Next Generation DNA Sequencing and the Future of Genomic Medicine
Abstract
:1. The first era of DNA sequencing: Sanger chemistry
2. Next generation DNA sequencing
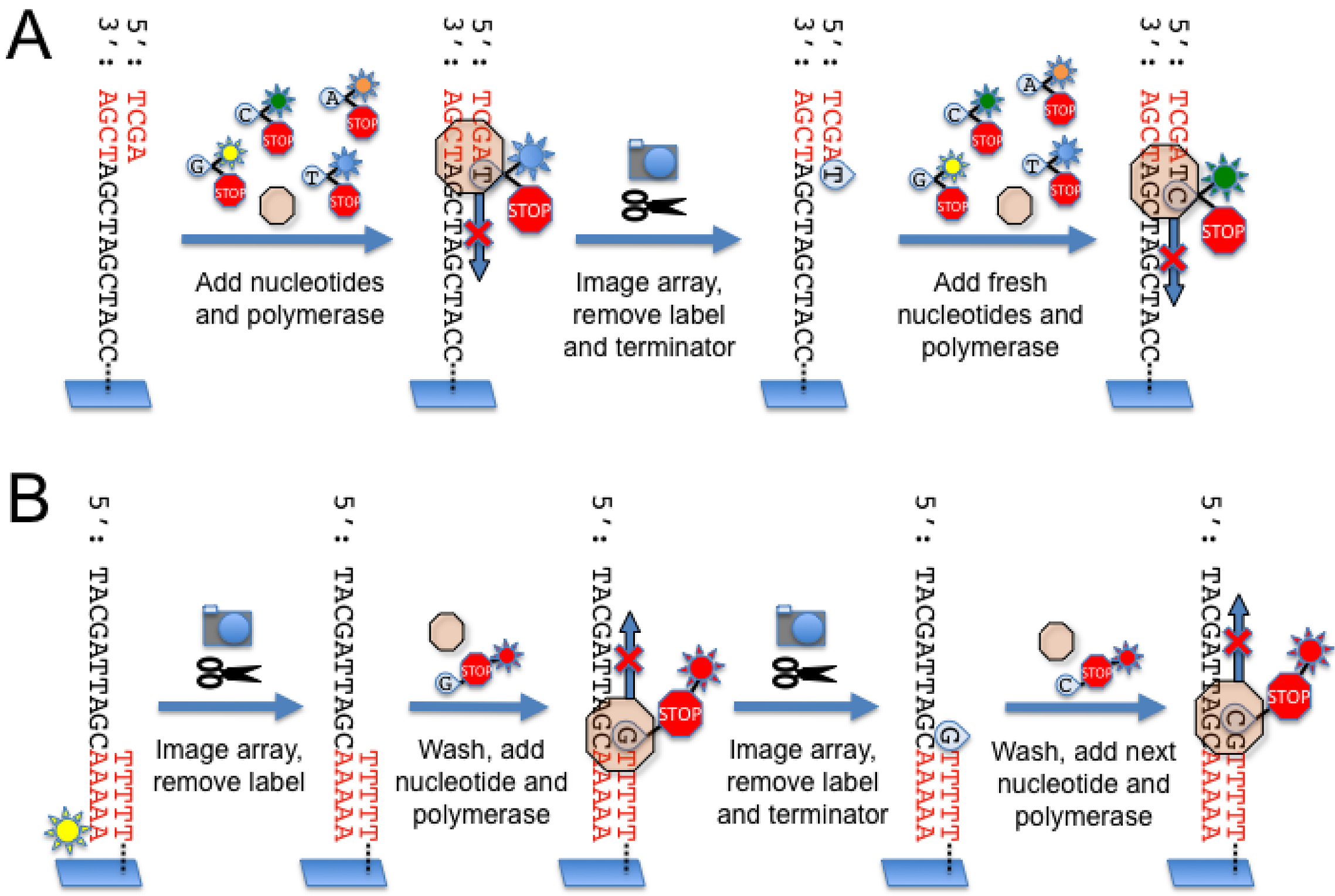
2.1. Roche/454 Life Sciences
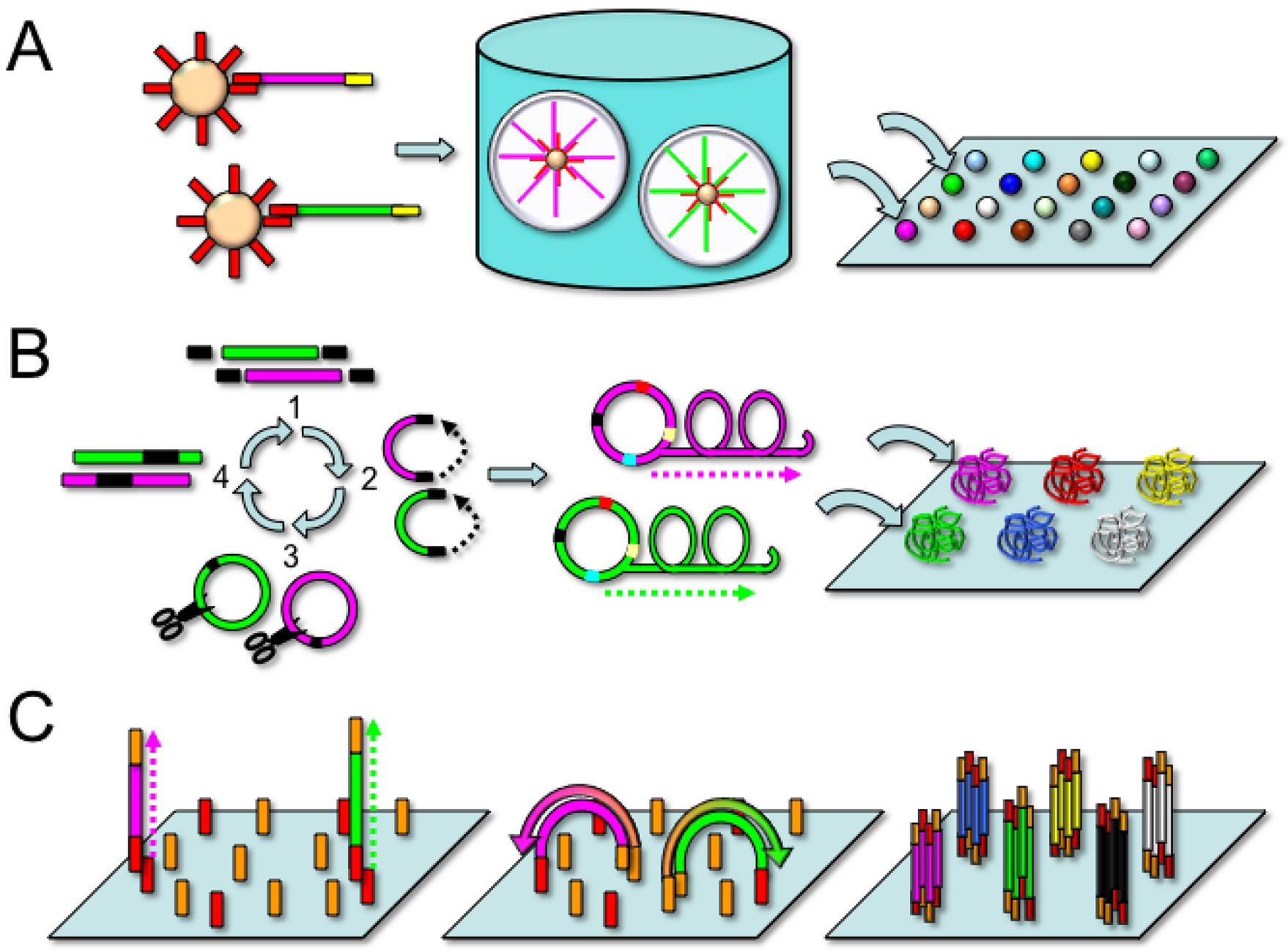

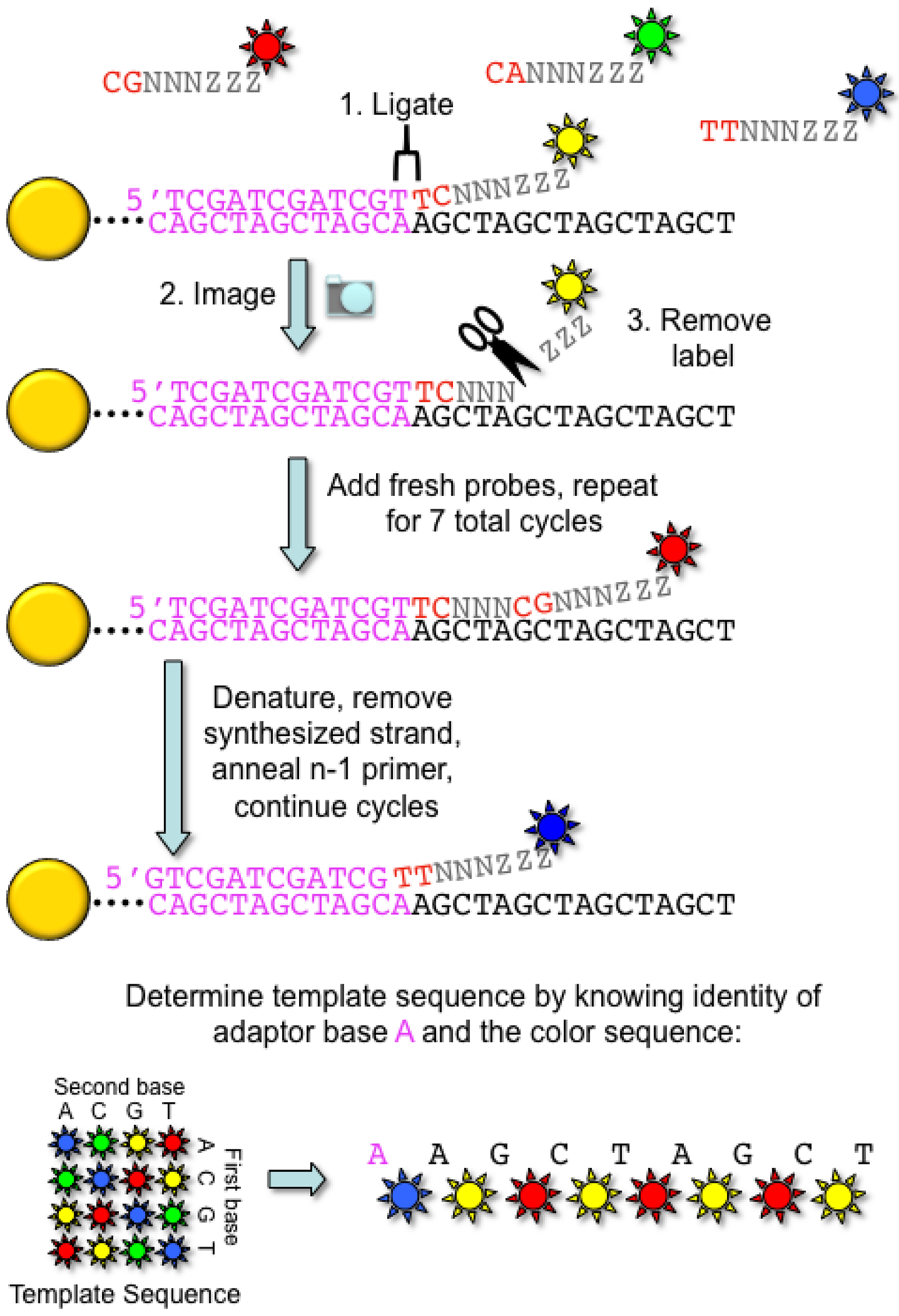
2.2. Applied Biosystems/SOLiD
2.3. Complete Genomics
2.4. Illumina Genome Analyzer
2.5. Helicos
