Abstract
Nucleophosmin (NPM1) mutations occurring in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) (about 50 so far identified) cluster almost exclusively in exon 12 and lead to common changes at the NPM1 mutants C-terminus, i.e., loss of tryptophans 288 and 290 (or 290 alone) and creation of a new nuclear export signal (NES), at the bases of exportin-1(XPO1)-mediated aberrant cytoplasmic NPM1. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) detects cytoplasmic NPM1 and is predictive of the molecular alteration. Besides IHC and molecular sequencing, Western blotting (WB) with anti-NPM1 mutant specific antibodies is another approach to identify NPM1-mutated AML. Here, we show that among 382 AML cases with NPM1 exon 12 mutations, one was not recognized by WB, and describe the discovery of a novel combination of two mutations involving exon 12. This appeared as a conventional mutation A with the known TCTG nucleotides insertion/duplication accompanied by a second event (i.e., an 8-nucleotide deletion occurring 15 nucleotides downstream of the TCTG insertion), resulting in a new C-terminal protein sequence. Strikingly, the sequence included a functional NES ensuring cytoplasmic relocation of the new mutant supporting the role of cytoplasmic NPM1 as critical in AML leukemogenesis.
1. Introduction
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with nucleophosmin (NPM1) gene mutations is the most frequent AML among adult patients, accounting for about one third (27–35%) of all AML [1]. NPM1-mutated AML is characterized by cytoplasmic positivity for NPM1 at immunohistochemical bone marrow trephine analysis, hence also the name NPMc+ AML [1]. NPM1-mutated AML displays peculiar biological and clinical features [1,2] that lead to its inclusion as a provisional entity first, and then as a definitive distinct entity in the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of the myeloid neoplasms [3].
NPM1 is a multifunctional protein [4], essential for life [5], localized in the nucleolus, where it represents one of the most abundant proteins [6] and plays a key role in ribosome biogenesis, but also with shuttling activity between the cytoplasm and the nucleus, serving as molecular chaperone for both nucleic acids and proteins [4]. NPM1 acts also as a nucleolar stress sensor, and as a regulator of p14ARF and p53 key tumor suppressors [4].
NPM1 mutations are specific for AML [1] and highly stable during the course of the disease and at relapse [7], and never found in normal subjects [8], suggesting they are gatekeeper genetic lesions in AML. Indeed, NPM1 mutation drives leukemia in mice when co-expressed with commonly co-occurring mutations [9]. NPM1 mutations in AML are consistently heterozygous [1]. An amount of wild-type NPM1 is always detectable in the nucleolus of NPM1-mutated leukemic cells, strongly suggesting that it may be required for their survival [10]. This is in keeping with the observation that the complete knockdown of NPM1 alleles is embryonic lethal in mice [5].
NPM1 shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm thank to specific protein domains including two nuclear localization signals (NLS), a C-terminal nucleolar localization signal (NoLS) and two intramolecular nuclear export signal (NES) motifs [2,11,12]. At the steady state, signals driving NPM1 into the nucleolus/nucleus are prevalent over the export of the protein, which is mediated by the interaction of NES domains in NPM1 with the exportin 1(XPO1) protein [12].
In NPM1-mutated AML, this equilibrium is altered as the consequence of the gene mutation that occurs almost exclusively in the last exon of the gene (exon 12) causing changes at the C-terminus end of the protein, including loss of the NoLS and acquisition of a new NES, resulting in an aberrant dislocation of NPM1 in the cytoplasm of AML cells [1,13,14]. This also occurs with the rarest mutations not involving exon 12 (i.e., exon 5, 9 and 11) [15,16,17].
We have previously shown that cytoplasmic NPM1 and its interaction with exportin 1(XPO1) are essential for the maintenance of leukemic phenotype [18].
Here, we describe an interesting new combination of NPM1 mutations in exon 12, leading to a mutated amino acid sequence at the C-terminus end, with loss of the NoLS of the wild type protein and creation of a NES motif, as shown for all the other exon 12 mutations [2,13,14].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Samples
From 2005 to 2019, 929 AML patient samples referred to our center were studied by immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blot (WB) with an anti-NPM1 mutant antibody, and NPM1 exon 12 sequencing, as routine diagnostic procedures, as previously reported [1,17,19,20,21] (Figure 1). The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and informed consent was obtained from each patient to perform diagnostic examinations.
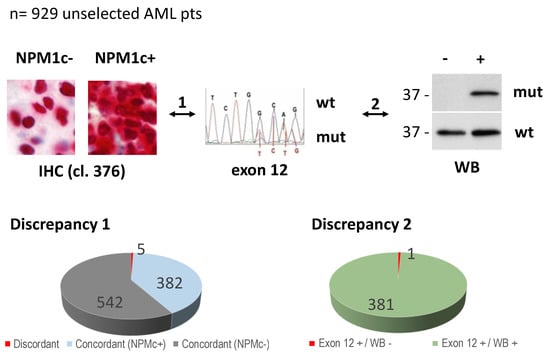
Figure 1.
