Non-Syndromic Autosomal Dominant Hearing Loss: The First Italian Family Carrying a Mutation in the NCOA3 Gene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
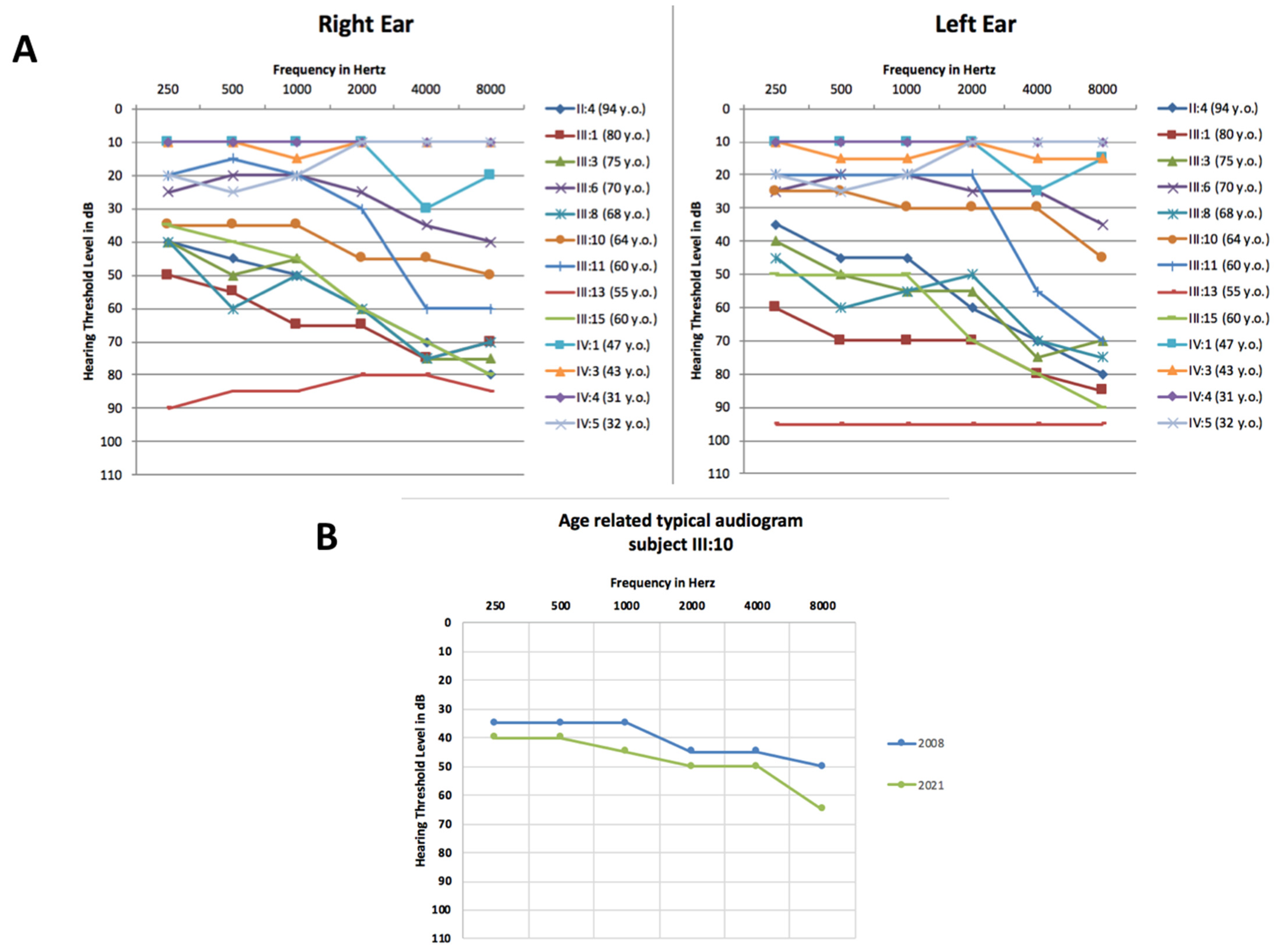
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Korver, A.M.; Smith, R.J.; Van Camp, G.; Schleiss, M.R.; Bitner-Glindzicz, M.A.; Lustig, L.R.; Usami, S.I.; Boudewyns, A.N. Congenital hearing loss. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vona, B.; Doll, J.; Hofrichter, M.; Haaf, T. Non-syndromic hearing loss: Clinical and diagnostic challenges. Med. Genet. 2020, 32, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.; Koboldt, D.C.; Barrie, E.S.; Crist, E.R.; García García, G.; Mezzavilla, M.; Faletra, F.; Mihalic Mosher, T.; Wilson, R.K.; Blanchet, C.; et al. Mutations in PLS1, encoding fimbrin, cause autosomal dominant nonsyndromic hearing loss. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 2286–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, N.; Moteki, H.; Takahashi, M.; Nishio, S.Y.; Arai, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Oridate, N.; Usami, S. An effective screening strategy for deafness in combination with a next-generation sequencing platform: A consecutive analysis. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 61, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan-Heggen, C.M.; Smith, R.J. Navigating genetic diagnostics in patients with hearing loss. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2016, 28, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vona, B.; Nanda, I.; Hofrichter, M.A.; Shehata-Dieler, W.; Haaf, T. Non-syndromic hearing loss gene identification: A brief history and glimpse into the future. Mol. Cell. Probes 2015, 29, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, R.S.; Dantas, V.; Alves, L.U.; Batissoco, A.C.; Oiticica, J.; Lawrence, E.A.; Kawafi, A.; Yang, Y.; Nicastro, F.S.; Novaes, B.C.; et al. NCOA3 identified as a new candidate to explain autosomal dominant progressive hearing loss. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 29, 3691–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abecasis, G.R.; Cherny, S.S.; Cookson, W.O.; Cardon, L.R. Merlin--rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iossifov, I.; O’Roak, B.J.; Sanders, S.J.; Ronemus, M.; Krumm, N.; Levy, D.; Stessman, H.A.; Witherspoon, K.T.; Vives, L.; Patterson, K.E.; et al. The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder. Nature 2014, 515, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmicki, J.A.; Samocha, K.E.; Howrigan, D.P.; Sanders, S.J.; Slowikowski, K.; Lek, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Cutler, D.J.; Devlin, B.; Roeder, K.; et al. Refining the role of de novo protein-truncating variants in neurodevelopmental disorders by using population reference samples. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, M.L.; Dancik, G.M.; Im, K.M.; Edwards, M.G.; Turan, S.; Brown, J.