Circular RNA UVRAG Mediated by Alternative Splicing Factor NOVA1 Regulates Adhesion and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
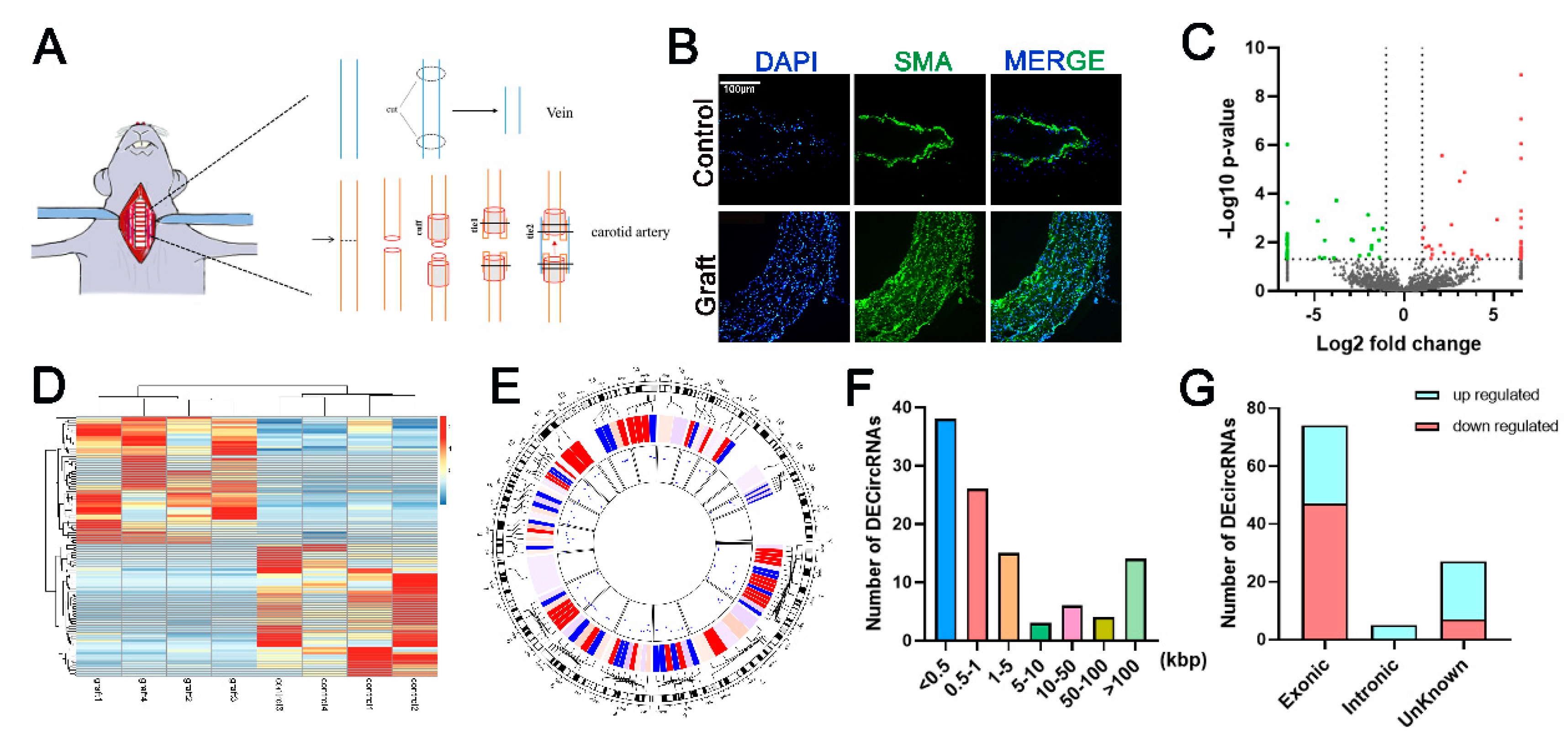
2.1. Establishment of Vein Graft Model
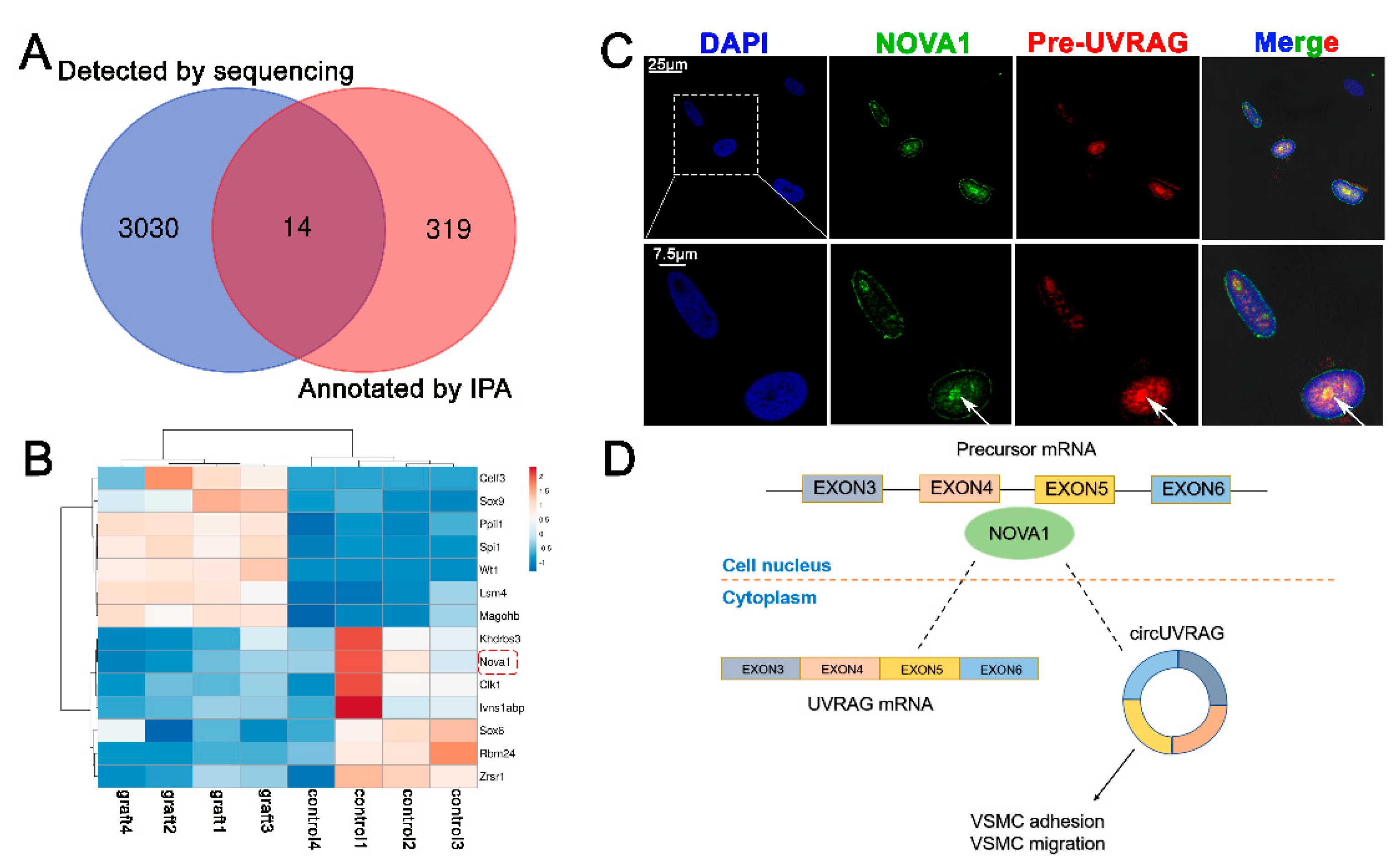
2.2. High-Throughput Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. The Culture of VSMCs
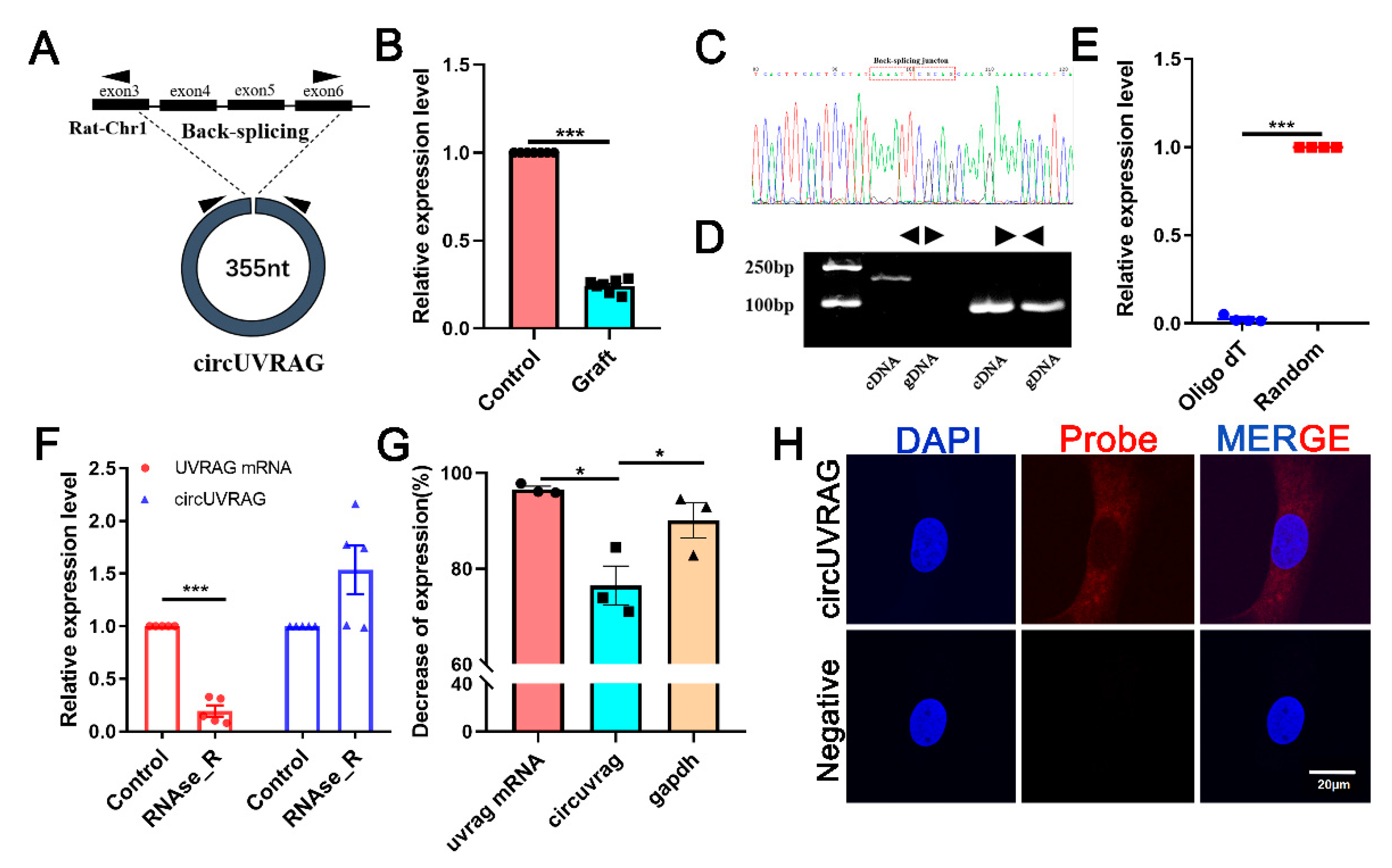
2.4. Immunofluorescence and Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
2.5. RNase R Digestion and Actinomycin D Treatment
2.6. Cell Adhesion and Migration
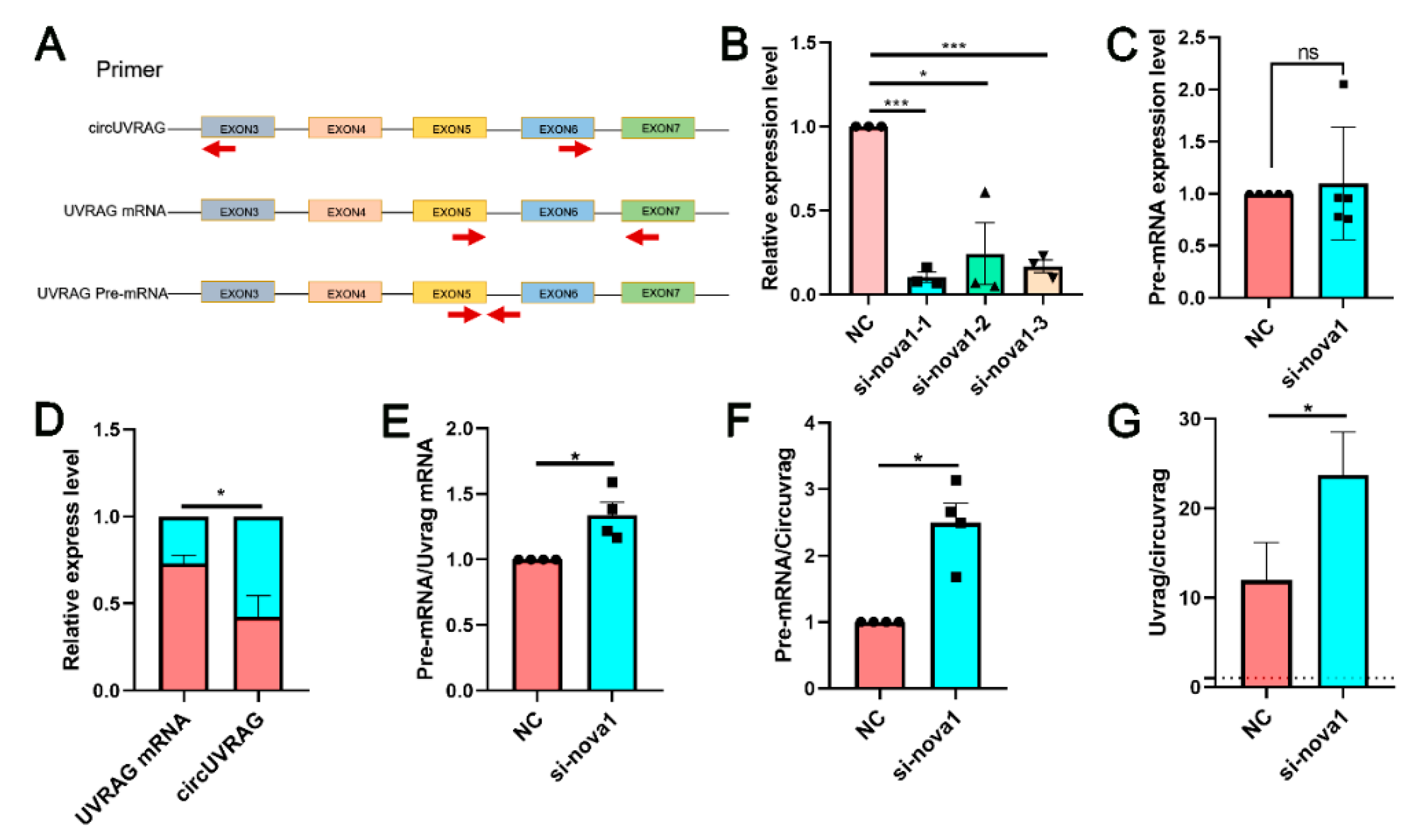
2.7. SiRNA Transfection
2.8. RNA Extraction and qPCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Characterization of Differentially Expressed Circular RNA
3.2. The Expression and Location of circUVRAG in VSMCs
3.3. Knockdown of circUVRAG Inhibits VSMCs Adhesion and Migration
3.4. The Splicing Factor NOVA1 Co-Localizes with UVRAG pre-mRNA in the Nucleus
3.5. Silencing NOVA1 Reduced the Expression of circUVRAG and Linear UVRAG mRNA without Affecting the Expression of UVRAG pre-mRNA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CABG | Coronary artery bypass graft |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DE circRNA | Differentially expressed circRNA |
| DE mRNA | Differentially expressed mRNA |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| FISH | Fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| gDNA | Genomic DNA |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis |
| NC | Negative control |
| NOVA1 | Neuro-oncological ventral antigen 1 |
| PCI | Percutaneous transluminal coronary intervention |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RBP | RNA binding protein |
| SMA | Smooth muscle α-actin |
| VGs | Vein grafts |
