Prenatal Diagnosis of PPP2R1A-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorders Using Whole Exome Sequencing: Clinical Report and Review of Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
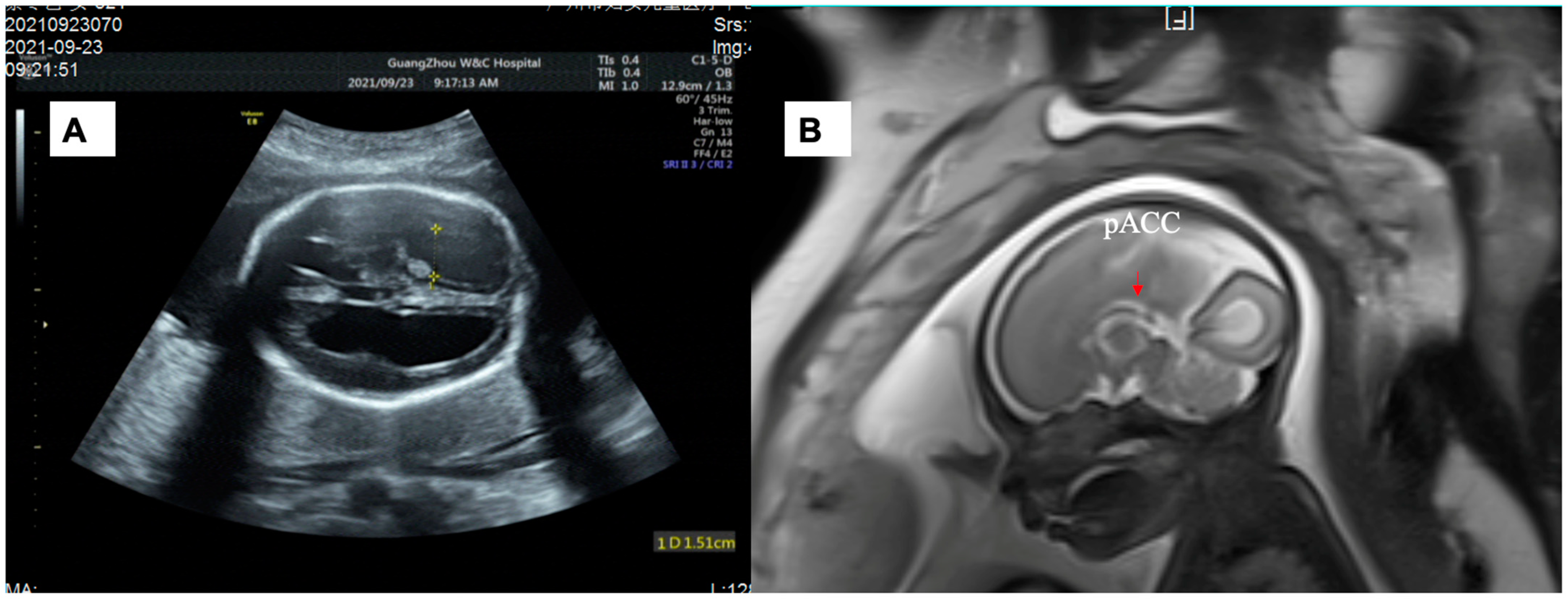
2.1. Case Presentation
2.2. Whole Exome Sequencing
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seshacharyulu, P.; Pandey, P.; Datta, K.; Batra, S.K. Phosphatase: PP2A structural importance, regulation and its aberrant expression in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmings, B.A.; Adams-Pearson, C.; Maurer, F.; Muller, P.; Goris, J.; Merlevede, W.; Hofsteenge, J.; Stone, S.R. α- and β-forms of the 65-kDa subunit of protein phosphatase 2A have a similar 39 amino acid repeating structure. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 3166–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, U.S.; Xu, W. Crystal structure of a protein phosphatase 2A heterotrimeric holoenzyme. Nature 2007, 445, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbinnen, I.; Vaneynde, P.; Reynhout, S.; Lenaerts, L.; Derua, R.; Houge, G.; Janssens, V. Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) mutations in brain function, development, and neurologic disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2021, 49, 1567–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Nie, Z.; Lei, T.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Han, J.; Pan, M.; Zhen, L.; et al. Whole exome sequencing as a diagnostic adjunct to clinical testing in fetuses with structural abnormalities. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2018, 51, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houge, G.; Haesen, D.; Vissers, L.E.L.M.; Mehta, S.; Parker, M.J.; Wright, M.; Vogt, J.; McKee, S.; Tolmie, J.L.; Cordeiro, N.; et al. B56δ-related protein phosphatase 2A dysfunction identified in patients with intellectual disability. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3051–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.; Caruso, P.; Karaa, A. A Newborn with Severe Ventriculomegaly: Expanding the PPP2R1A Gene Mutation Phenotype. J. Pediatr. Genet. 2019, 08, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Jia, Z.; Xi, H.; Mao, X. A De Novo Variant Identified in the PPP2R1A Gene in an Infant Induces Neurodevelopmental Abnormalities. Neurosci. Bull. 2020, 36, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaerts, L.; Reynhout, S.; Verbinnen, I.; Laumonnier, F.; Toutain, A.; Bonnet-Brilhault, F.; Hoorne, Y.; Joss, S.; Chassevent, A.K.; Smith-Hicks, C.; et al. The broad phenotypic spectrum of PPP2R1A-related neurodevelopmental disorders correlates with the degree of biochemical dysfunction. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruxmohan, S.; Quinonez, J.; Yadav, R.S.; Shrestha, S.; Poudel, S.; Stein, J.D. Refractory Epilepsy in a Toddler with PPP2R1A Gene Mutation and Congenital Hydrocephalus. Cureus 2021, 13, e19988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melas, M.; Mathew, M.T.; Mori, M.; Jayaraman, V.; Wilson, S.A.; Martin, C.; Jacobson-Kelly, A.E.; Kelly, B.J.