The SNP-Based Profiling of Montecristo Feral Goat Populations Reveals a History of Isolation, Bottlenecks, and the Effects of Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Construction and Filtering
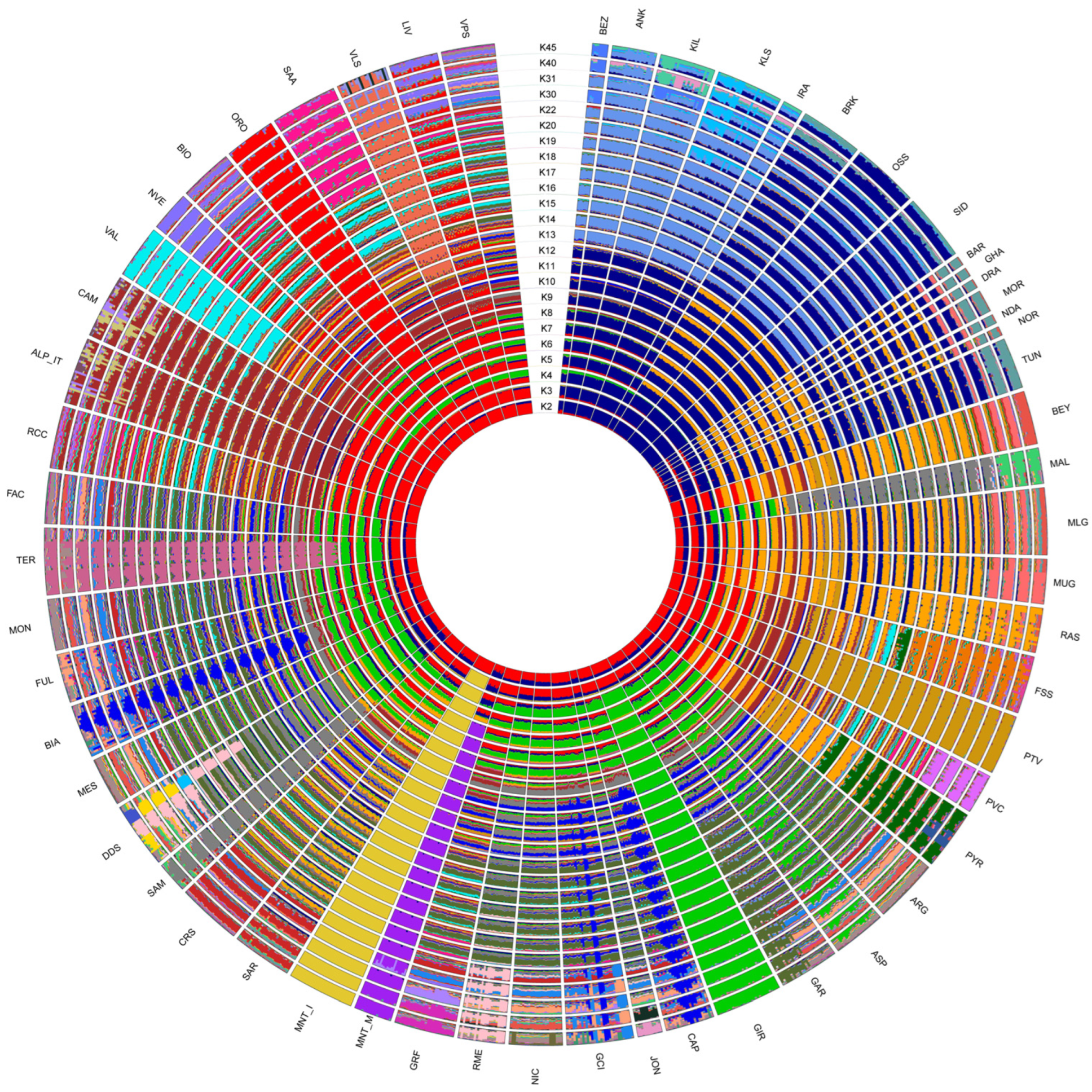
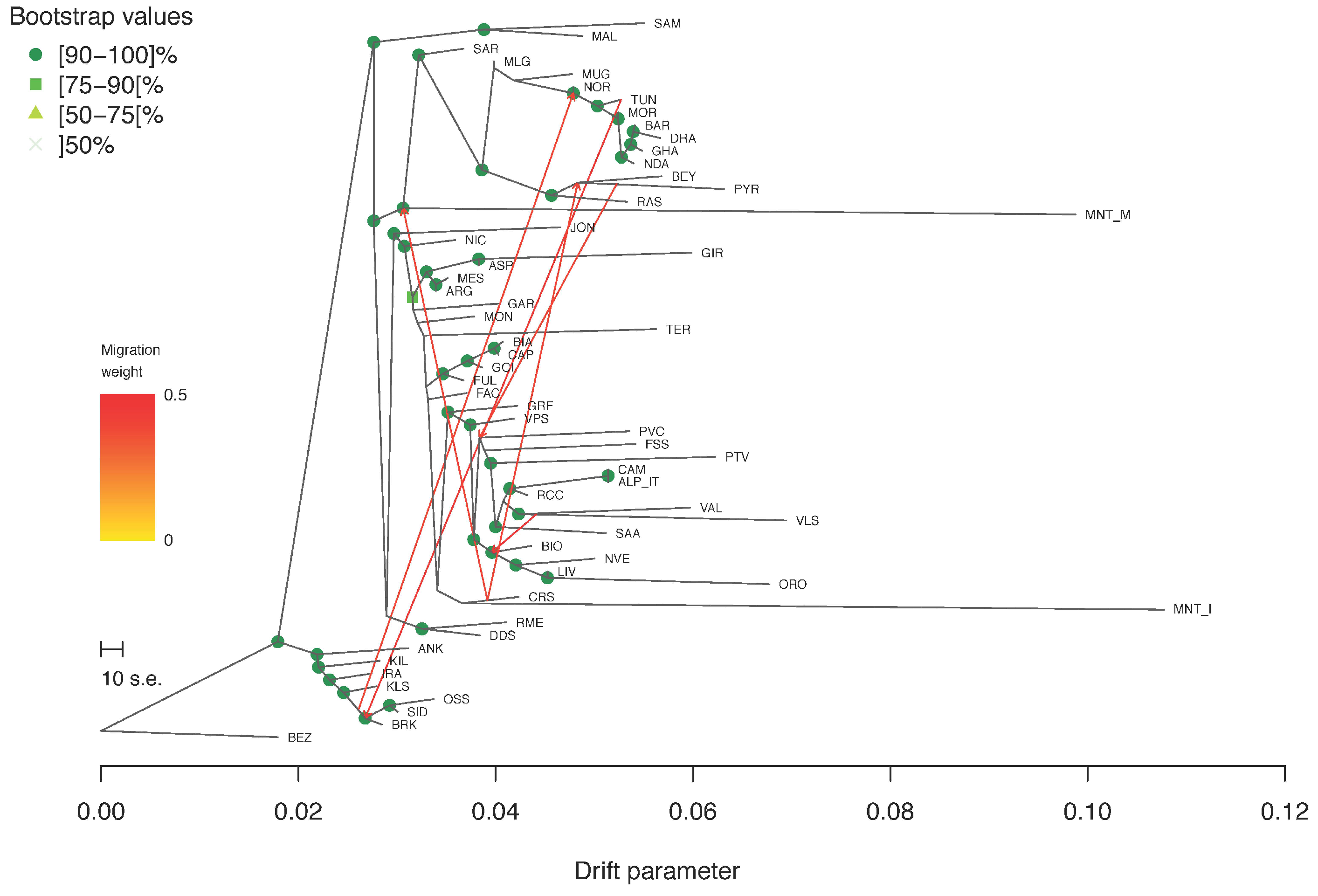
2.2. Estimation of Genetic Diversity, Population Structure and Migration Events
2.3. Runs of Homozygosity and Heterozygosity-Rich Regions
2.4. Approximate Bayesian Computation
3. Results
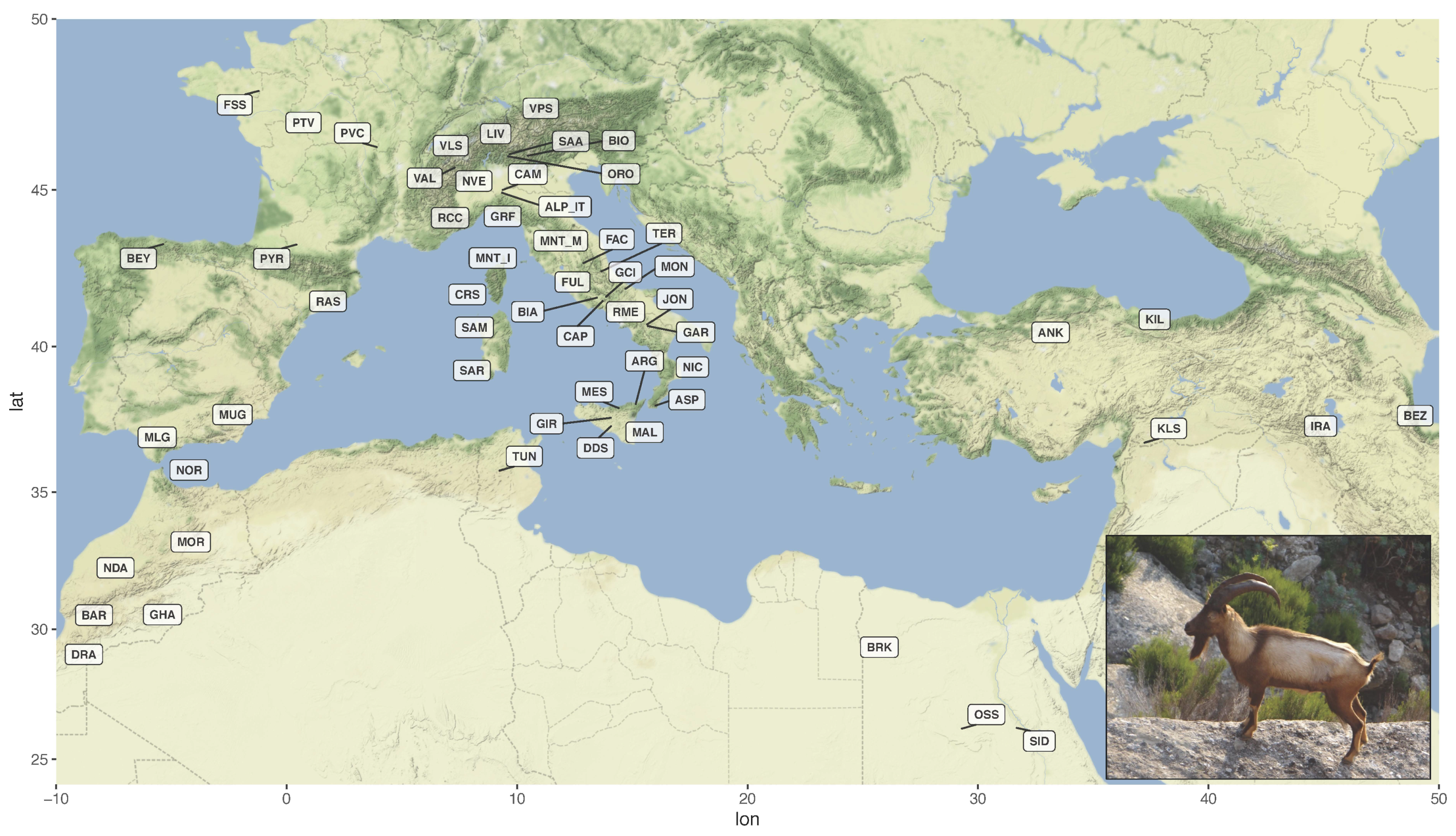
3.1. Dataset Construction and Filtering
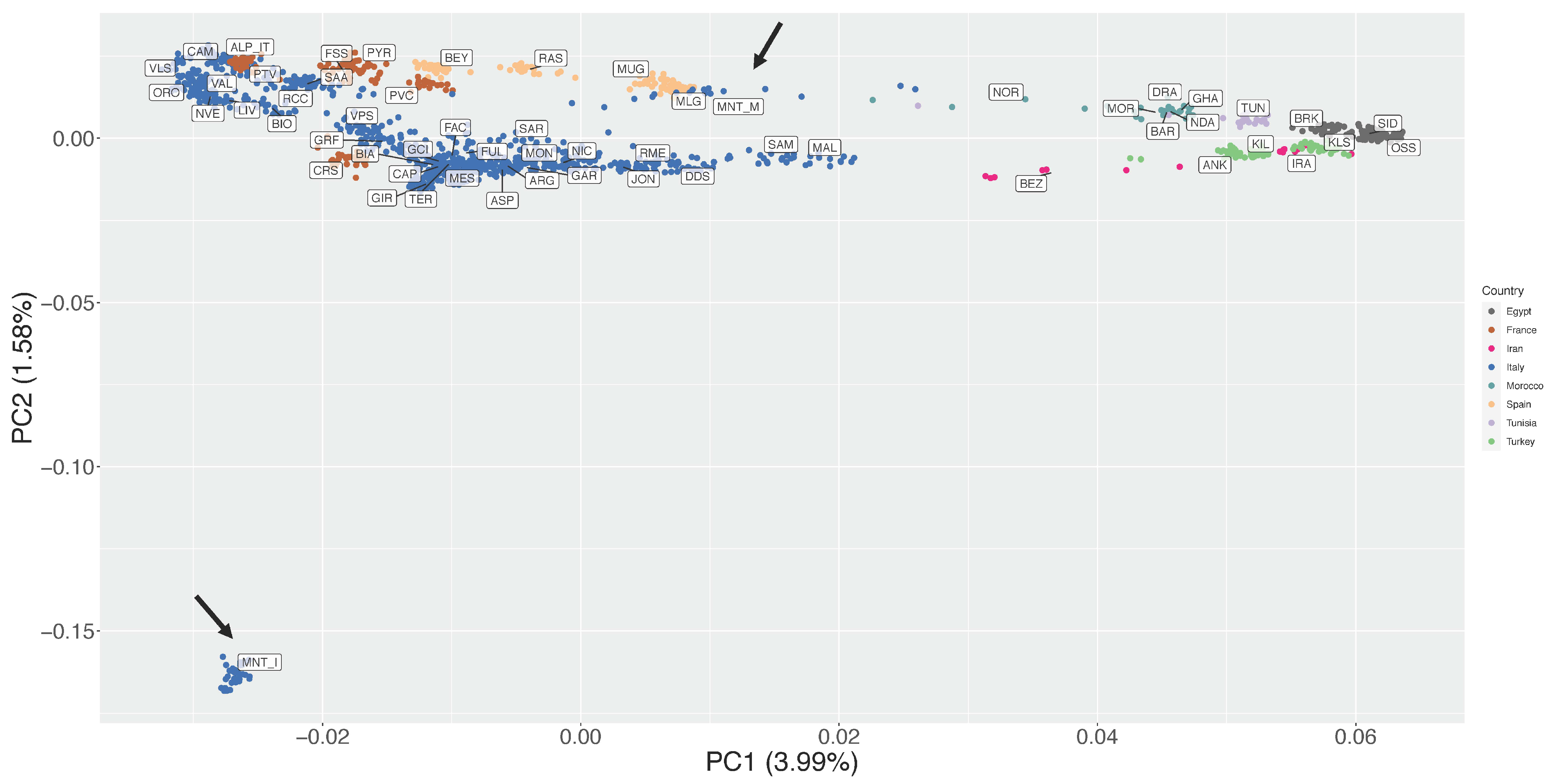
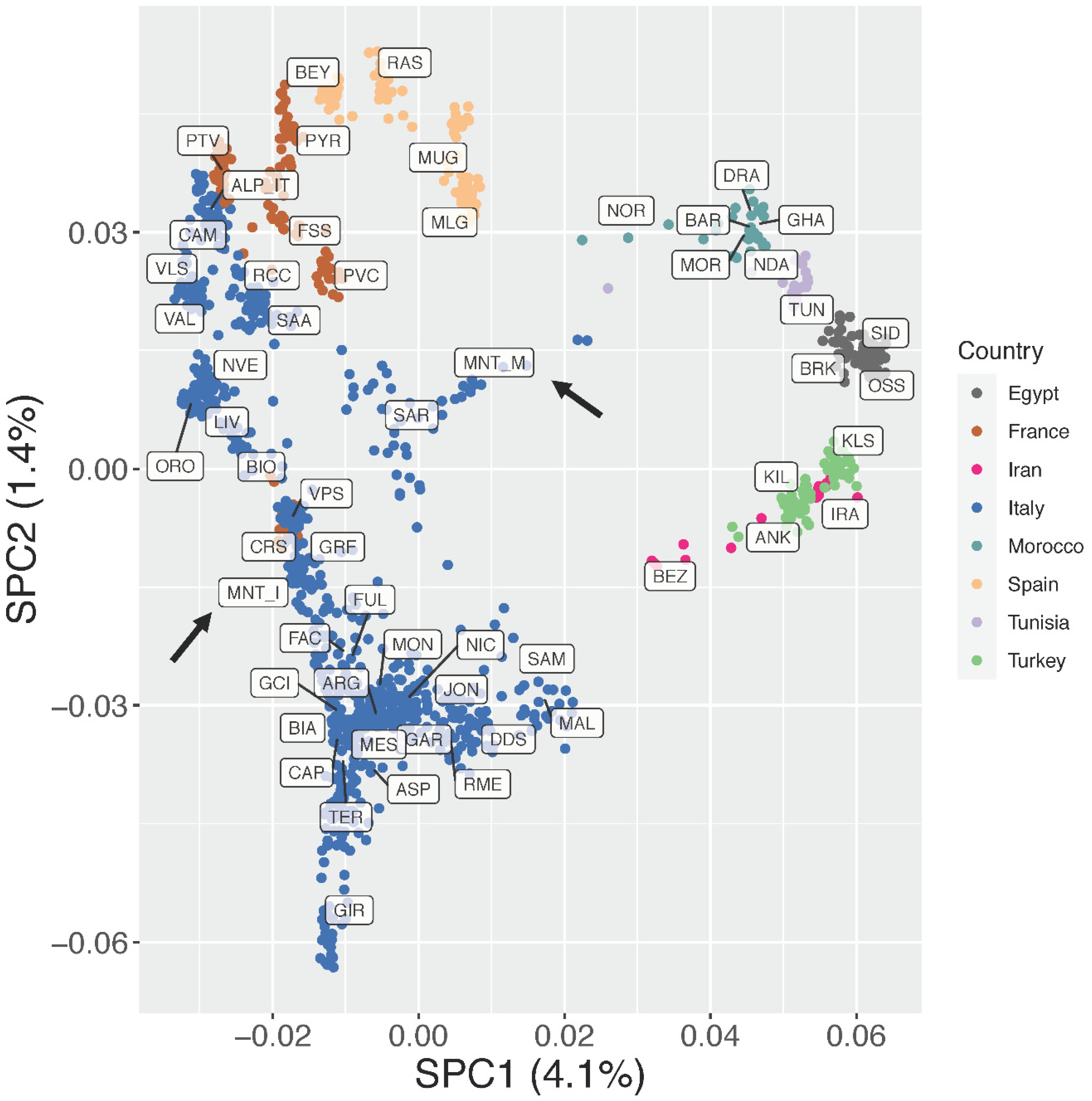
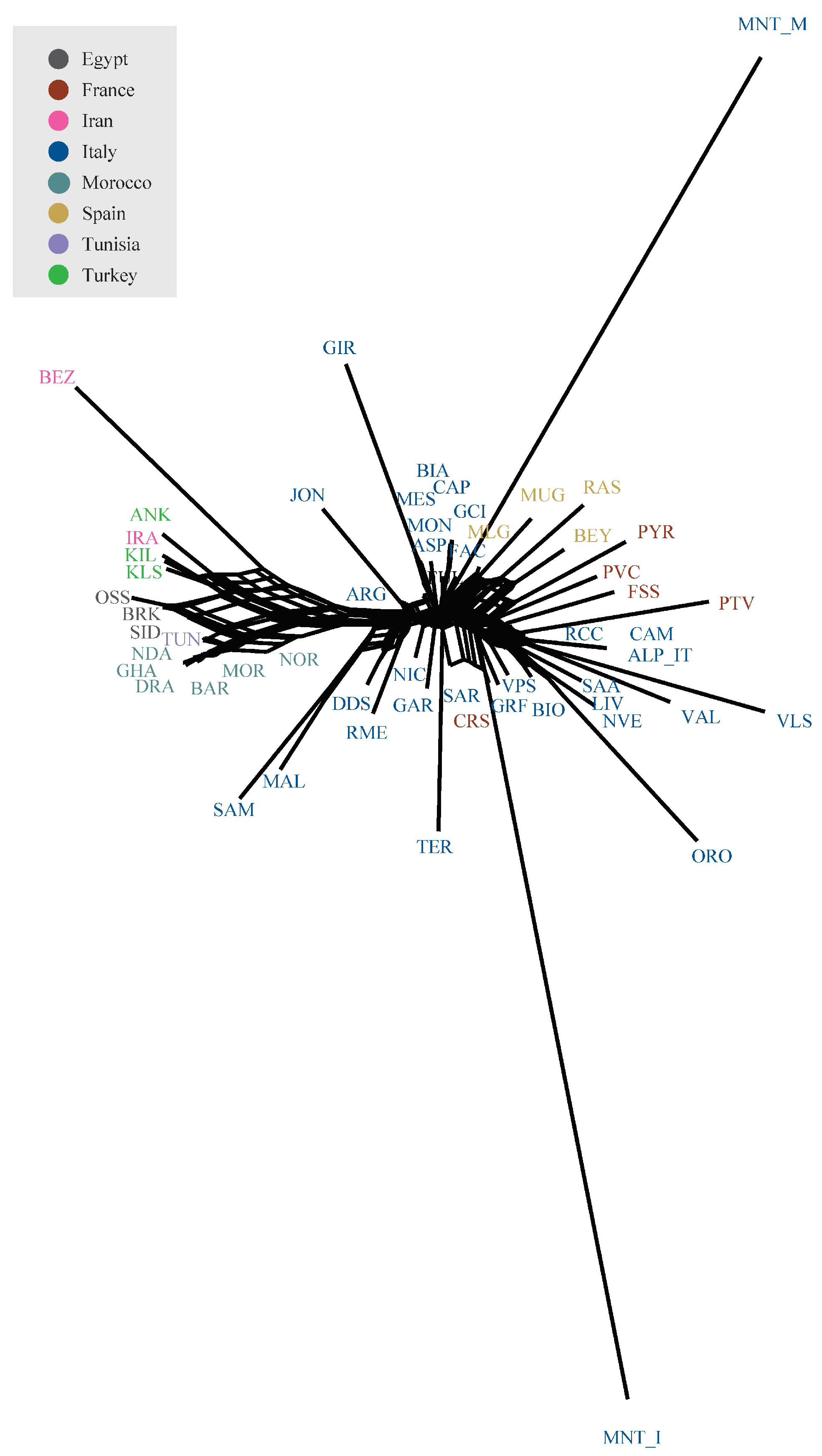
3.2. Estimation of Genetic Diversity, Population Structure, and Migration Events
3.3. Runs of Homozygosity and Heterozygosity-Rich Regions
3.4. Approximate Bayesian Computation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horwitz, L.K.; Bar-Gal, G.K. The Origin and Genetic Status of Insular Caprines in the Eastern Mediterranean: A Case Study of Free-Ranging Goats (Capra aegagrus cretica) on Crete. Hum. Evol. 2006, 21, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pavan, M. Montecristo riserva naturale. Ist. Entomol. Agrar. Pavia/Tipografia Meroni Albese (Como) 1971, 36. Available online: http://www.pngp.it/sites/default/files/libri_20170915.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- European Committee for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources. Montecristo Island Nature Reserve—Application for the European Diploma. 