. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9954–9964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.G.; Kawaoka, Y.; Bean, W.J. Molecular changes in a/chicken/pennsylvania/83 (H5N2) influenza virus associated with acquisition of virulence. Virology 1986, 149, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, K.L.; Fried, V.A.; Ando, M.; Webster, R.G. Glycosylation affects cleavage of an H5N2 influenza virus hemagglutinin and regulates virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, C.; Hall, H.; Huang, J.; Klimov, A.; Cox, N.; Hay, A.; Gregory, V.; Cameron, K.; Lim, W.; Subbarao, K. Characterization of the surface proteins of influenza A (H5N1) viruses isolated from humans in 1997–1998. Virology 1999, 254, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, S.; Larcher, T.; Cormier-Aline, F.; Soubieux, D.; Su, B.; Guigand, L.; Labrosse, B.; Cherel, Y.; Quéré, P.; Marc, D.; et al. A genetically engineered waterfowl influenza virus with a deletion in the stalk of the neuraminidase has increased virulence for chickens. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosaad, Z.; Arafa, A.; Hussein, H.A.; Shalaby, M.A. Mutation signature in neuraminidase gene of avian influenza H9N2/G1 in Egypt. Virusdisease 2017, 28, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Cui, J.-Q.; He, X.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Yao, K.-C.; Cao, S.-J.; Huang, Y. Genetic and antigenic evolution of H9N2 subtype avian influenza virus in domestic chickens in southwestern China, 2013–2016. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.; Yaqub, T.; Reddy, K.; McCauley, J.W. Novel genotypes of H9N2 Influenza A viruses isolated from poultry in Pakistan containing NS genes similar to highly pathogenic H7N3 and H5N1 viruses. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suttie, A.; Deng, Y.-M.; Greenhill, A.R.; Dussart, P.; Horwood, P.F.; Karlsson, E.A. Inventory of molecular markers affecting biological characteristics of avian influenza A viruses. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 739–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nao, N.; Kajihara, M.; Manzoor, R.; Maruyama, J.; Yoshida, R.; Muramatsu, M.; Miyamoto, H.; Igarashi, M.; Eguchi, N.; Sato, M.; et al. A single amino acid in the M1 protein responsible for the different pathogenic potentials of H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus strains. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Peng, C.; Luo, J.; Wang, C.; Han, L.; Wu, B.; Ji, G.; He, H. Adamantane-resistant influenza A viruses in the world (1902–2013): Frequency and distribution of M2 gene mutations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.K.; Yong, C.Y.; Tan, W.S.; Yeap, S.K.; Omar, A.R.; Razak, M.A.; Ho, K.L. An influenza A vaccine based on the extracellular domain of matrix 2 protein protects BALB/C mice against H1N1 and H3N2. Vaccines 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninyio, N.N.; Ho, K.L.; Omar, A.R.; Tan, W.S.; Iqbal, M.; Mariatulqabtiah, A.R. Virus-like particle vaccines: A prospective panacea against an avian influenza panzootic. Vaccines 2020, 8, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.; Jang, Y.; Kwon, S.; Lee, C.; Han, G.; Seong, B. Glycosylation of hemagglutinin and neuraminidase of influenza A virus as signature for ecological spillover and adaptation among influenza reservoirs. Viruses 2018, 10, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hervé, P.