Evolution, Expression and Meiotic Behavior of Genes Involved in Chromosome Segregation of Monotremes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
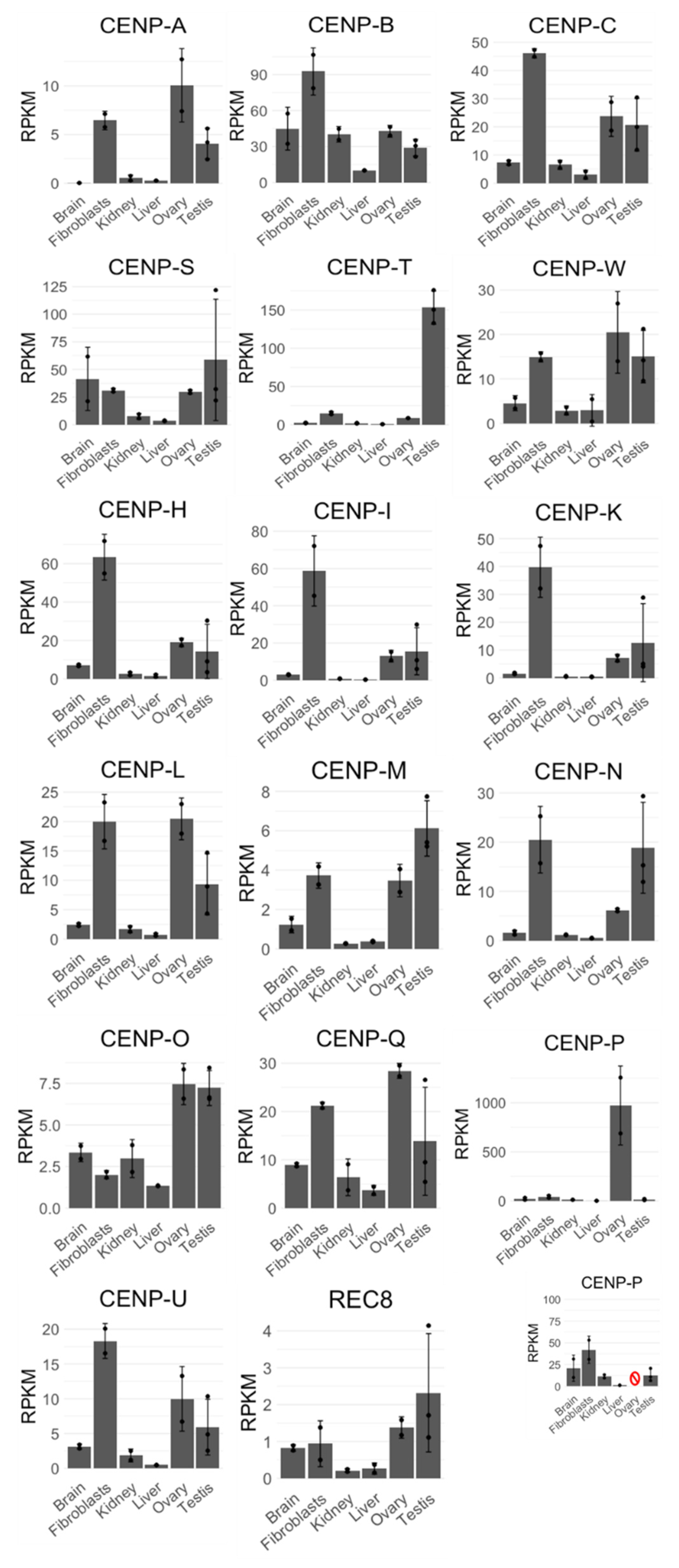
2.1. Bioinformatic Analysis, Transcriptome Mapping, and Expression Analysis
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Preparation of Meiotic Cells
2.4. Immunostaining
3. Results
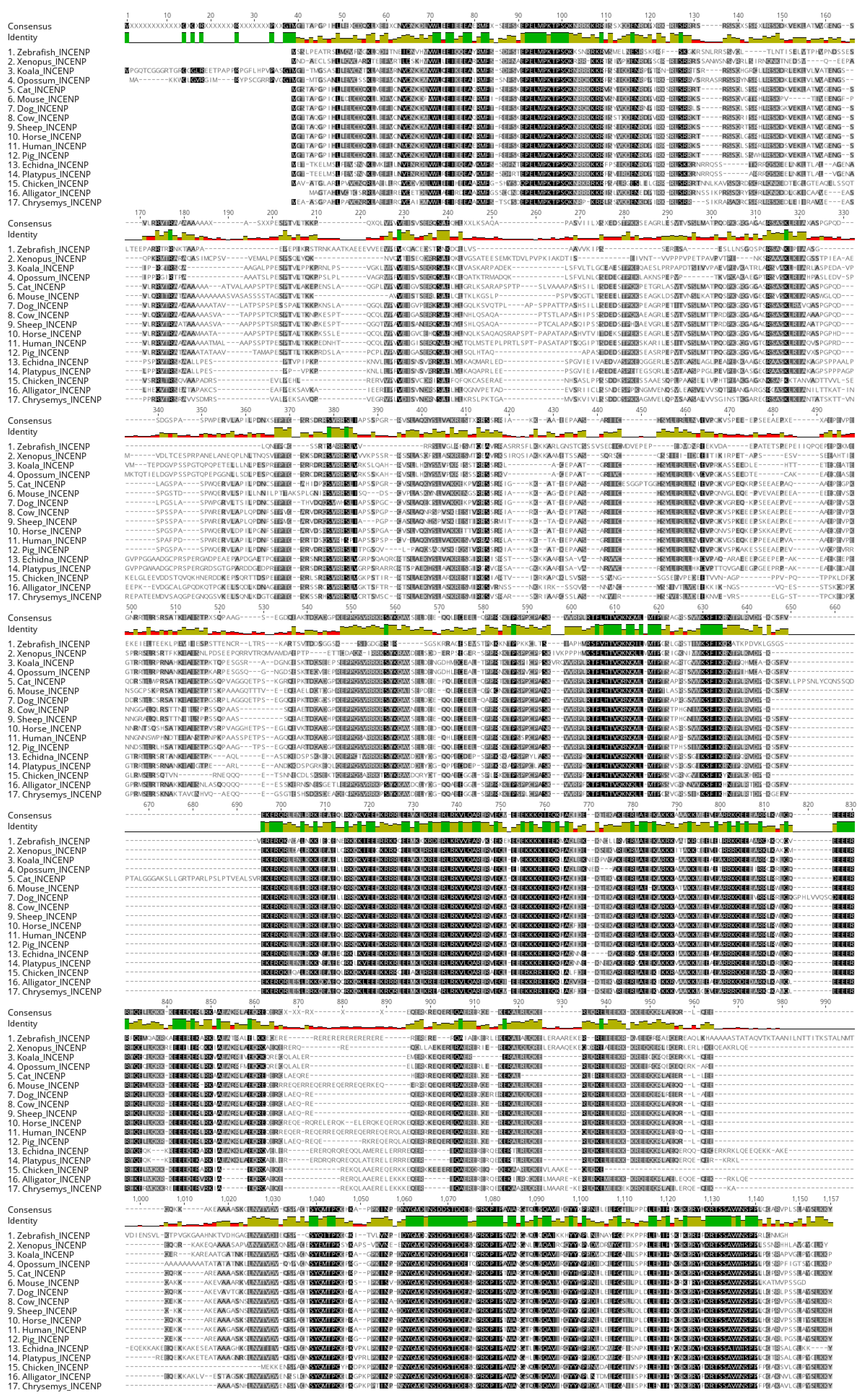
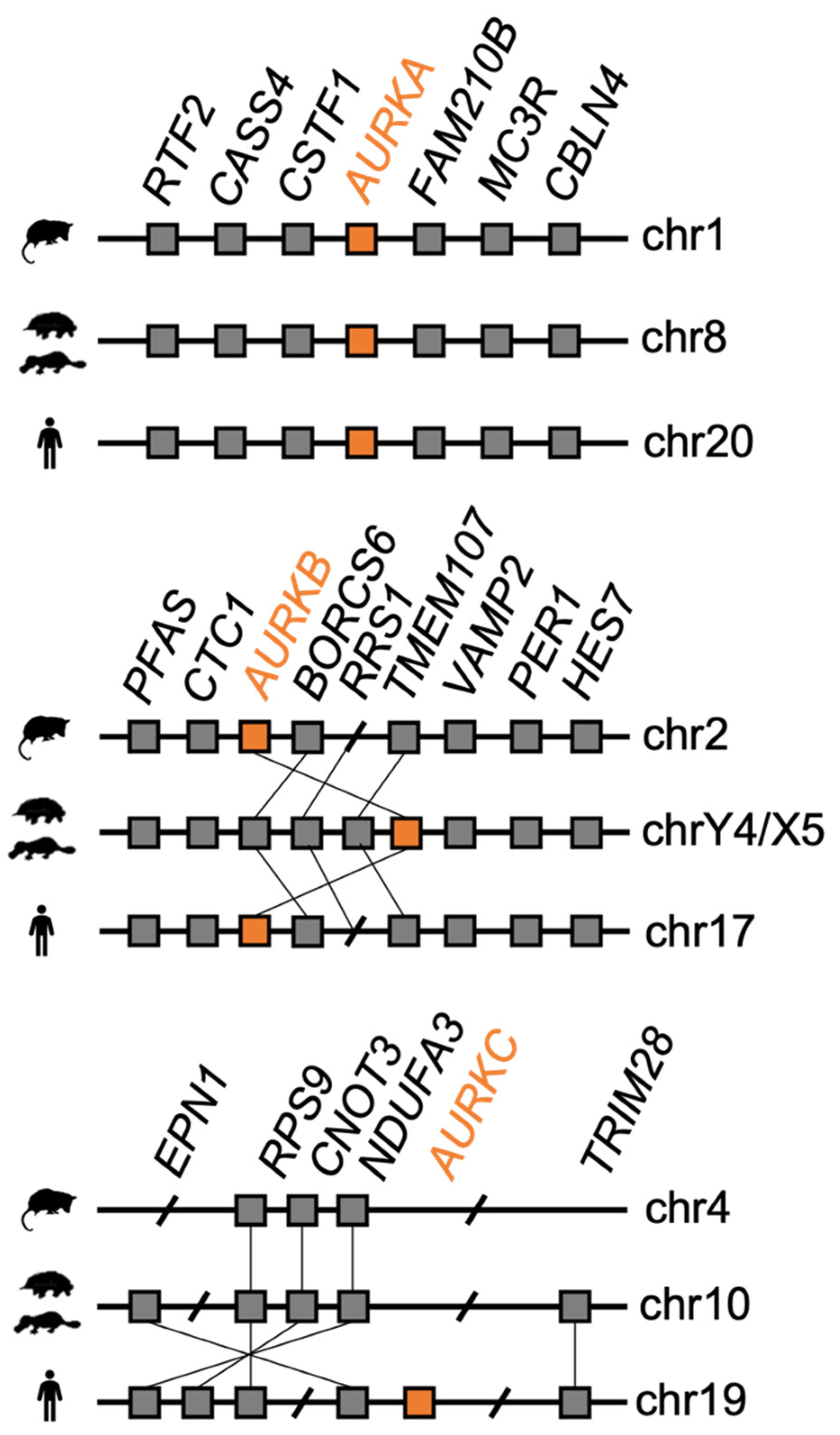
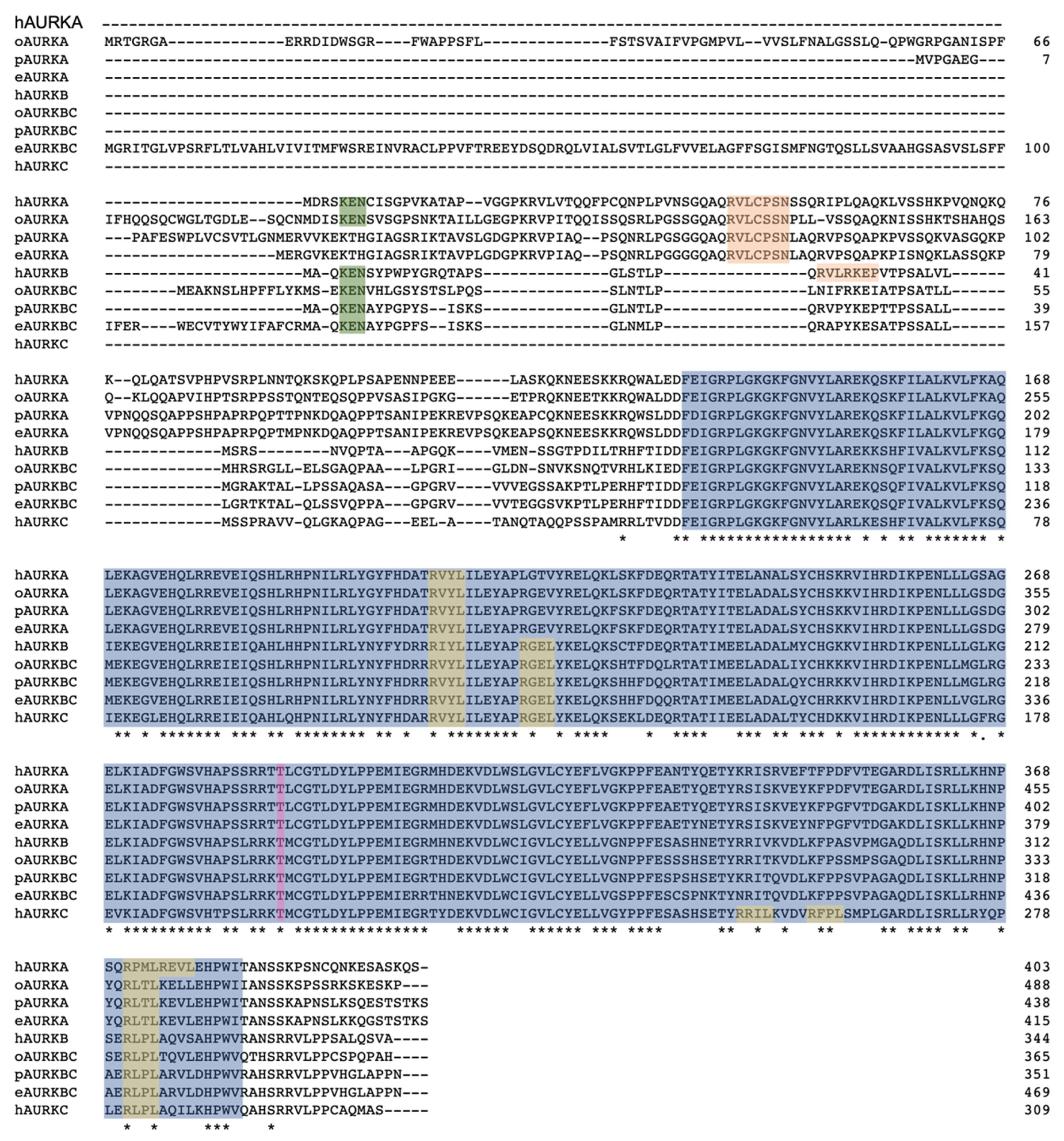
3.1. Analysis of Monotreme AURK Genes
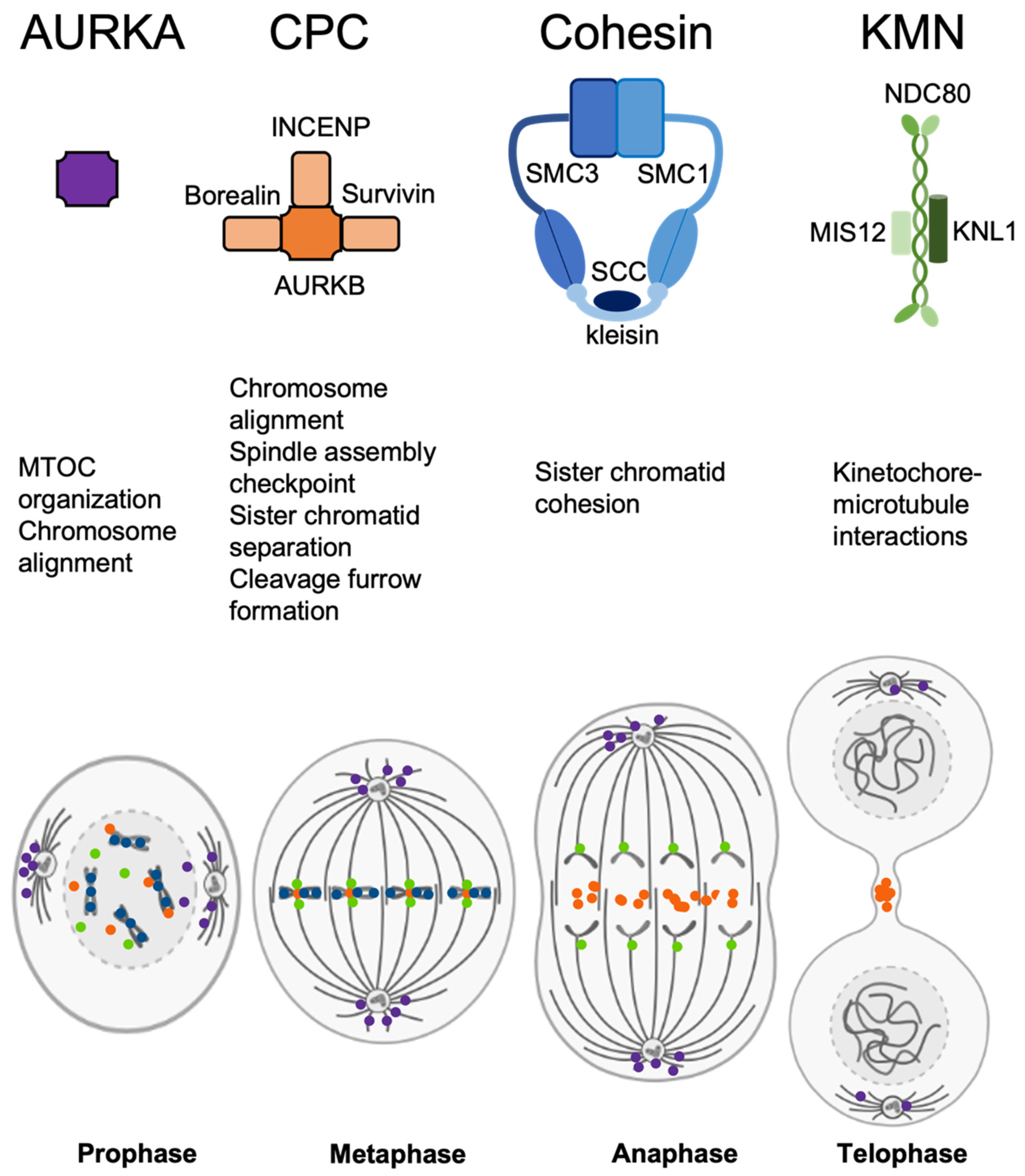
3.2. Analysis of CPC and Chromosome-Segregation-Related Proteins
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Rens, W.; O'Brien, P.C.; Grützner, F.; Clarke, O.; Graphodatskaya, D.; Tsend-Ayush, E.; Trifonov, V.; Skelton, H.; Wallis, M.C.; Johnston, S.; et al. The multiple sex chromosomes of platypus and echidna are not completely identical and several share homology with the avian Z. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruetzner, F.; Ashley, T.; Rowell, D.; Graves, J. How did the platypus get its sex chromosome chain? A comparison of meiotic multiples and sex chromosomes in plants and animals. Chromosoma 2005, 115, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeling, J.M.; Farmer, A.A.; Mansfield, A.; Cho, H.; Choudhary, M. Differential selective pressures experienced by the aurora kinase gene family. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bolanos-Garcia, V.M. Aurora kinases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 1572–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, Y.; Okumura, E.; Hosoya, T.; Hirota, T.; Kishimoto, T. A single starfish Aurora kinase performs the combined functions of Aurora-A and Aurora-B in human cells. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 3978–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, A.L.; Drutovic, D.; Vazquez, B.N.; El Yakoubi, W.; Gentilello, A.S.; Malumbres, M.; Solc, P.; Schindler, K. Genetic Interactions between the Aurora Kinases reveal new requirements for AURKB and AURKC during Oocyte Meiosis. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 3458–3468.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, A.L.; Schindler, K. Specialize and divide (Twice): Functions of three Aurora kinase homologs in Mammalian Oocyte Meiotic maturation. Trends Genet. 2017, 33, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alfaro, E.; López-Jiménez, P.; González-Martínez, J.; Malumbres, M.; Suja, J.A.; Gómez, R. PLK1 regulates centrosome migration and spindle dynamics in male mouse meiosis. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e51030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellard, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Shults, C.; Zhao, X.; McKay, M.; Murray, S.A.; Jordan, P.W. Overlapping roles for PLK1 and Aurora A during meiotic centrosome biogenesis in mouse spermatocytes. EMBO Rep. 2021, e51023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, K.; Katayama, H.; Hawke, D.H.; Sen, S. Aurora-C interactions with survivin and INCENP reveal shared and distinct features compared with Aurora-B chromosome passenger protein complex. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, M.T.; Viera, A.; Gómez, R.; Page, J.; Carmena, M.; Earnshaw, W.; Rufas, J.S.; Suja, J.A. Dynamic relocalization of the chromosomal passenger complex proteins inner centromere protein (INCENP) and Aurora-B kinase during male mouse meiosis. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 961–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gassmann, R.; Carvalho, A.; Henzing, A.J.; Ruchaud, S.; Hudson, D.F.; Honda, R.; Nigg, E.A.; Gerloff, D.L.; Earnshaw, W.C. Borealin: A novel chromosomal passenger required for stability of the bipolar mitotic spindle. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 166, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheeseman, I.M. The kinetochore. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2014, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinshaw, S.M.; Harrison, S.C. Kinetochore function from the bottom up. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revenkova, E.; Eijpe, M.; Heyting, C.; Gross, B.; Jessberger, R. Novel meiosis-specific isoform of mammalian SMC1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 6984–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rankin, S. Complex elaboration: Making sense of meiotic cohesin dynamics. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 2426–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cruz, R.; Brieno, M.A.; Roig, I.; Grossmann, M.; Velilla, E.; Pujol, A.; Cabero, L.; Pessarrodona, A.; Barbero, J.L.; Garcia Caldes, M. Dynamics of cohesin proteins REC8, STAG3, SMC1β and SMC3 are consistent with a role in sister chromatid cohesion during meiosis in human oocytes. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 2316–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanneti, N.S.; Landy, K.; Joyce, E.F.; McKim, K.S. A pathway for synapsis initiation during zygotene in Drosophila oocytes. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casey, A.E.; Daish, T.J.; Barbero, J.L.; Grützner, F. Differential cohesin loading marks paired and unpaired regions of platypus sex chromosomes at prophase I. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Shearwin-Whyatt, L.; Li, J.; Song, Z.; Hayakawa, T.; Stevens, D.; Fenelon, J.C.; Peel, E.; Cheng, Y.; Pajpach, F.; et al. Platypus and echidna genomes reveal mammalian biology and evolution. Nature 2021, 592, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrigley, J.M.; Graves, J. Two monotreme cell lines, derived from female platypuses (Ornithorhynchus anatinus; Monotremata, mammalia). Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 1984, 20, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glotzer, M.; Murray, A.W.; Kirschner, M.W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature 1991, 349, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, R.W.; Glotzer, M.; Kirschner, M.W. Mutagenic analysis of the destruction signal of mitotic cyclins and structural characterization of ubiquitinated intermediates. Mol. Biol. Cell 1996, 7, 1343–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfleger, C.M.; Kirschner, M.W. The KEN box: An APC recognition signal distinct from the D box targeted by Cdh1. Genome Res. 2000, 14, 655–665. [Google Scholar]
- Pfleger, C.M.; Lee, E.; Kirschner, M.W. Substrate recognition by the Cdc20 and Cdh1 components of the anaphase-promoting complex. Genes Dev. 2021, 15, 2396–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crane, R.; Kloepfer, A.; Ruderman, J.V. Requirements for the destruction of human Aurora-A. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 5975–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zachariae, W. Destruction with a box: Substrate recognition by the anaphase-promoting complex. Mol. Cell 2004, 13, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littlepage, L.E.; Ruderman, J.V. Identification of a new APC/C recognition domain, the A box, which is required for the Cdh1-dependent destruction of the kinase Aurora-A during mitotic exit. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2274–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willems, E.; Dedobbeleer, M.; Digregorio, M.; Lombard, A.; Lumapat, P.N.; Rogister, B. The functional diversity of Aurora kinases: A comprehensive review. Cell Div. 2018, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deakin, J.E.; Hore, T.A.; Koina, A.; Graves, J.A.M. The status of dosage compensation in the multiple X chromosomes of the platypus. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daish, T.J.; Casey, A.E.; Grützner, F. Lack of sex chromosome specific meiotic silencing in platypus reveals origin of MSCI in therian mammals. BMC Biol. 2015, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pajpach, F.; Shearwin-Whyatt, L.; Grützner, F. Evolution, Expression and Meiotic Behavior of Genes Involved in Chromosome Segregation of Monotremes. Genes 2021, 12, 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091320
Pajpach F, Shearwin-Whyatt L, Grützner F. Evolution, Expression and Meiotic Behavior of Genes Involved in Chromosome Segregation of Monotremes. Genes. 2021; 12(9):1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091320
Chicago/Turabian StylePajpach, Filip, Linda Shearwin-Whyatt, and Frank Grützner. 2021. "Evolution, Expression and Meiotic Behavior of Genes Involved in Chromosome Segregation of Monotremes" Genes 12, no. 9: 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091320
APA StylePajpach, F., Shearwin-Whyatt, L., & Grützner, F. (2021). Evolution, Expression and Meiotic Behavior of Genes Involved in Chromosome Segregation of Monotremes. Genes, 12(9), 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091320