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; et al. Somatic variation as an incidental finding in the pediatric next-generation sequencing era. Mol. Case Stud. 2021, 7, a6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, J.; McMullan, D.J.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Rinck, G.; Hamilton, S.J.; Quinlan-Jones, E.; Prigmore, E.; Keelagher, R.; Best, S.K.; Carey, G.K.; et al. Prenatal exome sequencing analysis in fetal structural anomalies detected by ultrasonography (PAGE): A cohort study. Lancet 2019, 393, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovski, S.; Aggarwal, V.; Giordano, J.L.; Stosic, M.; Wou, K.; Bier, L.; Spiegel, E.; Brennan, K.; Stong, N.; Jobanputra, V.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing in the evaluation of fetal structural anomalies: A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2019, 393, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heide, S.; Keren, B.; Billette, D.V.T.; Chantot-Bastaraud, S.; Depienne, C.; Nava, C.; Mignot, C.; Jacquette, A.; Fonteneau, E.; Lejeune, E.; et al. Copy Number Variations Found in Patients with a Corpus Callosum Abnormality and Intellectual Disability. J. Pediatr. 2017, 185, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, S.; D’Antonio, F.; Homfray, T.; Rich, P.; Pilu, G.; Bhide, A.; Thilaganathan, B.; Papageorghiou, A.T. Counseling in fetal medicine: Agenesis of the corpus callosum. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2012, 40, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siffredi, V.; Anderson, V.; McIlroy, A.; Wood, A.G.; Leventer, R.J.; Spencer-Smith, M.M. A Neuropsychological Profile for Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum? Cognitive, Academic, Executive, Social, and Behavioral Functioning in School-Age Children. J. Int. Neuropsych. Soc. 2018, 24, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.J.; Sherr, E.H.; Barkovich, A.J.; Richards, L.J. Clinical, genetic and imaging findings identify new causes for corpus callosum development syndromes. Brain 2014, 137, 1579–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, M.C.; Boekhorst, F.; Mancini, G.M.; Smit, L.S.; Groenenberg, I.A.L.; Dudink, J.; de Vries, F.A.T.; Go, A.T.J.I.; Galjaard, R.J.H. Advanced genomic testing may aid in counseling of isolated agenesis of the corpus callosum on prenatal ultrasound. Prenat. Diag. 2017, 37, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heide, S.; Spentchian, M.; Valence, S.; Buratti, J.; Mach, C.; Lejeune, E.; Olin, V.; Massimello, M.; Lehalle, D.; Mouthon, L.; et al. Prenatal exome sequencing in 65 fetuses with abnormality of the corpus callosum: Contribution to further diagnostic delineation. Genet Med. 2020, 22, 1887–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.Y.; She, Q.; Fu, F.; Zhen, L.; Li, R.; Yu, Q.X.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.S.; Cheng, K.; Zhou, H.; et al. Prenatal exome sequencing in fetuses with callosal anomalies. Prenat. Diag. 2022. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.deciphergenomics.org/ (accessed on 30 November 2022).

