Expression Analysis and Serodiagnostic Potential of Microneme Proteins 1 and 3 in Eimeria stiedai
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parasites and Animals
2.2. Serum
2.3. Bioinformatics Analyses, Cloning and Sequencing of EsMIC1 and EsMIC3
2.4. mRNA Expression Analyses of EsMIC1 and EsMIC3 at Different Developmental Stages of E. stiedai
2.5. Expression and Purification of rEsMIC1 and rEsMIC3
2.6. Western Blotting Analyses
2.7. Development of Indirect ELISAs
2.8. Sensitivity and Specificity of Indirect ELISAs
2.9. Early Diagnostic Potential Evaluation of Indirect ELISAs
2.10. Statistical Analyses
2.11. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
3. Results
3.1. Cloning, Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analyses of EsMIC1 and EsMIC3
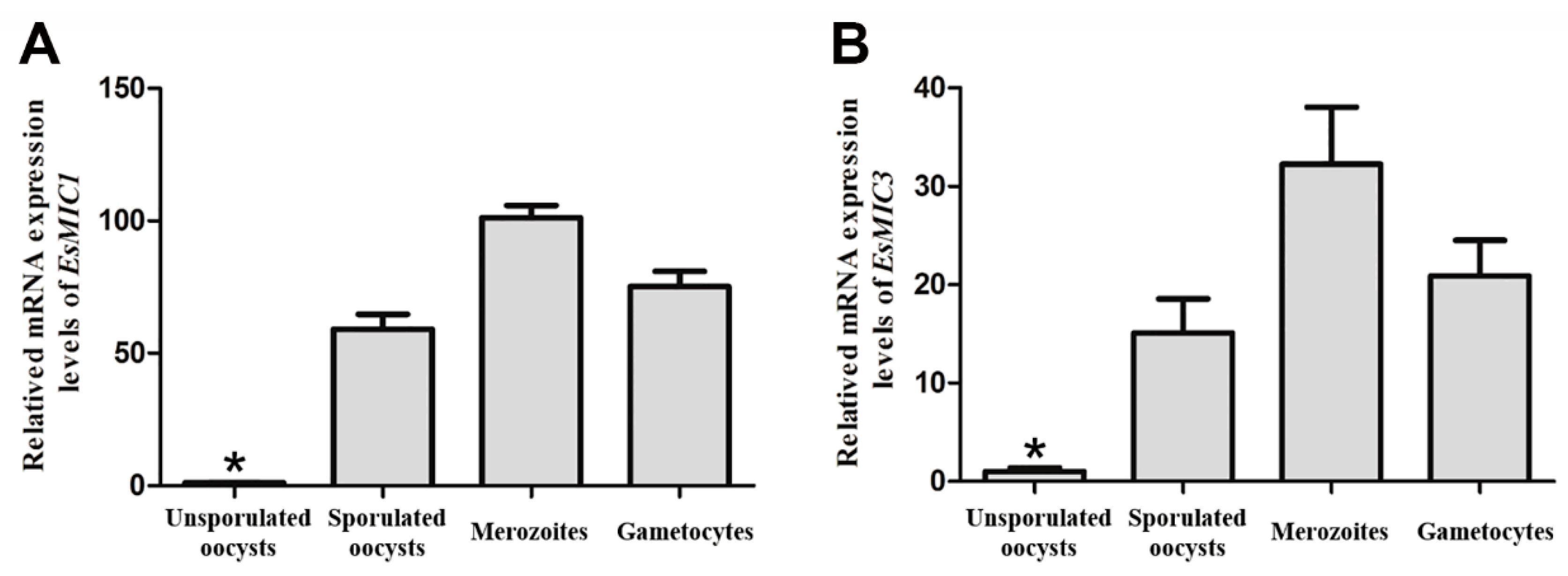
3.2. mRNA Expression of EsMIC1 and EsMIC3 at Different Developmental Stages of E. stiedai
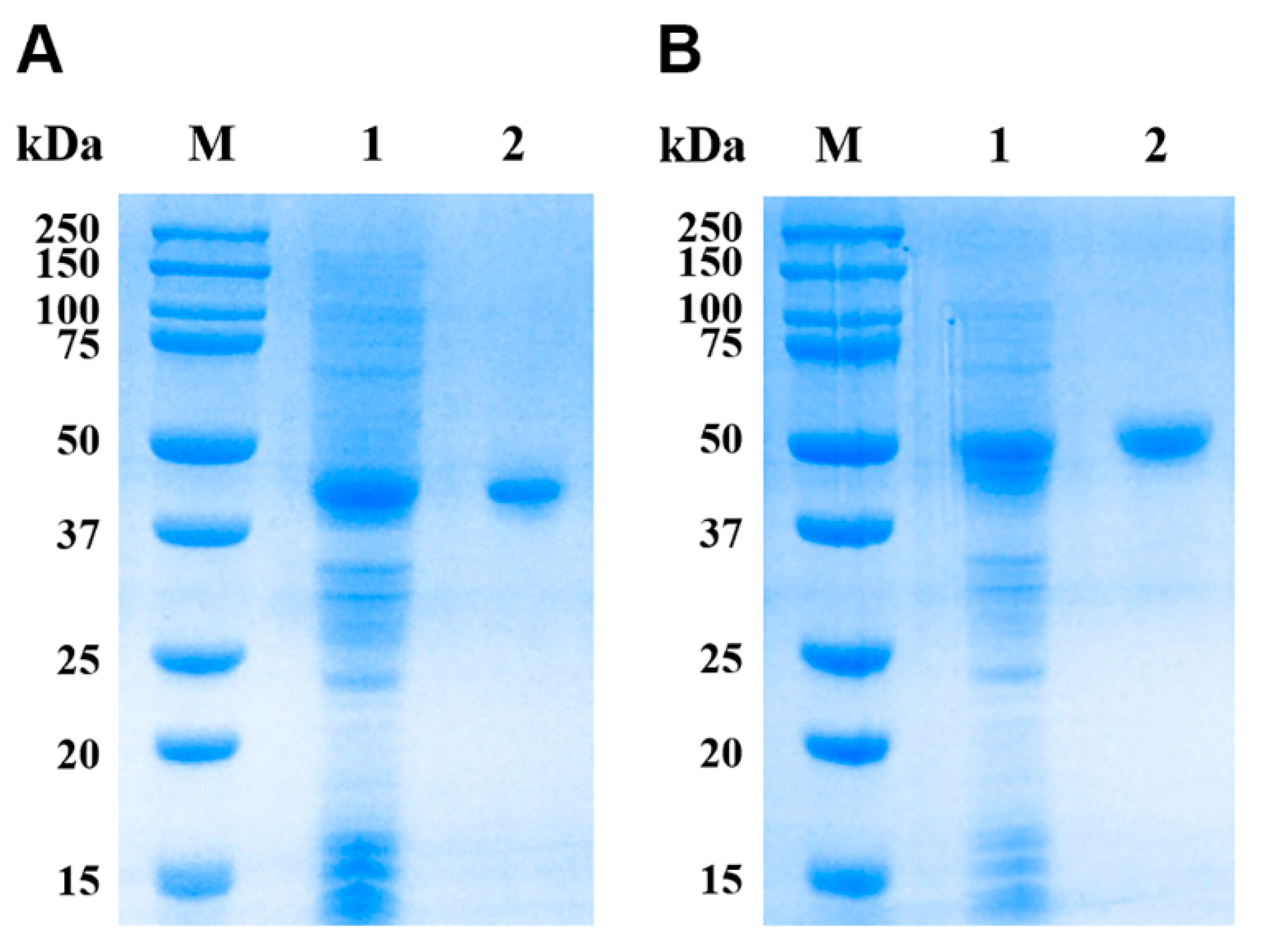
3.3. Expression and Purification of rEsMIC1 and rEsMIC3
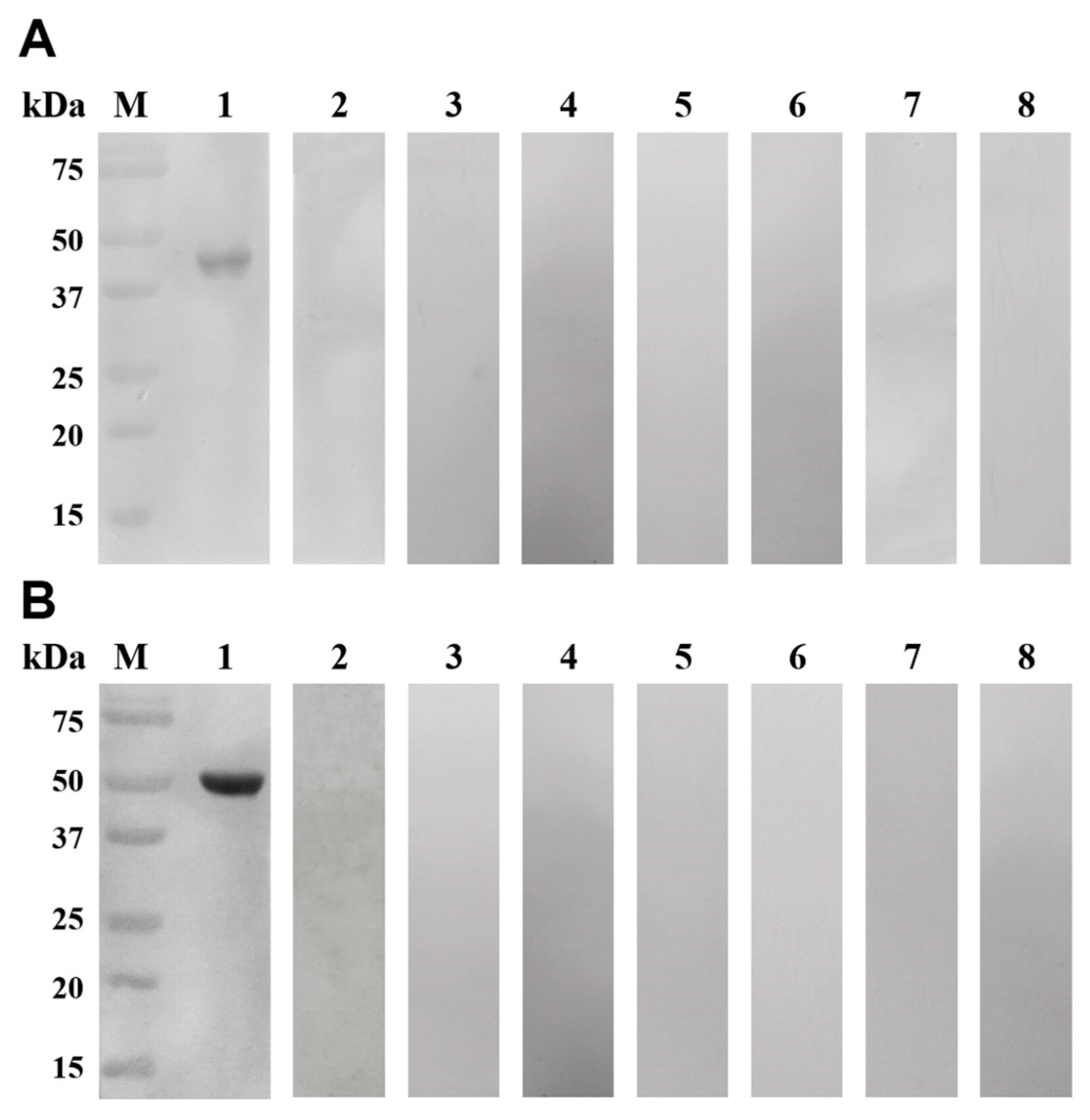
3.4. Western Blotting Analyses
3.5. Establishment of Indirect ELISA
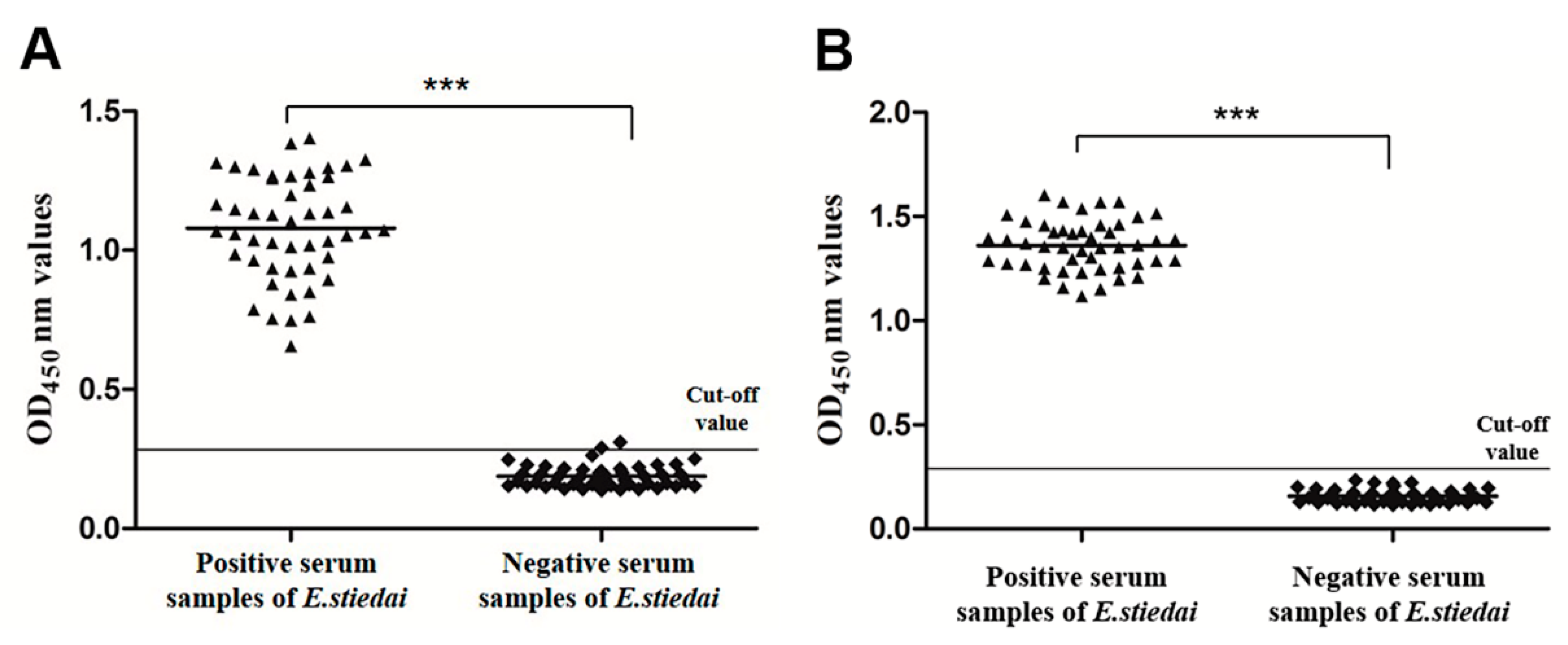
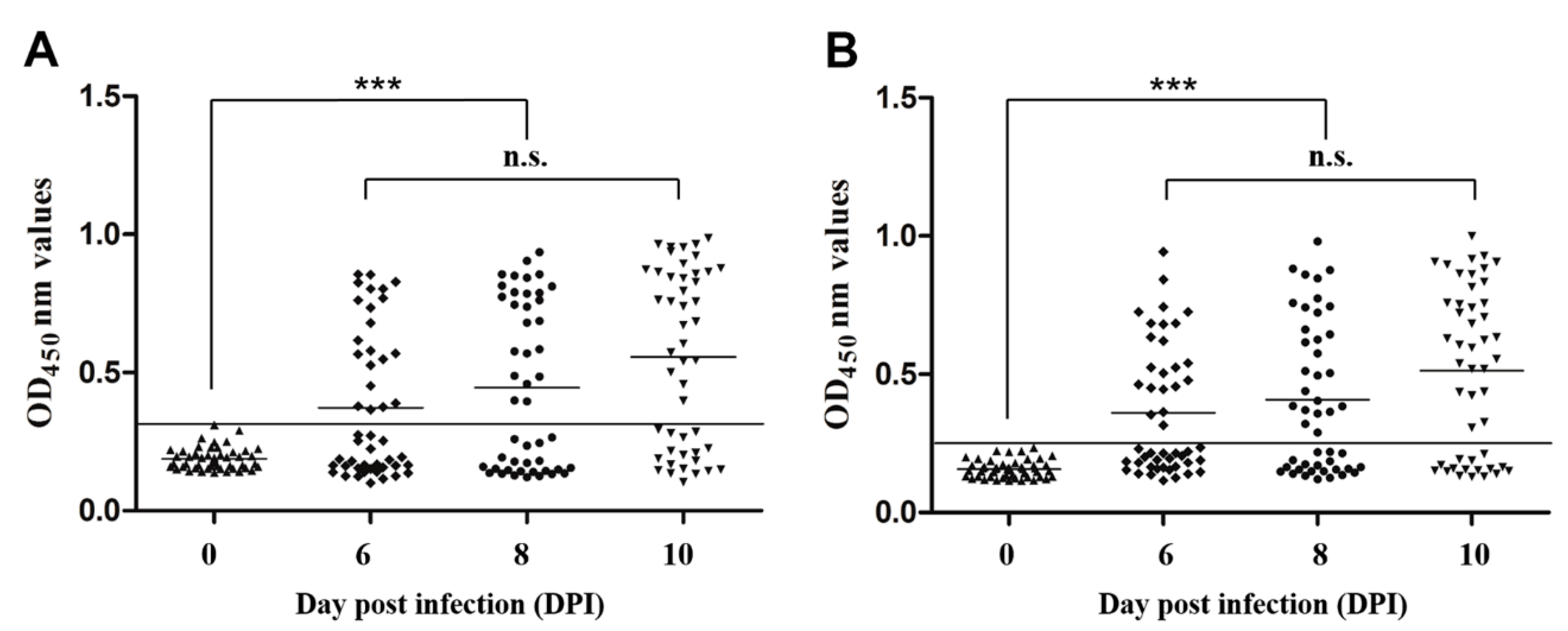
3.6. Sensitivity and Specificity of Indirect ELISA
3.7. Early Diagnostic Potential of Indirect ELISAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mäkitaipale, J.; Karvinen, I.; Virtala, A.M.K.; Näreaho, A. Prevalence of intestinal parasites and risk factor analysis for Eimeria infections in Finnish pet rabbits. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2017, 9, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Pakandl, M. Coccidia of rabbit: A review. Folia Parasitol. 2009, 56, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, F.; Yin, G.; Liu, X.; Suo, X.; Qin, Y. Large-scale survey of the prevalence of Eimeria infections in domestic rabbits in China. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asherson, G.L.; Rose, M.E. Autoantibody production in rabbits: III. The effect of infection with Eimeria stiedae and its relation to natural antibody. Immunology 1963, 6, 207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singla, L.D.; Juyal, P.D.; Sandhu, B.S. Pathology and therapy in naturally Eimeria stiedae-infected rabbits. J. Protozool. Res. 