Family-Based Genome-Wide Association Study of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Middle Eastern Families
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Genotyping
2.3. Genome-Wide Association Analysis
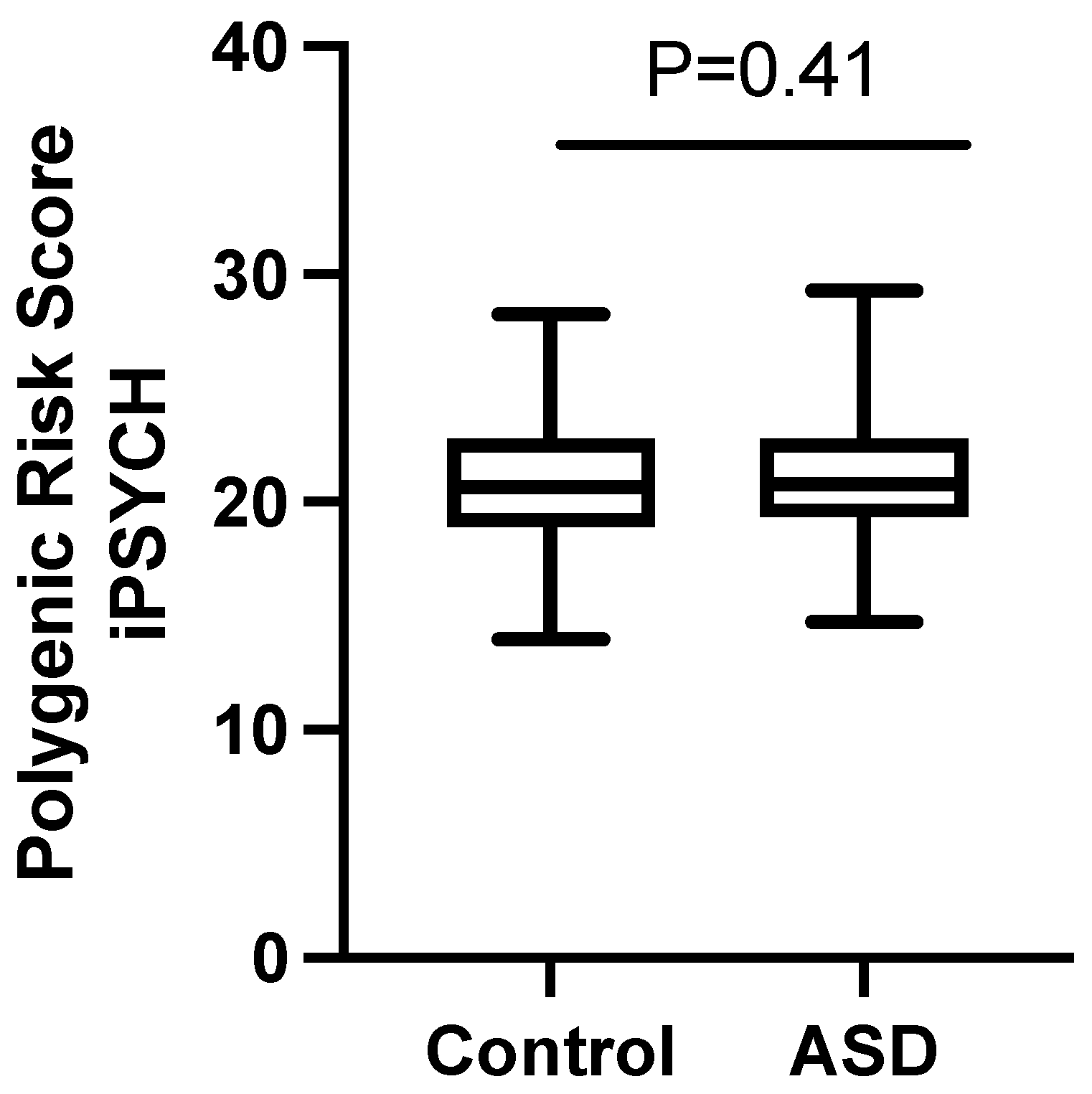
2.4. Polygenic Risk Score Analysis
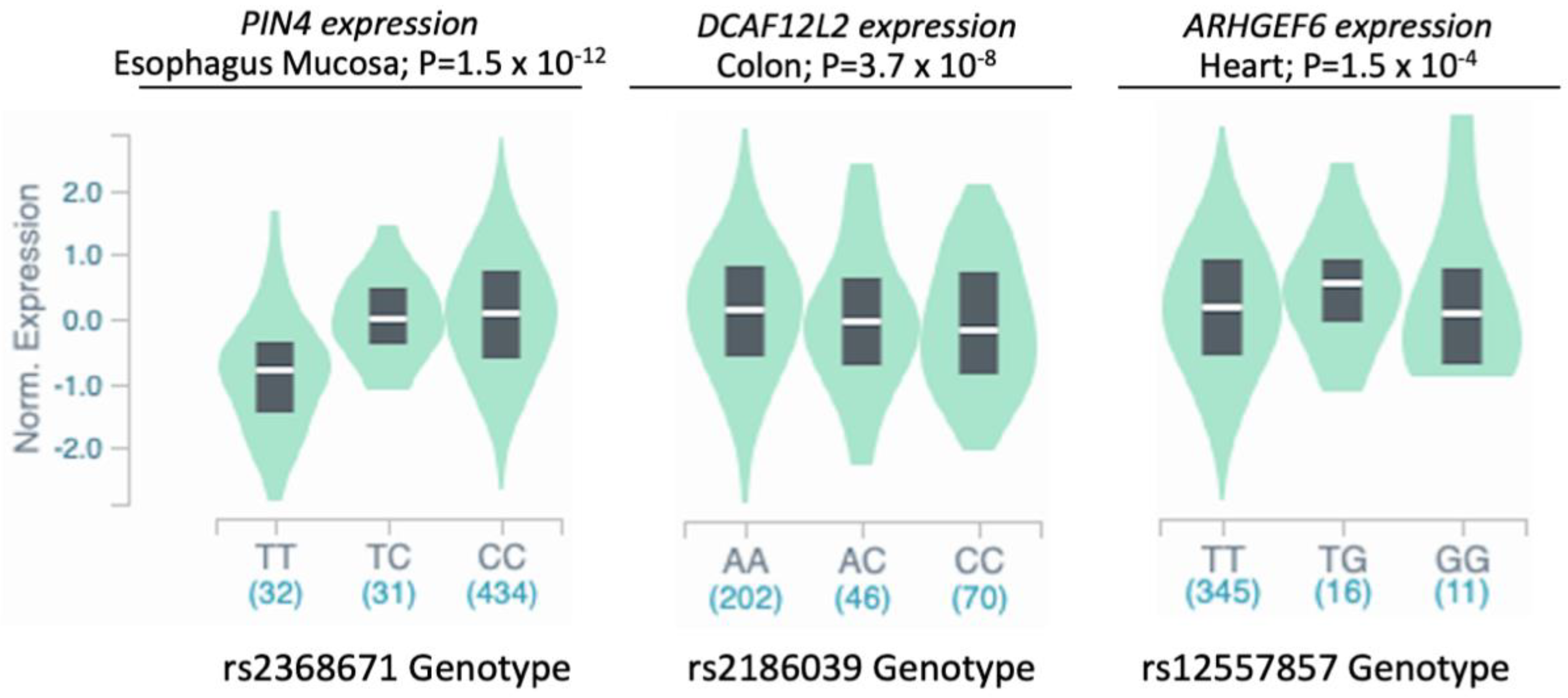
2.5. Expression Quantitative Trait Locus (eQTL) Analysis
3. Results
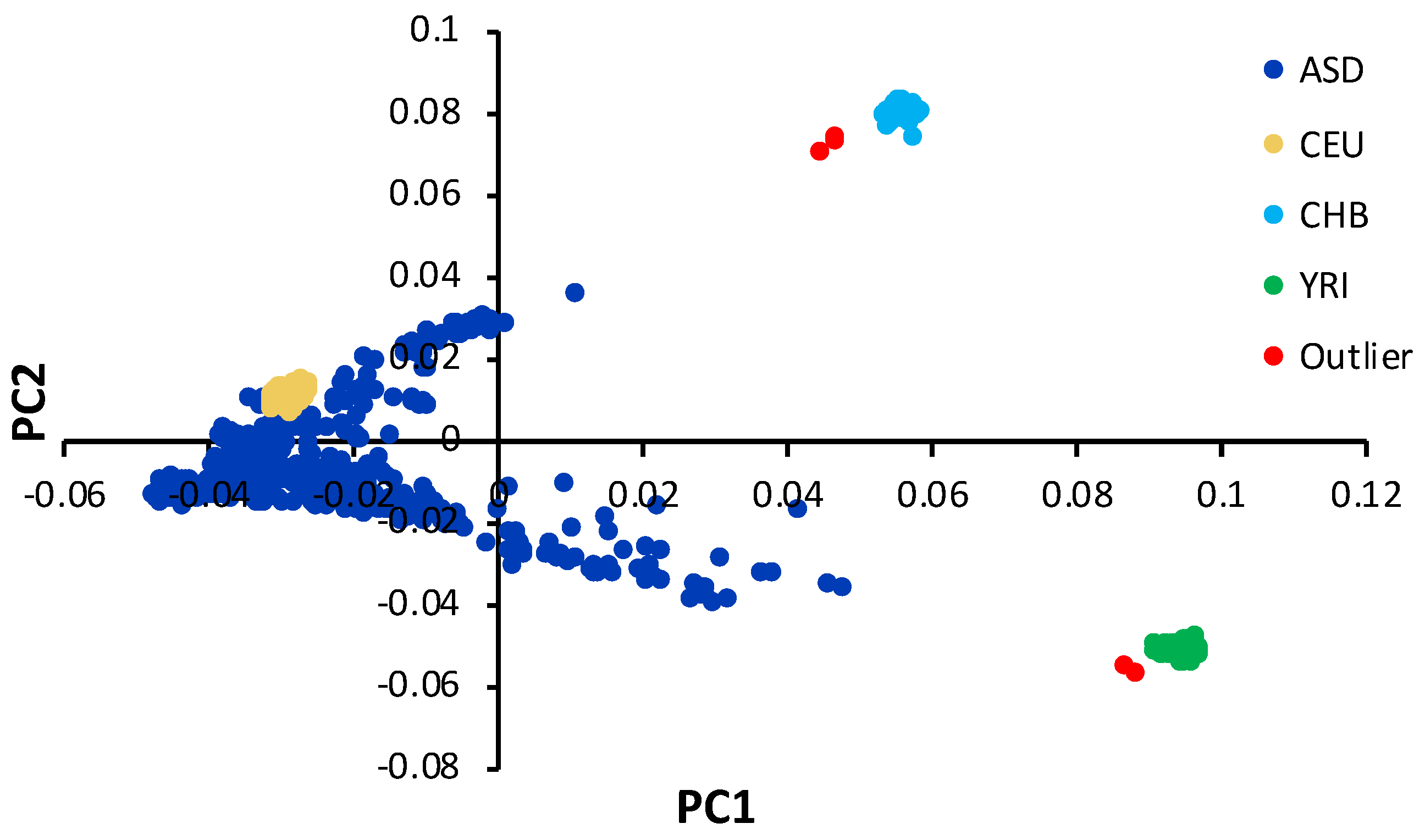
3.1. Characterstics of Study Subjects
3.2. Genome-Wide Association Analysis of ASD
3.3. Replication of Loci Reported in Previous GWAS of ASD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association Division of Research. Highlights of Changes from DSM-IV to DSM-5. Focus 2013, 11, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S.E.; Mandell, D.S.; Schultz, R.T. Autism. Lancet 2009, 374, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaban, F.; Aldosari, M.; Al-Shammari, H.; El-Hag, S.; Ghazal, I.; Tolefat, M.; Ali, M.; Kamal, M.; Aati, N.A.; Abeidah, M.; et al. Prevalence and correlates of autism spectrum disorder in Qatar: A national study. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2019, 60, 1254–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, P.J.; Zhang, W.-B.; Mok, R.S.; Zaslavsky, K.; Deneault, E.; D’Abate, L.; Rodrigues, D.C.; Yuen, R.K.; Faheem, M.; Mufteev, M.; et al. Synaptic Dysfunction in Human Neurons With Autism-Associated Deletions in PTCHD1-AS. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, S.; Pang, N.; Deng, X.; Yang, L.; He, F.; Wu, L.; Chen, C.; Yin, F.; Peng, J. Synaptopathology Involved in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.D.; Li, D.D.; Keown, C.L.; Lee, A.; Johnson, R.T.; Angkustsiri, K.; Rogers, S.J.; Müller, R.-A.; Amaral, D.G.; Nordahl, C.W. Functional Connectivity of the Amygdala Is Disrupted in Preschool-Aged Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2016, 55, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivito, G.; Clausi, S.; Laghi, F.; Tedesco, A.M.; Baiocco, R.; Mastropasqua, C.; Molinari, M.; Cercignani, M.; Bozzali, M.; Leggio, M. Resting-State Functional Connectivity Changes Between Dentate Nucleus and Cortical Social Brain Regions in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Cerebellum 2016, 16, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, A.; Le Couteur, A.; Gottesman, I.; Bolton, P.; Simonoff, E.; Yuzda, E.; Rutter, M. Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: Evidence from a British twin study. Psychol. Med. 1995, 25, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, R.E.; Law, J.K.; Yenokyan, G.; Mcgready, J.; Kaufmann, W.E.; Law, P.A. Characteristics and Concordance of Autism Spectrum Disorders Among 277 Twin Pairs. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2009, 163, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadybekov, A.; Tian, C.; Arnesano, C.; Katritch, V.; Herring, B.E. An autism spectrum disorder-related de novo mutation hotspot discovered in the GEF1 domain of Trio. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T.N.; Coe, B.P.; Dickel, D.E.; Hoekzema, K.; Nelson, B.J.; Zody, M.C.; Kronenberg, Z.N.; Hormozdiari, F.; Raja, A.; Pennacchio, L.A.; et al. Genomic Patterns of De Novo Mutation in Simplex Autism. Cell 2017, 171, 710–722.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, R.K.C.; Merico, D.; Bookman, M.; Howe, J.L.; Thiruvahindrapuram, B.; Patel, R.V.; Whitney, J.; Deflaux, N.; Bingham, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Whole genome sequencing resource identifies 18 new candidate genes for autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.-Y.; Lin, K.; Zhu, L.; Werling, D.M.; Dong, S.; Brand, H.; Wang, H.Z.; Zhao, X.; Schwartz, G.B.; Collins, R.L.; et al. Genome-wide de novo risk score implicates promoter variation in autism spectrum disorder. Science 2018, 362, eaat6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glessner, J.T.; Wang, K.; Cai, G.; Korvatska, O.; Kim, C.E.; Wood, S.; Zhang, H.; Estes, A.; Brune, C.W.; Bradfield, J.P.; et al. Autism genome-wide copy number variation reveals ubiquitin and neuronal genes. Nature 2009, 459, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Pagnamenta, A.T.; Klei, L.; Anney, R.; Merico, D.; Regan, R.; Conroy, J.; Magalhaes, T.R.; Correia, C.; Abrahams, B.S.; et al. Functional impact of global rare copy number variation in autism spectrum disorders. Nature 2010, 466, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Roak, B.J.; Stessman, H.A.; Boyle, E.A.; Witherspoon, K.T.; Martin, B.; Lee, C.; Vives, L.; Baker, C.; Hiatt, J.B.; Nickerson, D.A.; et al. Recurrent de novo mutations implicate novel genes underlying simplex autism risk. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebat, J.; Lakshmi, B.; Malhotra, D.; Troge, J.; Lese-Martin, C.; Walsh, T.; Yamrom, B.; Yoon, S.; Krasnitz, A.; Kendall, J.; et al. Strong Association of De Novo Copy Number Mutations with Autism. Science 2007, 316, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaugler, T.; Klei, L.; Sanders, S.J.; Bodea, C.A.; Goldberg, A.P.; Lee, A.B.; Mahajan, M.C.; Manaa, D.; Pawitan, Y.; Reichert, J.G.; et al. Most genetic risk for autism resides with common variation. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Ma, D.; Bucan, M.; Glessner, J.T.; Abrahams, B.S.; Salyakina, D.; Imielinski, M.; Bradfield, J.P.; Sleiman, P.M.A.; et al. Common genetic variants on 5p14.1 associate with autism spectrum disorders. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 459, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Salyakina, D.; Jaworski, J.M.; Konidari, I.; Whitehead, P.L.; Andersen, A.N.; Hoffman, J.D.; Slifer, S.H.; Hedges, D.J.; Cukier, H.N.; et al. A Genome-wide Association Study of Autism Reveals a Common Novel Risk Locus at 5p14.1. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2009, 73, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, L.A.; The Gene Discovery Project of Johns Hopkins & the Autism Consortium; Arking, D.E. A genome-wide linkage and association scan reveals novel loci for autism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 461, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anney, R.; Klei, L.; Pinto, D.; Regan, R.; Conroy, J.; Magalhaes, T.R.; Correia, C.; Abrahams, B.S.; Sykes, N.; Pagnamenta, A.T.; et al. A genome-wide scan for common alleles affecting risk for autism. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 4072–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grove, J.; Ripke, S.; Als, T.D.; Mattheisen, M.; Walters, R.K.; Won, H.; Pallesen, J.; Agerbo, E.; Andreassen, O.A.; Anney, R.; et al. Identification of common genetic risk variants for autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Autism Spectrum Disorders Working Group of The Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Meta-analysis of GWAS of over 16,000 individuals with autism spectrum disorder highlights a novel locus at 10q24.32 and a significant overlap with schizophrenia. Mol. Autism 2017, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, J.J.; Glessner, J.T.; Hakonarson, H. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Autism Incorporating Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised, Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, and Social Responsiveness Scale. Child Dev. 2012, 84, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anney, R.; Klei, L.; Pinto, D.; Almeida, J.; Bacchelli, E.; Baird, G.; Bolshakova, N.; Bölte, S.; Bolton, P.F.; Bourgeron, T.; et al. Individual common variants exert weak effects on the risk for autism spectrum disorders. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 4781–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Ou, J.; Li, K.; Guo, H.; Hu, Z.; Bai, T.; Zhao, J.; Xia, K.; Zhang, F. Genome-wide association analysis of autism identified multiple loci that have been reported as strong signals for neuropsychiatric disorders. Autism Res. 2020, 13, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, P.-H.; Chuang, L.-C.; Su, M.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Wu, J.-Y.; Yen, C.-J.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Liu, S.-K.; Chou, M.-C.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study for Autism Spectrum Disorder in Taiwanese Han Population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-C.; Yoo, H.J.; Park, M.; Cho, I.H.; Kim, B.-N.; Kim, J.-W.; Shin, M.-S.; Park, T.-W.; Son, J.-W.; Chung, U.-S.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Scan of Korean Autism Spectrum Disorders with Language Delay: A Preliminary Study. Psychiatry Investig. 