Identification, Expression, and Functions of the Somatostatin Gene Family in Spotted Scat (Scatophagus argus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cloning of the Somatostatin Genes of S. argus
2.2. Identification of SSTs from Representative Vertebrate Species
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis and Amino Acid Alignment
2.4. Syntenic Analyses
2.5. Tissue Specific Analysis of SST Gene Expression by qRT-PCR
2.6. Expression of Igf-1 and Igf-2 in the Liver After Injection with SSTs
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the SST Gene Family in S. argus
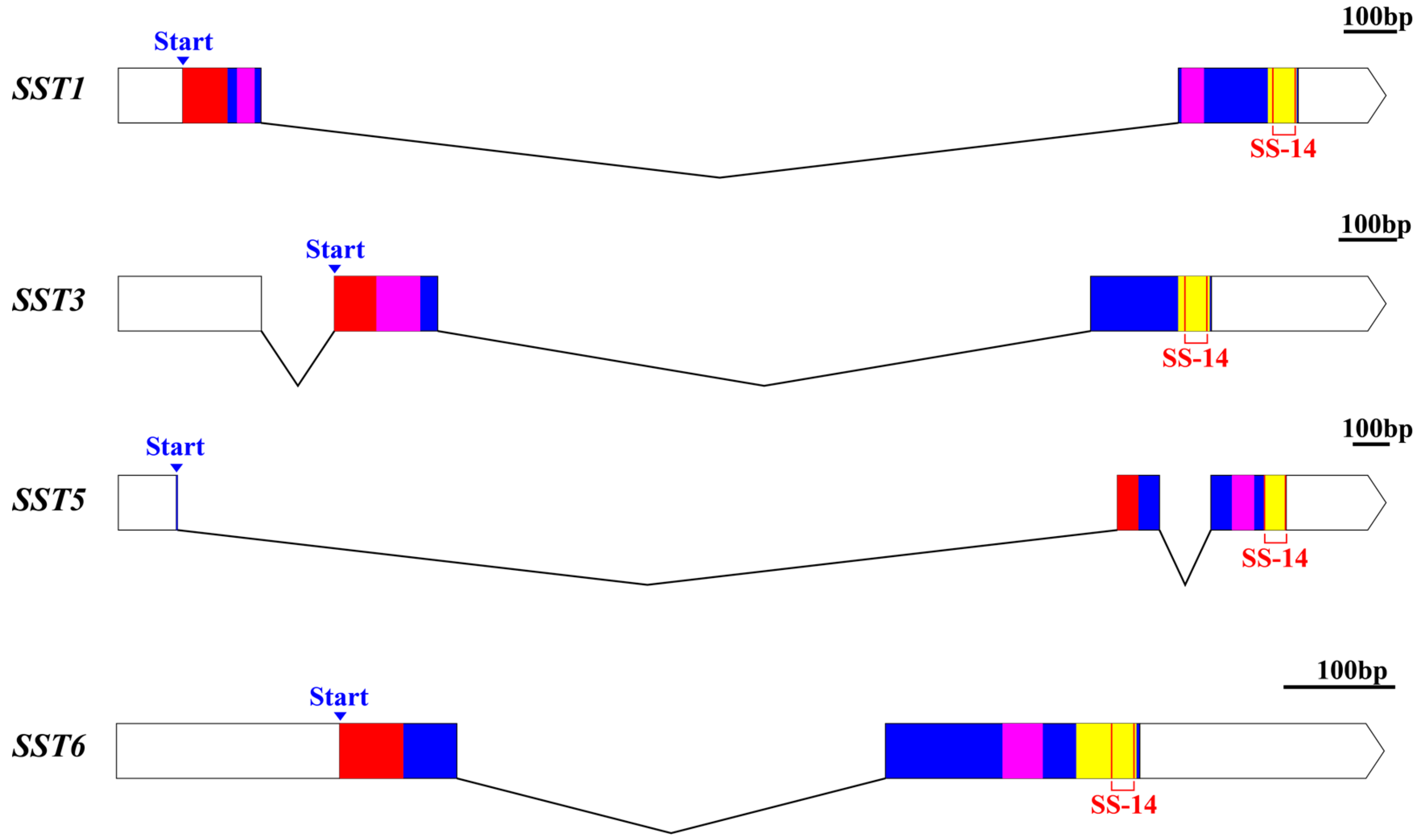
3.2. Gene Structures and Conserved Domains
3.3. Phylogenetic and Syntenic Analyses of S. argus SST Genes
3.4. Tissue Specific Distribution of SST Gene Expression
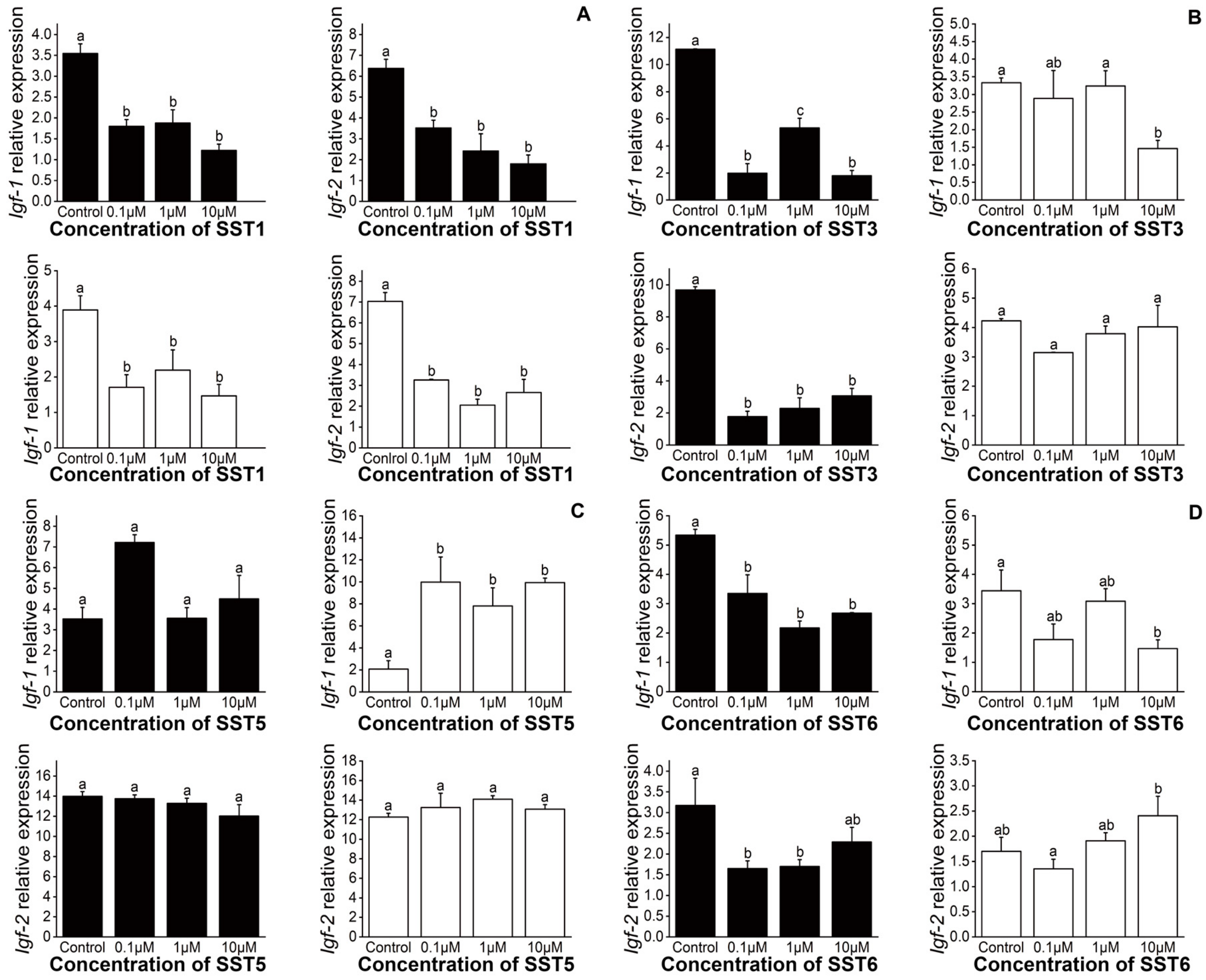
3.5. Effects of SSTs on the Expression of Igf-1 and Igf-2 in Liver Samples Incubated with S. argus In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Very, N.; Sheridan, M. The Role of Somatostatins in the Regulation of Growth in Fish. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 27, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, Y.C. Somatostatin and Its Receptor Family. Front. Neuroendocr. 1999, 20, 157–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazeau, P.; Vale, W.; Burgus, R.; Ling, N.; Butcher, M.; Rivier, J.; Guillemin, R. Hypothalamic Polypeptide That Inhibits the Secretion of Immunoreactive Pituitary Growth Hormone. Science 1973, 179, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, M.A.; Kittilson, J.D.; Slagter, B.J. Structure-Function Relationships of the Signaling System for the Somatostatin Peptide Hormone Family1. Am. Zoöl. 2000, 40, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sheridan, M.A.; Eilertson, C.D.; Kerstetter, T.H. Changes in plasma somatostatin associated with seawater adaptation and stunting of coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch. Aquaculture 1998, 168, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppinga, J.; Kittilson, J.; McCormick, S.D.; Sheridan, M.A. Effects of somatostatin on the growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor axis and seawater adaptation of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2007, 273, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Very, N.M.; Kittilson, J.D.; Klein, S.E.; Sheridan, M.A. Somatostatin inhibits basal and growth hormone-stimulated hepatic insulin-like growth factor-I production. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2008, 281, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, P.C.; Pollock, H.G.; Elliott, W.M.; Youson, J.H.; Plisetskaya, E.M. Isolation and characterization of a variant somatostatin-14 and two related somatostatins of 34 and 37 residues from lamprey (Petromyzon marinus). J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 15809–15814. [Google Scholar]