3. ird generation” DNA sequencing
3.1. Real time single molecule sequencing
3.2. DNA sequencing by direct physical methods
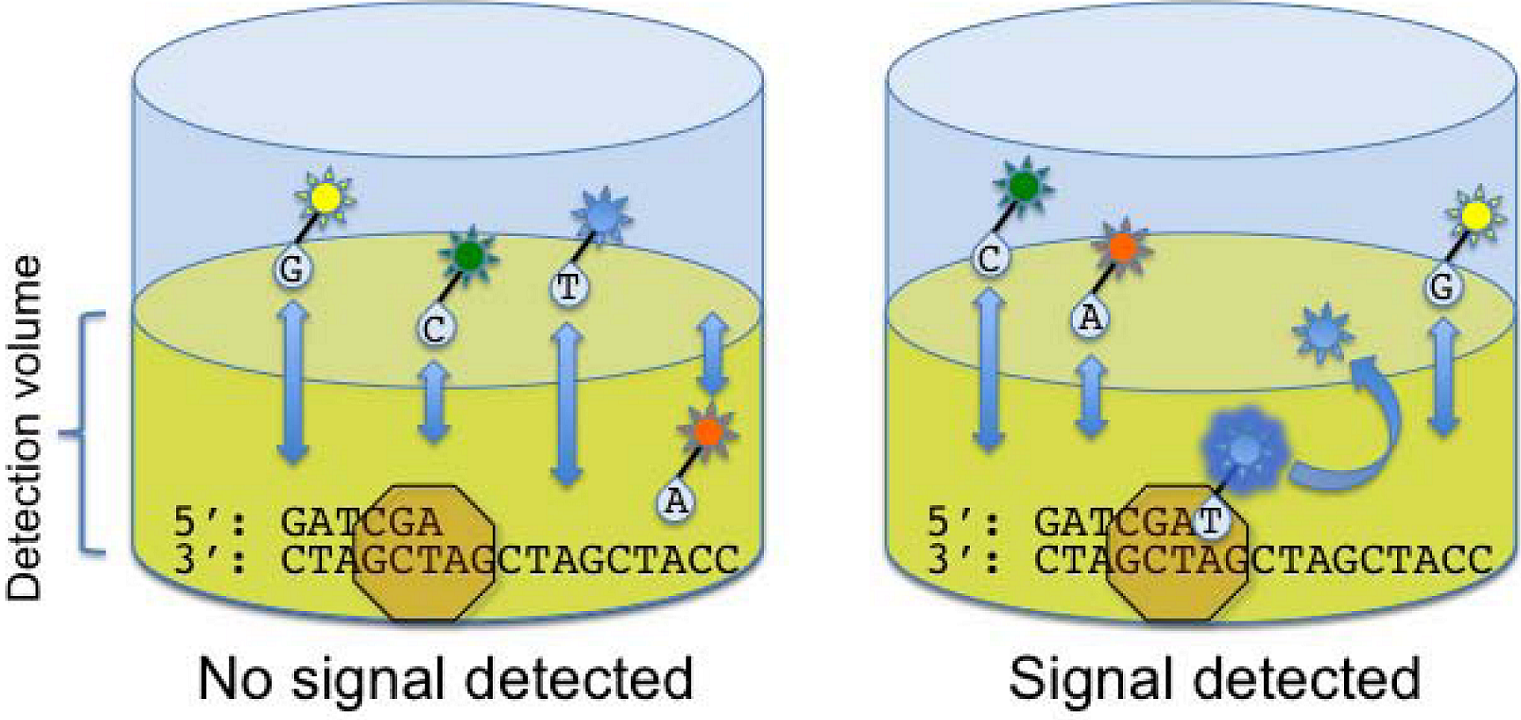
4. Genomic enrichment strategies
5. Data processing
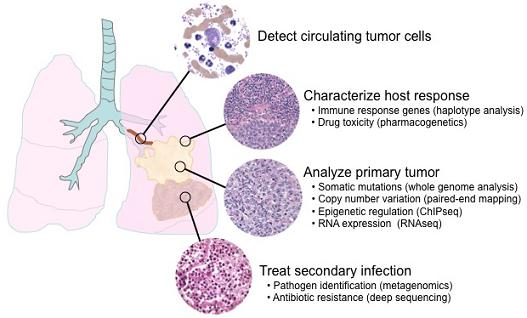
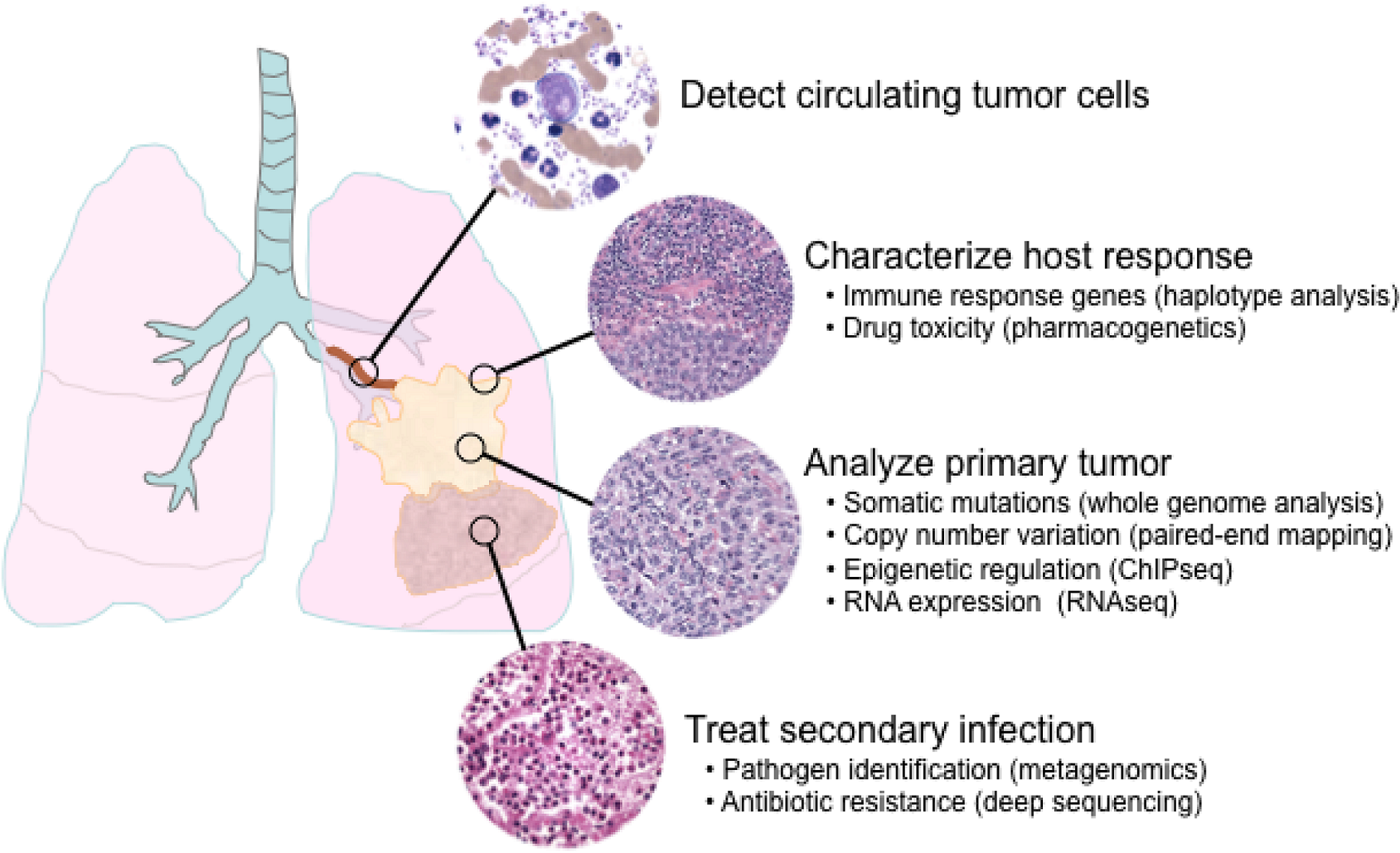
6. Applications of next-generation sequencing for clinical diagnostics
6.1. Single nucleotide polymorphisms and somatic mutations
6.2. Haplotype analysis
6.3. Copy number variation
6.4. Epigenetics
6.5. Transcriptome analysis
6.6. Metagenomics and minimal residual disease detection
7. Whole genome analysis and clinical diagnosis
7.1. Accuracy
7.2. Genotype/phenotype correlation
7.3. Clinical utility
7.4. Ethical issues
8. Conclusions
- empirical evidence of clinical utility to maximize the benefits and minimize the risk of harm.
