Abstract
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) reportedly influence the effect of nivolumab in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between the clinical outcomes of patients with mRCC and SNPs in programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) protein-coding gene (PDCD1) and explore any potential correlation with patient prognosis and incidence of immune-related adverse events (irAEs). In total, 106 patients with mRCC, who were treated with nivolumab alone (n = 59) or nivolumab and ipilimumab (n = 47), were enrolled in the study. Three SNPs in the PDCD1 gene, namely PD-1.3, PD-1.5, and PD-1.6, were assessed. Patients harboring the PD-1.6 G allele experienced more severe (odds ratio, 3.390; 95% confidence interval 1.517–7.756; p = 0.003) and multiple (OR, 2.778; 95% CI, 1.020–6.993 p = 0.031) irAEs than those harboring the AA genotype. Thus, the existence of the PDCD1 PD-1.6 polymorphism (G allele) was associated with the occurrence of severe and multiple irAEs in patients with mRCC. Further evaluation of PDCD1 polymorphisms might help identify patients experiencing irAE by nivolumab treatment.
1. Introduction
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is more common in males above 60 years of age [1], and 20–30% of patients with RCC already display the metastatic phenotype at the time of diagnosis. Survival rates for patients with metastatic RCC (mRCC) have remarkably improved since the introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Nivolumab, a novel anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) antibody, has been applied in standard therapeutic regimens for patients with mRCC as second-line therapy and others [2]. Additionally, first-line nivolumab combination therapy with cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 inhibitor or first-line cabozantinib therapy has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, and these drugs are expected to contribute towards a better clinical outcome in patients with mRCC [3,4]. However, the immune-related adverse events (irAEs), which are undesirable effects of these therapies, remain unresolved. In three pivotal trials, CheckMate 025, CheckMate 214, and CheckMate 9ER, 19%, 46%, and 19.1% of patients experienced Grade 3 or higher irAE, and 8%, 22%, and 12.2% discontinued treatment, respectively [2,3,4]. Some irAEs can induce life-threatening events, such as myocarditis or myasthenia gravis [5,6,7].
Some studies have recently shown that the manifestation of an irAE and a durable therapeutic response might be related to each other [8,9]. In contrast, steroid treatment applied to cope with irAEs can reduce favorable antitumor effects [10]. Such a paradoxical situation has been frequently observed in clinical settings [11,12]. The manifestation of nivolumab toxicity can vary and is difficult to predict prior to treatment initiation [12,13]. As inhibition of PD-1 by nivolumab induces host immunity upregulation, the patient’s genetic background may play a crucial role in determining the effect of nivolumab [14].
Identifying biological markers for predicting the clinical effect and safety of therapeutic agents is highly desirable because of the increasing number of treatment options for advanced renal cancer. Although ICIs are available, a definitive strategy for treatment, including the appropriate choice or combination of agents with respect to patients’ health background, has not been developed. There are several approaches to identify clinically useful genetic variations. For instance, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) reportedly influence the effect of nivolumab [15]. A SNP is a genomic variant at a single base position in the DNA and may influence promoter activity (gene expression), messenger RNA (mRNA) conformation (stability), and subcellular localization of mRNAs and/or proteins and hence may affect the development of disease. Some studies have shown that SNPs in the PD-1 protein-coding gene, PDCD1, are related to a better survival rate [16] or worsened toxicity [17] in patients with malignancies treated by nivolumab.