1986. Available online: https://rm.coe.int/group-of-specialists-on-protected-areas-montecristo-island-nature-rese/16808aa975 (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Doro, M.G.; Casu, G.; Leoni, G.G.; Naitana, S.; Pirastu, M.; Novelletto, A.; Fraticelli, F. The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the Montecristo goat. Livest. Sci. 2016, 188, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciani, F.; Masseti, M. Considerazioni sull’origine della popolazione ircina dell’isola di Montecristo, nel Mar Tirreno settentrionale. Elementi per un confronto cronologico-culturale con l’antica diffusione artificiale dell’egagro (Capra aegagrus Erxleben, 1777) nelle isole del. Atti Conv. Genet. Conserv. fauna Suppl. Ric. Biol. Selvag. 1991, 18, 123–133. [Google Scholar]
- Masseti, M. The wild goat, Capra aegagrus Erxleben, 1777, of the island of Montecristo (Northern Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy): Does it still exist? Mammalia 2016, 80, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boitani, L.; Lovari, S.; Vigna Taglianti, A. Mammalia III. Carnivora, artiodactyla. Edagricole-New Business Media. 2003. Available online: https://www.ibs.it/mammalia-iii-carnivora-artiodactyla-libro-vari/e/9788850648795 (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Masseti, M. The wild goats Capra aegagrus Erxleben, 1777 of the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Atlantic Ocean islands. Mamm. Rev. 2009, 39, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, S.; Sauli, G. Montecristo. Nat. E Mont. 1976, 23, 7–27. [Google Scholar]