- profound leap in bio-computational infrastructure and the development of comprehensive programs that aid in the interpretation of massive amounts of genomic data.
- standards and laboratory guidelines to help with the clinical interpretation of the results and to facilitate appropriate medical decisions based on this information.
- medical students, physicians, laboratory technologists and other health care professionals in these methods.
- physicians, patients, and policy makers in the possibilities and limitations of these technologies, as well as the ethical issues surrounding their use.
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Maxam, A.M.; Gilbert, W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1977, 74, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.M.; Sanders, J.Z.; Kaiser, R.J.; Hughes, P.; Dodd, C.; Connell, C.R.; Heiner, C.; Kent, S.B.; Hood, L.E. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature 1986, 321, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gocayne, J.; Robinson, D.A.; FitzGerald, M.G.; Chung, F.Z.; Kerlavage, A.R.; Lentes, K.U.; Lai, J.; Wang, C.D.; Fraser, C.M.; Venter, J.C. Primary structure of rat cardiac beta-adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors obtained by automated DNA sequence analysis: further evidence for a multigene family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1987, 84, 8296–8300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, J.C.; Adams, M.D.; Myers, E.W.; Li, P.W.; Mural, R.J.; Sutton, G.G.; Smith, H.O.; Yandell, M.; Evans, C.A.; Holt, R.A.; et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science 2001, 291, 1304–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emrich, C.A.; Tian, H.; Medintz, I.L.; Mathies, R.A. Microfabricated 384-lane capillary array electrophoresis bioanalyzer for ultrahigh-throughput genetic analysis. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5076–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kommedal, O.; Karlsen, B.; Saebo, O. Analysis of mixed sequencing chromatograms and its application in direct 16S rRNA gene sequencing of polymicrobial samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3766–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margulies, M.; Egholm, M.; Altman, W.E.; Attiya, S.; Bader, J.S.; Bemben, L.A.; Berka, J.; Braverman, M.S.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, Z.; et al. Genome sequencing in microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors. Nature 2005, 437, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ronaghi, M.; Karamohamed, S.; Pettersson, B.; Uhlen, M.; Nyren, P. Real-time DNA sequencing using detection of pyrophosphate release. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 242, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronaghi, M.; Uhlen, M.; Nyren, P. A sequencing method based on real-time pyrophosphate. Science 1998, 281, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shendure, J.; Porreca, G.J.; Reppas, N.B.; Lin, X.; McCutcheon, J.P.; Rosenbaum, A.M.; Wang, M.D.; Zhang, K.; Mitra, R.D.; Church, G.M. Accurate multiplex polony sequencing of an evolved bacterial genome. Science 2005, 309, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Church Laboratory. Polony sequencing protocols. Available online: http://openwetware.org/wiki/Church_Lab:PoloProt (accessed April 2010).
- Drmanac, R.; Sparks, A.B.; Callow, M.J.; Halpern, A.L.; Burns, N.L.; Kermani, B.G.; Carnevali, P.; Nazarenko, I.; Nilsen, G.B.; Yeung, G.; et al. Human genome sequencing using unchained base reads on self-assembling DNA nanoarrays. Science. 2010, 327, pp. 78–81. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adessi, C.; Matton, G.; Ayala, G.; Turcatti, G.; Mermod, J.J.; Mayer, P.; Kawashima, E. Solid phase DNA amplification: characterisation of primer attachment and amplification mechanisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedurco, M.; Romieu, A.; Williams, S.; Lawrence, I.; Turcatti, G. BTA, a novel reagent for DNA attachment on glass and efficient generation of solid-phase amplified DNA colonies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, D.R.; Balasubramanian, S.; Swerdlow, H.P.; Smith, G.P.; Milton, J.; Brown, C.G.; Hall, K.P.; Evers, D.J.; Barnes, C.L.; Bignell, H.R.; et al. Accurate whole human genome sequencing using reversible terminator chemistry. Nature 2008, 456, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, M.A.; Kozarewa, I.; Smith, F.; Scally, A.; Stephens, P.J.; Durbin, R.; Swerdlow, H.; Turner, D.J. A large genome center's improvements to the Illumina sequencing system. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braslavsky, I.; Hebert, B.; Kartalov, E.; Quake, S.R. Sequence information can be obtained from single DNA molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003, 100, 3960–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, T.D.; Buzby, P.R.; Babcock, H.; Beer, E.; Bowers, J.; Braslavsky, I.; Causey, M.; Colonell, J.; Dimeo, J.; Efcavitch, J.W.; Giladi, E.; Gill, J.; Healy, J.; Jarosz, M.; Lapen, D.; Moulton, K.; Quake, S.R.; Steinmann, K.; Thayer, E.; Tyurina, A.; Ward, R.; Weiss, H.; Xie, Z. Single-molecule DNA sequencing of a viral genome. Science 2008, 320, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pushkarev, D.; Neff, N.F.; Quake, S.R. Single-molecule sequencing of an individual human genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, J.; Mitchell, J.; Beer, E.; Buzby, P.R.; Causey, M.; Efcavitch, J.W.; Jarosz, M.; Krzymanska-Olejnik, E.; Kung, L.; Lipson, D.; Lowman, G.M.; Marappan, S.; McInerney, P.; Platt, A.; Roy, A.; Siddiqi, S.M.; Steinmann, K.; Thompson, J.F. Virtual terminator nucleotides for next-generation DNA sequencing. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branton, D.; Deamer, D.W.; Marziali, A.; Bayley, H.; Benner, S.A.; Butler, T.; Di Ventra, M.; Garaj, S.; Hibbs, A.; Huang, X.; Jovanovich, S.B.; Krstic, P.S.; Lindsay, S.; Ling, X.S.; Mastrangelo, C.H.; Meller, A.; Oliver, J.S.; Pershin, Y.V.; Ramsey, J.M.; Riehn, R.; Soni, G.V.; Tabard-Cossa, V.; Wanunu, M.; Wiggin, M.; Schloss, J.A. The potential and challenges of nanopore sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, J.; Fehr, A.; Gray, J.; Luong, K.; Lyle, J.; Otto, G.; Peluso, P.; Rank, D.; Baybayan, P.; Bettman, B.; et al. Real-time DNA sequencing from single polymerase molecules. Science 2009, 323, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flusberg, B.A.; Webster, D.R.; Lee, J.H.; Travers, K.J.; Olivares, E.C.; Clark, T.A.; Korlach, J.; Turner, S.W. Direct detection of DNA methylation during single-molecule, real-time sequencing. Nat. Methods. 9 5 2010. Available online: http://www.nature.com/naturemethods (accessed May 2010).