Many SNPs in the PDCD1 gene have been previously analyzed. The SNP PD-1.3 located in intron 4 (rs11568821) was first described by Prokunina et al. to be associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus [14]. An allele of SNP PD-1.3 may alter a binding site of runt-related transcription factor 1 located in an intronic enhancer region and has been thought to increase susceptibility to autoimmunity [18]. Another SNP, PD-1.5, in exon 5 (rs2227981) has been shown to be associated with ankylosing spondylitis [19]. Other studies have further shown that PD-1 expression in CD4+ T cells is significantly lower in individuals with PD-1.5 CC genotype than in those with PD-1.5 CT and PD-1.5 TT genotypes [20]. PD-1.6 is an SNP in the 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) of PD-1 (rs10204525) and is reportedly associated with susceptibility and disease progression in chronic hepatitis B virus infection [21]. The PD-1.6 polymorphism reportedly alters cytokine production and PD-1 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells [22]. Nevertheless, a definitive overview of PDCD1 SNP frequencies largely remains elusive owing to a large variation among different ethnic groups and a relative paucity of extensive studies [23]. In addition, no study has demonstrated the association between PDCD1 SNPs and the clinical outcomes of patients with mRCC treated with nivolumab. Therefore, we aimed to investigate three common SNPs in PDCD1 in Japanese patients with mRCC and their potential association with the clinical outcomes of patients treated with nivolumab. Our findings could form the basis for further evaluation of PDCD1 polymorphisms, which might help identify patients benefitting from nivolumab treatment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
This retrospective study included 106 patients with mRCC treated with first-line, second-line, or other nivolumab regimens, between March 2013 and March 2019. Treatments were administered without any interruptions between cycles unless disease progression or intolerable toxicities were observed. Patients were classified according to the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium (IMDC) risk scoring system prior to nivolumab regimen initiation. The choice of first- or second-line systemic therapy was based on the IMDC risk score, performance status, disease extent, comorbidity presence, previous treatment, and individual preferences. Some patients underwent metastasectomies. The response to the nivolumab regimen was evaluated according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumor (RECIST), version 1.1. The assessment interval for individual patients was scheduled by the attending physicians. All adverse events (AEs) were graded in concordance with the National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria (NCI-CTC), version 5.0. We obtained AE documentation from the patient medical records and investigated the relationship between SNPs and AEs of ≥ Grade 2. Patients who had more than three ≥ Grade 2 AEs were defined as having multiple AEs. All AEs leading to nivolumab treatment termination were noted.
2.2. Genetic Analysis
We analyzed three representative SNPs, namely PD-1.3 (rs11568821), PD-1.5 (rs2227981), and PD-1.6 (rs10204525), in the PDCD1 gene. The relationships between these SNPs and patient survival and clinical outcome, including progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), best objective response (BOR), and AEs, were evaluated. DNA was extracted from peripheral blood samples using a QIAamp Blood kit (Cat. No. ID 51104, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and stored at −20 °C until analysis. We followed its protocol handbook. Each SNP was genotyped using the PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism method. Primer sequences, restriction enzymes, and PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism product sizes are presented in Table S1. PD-1.6 was amplified as described previously by Direskeneli et al. using PCR [24], and the primers for PD-1.3 and PD-1.5 were designed using Primer 3Plus (https://www.bioinformatics.nl/cgi-bin/primer3plus/primer3plus.cgi: accessed on 1 November 2018). DNA was amplified in a VeritiTM thermal cycler (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA): starting with an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 58 °C for 30 s, and elongation at 72 °C for 30 s, and, at last, a final elongation at 72 °C for 10 min.
2.3. Statistical Analyses
PFS was defined as the time between initiation of nivolumab treatment and disease progression or death, as confirmed by radiological images or clear clinical manifestation of progressive disease (PD). OS was defined as the time between nivolumab treatment initiation and death. The data records were closed upon patient death or final follow-up. The data are expressed as the median and range, and differences with a p-value < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. The chi-square test was used to examine differences in categorical data. PFS and OS data were stratified using the Kaplan–Meier method and analyzed using the log-rank test. The Cox proportional hazard regression model was used for the analysis of hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). To reduce the effects of selection biases and potential confounders in this observational study, we performed multiple logistic regression analyses. A multivariate analysis was performed to determine the odds ratios (ORs) and 95% CIs for factors with p-value < 0.1 in the univariate analysis. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS statistical software, version 26.0 (SPSS Japan Inc., Tokyo, Japan). To test the population homogeneity among the subjects, the genotype frequencies of each polymorphism were tested against the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium using the chi-square test.
