Identification of Missense Variants Affecting Carcass Traits for Hanwoo Precision Breeding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, SNP Genotyping, and Quality Control
2.2. Imputation, Lift-Over, and Annotation
2.3. Variance Component Estimation of Genome Regions
2.4. Exon-Specific Association Test (ESAS)
2.5. Favorable and Unfavorable Haplotypes
2.6. Genomic Prediction
2.7. Prediction of Damaging Causal Mutations and Structure
3. Results
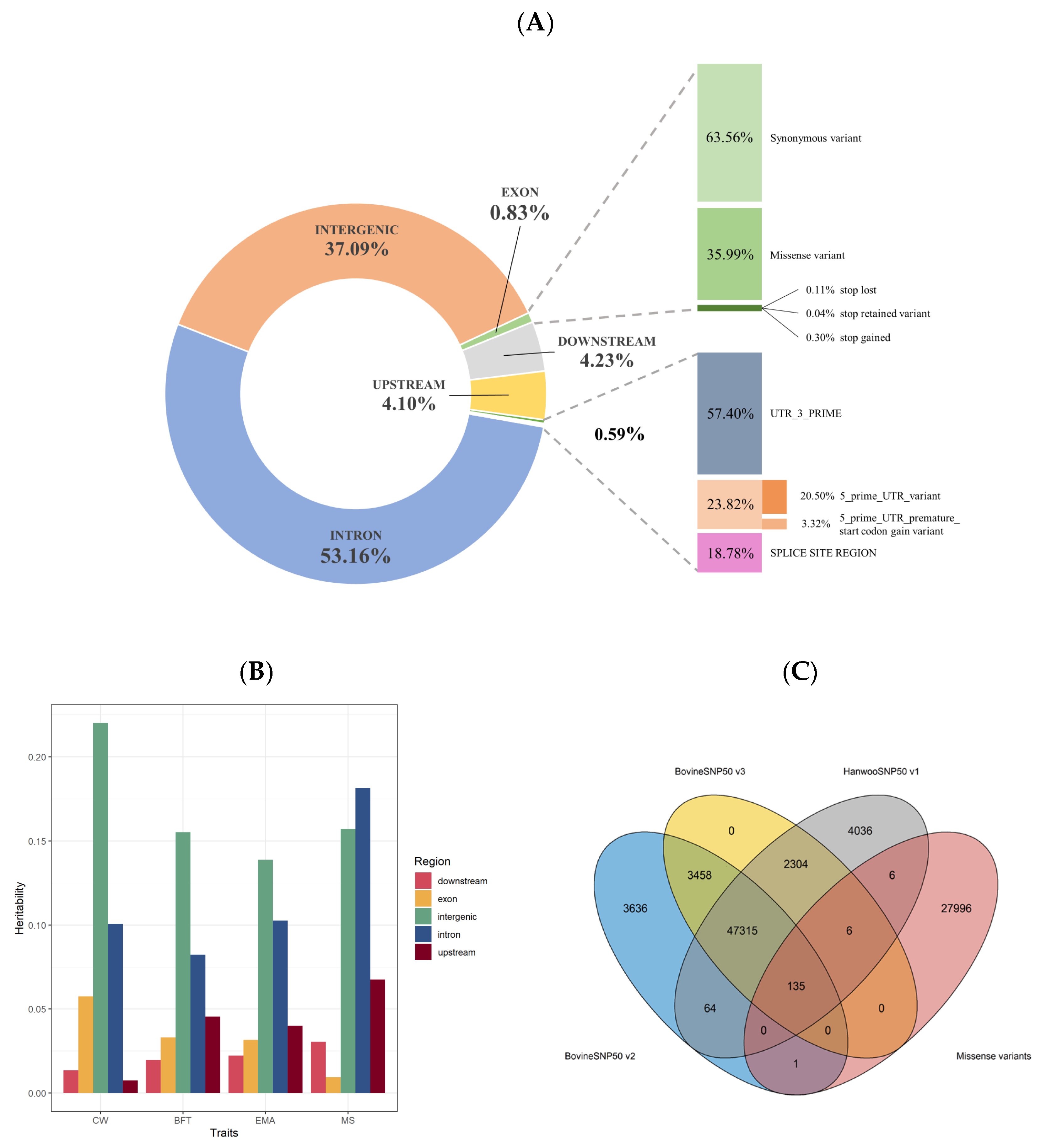
3.1. Genome Partitioning of Genetic Variation
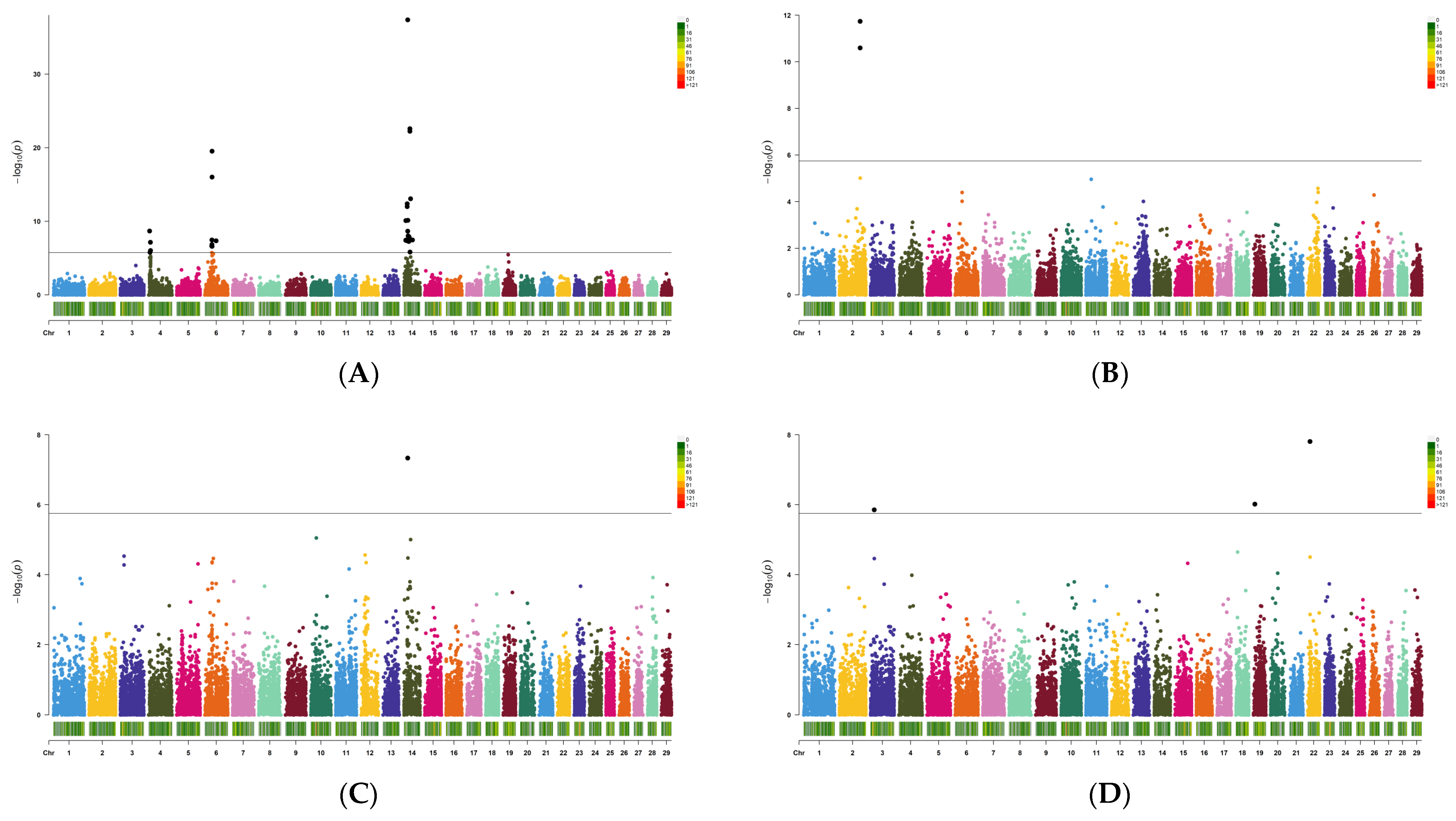
3.2. Identification of Candidate Causal Variants
3.3. Explanatory Power of Candidate SNPs
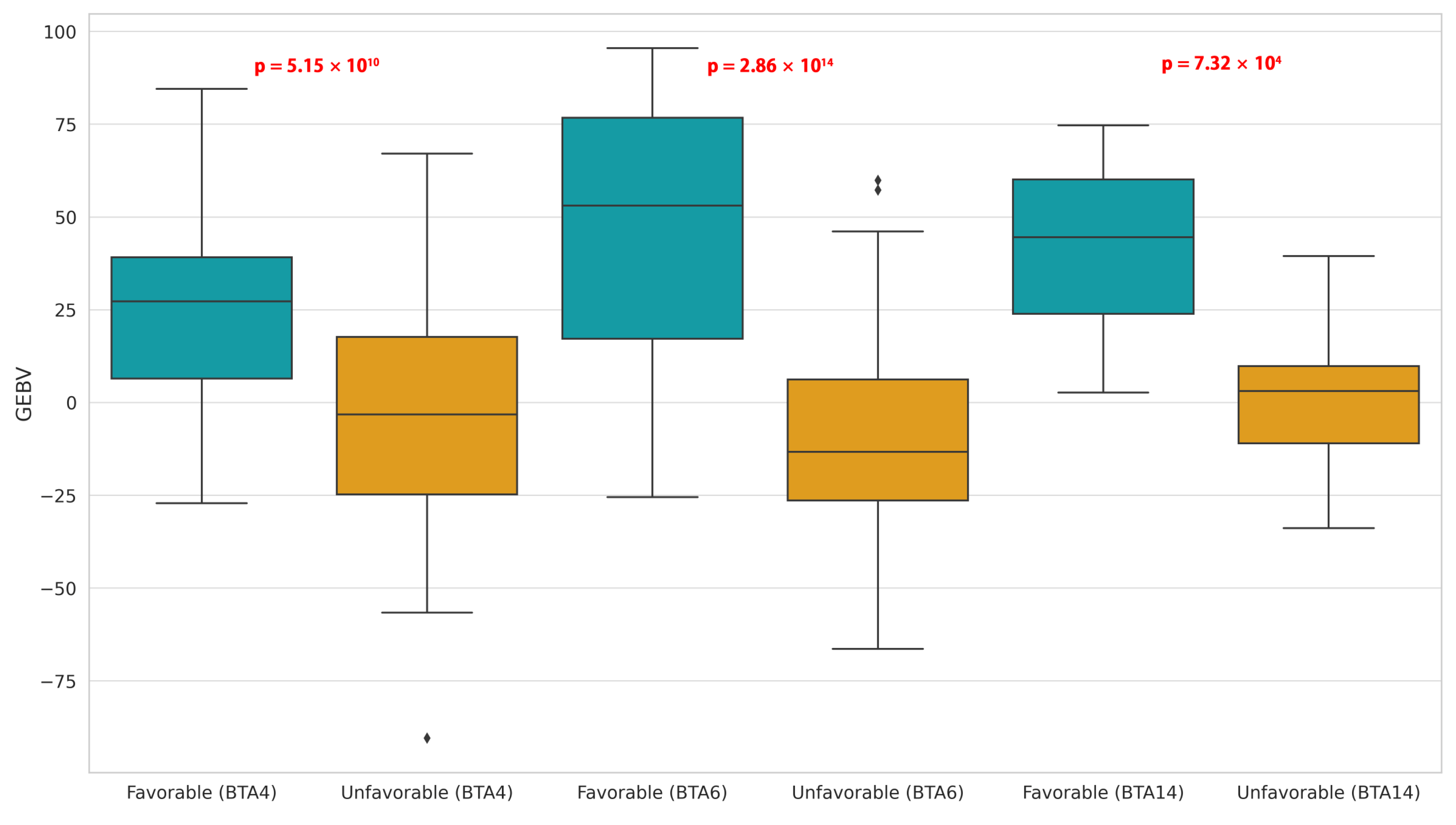
3.4. Favorable and Unfavorable Homozygous Haplotypes
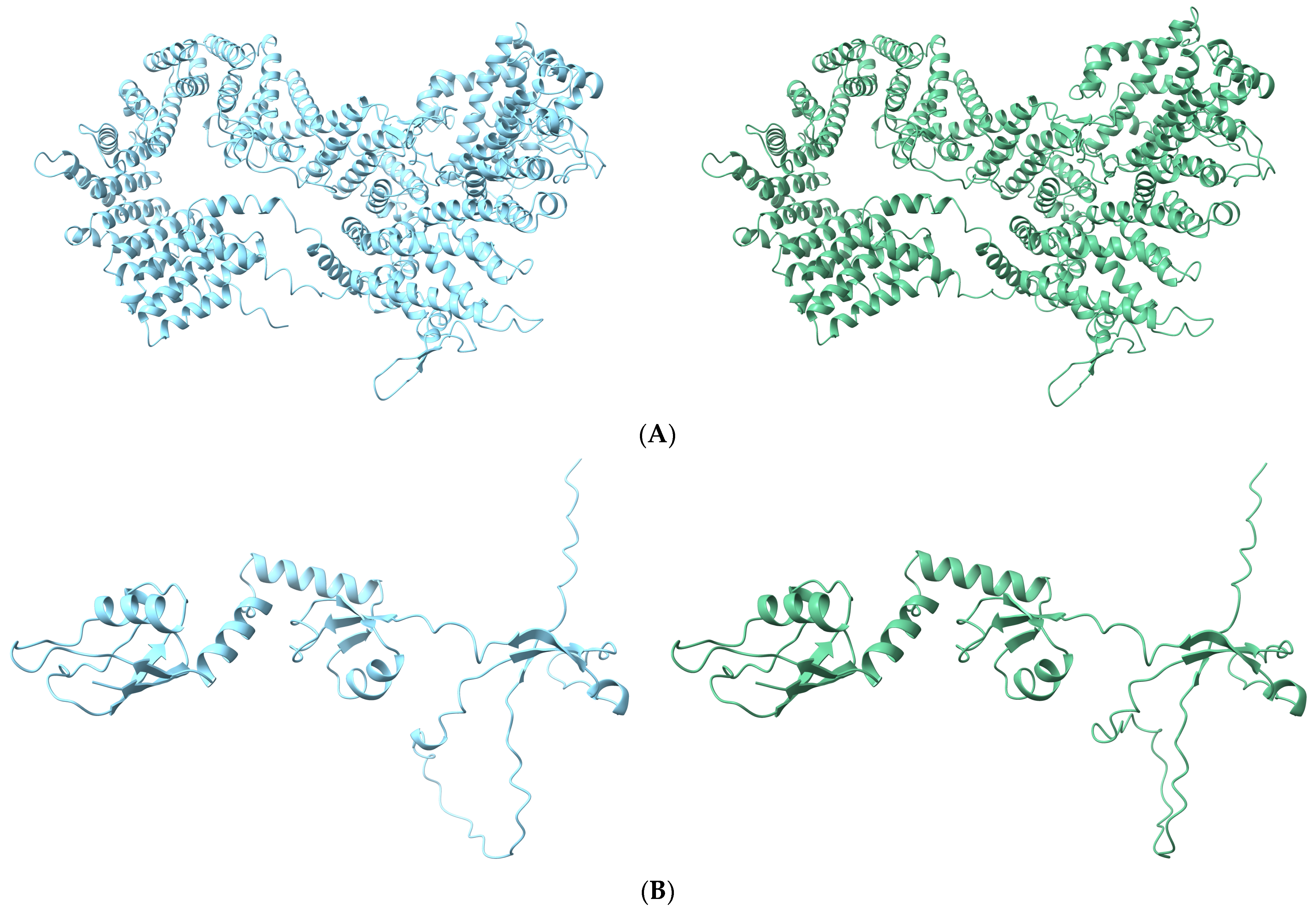
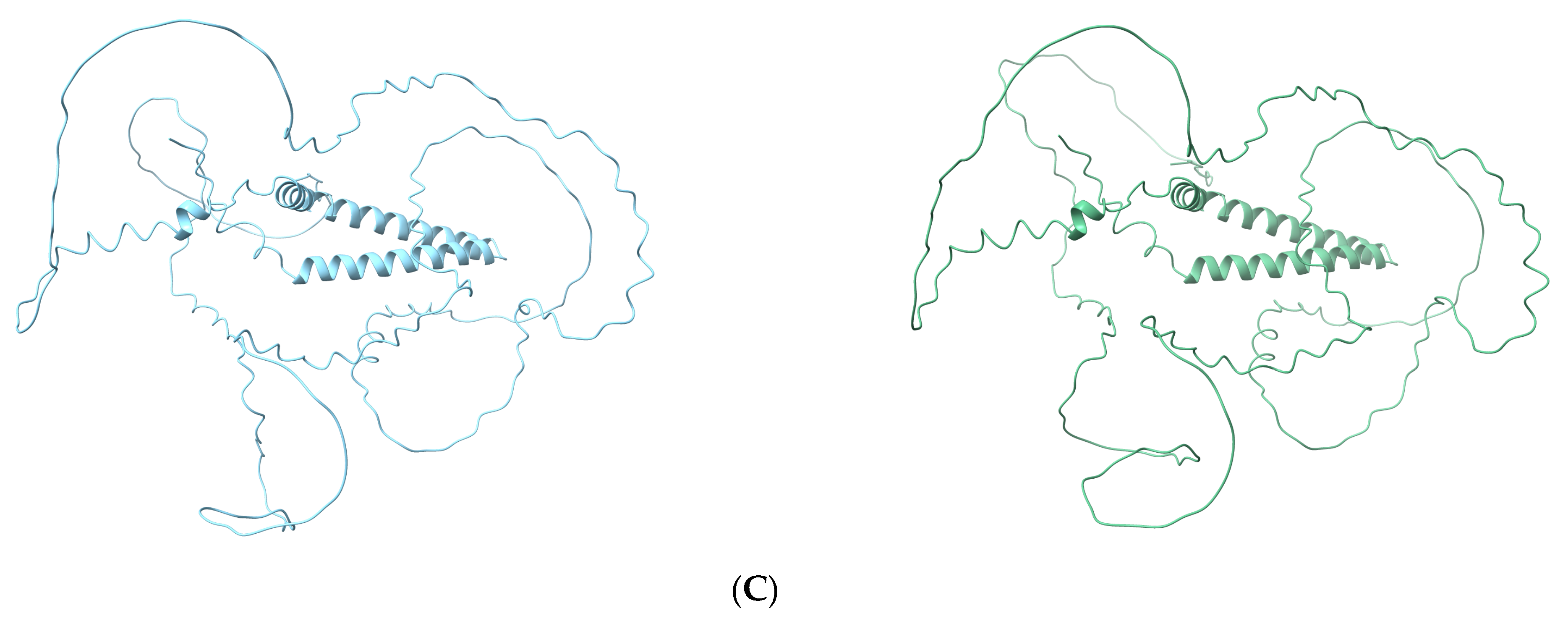
3.5. Effects of Causal Variants on Protein Structure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edea, Z.; Jeoung, Y.H.; Shin, S.-S.; Ku, J.; Seo, S.; Kim, I.-H.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, K.-S. Genome-wide association study of carcass weight in commercial Hanwoo cattle. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koufariotis, L.; Chen, Y.-P.P.; Bolormaa, S.; Hayes, B.J. Regulatory and coding genome regions are enriched for trait associated variants in dairy and beef cattle. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVean, G.A.; Altshuler, D.M.; Durbin, R.M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Bentley, D.R.; Chakravarti, A.; Clark, A.G.; Donnelly, P.; Eichler, E.E.; Flicek, P.; et al. An integrated map of genetic variation from 1092 human genomes. Nature 2012, 491, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daetwyler, H.D.; Capitan, A.; Pausch, H.; Stothard, P.; Van Binsbergen, R.; Brøndum, R.F.; Liao, X.; Djari, A.; Rodriguez, S.C.; Grohs, C. Whole-genome sequencing of 234 bulls facilitates mapping of monogenic and complex traits in cattle. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Cole, J.B.; Freebern, E.; Da, Y.; VanRaden, P.M.; Ma, L. Functional annotation and Bayesian fine-mapping reveals candidate genes for important agronomic traits in Holstein bulls. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freebern, E.; Santos, D.J.; Fang, L.; Jiang, J.; Parker Gaddis, K.L.; Liu, G.E.; VanRaden, P.M.; Maltecca, C.; Cole, J.B.; Ma, L. GWAS and fine-mapping of livability and six disease traits in Holstein cattle. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; de las Heras-Saldana, S.; Moghaddar, N.; Lee, S.H.; Lim, D.; van der Werf, J.H. Genome-wide association study for carcass traits in Hanwoo cattle using additional relatives’ information of non-genotyped animals. Anim. Genet. 2022, 53, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Macciardi, F.; Subramanian, A.; Guffanti, G.; Potkin, S.G.; Yu, Z.; Xie, X. SNP-based pathway enrichment analysis for genome-wide association studies. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, C.; Jiang, J.; Paul, D.; Zhao, H. Variance estimation and confidence intervals from genome-wide association studies through high-dimensional misspecified mixed model analysis. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2022, 220, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaid, D.J.; Chen, W.; Larson, N.B. From genome-wide associations to candidate causal variants by statistical fine-mapping. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schork, A.J.; Thompson, W.K.; Pham, P.; Torkamani, A.; Roddey, J.C.; Sullivan, P.F.; Kelsoe, J.R.; O’Donovan, M.C.; Furberg, H.; Tobacco; et al. All SNPs are not created equal: Genome-wide association studies reveal a consistent pattern of enrichment among functionally annotated SNPs. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreassen, O.A.; Thompson, W.K.; Schork, A.J.; Ripke, S.; Mattingsdal, M.; Kelsoe, J.R.; Kendler, K.S.; O’Donovan, M.C.; Rujescu, D.; Werge, T. Improved detection of common variants associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder using pleiotropy-informed conditional false discovery rate. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöstedt, E.; Zhong, W.; Fagerberg, L.; Karlsson, M.; Mitsios, N.; Adori, C.; Oksvold, P.; Edfors, F.; Limiszewska, A.; Hikmet, F. An atlas of the protein-coding genes in the human, pig, and mouse brain. Science 2020, 367, eaay5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindorff, L.A.; Sethupathy, P.; Junkins, H.A.; Ramos, E.M.; Mehta, J.P.; Collins, F.S.; Manolio, T.A. Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9362–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindt, A.S.; Navarro, P.; Semple, C.A.; Haley, C.S. The genomic signature of trait-associated variants. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosino, M.; Novak, L.; Pasquo, A.; Chiaraluce, R.; Turina, P.; Capriotti, E.; Consalvi, V. Analysis and Interpretation of the Impact of Missense Variants in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Henikoff, S.; Ng, P.C. Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.C.; Henikoff, S. Predicting the Effects of Amino Acid Substitutions on Protein Function. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2006, 7, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.; Simpkin, A.J.; Hartmann, M.D.; Rigden, D.J.; Keegan, R.M.; Lupas, A.N. High-accuracy protein structure prediction in CASP14. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2021, 89, 1687–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadi, M.; Anyango, S.; Deshpande, M.; Nair, S.; Natassia, C.; Yordanova, G.; Yuan, D.; Stroe, O.; Wood, G.; Laydon, A.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: Massively expanding the structural coverage of protein-sequence space with high-accuracy models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, D439–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadi, M.; Velankar, S. The impact of AlphaFold Protein Structure Database on the fields of life sciences. Proteomics 2022, 23, 2200128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.H.; Shatkay, H. An integrative scoring system for ranking SNPs by their potential deleterious effects. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juran, B.D.; Lazaridis, K.N. Genomics in the post-GWAS era. In Seminars in Liver; Thieme Medical Publishers: Leipzig, Germany, 2011; pp. 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Forer, L.; Schönherr, S.; Sidore, C.; Locke, A.E.; Kwong, A.; Vrieze, S.I.; Chew, E.Y.; Levy, S.; McGue, M.; et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Manolio, T.A.; Pasquale, L.R.; Boerwinkle, E.; Caporaso, N.; Cunningham, J.M.; De Andrade, M.; Feenstra, B.; Feingold, E.; Hayes, M.G. Genome partitioning of genetic variation for complex traits using common SNPs. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.; Chasman, D.I.; Smith, J.D.; Mora, S.; Ridker, P.M.; Nickerson, D.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Stephens, M. A multivariate genome-wide association analysis of 10 LDL subfractions, and their response to statin treatment, in 1868 Caucasians. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, M.; Smith, N.J.; Donnelly, P. A New Statistical Method for Haplotype Reconstruction from Population Data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 68, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, M.; Scheet, P. Accounting for Decay of Linkage Disequilibrium in Haplotype Inference and Missing-Data Imputation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 76, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misztal, I.; Tsuruta, S.; Strabel, T.; Auvray, B.; Druet, T.; Lee, D. BLUPF90 and related programs (BGF90). In Proceedings of the 7th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production, Montpellier, France, 19–23 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- VanRaden, P.M. Efficient Methods to Compute Genomic Predictions. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4414–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdita, M.; Schütze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Iqbal, A.; Kim, J.-J. A whole genome association study to detect additive and dominant single nucleotide polymorphisms for growth and carcass traits in Korean native cattle, Hanwoo. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikanth, K.; Lee, S.-H.; Chung, K.-Y.; Park, J.-E.; Jang, G.-W.; Park, M.-R.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, T.-H.; Chai, H.-H.; Park, W.C.; et al. A Gene-Set Enrichment and Protein–Protein Interaction Network-Based GWAS with Regulatory SNPs Identifies Candidate Genes and Pathways Associated with Carcass Traits in Hanwoo Cattle. Genes 2020, 11, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuiyan, M.S.A.; Lim, D.; Park, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Gondro, C.; Park, B.; Lee, S. Functional Partitioning of Genomic Variance and Genome-Wide Association Study for Carcass Traits in Korean Hanwoo Cattle Using Imputed Sequence Level SNP Data. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wayt, J.; Bretscher, A. Cordon Bleu serves as a platform at the basal region of microvilli, where it regulates microvillar length through its WH2 domains. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 2817–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Dominguez, R. Regulation of actin cytoskeleton dynamics in cells. Mol. Cells 2010, 29, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, L.; Bugyi, B.; Carlier, M.-F. Spire and Cordon-bleu: Multifunctional regulators of actin dynamics. Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 18, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, R.; Pinyol, R.; Reichenbach, N.; Custer, L.; Klingensmith, J.; Kessels, M.M.; Qualmann, B. Cordon-bleu is an actin nucleation factor and controls neuronal morphology. Cell 2007, 131, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm-Perry, A.K.; Sexten, A.K.; Kuehn, L.A.; Smith, T.P.L.; King, D.A.; Shackelford, S.D.; Wheeler, T.L.; Ferrell, C.L.; Jenkins, T.G.; Snelling, W.M.; et al. Association, effects and validation of polymorphisms within the NCAPG-LCORL locus located on BTA6 with feed intake, gain, meat and carcass traits in beef cattle. BMC Genet. 2011, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setoguchi, K.; Watanabe, T.; Weikard, R.; Albrecht, E.; Kühn, C.; Kinoshita, A.; Sugimoto, Y.; Takasuga, A. The SNP c.1326T > G in the non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit G (NCAPG) gene encoding a p.Ile442Met variant is associated with an increase in body frame size at puberty in cattle. Anim. Genet. 2011, 42, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randhawa, I.A.S.; Khatkar, M.S.; Thomson, P.C.; Raadsma, H.W. Composite Selection Signals for Complex Traits Exemplified Through Bovine Stature Using Multibreed Cohorts of European and African Bos taurus. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2015, 5, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindholm-Perry, A.K.; Kuehn, L.A.; Oliver, W.T.; Sexten, A.K.; Miles, J.R.; Rempel, L.A.; Cushman, R.A.; Freetly, H.C. Adipose and muscle tissue gene expression of two genes (NCAPG and LCORL) located in a chromosomal region associated with cattle feed intake and gain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80882. [Google Scholar]
- Ealy, A.D.; Yang, Q.E.; Ozawa, M.; Johnson, S.E. Expression Profiling and Potential Functions of Protein Kinase C Delta During Early Bovine Embryo Development. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 87, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiong, J.; Lan, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, J.; Fei, Z.; Zheng, X.; Chen, C. Role of PRKDC in cancer initiation, progression, and treatment. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-J.; Gavrilova, O.; Brown, A.L.; Soto, J.E.; Bremner, S.; Kim, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, S.; Um, J.