- The X PRIZE Foundation. Archon X PRIZE for genomics. Available online: http://genomics.xprize.org (accessed April 2010).
- Turner, E.H.; Ng, S.B.; Nickerson, D.A.; Shendure, J. Methods for genomic partitioning. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuzelaar, L.S.; Lancaster, O.; Pasche, J.P.; Kopal, G.; Brookes, A.J. MegaPlex PCR: a strategy for multiplex amplification. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 835–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varley, K.E.; Mitra, R.D. Nested Patch PCR enables highly multiplexed mutation discovery in candidate genes. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, F.; Stenberg, J.; Fredriksson, S.; Welch, K.; Zhang, M.; Nilsson, M.; Bicknell, D.; Bodmer, W.F.; Davis, R.W.; Ji, H. Multigene amplification and massively parallel sequencing for cancer mutation discovery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 9387–9392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, E.; Xuan, Z.; Balija, V.; Kramer, M.; Molla, M.N.; Smith, S.W.; Middle, C.M.; Rodesch, M.J.; Albert, T.J.; Hannon, G.J.; McCombie, W.R. Genome-wide in situ exon capture for selective resequencing. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.B.; Buckingham, K.J.; Lee, C.; Bigham, A.W.; Tabor, H.K.; Dent, K.M.; Huff, C.D.; Shannon, P.T.; Jabs, E.W.; Nickerson, D.A.; Shendure, J.; Bamshad, M.J. Exome sequencing identifies the cause of a mendelian disorder. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huse, S.M.; Huber, J.A.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L.; Welch, D.M. Accuracy and quality of massively parallel DNA pyrosequencing. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flicek, P.; Birney, E. Sense from sequence reads: methods for alignment and assembly. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, S6–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idury, R.M.; Waterman, M.S. A new algorithm for DNA sequence assembly. J. Comput. Biol. 1995, 2, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, J.T.; Wong, K.; Jackman, S.D.; Schein, J.E.; Jones, S.J.; Birol, I. ABySS: a parallel assembler for short read sequence data. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolio, T.A.; Collins, F.S. The HapMap and genome-wide association studies in diagnosis and therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2009, 60, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature 2005, 437, 1299–1320. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Ballinger, D.G.; Cox, D.R.; Hinds, D.A.; Stuve, L.L.; Gibbs, R.A.; Belmont, J.W.; Boudreau, A.; Hardenbol, P.; Leal, S.M.; et al. A second generation human haplotype map of over 3.1 million SNPs. Nature 2007, 449, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFramboise, T. Single nucleotide polymorphism arrays: a decade of biological, computational and technological advances. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 4181–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tassell, C.P.; Smith, T.P.; Matukumalli, L.K.; Taylor, J.F.; Schnabel, R.D.; Lawley, C.T.; Haudenschild, C.D.; Moore, S.S.; Warren, W.C.; Sonstegard, T.S. SNP discovery and allele frequency estimation by deep sequencing of reduced representation libraries. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.; Fang, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Kristiansen, K. SNP detection for massively parallel whole-genome resequencing. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, W.; Kozlowski, P.; Taillon, B.E.; Bouffard, P.; Holmes, A.J.; Janne, P.; Camposano, S.; Thiele, E.; Franz, D.; Kwiatkowski, D.J. Ultra deep sequencing detects a low rate of mosaic mutations in tuberous sclerosis complex. Hum. Genet. 2010, 127, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The 1000 Genomes Project. 1000 genomes: a deep catalog of human variation. Available online: http://www.1000genomes.org/page.php (accessed April 2010).
- Lupski, J.R.; Reid, J.G.; Gonzaga-Jauregui, C.; Rio Deiros, D.; Chen, D.C.; Nazareth, L.; Bainbridge, M.; Dinh, H.; Jing, C.; Wheeler, D.A.; McGuire, A.L.; Zhang, F.; Stankiewicz, P.; Halperin, J.J.; Yang, C.; Gehman, C.; Guo, D.; Irikat, R.K.; Tom, W.; Fantin, N.J.; Muzny, D.M.; Gibbs, R.A. Whole-genome sequencing in a patient with Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, J.C.; Glusman, G.; Smit, A.F.; Huff, C.D.; Hubley, R.; Shannon, P.T.; Rowen, L.; Pant, K.P.; Goodman, N.; Bamshad, M.; Shendure, J.; Drmanac, R.; Jorde, L.B.; Hood, L.; Galas, D.J. Analysis of genetic inheritance in a family quartet by whole-genome sequencing. Science 2010, 328, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, T.J.; Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Fulton, B.; McLellan, M.D.; Chen, K.; Dooling, D.; Dunford-Shore, B.H.; McGrath, S.; Hickenbotham, M.; et al. DNA sequencing of a cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukaemia genome. Nature 2008, 456, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Dooling, D.J.; Larson, D.E.; McLellan, M.D.; Chen, K.; Koboldt, D.C.; Fulton, R.S.; Delehaunty, K.D.; McGrath, S.D.; et al. Recurring mutations found by sequencing an acute myeloid leukemia genome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleasance, E.D.; Stephens, P.J.; O'Meara, S.; McBride, D.J.; Meynert, A.; Jones, D.; Lin, M.L.; Beare, D.; Lau, K.W.; Greenman, C.; et al. A small-cell lung cancer genome with complex signatures of tobacco exposure. Nature 2010, 463, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleasance, E.D.; Cheetham, R.K.; Stephens, P.J.; McBride, D.J.; Humphray, S.J.; Greenman, C.D.; Varela, I.; Lin, M.L.; Ordonez, G.R.; Bignell, G.R.; et al. A comprehensive catalogue of somatic mutations from a human cancer genome. Nature 2010, 463, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Cancer Genome Consortium. International cancer genome consortium overview. Available online: http://www.icgc.org (accessed April 2010).