2.4. Ethical Statement
All patients gave informed consent for this study, and the ethics committee of the Akita University Graduate School of Medicine and the Hirosaki Graduate School of Medicine approved the study (approved No. 1517 at Akita University Ethical Committee).
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
The patients’ clinical characteristics are described in Table 1. The median age was 69 years old (interquartile range [IQR]: 62–74 years old). All 106 patients were Japanese, and, among them, 85 were male (80%) and 21 were female (20%). Sixty-four (60%) patients had undergone radical nephrectomy prior to initiation of systemic therapies. Forty-seven (44%) patients were administered nivolumab and ipilimumab as first-line systemic therapy, whereas 59 were administered (56%) nivolumab as second-line therapy or at a later time point. Among the patients who received second-line or later therapies, 27 (26%) had previously been treated with one therapy and 15 (14%) with two or more therapies, and 17 (16%) patients showed no records of prior therapy. Based on the IMDC risk classification system, 15 patients (14%) were classified as favorable-risk, 47 (44%) as intermediate-risk, and 42 as poor-risk (40%). Twenty-nine (27%) patients had one metastatic site, 39 (37%) had two, and 38 (36%) had three or more. The sites of metastasis were the lungs (n = 79, 75%), bones (n = 36, 34%), lymph nodes (n = 30, 28%), adrenal glands (n = 15, 14%), liver (n = 14, 13%), brain (n = 10, 9%), and others (n = 27, 25%).

Table 1.
Patients’ characteristics.
3.2. Patient Outcomes and Genotypic Characteristics
The median follow-up period after nivolumab initiation was 18.8 months (IQR, 6.3–33.9 months). At the time of data analysis, 26 (25%) patients continued with nivolumab therapy. Forty-five (42%) patients stopped nivolumab treatment owing to disease progression, whereas 14 (13%) stopped treatment due to the occurrence of AEs. Thirty-seven patients (35%) had died at the time of data analysis. The estimated median PFS and OS were 5.0 (IQR, 2.7–17.4) and 18.8 (IQR, 6.3–33.9) months, respectively. The BOR assessment data are shown for 103 patients (Table 1). Three patients who did not receive the first evaluation (early discontinuation) were excluded. Eight patients (8%) exhibited complete response (CR), 30 (28%) showed partial response (PR), 39 (37%) showed stable disease (SD), and 26 (24%) showed PD. Fifty-three (50%) of 106 patients developed AEs ≥ Grade 2, and 14 (13%) patients discontinued nivolumab because of AEs (Table 1).
SNPs were successfully analyzed in the 106 patients. None of the patients had the PD-1.3 polymorphism. No significant relationship was observed between the genotypes of the two SNPs and PFS and OS (Table 2 and Figure 1). The distribution of SNPs in patients exhibiting CR + PR + SD vs. PD or in those displaying CR + PR vs. SD + PD was analyzed. No associations were detected between the clinical factors, SNPs, and the BOR (Table 3). Furthermore, there were no significant associations between clinical factors and polymorphisms and the risk of development of any AE (Table 4). In contrast, the incidence of ≥ Grade 2 irAEs was significantly higher in patients carrying the PD-1.6 G allele than in those carrying other genotypes (OR: 3.390, 95% CI: 1.517–7.576, p = 0.003; Table 4). In addition, patients harboring the PD-1.6 G allele had a significantly higher risk of multiple AEs than those harboring the AA genotype (OR: 2.778, 95% CI: 1.020–6.993, p = 0.031; Table 4). These instances of statistical significance were also confirmed by the logistic regression analysis performed to reduce selection biases and confounders (Table S2). Although clinical stage 3 (OR: 3.469, 95% CI: 1.135–10.602, p = 0.029), prior history of nephrectomy (OR: 2.780, 95% CI: 1.120–6.896, p = 0.027) and difference of treatment regimen (OR: 3.879, 95% CI: 1.500–10.033, p = 0.005) were significant factors in univariate analysis (Table 4), these significances disappeared with the multi-valuable analysis (Table S2).