2011, 8, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.; Rutter, M.; Le Couteur, A. Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised: A revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1994, 24, 659–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, C.; Risi, S.; Lambrecht, L.; Cook, E.H., Jr.; Leventhal, B.L.; DiLavore, P.C.; Pickles, A.; Rutter, M. The Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule—Generic: A Standard Measure of Social and Communication Deficits Associated with the Spectrum of Autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2000, 30, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurie, C.C.; Doheny, K.F.; Mirel, D.B.; Pugh, E.W.; Bierut, L.J.; Bhangale, T.; Boehm, F.; Caporaso, N.E.; Cornelis, M.C.; Edenberg, H.J.; et al. Quality control and quality assurance in genotypic data for genome-wide association studies. Genet. Epidemiology 2010, 34, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.A.M.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. GigaScience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulchenko, Y.S.; Ripke, S.; Isaacs, A.; Van Duijn, C.M. GenABEL: An R library for genome-wide association analysis. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1294–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, R.; McWhirter, R. Adjusting for Familial Relatedness in the Analysis of GWAS Data. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volumr 1526, pp. 175–190. [Google Scholar]
- Thareja, G.; The Qatar Genome Program Research (QGPR) Consortium; Al-Sarraj, Y.; Belkadi, A.; Almotawa, M.; Suhre, K.; Albagha, O.M.E. Whole genome sequencing in the Middle Eastern Qatari population identifies genetic associations with 45 clinically relevant traits. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakiola, M.; Strange, A.; Cordell, H.J.; Miller, E.N.; Pirinen, M.; Su, Z.; Mishra, A.; Mehrotra, S.; Monteiro, G.R.; Band, G.; et al. Common variants in the HLA-DRB1–HLA-DQA1 HLA class II region are associated with susceptibility to visceral leishmaniasis. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eu-Ahsunthornwattana, J.; Howey, R.A.; Cordell, H.J. Accounting for relatedness in family-based association studies: Application to Genetic Analysis Workshop 18 data. BMC Proc. 2014, 8, S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Taskesen, E.; Van Bochoven, A.; Posthuma, D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staley, J.R.; Blackshaw, J.; Kamat, M.A.; Ellis, S.; Surendran, P.; Sun, B.B.; Paul, D.S.; Freitag, D.; Burgess, S.; Danesh, J.; et al. PhenoScanner: A database of human genotype–phenotype associations. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3207–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, J.; Bowler, E.; Cerezo, M.; Gil, L.; Hall, P.; Hastings, E.; Junkins, H.; McMahon, A.; Milano, A.; Morales, J.; et al. The new NHGRI-EBI Catalog of published genome-wide association studies (GWAS Catalog). Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D896–D901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruim, R.J.; Welch, R.P.; Sanna, S.; Teslovich, T.M.; Chines, P.S.; Gliedt, T.P.; Boehnke, M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Willer, C.J. LocusZoom: Regional visualization of genome-wide association scan results. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2336–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Need, A.C.; Attix, D.K.; McEvoy, J.M.; Cirulli, E.T.; Linney, K.L.; Hunt, P.; Ge, D.; Heinzen, E.L.; Maia, J.M.; Shianna, K.V.; et al. A genome-wide study of common SNPs and CNVs in cognitive performance in the CANTAB. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4650–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firth, H.V.; Richards, S.M.; Bevan, A.P.; Clayton, S.; Corpas, M.; Rajan, D.; Van Vooren, S.; Moreau, Y.; Pettett, R.M.; Carter, N.P. DECIPHER: Database of Chromosomal Imbalance and Phenotype in Humans Using Ensembl Resources. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yntema, H.G.; Hamel, B.C.; Smits, A.P.; Van Roosmalen, T.; Helm, B.V.D.; Kremer, H.; Ropers, H.H.; Smeets, D.F.; Van Bokhoven, H. Localisation of a gene for non-specific X linked mental retardation (MRX46) to Xq25-q26. J. Med Genet. 1998, 35, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kutsche, K.; Yntema, H.; Brandt, A.; Jantke, I.; Nothwang, H.G.; Orth, U.; Boavida, M.G.; David, D.; Chelly, J.; Fryns, J.-P.; et al. Mutations in ARHGEF6, encoding a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rho GTPases, in patients with X-linked mental retardation. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsdale, J.; Thomas, J.; Salvatore, M.; Phillips, R.; Lo, E.; Shad, S.; Hasz, R.; Walters, G.; Garcia, F.; Young, N.; et al. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Wedow, R.; Okbay, A.; Kong, E.; Maghzian, O.; Zacher, M.; Nguyen-Viet, T.A.; Bowers, P.; Sidorenko, J.; Linnér, R.K.; et al. Gene discovery and polygenic prediction from a genome-wide association study of educational attainment in 1.1 million individuals. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Bayona, S.; Stracker, T.H. The Tousled-like kinases regulate genome and epigenome stability: Implications in development and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3827–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, S.H.; Reijnders, M.R.F.; Pfundt, R.; Yntema, H.G.; Kamsteeg, E.-J.; De Vries, P.; De Vries, B.B.A.; Willemsen, M.H.; Kleefstra, T.; Löhner, K.; et al. Meta-analysis of 2,104 trios provides support for 10 new genes for intellectual disability. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1194–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijnders, M.R.; Miller, K.A.; Alvi, M.; Goos, J.A.; Lees, M.M.; De Burca, A.; Henderson, A.; Kraus, A.; Mikat, B.; De Vries, B.B.; et al. De Novo and Inherited Loss-of-Function Variants in TLK2: Clinical and Genotype-Phenotype Evaluation of a Distinct Neurodevelopmental Disorder. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromer, M.; Pocklington, A.J.; Kavanagh, D.H.; Williams, H.J.; Dwyer, S.; Gormley, P.; Georgieva, L.; Rees, E.; Palta, P.; Ruderfer, D.M.; et al. De novo mutations in schizophrenia implicate synaptic networks. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 506, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iossifov, I.; O’Roak, B.J.; Sanders, S.J.; Ronemus, M.; Krumm, N.; Levy, D.; Stessman, H.A.; Witherspoon, K.T.; Vives, L.; Patterson, K.E.; et al. The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder. Nature 2014, 515, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritsen, M.B.; Als, T.D.; A Dahl, H.; Flint, T.J.; Wang, A.G.; Vang, M.; A Kruse, T.; Ewald, H.; Mors, O. A genome-wide search for alleles and haplotypes associated with autism and related pervasive developmental disorders on the Faroe Islands. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 11, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, D.; Van Dijk, A.; Pfundt, R.; Hoischen, A.; Merkx, G.; Gradek, G.; Lybæk, H.; Stray-Pedersen, A.; Brunner, H.; Houge, G. Severe Progressive Autism Associated with Two de novo Changes: A 2.6-Mb 2q31.1 Deletion and a Balanced t(14;21)(q21.1;p11.2) Translocation with Long-Range Epigenetic Silencing of LRFN5 Expression. Mol. Syndr. 2010, 1, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, S.H.; Folsom, T.D.; Thuras, P.D. Deficits in GABAB receptor system in schizophrenia and mood disorders: A postmortem study. Schizophr. Res. 2011, 128, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, D.J.; Hamilton-Nelson, K.L.; Sacharow, S.J.; Nations, L.; Beecham, G.W.; Kozhekbaeva, Z.M.; Butler, B.L.; Cukier, H.N.; Whitehead, P.L.; Ma, D.; et al. Evidence of novel fine-scale structural variation at autism spectrum disorder candidate loci. Mol. Autism 2012, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, F.F.; Myers, C.T.; Cossette, P.; Lemay, P.; Spiegelman, D.; Laporte, A.D.; Nassif, C.; Diallo, O.; Monlong, J.; Cadieux-Dion, M.; et al. High Rate of Recurrent De Novo Mutations in Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 664–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.; Jung, J.; Lee, Y.-N.; Lee, Y.; Cho, H.; Na Bs, E.; Hong, J.; Kim, E.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; et al. GABBR2mutations determine phenotype in rett syndrome and epileptic encephalopathy. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.; Barbosa, M.; Ameur, A.; Soares, G.; De Sá, J.; Dias, A.I.; Oliveira, G.; Cabral, P.; Temudo, T.; Calado, E.; et al. Identification of novel genetic causes of Rett syndrome-likephenotypes. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 53, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, A.; Miyake, N.; Tsurusaki, Y.; Fukai, R.; Miyatake, S.; Koshimizu, E.; Kushima, I.; Okada, T.; Morikawa, M.; Uno, Y.; et al. Integrative Analyses of De Novo Mutations Provide Deeper Biological Insights into Autism Spectrum Disorder. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbach, G.D.; Lord, C. The Simons Simplex Collection: A Resource for Identification of Autism Genetic Risk Factors. Neuron 2010, 68, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelson, J.J.; Shi, Y.; Gujral, M.; Zheng, H.; Malhotra, D.; Jin, X.; Jian, M.; Liu, G.; Greer, D.; Bhandari, A.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing in Autism Identifies Hot Spots for De Novo Germline Mutation. Cell 2012, 151, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, V.W.; Devlin, C.A.; Debski, J.J. ASD Phenotype—Genotype Associations in Concordant and Discordant Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins Stratified by Severity of Autistic Traits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study, D.D.D. Deciphering Developmental Disorders Study Prevalence and architecture of de novo mutations in developmental disorders. Nature 2017, 542, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harakalova, M.; Boogaard, M.-J.V.D.; Sinke, R.; Van Lieshout, S.; Van Tuil, M.C.; Duran, K.; Renkens, I.; Terhal, P.A.; De Kovel, C.; Nijman, I.J.; et al. X-exome sequencing identifies aHDAC8variant in a large pedigree with X-linked intellectual disability, truncal obesity, gynaecomastia, hypogonadism and unusual face. J. Med Genet. 2012, 49, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, A.D.; Moss, J.F.; Selicorni, A.; Bisgaard, A.-M.; Deardorff, M.A.; Gillett, P.M.; Ishman, S.L.; Kerr, L.M.; Levin, A.V.; Mulder, P.A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of Cornelia de Lange syndrome: First international consensus statement. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Msc, P.B.; Joset, P.; Steindl, K.; Oneda, B.; Gogoll, L.; Azzarello-Burri, S.; Sheth, F.; Datar, C.; Verma, I.C.; Puri, R.D.; et al. Elucidation of the phenotypic spectrum and genetic landscape in primary and secondary microcephaly. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 2043–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, E.B.; Kaul, V.; Paschall, J.; Church, D.M.; Bunke, B.; Kunig, D.; Moreno-De-Luca, D.; Moreno-De-Luca, A.; Mulle, J.G.; Warren, S.T.; et al. An evidence-based approach to establish the functional and clinical significance of copy number variants in intellectual and developmental disabilities. Genet. Med. 2011, 13, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Roak, B.J.; Vives, L.; Girirajan, S.; Karakoc, E.; Krumm, N.; Coe, B.P.; Levy, R.; Ko, A.; Lee, C.; Smith, J.A.B.; et al. Sporadic autism exomes reveal a highly interconnected protein network of de novo mutations. Nature 2012, 485, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jónsson, H.; Sulem, P.; Kehr, B.; Kristmundsdottir, S.; Zink, F.; Hjartarson, E.; Hardarson, M.T.; Hjorleifsson, K.E.; Eggertsson, H.P.; Gudjonsson, S.A.; et al. Parental influence on human germline de novo mutations in 1548 trios from Iceland. Nature 2017, 549, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
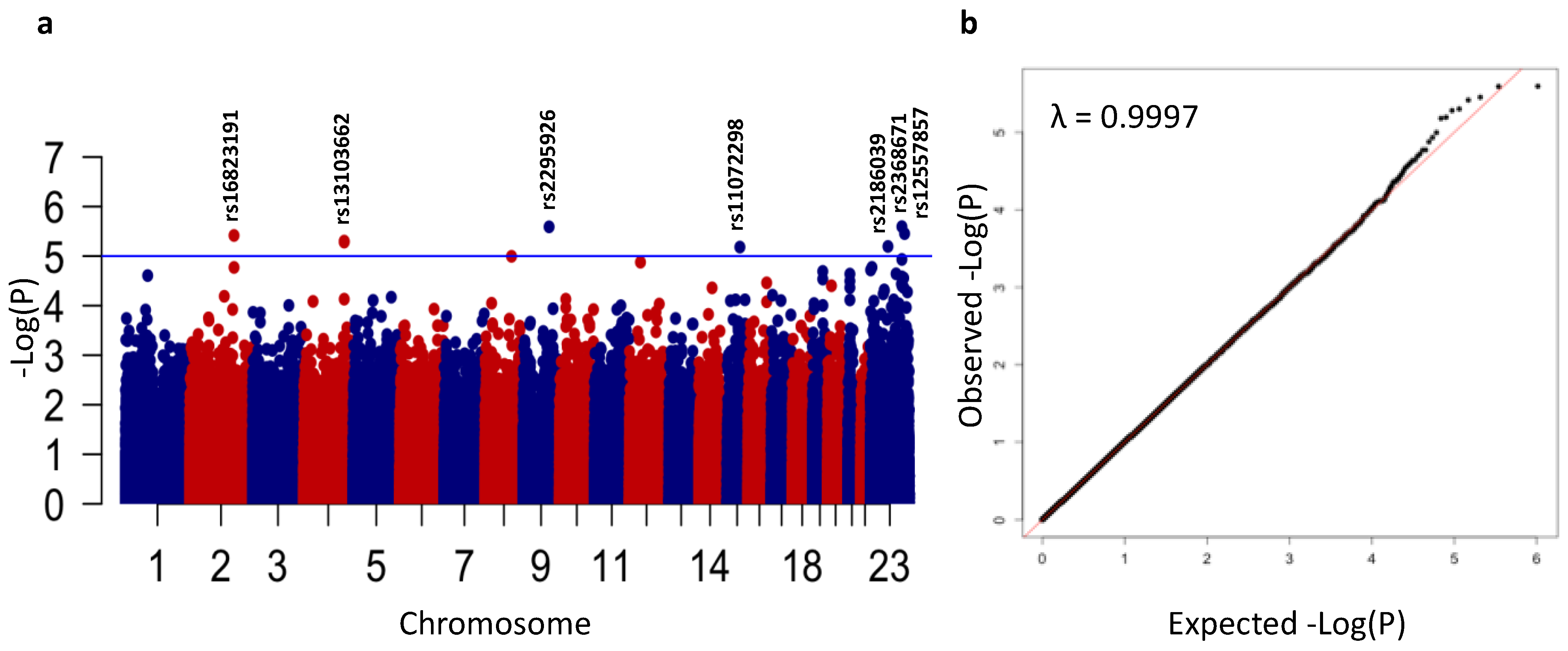
| SNP | Chr | Position | A1 | A2 | A1 Freq (%) | p | OR | 95% CI | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs16823191 | 2 | 171,930,818 | G | A | 6.0 | 3.8 × 10−6 | 1.22 | 1.09–1.36 | TLK1, GORASP2 |
| rs13103662 | 4 | 157,249,803 | A | G | 18.0 | 5.0 × 10−6 | 0.89 | 0.83–0.95 | --- |
| rs2295926 | 9 | 101,593,825 | G | A | 29.5 | 2.6 × 10−6 | 0.90 | 0.84–0.95 | GABBR2, ANKS6, GALNT12 |
| rs11072298 | 15 | 71,854,982 | A | C | 18.2 | 6.6 × 10−6 | 0.89 | 0.83–0.95 | THSD4 |
| rs2368671 | X | 71,523,650 | T | C | 8.1 | 6.4 × 10−6 | 1.15 | 1.06–1.24 | PIN4, ERCC6L, RPS4X, CITED1, HDAC8 |
| rs2186039 | X | 125,384,433 | C | A | 41.2 | 2.5 × 10−6 | 1.08 | 1.04–1.13 | DCAF12L2 |
| rs12557857 | X | 135,868,083 | G | T | 2.2 | 3.5 × 10−6 | 1.29 | 1.12–1.48 | ARHGEF6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Sarraj, Y.; Al-Dous, E.; Taha, R.Z.; Ahram, D.; Alshaban, F.; Tolfat, M.; El-Shanti, H.; Albagha, O.M.E. Family-Based Genome-Wide Association Study of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Middle Eastern Families. Genes 2021, 12, 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12050761
Al-Sarraj Y, Al-Dous E, Taha RZ, Ahram D, Alshaban F, Tolfat M, El-Shanti H, Albagha OME. Family-Based Genome-Wide Association Study of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Middle Eastern Families. Genes. 2021; 12(5):761. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12050761
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Sarraj, Yasser, Eman Al-Dous, Rowaida Z. Taha, Dina Ahram, Fouad Alshaban, Mohammed Tolfat, Hatem El-Shanti, and Omar M.E. Albagha. 2021. "Family-Based Genome-Wide Association Study of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Middle Eastern Families" Genes 12, no. 5: 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12050761
APA StyleAl-Sarraj, Y., Al-Dous, E., Taha, R. Z., Ahram, D., Alshaban, F., Tolfat, M., El-Shanti, H., & Albagha, O. M. E. (2021). Family-Based Genome-Wide Association Study of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Middle Eastern Families. Genes, 12(5), 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12050761