Study design and diagnostic discrepancies. Overall, 929 unselected AML patients were studied by multiple diagnostic approaches (i.e., immunohistochemistry, IHC; standard molecular analysis for NPM1 exon 12, and Western blotting with specific anti-NPM1 mutant antibody, WB). 1 indicates comparison between IHC and NPM1 exon 12-molecular analysis. 2 indicates comparison between NPM1 exon 12-molecular analysis and WB. wt: wild type (exon 12 wild type); mut: mutated (exon 12 mutation A and other non-A mutations). Discrepancy 1 indicates NPM1c+ at IHC and NPM1 exon 12 wild-type (reported in [17]). Discrepancy 2 indicates NPM1c+ with mutation in exon 12 (Exon 12 +), but Western blotting (WB) negative with anti-NPM1 mutant antibody, recognizing either NPM1 mutant A and other previously described non-A mutants [20].
2.2. Immunohistochemical Analysis
Immunohistochemistry was performed on human paraffin embedded bone marrow trephine samples, as previously described [1,19]. Briefly, samples were fixed in B5 (Bio-Optica) for 2 h and decalcified in ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (Osteodec; Bio-Optica, Milan, Italy) for 5 to 6 h. Antigen retrieval was carried out by microwaving in 0.1 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, pH 8.0. Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin was revealed using a mouse anti-NPM1 monoclonal antibody, recognizing the N-terminal part of NPM1 (mAb, clone 376, generated by B.F.) [1]. Notably, this is a pan-NPM1 antibody able to recognize either NPM1 wild-type or all the NPM1 mutants [1,17,21]. Other antigens used for diagnosis included: nucleolin (C23; mAb MS-3; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA), myeloperoxidase (rabbit antimyeloperoxidase antibody; Dako, Glostrup, Denmark), linker for activation of T cells (LAT; Dako, Glostrup, Denmark); macrophage-restricted CD68 (mouse mAb PG-M1 generated by B.F.), CD34 (mouse mAb, clone QBEnd10, Dako, Glostrup, Denmark), and Bcl-2 (mouse mAb, clone 124, Dako, Glostrup, Denmark). The antibody/antigen interaction was revealed by the alkaline phosphatase anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP) technique.
2.3. Detection of NPM1 Mutant Protein by Western Blot Analysis
WB analysis for NPM1 mutant protein was performed according to standard procedures, as previously described [20]. Lysates from 1−2 × 106 cells from either peripheral blood or bone marrow of patients were used for analysis, whilst protein lysate from the human leukemic cell line OCI-AML3 (carrying NPM1 mutation A) [22,23] was used as a positive control. The following antibodies were used: a rabbit polyclonal anti-NPM1 mutant antibody (produced by B.F.), recognizing NPM1 exon 12 mutants [20] and the-pan NPM1 antibody, clone 376 [1]. After incubation with the appropriate secondary antibody, the signal was revealed by enhanced chemoluminescence, according to manufacturer’s instructions (Immobilon Crescendo Western HRP substrate, Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA).
2.4. Sanger Sequencing of NPM1
Genomic DNA and total RNA were extracted from bone marrow samples with AllPrep DNA/RNA mini kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany). RNA was reverse-transcribed to generate cDNA for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction using RT-kit plus (ELITech Group, Puteaux, France), following manufacturer’s instructions. cDNA was amplified using NPM-Forward primer: 5′-GAAAAAGCGCCAGTGAAGAAA-3′, and NPM-reverse primer: 5′-TACCGTGTTTGATAAATGTTGTCCAGG-3′. The PCR was performed using Platinum Taq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) (Tm = 60 °C; 38 cycles) and subjected to Sanger sequencing according to standard protocol, using ABI 3500 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). The raw data obtained from the sequencer were analyzed with FinchTV 1.4.0 (Geospiza, Seattle, WA, USA) in order to obtain the nucleotide sequence.
2.5. Targeted Deep Sequencing
Genomic DNA was quantified with High-Sensitivity (HS) and Broad-Range (BR) Qubit assay on a Qubit 2.0 fluorometer (Invitrogen) and was subjected either to deep targeted sequencing of NPM1 gene to molecularly barcoded targeted sequencing of 42 genes recurrently mutated in myeloid neoplasms (QIAseq Targeted DNA Custom Panel–CDHS-31667Z-1041-QIAGEN) (Supplementary Table S1), using 35 ng of input DNA. Libraries, generated according to the manufacturer’s instructions, were sequenced on a Illumina MiSeq instrument 2 × 151 cycles for the myeloid panel, using MiSeq Reagent Kit v2 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) (mean unique depth of coverage was 1508×). Mapping and variant calling was performed with QIAGEN smCounter algorithm v2 with default settings [24], and variant annotation was performed with Illlumina Variant Studio 3.0. Sequencing variants were then subjected to the further following filters, and retained only if: (i) they passed the default filters of the Qiagen software; (ii) they were predicted to change the gene coding sequence, or they involved the conserved splice-site (i.e., the 4 nucleotides surrounding the exon-intron junction); (iii) they were not present in the Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC) database of normal individuals at a population frequency ≥1% (as provided by Illumina Variant Studio 3.0); (iv) they were present at an allele frequency >2%; and (v) if consisting in insertions or deletions, they were not located in homopolymeric stretches of 5 nucleotides or longer.
