Identification of Phosphorylated Amino Acids in Human TNRC6A C-Terminal Region and Their Effects on the Interaction with the CCR4-NOT Complex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Construction of Expression Constructs of Phosphorylated TNRC6A Mutants
2.2.1. TNRC6A Expression Construct with Myc-GFP Tag at N-Terminus
2.2.2. TNRC6A Expression Construct with FLAG-HA-SBP Tag at N-Terminus
2.2.3. Full-Length TNRC6A Expression Construct with FHS Tag at N-Terminus
2.3. Immunoprecipitation
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Detection of Phosphorylated Amino Acid Residues Using Phos-Tag SDS-PAGE
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
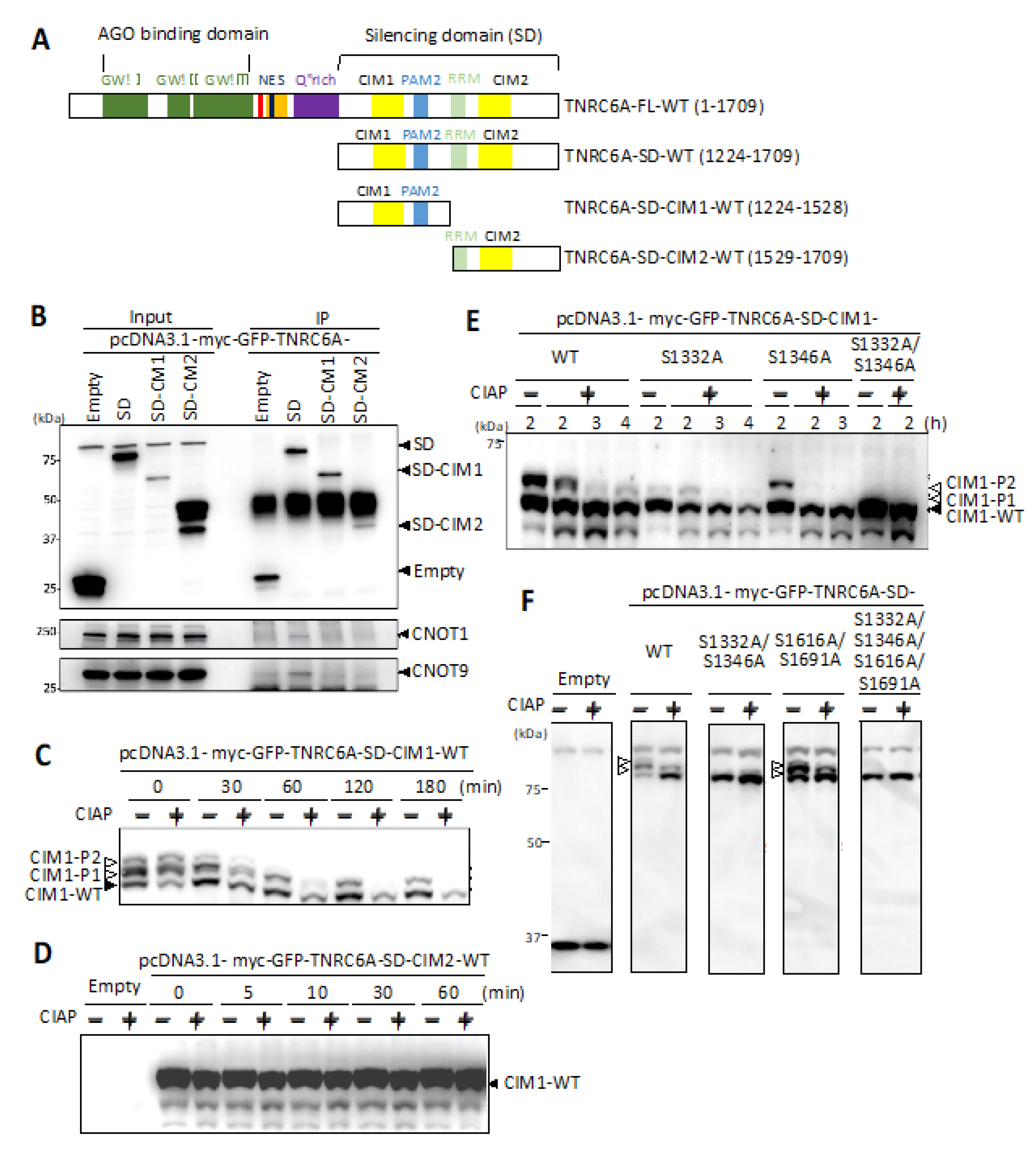
3.1. Interaction of C-Terminal Silencing Domain (SD) of TNRC6A with the Components Involved in the CCR4-NOT Complex
3.2. Identification of Phosphorylated Regions in the SD of TNRC6A
3.3. Identification of Phosphorylated Amino Acids in the Vicinity of the CIM1 Region
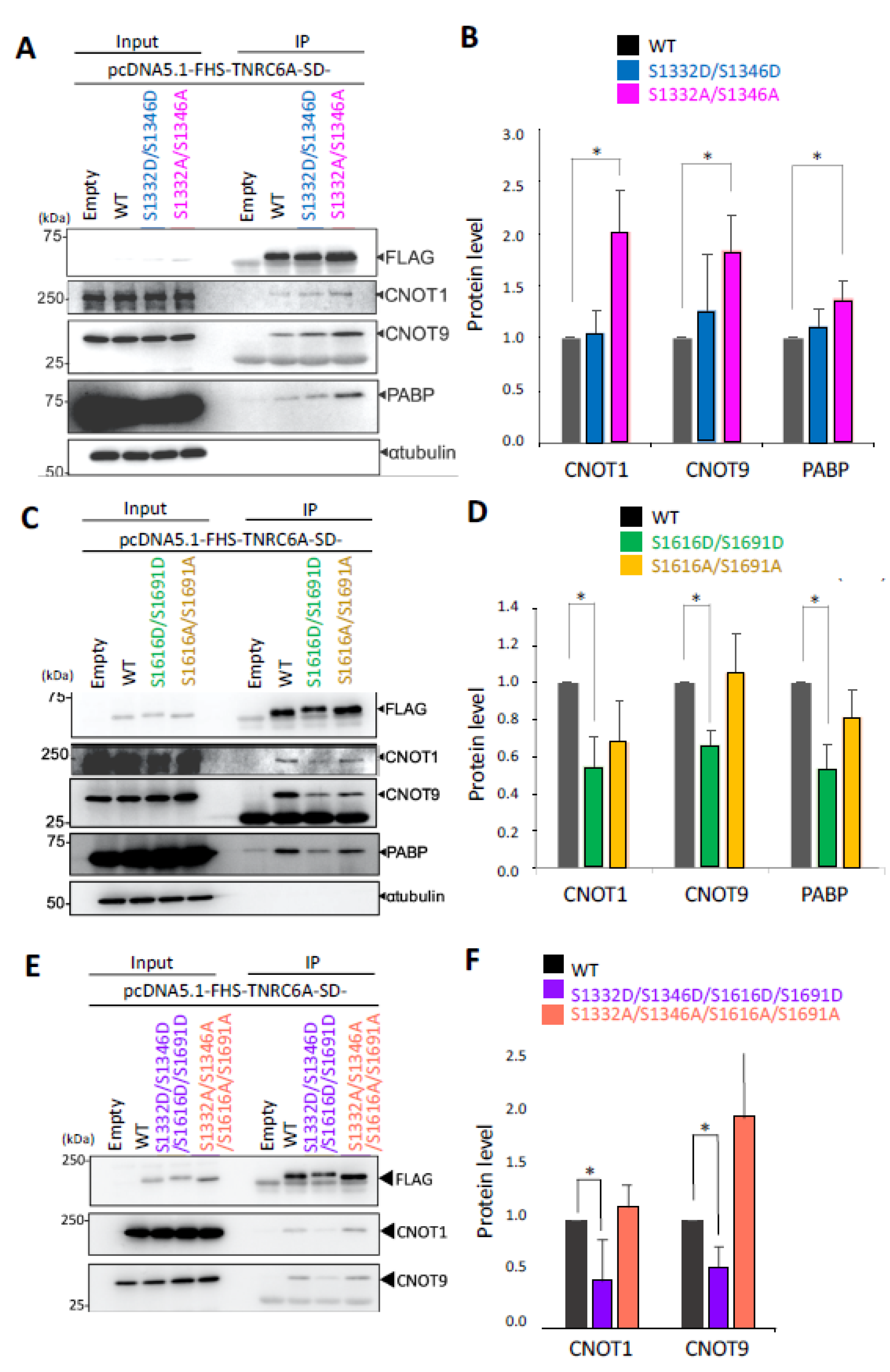
3.4. Effect of Phosphorylation in the SD Fragment on the Interaction with RNA Silencing-Related Factors
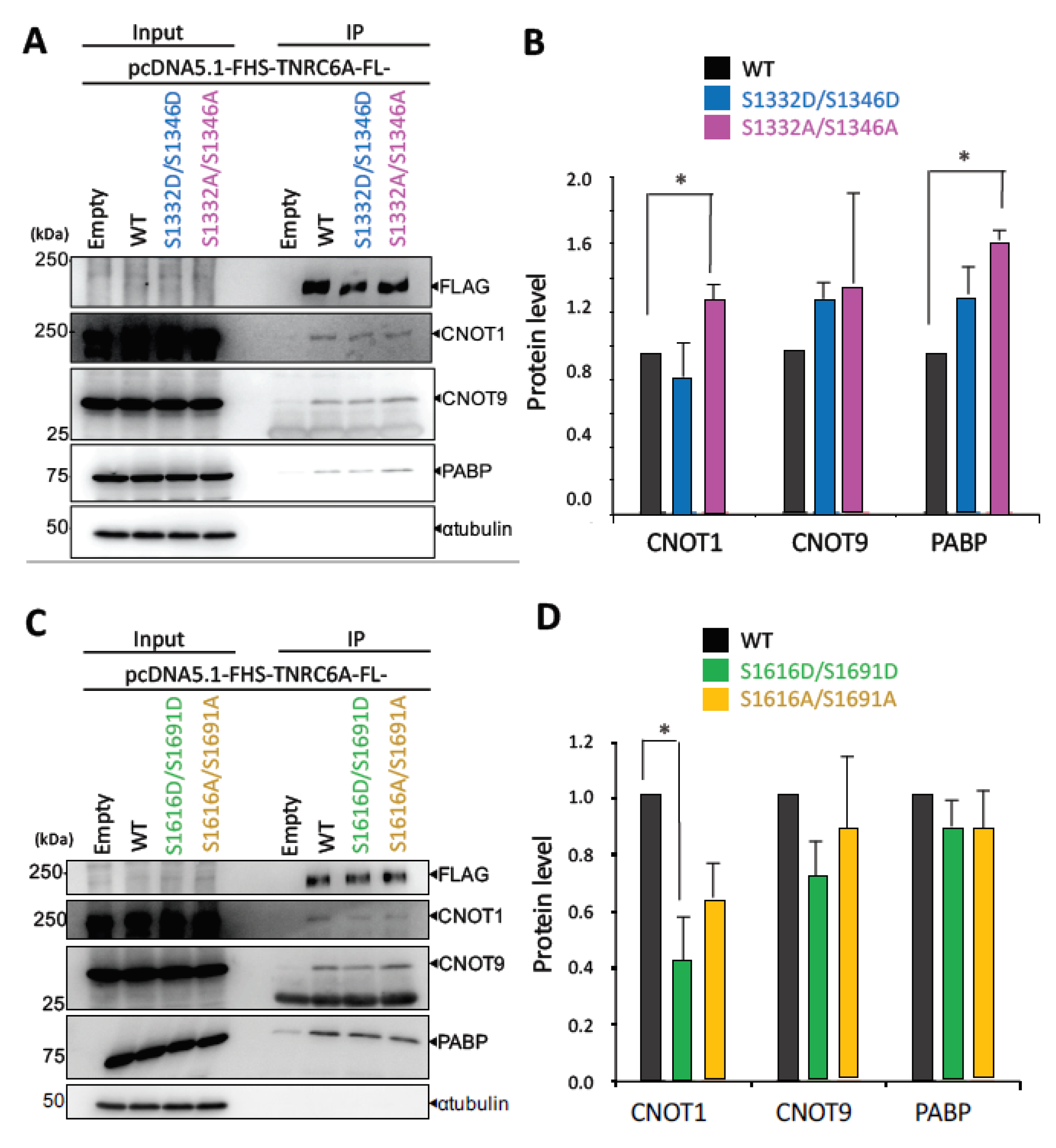
3.5. Effect of Phosphorylation of the SD in Full-Length (FL) TNRC6A on Interaction with RNA Silencing-Related Factors
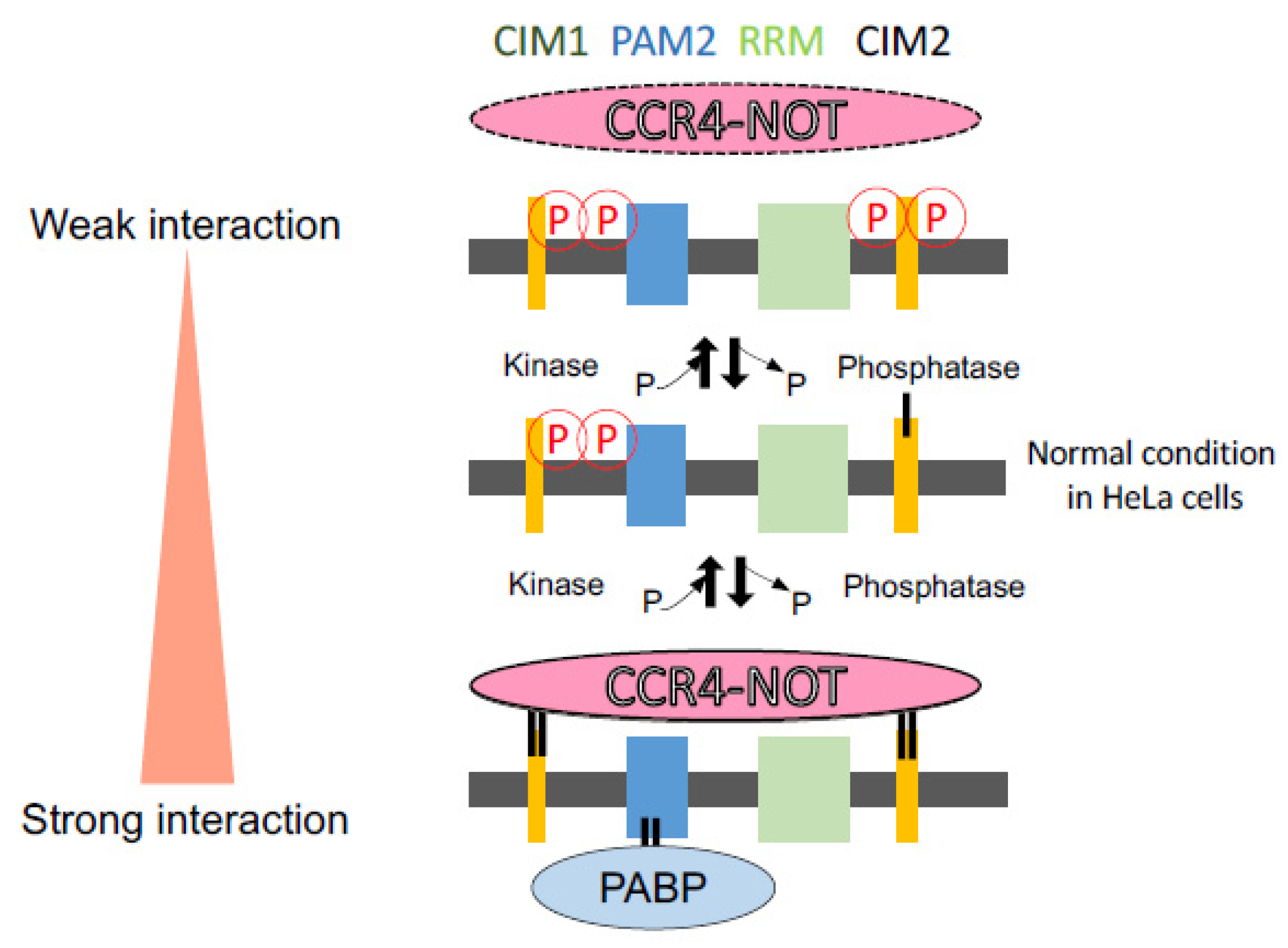
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenohabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamore, P.D.; Sharp, T.T.; Bartel, D.P. RNAi: Double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 2000, 101, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaucheret, H. Post-transcriptional small RNA pathways in plants: Mechanisms and regulations. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomari, Y.; Matranga, C.; Haley, B.; Martinez, N.; Zamore, P.D. A protein sensor for siRNA asymmetry. Science 2004, 306, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniataki, E.; Mourelatos, Z. A human, ATP-independent, RISC assembly machine fueled by pre-miRNA. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2979–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, J.; Jug, S.; Keller, S.; Gregory, R.I.; Diederichs, S. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnegan, E.F.; Pasquinelli, A.E. MicroRNA biogenesis: Regulating the regulators. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhart, B.J.; Slack, F.J.; Basson, M.; Pasquinelli, A.E.; Bettinger, J.C.; Rougbie, A.E.; Horvitz, H.R.; Ruvkun, G. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2000, 403, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Till, S.; Lejeune, E.; Thermann, R.; Bortfeld, M.; Hothorn, M.; Enderle, D.; Heinrich, C.; Hentze, M.W.; Ladurner, A.G. A conserved motif in Argonaute-interacting proteins mediates functional interactions through the Argonaute PIWI domain. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulalio, A.; Triischler, F.; Izaurralde, E. The GW182 protein family in animal cells: New insights into domains required for miRNA-mediated gene silencing. RNA 2009, 15, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzaretti, D.; Tournier, I.; Izzaurralde, E. The C-terminal domains of human TNRC6A, TNRC6B, TNRC6C silence bound transcripts independently of Argonaute proteins. RNA 2009, 15, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, S.L.; Li, S.; Abaal, G.Z.; Pauley, B.A.; Fritzler, M.J.; Chan, E.K.L. The C-terminal hald of human Ago2 binds to multiple GW-rich regions of GW182 and requires GW182 to mediate silencing. RNA 2009, 15, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takimoto, K.; Wakiyama, M.; Yokoyama, S. Mammalian