2000, 10, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, F.L.D.C.; Yamamoto, B.L.; Freitas, W.L.D.C.; Fagliari, J.J.; Almeida, K.D.S.; Machado, R.Z.; Machado, C.R. Systemic inflammatory response indicators in rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) experimentally infected with sporulated oocysts of Eimeria stiedai (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae). Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2011, 20, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jing, J.; Liu, C.; Zhu, S.X.; Jiang, Y.M.; Wu, L.C.; Song, H.Y.; Shao, Y.X. Pathological and ultrastructural observations and liver function analysis of Eimeria stiedai-infected rabbits. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 223, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyner, L.P.; Catchpole, J.; Berrett, S. Eimeria stiedai in rabbits: The demonstration of responses to chemotherapy. Res. Vet. Sci. 1983, 34, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, C.; Wu, B.; Li, J.; Gong, P.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Cai, X.; Zhang, X. Complete genome sequence and evolution analysis of Eimeria stiedai RNA virus 1, a novel member of the family Totiviridae. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 3571–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taee, M.N.K.; Al-Zubaidi, M.T.S. Protection against Eimeria stiedae in rabbits by using sonicated sporulated oocyst vaccine. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2017, 5, 579–585. [Google Scholar]
- Barriga, O.O.; Arnoni, J.V. Pathophysiology of hepatic coccidiosis in rabbits. Vet. Parasitol. 1981, 8, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mathal, E.M. Hepatic Coccidiosis of the Domestic Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus domesticus L.) in Saudi Arabia. World J. Zool. 2008, 3, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, U.C.; Fraga, J.S.; Licois, D.; Pakandl, M.; Gruber, A. Development of molecular assays for the identification of the 11 Eimeria species of the domestic rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 176, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivajothi, S.; Reddy, B.S.; Rayulu, V.C. Study on impression smears of hepatic coccidiosis