| NO. | Age, Sex at Evaluation | DNA Change | Protein Change | Corpus Callosum | Head Size | Ventricle | Other CNS Findings | Epilepsy | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.5 y, F | c.536C > T | p. P179L | Agenesis of the corpus callosum | - | - | - | - | [7] |
| 2 | 4 y, F | c.544C > T | p. R182W | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | - | ventriculomegaly | - | yes | [7] |
| 3 | 11 y, M | c.544C > T | p. R182W | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | - | - | - | yes | [7] |
| 4 | 1 y, F | c.544C > T | p. R182W | Agenesis of the corpus callosum | - | ventriculomegaly | delayed myelination | yes | [7] |
| 5 | 5 y, M | c.773G > A | p. R258H | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | - | - | delayed myelination | yes | [7] |
| 6 | Newborn, M | c.548G > A | p. R183Q | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | - | severe ventriculomegaly | pontocerebellar hypoplasia | yes | [8] |
| 7 | 9 mo, M | c.656C > T | p. S219L | Agenesis of the corpus callosum | - | ventriculomegaly | reduced brain parenchyma, delayed myelination in the white matter, peripheral and central auditory impairment | yes | [9] |
| 8 | 11 y, F | c.96C > G | p. I32M | - | - | - | - | yes | [10] |
| 9 | 4 y, M | c.421T > A | p. F141I | - | macrocephaly | - | - | - | [10] |
| 10 | 18 y, M | c.455C > T | p. S152F | - | - | - | - | - | [10] |
| 11 | 18 y, F | c.532A > T | p. T178S | - | macrocephaly | - | - | - | [10] |
| 12 | 12 y, M | c.533C > A | p, T178N | - | macrocephaly | - | - | - | [10] |
| 13 | 4 y, M | c.536C > T | p. P179L | Agenesis of the corpus callosum | microcephaly | ventriculomegaly | - | yes | [10] |
| 14 | 3 y 9 mo, M | c.539T > C | p. M180T | - | macrocephaly | - | - | - | [10] |
| 15 | 6 y, F | c.539T > C | p. M180T | - | macrocephaly | - | - | - | [10] |
| 16 | 2 y, F | c.539T > C | p. M180T | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | macrocephaly | - | delayed myelination | - | [10] |
| 17 | 23 y, F | c.539T > C | p. M180T | - | macrocephaly | - | periventricular leukomalacia | - | [10] |
| 18 | 2 y, M | c.539T > C | p. M180T | - | macrocephaly | - | - | - | [10] |
| 19 | 27 y, M | c.538A > G | p. M180V | - | macrocephaly | - | - | - | [10] |
| 20 | 20 y, M | c.538A > G | p. M180V | - | macrocephaly | - | - | - | [10] |
| 21 | 1 y 4mo, M | c.538A > G | p. M180V | - | macrocephaly | - | - | - | [10] |
| 22 | 10 mo, F | c.539T > A | p. M180K | - | - | - | - | yes | [10] |
| 23 | 9 y, F | c.539T > G | p. M180R | - | microcephaly | - | - | - | [10] |
| 24 | 6 y, F | c.544C > T | p. R182W | Agenesis of the corpus callosum | - | ventriculomegaly | - | yes | [10] |
| 25 | 4 y, M | c.544C > T | p. R182W | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | - | ventriculomegaly, hydrocephalus | - | - | [10] |
| 26 | 3 y, F | c.544C > T | p. R182W | Agenesis of the corpus callosum | - | ventriculomegaly | delayed myelination | yes | [10] |
| 27 | 2 y, M | c.547C > T | p. R183W | - | - | ventriculomegaly, hydrocephalus | - | yes | [10] |
| 28 | 20 y, M | c.656C > T | p. S219L | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | microcephaly | - | - | yes | [10] |