- Angelici, F.M.; Laurenti, A.; Nappi, A. A checklist of the mammals of small Italian islands. Hystrix Ital. J. Mammal. 2009, 20, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Toschi, A. Note sui vertebrati dell’isola di Montecristo. Compositori 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Raganella, E.P.; Lazzaro, L.; Gotti, C.; Baccetti, N. Piano di Gestione e Conservazione Della Capra di Montecristo: Sintesi del Contesto e Azioni. 2015. Available online: https://www.restoconlife.eu/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/Piano-di-gestione-della-capra-di-Montecristo.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Preserving the Biodiversity of the ‘Il Felcetone’ Farm in Tuscany. Available online: https://www.nandoandelsaperettifoundation.org/en/page.php/page.php?project=512 (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Zanichelli, F.; Giannini, F.; de Pietro, F.; Puppo, F. I Quaderni del Parco, documenti tecnici volume 2 PROGETTO LIFE+ MONTECRISTO 2010, Eradicazione di Componenti Florofaunistiche Aliene Invasive e Tutela di Specie e Habitat Nell’arcipelago Toscano. 2014. Available online: https://www.mite.gov.it/sites/default/files/archivio/allegati/life/life_pubblicazione_montecristo2010.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Gippoliti, S. The wild goat of Montecristo Island: Did it ever exist? Mammalia 2016, 80, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosser-Klopp, G.; Bardou, P.; Bouchez, O.; Cabau, C.; Crooijmans, R.; Dong, Y.; Donnadieu-Tonon, C.; Eggen, A.; Heuven, H.C.M.; Jamli, S.; et al. Design and characterization of a 52K SNP chip for goats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortellari, M.; Barbato, M.; Talenti, A.; Bionda, A.; Carta, A.; Ciampolini, R.; Ciani, E.; Crisà, A.; Frattini, S.; Lasagna, E.; et al. The climatic and genetic heritage of Italian goat breeds with genomic SNP data. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoloso, L.; The Italian Goat Consortium; Bomba, L.; Colli, L.; Negrini, R.; Milanesi, M.; Mazza, R.; Sechi, T.; Frattini, S.; Talenti, A.; et al. Genetic diversity of Italian goat breeds assessed with a medium-density SNP chip. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2015, 47, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, A.; The AdaptMap Consortium; Nicolazzi, E.L.; Van Tassell, C.P.; Rothschild, M.F.; Colli, L.; Rosen, B.D.; Sonstegard, T.S.; Crepaldi, P.; Tosser-Klopp, G.; et al. AdaptMap: Exploring goat diversity and adaptation. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanesi, M.; Capomaccio, S.; Vajana, E.; Bomba, L.; Garcia, J.F.; Ajmone-Marsan, P.; Colli, L. BITE: An R package for biodiversity analyses. bioRxiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colli, L.; The AdaptMap Consortium; Milanesi, M.; Talenti, A.; Bertolini, F.; Chen, M.; Crisà, A.; Daly, K.G.; Del Corvo, M.; Guldbrandtsen, B.; et al. Genome-wide SNP profiling of worldwide goat populations reveals strong partitioning of diversity and highlights post-domestication migration routes. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2017. Available online: http://r.meteo.uni.wroc.pl/web/packages/dplR/vignettes/intro-dplR.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Huson, D.H.; Bryant, D. Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.H.