- Fukusumi, S.; Kitada, C.; Takekawa, S.; Kizawa, H.; Sakamoto, J.; Miyamoto, M.; Hinuma, S.; Kitano, K.; Fujino, M. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Human Cortistatin-like Peptide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 232, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lecea, L.; Criado, J.R.; Prospéro-García, O.; Gautvik, K.M.; Schweitzer, P.; Danielson, P.E.; Dunlop, C.L.M.; Siggins, G.R.; Henriksen, S.J.; Sutcliffe, J.G. A cortical neuropeptide with neuronal depressant and sleep-modulating properties. Nature 1996, 381, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabucchi, M.; Tostivint, H.; Lihrmann, I.; Blähser, S.; Vallarino, M.; Vaudry, H. Characterization of the cDNA encoding a somatostatin variant in the chicken brain: Comparison of the distribution of the two somatostatin precursor mRNAs. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 461, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabucchi, M.; Lihrmann, I.; Vallarino, M.; Vaudry, H. Molecular cloning of the cDNAs and distribution of the mRNAs encoding two somatostatin precursors in the African lungfish Protopterus annectens. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 410, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Li, W.S.; Lin, H.R. Polygenic expression of somatostatin in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides): Molecular cloning and distribution of the mRNAs encoding three somatostatin precursors. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2005, 241, 62–72. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Yu, X.; Pang, M.; Liu, H.; Tong, J. Molecular characterization and expression of three preprosomatostatin genes and their association with growth in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 182, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, F.B.; Kenigfest, N.B.; Mazan, S.; Tostivint, H. Molecular cloning of the cDNAs encoding three somatostatin variants in the dogfish (Scylorhinus canicula). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 180, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tostivint, H.; Dettaï, A.; Quan, F.B.; Ravi, V.; Tay, B.-H.; Rodicio, M.C.; Mazan, S.; Venkatesh, B.; Kenigfest, N.B. Identification of three somatostatin genes in lampreys. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 237, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, J.V.O.D.; Adriaensen, D.; Van Nassauw, L.; Timmermans, J.-P. The role(s) of somatostatin, structurally related peptides and somatostatin receptors in the gastrointestinal tract: A review. Regul. Pept. 2009, 156, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostivint, H.; Lihrmann, I.; Bucharles, C.; Vieau, D.; Coulouarn, Y.; Fournier, A.; Conlon, J.M.; Vaudry, H. Occurrence of two somatostatin variants in the frog brain: Characterization of the cDNAs, distribution of the mRNAs, and receptor-binding affinities of the peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12605–12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudry, H.; Chartrel, N.; Conlon, J.M. Isolation of [Pro2,Met13]Somatostatin-14 and somatostatin-14 from the frog brain reveals the existence of a somatostatin gene family in a tetrapod. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 188, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Lin, H. The evolution of somatostatin in vertebrates. Gene 2010, 463, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostivint, H.; Lihrmann, I.; Vaudry, H. New insight into the molecular evolution of the somatostatin family. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2008, 286, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tostivint, H.; Daza, D.O.; Bergqvist, C.A.; Quan, F.B.; Bougerol, M.; Lihrmann, I.; Larhammar, D. MOLECULAR EVOLUTION OF GPCRS: Somatostatin/urotensin II receptors. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 52, T61–T86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.; Furlong, M.; Sim, M.; Cho, M.; Park, S.; Cho, E.B.; Reyes-Alcaraz, A.; Hwang, J.-I.; Kim, J.; Seong, J.Y. Prevertebrate Local Gene Duplication Facilitated Expansion of the Neuropeptide GPCR Superfamily. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2803–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dehal, P.; Boore, J.L. Two rounds of whole genome duplication in the ancestral vertebrate. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, N.H.; Butts, T.; Ferrier, D.E.K.; Furlong, R.F.; Hellsten, U.; Kawashima, T.; Robinson-Rechavi, M.; Shoguchi, E.; Terry, A.; Yu, J.-K.; et al. The amphioxus genome and the evolution of the chordate karyotype. Nature 2008, 453, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Peer, Y.; Maere, S.; Meyer, A. 2R or not 2R is not the question anymore. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostivint, H.; Gaillard, A.-L.; Mazan, S.; Pézeron, G. Revisiting the evolution of the somatostatin family: Already five genes in the gnathostome ancestor. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 279, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostivint, H.; Joly, L.; Lihrmann, I.; Ekker, M.; Vaudry, H. Chromosomal localization of three somatostatin genes in zebrafish. Evidence that the [Pro2]-somatostatin-14 isoform and cortistatin are encoded by orthologous genes. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 33, R1–R8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, G.; Radhakrishnan, C.K. Food, Feeding Habits and Biochemical Composition of Scatophagus argus. Turkish J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 11, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazilou, A.; Chenary, F.; Morovvati, H.; Zolgarneine, H. Time course of saltwater adaptation in Spotted Scat (Scatophagus argus) (Pisces): A histomorphometric approach. Ital. J. Zool. 2011, 78, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S. An Overview on Morphology, Biology, and Culture of Spotted Scat Scatophagus argus (Linnaeus 1766). Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2016, 24, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, F.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Allen, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Bennett, R.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Boddu, S.; et al. Ensembl 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D745–D751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, E.W.; Agarwala, R.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Canese, K.; Clark, K.; Connor, R.; Fiorini, N.; Funk, K.; Hefferon, T.; et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D23–D28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Deng, S.