2.6. Genomic DNA NPM1 Fragment Analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted with Maxwell (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), quantified using a ND-1000 apparatus (Nanodrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA), and amplified with the NPM-Forward primer: FAM 5′-AGGACAGCCAGATATCAACTGTTAC-3′ and NPM-Reverse primer: 5′-AGTTAACTCTCTGGTGGTAGAATGAAA-3′. Reactions of 25 μL contained 10 ng of genomic DNA, primers (0.8 µM each), deoxynucleoside-5′-triphosphates (0.25 mM, each), MgCl2 (1.5 mM), 6.25% of Dimethyl sulfoxide, 0.4 U of Taq-Gold DNA polymerase, and 10× buffer (AmpliTaq DNA polymerase, Applied Biosystem Inc.). Cycling conditions were: 1 cycle, 7 min at 94 °C; 30 cycles, 60 s at 95 °C, 40 s at 55 °C, and 90 s at 72 °C; and 1 cycle, 5 min at 72 °C. 1 μL polymerase-chain-reaction (PCR) product was mixed with 9 μL of HiDi formamide (Applied Biosystems, Inc.) and 0.3 μL Liz Size Standard (Applied Biosystems, Inc.) and heated at 95 °C for 2 min. The samples were run on an ABI 3500 Genetic Analyzer T (Applied Biosystems, Inc.). PCR products and internal standards were detected using filter set D. Raw data were analyzed with GeneMapper v4.0 software (Applied Biosystems, Inc.).
2.7. pEGFP-C1-NPM1 Plasmid Constructs, Cell Transfection and Immunofluorescence Analysis
Generation of the specific plasmids and constructs cloning were commissioned to GeneScript (Piscataway, NJ, USA) once provided with the plasmid pEGFP-C1-NPM1wt as a template and sequence information. For ectopic expression of the GFP-NPM1 fusion proteins, the murine fibroblasts cell line NIH-3T3 were transiently transfected with plasmids: p-EGFP-C1 empty vector, p-EGFP-C1-NPM1wt and p-EGFP-C1-NPM1mutA, as controls, and the p-EGFP-C1-NPM1_new mutant. The subcellular localization of the GFP-NPM1 fusion proteins was analyzed by confocal microscopy [13,25]. Treatment with the specific exportin-1/XPO1 inhibitor leptomycin B (20 ng/mL for 5 h) (Merck Biosciences Ltd.,Darmstadt, Germany) of NIH-3T3 overexpressing the new GFP-NPM1 fusion protein was used to evaluate the NES dependence of its subcellular localization, as previously reported [13,25]. For confocal microscopy studies, transfected NIH-3T3 cells, grown on glass coverslips, were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, pH 7.4 (10 min), air dried and flipped onto standard glass slides with Mowiol mounting medium (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Nuclei were stained with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) fluorescent stain in Prolong Gold mounting reagent (Molecular Probes by Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) following standard procedures. Confocal analysis was done with a Zeiss LSM 800 confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany) using 488 nm (for eGFP) laser line for excitation.
2.8. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RTq-PCR) for NPM1 Mutation A
RTq-PCR for NPM1 mutation A was performed using the commercially available ipsogen® NPM1 mutA MutaQuant® kit (#677513; QIAGEN GmbH, Hilden, Germany), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. An endogenous control (transcript from Abelson, ABL) is amplified from the sample together with the NPM1 mutA transcript. Standard curves of known amounts of both the endogenous ABL control and NPM1 mutA cDNA allow the calculation of the ratio of NPM1 mutA signal to endogenous ABL signal in each sample. The kit allows quantification of NPM1 mutA transcripts for minimal residual disease (MRD) monitoring. Notably, the specificity of the kit is based on the use of specific reverse primers for the NPM1mutA allele.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of a New NPM1 Mutation Involving Exon 12
In our previously reported study [17], 387 out of the 929 bone marrow samples analyzed (41.6%) showed cytoplasmic positivity for NPM1 (NPMc+) at IHC (Figure 1). Five out of 387 (1.3%) NPMc+ AML cases harbored rare NPM1 non-exon 12 mutations, specifically in exon 9 (n = 1), exon 11 (n = 1) and exon 5 (n = 3) [17] (Discrepancy 1, Figure 1). Of course, these rare non-exon 12 mutants were not recognized at WB analysis by the anti-NPM1 mutant antibody that was raised against the C-terminus of mutant A [20]. Instead, all cases with mutation in exon 12, but one, were recognized by the anti-NPM1 mutant antibody at WB confirming the value of this methodological approach in identifying at least the great majority of NPM1 mutant proteins in AML samples and in predicting the underlying mutation in NPM1 exon 12 [20] (Discrepancy 2, Figure 1).