Table 2.
Association between survival outcome and PDCD1 polymorphism.
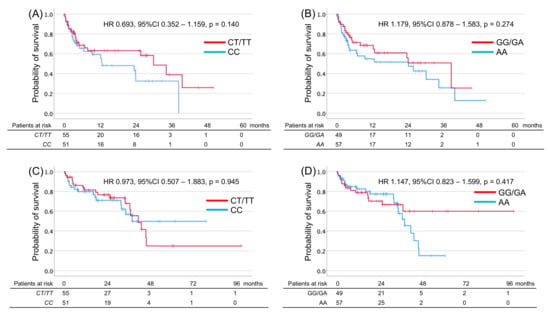
Figure 1.
Kaplan–Meier estimates of progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients and harboring T allele of PDCD1 rs2227981 (PD-1.5) and G allele of PDCD1 rs10204525 (PD-1.6). PFS (A,B) or OS (C,D) according to PDCD1 genotype in PD-1.5 (A,C) or PD-1.6 (B,D).

Table 3.
Distributions of clinical factors and PDCD1 polymorphisms for the response.

Table 4.
Association between adverse events and clinical factors and polymorphisms in PDCD1 gene.
4. Discussion
Presently, as the known candidate targets of nivolumab mainly originate from the tumor and the surrounding tumor microenvironment, programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in tumor cells measured by immunohistochemistry could predict responses to ICIs [25]. However, tumors that do not express detectable levels of PD-L1 on the cell surface can also respond to ICIs [3]. A recent study reported that PD-L1 expression is altered even during the course of clinical treatment [26]. This observation might lead to the notion that PD-L1 expression measured by immunohistochemistry cannot be reliable as a predictive biomarker of therapeutic response. Therefore, the development of better biomarkers for predicting responses to nivolumab therapy is necessary to help clinical decision-making and potentially expose fewer patients to inadequate treatments and the associated toxicities and costs [27,28].
In this study, we analyzed the potential of three PD-1 SNPs as a predictive biomarker of nivolumab therapeutic outcome in patients with mRCC, because PD-1 is the primary target of this anti-PD-1 antibody [29]. PD-1, which is broadly expressed in multiple cell types, including T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages, plays a role in down-regulating T-cell responses, leading to immune suppression. Inhibition of PD-1 by nivolumab is a key aspect of the PD-1 pathway during signal induction [30]. The PD-1 protein is encoded by PDCD1 and is expressed on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. The functions of PD-1 polymorphisms have not yet been fully investigated; however, they may modify anti-tumor immunity and affect the response to ICIs [31].
As PD-1.6 G > A polymorphism is located at the 3′-UTR, it may affect transcriptional initiation, resulting in a decreased expression of PD-1 [32]. Although the PD-1.6 A allele is a minor allele among Caucasians (at most, 10%), the A allele is the major allele in Asian populations, appearing in 60–70% of the individuals [33]. The promotion of an immunosuppressive phenotype by PD-1.6 G > A polymorphism may also contribute to tumor development; nonetheless, this has not yet been characterized [31]. Zhang et al. reported that the PD-1.6 A allele increases PD-1 expression [21]. In the regulatory pathway, miRNA-4717 plays a crucial role [21]; miRNA-4717 has demonstrated allele-specific influence on luciferase activity in a dose-dependent manner in cells transfected with vectors containing different PD-1.6 G alleles. In patients with the PD-1.6 GG genotype, miRNA-4717 mimics a significantly decreased PD-1 expression [21]. In general, a high PD-1 expression seems to be related to a substantial antitumor effect and the development of irAEs induced by nivolumab administration [15]. However, the quantity of PD-1 protein is reduced in children with new-onset autoimmune diseases and type I diabetes compared with those negative for auto-antibody (AAB) presence [34]. Interestingly, the proportion of circulating FOXP3+ regulatory T cells expressing PD-1 has also been found to be reduced in children with an AAB-positive at-risk status compared with those in the control group showing an AAB-negative status [34]. This finding might support the argument that patients carrying the PD-1.6 G allele develop irAEs more frequently than those carrying the AA genotype. These significant associations suggest that individualized treatment strategies should be possible for patients carrying the PD-1.6 G allele. Although the PD-1.5 T allele showed poor survival outcomes in melanoma patients [16], no significant survival impact was observed in our study. Patients who carried a PD-1.5 T allele were significantly associated with lower mRNA expression of PDCD1 in subcutaneous adipose tissue, not in lung nor liver as major metastatic organs by RCC [16]. This tissue specificity of mRNA expression might cause a different result in our study.
