Integrated Full-Length Transcriptome and RNA-Seq to Identify Immune System Genes from the Skin of Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
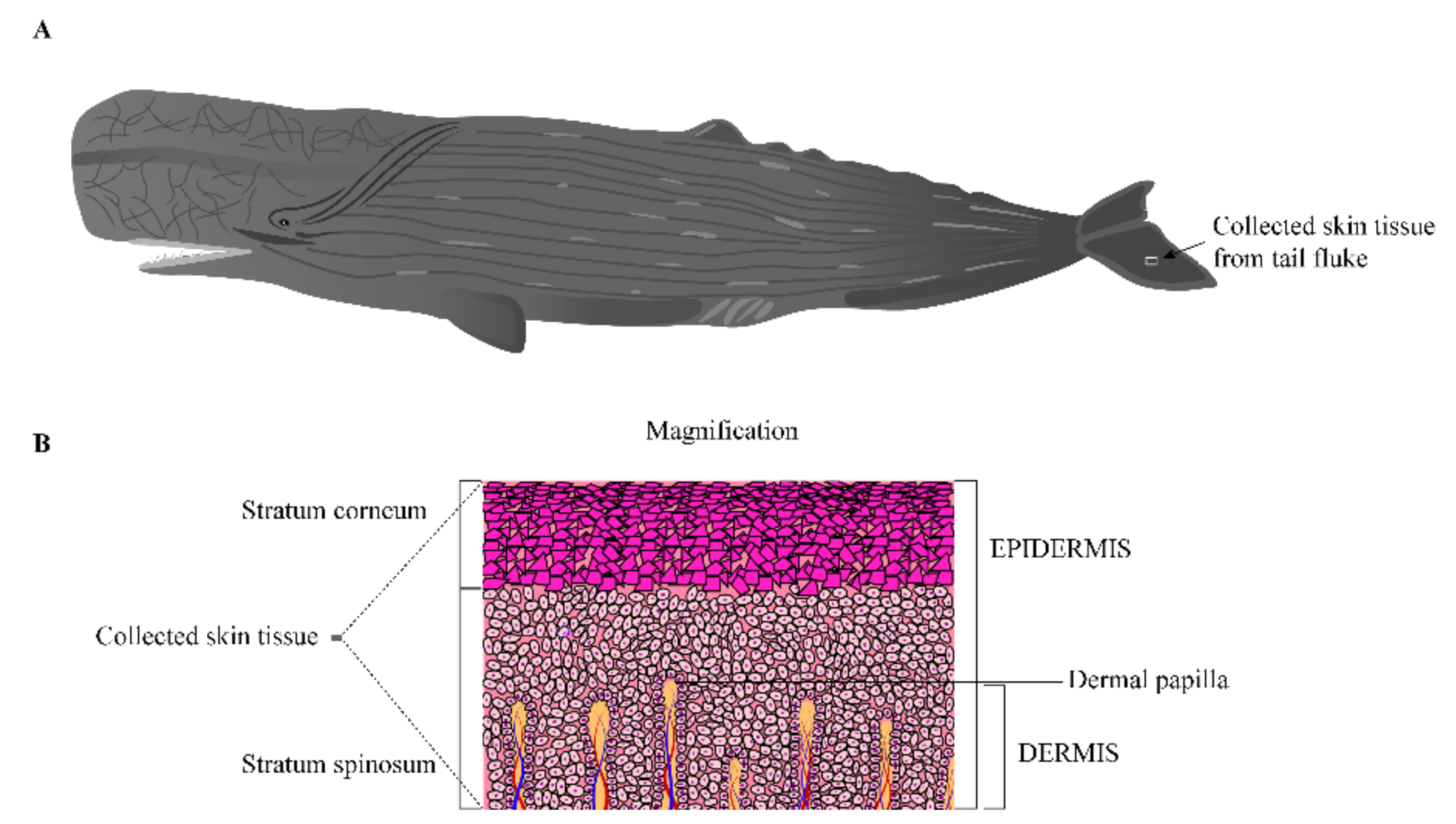
2.1. Animal and Tissue Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction and Quantification
2.3. PacBio Iso-Seq Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.4. RNA-seq Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis of PacBio Data and RNA-seq Data
2.6. Quantification and Annotation of Gene Expression Levels
2.7. Sequence Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Full-Length Transcripts from the Skin of Sperm Whale
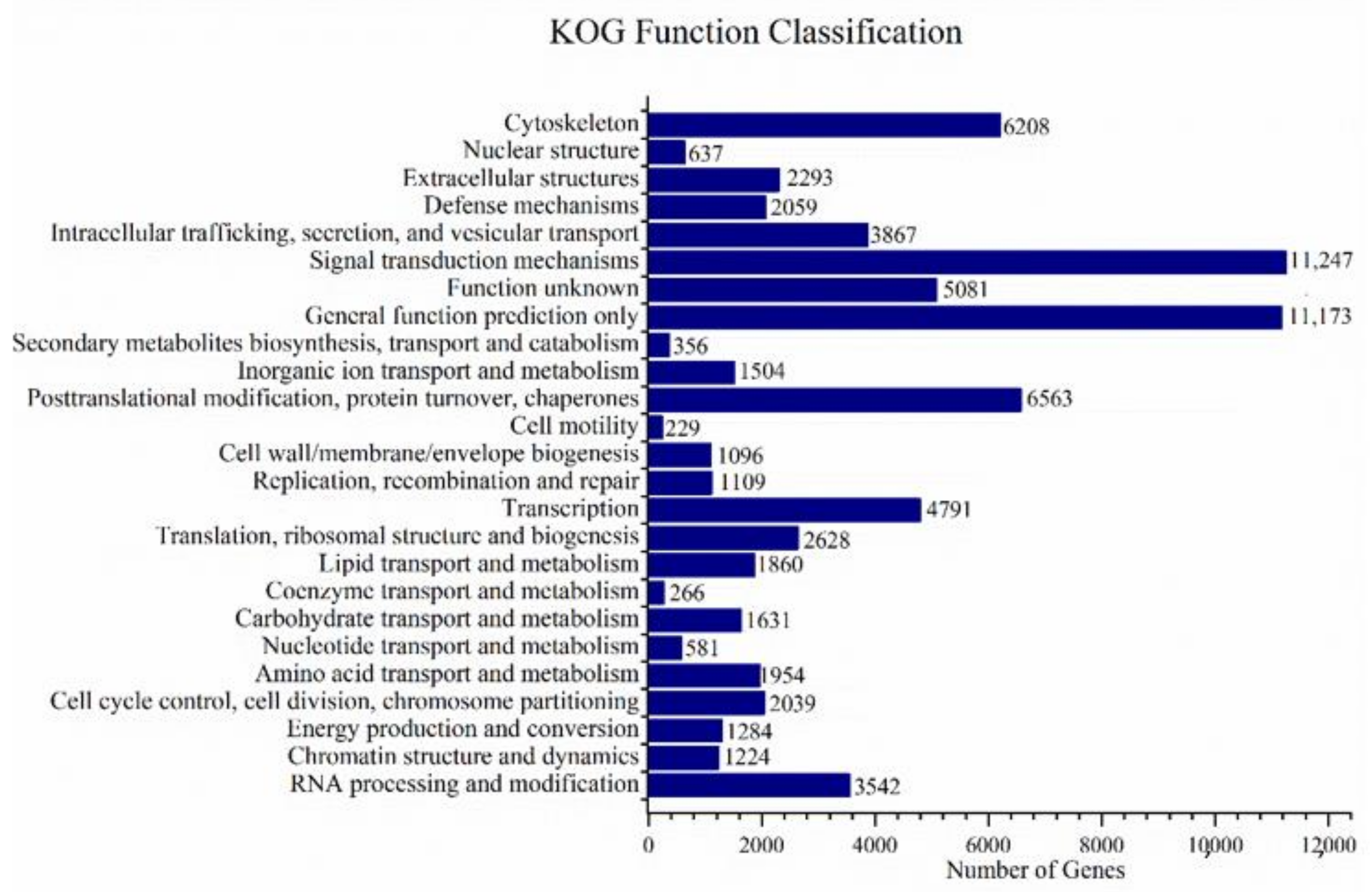
3.2. Annotations and Analysis of Full-Length Transcriptome
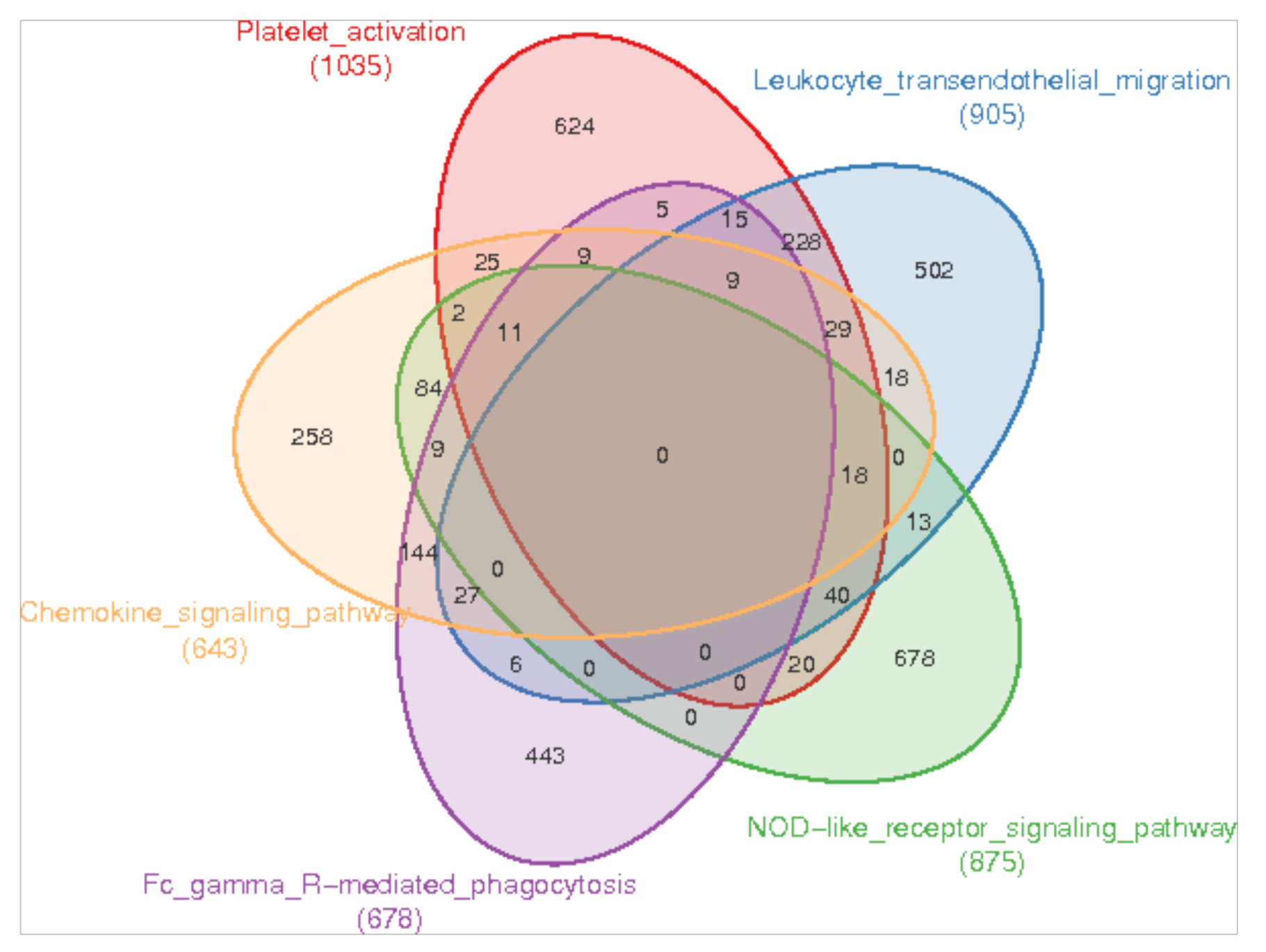
3.3. Enrichment of Immune-Related Pathways in the Skin of Sperm Whale
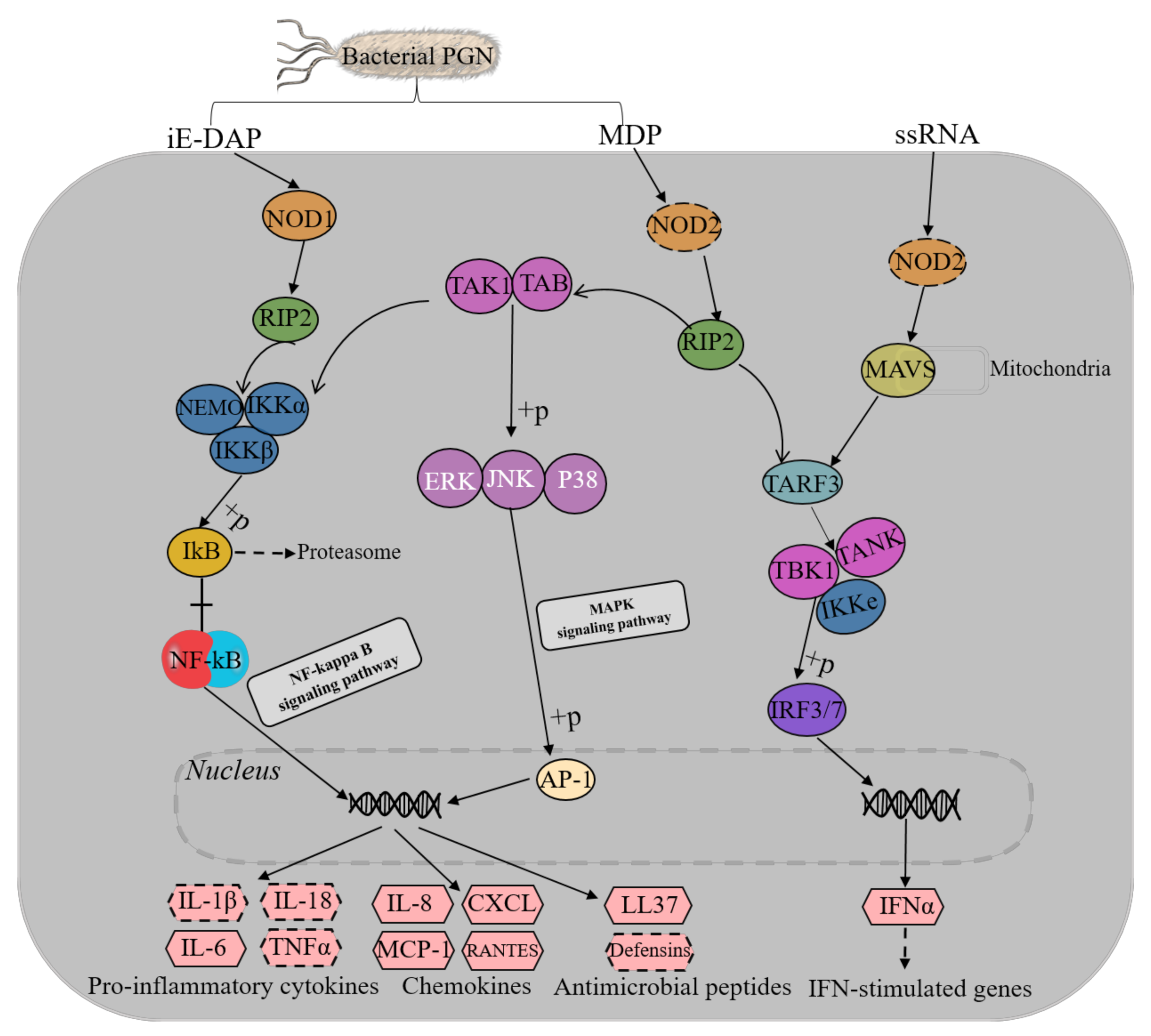
3.4. NOD-Like Receptor Signaling Pathway
3.5. Structural and Evolutional Analysis of NOD1 Gene in Sperm Whale
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

| Species Name | Protein ID | Length (Amino Acids) |
|---|---|---|
| Tursiops truncatus | XP_019781619.1 | 953 |
| Lagnorhynchus obliquidens | XP_026958076.1 | 953 |
| Globicephla melas | XP_030713315.1 | 953 |
| Orcinus orca | XP_033284214.1 | 953 |
| Phocoena sinus | XP_032499084.1 | 972 |
| Neophocaena asiaeorientalis | XP_024610766.1 | 963 |
| Monodon monoceros | XP_029089062.1 | 953 |
| Delphinapterus leucas | XP_022439858.1 | 953 |
| Lipotes vexillifer | XP_007466161.1 | 953 |
| Physeter macrocephalus | Isoform_6383 | 958 |
| Odocoileus virginianus texanus | XP_020748129.1 | 954 |
| Balaenoptera acutorostrata | XP_028020573.1 | 818 |
| Balaenoptera musculus | XP_036718877.1 | 953 |
| Ovis aries | XP_004007979.2 | 954 |
| Bubalus bubalis | XP_006055719.1 | 954 |
| Bos taurus | XP_005205565.2 | 954 |
| Camelus bactrianus | XP_010969658.1 | 953 |
| Sus scrofa | NP_001107749.1 | 953 |
| Anolis carolinensis | XP_003222248.2 | 950 |
| Equus caballus | XP_023495227.1 | 897 |
| Tupaia chinensis | ELW67927.1 | 1109 |
| Homo sapiens | AAD28350.1 | 953 |
| Oryctolagus cuniculus | XP_002713781.1 | 953 |
| Mus musculus | AAN52479.1 | 953 |
| Ornithorhynchus anatinus | XP_001512159.2 | 950 |
| Gallus gallus | NP_001305367.1 | 951 |
| Danio rerio | XP_002665106.3 | 940 |
| Xenopus tropicalis | XP_031759856.1 | 945 |
| Canis lupus familiaris | XP_013974568.1 | 964 |
| Vulpes vulpes | XP_025874889.1 | 953 |
| Proteins/Enzymes Name | Genes ID in This Transcriptome | *** FPKM (Min–Max) | Sequence Alignment Identity Percentage (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physeter macrocephalus | Lipotes vexillifer | Tursiops truncatus | |||
| Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 1 (NOD1) | Isoform_6383 Isoform_44218 Isoform_24661 Isoform_40056 | 0.41–7.56 | 100.00 (XP_023984584.1) 100.00 (XP_023984584.1) 100.00 (XP_023984584.1) 92.05 (XP_023984584.1) | 96.41 (XP_007466161.1) 98.94 (XP_007466161.1) 98.52 (XP_007466161.1) 90.73 (XP_007466161.1) | 96.73 (XP_019781619.1) 97.88 (XP_033719017.1) 97.78 (XP_019781638.1) 90.07 (XP_033719017.1) |
| Interleukin 6(IL-6) | Isoform_60901 Isoform_23835 | 1.32–1.59 | 100.00 (XP_007105488.3) 100.00 (XP_007105488.3) | NM NM | 100.00 (XP_019778462.1) 100.00 (XP_019778462.1) |
| Interleukin 8 (IL-8) | Isoform_34284 | 2.71 | 100.00 (XP_007126317.1) | 98.02 (XP_007467625.1) | 96.04 (NP_001267571.1) |
| C–X–C motif chemokine 2 (CXCL2) C–X–C motif chemokine 3 (CXCL3) | Isoform_67128 Isoform_70740 Isoform_34284 Isoform_69403 Isoform_45444 | 0.79–7.18 2.29-3.46 2.29-3.46 | 98.53 (XP_023971193.1) 98.53 (XP_023971193.1) 98.44 (XP_023971204.1) 98.41 (XP_007126322.2) 98.44 (XP_007126322.2) | 96.88 (NP_007463281.1) 96.88 (NP_007463281.1) 96.88 (NP_007463281.1) NM NM | 94.12 (NP_004331677.2) 94.12 (NP_004331677.2) 93.75 (NP_004331677.2) NM NM |