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, C.; Owens, C.; Costello, J.C.; Guo, G.; et al. Concurrent alterations in TERT, KDM6A, and the BRCA pathway in bladder cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4935–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Ivanchenko, M.V.; Al Jandal, H.; Cicconet, M.; Indzhykulian, A.A.; Corey, D.P. PKHD1L1 is a coat protein of hair-cell stereocilia and is required for normal hearing. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using PolyPhen-2. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2013, 76, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Rödelsperger, C.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limongelli, I.; Marini, S.; Bellazzi, R. PaPI: Pseudo amino acid composition to score human protein-coding variants. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, D.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X. DANN: A deep learning approach for annotating the pathogenicity of genetic variants. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, A.M.; DiStefano, M.T.; Hemphill, S.E.; Cushman, B.J.; Grant, A.R.; Siegert, R.K.; Shen, J.; Chapin, A.; Boczek, N.J.; Schimmenti, L.A.; et al. ClinGen Hearing Loss Clinical Domain Working Group Expert specification of the ACMG/AMP variant interpretation guidelines for genetic hearing loss. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 1593–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Gilbert, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhen, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y. Association of NCOA3 polymorphisms with Dyslipidemia in the Chinese Han population. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Guo, J.; Kang, S.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Qi, X. NCOA3 Loss Disrupts Molecular Signature of Chondrocytes and Promotes Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis Progression. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 49, 2396–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwinska-Kowalska, M. Hearing. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 131, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Mean Target Coverage (Mean Base Coverage Depth) | Coverage Uniformity (Percentage of Bases with a Coverage Depth > 0.2 × Mean_Coverage) | % Target Bases 10X (Percentage of Target Bases with Coverage above 10X) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| II:3 | 78.469824 | 97.5476 | 97.4332 |
| II:4 | 77.629201 | 95.2360 | 98.0183 |
| II:5 | 79.013458 | 96.1209 | 97.0431 |
| III:1 | 77.012397 | 98.0127 | 96.0126 |
| III:3 | 78.723768 | 97.5421 | 98.3218 |
| III:5 | 77.629071 | 96.9301 | 97.9854 |
| III:6 | 77.204720 | 95.9183 | 97.4510 |
| III:7 | 75.927492 | 96.5333 | 96.9981 |
| III:8 | 76.638206 | 98.1426 | 95.4832 |
| III:9 | 78.656329 | 95.6721 | 96.9453 |