Nevertheless, this study has a few potential limitations. First, due to the retrospective study design, the treatment schedule, AE management, and timings for objective assessments could not be unified. Second, a validation study confirming the results of the SNP analysis was not conducted in the present study, which remains essential. Third, this study included patients treated with nivolumab monotherapy and ipilimumab and nivolumab combination therapy. The data from patients treated with the combination therapy might be affected by other factors, such as cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4-related genomic polymorphisms. Lastly, the major limitation is the lack of statistical power calculation, which might have led to a type II error because of the small sample size. However, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to report the clinical value of PDCD1 SNPs in patients with mRCC who were treated with nivolumab. Further research is warranted to address the clinical implications of PDCD1 SNPs in patients with mRCC.
5. Conclusions
Our retrospective assessment of SNPs in PDCD1 as predictive markers of nivolumab toxicity in Japanese patients with mRCC suggested that the PD-1.6 G allele of PDCD1 might be associated with increased severity and multiplicity of AEs. Upon further validation of our findings using a larger sample size, alternative mRCC treatment approaches based on PDCD1 SNPs could be established in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/genes13071204/s1, Table S1: Primers and PCR conditions for SNP typing of polymorphic variants of PDCD1 gene, Table S2: Prognostic values of clinical variables and PDCD1 polymorphism for predicting grade 2 or higher irAE and multiple irAEs in 106 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma analyzed by using multivariate logistic regression models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K. and K.N.; Methodology, M.K., K.N. and T.H.; Software, Validation, S.H. and C.O.; Formal Analysis, K.N.; Investigation, M.K. and K.N.; Resources, K.N.; Data Curation, Y.M., Y.S., H.S., S.K., R.Y., A.K., T.N., M.S. and S.N.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.K. and K.N.; Writing—Review & Editing, K.N. and T.H.; Visualization, M.K. and K.N.; Supervision, K.N., C.O. and T.H.; Project Administration, M.K. and K.N.; Funding Acquisition, K.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research, Japan grant numbers 17K11121 and 20K09553.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Akita University Hospital and that of the other participating institutions (Approval Code:1517; Approval Date: 11 April 2016).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Yoko Mitobe and Yukiko Sugiyama for their assistance in data collection.
