Susceptibility of Field-Collected Nyssorhynchus darlingi to Plasmodium spp. in Western Amazonian Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Adult Mosquito Collection
2.2. Mosquito Processing and NextRAD
2.3. Variant Calling
2.4. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS)
2.5. Genetic Structure Testing
2.6. Protein Sequence Comparisons
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, M.U.; Castro, M.C. Challenges for Malaria Elimination in Brazil. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SVS Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde: Boletins Epidemiológicos. 2017. Available online: http://portalms.saude.gov.br/saude-de-a-z/malaria (accessed on 20 June 2021).
- Prussing, C.; Emerson, K.J.; Bickersmith, S.A.; Sallum, M.A.M.; Conn, J.E. Minimal Genetic Differentiation of the Malaria Vector Nyssorhynchus darlingi Associated with Forest Cover Level in Amazonian Brazil. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Technical Document. Malaria Country Profile: Brazil. 2018. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/malaria/country-profiles/2018/profile_bra_en.pdf (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Barbosa, L.M.C.; Souto, R.N.P.; Dos Anjos Ferreira, R.M.; Scarpassa, V.M. Behavioral Patterns, Parity Rate and Natural Infection Analysis in Anopheline Species Involved in the Transmission of Malaria in the Northeastern Brazilian Amazon Region. Acta Trop. 2016, 164, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, M.; Saavedra, M.P.; Bickersmith, S.A.; Prussing, C.; Michalski, A.; Tong Rios, C.; Vinetz, J.M.; Conn, J.E. Intensive Trapping of Blood-Fed Anopheles darlingi in Amazonian Peru Reveals Unexpectedly High Proportions of Avian Blood-Meals. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Lerma, J.; Solarte, Y.A.; Giraldo-Calderón, G.I.; Quiñones, M.L.; Ruiz-López, F.; Wilkerson, R.C.; González, R. Malaria Vector Species in Colombia: A Review. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2011, 106 (Suppl. 1), 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Díaz, N.; Conn, J.E.; Correa, M.M. Behavior and Population Structure of Anopheles darlingi in Colombia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 39, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prussing, C.; Moreno, M.; Saavedra, M.P.; Bickersmith, S.A.; Gamboa, D.; Alava, F.; Schlichting, C.D.; Emerson, K.J.; Vinetz, J.M.; Conn, J.E. Decreasing Proportion of Anopheles darlingi Biting Outdoors between Long-Lasting Insecticidal Net Distributions in Peri-Iquitos, Amazonian Peru. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sallum, M.A.M.; Conn, J.E.; Bergo, E.S.; Laporta, G.Z.; Chaves, L.S.M.; Bickersmith, S.A.; de Oliveira, T.M.P.; Figueira, E.A.G.; Moresco, G.; Olívêr, L.; et al. Vector Competence, Vectorial Capacity of Nyssorhynchus darlingi and the Basic Reproduction Number of Plasmodium Vivax in Agricultural Settlements in the Amazonian Region of Brazil. Malar. J. 2019, 18, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- della Torre, A.; Fanello, C.; Akogbeto, M.; Dossou-yovo, J.; Favia, G.; Petrarca, V.; Coluzzi, M. Molecular Evidence of Incipient Speciation within Anopheles gambiae S.s. in West Africa. Insect Mol. Biol. 2001, 10, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.; Conn, J.E.; Alonso, D.P.; Vinetz, J.M.; Emerson, K.J.; Ribolla, P.E.M. Microgeographical Structure in the Major Neotropical Malaria Vector Anopheles darlingi Using Microsatellites and SNP Markers. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morlais, I.; Ponçon, N.; Simard, F.; Cohuet, A.; Fontenille, D. Intraspecific Nucleotide Variation in Anopheles gambiae: New Insights into the Biology of Malaria Vectors. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 71, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, R.A.; Subramanian, G.M.; Halpern, A.; Sutton, G.G.; Charlab, R.; Nusskern, D.R.; Wincker, P.; Clark, A.G.; Ribeiro, J.M.C.; Wides, R.; et al. The Genome Sequence of the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Science 2002, 298, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christophides, G.K.; Zdobnov, E.; Barillas-Mury, C.; Birney, E.; Blandin, S.; Blass, C.; Brey, P.T.; Collins, F.H.; Danielli, A.; Dimopoulos, G.; et al. Immunity-Related Genes and Gene Families in Anopheles gambiae. Science 2002, 298, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riehle, M.M.; Markianos, K.; Niaré, O.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Touré, A.M.; Podiougou, B.; Oduol, F.; Diawara, S.; Diallo, M.; et al. Natural Malaria Infection in Anopheles gambiae Is Regulated by a Single Genomic Control Region. Science 2006, 312, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos, M.; Alonso, D.P.; Conn, J.E.; Vinetz, J.M.; Emerson, K.J.; Ribolla, P.E.M. Genetic Diversity of Nyssorhynchus (Anopheles) darlingi Related to Biting Behavior in Western Amazon. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altamiranda-Saavedra, M.; Conn, J.E.; Correa, M.M. Genetic Structure and Phenotypic Variation of Anopheles darlingi in Northwest Colombia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 56, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinotti, O.; Cerqueira, G.C.; de Almeida, L.G.P.; Ferro, M.I.T.; da Loreto, E.L.S.; Zaha, A.; Teixeira, S.M.R.; Wespiser, A.R.; Almeida, E.; Silva, A.; et al. The Genome of Anopheles darlingi, the Main Neotropical Malaria Vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 7387–7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickersmith, S.A.; Lainhart, W.; Moreno, M.; Chu, V.M.; Vinetz, J.M.; Conn, J.E. A Sensitive, Specific and Reproducible Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Method for Detection of Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum Infection in Field-Collected Anophelines. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laporta, G.Z.; Burattini, M.N.; Levy, D.; Fukuya, L.A.; de Oliveira, T.M.P.; Maselli, L.M.F.; Conn, J.E.; Massad, E.; Bydlowski, S.P.; Sallum, M.A.M. Plasmodium falciparum in the Southeastern Atlantic Forest: A Challenge to the Bromeliad-Malaria Paradigm? Malar. J. 2015, 14, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giraldo-Calderón, G.I.; Emrich, S.J.; MacCallum, R.M.; Maslen, G.; Dialynas, E.; Topalis, P.; Ho, N.; Gesing, S.; Madey, G.; VectorBase Consortium; et al. VectorBase: An Updated Bioinformatics Resource for Invertebrate Vectors and Other Organisms Related with Human Diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D707–D713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H. A Statistical Framework for SNP Calling, Mutation Discovery, Association Mapping and Population Genetical Parameter Estimation from Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The Variant Call Format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- R Development Core Team. The R Reference Manual: Base Package; Network Theory Limited: Surrey, UK, 2003; ISBN 9780954612009. [Google Scholar]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.G. Cytochromes P450 and Insecticide Resistance. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 29, 757–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranson, H.; Claudianos, C.; Ortelli, F.; Abgrall, C.; Hemingway, J.; Sharakhova, M.V.; Unger, M.F.; Collins, F.H.; Feyereisen, R. Evolution of Supergene Families Associated with Insecticide Resistance. Science 2002, 298, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Li, T.; Feng, X.; Li, M.; Liu, S.; Liu, N. Multiple Cytochrome P450 Genes: Conferring High Levels of Permethrin Resistance in Mosquitoes, Culex quinquefasciatus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchouakui, M.; Mugenzi, L.M.J.; Wondji, M.J.; Tchoupo, M.; Njiokou, F.; Wondji, C.S. Combined over-Expression of Two Cytochrome P450 Genes Exacerbates the Fitness Cost of Pyrethroid Resistance in the Major African Malaria Vector Anopheles funestus. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 173, 104772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoh, M.G.; Gaude, T.; Prud’homme, S.M.; Riaz, M.A.; David, J.-P.; Reynaud, S. Molecular Bases of P450-Mediated Resistance to the Neonicotinoid Insecticide Imidacloprid in the Mosquito Aedes aegypti. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 236, 105860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.-P.; Strode, C.; Vontas, J.; Nikou, D.; Vaughan, A.; Pignatelli, P.M.; Louis, C.; Hemingway, J.; Ranson, H. The Anopheles Gambiae Detoxification Chip: A Highly Specific Microarray to Study Metabolic-Based Insecticide Resistance in Malaria Vectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4080–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, P.; Donnelly, M.J.; Ranson, H. Transcription Profiling of a Recently Colonised Pyrethroid Resistant Anopheles gambiae Strain from Ghana. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikou, D.; Ranson, H.; Hemingway, J. An Adult-Specific CYP6 P450 Gene Is Overexpressed in a Pyrethroid-Resistant Strain of the Malaria Vector, Anopheles gambiae. Gene 2003, 318, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, V.A.; Pignatelli, P.; Moore, J.D.; Wagstaff, S.; Ranson, H. The Transcription Factor Maf-S Regulates Metabolic Resistance to Insecticides in the Malaria Vector Anopheles gambiae. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiwat, H.; Bretas, G. Ecology of Anopheles darlingi Root with Respect to Vector Importance: A Review. Parasit. Vectors 2011, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Arakane, Y.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Kramer, K.J.; Ma, E.; Zhu, K.Y. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Chitinase-like Gene Cluster (AgCht5) Possibly Derived from Tandem Duplications in the African Malaria Mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filho, B.P.D.; Lemos, F.J.A.; Secundino, N.F.C.; Páscoa, V.; Pereira, S.T.; Pimenta, P.F.P. Presence of Chitinase and Beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase in the Aedes aegypti. a Chitinolytic System Involving Peritrophic Matrix Formation and Degradation. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zheng, S.; Cheng, X.; Ladd, T.; Lingohr, E.J.; Krell, P.J.; Arif, B.M.; Retnakaran, A.; Feng, Q. A Molt-Associated Chitinase cDNA from the Spruce Budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Arakane, Y.; Beeman, R.W.; Kramer, K.J.; Muthukrishnan, S. Functional Specialization among Insect Chitinase Family Genes Revealed by RNA Interference. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6650–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Arakane, Y.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Kramer, K.J.; Ma, E.; Zhu, K.Y. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Chitinase and Chitinase-Like Genes in the African Malaria Mosquito (Anopheles gambiae). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dinglasan, R.R.; Devenport, M.; Florens, L.; Johnson, J.R.; McHugh, C.A.; Donnelly-Doman, M.; Carucci, D.J.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Jacobs-Lorena, M. The Anopheles gambiae Adult Midgut Peritrophic Matrix Proteome. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patra, K.P.; Kaur, H.; Kolli, S.K.; Wozniak, J.M.; Prieto, J.H.; Yates, J.R.; Gonzalez, D.J.; Janse, C.J.; Vinetz, J.M. A Hetero-Multimeric Chitinase-Containing Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium gallinaceum Ookinete-Secreted Protein Complex Involved in Mosquito Midgut Invasion. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 615343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanath, V.K.; Gore, S.T.; Valiyaparambil, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Lakshminarasimhan, A. Plasmodium Chitinases: Revisiting a Target of Transmission-Blockade against Malaria. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Cabib, E.; Miller, L.H. Malaria Parasite Chitinase and Penetration of the Mosquito Peritrophic Membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2807–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, C.; Lambrechts, L.; Rousset, F.; Abate, L.; Nsango, S.E.; Fontenille, D.; Morlais, I.; Cohuet, A. Polymorphisms in Anopheles gambiae immune genes associated with natural resistance to Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 16, e1001112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redmond, S.N.; Eiglmeier, K.; Mitri, C.; Markianos, K.; Guelbeogo, W.M.; Gneme, A.; Isaacs, A.T.; Coulibaly, B.; Brito-Fravallo, E.; Maslen, G.; et al. Association mapping by pooled sequencing identifies TOLL 11 as a protective factor against Plasmodium falciparum in Anopheles gambiae. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riehle, M.M.; Bukhari, T.; Gneme, A.; Guelbeogo, W.M.; Coulibaly, B.; Fofana, A.; Pain, A.; Bischoff, E.; Renaud, F.; Beavogui, A.H.; et al. The Anopheles gambiae 2La chromosome inversion is associated with susceptibility to Plasmodium falciparum in Africa. elife 2017, 23, e25813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
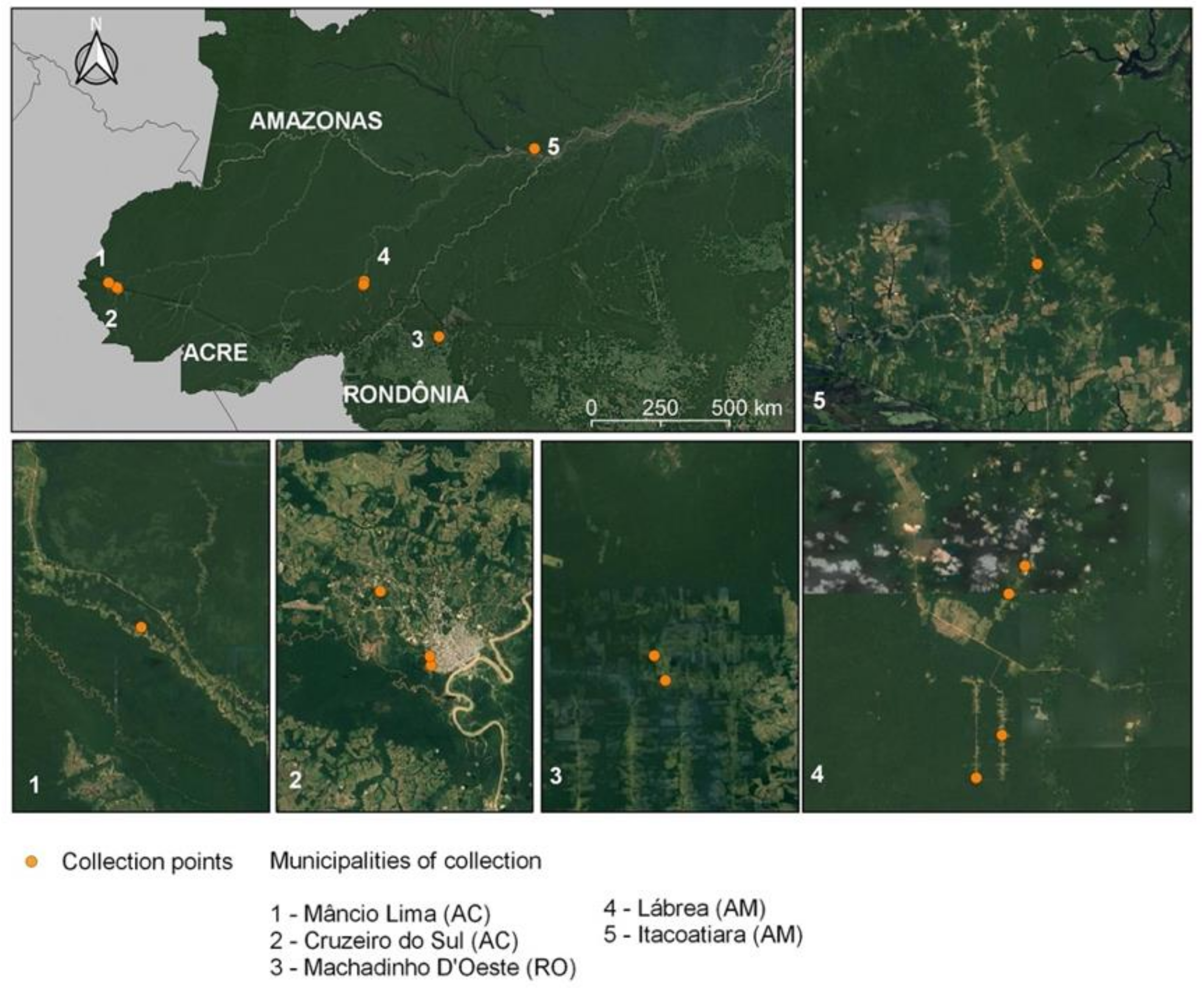
| Municipality | State | P. vivax | P. falciparum | Negative | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cruzeiro do Sul | Acre | 17 | - | 17 | 34 |
| Mâncio Lima | Acre | - | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Lábrea | Amazonas | 3 | 9 | 6 | 18 |
| Machadinho D’Oeste | Rondônia | 5 | - | 4 | 9 |
| Itacoatiara | Amazonas | 1 | - | 1 | 2 |
| Total | 26 | 26 | 10 | 29 | 65 |
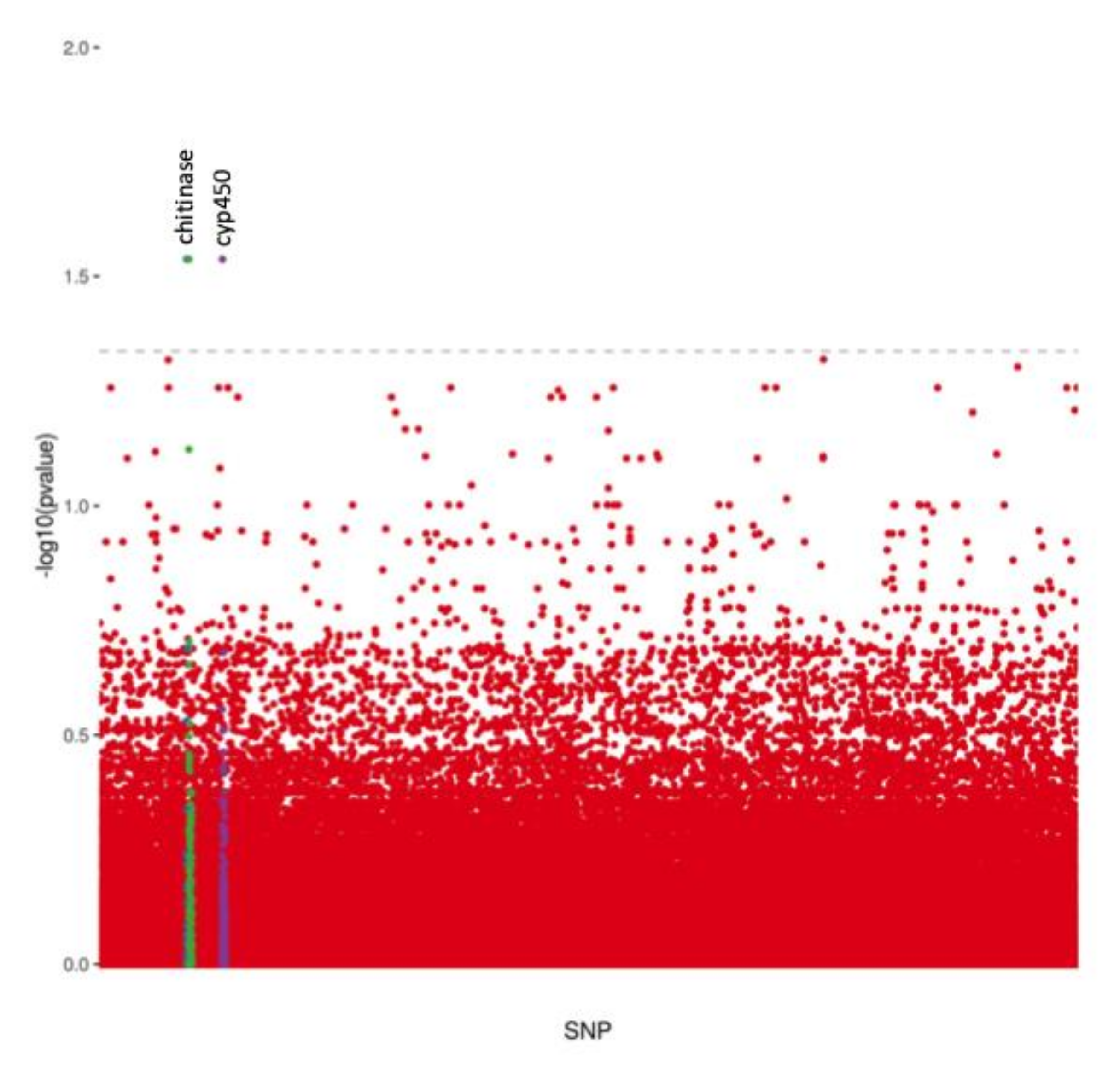
| Scaffold | Position | Ref | Alt | Adjacent Genes | Distance to Adjacent Gene (bp) | pFDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADMH02000716 | 10,949 | G | C | cyp450 | 56 | 0.029 |
| ADMH02002098 | 10,391 | T | A | Chitinase | 71,655 | 0.029 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alonso, D.P.; Alvarez, M.V.N.; Ribolla, P.E.M.; Conn, J.E.; de Oliveira, T.M.P.; Sallum, M.A.M. Susceptibility of Field-Collected Nyssorhynchus darlingi to Plasmodium spp. in Western Amazonian Brazil. Genes 2021, 12, 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111693
Alonso DP, Alvarez MVN, Ribolla PEM, Conn JE, de Oliveira TMP, Sallum MAM. Susceptibility of Field-Collected Nyssorhynchus darlingi to Plasmodium spp. in Western Amazonian Brazil. Genes. 2021; 12(11):1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111693
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlonso, Diego Peres, Marcus Vinicius Niz Alvarez, Paulo Eduardo Martins Ribolla, Jan E. Conn, Tatiane Marques Porangaba de Oliveira, and Maria Anice Mureb Sallum. 2021. "Susceptibility of Field-Collected Nyssorhynchus darlingi to Plasmodium spp. in Western Amazonian Brazil" Genes 12, no. 11: 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111693
APA StyleAlonso, D. P., Alvarez, M. V. N., Ribolla, P. E. M., Conn, J. E., de Oliveira, T. M. P., & Sallum, M. A. M. (2021). Susceptibility of Field-Collected Nyssorhynchus darlingi to Plasmodium spp. in Western Amazonian Brazil. Genes, 12(11), 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111693