- Sabeti, P.C.; Varilly, P.; Fry, B.; Lohmueller, J.; Hostetter, E.; Cotsapas, C.; Xie, X.; Byrne, E.H.; McCarroll, S.A.; Gaudet, R.; et al. Genome-wide detection and characterization of positive selection in human populations. Nature 2007, 449, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersdorf, E.W. HLA matching in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2004, 11, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, C.; Danzer, M.; Hackl, C.; Kopal, G.; Hufnagl, P.; Hofer, K.; Polin, H.; Stabentheiner, S.; Proll, J. Rapid high-throughput human leukocyte antigen typing by massively parallel pyrosequencing for high-resolution allele identification. Hum. Immunol. 2009, 70, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, G.; Higuchi, R.; Hoglund, B.; Goodridge, D.; Sayer, D.; Trachtenberg, E.A.; Erlich, H.A. High-resolution, high-throughput HLA genotyping by next-generation sequencing. Tissue Antigens 2009, 74, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iafrate, A.J.; Feuk, L.; Rivera, M.N.; Listewnik, M.L.; Donahoe, P.K.; Qi, Y.; Scherer, S.W.; Lee, C. Detection of large-scale variation in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebat, J.; Lakshmi, B.; Troge, J.; Alexander, J.; Young, J.; Lundin, P.; Maner, S.; Massa, H.; Walker, M.; Chi, M.; Navin, N.; Lucito, R.; Healy, J.; Hicks, J.; Ye, K.; Reiner, A.; Gilliam, T.C.; Trask, B.; Patterson, N.; Zetterberg, A.; Wigler, M. Large-scale copy number polymorphism in the human genome. Science 2004, 305, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankiewicz, P.; Lupski, J.R. Structural variation in the human genome and its role in disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 2010, 61, 437–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Gu, W.; Hurles, M.E.; Lupski, J.R. Copy number variation in human health, disease, and evolution. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 451–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbel, J.O.; Urban, A.E.; Affourtit, J.P.; Godwin, B.; Grubert, F.; Simons, J.F.; Kim, P.M.; Palejev, D.; Carriero, N.J.; Du, L.; Taillon, B.E.; Chen, Z.; Tanzer, A.; Saunders, A.C.; Chi, J.; Yang, F.; Carter, N.P.; Hurles, M.E.; Weissman, S.M.; Harkins, T.T.; Gerstein, M.B.; Egholm, M.; Snyder, M. Paired-end mapping reveals extensive structural variation in the human genome. Science 2007, 318, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, P.J.; Stephens, P.J.; Pleasance, E.D.; O'Meara, S.; Li, H.; Santarius, T.; Stebbings, L.A.; Leroy, C.; Edkins, S.; Hardy, C.; Teague, J.W.; Menzies, A.; Goodhead, I.; Turner, D.J.; Clee, C.M.; Quail, M.A.; Cox, A.; Brown, C.; Durbin, R.; Hurles, M.E.; Edwards, P.A.; Bignell, G.R.; Stratton, M.R.; Futreal, P.A. Identification of somatically acquired rearrangements in cancer using genome-wide massively parallel paired-end sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, P.J.; McBride, D.J.; Lin, M.L.; Varela, I.; Pleasance, E.D.; Simpson, J.T.; Stebbings, L.A.; Leroy, C.; Edkins, S.; Mudie, L.J.; et al. Complex landscapes of somatic rearrangement in human breast cancer genomes. Nature 2009, 462, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.; Percharde, M.; Coley, H.M.; Webb, A.; Crook, T. The context and potential of epigenetics in oncology. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggerholm, A.; Holm, M.S.; Guldberg, P.; Olesen, L.H.; Hokland, P. Promoter hypermethylation of p15INK4B, HIC1, CDH1, and ER is frequent in myelodysplastic syndrome and predicts poor prognosis in early-stage patients. Eur. J. Haematol. 2006, 76, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, M.F.; Loda, M.; Gaida, G.M.; Lipman, J.; Mishra, R.; Goldman, H.; Jessup, J.M.; Kolodner, R. Methylation of the hMLH1 promoter correlates with lack of expression of hMLH1 in sporadic colon tumors and mismatch repair-defective human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.F.; de Tribolet, N.; Weller, M.; Kros, J.M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Mason, W.; Mariani, L.; Bromberg, J.E.; Hau, P.; Mirimanoff, R.O.; Cairncross, J.G.; Janzer, R.C.; Stupp, R. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, A.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Gu, H.; Wernig, M.; Hanna, J.; Sivachenko, A.; Zhang, X.; Bernstein, B.E.; Nusbaum, C.; Jaffe, D.B.; Gnirke, A.; Jaenisch, R.; Lander, E.S. Genome-scale DNA methylation maps of pluripotent and differentiated cells. Nature 2008, 454, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Korshunova, Y.; Maloney, R.K.; Lakey, N.; Citek, R.W.; Bacher, B.; Budiman, A.; Ordway, J.M.; McCombie, W.R.; Leon, J.; Jeddeloh, J.A.; McPherson, J.D. Massively parallel bisulphite pyrosequencing reveals the molecular complexity of breast cancer-associated cytosine-methylation patterns obtained from tissue and serum DNA. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piekarz, R.L.; Bates, S.E. Epigenetic modifiers: basic understanding and clinical development. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3918–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.J.; Larsen, P.L.; Varshavsky, A. Mapping protein-DNA interactions in vivo with formaldehyde: evidence that histone H4 is retained on a highly transcribed gene. Cell 1988, 53, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, B.; Robert, F.; Wyrick, J.J.; Aparicio, O.; Jennings, E.G.; Simon, I.; Zeitlinger, J.; Schreiber, J.; Hannett, N.; Kanin, E.; Volkert, T.L.; Wilson, C.J.; Bell, S.P.; Young, R.A. Genome-wide location and function of DNA binding proteins. Science 2000, 290, 2306–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, P.J. ChIP-seq: advantages and challenges of a maturing technology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barski, A.; Cuddapah, S.; Cui, K.; Roh, T.Y.; Schones, D.E.; Wang, Z.; Wei, G.; Chepelev, I.; Zhao, K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 2007, 129, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, G.; Hirst, M.; Bainbridge, M.; Bilenky, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, T.; Euskirchen, G.; Bernier, B.; Varhol, R.; Delaney, A.; Thiessen, N.; Griffith, O.L.; He, A.; Marra, M.; Snyder, M.; Jones, S. Genome-wide profiles of STAT1 DNA association using chromatin immunoprecipitation and massively parallel sequencing. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, T.S.; Ku, M.; Jaffe, D.B.; Issac, B.; Lieberman, E.; Giannoukos, G.; Alvarez, P.; Brockman, W.; Kim, T.K.; Koche, R.P.; Lee, W.; Mendenhall, E.; O'Donovan, A.; Presser, A.; Russ, C.; Xie, X.; Meissner, A.; Wernig, M.; Jaenisch, R.; Nusbaum, C.; Lander, E.S.; Bernstein, B.E. Genome-wide maps of chromatin state in pluripotent and lineage-committed cells. Nature 2007, 448, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, E.; Friedman, N.; Koller, D.; Regev, A. A module map showing conditional activity of expression modules in cancer. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Vijver, M.J.; He, Y.D.; van't Veer, L.J.; Dai, H.; Hart, A.A.; Voskuil, D.W.; Schreiber, G.J.; Peterse, J.L.; Roberts, C.; Marton, M.J.; Parrish, M.; Atsma, D.; Witteveen, A.; Glas, A.; Delahaye, L.; van der Velde, T.; Bartelink, H.; Rodenhuis, S.; Rutgers, E.T.; Friend, S.H.; Bernards, R. A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, S.; Shak, S.; Tang, G.; Kim, C.; Baker, J.; Cronin, M.; Baehner, F.L.; Walker, M.G.; Watson, D.; Park, T.; Hiller, W.; Fisher, E.R.; Wickerham, D.L.; Bryant, J.; Wolmark, N. A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipshutz, R.J.; Fodor, S.P.; Gingeras, T.R.; Lockhart, D.J. High density synthetic oligonucleotide arrays. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schena, M.; Shalon, D.; Davis, R.W.; Brown, P.O. Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science 1995, 270, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tinker, A.V.; Boussioutas, A.; Bowtell, D.D. The challenges of gene expression microarrays for the study of human cancer. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.H.; Weng, Z.; Witten, D.M.; Zhu, S.; Foley, J.W.; Lacroute, P.; Smith, C.L.; Tibshirani, R.; van de Rijn, M.; Sidow, A.; West, R.B. 3’-end sequencing for expression quantification (3SEQ) from archival tumor samples. PLoS One 2010, 5, e8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, M.; Schulz, M.H.; Richard, H.; Magen, A.; Klingenhoff, A.; Scherf, M.; Seifert, M.; Borodina, T.; Soldatov, A.; Parkhomchuk, D.; Schmidt, D.; O'Keeffe, S.; Haas, S.; Vingron, M.; Lehrach, H.; Yaspo, M.L. A global view of gene activity and alternative splicing by deep sequencing of the human transcriptome. Science 2008, 321, 956–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, R.; Bainbridge, M.; Fejes, A.; Hirst, M.; Krzywinski, M.; Pugh, T.; McDonald, H.; Varhol, R.; Jones, S.; Marra, M. Profiling the HeLa S3 transcriptome using randomly primed cDNA and massively parallel short-read sequencing. Biotechniques 2008, 45, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, C.A.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; Cao, X.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Han, B.; Jing, X.; Sam, L.; Barrette, T.; Palanisamy, N.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Transcriptome sequencing to detect gene fusions in cancer. Nature 2009, 458, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.P.; Kobel, M.; Senz, J.; Morin, R.D.; Clarke, B.A.; Wiegand, K.C.; Leung, G.; Zayed, A.; Mehl, E.; Kalloger, S.E.; et al. Mutation of FOXL2 in granulosa-cell tumors of the ovary. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2719–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygaard, S.; Jacobsen, A.; Lindow, M.; Eriksen, J.; Balslev, E.; Flyger, H.; Tolstrup, N.; Moller, S.; Krogh, A.; Litman, T. Identification and analysis of miRNAs in human breast cancer and teratoma samples using deep sequencing. BMC Med. Genomics 2009, 2, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Wyman, S.K.; Parkin, R.K.; Mitchell, P.S.; Fritz, B.R.; O'Briant, K.; Godwin, A.K.; Urban, N.; Drescher, C.W.; Knudsen, B.S.; Tewari, M. Repertoire of microRNAs in epithelial ovarian cancer as determined by next generation sequencing of small RNA cDNA libraries. PLoS One 2009, 4, e5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uziel, T.; Karginov, F.V.; Xie, S.; Parker, J.S.; Wang, Y.D.; Gajjar, A.; He, L.; Ellison, D.; Gilbertson, R.J.; Hannon, G.; Roussel, M.F. The miR-17~92 cluster collaborates with the Sonic Hedgehog pathway in medulloblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009, 106, 2812–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, C.M.; Hoffmann, S.; Darfeuille, F.; Reignier, J.; Findeiss, S.; Sittka, A.; Chabas, S.; Reiche, K.; Hackermuller, J.; Reinhardt, R.; Stadler, P.F.; Vogel, J. The primary transcriptome of the major human pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 2010, 464, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, S.B.; Sammeth, M.; Gutierrez-Arcelus, M.; Lach, R.P.; Ingle, C.; Nisbett, J.; Guigo, R.; Dermitzakis, E.T. Transcriptome genetics using second generation sequencing in a Caucasian population. Nature 2010, 464, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickrell, J.K.; Marioni, J.C.; Pai, A.A.; Degner, J.F.; Engelhardt, B.E.; Nkadori, E.; Veyrieras, J.B.; Stephens, M.; Gilad, Y.; Pritchard, J.K. Understanding mechanisms underlying human gene expression variation with RNA sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muldrew, K.L. Molecular diagnostics of infectious diseases. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2009, 21, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrosino, J.F.; Highlander, S.; Luna, R.A.; Gibbs, R.A.; Versalovic, J. Metagenomic pyrosequencing and microbial identification. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, G.; Druce, J.; Du, L.; Tran, T.; Birch, C.; Briese, T.; Conlan, S.; Quan, P.L.; Hui, J.; Marshall, J.; Simons, J.F.; Egholm, M.; Paddock, C.D.; Shieh, W.J.