Conflicts of Interest
Habuchi received honoraria from Novartis Pharma, Pfizer Co., GlaxoSmithKline, and Ono Pharma Co. The other authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, nor in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Thompson, R.H.; Ordonez, M.A.; Iasonos, A.; Secin, F.P.; Guillonneau, B.; Russo, P.; Touijer, K. Renal cell carcinoma in young and old patients—Is there a difference? J. Urol. 2008, 180, 1262–1266, discussion 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; George, S.; Hammers, H.J.; Srinivas, S.; Tykodi, S.S.; Sosman, J.A.; Procopio, G.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. Nivolumab versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Aren Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthelemy, P.; Porta, C.; George, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Powles, T.; Burotto, M.; Escudier, B.; Bourlon, M.T.; Zurawski, B.; Oyervides Juarez, V.M.; Hsieh, J.J.; Basso, U.; Shah, A.Y.; et al. Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Marone, G.; Mercurio, V.; Galdiero, M.R.; Bonaduce, D.; Tocchetti, C.G. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Cardiac Toxicity: An Emerging Issue. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Kawai, S.; Ota, T.; Tsukuda, H.; Fukuoka, M. Myasthenia gravis induced by nivolumab in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: A case report and literature review. Immunotherapy 2017, 9, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, S.; Nishida, S.; Miyazato, M.; Goya, M.; Saito, S. A case report of nivolumab-induced myasthenia gravis and myositis in a metastatic renal cell carcinoma patient. Urol. Case Rep. 2020, 29, 101105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, H.; Takagi, T.; Kondo, T.; Homma, C.; Tachibana, H.; Fukuda, H.; Yoshida, K.; Iizuka, J.; Kobayashi, H.; Okumi, M.; et al. Association between immune-related adverse events and prognosis in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with nivolumab. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2019, 37, 355.e321–355.e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, M.G.; Pipitone, S.; Venturelli, M.; Baldessari, C.; Porta, C.; Iannuzzi, F.; Basso, U.; Scagliarini, S.; Zucali, P.A.; Galli, L.; et al. Correlation Between Immune-related Adverse Event (IRAE) Occurrence and Clinical Outcome in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma (mRCC) Treated with Nivolumab: IRAENE Trial, an Italian Multi-institutional Retrospective Study. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2020, 18, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, E.Y.; Merl, M.Y.; Lin, K. The impact of corticosteroid use during anti-PD1 treatment. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 26, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numakura, K.; Horikawa, Y.; Kamada, S.; Koizumi, A.; Nara, T.; Chiba, S.; Kanda, S.; Saito, M.; Narita, S.; Inoue, T.; et al. Efficacy of anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab in Japanese patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A retrospective multicenter analysis. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 11, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Numakura, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Hatakeyama, S.; Naito, S.; Horikawa, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Kamada, S.; Muto, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Koizumi, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nivolumab for renal cell carcinoma in patients over 75 years old from multiple Japanese institutes. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinata, N.; Yonese, J.; Masui, S.; Nakai, Y.; Shirotake, S.; Tatsugami, K.; Inamoto, T.; Nozawa, M.; Ueda, K.; Etsunaga, T.; et al. A multicenter retrospective study of nivolumab monotherapy in previously treated metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients: Interim analysis of Japanese real-world data. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokunina, L.; Castillejo-Lopez, C.; Oberg, F.; Gunnarsson, I.; Berg, L.; Magnusson, V.; Brookes, A.J.; Tentler, D.; Kristjansdottir, H.; Grondal, G.; et al. A regulatory polymorphism in PDCD1 is associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in humans. Nat. Genet. 2002, 32, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de With, M.; Hurkmans, D.P.; Oomen-de Hoop, E.; Lalouti, A.; Bins, S.; El Bouazzaoui, S.; van Brakel, M.; Debets, R.; Aerts, J.; van Schaik, R.H.N.; et al. Germline Variation in PDCD1 Is Associated with Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma Treated with Anti-PD-1 Monotherapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomizo, T.; Ozasa, H.; Tsuji, T.; Funazo, T.; Yasuda, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Yagi, Y.; Sakamori, Y.; Nagai, H.; Hirai, T.; et al. Clinical Impact of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in PD-L1 on Response to Nivolumab for Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bins, S.; Basak, E.A.; El Bouazzaoui, S.; Koolen, S.L.W.; Oomen-de Hoop, E.; van der Leest, C.H.; van der Veldt, A.A.M.; Sleijfer, S.; Debets, R.; van