-L.; Lorin, V.; Jouvion, G.; Da Costa, B.; Escriou, N. Addition of N-glycosylation sites on the globular head of the H5 hemagglutinin induces the escape of highly pathogenic avian influenza A H5N1 viruses from vaccine-induced immunity. Virology 2015, 486, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, J.L.; Gilbertson, B.P.; Trifkovic, S.; Brown, L.E.; McKimm-Breschkin, J.L. Influenza virus neuraminidase structure and functions. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, F.; Xiong, C.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, Q. Could a deletion in neuraminidase stalk strengthen human tropism of the novel avian influenza virus H7N9 in China, 2013? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Direction | Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA | Forward | TATTCGTCTCAGGGAGCAAAAGCAAGGG | 1733 | [14] |
| Reverse | ATATCGTCTCGTATTAGTAGAAA CAAGGGTGTTTT | |||
| NA | Forward | TATTGGTCTCAGGGAGCAAAAGCA GGAGTAGGAGT | 1431 | [14] |
| Reverse | ATATGGTCTCGTATTAGTAGAAAC AAGGAGTTTTTT | |||
| M | Forward | TATTCGTCTCAGGGGCAAAAGCAGGTAG | 1027 | [14] |
| Reverse | ATATCGTCTCGTATTAGTAGAAAC AAGGTAGTTTTT | |||
| N2 | Forward Reverse | GCATGGTCCAGTTCAAGTTG CCTTTCCAGTTGTCTCTGCA | 362 | [15] |
| Strain | Cleavage Site | Molecular Criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| (A/duck/Malaysia/8443/2004(H5N2)) | PQRE----TRGL | LPAI | This study |
| (A/duck/Japan/9UO036/2009(H5N2)) | PQRE----TRGL | LPAI | JX673924.1 |
| (A/duck/Hokkaido/193/04(H5N3)) | PQRE----TRGL | LPAI | AB241625.1 |
| (A/migratoryduck/Jiang Xi/13487/2005(H5N3)) | PQRE----TRGL | LPAI | EF597260.1 |
| (A/turkey/Italy/1325/2005(H5N2)) | PQRE----TRGL | LPAI | CY022629.1 |
| (A/duck/Malaysia/F118-08-04/2004(H5N2)) | PQRE----TRGL | LPAI | DQ104701.1 |
| (A/duck broiler/Malaysia/F189/07/04(H5N2)) | PQRE----TRGL | LPAI | DQ122147.1 |
| (A/mallard/Ohio/11OS2229/2011(H5N2)) | PQRE----TRGL | LPAI | CY132453.1 |
| (A/duck/New York/483239/2007(H5N2)) | PQKE----TKGL | LPAI | GU049935.1 |
| (A/mallard/British Columbia/07826/2005(H5N2)) | PQRE----TRGL | LPAI | CY047496.1 |
| (A/duck/Hokkaido/W103/2017(H5N2)) | PQRE----TRGL | LPAI | MK592509.1 |
| (A/duck/Hebei/0908/2009(H5N2)) | PQIEGRRRKRGL | HPAI | JQ041399.1 |
| (A/goose/Guangdong/1/1996(H5N1)) | PQRERRRKKRGL | HPAI | NC_007362.1 |
| (A/duck/Guangdong/40/2000(H5N1)) | PQRERRRKKRGL | HPAI | AY585374.1 |
| (A/duck/Guangxi/53/2002(H5N1)) | PQRERRRKKRGL | HPAI | AY585366.1 |
| (A/duck/Guangzhou/20/2005(H5N1)) | PQRERRRKKRGL | HPAI | DQ320901.1 |
| (A/duck/Cambodia/D3KP/2006(H5N1)) | PQRERRRKKRGL | HPAI | HQ200519.1 |
| (A/duck/Thailand/TS04/2006(H5N1)) | PQRERRRKKRGL | HPAI | JQ794470.1 |
| Virus Strain | Amino Acid Position | Reference | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 113 | 124 | 142 | 154 | 228 | 233 | 337–349 (Cleavage Site) | ||
| A/duck/Malaysia/8443/2004(H5N2) | D | T | D | N | S | P | PQRETR---GLF | |
| (A/duck/Guangzhou/20/2005(H5N1)) | D | I | E | L | K | S | PQRERRRKKRGLF | |
| (A/duck/Thailand/TS04/2006(H5N1)) | D | I | E | L | R | S | PQRERRRKKRGLF | |
| (A/duck/Hebei/0908/2009(H5N2)) | D | I | E | L | K | S | PQIEGRRRKRGLF | |
| A/spotbill duck/Xuyi/18/2005(H5N2) | D | I | E | N | K | S | PQRERRRKKRGLF | |
| Virus Strains | Potential N-Gly-Position | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Globular Domain | Stalk Domain | |||||||||||||||
| 39 | 88 | 156 | 170 | 179 | 181 | 209 | 252 | 289 | 26 | 27 | 302 | 496 | 500 | 555 | 559 | |
| A/duck/Malaysia/8443/2004(H5N2) | NVTV | - | - | - | - | NNTN | - | - | - | NNST | NSTE | NSTM | NGTY | - | NGSL | - |
| A/duck/Hebei/0908/2009(H5N2) | NVTV | NVSE | NPSF | NSTY | NYTN | - | - | - | - | NNST | NSTE | NSSM | - | NGTY | - | NGSL |
| A/spotbill duck/Xuyi/18/2005(H5N2) | NVTV | - | - | NSTY | - | NNTN | - | - | - | NNST | NSTE | NSSM | - | NGTY | - | NGSL |