in rabbits. J. Parasit. Dis. 2016, 40, 906–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, D.; Dubremetz, J.F.; Lebrun, M. Microneme proteins: Structural and functional requirements to promote adhesion and invasion by the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healer, J.; Crawford, S.; Ralph, S.; McFadden, G.; Cowman, A.F. Independent translocation of two micronemal proteins in developing Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 5751–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, N.; Naguleswaran, A.; Cannas, A.; Vonlaufen, N.; Bienz, M.; Björkman, C.; Bohne, W.; Hemphill, A. Identification of a Neospora caninum microneme protein (NcMIC1) which interacts with sulfated host cell surface glycosaminoglycans. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3187–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.; Shirley, M.; Tomley, F. Mapping and expression of microneme genes in Eimeria tenella. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, V.B.; Tomley, F.M. Microneme proteins in Apicomplexans. Subcell. Biochem. 2008, 47, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, H.; Tolia, N.H. Getting in: The structural biology of malaria invasion. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomley, F.M.; Soldati, D.S. Mix and match modules: Structure and function of microneme proteins in apicomplexan parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2001, 17, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Tao, G.; Bao, G.; Suo, J.; Hao, L.; Fu, Y.; Suo, X. Stable transfection of Eimeria intestinalis and investigation of its life cycle, reproduction and immunogenicity. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ORF Finder. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/ (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- SignalP 5.0 Server. Available online: http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/Services/SignalP/ (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- TMHMM Server v. 2.0. Available online: http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/ (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- ExPASy ProtParam Tool. Available online: https://web.expasy.org/protparam/ (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- Crowther, J.R. The ELISA Guidebook; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 149. [Google Scholar]