-P.; Chen, H.-P.; Jiang, D.-N.; Tian, C.-X.; Yang, W.; Wu, T.-L.; Zhu, C.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.-L. Phoenixin participated in regulation of food intake and growth in spotted scat, Scatophagus argus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 226, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, J.; Tostivint, H.; Vaudry, H. Somatostatin- and urotensin II-related peptides: Molecular diversity and evolutionary perspectives. Regul. Pept. 1997, 69, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidah, N.G.; Chrétien, M. Proprotein and prohormone convertases: A family of subtilases generating diverse bioactive polypeptides. Brain Res. 1999, 848, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabucchi, M.; Tostivint, H.; Lihrmann, I.; Sollars, C.; Vallarino, M.; Dores, R.M.; Vaudry, H. Polygenic expression of somatostatin in the sturgeon Acipenser transmontanus: Molecular cloning and distribution of the mRNAs encoding two somatostatin precursors. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010, 443, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunker, W.K.; Smith, S.; Graves, C.; Davis, P.J.; Unniappan, S.; Rivier, J.E.; Peter, R.E.; Chang, J.P. Endogenous Hypothalamic Somatostatins Differentially Regulate Growth Hormone Secretion from Goldfish Pituitary Somatotropes in Vitro. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 4031–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holstein, B.; Cederberg, C. Effect of somatostatin on basal and stimulated gastric secretion in the cod, Gadus morhua. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 1988, 254, G183–G188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J. Evolution by gene duplication: An update. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, J. Rapid Subfunctionalization Accompanied by Prolonged and Substantial Neofunctionalization in Duplicate Gene Evolution. Genetics 2005, 169, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet, F.G.; Crollius, H.R.; Paris, M.; Aury, J.-M.; Gibert, P.; Jaillon, O.; Laudet, V.; Robinson-Rechavi, M. Gene Loss and Evolutionary Rates Following Whole-Genome Duplication in Teleost Fishes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1808–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, T.A.; Fraser, R.A.; Andrews, P.; Peter, R. The influence of mammalian and teleost somatostatins on the secretion of growth hormone from goldfish (Carassius auratus L.) pituitary fragments in vitro. Regul. Pept. 1987, 17, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, H.; Bradshaw, R.A.; Bates, O.J.; Permutt, A. Amino acid sequence of catfish pancreatic somatostatin I. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 2251–2254. [Google Scholar]