| C–C motif chemokine 2 (MCP-1) | Isoform_85283 Isoform_14905 Isoform_68475 | 0.08–3.03 | 100.00 (XP_007467625.1) 91.11 (XP_023983766.1) 98.44 (XP_023983766.1) | 90.36 (XP_007458436.1) 82.22 (XP_007458436.1) 89.80 (XP_007458436.1) | NM NM NM |
| Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (LL37) | Isoform_27979 Isoform_90183 Isoform_92246 | 0.11–15.39 | 100.00 (XP_007101317.2) 100.00 (XP_007101317.2) 100.00 (XP_007101317.2) | 90.91 (XP_007446211.1) 89.94 (XP_007446211.1) 77.99 (XP_007446211.1) | 93.94 (XP_033720747.1) 88.89 (XP_033720747.1) 90.35 (XP_033720747.1) |
| transcription factor AP-1 (AP-1) Interferon α (IFNα) | Isoform_38241 Isoform_63047 Isoform_56853 Isoform_75661 | 0.25–264.37 1.04 | 100.00 (XP_023975690.1) 100.00 (XP_023975690.1) 80.97 (XP_023975690.1) 100.00 (XP_023982688.1) | 100.00 (XP_007462636.1) 100.00 (XP_007462636.1) NM 58.90 (XP_007455007.1) | 100.00 (XP_019797942.2) 100.00 (XP_019797942.2) NM 97.22 (AFH89765.1) |
| Receptor-interacting serine/threonine–protein kinase 2 (RIP2) | Isoform_20477 Isoform_25948 Isoform_60840 Isoform_78887 | 0.71–1.52 | 100.00 (XP_023982836.1) 100.00 (XP_023982836.1) 100.00 (XP_023982837.1) 100.00 (XP_023982837.1) | 98.33 (XP_007446375.1) 98.33 (XP_007446375.1) 97.07 (XP_007446375.1) 98.39 (XP_007446375.1) | 97.95 (XP_033699058.1) 97.95 (XP_033699058.1) 96.31 (XP_033699060.1) 98.39 (XP_033699059.1) |
| transcription factor p65(RELA) | Isoform_11257 Isoform_15246 Isoform_14067 Isoform_35442 | 0.08–10.86 | 100.00 (XP_023989099.1) 87.06 (XP_023989099.1) 99.64 (XP_007128247.1) 100.00 (XP_007128247.1) | 96.01 (XP_007462051.1) 87.06 (XP_007462053.1) 96.01 (XP_007462052.1) 94.46 (XP_007462051.1) | NM NM NM NM |
| Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit (NFKB1) | Isoform_2285 Isoform_78940 | 1.34–3.73 | 100.00 (XP_023982362.1) 100.00 (XP_023982361.1) | 95.21 (XP_007463876.1) 97.52 (XP_007463874.1) | 91.78 (XP_019782050.1) 96.88 (XP_019782049.1) |
| Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit β (Ikkβ) | Isoform_16029 Isoform_3742 | 0.64–2.16 | 99.44 (XP_028341955.1) 99.73 (XP_028341955.1) | 97.32 (XP_007455533.1) 98.02 (XP_007455533.1) | 96.78 (XP_033704813.1) 98.02 (XP_033704810.1) |
| Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit α (Ikkα) | Isoform_69638 Isoform_28559 | 0.25–3.37 | 100.00 (XP_028337608.1) 100.00 (XP_028337608.1) | 100.00 (XP_007117682.1) 97.84 (XP_007470397.1) | 100.00 (XP_033697982.1) 99.27 (XP_033697983.1) |
| NF-kappa-B inhibitor α (NFKBIA) | Isoform_44406 Isoform_62842 Isoform_57121 Isoform_5319 | 0.03–66.12 | 100.00 (XP_007119015.1) 100.00 (XP_007119015.1) 100.00 (XP_007119015.1) 89.70 (XP_007119015.1) | 95.54 (XP_007464888.1) 93.87 (XP_007464888.1) 95.37 (XP_007464888.1) NM | NM NM NM NM |
| NF-kappa-B inhibitor β(NFKBIB) | Isoform_64970 Isoform_49218 Isoform_61453 Isoform_30066 | 0.36–16.21 | 100.00 (XP_007114641.1) 99.46 (XP_007114641.2) 100.00 (XP_007114641.2) 100.00 (XP_007114641.2) | 98.58 (XP_007464742.1) 97.27 (XP_007464742.1) 99.08 (XP_007464742.1) 98.71 (XP_007464742.1) | 98.58 (XP_019796701.1) 97.28 (XP_019796701.1) 98.18 (XP_019796701.1) 98.39 (XP_019796701.1) |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 (TAK1) | Isoform_11038 Isoform_3956 Isoform_6441 | 0.39–2.85 | 100.00 (XP_007126290.1) 100.00 (XP_007126290.1) 100.00 (XP_007126290.1) | NM NM NM | NM NM NM |