- ARRIVE Guidelines Home Page. Available online: http://www.nc3rs.org.uk/arrive-guidelines (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- Dowse, T.; Soldati, D. Host cell invasion by the apicomplexans: The significance of microneme protein proteolysis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Cui, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, S.; Huang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhao, H.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Han, H.; et al. Molecular characterization and protective efficacy of the microneme 2 protein from Eimeria tenella. Parasite 2018, 25, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Simpson, P.; Bumstead, J.; Tomley, F.; Matthews, S. Complete NMR assignments for the second microneme adhesive repeat (MAR) domain from Eimeria tenella microneme protein EtMIC3. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2009, 3, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holec, L.; Gąsior, A.; Brillowska-Dąbrowska, A.; Kur, J. Toxoplasma gondii: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using different fragments of recombinant microneme protein 1 (MIC1) for detection of immunoglobulin G antibodies. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 119, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, M.H.; Liu, B.; Henry, M.; Liew, L.; Matthews, S.J.; Carruthers, V.B. Structural basis of Toxoplasma gondii MIC2-associated protein interaction with MIC2. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1432–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, F.C.; Zhou, C.X.; Zhu, X.Q. Research advances in interactions related to Toxoplasma gondii microneme proteins. Exp. Parasitol. 2017, 176, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Oh, S.S.; Chishti, A.H. A Presenilin-like protease associated with Plasmodium falciparum micronemes is involved in erythrocyte invasion. Mol. Biochem. Parasit. 2008, 158, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; More, K.R.; Chitnis, C.E. Role of calcineurin and actin dynamics in regulated secretion of microneme proteins in Plasmodium falciparum merozoites during erythrocyte invasion. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Qu, G.; Cao, L.; Li, Q.; Fetterer, R.; Feng, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, G.; Qi, D.; Zhang, X.; et al. Characterization of Neospora caninum microneme protein 10 (NcMIC10) and its potential use as a diagnostic marker for neosporosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 187, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Fu, Y.; Nan, H.; Liu, Q. Identification and characterization of a microneme protein (NcMIC6) in Neospora caninum. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Dalloul, R.A.; Min, W.; Sato, T.; Yasuda, A.; Lillehoj, E.P. In ovo vaccination with the Eimeria tenella EtMIC2 gene induces protective immunity against coccidiosis. Vaccine 2005, 23, 3733–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periz, J.; Gill, A.C.; Hunt, L.; Brown, P.; Tomley, F.M. The microneme proteins EtMIC4 and EtMIC5 of Eimeria tenella form a novel, ultra-high molecular mass protein complex that binds target host cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 16891–16898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, P.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Display of Eimeria tenella EtMic2 protein on the surface of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a potential oral vaccine against chicken coccidiosis. Vaccine 2014, 32, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomley, F.M.; Clarke, L.E.; Kawazoe, U.; Dijkema, R.; Kok, J.J. Sequence of the gene encoding an immunodominant microneme protein of Eimeria tenella. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1991, 49, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Shi, W.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhao, X. Preparation and initial application of monoclonal antibodies that recognize Eimeria tenella microneme proteins 1 and 2. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 4151–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbe, M.; de Venevelles, P.; Girard-Misguich, F.; Bourdieu, C.; Guillaume, A.; Pery, P. Eimeria tenella microneme protein EtMIC3: Identification, localisation and role in host cell infection. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2005, 140, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novaes, J.; Rangel, L.T.L.; Ferro, M.; Abe, R.Y.; Manha, A.P.; de Mello, J.C.; Varuzza, L.; Durham, A.M.; Madeira, A.M.B.; Gruber, A. A comparative transcriptome analysis reveals expression profiles conserved across three Eimeria spp. of domestic fowl and associated with multiple developmental stages. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, N.S.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liao, S.Q.; Wu, C.Y.; Lv, M.N.; Li, J.; Tong, Z.X.; Sun, M.F. Partial protective of chickens against Eimeria tenella challenge with recombinant EtMIC-1 antigen. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Lv, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, F.; Zhao, X. Evaluation of immune protective efficacies of Eimeria tenella EtMic1 polypeptides with different domain recombination displayed on yeast surface. Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 155, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grès, V.; Voza, T.; Chabaud, A.; Landau, I. Coccidiosis of the wild rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in France. Parasite 2003, 10, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shahawi, G.A.; El-Fayomi, H.M.; Abdel-Haleem, H.M. Coccidiosis of domestic rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in Egypt: Light microscopic study. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, G.; Goraya, M.U.; Huang, J.; Suo, X.; Huang, Z.; Liu, X. Survey of coccidial infection of rabbits in Sichuan Province, Southwest China. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-El-Ezz, N.M.T.; Megeed, K.N.A.; Mahdy, O.A.; Hassan, S.E. ELISA assessment in the diagnosis of hepatic coccidiosis in experimentally infected rabbits. Glob. Vet. 2012, 9, 517–523. [Google Scholar]
- Onaga, H.; Saeki, H.; Hoshi, S.; Ueda, S. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serodiagnosis of coccidiosis in chickens: Use of a single serum dilution. Avian Dis. 1986, 30, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, O.; Onaga, H.; Nakamura, T. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with the recombinant merozoite protein as antigen for detection of antibodies to Eimeria necatrix. Avian Dis. 2003, 47, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cere, N.; Humbert, J.F.; Licois, D.; Corvione, M.; Afanassieff, M.; Chanteloup, N. A new approach for the identification and the diagnosis of Eimeria media parasite of the rabbit. Exp. Parasitol. 1996, 82, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Gong, D.; Ma, L.A.; Nie, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, B.; Zhao, J. Evaluation of a recombinant MIC3 based latex agglutination test for the rapid serodiagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in swines. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 158, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | qRT-PCR Primer Sequences | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| EsMIC1 | F: 5′-TGACAGGAATGAGCGACAGTTGC-3′ | 99 |
| R: 5′-CGGCGGCCTCGAGAATGTTG-3′ | ||
| EsMIC3 | F: 5′-CTCGATCACCAGATGCCAAGTCAG-3′ | 141 |
| R: 5′-CACGCCTCCTCGCCATTCAC-3′ | ||
| 18S ribosomal RNA | F: 5′-GGAGTTGACGAAAGGGCACCAC-3′ | 113 |
| R: 5′-GCCATGCACCACCACCCATAG-3′ |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, W.; Shen, N.; Xiao, J.; Tao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Angel, C.; Gu, X.; Xie, Y.; He, R.; Jing, B.; et al. Expression Analysis and Serodiagnostic Potential of Microneme Proteins 1 and 3 in Eimeria stiedai. Genes 2020, 11, 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11070725
Wei W, Shen N, Xiao J, Tao Y, Luo Y, Angel C, Gu X, Xie Y, He R, Jing B, et al. Expression Analysis and Serodiagnostic Potential of Microneme Proteins 1 and 3 in Eimeria stiedai. Genes. 2020; 11(7):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11070725
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Wenrui, Nengxing Shen, Jie Xiao, Yuanyuan Tao, Yuejun Luo, Christiana Angel, Xiaobin Gu, Yue Xie, Ran He, Bo Jing, and et al. 2020. "Expression Analysis and Serodiagnostic Potential of Microneme Proteins 1 and 3 in Eimeria stiedai" Genes 11, no. 7: 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11070725
APA StyleWei, W., Shen, N., Xiao, J., Tao, Y., Luo, Y., Angel, C., Gu, X., Xie, Y., He, R., Jing, B., Peng, X., & Yang, G. (2020). Expression Analysis and Serodiagnostic Potential of Microneme Proteins 1 and 3 in Eimeria stiedai. Genes, 11(7), 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11070725