| III:10 | 76.739260 | 98.2310 | 97.0034 |
| III:11 | 78.739279 | 96.9231 | 95.8741 |
| III:13 | 78.317429 | 97.8342 | 96.7632 |
| III:15 | 79.125820 | 96.7631 | 97.1632 |
| Subject | Affection | Variants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALDH1B1 NM_000692.5 | SMC2 NM_001042550.2 | NCO3 NM_181659.3 | MBD2 NM_015832.6 | KCNH6 NM_030779.4 | PKHD1L1 NM_177531.4 | ||
| c.G1087A | c.A1514G | c.G2909C | c.G707T | c.G263T | c.T9722A | ||
| II-3 (male, 92 y.o) | healthy | G/G | A/A | G/G | G/G | false positive | T/T |
| II-4 (female, 94 y.o.) | affected | G/A | A/G | G/C | G/T | false positive | T/A |
| II-5 (male, 88 y.o.) | affected | G/A | A/G | G/C | G/T | false positive | T/A |
| III-1 (male, 80 y.o.) | affected | G/A | A/G | G/C | G/T | false positive | T/T |
| III-3 (female, 75 y.o.) | affected | G/A | A/G | G/C | G/T | false positive | T/A |
| III-5 (male, 71 y.o.) | affected | G/G | A/A | G/C | G/G | false positive | T/T |
| III-6 (male, 70 y.o.) | affected | G/G | A/G | G/C | G/G | false positive | T/T |
| III-7 (female, 68 y.o.) | affected | G/A | A/G | G/C | G/G | false positive | T/T |
| III-8 (female, 70 y.o.) | affected | G/G | A/G | G/G | G/G | false positive | T/T |
| III-9 (male, 68 y.o.) | healthy | G/G | A/G | G/G | G/T | false positive | T/T |
| III-10 (male, 64 y.o.) | affected | G/A | A/G | G/C | G/T | false positive | T/A |
| III-11 (male, 60 y.o.) | affected | G/G | A/G | G/C | G/G | false positive | T/T |
| III-13 (female, 56 y.o.) | affected | G/A | A/G | G/C | G/T | false positive | T/A |
| III-15 (male, 60 y.o.) | affected | G/A | A/G | G/C | G/T | false positive | T/A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tesolin, P.; Morgan, A.; Notarangelo, M.; Ortore, R.P.; Concas, M.P.; Notarangelo, A.; Girotto, G. Non-Syndromic Autosomal Dominant Hearing Loss: The First Italian Family Carrying a Mutation in the NCOA3 Gene. Genes 2021, 12, 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071043
Tesolin P, Morgan A, Notarangelo M, Ortore RP, Concas MP, Notarangelo A, Girotto G. Non-Syndromic Autosomal Dominant Hearing Loss: The First Italian Family Carrying a Mutation in the NCOA3 Gene. Genes. 2021; 12(7):1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071043
Chicago/Turabian StyleTesolin, Paola, Anna Morgan, Michela Notarangelo, Rocco Pio Ortore, Maria Pina Concas, Angelantonio Notarangelo, and Giorgia Girotto. 2021. "Non-Syndromic Autosomal Dominant Hearing Loss: The First Italian Family Carrying a Mutation in the NCOA3 Gene" Genes 12, no. 7: 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071043
APA StyleTesolin, P., Morgan, A., Notarangelo, M., Ortore, R. P., Concas, M. P., Notarangelo, A., & Girotto, G. (2021). Non-Syndromic Autosomal Dominant Hearing Loss: The First Italian Family Carrying a Mutation in the NCOA3 Gene. Genes, 12(7), 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071043