The single case not recognized by WB, hereinafter referred to as pt. Rm (patient sample from Rome, Italy) (Figure 2), was further investigated. IHC analysis on pt. Rm bone marrow biopsy showed diffuse infiltration by leukemic blasts with evident positivity at cytoplasmic level for NPM1 (NPM1 (Figure 2a). Myelo-monocytic blasts appeared negative for CD34 (Figure 2a), as typically observed in NPM1-mutated AML [1]. Additionally, Bcl-2 protein appeared overexpressed (not shown), as observed in the great majority of AML at diagnosis. Dysplastic megakaryocytes were detected in clusters (Figure 2a). As mentioned, WB analysis with anti-NPM1 mutant antibody was negative (Figure 2b).
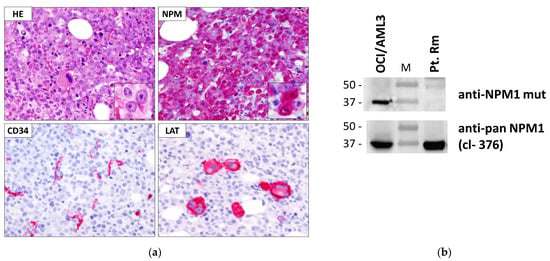
Figure 2.
(a) Immunohistochemical staining of bone marrow trephine from pt. Rm. HE: hematoxylin-eosin staining; NPM: mouse monoclonal anti-panNPM1, clone 376; CD34: anti-CD34 mAb (to note, blood vessels in tissue sections are used as positive control for CD34 staining). LAT: linker for activation of T cell (marker for megakaryocytes); APAAP technique; hematoxylin counterstaining. Images were collected using an Olympus B61 microscope with a UPlanApo 40×/0.85U and UPlan FI 100×/1.3 NA oil objective for the insets; Camedia 4040, Dp_soft Version 3.2; and Adobe Photoshop CC 2019; (b) WB analysis of total protein extracts from pt. Rm. OCI/AML3: positive control for NPM1 mutant A expression. M: molecular weight marker.
Interestingly, Sanger and deep targeted sequencing of NPM1 performed on the genomic DNA extracted from pt. Rm peripheral blood (PB) showed the insertion/duplication of the 4 nucleotides (nt) TCTG characterizing the most common NPM1 mutation type A (NM_002520.6:c.860_863dupTCTG) [1], that, however, was accompanied (15 nucleotides downstream) by a deletion of eight nucleotides (NM_002520.6:c.879_*1delTCTTTAAG), a composite genetic event not previously described (Supplementary Table S1). Specifically, the variant allelic frequencies (VAFs) for the 4-nt TCTG insertion/duplication and the new 8-nt deletion were 16% and 20.5%, respectively, in keeping with the about 40% AML blasts representation in the analyzed patient’s sample (considering that NPM1 mutation are heterozygous) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Biological and clinical features of AML patient with NPM1 mutation Rm.
To confirm that the two events (4-nt insertion and 8-nt deletion) occurred in the same allele of NPM1 gene, we performed genomic DNA fragment analysis for NPM1 exon 12 of the pt. Rm sample in parallel with either wild type or mutation A control (Figure 3). As expected, in the pt. Rm sample, the electropherogram revealed two fragment peaks, one of the same size of the wild type, and the other 4 nt shorter, being the result of the composite 4 nt insertion/8 nt deletion. No peaks of other sizes, and in particular no peak corresponding to mutant A, were evident. These data prove that indeed the 4 nt TCTG insertion/duplication and the new 8 nt deletion occurred in the same allele of NPM1 gene. Quantitation of the mutation Rm peak indicated a 21% VAF, in line with the values obtained by deep targeted sequencing of NPM1 (Figure 3, Supplementary Table S1).
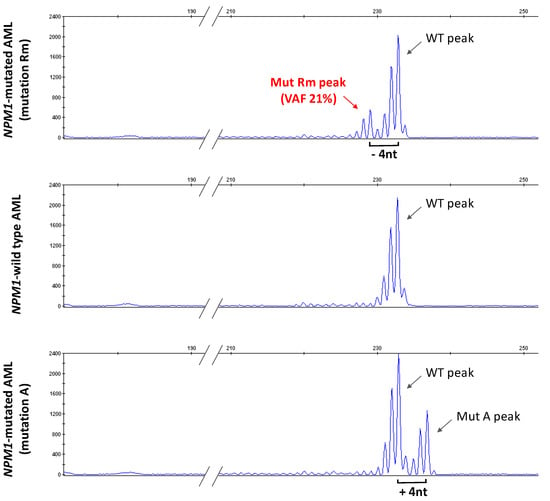
Figure 3.
Genomic DNA NPM1 fragment analysis. Electropherograms of genomic DNA fragments of NPM1 exon 12 extracted from PB of the AML patient Rm (upper panel), AML sample with wild type NPM1 (middle panel) and AML sample with NPM1 mutation A (lower panel). Peaks corresponding to WT (wild type), mutant A (Mut A) and mutant Rm (Mut Rm) are indicated. Fragments from Mut Rm are 4 nucleotides shorter (−4 nt) than WT. Fragments from Mut A are 4 nucleotides longer (+4 nt) than WT. The variant allelic frequency (VAF) of the Rm mutated allele is shown.
Occurring on the same NPM1 allele, the 8 nt frame-shifting deletion, which on its own would just replace the last protein amino acid (L294K; Supplementary Table S1), when combined with the preceding mutation A (4 nt TCTG insertion) leads to elimination of the ‘planned’ stop codon typical of mutation A (W288CfsTer12) and introduces an earlier ‘new’ stop codon (W288CfsTer11; Figure 4a).