- Very, N.M.; Sheridan, M.A. Somatostatin inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I receptor expression in the gill of a teleost fish (Oncorhynchus mykiss). FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 4773–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Jia, J.; Yang, G.; Qin, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, C.; Li, W. In vitro effects of somatostatin on the growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor axis in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 237, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Species | Gene | Accession | Chr. | Position | Intron Number | Length (aa) | Mol. Wt. (KDa) | pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scatophagusargus | SST1 | MN503273 | linkage group 4 | 1,497,913–1,500,200 | 1 | 123 | 13.50858 | 5.927 |
| SST3 | MN503274 | linkage group 4 | 1,509,010–1,511,180 | 2 | 127 | 14.18519 | 7.087 | |
| SST5 | MN503275 | linkage group 23 | 6,586,660–6,590,089 | 2 | 106 | 12.14712 | 5.137 | |
| SST6 | MN503272 | linkage group 8 | 28,731,379–28,732,313 | 1 | 110 | 12.32939 | 7.054 | |
| Danio rerio | SST1 | ENSDARG00000040799 | 15 | 36,156,986–36,158,851 | 1 | 114 | 12.44737 | 6.573 |
| SST3 | ENSDARG00000033161 | 15 | 36,115,955–36,120,277 | 1 | 119 | 13.77676 | 5.743 | |
| SST5 | XM_001333046 | 7 | 19,971,621–19,975,163 | 1 | 107 | 12.39434 | 6.564 | |
| SST6 | ENSDARG00000031649 | 23 | 28,731,379–28,732,313 | 1 | 111 | 12.50558 | 6.636 | |
| Ictalurus punctatus | SST1 | ENSIPUT00000002347.1 | 17 | 13,328,384–13,330,108 | 1 | 114 | 12.41834 | 6.556 |
| SST3 | ENSIPUG00000001600 | 17 | 13,313,346–13,315,085 | 1 | 118 | 13.19919 | 6.906 | |
| SST5 | NC_030422.1 | 7 | 16,459,454–16,460,769 | 1 | 101 | 11.59656 | 7.196 | |
| SST6 | ENSIPUG00000009885 | 15 | 20,806,961–20,808,421 | 1 | 109 | 12.42848 | 5.960 | |
| Lepisosteus oculatus | SST1 | ENSLOCG00000009439 | LG14 | 19,404,762–19,407,399 | 1 | 114 | 12.47024 | 5.443 |
| SST3 | ENSLOCG00000009445 | LG14 | 19,441,987–19,443,409 | 1 | 116 | 13.18407 | 7.085 | |
| SST5 | XM_006627348 | LG2 | 57,923,010–57,929,171 | 1 | 122 | 13.45959 | 9.055 | |
| SST6 | XP_006642047.1 | LG25 | 11,726,683–11,728,536 | 1 | 109 | 12.13611 | 7.049 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, P.; Tian, C.; Lin, X.; Jiang, D.; Shi, H.; Chen, H.; Deng, S.; Zhu, C.; Li, G. Identification, Expression, and Functions of the Somatostatin Gene Family in Spotted Scat (Scatophagus argus). Genes 2020, 11, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020194
Feng P, Tian C, Lin X, Jiang D, Shi H, Chen H, Deng S, Zhu C, Li G. Identification, Expression, and Functions of the Somatostatin Gene Family in Spotted Scat (Scatophagus argus). Genes. 2020; 11(2):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020194
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Peizhe, Changxu Tian, Xinghua Lin, Dongneng Jiang, Hongjuan Shi, Huapu Chen, Siping Deng, Chunhua Zhu, and Guangli Li. 2020. "Identification, Expression, and Functions of the Somatostatin Gene Family in Spotted Scat (Scatophagus argus)" Genes 11, no. 2: 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020194
APA StyleFeng, P., Tian, C., Lin, X., Jiang, D., Shi, H., Chen, H., Deng, S., Zhu, C., & Li, G. (2020). Identification, Expression, and Functions of the Somatostatin Gene Family in Spotted Scat (Scatophagus argus). Genes, 11(2), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11020194