| A/duck/Guangzhou/20/2005(H5N1) | NVTV | - | - | - | - | NNTN | NPTT | - | - | NNST | NSTE | NSSM | - | NGTY | - | NGSL |
| A/duck/Thailand/TS04/2006(H5N1) | NVTV | - | - | NSTY | - | NNTN | NPTT | - | - | NNST | NSTE | NSSM | - | NGTY | - | NGSL |
| Virus | Deletion of the Stalk Region | Haemadsorbing Site | Active Centre | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 366–373 | 399–404 | 431–433 | 140–157 | ||
| (A/Duck/Malaysia/8443/2004(H5N2)) | NO | ISKDSRSG | DNSNWS | PQE | LDNKHSNGTIHDRIPHRTL |
| (A/duck/Hebei/0908/2009(H5N2)) | NO | ISKDSRSG | DNSNWS | PQE | LNNKHSNGTIHDRIPNRTL |
| A/spotbill duck/Xuyi/18/2005(H5N2) | NO | ISKDSRSG | DNNNWS | PQE | LDNKHSNGTIHDRIPHRTL |
| (A/chicken/Shandong/S3/2014(H5N2)) | 63–65 | IKSDLRSG | DSESWS | PRE | LKNKHSNGTTHDRIPHRTL |
| (A/chicken/Hebei/1102-MA/2010(H5N2)) | 63–65 | IKSDSRSG | DSDSWS | PQE | LRNKHSNGTTHDRIPHRTL |
| Virus Strain | Potential N-Gly-Position | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 61 | 66 | 69 | 70 | 83 | 86 | 143 | 146 | 155 | 197 | 200 | 231 | 234 | 242 | 261 | 402 | |
| (A/Duck/Malaysia/8443/2004(H5N2)) | NIT | - | NNT | - | - | - | - | NGT | - | - | NAT | - | NGT | - | - | NWS |
| (A/duck/Hebei/0908/2009(H5N2)) | NIT | - | NNT | NTT | - | NWS | - | NGT | NRT | - | NAT | - | NGT | - | - | NWS |
| A/spotbill duck/Xuyi/18/2005(H5N2) | NIT | - | NNT | NTT | - | - | - | NGT | - | - | NAT | NGT | - | - | - | NWS |
| A/chicken/Shandong/S3/2014(H5N2)) | - | NST | - | - | NWS | - | NGT | - | - | NAT | - | NGT | - | NAS | NVS | - |
| (A/chicken/Hebei/1102-MA/2010(H5N2)) | - | NST | - | - | NWS | - | NGT | - | - | NAT | - | NGT | - | - | NIS | - |
| Virus Strain | Protein and the Specific Amino Acid Markers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | |||||||
| N30D | I43M | T215A | L26F | I/V27A/T/S | A30V/T/S | S31N/G | G34E | |
| Increased Virulence in Mice | Increased Virulence in Mice, Chickens, and Ducks | Increased Virulence in Mice | Increased Resistance to Amantadine and Rimantadine | |||||
| A/duck/Malaysia/8443/2004(H5N2) | D | M | A | L | V | A | S | G |
| A/duck/Guangzhou/20/2005(H5N1) | D | M | A | - | - | - | - | - |
| A/duck/Thailand/TS04/2006(H5N1) | D | M | A | L | V | A | N | G |
| A/duck/Hebei/0908/2009(H5N2) | D | M | A | L | V | A | S | G |
| A/chicken/Hebei/1102-MA/2010(H5N2)) | D | M | A | L | V | A | N | G |
| A/chicken/Shandong/S3/2014(H5N2) | D | M | A | L | V | A | N | G |
| A/chicken/Jiangsu/1001/2013(H5N2) | D | M | A | L | V | A | N | G |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizal, F.A.; Ho, K.L.; Omar, A.R.; Tan, W.S.; Mariatulqabtiah, A.R.; Iqbal, M. Sequence Analysis of the Malaysian Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus Strain H5N2 from Duck. Genes 2023, 14, 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101973
Rizal FA, Ho KL, Omar AR, Tan WS, Mariatulqabtiah AR, Iqbal M. Sequence Analysis of the Malaysian Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus Strain H5N2 from Duck. Genes. 2023; 14(10):1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101973
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizal, Fatin Ahmad, Kok Lian Ho, Abdul Rahman Omar, Wen Siang Tan, Abdul Razak Mariatulqabtiah, and Munir Iqbal. 2023. "Sequence Analysis of the Malaysian Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus Strain H5N2 from Duck" Genes 14, no. 10: 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101973
APA StyleRizal, F. A., Ho, K. L., Omar, A. R., Tan, W. S., Mariatulqabtiah, A. R., & Iqbal, M. (2023). Sequence Analysis of the Malaysian Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus Strain H5N2 from Duck. Genes, 14(10), 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101973