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickrell, J.K.; Pritchard, J.K. Inference of Population Splits and Mixtures from Genome-Wide Allele Frequency Data. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitak, R.R. OptM: An R package to optimize the number of migration edges using threshold models. J. Hered. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) Version 3.6. Distributed by the Author. 2004. Available online: http://www.evolution.gs.washington.edu/phylip.html (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Barbato, M.; Orozco-terWengel, P.; Tapio, M.; Bruford, M.W. SNeP: A tool to estimate trends in recent effective population size trajectories using genome-wide SNP data. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortellari, M.; Bionda, A.; Negro, A.; Frattini, S.; Mastrangelo, S.; Somenzi, E.; Lasagna, E.; Sarti, F.M.; Ciani, E.; Ciampolini, R.; et al. Runs of homozygosity in the Italian goat breeds: Impact of management practices in low-input systems. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2021, 53, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biscarini, F.; Cozzi, P.; Gaspa, G.; Marras, G. detectRUNS: An R package to detect runs of homozygosity and heterozygosity in diploid genomes. CRAN 2019, 8, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, P.A.S.; Suárez-Vega, A.; Marras, G.; Cánovas, Á. GALLO: An R package for genomic annotation and integration of multiple data sources in livestock for positional candidate loci. Gigascience 2020, 9, giaa149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, F.; Durif, G.; Raynal, L.; Lombaert, E.; Gautier, M.; Vitalis, R.; Marin, J.; Estoup, A. Extending approximate Bayesian computation with supervised machine learning to infer demographic history from genetic polymorphisms using DIYABC Random Forest. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 2598–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, T.F.; The AdaptMap Consortium; Amills, M.; Bertolini, F.; Rothschild, M.; Marras, G.; Boink, G.; Jordana, J.; Capote, J.; Carolan, S.; et al. Patterns of homozygosity in insular and continental goat breeds. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugo, G.P.; Browett, S.; Randhawa, I.; Howard, D.J.; Mullen, M.P.; Richardson, I.W.; Park, S.D.E.; Magee, D.A.; Scraggs, E.; Dover, M.J.; et al. A Population Genomics Analysis of the Native Irish Galway Sheep Breed. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selli, A.; Ventura, R.V.; Fonseca, P.A.S.; Buzanskas, M.E.; Andrietta, L.T.; Balieiro, J.C.C.; Brito, L.F. Detection and Visualization of Heterozygosity-Rich Regions and Runs of Homozygosity in Worldwide Sheep Populations. Animals 2021, 11, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, S.; Di Gerlando, R.; Sardina, M.; Sutera, A.; Moscarelli, A.; Tolone, M.; Cortellari, M.; Marletta, D.; Crepaldi, P.; Portolano, B. Genome-wide patterns of homozygosity reveal the conservation status in five italian goat populations. Animals 2021, 11, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandolo, W.; Mészáros, G.; Banda, L.J.; Gondwe, T.N.; Lamuno, D.; Mulindwa, H.A.; Nakimbugwe, H.N.; Wurzinger, M.; Utsunomiya, Y.T.; Woodward-Greene, M.; et al. Timing and extent of inbreeding in African goats. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burren, A.; Neuditschko, M.; Signer-Hasler, H.; Frischknecht, M.; Reber, I.; Menzi, F.; Drögemüller, C.; Flury, C. Genetic diversity analyses reveal first insights into breed-specific selection signatures within Swiss goat breeds. Anim. Genet. 2016, 47, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagawa, Y.; Nishimura, H.; Tsujimura, A.; Matsuoka, Y.; Matsumiya, K.; Okuyama, A.; Nishimune, Y.; Tanaka, H. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms and mutation analyses of the TNP1 and TNP2 genes of fertile and infertile human male populations. J. Androl. 2005, 26, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansbach, C.E.; Bétous, R.; Lovejoy, C.A.; Glick, G.G.; Cortez, D. The annealing helicase SMARCAL1 maintains genome integrity at stalled replication forks. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 2405–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Liu, X.; Gebreselassie, G.; Abied, A.; Ma, Q.; Ma, Y. Genome-wide association analysis reveals the genetic locus for high reproduction trait in Chinese Arbas Cashmere goat. Genes Genom. 2020, 42, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E, G.-X.; Zhao, Y.-J.; Huang, Y.-F. Huang, Selection signatures of litter size in Dazu black goats based on a whole genome sequencing mixed pools strategy. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 5517–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, W.-R.; Lv, F.-H.; He, S.-G.; Tian, S.; Peng, W.-F.; Sun, Y.-W.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Tu, X.-L.; Zhang, M.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Native Sheep Provides Insights into Rapid Adaptations to Extreme Environments. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2576–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Somenzi, E.; Senczuk, G.; Ciampolini, R.; Cortellari, M.; Vajana, E.; Tosser-Klopp, G.; Pilla, F.; Ajmone-Marsan, P.; Crepaldi, P.; Colli, L. The SNP-Based Profiling of Montecristo Feral Goat Populations Reveals a History of Isolation, Bottlenecks, and the Effects of Management. Genes 2022, 13, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13020213
Somenzi E, Senczuk G, Ciampolini R, Cortellari M, Vajana E, Tosser-Klopp G, Pilla F, Ajmone-Marsan P, Crepaldi P, Colli L. The SNP-Based Profiling of Montecristo Feral Goat Populations Reveals a History of Isolation, Bottlenecks, and the Effects of Management. Genes. 2022; 13(2):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13020213
Chicago/Turabian StyleSomenzi, Elisa, Gabriele Senczuk, Roberta Ciampolini, Matteo Cortellari, Elia Vajana, Gwenola Tosser-Klopp, Fabio Pilla, Paolo Ajmone-Marsan, Paola Crepaldi, and Licia Colli. 2022. "The SNP-Based Profiling of Montecristo Feral Goat Populations Reveals a History of Isolation, Bottlenecks, and the Effects of Management" Genes 13, no. 2: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13020213
APA StyleSomenzi, E., Senczuk, G., Ciampolini, R., Cortellari, M., Vajana, E., Tosser-Klopp, G., Pilla, F., Ajmone-Marsan, P., Crepaldi, P., & Colli, L. (2022). The SNP-Based Profiling of Montecristo Feral Goat Populations Reveals a History of Isolation, Bottlenecks, and the Effects of Management. Genes, 13(2), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13020213