| VSMCs | Vascular smooth muscle cells |
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; et al. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, F.J.; Sousa-Uva, M.; Ahlsson, A.; Alfonso, F.; Banning, A.P.; Benedetto, U.; Byrne, R.A.; Collet, J.P.; Falk, V.; Head, S.J.; et al. ESC Scientific Document Group. 2018 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 87–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parang, P.; Arora, R. Coronary vein graft disease: Pathogenesis and prevention. Can. J. Cardiol. 2009, 25, e57–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, E.; de Souza, D.R.; Böning, A.; Liakopoulos, O.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Pepper, J.; Gibson, C.M.; Perrault, L.P.; Wolf, R.K.; Kim, K.B.; et al. Saphenous vein grafts in contemporary coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, C.; Zang, H.; Qi, L.; Azhar, M.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.; Cai, G.; Weiser-Evans, M.C.M.; Cui, T. Mature Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells, but Not Endothelial Cells, Serve as the Major Cellular Source of Intimal Hyperplasia in Vein Grafts. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1870–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.X.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yin, Q.F.; Wei, J.; Yao, R.W.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Coordinated circRNA Biogenesis and Function with NF90/NF110 in Viral Infection. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnerio, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cheloni, G.; Panella, R.; Mae Katon, J.; Simpson, M.; Matsumoto, A.; Papa, A.; Loretelli, C.; Petri, A.; et al. Intragenic antagonistic roles of protein and circRNA in tumorigenesis. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwecka, M.; Glažar, P.; Hernandez-Miranda, L.R.; Memczak, S.; Wolf, S.A.; Rybak-Wolf, A.; Filipchyk, A.; Klironomos, F.; Cerda Jara, C.A.; Fenske, P.; et al. Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science 2017, 357, eaam8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aufiero, S.; Reckman, Y.J.; Pinto, Y.M.; Creemers, E.E. Circular RNAs open a new chapter in cardiovascular biology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yang, F.; Zhao, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y. Circular RNA circCHFR Facilitates the Proliferation and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle via miR-370/FOXO1/Cyclin D1 Pathway. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Li, X.; Zheng, H.; Si, X.; Li, B.; Wei, G.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liao, W.; et al. Loss of Super-Enhancer-Regulated circRNA Nfix Induces Cardiac Regeneration After Myocardial Infarction in Adult Mice. Circulation 2019, 139, 2857–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, I.F.; Climent, M.; Quintavalle, M.; Farina, F.M.; Schorn, T.; Zani, S.; Carullo, P.; Kunderfranco, P.; Civilini, E.; Condorelli, G.; et al. Circ_Lrp6, a Circular RNA Enriched in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells, Acts as a Sponge Regulating miRNA-145 Function. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Liu, H.S.; Wang, F.W.; Hu, T.; Liang, Z.X.; Lan, N.; He, X.W.; Zheng, X.B.; Wu, X.J.; Xie, D.; et al. circCAMSAP1 Promotes Tumor Growth in Colorectal Cancer via the miR-328-5p/E2F1 Axis. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 914–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldolesi, J. Alternative Splicing by NOVA Factors: From Gene Expression to Cell Physiology and Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Störchel, P.H.; Thümmler, J.; Siegel, G.; Aksoy-Aksel, A.; Zampa, F.; Sumer, S.; Schratt, G. A large-scale functional screen identifies Nova1 and Ncoa3 as regulators of neuronal miRNA function. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 2237–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludlow, A.T.; Wong, M.S.; Robin, J.D.; Batten, K.; Yuan, L.; Lai, T.P.; Dahlson, N.; Zhang, L.; Mender, I.; Tedone, E.; et al. NOVA1 regulates hTERT splicing and cell growth in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Bao, H.; Yan, Z.Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Yao, Q.P.; Shi, Q.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, K.X.; Shen, B.R.; et al. MicroRNA-33 protects against neointimal hyperplasia induced by arterial mechanical stretch in the grafted vein. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadey, K.; Lopes, J.; Bendeck, M.; George, S. Role of smooth muscle cells in coronary artery bypass grafting failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, J.R.W.; Jacquemet, G. Cell matrix adhesion in cell migration. Essays Biochem. 2019, 63, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.P.; Liu, Z.; Yao, A.H.; Liu, J.T.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.S.; Han, Y.; Jiang, Z.L.; Qi, Y.X. Circular RNA circTET3 mediates migration of rat vascular smooth muscle cells by targeting miR-351-5p. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 6831–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Z.H.; Chang, N.B.; Yao, Q.P.; Li, T.; Zhu, X.L.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, M.J.; Cheng, Y.S.; Jiang, R.; Jiang, J. Suppression of circDcbld1 Alleviates Intimal Hyperplasia in Rat Carotid Artery by Targeting miR-145-3p/Neuropilin-1. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Xia, L.; Fan, S.; Zheng, J.; Qin, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Tao, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, K.; et al. Circular RNA CircMAP3K5 Acts as a MicroRNA-22-3p Sponge to Promote Resolution of Intimal Hyperplasia Via TET2-Mediated Smooth Muscle Cell Differentiation. Circulation 2021, 143, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, M.L.; Zhao, X.S.; Zhao, H.Y.; Suzuki, T.; Wen, J.K. A Novel Regulatory Mechanism of Smooth Muscle α-Actin Expression by NRG-1/circACTA2/miR-548f-5p Axis. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wu, S.; Wu, X.; Zhou, X.; Jin, S.; Jiang, H. Silencing circular RNA UVRAG inhibits bladder cancer growth and metastasis by targeting the microRNA-223/fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 axis. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Guo, W.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Luo, Y.; Lyu, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Panda, A.C.; Munk, R.; Grammatikakis, I.; Dudekula, D.B.; De, S.; Kim, J.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Martindale, J.L.; et al. Identification of HuR target circular RNAs uncovers suppression of PABPN1 translation by CircPABPN1. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdt, L.M.; Stahringer, A.; Sass, K.; Pichler, G.; Kulak, N.A.; Wilfert, W.; Kohlmaier, A.; Herbst, A.; Northoff, B.H.; Nicolaou, A.; et al. Circular non-coding RNA ANRIL modulates ribosomal RNA maturation and atherosclerosis in humans. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Yuan, Z.; Du, K.Y.; Fang, L.; Lyu, J.; Zhang, C.; He, A.; Eshaghi, E.; Zeng, K.; Ma, J.; et al. Translation of yes-associated protein (YAP) was antagonized by its circular RNA via suppressing the assembly of the translation initiation machinery. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 2758–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Lin, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, X. Circular RNA circITGA7 inhibits colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by modulating the Ras pathway and upregulating transcription of its host gene ITGA7. J. Pathol. 2018, 246, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Dou, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.H.; Cui, Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Yong, Y.T.; Liu, Y.B.; Hu, H.J.; et al. circ-Sirt1 controls NF-κB activation via sequence-specific interaction and enhancement of SIRT1 expression by binding to miR-132/212 in vascular smooth muscle cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3580–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.U.; Agarwal, V.; Guo, H.; Bartel, D.P. Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, K.; Kapoor, U.; Amman, F.; Picardi, E.; Martin, D.; Bajad, P.; Jantsch, M.F. A high resolution A-to-I editing map in the mouse identifies editing events controlled by pre-mRNA splicing. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CircRNA | Protein | RPIseq | lncPro | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | SVM | Value | ||
| CircUVRAG | NOVA1 | 0.75 | 0.85 | 66.5614 |
| CircUVRAG | CELF3 | 0.8 | 0.93 | 44.1834 |
| CircUVRAG | CLK1 | 0.75 | 0.91 | 63.512 |
| CircUVRAG | IVNS1ABP | 0.75 | 0.78 | 41.1168 |
| CircUVRAG | KHDRBS3 | 0.8 | 0.93 | 34.8158 |
| CircUVRAG | LSM4 | 0.75 | 0.862 | 31.5662 |
| CircUVRAG | MAGOHB | 0.75 | 0.677 | 34.8675 |