-H.; Koch, L.G. DNA-PK promotes the mitochondrial, metabolic, and physical decline that occurs during aging. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1135–1146.e1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimering, M.B.; Delic, V.; Citron, B.A. Gene expression changes in a model neuron cell line exposed to autoantibodies from patients with traumatic brain injury and/or Type 2 diabetes. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 4365–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C.; Wang, H.; Liao, Q.; Khan, R.; Raza, S.H.A.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; Cheng, G.; Tian, W.; Li, Y. Genome-wide analysis reveals the effects of artificial selection on production and meat quality traits in Qinchuan cattle. Genomics 2019, 111, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettre, G.; Jackson, A.U.; Gieger, C.; Schumacher, F.R.; Berndt, S.I.; Sanna, S.; Eyheramendy, S.; Voight, B.F.; Butler, J.L.; Guiducci, C.; et al. Identification of ten loci associated with height highlights new biological pathways in human growth. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.R.; Esko, T.; Yang, J.; Vedantam, S.; Pers, T.H.; Gustafsson, S.; Chu, A.Y.; Estrada, K.; Luan, J.A.; Kutalik, Z.; et al. Defining the role of common variation in the genomic and biological architecture of adult human height. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.; Metter, E.J.; Ferrucci, L.; Roth, S.M. Activin-type II receptor B (ACVR2B) and follistatin haplotype associations with muscle mass and strength in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 2142–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trait | Chr:Pos | Allele | RefSNPID | Gene | SNPeffect | SE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CW | 4:4857791 | A/G | rs210475204 | COBL | 6.507 | 1.09 | 2.195 × 10−9 |
| 4:9502576 | C/T | rs445255852 | LRRD1 | 6.653 | 1.24 | 7.130 × 10−8 | |
| 4:9875221 | G/A | rs379759182 | RBM48 | 4.342 | 0.89 | 9.806 × 10−7 | |
| 4:7208133 | C/T | rs516634298 | ABCA13 | 3.780 | 0.79 | 1.666 × 10−6 | |
| 6:37403795 | T/C | rs109696064 | LCORL | 13.712 | 1.49 | 3.011 × 10−20 | |
| 6:37343379 | G/T | rs109570900 | NCAPG | 11.838 | 1.43 | 9.919 × 10−17 | |
| 6:36630884 | T/C | rs383697460 | PKD2 | 15.613 | 2.83 | 3.458 × 10−8 | |
| 6:58146321 | G/A | rs797342426 | Hypothetical | 14.673 | 2.68 | 4.520 × 10−8 | |