GW182 contains multiple Argonaute-binding sites and functions in microRNA-mediated translational repression. RNA 2009, 15, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzuoglu-Ozturk, D.; Huntzinger, E.; Schmidt, S.; Izaurralde, E. The Caenorhabditis elegans GW182 protein AIN-1 interacts with PAB-1 and subunits of the PAN2-PAN3 and CCR4-NOT deadenylase complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 5651–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, K.; Nishi, A.; Nagasawa, T.; Ui-Tei, K. Human TNRC6A is an Argonaute-navigator protein for microRNA-mediated gene silencing in the nucleus. RNA 2013, 19, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, K.; Takahashi, T.; Suzawa, M.; Miyakawa, T.; Nagasawa, T.; Ming, Y.; Tanokura, M.; Ui-Tei, K. Control of the localization and function of a miRNA silencing component TNRC6A by Argonaute protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 9856–9873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niaz, S.; Hussain, M.U. Role of GW182 protein in the cell. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 101, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eystathioy, T.; Chan, E.K.L.; Tenenbaum, S.A.; Keenes, J.D.; Griffith, K.; Marvin, J.; Fritzler, M.J. A phosphorylated cytoplasmic autoantigen, GW182, associates with a unique population of human mRNAs within novel cytoplasmic speckles. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 1338–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakymiw, A.; Lian, S.; Eystathioy, T.; Li, S.; Satoh, M.; Hamel, J.C.; Fritzler, M.J.; Chan, E.K.L. Disruption of GW bodies impairs mammalian RNA interference. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Valencia-Sanchez, M.A.; Hannon, G.J.; Parker, R. MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to mammalian P-bodies. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, G.L.; Blau, H.M. Argonaute 2/RISC resides in sites of mammalian mRNA decay known as a cytoplasmic bodies. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horman, S.R.; Janas, M.M.; Litterst, C.; Wang, B.; MacRae, I.J.; Morrissey, D.V.; Graves, P.; Luo, B.; Umesalma, S.; Qi, H.H.; et al. Akt-mediated phosphorylation of argonaute 2 downregulates cleavage and upregulates translational repression of microRNA targets. Mol Cell. 2013, 50, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Palma, S.D.; Preisinger, C.; Peng, M.; Polat, A.N.; Heck, A.J.R.; Mohammed, S. Toward a comprehensive characterization of a human cancer cell phosphoproteome. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertins, P.; Qiao, J.W.; Patel, J.; Udeshi, N.D.; Clauser, K.R.; Mani, D.R.; Burgess, M.W.; Gillette, M.A.; Jaffe, J.D.; Carr, S.A. Integrated proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications by serial enrichment. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; D’Souza, R.C.J.; Tyanova, S.; Schaab, C.; Wisneewski, J.R.; Cox, J.; Mann, M. Ultradeep human phosphoproteome reveals a distinct regulatory nature of Tyr and Ser/Thr-based signaling. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertins, P.; Mani, D.R.; Ruggles, K.V.; Gillette, M.A.; Clauser, K.R.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Qiao, J.W.; Cao, S.; Petralia, F.; et al. Proteogenomics connects somatic mutations to signaling in breast cancer. Nature 2016, 534, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzawa, M.; Noguchi, K.; Nishi, K.; Kozuka-Hata, H.; Oyama, M.; Ui-Tei, K. Comprehensive identification of nuclear and cytoplasmic TNRC6A-associating proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 