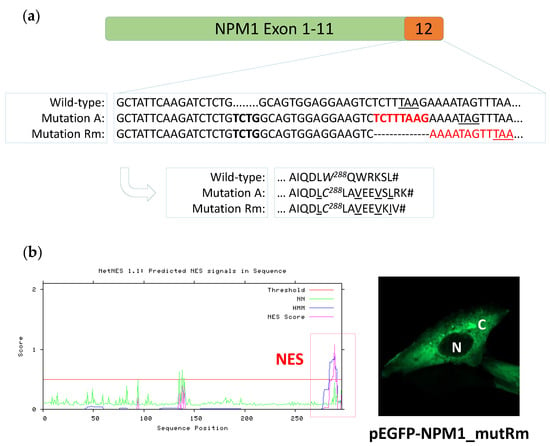
Figure 4.
The new NPM1 mutation Rm disrupts the NoLS and inserts a C-terminal NES. (a) Nucleotide sequences of exon 12 in NPM1 wild-type, mutation A and new composite mutation Rm, and corresponding predicted protein sequences (arrow). The 4 nucleotide insertion TCTG in mutation A and mutation Rm is highlighted in bold black. The 8 nucleotides lost in composite mutation Rm are highlighted in bold red. The C-terminal NES motifs in mutant A and mutant Rm are underlined. (b) Left, NES motif prediction in the new NPM1 mutant Rm. The newly acquired C-terminal NES is highlighted in the red box. Right, representative image of NIH-3T3 overexpressing the new GFP-NPM1 mutant Rm fusion protein. Images were acquired using a Zeiss LSM 800 confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss) with a 488-nm (for eGFP) laser line for excitation, and a 63×/1.4 OIL Plan-Apochromat objective. N: nucleus; C: cytoplasm.
3.2. The New NPM1 Mutant Protein Displays a New C-Terminal Nuclear Export Signal (NES) Motif
We then analyzed the consequences of this new composite mutation at the protein level. The two events described above result in a new mutant NPM1 protein (W288CfsTer11), here named Rm, 297 amino acid long, with a C-terminal sequence differing from the mutant A only for the last amino acids (mutRm_288CLAVEEVKIV versus mutA_288CLAVEEVSLRK) (Figure 4a). In particular, protein sequence prediction indicates that, as for NPM1 mutant A, the new NPM1 mutant Rm loses the nucleolar localization signal (NoLS), with the loss, in particular, of both tryptophans 288 and 290 typical of the wild-type NPM1 protein, whilst it acquires a theoretical new NES. Indeed, a search for acquisition of a NES motif in the new mutant protein sequence, performed by applying the NES detection NetNES 1.1 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetNES, accessed date: 17 August 2021), identified a C-terminal NES with high score (LVVI) (Figure 4b, left). To confirm its predicted cytoplasmic localization, the Rm mutant was expressed as GFP-NPM1 fusion protein in NIH-3T3 cells and its subcellular localization analyzed at confocal microscopy. As expected by the newly acquired C-terminal NES and the concomitant loss of NoLS, the Rm mutant is localized in the cytoplasm (Figure 4b, right).
3.3. The New NPM1 Mutant Protein Locates in the Cytoplasm in a NES-Dependent Manner
To demonstrate that the Rm mutant locates in the cytoplasm in a NES-dependent manner, its subcellular localization, as a GFP-NPM1 fusion protein in NIH-3T3 cells, was analyzed at confocal microscopy, either in presence or absence of the exportin-1(XPO1) inhibitor leptomycin B. Whilst in untreated cells, green fluorescence was detected only in the cytoplasm, relocation into the nucleoplasm was observed upon leptomycin B treatment, confirming it is a NES-dependent phenomenon (Figure 5). To note, as expected in NIH-3T3 overexpression system, upon relocation of the Rm mutant into the nucleus, nucleoli are spared most likely due to the loss of NoLS, as happens with NPM1 mutant A (Figure 5).
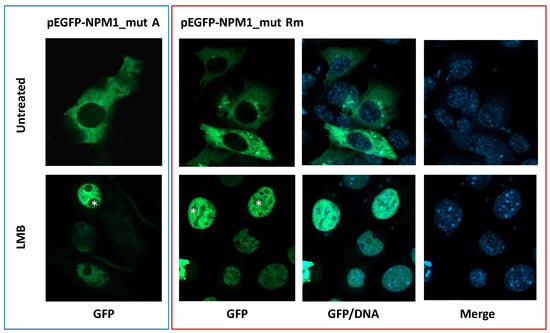
Figure 5.
The subcellular localization of the new NPM1 mutant Rm is NES-dependent. NIH-3T3 overexpressing either the GFP-NPM1 mutant A or the new GFP-NPM1 mutant Rm fusion proteins. Untreated: vehicle. LMB: leptomycin B. GFP: green fluorescence protein (of the GFP-NPM1 fusion protein). DNA: indicates stained nuclei (blue). Images were acquired using a Zeiss LSM 800 confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss) with a 488-nm (for eGFP) laser line for excitation, and a 63×/1.4 OIL Plan-Apochromat objective. Asterisk: nucleoli spaces.