| TAK1-binding protein 3(TAB3) | Isoform_24688 | 1.38 | 99.81 (XP_023972426.1) | 98.85 (XP_007456911.1) | NM |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3(ERK) | Isoform_43270 Isoform_52694 Isoform_78038 | 2.06–23.34 | NM NM NM | 98.87 (XP_007452842.1) 100.00 (XP_007452842.1) 100.00 (XP_007452842.1) | NM NM NM |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 9 (MAPK9) (JNK) | Isoform_51119 Isoform_55328 | 0.43–1.36 | 100.00 (XP_023972057.1) 99.57 (XP_023972058.1) | 99.59 (XP_007465571.1) 99.13 (XP_007465571.1) | NM NM |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 (MAPK8) (JNK) | Isoform_76485 | 0.05 | NM | 98.82 (XP_007446292.1) | NM |
| P38 MAP kinase 11 (P38 β) P38 MAP kinase 12 (P38 γ) P38 MAP kinase 13 (P38 δ) | Isoform_54378 Isoform_28186 Isoform_36890 Isoform_46157 Isoform_9786 Isoform_5589 Isoform_11611 Isoform_12832 Isoform_13409 | 1.77 0.36–3.83 0.06–20.27 | 75.34 (XP_023983249.1) 100.00 (XP_028346617.1) 59.13 (XP_028346617.1) 96.18 (XP_028346617.1) 100.00 (XP_023977640.1) 100.00 (XP_023977640.1) 95.60 (XP_023977640.1) 100.00 (XP_023977640.1) 100.00 (XP_023977640.1) | 73.97 (XP_007454143.1) 97.90 (XP_007453950.1) 56.15 (XP_007467328.1) 94.24 (XP_007453950.1) 96.06 (XP_007467328.1) 96.17 (XP_007467328.1) 93.41 (XP_007467328.1) 96.06 (XP_007467328.1) 94.17 (XP_007467328.1) | NM 98.51 (XP_033721676.1) 56.92 (XP_019805222.1) 94.96 (XP_033721674.1) 95.07 (XP_004313866.1) 95.08 (XP_004313866.1) 92.31 (XP_004313866.1) 95.07 (XP_004313866.1) 95.15 (XP_019805222.1) |
| Mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS) | Isoform_11457 Isoform_8429 | 0.19–1.83 | NM NM | 94.08 (XP_007454896.1) 94.08 (XP_007454896.1) | 92.91 (XP_033695234.1) 92.01 (XP_033695233.1) |
| TAK1-binding protein 3 (TAB3) | Isoform_24688 | 0.99 | 99.81 (XP_023972426.1) | 98.85 (XP_007456911.1) | NM |
| Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit epsilon (IKKe) | Isoform_49506 Isoform_42897 Isoform_44117 Isoform_39392 Isoform_73428 | 0.51–1.29 | NM NM NM NM 100.00 (XP_028342232.1) | 78.84 (XP_007470765.1) 95.02 (XP_007470765.1) 93.63 (XP_007470765.1) 94.96 (XP_007470765.1) 94.32 (XP_007470765.1) | NM NM NM NM NM |
| TRAF family member-associated NF-kappa-B activator (TANK) | Isoform_44877 Isoform_30925 Isoform_67916 Isoform_35515 | 0.03–1.95 | NM 98.86 (XP_007107800.2) 100.00 (XP_028334198.1) 100.00 (XP_028334197.1) | 96.77 (XP_019778469.1) 96.80 (XP_019778470.1) 96.77 (XP_007457066.1) 95.12 (XP_007457065.1) | NM 94.65 (XP_019778476.1) 97.42 (XP_019778476.1) 95.89 (XP_019778469.1) |
| Interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) | Isoform_25349 Isoform_45963 Isoform_65550 Isoform_73641 Isoform_51357 | 0.6–3.42 | 93.54 (XP_007112499.1) 100.00 (XP_007112499.1) 100.00 (XP_007112499.1) 95.52 (XP_007112501.1) 100.00 (XP_007112498.1) | 87.76 (XP_007463434.1) 94.78 (XP_007463434.1) 95.08 (XP_007463433.1) 96.22 (XP_007463435.1) 95.93 (XP_007463434.1) | 87.41 (XP_033701337.1) NM95.04 (XP_033701337.1) 84.82 (XP_033701337.1) 95.69 (XP_033701337.1) |
| Interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit γ (NEMO) C–C motif chemokine 5 (CCL5/RANTES) TNF receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3) | Isoform_16065 Isoform_57550 Isoform_32564 Isoform_44904 Isoform_30772 Isoform_32236 Isoform_33819 Isoform_86381 Isoform_14574 | 0.4–1.62 0.13–2.14 0.85 0.1 | 100.00 (XP_028341713.1) 87.47 (XP_028341711.1) 87.47 (XP_028341711.1) 100.00 (XP_028341713.1) NM NM NM 100.00 (XP_028355421.1) NM | 95.04 (XP_007465980.1) 84.88 (XP_007465980.1) 93.44 (XP_007465980.1) 86.14 (XP_007465980.1) 92.79 (XP_007457510.1) 93.45 (XP_007457510.1) 93.45 (XP_007457510.1) 96.83 (XP_007447107.1) 93.04 (XP_007455372.1) | 96.17 (XP_033717457.1) NM95.29 (XP_033717454.1) 95.32 (XP_033717457.1) 92.48 (XP_033705598.1) 93.45 (XP_033705598.1) 93.45 (XP_033705598.1) 95.24 (XP_004322904.1) 94.39 (XP_019776547.2) |
References