3319–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, M.R.; Cieplak, M.K.; Frank, F.; Morita, M.; Green, J.; Srikumar, T.; Nagar, B.; Yamamoto, T.; Raught, B.; Duchaine, T.F.; et al. miRNA-mediated deadenylation is orchestrated by GW182 through two conserved motifs that interact with CCR4-NOT. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zekri, L.; Huntzinger, E.; Heimsadt, S.; Izaurralde, E. The silencing domain of GW182 interacts with PABPC1 to promote translational repression and degradation of microRNA targets and is required for target release. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 6220–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntzinger, E.; Braun, J.E.; Heimstadt, S.; Zekri, L.; Izaurralde, E. Two PABPC1-bidnign sites in GW182 proteins promote miRNA-mediated gene silencing. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 4146–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntzinger, E.; Kuzuoglu-Ozturk, D.; Braun, J.E.; Eulalio, A.; Wohlbold, L.; Izaurralde, E. The interactions of GW182 proteins with PABP and deadenylases are required for both translational repression and degradation of miRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 978–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, G.; Safaee, N.; Rosenauer, A.; Gehring, K. Structural basis of binding of P-body-associated proteins GW182 and ataxin-2 by the Mlle domain of poly(A)-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 13599–13606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.E.; Huntzinger, E.; Fauser, M.; Izaurralde, E. GW182 proteins directly recruit cytoplasmic deadenylase complexes to miRNA target. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekulaeva, M.; Matys, H.; Zipprich, J.T.; Attig, J.; Colic, M.; Parker, R.; Fillipowicz, W. miRNA repression involves GW182-mediated recruitment of CCR4-NOT through conserved W-containing motifs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collart, M.A.; Panasenko, O.O. The Cer4-Not complex. Gene 2012, 492, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, M.; Boland, A.; Huntzinger, E.; Weichenrieder, O.; Izaurralde, E. Structure of the PAN3 pseudokinase reveals the basis for interactions with the PAN2 deadenylase and the GW182 proteins. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Boland, A.; Kuzuoglu-Ozturk, D.; Bawankar, P.; Loh, B.; Chang, C.-T.; Weichenrieder, O.; Izaurralde, E. A DDX6-CNOT1 complex and W-binding pockets in CNOT9 reveal direct links between miRNA target recognition and silencing. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zekri, L.; Kuzuoglu-Ozturk, D.; Izaurralde, E. GW182 proteins cause PABP dissociation from silenced miRNA targets in the absence of deadenylation. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Sankala, H.; Zhang, X.; Graves, P.R. Phophorylation of Argonaute 2 at serine-387 facilitates its localization to processing bodies. Biochem. J. 2008, 413, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruepp, M.-D.; Aringhieri, C.; Vivarelli, S.; Cardinale, S.; Paro, S.; Schumperli, D.; Barabiono, S.M.L. Mammalian pre-mRNA 3’ end processing factor CF I m 68 functions in mRNA export. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 5211–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudel, S.; Wang, Y.; Lenobel, R.; Korner, R.; Hsiao, H.H.; Urlaub, H.; Patel, D.; Meister, G. Phosphorylation of human Argonaute proteins affects small RNA binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 2330–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, M.; Furuta, T.; Suen, K.M.; Gonzalez, G.; Liu, B.; Kalia, A.; Ladbury, J.E.; Fire, A.Z.; Skeath, J.B.; Arur, S. A requirement for ERK-dependent Dicer phosphorylation in coordinating oocyte-to-embryo transition in C. elegans. Dev. Cell 2014, 31, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.