3.4. Detection of NPM1 Mutant Rm Transcripts by q-RT-PCR for NPM1 Mutation A
Since, as described above, NPM1 mutation Rm is characterized by the insertion/duplication of the 4 nucleotides TCTG typical of NPM1 mutation type A (i.e., NM_002520.6:c.860_863dupTCTG) with conservation of the following 15 nucleotides sequence before the eight nucleotide deletion (i.e., NM_002520.6:c.879_*1delTCTTTAAG), we hypothesized that it was identifiable applying the q-RT-PCR assay designed specifically for mutation A and used for diagnostic purposes and minimal residual disease (MRD) monitoring. Indeed, NPM1 mutant Rm transcripts could be detected and quantified (NPM1mutRm = 506 copies/100 Abl) as it occurs for the classical NPM1 mutation A (Table 1).
3.5. Characteristics of AML Carrying NPM1 Mutation Rm
We then analyzed whether patient carrying NPM1 mutation Rm displayed characteristics typical of the most common AML with NPM1 mutation A. Besides NPM1 cytoplasmic positivity at IHC, other biological characteristics in common with other NPM1-mutated AML include de novo occurrence, hyperleukocytosis, CD34-negativity, morphological pattern myelo-monocytic phenotype, increased dysplastic megakaryocytes [26,27,28], and normal karyotype [29] (Table 1). Among other genes frequently mutated in NPM1-mutated AML, FLT3 was wild-type in pt. Rm, as well as epigenetic genes DNMT3A and IDH1/2, whilst TET2 resulted as mutated with a variant allelic frequency, VAF of 47.2%. Other co-occurring mutations included mutations in SRSF2 (VAF, 50.2%) and ASXL1 (at lower VAF, 8.7%), frequently found in elderly patients [30] (Supplementary Table S2). The VAF values for either TET2 or SRSF2 mutations, much higher than NPM1 mutations (VAF 16/20.5%) and involving almost the totality of the sample cells, suggest NPM1 mutations arose on a background of a TET2/SRSF2-positive disease.
4. Discussion
Here, we report the description of a new mutation involving exon 12 of NPM1 gene in a patient with diagnosis of AML. As compared to the other variants of exon 12 mutations, this appears peculiar since it introduces the same 4 nucleotides insertion (i.e., TCTG) as mutation A but, due to an accompanying downstream eight-nucleotide deletion, the last amino acids are different.
Nevertheless, as it happens for all NPM1 mutations, a newly acquired functional C-terminal NES mediated the cytoplasmic accumulation of the new composite mutant.
Whether these two different genetic events occurred simultaneously or independently can be a matter of speculation, given that the two events are separated by 15 nucleotides and the mechanism hypothesized as underlying the four-nucleotide insertion identical to mutation A (i.e., illegitimate activity of the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase [31]) is unlikely to explain the following 8-nucleotide deletion. The fact that allele frequency for the eight-nucleotide deletion resulted, upon molecularly barcoded deep sequencing, somewhat higher than the upstream four-nucleotide insertion (20.5% versus 16.1%, respectively) (Supplementary Table S2) might lead to the hypothesis that the eight-nucleotide deletion developed first. However, we can not exclude that, although VAF estimate based on barcoded deep sequencing are generally very accurately determined, the slightly higher VAF of the deletion (4%) could be due to bioinformatics parameters of the variant calling pipeline.
Nevertheless, it would be interesting to dissect in proper experimental models the functional consequences of the 8 nt deletion on its own and the new composite mutation.
The discovery of this new composite mutation involving NPM1 exon 12 has been made by the application of different diagnostic assays, i.e., immunohistochemistry, molecular analysis (PCR, DNA fragments analysis, deep targeted NGS) and Western blotting, which, more than alternatives, could be considered complementary techniques for an accurate diagnosis [32]. Strikingly, despite a very similar C-terminal protein sequence as mutant A, this mutant was not identified by the anti-NPM1 mutant A antibody (able to recognize almost all the NPM1 exon 12 mutants) at WB, suggesting the last amino acids of NPM1 mutant A (i.e., 295SLRK) are important for the antibody reactivity. On the other hand, in contrast to what observed with all the other known exon 12 mutations, the NPM1 mutant Rm transcripts are detectable and quantifiable by qRT-PCR designed for NPM1 mutation A (Table 1), suggesting this assay can be used for MRD monitoring in case of NPM1 mutation Rm.
Biologically, this report reinforces the concept of NPM1 as ‘born-to be-exported’ in NPM1-mutated AML, meaning that only those mutations that lead to exportin-1(XPO1)/NPM1 mutant interaction and the following dislocation of NPM1 in the cell cytoplasm are selected to develop leukemia [13,17,18].
In summary, this case underlies on one side the biologic significance of the event ‘cytoplasmic positivity of NPM1′ as critical for leukemogenesis in AML, and on the other side the value of using several different techniques in routine diagnostics in order to recognize rare cases leading to similar alterations and define the strategy for MRD monitoring [17,21,32].