Schaik, R.H.N.; et al. Association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms and adverse events in nivolumab-treated non-small cell lung cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salmaninejad, A.; Khoramshahi, V.; Azani, A.; Soltaninejad, E.; Aslani, S.; Zamani, M.R.; Zal, M.; Nesaei, A.; Hosseini, S.M. PD-1 and cancer: Molecular mechanisms and polymorphisms. Immunogenetics 2018, 70, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Deng, C.; Li, J.; Wen, X.; Wu, Z.; Hu, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.; et al. The associations between PD-1, CTLA-4 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis: A meta-analysis and systemic review. Rheumatol. Int. 2016, 36, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, R.; Haseda, F.; Tsutsumi, C.; Hiromine, Y.; Noso, S.; Kawabata, Y.; Mitsui, S.; Terasaki, J.; Ikegami, H.; Imagawa, A.; et al. Low programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) expression in peripheral CD4+ T cells in Japanese patients with autoimmune type 1 diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 180, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Li, N.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Li, F.; Yang, C.; Han, Q.; Lv, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z. microRNA-4717 differentially interacts with its polymorphic target in the PD1 3′ untranslated region: A mechanism for regulating PD-1 expression and function in HBV-associated liver diseases. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18933–18944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Li, N.; Li, F.; Zhou, Z.; Sang, J.; Chen, Y.; Han, Q.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Z. Immune checkpoint proteins PD-1 and TIM-3 are both highly expressed in liver tissues and correlate with their gene polymorphisms in patients with HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine 2016, 95, e5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Yamada, R.; Kobayashi, K.; Kawaida, R.; Yamamoto, K. Ethnic differences in allele frequency of autoimmune-disease-associated SNPs. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 50, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Direskeneli, H.; Tuna-Erdogan, E.; Gunduz, F.; Bandurska-Luque, A.; Alparslan, B.; Kebe, M.; Uyar, F.A.; Bicakcigil, M.; Aksu, K.; Kamali, S.; et al. PDCD1 polymorphisms are not associated with Takayasu’s arteritis in Turkey. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2012, 30, S11–S14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pignon, J.C.; Jegede, O.; Shukla, S.A.; Braun, D.A.; Horak, C.E.; Wind-Rotolo, M.; Ishii, Y.; Catalano, P.J.; Grosha, J.; Flaifel, A.; et al. irRECIST for the Evaluation of Candidate Biomarkers of Response to Nivolumab in Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Analysis of a Phase II Prospective Clinical Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2174–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, J.; Han, G.; Schalper, K.A.; Carvajal-Hausdorf, D.; Pelekanou, V.; Rehman, J.; Velcheti, V.; Herbst, R.; LoRusso, P.; Rimm, D.L. Quantitative Assessment of the Heterogeneity of PD-L1 Expression in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, T.; Masuda, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Numao, N.; Yonese, J. Biomarkers to predict prognosis and response to checkpoint inhibitors. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 22, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, Y.; Slattery, T.D.; Pickering, L.M. Individualizing Systemic Therapies in First Line Treatment and beyond for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Tupikowski, K.; Jasek, M.; Tomkiewicz, A.; Witkowicz, A.; Ptaszkowski, K.; Karpinski, P.; Zdrojowy, R.; Halon, A.; Karabon, L. SNP-SNP Interaction in Genes Encoding PD-1/PD-L1 Axis as a Potential Risk Factor for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, A.H.; Pauken, K.E. The diverse functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Jasek, M.; Karabon, L. Immune Checkpoint Molecules-Inherited Variations as Markers for Cancer Risk. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 606721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Duan, S.; Han, Q.; Li, Z.; Lv, Y.; Chen, J.; Lou, S.; Li, N. Association of polymorphisms of programmed cell death-1 gene with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hum. Immunol. 2010, 71, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldafashi, N.; Darlay, R.; Shukla, R.; McCain, M.V.; Watson, R.; Liu, Y.L.; McStraw, N.; Fathy, M.; Fawzy, M.A.; Zaki, M.Y.W.; et al. A PDCD1 Role in the Genetic Predisposition to NAFLD-HCC? Cancers 2021, 13, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchione, A.; Di Fonte, R.; Gerosa, J.; Jofra, T.; Cicalese, M.P.; Napoleone, V.; Ippolito, E.; Galvani, G.; Ragogna, F.; Stabilini, A.; et al. Reduced PD-1 expression on circulating follicular and conventional FOXP3+ Treg cells in children with new onset type 1 diabetes and autoantibody-positive at-risk children. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 211, 108319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).