-L.; Chadee, A.B.; Chen, C.-Y.A.; Zhang, Y.; Shyu, A.-B. Phosphorylation at intrinsically disordered region of PAM2 motif-containing proteins modulates their interactions with PABPC1 and influences mRNA fate. RNA 2013, 19, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
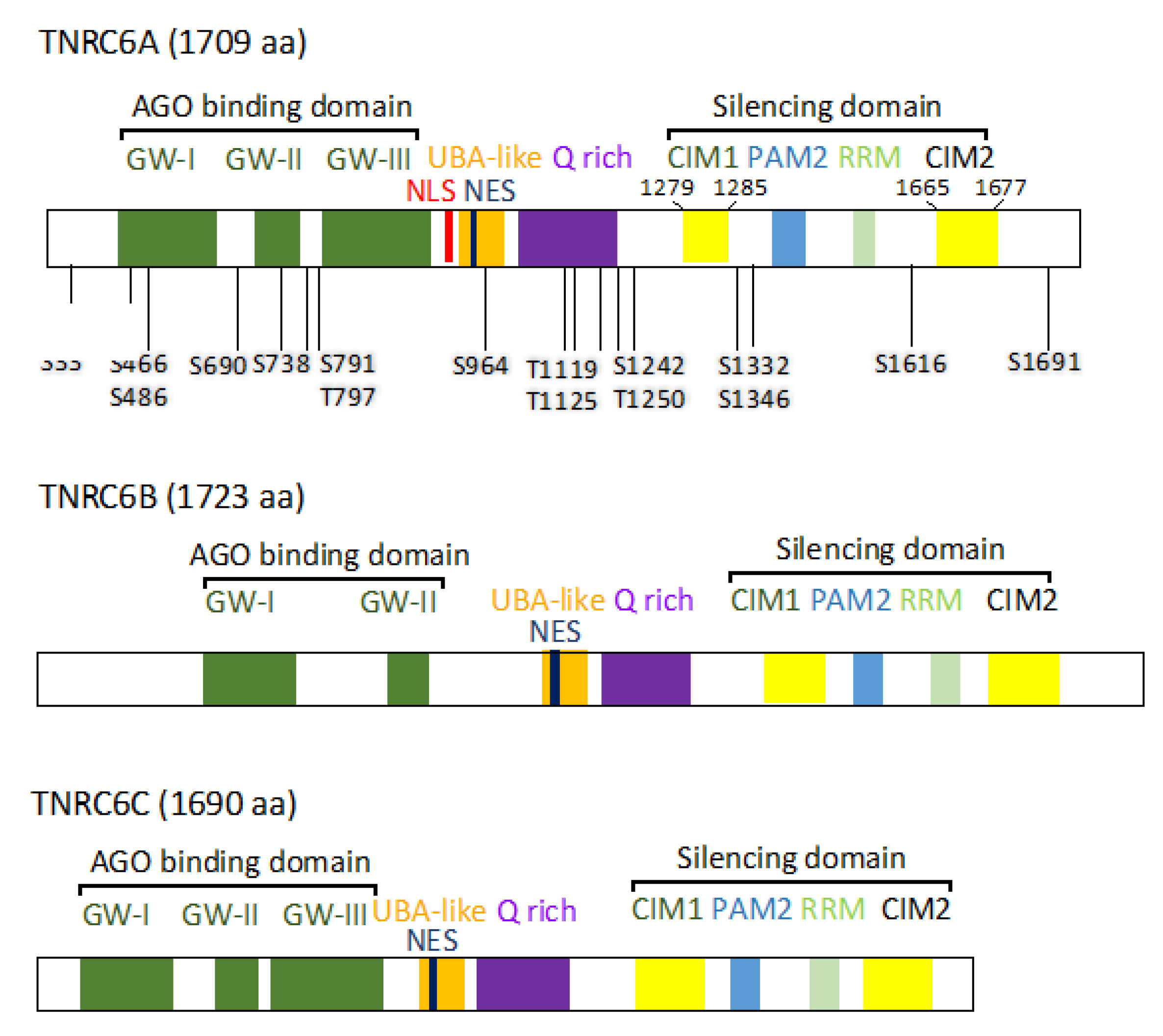
| Amino Acid Positions | Amino Acid | Sequence | References (>5) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 486 | S | TAWDTETsPRGERKT | 9 |
| 690 | S | DSSKPVSsPDWNKQQ | 7 |
| 738 | S | PTGWEEPsPESIRRK | 14 |
| 964 | S | NISFSRDsPEENVQS | 7 |
| 1332 | S | NSSTSPAsPPGSIGD | 7 |
| 1346 | S | DGWPRAKsPNGSSSV | 7 |
| 1378 | Y | IDPETDPyVTPGSVI | 7 |
| 1451 | S | SDSKLTWsPGSVTNT | 7 |
| 1616 | S | QSQSLTPsPGWQSLG | 6 |
| 1691 | S | PRGISSPsPINAFLS | 6 |
| Amino Acid Position | Motif | Sequence | Modification | Highest pRS Probability (>0.9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S33 | DGLRNsTGLGSQNK | S6(Phospho) | 0.990217268 | |
| S466 | Ago binding domain | VLsNSGWGQTPIK | S3(Phospho) | 0.999568224 |
| S486 | Ago binding domain | QNTAWDTETsPR | S10(Phospho) | 0.999141693 |
| S690 | Ago binding domain | SNQSLGWGDSSKPVSsPDWNK | S16(Phospho) | 0.990312636 |
| S738 | Ago binding domain | EEEPTGWEEPsPESIRR | S11(Phospho) | 0.184156224 |
| T791 | Ago binding domain | SDQQAQVHQLLtPASAISNK | T12(Phospho) | 0.966504514 |
| S797 | Ago binding domain | SDQQAQVHQLLTPASAIsNK | S18(Phospho) | 0.999999821 |
| S964 | UBS-like | QFSNISFSRDsPEENVQSNK | S11(Phospho) | 0.917854786 |
| S1119 | Q rich | AQVPPPLLsPQVPVSLLK | S9(Phospho) | 0.999998212 |