- Uhen, M.D. The Origin (s) of Whales. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2010, 38, 189–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, H. Sperm Whales: Social Evolution in the Ocean; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jaquet, N.; Whitehead, H. Scale-dependent correlation of sperm whale distribution with environmental features and productivity in the South Pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 135, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewissen, J.G.M.; Cooper, L.N.; George, J.C.; Bajpai, S. From Land to Water: The Origin of Whales, Dolphins, and Porpoises. Evol. Educ. Outreach 2009, 2, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreer, J.F.; Kovacs, K.M. Allometry of diving capacity in air-breathing vertebrates. Can. J. Zool. 1997, 75, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeman, M.E.; Hebsgaard, M.B.; Fordyce, R.E.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Rabosky, D.L.; Nielsen, R.; Rahbek, C.; Glenner, H.; Sørensen, M.V.; Willerslev, E. Radiation of Extant Cetaceans Driven by Restructuring of the Oceans. Syst. Biol. 2009, 58, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, W.C.; Kuderna, L.; Alexander, A.; Catchen, J.; Pérez-Silva, J.G.; López-Otín, C.; Quesada, V.; Minx, P.; Tomlinson, C.; Montague, M.J.; et al. The Novel Evolution of the Sperm Whale Genome. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 3260–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, B.; Baird, R.; Barlow, J.; Dawson, S.; Ford, J.; Mead, J. Physeter Macrocephalus (Amended version of 2008 Assessment). IUCN Red List Threat. Species 2019, 2307–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A.E. Innate host defense mechanisms of fish against viruses and bacteria. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2001, 25, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, B.; Song, G.; Li, T.; Bin, C.Z. De Novo Assembly of Mud Loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) skin transcriptome to identify putative genes involved in immunity and epidermal mucus secretion. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidenberg, J.S. Anatomical adaptations of aquatic mammals. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2007, 290, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.T.J.; Cotton, J.A.; Kirwan, J.D.; Teeling, E.C.; Rossiter, S.J. Parallel signatures of sequence evolution among hearing genes in echolocating mammals: An emerging model of genetic convergence. Heredity 2012, 108, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Hu, B.; Zheng, J.; Xiao, W.; Hao, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, D. Physicochemical Evolution and Molecular Adaptation of the Cetacean Osmoregulation-related Gene UT-A2 and Implications for Functional Studies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Guise, S.; Ross, P.S.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Martineau, D.; Beland, P.; Fournier, M. Immune functions in beluga whales (Delphinapterus leucas): Evaluation of natural killer cell activity. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1997, 58, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Beineke, A.; Siebert, U.; Wohlsein, P.; Baumgärtner, W. Immunology of whales and dolphins. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 133, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabka, T.S.; Romano, T.A. Distribution of MHC II (+) cells in skin of the Atlantic bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus): An initial investigation of dolphin dendritic cells. Anat. Rec. 2003, 273A, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunardi, D.; Abelli, L.; Panti, C.; Marsili, L.; Fossi, M.C.; Mancia, A. Transcriptomic analysis of bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) skin biopsies to assess the effects of emerging contaminants. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 114, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, D.; Jia, K.; Xia, J.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Yi, M. De novo Assembly of the Indo-Pacific Humpback Dolphin Leucocyte Transcriptome to Identify Putative Genes Involved in the Aquatic Adaptation and Immune Response. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishengoma, E.; Agaba, M. Evolution of toll-like receptors in the context of terrestrial ungulates and cetaceans diversification. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Seim, I.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ren, W.; Xu, S.; Yang, G. Distinct evolution of toll-like receptor signaling pathway genes in cetaceans. Genes Genom. 2019, 41, 1417–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbridge, L.M.; O’Riordan, M.X.D. Innate recognition of intracellular bacteria. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2006, 19, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, L.; Warner, N.; Viani, K.; Nuñez, G. Function of Nod-like receptors in microbial recognition and host defense. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 227, 106–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, D.; Gao, Y.; Chu, Q.; Cui, J.; Xu, T. NOD1 is the innate immune receptor for iE-DAP and can activate NF-κB pathway in teleost fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 76, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.H.; Reimer, T.; Kim, Y.-G.; Nuñez, G. NOD-like receptors (NLRs): Bona fide intracellular microbial sensors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, S.R.; Blossom, D. NLRs, inflammasomes, and viral infection. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Yang, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-G.; Fujimoto, Y.; Nuñez, G.; Fukase, K.; Inohara, N. Differential Release and Distribution of Nod1 and Nod2 Immunostimulatory Molecules among Bacterial Species and Environments. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29054–29063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanneganti, T.D.; Lamkanfi, M.; Núñez, G. Intracellular NOD-like Receptors in Host Defense and Disease. Immunity 2007, 27, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, F.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, X.; Yu, R.-Q.; Wu, Y. Tissue distribution of organic contaminants in stranded pregnant sperm whale (Physeter microcephalus) from the Huizhou coast of the South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 144, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wu, M.; Mou, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Ding, L.; Luo, J. Comparative transcriptomics provides novel insights into the mechanisms of selenium tolerance in the hyperaccumulator plant Cardamine hupingshanensis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, W. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 3, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talón, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevillon, E.; Silventoinen, V.; Pillai, S.; Harte, N.; Mulder, N.; Apweiler, R.; Lopez, R. InterProScan: Protein domains identifier. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W116–W120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ciclitira, P.; Messing, J. PacBio sequencing of gene families—A case study with wheat gluten genes. Gene 2014, 533, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponting, C.P.; Schultz, J.; Milpetz, F.; Bork, P. SMART: Identification and annotation of domains from signalling and extracellular protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inohara, N.; Koseki, T.; Del, P.L.; Hu, Y.; Yee, C.; Chen, S.; Carrio, R.; Merino, J.; Liu, D.; Ni, J.; et al. Nod1, an Apaf-1-like activator of caspase-9 and nuclear factor-kappaB. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 14560–14567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, Y.; Inohara, N.; Benito, A.; Chen, F.F.; Yamaoka, S.; Núñez, G. Nod2, a Nod1/Apaf-1 Family Member That Is Restricted to Monocytes and Activates NF-κB. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 4812–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guang, Y.; Ran, T.; ShiXia, X.U.; WenHua, R. Molecular adaptation mechanism of secondary aquatic life in cetaceans. Sci. China Ser. C 2019, 49, 380–391. [Google Scholar]
- Matejuk, A. Skin Immunity. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2018, 66, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, G.K.; Grayson, S.; Brown, B.E.; Elias, P.M. Lipokeratinocytes of the epidermis of a cetacean (Phocena phocena). Cell Tissue Res. 1986, 246, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Montie, E.W.; Fair, P.A.; Bossart, G.D.; Mitchum, G.B.; Houde, M.; Muir, D.C.G.; Letcher, R.J.; McFee, W.E.; Starczak, V.R.; Stegeman, J.J.; et al. Cytochrome P4501A1 expression, polychlorinated biphenyls and hydroxylated metabolites, and adipocyte size of bottlenose dolphins from the Southeast United States. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 86, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegers, U.; Meyer, W. A preliminary approach to epidermal antimicrobial defense in the Delphinidae. Mar. Biol. 2004, 144, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theissinger, K.; Falckenhayn, C.; Blande, D.; Toljamo, A.; Gutekunst, J.; Makkonen, J.; Jussila, J.; Lyko, F.; Schrimpf, A.; Schulz, R.; et al. De Novo assembly and annotation of the freshwater crayfish Astacus astacus transcriptome. Mar. Genom. 2016, 28, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.; Watanabe, L.; Vianez, J.; Nunes, M.; Cardoso, J.; Lima, C.; Schneider, H.; Sampaio, I. Comparative analysis of the transcriptome of the Amazonian fish species Colossoma macropomum (tambaqui) and hybrid tambacu by next generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scannapieco, A.C.; Conte, C.A.; Rivarola, M.; Wulff, J.P.; Muntaabski, I.; Ribone, A.; Milla, F.; Cladera, J.L.; Lanzavecchia, S.B. Transcriptome analysis of Anastrepha fraterculus sp. 1 males, females, and embryos: Insights into development, courtship, and reproduction. BMC Genet. 2020, 21, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Nie, X.; Liu, Q.; Xie, F.; Shang, D. Transcriptome Analysis and Identification of Genes Related to Immune Function in Skin of the Chinese Brown Frog. Zool. Sci. 2009, 26, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueiro, M.C.; Bagnato, E.; Palacios, M.G. Parasite infection and immune and health-state in wild fish exposed to marine pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lv, Z.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, X.; Shao, Y.; Chang, Y. Transcriptome profiling reveals key roles of phagosome and NOD-like receptor pathway in spotting diseased Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.R. Structure of fish Toll-like receptors (TLR) and NOD-like receptors (NLR). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 1602–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 1, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botos, I.; Segal, D.M.; Davies, D.R. The Structural Biology of Toll-like Receptors. Structure 2011, 19, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, G.; Veronica, S.; Peter, D.E. Human and chicken TLR pathways: Manual curation and computer-based orthology analysis. Mamm. Genome 2011, 22, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, W.; Zhou, K.; Yang, G. Adaptive evolution and functional constraint at TLR4 during the secondary aquatic adaptation and diversification of cetaceans. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yu, M.; Tong, S.; Jia, K.; Liu, R.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Ning, Z. Tissue-specific expression of the NOD-like receptor protein 3 in BALB/c mice. J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 15, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.V.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Kucuktas, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Sha, Z.; Terhune, J.; Peatman, E.; Liu, Z. Pathogen recognition receptors in channel catfish: I. Identification, phylogeny and expression of NOD-like receptors. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 37, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Kinio, A.; Saleh, M. Function of NOD-like receptors in immunity and disease. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2010, 11, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, G.; Zhuang, W.; Wang, T.; Lian, G.; Luo, L.; Ye, C.; Wang, H.; Xie, L. Transcriptomic analysis identifies Toll-like and Nod-like pathways and necroptosis in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 11409–11421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, R.G.; Milutinovic, S.; Reed, J.C. Roles of NOD1 (NLRC1) and NOD2 (NLRC2) in innate immunity and inflammatory diseases. Biosci. Rep. 2012, 32, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbah, A.; Chang, T.H.; Harnack, R.; Frohlich, V.; Tominaga, K.; Dube, P.H.; Xiang, Y.; Bose, S. Activation of innate immune antiviral responses by Nod2. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupfer, C.; Thomas, P.G.; Kanneganti, T.-D. Nucleotide Oligomerization and Binding Domain 2-Dependent Dendritic Cell Activation Is Necessary for Innate Immunity and Optimal CD8+ T Cell Responses to Influenza A Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 8946–8955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedoszytko, B.; Sokołowska-Wojdyło, M.; Ruckemann-Dziurdzińska, K.; Roszkiewicz, J.; Nowicki, R.J. Chemokines and cytokines network in the pathogenesis of the inflammatory skin diseases: Atopic dermatitis, psoriasis and skin mastocytosis. Postȩpy Dermatol. Alergol. 2014, 2, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.V.; Ni, J.; Dixit, V.M. RIP2 is a Novel NF-κB-activating and Cell Death-inducing Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 16968–16975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Inohara, N.; Hernandez, L.D.; Galán, J.E.; Núñez, G.; Janeway, C.A.; Medzhitov, R.; Flavell, R.A. RICK/Rip2/CARDIAK mediates signalling for receptors of the innate and adaptive immune systems. Nature 2002, 416, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inohara, N.; Koseki, T.; Lin, J.; Del Peso, L.; Lucas, P.C.; Chen, F.F.; Ogura, Y.; Núñez, G. An Induced Proximity Model for NF-κB Activation in the Nod1/RICK and RIP Signaling Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 27823–27831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strober, W.; Murray, P.J.; Kitani, A.; Watanabe, T. Signalling pathways and molecular interactions of NOD1 and NOD2. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-G.; McDonald, C.; Kanneganti, T.-D.; Hasegawa, M.; Body-Malapel, M.; Inohara, N.; Núñez, G. RICK/RIP2 Mediates Innate Immune Responses Induced through Nod1 and Nod2 but Not TLRs. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2380–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nembrini, C.; Kisielow, J.; Shamshiev, A.T.; Tortola, L.; Coyle, A.J.; Kopf, M.; Marsland, B.J. The Kinase Activity of Rip2 Determines Its Stability and Consequently Nod1- and Nod2-mediated Immune Responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19183–19188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windheim, M.; Lang, C.; Peggie, M.; Plater, L.A.; Cohen, P. Molecular mechanisms involved in the regulation of cytokine production by muramyl dipeptide. Biochem. J. 2007, 404, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Ghosh, S. NF-κB, An Evolutionarily Conserved Mediator of Immune and Inflammatory Responses. In Mechanisms of Lymphocyte Activation and Immune Regulation X; Gupta, S., Paul, W.E., Steinman, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 560, pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, G.; Haas, D.A.; Farrell, P.J.; Pichlmair, A.; Bowie, A.G. Poxvirus Protein MC132 from Molluscum Contagiosum Virus Inhibits NF-κB Activation by Targeting p65 for Degradation. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8406–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasgow, J.N.; Wood, T.; Perez-Polo, J.R. Identification and characterization of nuclear factor kappaB binding sites in the murine bcl-x promoter. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, M.B.; Schreck, R.; Baeuerle, P.A. NF-kappa B contacts DNA by a heterodimer of the p50 and p65 subunit. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beinke, S. Structure-Function Analysis of NF-κB1 p105. Ph.D. Thesis, University College London, London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, N.D. The Rel/NF-kappa B family: Friend and foe. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elewaut, D.; Di Donato, J.A.; Kim, J.M.; Truong, F.; Eckmann, L.; Kagnoff, M.F. NF-κB is a central regulator of the intestinal epithelial cell innate immune response induced by infection with enteroinvasive bacteria. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Schattenberg, J.M.; Czaja, M.J. TNF/TNF Receptors; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 161–177. [Google Scholar]
- Inohara, N.; Núñez, G. NODs: Intracellular proteins involved in inflammation and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | Read of Insert | Total Transcripts | Mean Length (bp) | N50 (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 1,056,247 | 96,350 | 1705 | 1996 |
| Sequence Size (bp) | UniGene Number |
|---|---|
| 200–500 | 16,252 |
| 500–1000 | 7251 |
| 1000–2000 | 6444 |
| 2000–3000 | 3192 |
| ≥3000 | 2843 |
| Total | 35,982 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Aierken, R.; Kang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Q.; Fan, Z.; Zhen, Y.; Zhao, L. Integrated Full-Length Transcriptome and RNA-Seq to Identify Immune System Genes from the Skin of Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus). Genes 2021, 12, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020233
Wang D, Li Y, Aierken R, Kang Q, Wang X, Zeng Q, Fan Z, Zhen Y, Zhao L. Integrated Full-Length Transcriptome and RNA-Seq to Identify Immune System Genes from the Skin of Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus). Genes. 2021; 12(2):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020233
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Daling, Ying Li, Reyilamu Aierken, Qi Kang, Xianyan Wang, Qianhui Zeng, Zhichang Fan, Yu Zhen, and Liyuan Zhao. 2021. "Integrated Full-Length Transcriptome and RNA-Seq to Identify Immune System Genes from the Skin of Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus)" Genes 12, no. 2: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020233
APA StyleWang, D., Li, Y., Aierken, R., Kang, Q., Wang, X., Zeng, Q., Fan, Z., Zhen, Y., & Zhao, L. (2021). Integrated Full-Length Transcriptome and RNA-Seq to Identify Immune System Genes from the Skin of Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus). Genes, 12(2), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020233