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/genes12091426/s1, Table S1: Genes subjected to targeted deep sequencing (QIAseq Targeted DNA Custom panel-QIAGEN (CDHS-31667Z-1041), Table S2: List of somatic mutations by barcoded-targeted NGS of myeloid recurrent genes in peripheral blood of AML patient Rm.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.P.M. and B.F.; methodology, E.T. and M.P.M.; validation, formal analysis, A.V., R.R., G.M., M.G.M., P.S., E.T., M.P.M.; sample collection, O.A. and G.A.; writing—original draft preparation, A.V. and R.R.; writing—review and editing, B.F. and M.P.M.; supervision, P.S., E.T. and M.P.M.; funding acquisition, B.F. and M.P.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by AIRC IG 2016 n.18568 (to B.F.), ERC Adv Grant 2016 n. 740230 (to B.F.) and ERC Cons Grant 2016 n. 725725 (to M.P.M.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, as it was retrospective in nature and performed on routine diagnostic samples.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
For original data, please contact maria.martelli@unipg.it.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Alessia Tabarrini and Barbara Bigerna for technical support in IHC analysis. We thank Claudia Tibidò and Laura Pinacoli for secretarial assistance. In memory of Roberta Pacini.
Conflicts of Interest
B.F. licensed a patent on NPM1 mutants (n. 102004901256449). B.F. and M.P.M. declare honoraria from Rasna Therapeutics, Inc for scientific advisor activities. M.P.M. also declares honoraria/consultancy at scientific advisory board for Abbvie, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Jazz Pharmaceuticals. O.A. declares honoraria/consultancy at scientific advisory board for Janssen, Novartis, Celgene, Amgen. P.S. declares honoraria/consultancy at scientific advisory board for Abbvie, Janssen, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Incyte. The other authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Falini, B.; Mecucci, C.; Tiacci, E.; Alcalay, M.; Rosati, R.; Pasqualucci, L.; La Starza, R.; Diverio, D.; Colombo, E.; Santucci, A.; et al. Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Nicoletti, I.; Martelli, M.F.; Mecucci, C. Acute myeloid leukemia carrying cytoplasmic/mutated nucleophosmin (NPMc+ AML): Biologic and clinical features. Blood 2007, 109, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisendi, S.; Mecucci, C.; Falini, B.; Pandolfi, P.P. Nucleophosmin and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisendi, S.; Bernardi, R.; Rossi, M.; Cheng, K.; Khandker, L.; Manova, K.; Pandolfi, P.P. Role of nucleophosmin in embryonic development and tumorigenesis. Nature 2005, 437, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulon, S.; Westman, B.J.; Hutten, S.; Boisvert, F.M.; Lamond, A.I. The nucleolus under stress. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Martelli, M.P.; Mecucci, C.; Liso, A.; Bolli, N.; Bigerna, B.; Pucciarini, A.; Pileri, S.; Meloni, G.; Martelli, M.F.; et al. Cytoplasmic mutated nucleophosmin is stable in primary leukemic cells and in a xenotransplant model of NPMc+ acute myeloid leukemia in SCID mice. Haematologica 2008, 93, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKerrell, T.; Park, N.; Moreno, T.; Grove, C.S.; Ponstingl, H.; Stephens, J.; Crawley, C.; Craig, J.; Scott, M.A.; Hodkinson, C.; et al. Leukemia-associated somatic mutations drive distinct patterns of age-related clonal hemopoiesis. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Sportoletti, P. A scale of bad co-mutations in NPM1-driven AML. Blood 2017, 130, 1877–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Martelli, M.P. NPM1-mutated AML: Targeting by disassembling. Blood 2011, 118, 2936–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hingorani, K.; Szebeni, A.; Olson, M.O. Mapping the functional domains of nucleolar protein B23. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 24451–24457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Wang, X.W. Temporal and spatial control of nucleophosmin by the Ran-Crm1 complex in centrosome duplication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolli, N.; Nicoletti, I.; De Marco, M.F.; Bigerna, B.; Pucciarini, A.; Mannucci, R.; Martelli, M.P.; Liso, A.; Mecucci, C.; Fabbiano, F.; et al. Born to be exported: COOH-terminal nuclear export signals of different strength ensure cytoplasmic accumulation of nucleophosmin leukemic mutants. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6230–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Albiero, E.; Bolli, N.; De Marco, M.F.; Madeo, D.; Martelli, M.; Nicoletti, I.; Rodeghiero, F. Aberrant cytoplasmic expression of C-terminal-truncated NPM leukaemic mutant is dictated by tryptophans loss and a new NES motif. Leukemia 2007, 21, 2052–2054; author reply 2054; discussion 2055–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, A.R.; Colombo, E.; Luzi, L.; Martinelli, P.; Volorio, S.; Bernard, L.; Meani, N.; Bergomas, R.; Alcalay, M.; Pelicci, P.G. Cytoplasmic localization of NPM in myeloid leukemias is dictated by gain-of-function mutations that create a functional nuclear export signal. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4376–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiero, E.; Madeo, D.; Bolli, N.; Giaretta, I.; Bona, E.D.; Martelli, M.F.; Nicoletti, I.; Rodeghiero, F.; Falini, B. Identification and functional characterization of a cytoplasmic nucleophosmin leukaemic mutant generated by a novel exon-11 NPM1 mutation. Leukemia 2007, 21, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, M.P.; Rossi, R.; Venanzi, A.; Meggendorfer, M.; Perriello, V.M.; Martino, G.; Spinelli, O.; Ciurnelli, R.; Varasano, E.; Brunetti, L.; et al. Novel Npm1 Exon 5 Mutations and Gene Fusions Leading to Aberrant Cytoplasmic Nucleophosmin in Aml. Blood 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, L.; Gundry, M.C.; Sorcini, D.; Guzman, A.G.; Huang, Y.H.; Ramabadran, R.; Gionfriddo, I.; Mezzasoma, F.; Milano, F.; Nabet, B.; et al. Mutant NPM1 Maintains the Leukemic State through HOX Expression. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Martelli, M.P.; Bolli, N.; Bonasso, R.; Ghia, E.; Pallotta, M.T.; Diverio, D.; Nicoletti, I.; Pacini, R.; Tabarrini, A.; et al. Immunohistochemistry predicts nucleophosmin (NPM) mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2006, 108, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, M.P.; Manes, N.; Liso, A.; Pettirossi, V.; Verducci Galletti, B.; Bigerna, B.; Pucciarini, A.; De Marco, M.F.; Pallotta, M.T.; Bolli, N.; et al. A western blot assay for detecting mutant nucleophosmin (NPM1) proteins in acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia 2008, 22, 2285–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Falini, B.; Brunetti, L.; Martelli, M.P. How I diagnose and treat NPM1-mutated AML. Blood 2021, 137, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quentmeier, H.; Martelli, M.P.; Dirks, W.G.; Bolli, N.; Liso, A.; Macleod, R.A.; Nicoletti, I.; Mannucci, R.; Pucciarini, A.; Bigerna, B.; et al. Cell line OCI/AML3 bears exon-12 NPM gene mutation-A and cytoplasmic expression of nucleophosmin. Leukemia 2005, 19, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiacci, E.; Spanhol-Rosseto, A.; Martelli, M.P.; Pasqualucci, L.; Quentmeier, H.; Grossmann, V.; Drexler, H.G.; Falini, B. The NPM1 wild-type OCI-AML2 and the NPM1-mutated OCI-AML3 cell lines carry DNMT3A mutations. Leukemia 2012, 26, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Gu, X.; Padmanabhan, R.; Wu, Z.; Peng, Q.; DiCarlo, J.; Wang, Y. smCounter2: An accurate low-frequency variant caller for targeted sequencing data with unique molecular identifiers. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Bolli, N.; Shan, J.; Martelli, M.P.; Liso, A.; Pucciarini, A.; Bigerna, B.; Pasqualucci, L.; Mannucci, R.; Rosati, R.; et al. Both carboxy-terminus NES motif and mutated tryptophan(s) are crucial for aberrant nuclear export of nucleophosmin leukemic mutants in NPMc+ AML. Blood 2006, 107, 4514–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Liso, A.; Martelli, M.P.; Bolli, N.; Pacini, R.; Tabarrini, A.; Carini, M.; Bigerna, B.; Pucciarini, A.; Mannucci, R.; et al. Mutated nucleophosmin detects clonal multilineage involvement in acute myeloid leukemia: Impact on WHO classification. Blood 2006, 108, 4146–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falini, B.; Macijewski, K.; Weiss, T.; Bacher, U.; Schnittger, S.; Kern, W.; Kohlmann, A.; Klein, H.U.; Vignetti, M.; Piciocchi, A.; et al. Multilineage dysplasia has no impact on biologic, clinicopathologic, and prognostic features of AML with mutated nucleophosmin (NPM1). Blood 2010, 115, 3776–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sportoletti, P.; Varasano, E.; Rossi, R.; Bereshchenko, O.; Cecchini, D.; Gionfriddo, I.; Bolli, N.; Tiacci, E.; Intermesoli, T.; Zanghi, P.; et al. The human NPM1 mutation A perturbs megakaryopoiesis in a conditional mouse model. Blood 2013, 121, 3447–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2059–2074. [CrossRef]
- Eisfeld, A.K.; Kohlschmidt, J.; Mrozek, K.; Blachly, J.S.; Walker, C.J.; Nicolet, D.; Orwick, S.; Maharry, S.E.; Carroll, A.J.; Stone, R.M.; et al. Mutation patterns identify adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia aged 60 years or older who respond favorably to standard chemotherapy: An analysis of Alliance studies. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrow, J.; Dyer, S.A.; Akiki, S.; Griffiths, M.J. Molecular roulette: Nucleophosmin mutations in AML are orchestrated through N-nucleotide addition by TdT. Blood 2019, 134, 2291–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Martelli, M.P.; Pileri, S.A.; Mecucci, C. Molecular and alternative methods for diagnosis of acute myeloid leukemia with mutated NPM1: Flexibility may help. Haematologica 2010, 95, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).