| S1125 | Q rich | AQVPPPLLSPQVPVsLLK | S15(Phospho) | 0.981702089 |
| T1217 | Q rich | QQtPPSQQQPLHQPAMK | T3(Phospho) | 0.99997437 |
| T1242 | Silencing domain | SFLDNVMPHTtPELQK | T11(Phospho) | 0.998789012 |
| S1250 | Silencing domain | GPsPINAFSNFPIGLNSNLNVNMDMNSIK | S3(Phospho) | 0.997624218 |
| S1332 | Silencing domain | LEESPFVPYDFMNSSTSPAsPPGSIGDGWPR | S20(Phospho) | 0.998691678 |
| S1346 | Silencing domain | AKsPNGSSSVNWPPEFRPGEPWK | S3(Phospho) | 0.943672001 |
| S1616 | Silencing domain | FFAQSQSLTPsPGWQSLGSSQSR | S11(Phospho) | 0.999580026 |
| S1691 | Silencing domain | GISSPsPINAFLSVDHLGGGGESM | S6(Phospho) | 0.97981894 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munakata, F.; Suzawa, M.; Ui-Tei, K. Identification of Phosphorylated Amino Acids in Human TNRC6A C-Terminal Region and Their Effects on the Interaction with the CCR4-NOT Complex. Genes 2021, 12, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020271
Munakata F, Suzawa M, Ui-Tei K. Identification of Phosphorylated Amino Acids in Human TNRC6A C-Terminal Region and Their Effects on the Interaction with the CCR4-NOT Complex. Genes. 2021; 12(2):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020271
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunakata, Fusako, Masataka Suzawa, and Kumiko Ui-Tei. 2021. "Identification of Phosphorylated Amino Acids in Human TNRC6A C-Terminal Region and Their Effects on the Interaction with the CCR4-NOT Complex" Genes 12, no. 2: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020271
APA StyleMunakata, F., Suzawa, M., & Ui-Tei, K. (2021). Identification of Phosphorylated Amino Acids in Human TNRC6A C-Terminal Region and Their Effects on the Interaction with the CCR4-NOT Complex. Genes, 12(2), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020271