| 6:36880429 | C/T | rs716537943 | IBSP | 7.977 | 1.52 | 1.490 × 10−7 | |
| 6:36028197 | G/A | rs383620650 | FAM13A | 8.228 | 1.59 | 2.346 × 10−7 | |
| 6:37237698 | T/C | rs210785796 | FAM184B | −4.537 | 0.88 | 2.626 × 10−7 | |
| 14:19524263 | T/C | rs449968016 | PRKDC | 16.417 | 1.27 | 4.337 × 10−38 | |
| 14:30393332 | C/A | rs109953090 | DNAJC5B | 10.964 | 1.10 | 2.686 × 10−23 | |
| 14:30518533 | T/C | rs381116984 | CRH | 10.866 | 1.10 | 5.889 × 10−23 | |
| 14:33878123 | A/G | rs464130691 | NCOA2 | 10.022 | 1.34 | 8.765 × 10−14 | |
| 14:16328530 | A/G | rs471616366 | Hypothetical | 10.655 | 1.47 | 4.335 × 10−13 | |
| 14:16641005 | C/T | rs211636635 | TBC1D31 | 10.450 | 1.47 | 1.045 × 10−12 | |
| 14:16698021 | G/T | rs208131933 | TBC1D31 | 10.450 | 1.47 | 1.045 × 10−12 | |
| 14:19984551 | A/G | rs109071668 | PPDPFL | 4.505 | 0.69 | 7.512 × 10−11 | |
| 14:9051405 | A/T | rs209264955 | HHLA1 | 5.423 | 0.84 | 8.386 × 10−11 | |
| 14:19372860 | T/C | rs210839501 | SPIDR | 3.949 | 0.66 | 2.213 × 10−9 | |
| 14:21195722 | G/T | rs380004533 | ST18 | −4.275 | 0.75 | 9.922 × 10−9 | |
| 14:26475692 | A/G | rs381829093 | CHD7 | −4.136 | 0.73 | 1.314 × 10−8 | |
| 14:31303419 | G/A | rs109820067 | CSPP1 | −3.879 | 0.70 | 2.738 × 10−8 | |
| 14:43787543 | A/G | rs380389290 | Hypothetical | 5.905 | 1.07 | 3.557 × 10−8 | |
| 14:9111310 | T/C | rs209285140 | OC90 | 4.037 | 0.73 | 3.609 × 10−8 | |
| 14:9111217 | A/G | rs210209375 | OC90 | 4.036 | 0.73 | 3.659 × 10−8 | |
| 14:16590597 | T/C | rs207540257 | FAM83A | 6.487 | 1.18 | 3.713 × 10−8 | |
| 14:16590776 | T/C | rs380808409 | FAM83A | 6.487 | 1.18 | 3.713 × 10−8 | |
| 14:9111232 | G/A | rs207841625 | OC90 | 3.968 | 0.72 | 4.009 × 10−8 | |
| 14:16609068 | T/A | rs210725961 | FAM83A | 6.441 | 1.18 | 4.470 × 10−8 | |
| 14:24756697 | T/C | rs136157938 | SDCBP | −3.559 | 0.66 | 5.573 × 10−8 | |
| 14:30837447 | C/T | rs109134892 | MYBL1 | −3.230 | 0.67 | 1.567 × 10−6 | |
| BFT | 2:107160304 | G/T | rs109446852 | ZFAND2B | 0.799 | 0.11 | 1.840 × 10−12 |
| 2:107114443 | A/G | rs383795443 | SLC23A3 | 0.768 | 0.12 | 2.549 × 10−11 | |
| EMA | 14:19524263 | T/C | rs449968016 | PRKDC | 1.644 | 0.30 | 4.617 × 10−8 |
| MS | 3:19028381 | G/A | rs210416891 | MRPL9 | 0.251 | 0.05 | 1.408 × 10−6 |
| 19:7310638 | G/C | rs799291287 | ANKFN1 | −0.234 | 0.05 | 9.683 × 10−7 | |
| 22:11849704 | G/C | rs799031002 | ACVR2B | 0.298 | 0.05 | 1.567 × 10−8 |