| 29 | 2 y 4 mo, M | c.656C > T | p. S219L | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | - | ventriculomegaly | - | yes | [10] |
| 30 | 7 y, M | c.656C > T | p. S219L | - | - | - | [10] | ||
| 31 | 4 y, F | c.658G > A | p. V220M | Agenesis of the corpus callosum | - | ventriculomegaly | - | yes | [10] |
| 32 | 7 y, F | c.658G > A | p. V220M | Agenesis of the corpus callosum | microcephaly | ventriculomegaly | - | yes | [10] |
| 33 | 3 y, M | c.658G > A | p. V220M | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | - | - | periventricular leukomalacia, delayed myelination | - | [10] |
| 34 | 4 y, M | c.658G > A | p. V220M | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | - | periventricular leukomalacia | - | [10] | |
| 35 | 4 y, M | c.773G > A | p. R258H | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | microcephaly | ventriculomegaly | - | yes | [10] |
| 36 | 1 y 6 mo, M | c.773G > A | p. R258H | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | microcephaly | - | - | - | [10] |
| 37 | 1 y 1 mo, M | c.772C > A | p. R258S | Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum | microcephaly | - | - | - | [10] |
| 38 | 14 mo, M | - | - | hypoplastic/absent corpus callosum | macrocephaly | hydrocephalus | pontocerebellar hypoplasia | yes | [11] |
| 39 | 16 mo, M | c.773G > A | p. R258H | - | microcephaly | ventriculomegaly and enlarged third ventricle | - | - | [12] |
| 40 | 26+ gestation weeks, M | c.544C > T | p. R182W | partial agenesis of the corpus callosum | - | severe lateral ventriculomegaly | - | - | our study |
| 41 | 25+ gestation weeks, M | c.547C > T | p. R183W | - | macrocephaly | severe lateral and third ventriculomegaly | - | - | our study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, T.; Zhen, L.; Yang, X.; Pan, M.; Fu, F.; Han, J.; Li, L.; Li, D.; Liao, C. Prenatal Diagnosis of PPP2R1A-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorders Using Whole Exome Sequencing: Clinical Report and Review of Literature. Genes 2023, 14, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010126
Lei T, Zhen L, Yang X, Pan M, Fu F, Han J, Li L, Li D, Liao C. Prenatal Diagnosis of PPP2R1A-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorders Using Whole Exome Sequencing: Clinical Report and Review of Literature. Genes. 2023; 14(1):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010126
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Tingying, Li Zhen, Xin Yang, Min Pan, Fang Fu, Jin Han, Lushan Li, Dongzhi Li, and Can Liao. 2023. "Prenatal Diagnosis of PPP2R1A-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorders Using Whole Exome Sequencing: Clinical Report and Review of Literature" Genes 14, no. 1: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010126
APA StyleLei, T., Zhen, L., Yang, X., Pan, M., Fu, F., Han, J., Li, L., Li, D., & Liao, C. (2023). Prenatal Diagnosis of PPP2R1A-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorders Using Whole Exome Sequencing: Clinical Report and Review of Literature. Genes, 14(1), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010126