| CircUVRAG | PPIL1 | 0.8 | 0.851 | 54.9877 |
| CircUVRAG | RBM24 | 0.65 | 0.768 | 57.5284 |
| CircUVRAG | SOX6 | 0.75 | 0.94 | 58.9258 |
| CircUVRAG | SOX9 | 0.75 | 0.888 | 49.6005 |
| CircUVRAG | SPI1 | 0.65 | 0.843 | 32.2629 |
| CircUVRAG | WT1 | 0.7 | 0.91 | 48.7542 |
| CircUVRAG | ZRSR1 | 0.75 | 0.926 | 57.8013 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Lou, Y.; Cui, J.-C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.-T.; Yuan, Y.; Han, Y.; Huo, Y.-L.; Qi, Y.-X.; Jiang, Z.-L.; et al. Circular RNA UVRAG Mediated by Alternative Splicing Factor NOVA1 Regulates Adhesion and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Genes 2021, 12, 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030418
Liu Z, Lou Y, Cui J-C, Chen Y, Liu J-T, Yuan Y, Han Y, Huo Y-L, Qi Y-X, Jiang Z-L, et al. Circular RNA UVRAG Mediated by Alternative Splicing Factor NOVA1 Regulates Adhesion and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Genes. 2021; 12(3):418. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030418
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ze, Yue Lou, Jia-Chen Cui, Yi Chen, Ji-Ting Liu, Ying Yuan, Yue Han, Yun-Long Huo, Ying-Xin Qi, Zong-Lai Jiang, and et al. 2021. "Circular RNA UVRAG Mediated by Alternative Splicing Factor NOVA1 Regulates Adhesion and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells" Genes 12, no. 3: 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030418
APA StyleLiu, Z., Lou, Y., Cui, J.-C., Chen, Y., Liu, J.-T., Yuan, Y., Han, Y., Huo, Y.-L., Qi, Y.-X., Jiang, Z.-L., & Yao, Q.-P. (2021). Circular RNA UVRAG Mediated by Alternative Splicing Factor NOVA1 Regulates Adhesion and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Genes, 12(3), 418. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030418