| Trait | CHROM | RefSNPID | Gene | %V(g) | %V(p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CW | BTA4 | rs210475204 | COBL | 1.634 | 0.005 |
| BTA6 | rs109696064 | LCORL | 4.495 | 0.014 | |
| BTA14 | rs449968016 | PRKDC | 8.470 | 0.026 | |
| BFT | BTA2 | rs109446852 | ZFAND2B | 2.075 | 0.006 |
| EMA | BTA14 | rs449968016 | PRKDC | 1.728 | 0.005 |
| MS | BTA3 | rs210416891 | MRPL9 | 1.104 | 0.004 |
| BTA19 | rs799291287 | ANKFN1 | 0.566 | 0.002 | |
| BTA22 | rs799031002 | ACVR2B | 1.187 | 0.004 |
| Trait | Protein | HGVS | Predicted Classification 1 | Damaging Score 2 | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CW | COBL | p.Arg660Gln | No damage | 0.007 | 0.96 | 0.75 |
| LCORL | p.Glu485Lys | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | |
| PRKDC | p.Ala895Thr | Probably damaging | 0.988 | 0.73 | 0.96 | |
| BFT | ZFAND2B | p.Leu117Arg | No damage | 0.000 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| EMA | PRKDC | p.Ala895Thr | Probably damaging | 0.988 | 0.73 | 0.96 |
| MS | MRPL9 | p.Thr226Ala | Probably damaging | 0.998 | 0.27 | 0.99 |
| ANKFN1 | p.Leu174Val | Probably damaging | 0.961 | 0.78 | 0.95 | |
| ACVR2B | p.Thr395Ser | Possibly damaging | 0.734 | 0.85 | 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.J.; Kim, Y.; Dinh, P.T.N.; Chung, Y.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, I.; Lee, S.H. Identification of Missense Variants Affecting Carcass Traits for Hanwoo Precision Breeding. Genes 2023, 14, 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101839
Lee DJ, Kim Y, Dinh PTN, Chung Y, Lee D, Kim Y, Lee SH, Choi I, Lee SH. Identification of Missense Variants Affecting Carcass Traits for Hanwoo Precision Breeding. Genes. 2023; 14(10):1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101839
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dong Jae, Yoonsik Kim, Phuong Thanh N. Dinh, Yoonji Chung, Dooho Lee, Yeongkuk Kim, Soo Hyun Lee, Inchul Choi, and Seung Hwan Lee. 2023. "Identification of Missense Variants Affecting Carcass Traits for Hanwoo Precision Breeding" Genes 14, no. 10: 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101839
APA StyleLee, D. J., Kim, Y., Dinh, P. T. N., Chung, Y., Lee, D., Kim, Y., Lee, S. H., Choi, I., & Lee, S. H. (2023). Identification of Missense Variants Affecting Carcass Traits for Hanwoo Precision Breeding. Genes, 14(10), 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101839