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Catton, M.; Lipkin, W.I. A new arenavirus in a cluster of fatal transplant-associated diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margeridon-Thermet, S.; Shulman, N.S.; Ahmed, A.; Shahriar, R.; Liu, T.; Wang, C.; Holmes, S.P.; Babrzadeh, F.; Gharizadeh, B.; Hanczaruk, B.; Simen, B.B.; Egholm, M.; Shafer, R.W. Ultra-deep pyrosequencing of hepatitis B virus quasispecies from nucleoside and nucleotide reverse-transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI)-treated patients and NRTI-naive patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.; Chiarella, J.; Simen, B.B.; Hanczaruk, B.; Egholm, M.; Landry, M.L.; Dieckhaus, K.; Rosen, M.I.; Kozal, M.J. Low-abundance HIV drug-resistant viral variants in treatment-experienced persons correlate with historical antiretroviral use. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Maeda, N.; Miron, I.M.; Yoh, M.; Izutsu, K.; Kataoka, C.; Honda, T.; Yasunaga, T.; Nakaya, T.; Kawai, J.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Horii, T.; Iida, T. Metagenomic diagnosis of bacterial infections. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1784–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radich, J.P.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Chan, W.C.; Croce, C.M.; Czuczman, M.S.; Erba, H.P.; Horning, S.J.; Houldsworth, J.; Smith, B.D.; Snyder, D.S.; Sundar, H.M.; Wetzler, M.; Winter, J.N. NCCN task force report: molecular markers in leukemias and lymphomas. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2009, 7 (Suppl. 4), S1-34, quiz S35-36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allan, A.L.; Keeney, M. Circulating tumor cell analysis: technical and statistical considerations for application to the clinic. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 426218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Druker, B.J. Translation of the Philadelphia chromosome into therapy for CML. Blood 2008, 112, 4808–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Diehl, F.; Schmidt, K.; Clouser, C.; Duncan, C.; Antipova, A.; Lee, C.; McKernan, K.; De La Vega, F.M.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Diaz Jr., L.A.; Velculescu, V.E. Development of personalized tumor biomarkers using massively parallel sequencing. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 20ra14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyd, S.D.; Marshall, E.L.; Merker, J.D.; Maniar, J.M.; Zhang, L.N.; Sahaf, B.; Jones, C.D.; Simen, B.B.; Hanczaruk, B.; Nguyen, K.D.; Nadeau, K.C.; Egholm, M.; Miklos, D.B.; Zehnder, J.L.; Fire, A.Z. Measurement and clinical monitoring of human lymphocyte clonality by massively parallel VDJ pyrosequencing. Sci. Transl. Med. 2009, 1, 12ra23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parameswaran, P.; Jalili, R.; Tao, L.; Shokralla, S.; Gharizadeh, B.; Ronaghi, M.; Fire, A.Z. A pyrosequencing-tailored nucleotide barcode design unveils opportunities for large-scale sample multiplexing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elstein, A.S.; Schwartz, A. Clinical problem solving and diagnostic decision making: selective review of the cognitive literature. Brit. Med. J. 2002, 324, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isler, J.A.; Vesterqvist, O.E.; Burczynski, M.E. Analytical validation of genotyping assays in the biomarker laboratory. Pharmacogenomics 2007, 8, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, T.; Mueller, B.U. Complexity of CEBPA dysregulation in human acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5303–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrijver, I. Hereditary non-syndromic sensorineural hearing loss: transforming silence to sound. J. Mol. Diagn. 2004, 6, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelsell, D.P.; Dunlop, J.; Stevens, H.P.; Lench, N.J.; Liang, J.N.; Parry, G.; Mueller, R.F.; Leigh, I.M. Connexin 26 mutations in hereditary non-syndromic sensorineural deafness. Nature 1997, 387, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballana, E.; Ventayol, M.; Rabionet, R.; Gasparini, P.; Estivill, X. Connexins and deafness homepage. Available online: http://davinci.crg.es/deafness/index.php (accessed April 2010). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.W.; Deans, M.R.; Kelsell, D.P.; Paul, D.L. Connexin mutations in deafness. Nature 1998, 394, 630–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramensky, V.; Bork, P.; Sunyaev, S. Human non-synonymous SNPs: server and survey. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3894–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binkley, J.; Karra, K.; Kirby, A.; Hosobuchi, M.; Stone, E.A.; Sidow, A. ProPhylER: a curated online resource for protein function and structure based on evolutionary constraint analyses. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, L.; Gopinath, G.; Gillespie, M.; Caudy, M.; Croft, D.; de Bono, B.; Garapati, P.; Hemish, J.; Hermjakob, H.; Jassal, B.; Kanapin, A.; Lewis, S.; Mahajan, S.; May, B.; Schmidt, E.; Vastrik, I.; Wu, G.; Birney, E.; Stein, L.; D'Eustachio, P. Reactome knowledgebase of human biological pathways and processes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D619–D622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer-Mehren, A.; Furlong, L.I.; Rautschka, M.; Sanz, F. From SNPs to pathways: integration of functional effect of sequence variations on models of cell signalling pathways. BMC Bioinformatics 2009, 10 (Suppl. 8), S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, M.J.; McBride, C.M.; Schully, S.D.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Feero, W.G.; Janssens, A.C.; Gwinn, M.; Simons-Morton, D.G.; Bernhardt, J.M.; Cargill, M.; et al. The Scientific Foundation for personal genomics: recommendations from a National Institutes of Health-Centers for Disease Control and Prevention multidisciplinary workshop. Genet. Med. 2009, 11, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sconce, E.A.; Khan, T.I.; Wynne, H.A.; Avery, P.; Monkhouse, L.; King, B.P.; Wood, P.; Kesteven, P.; Daly, A.K.; Kamali, F. The impact of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genetic polymorphism and patient characteristics upon warfarin dose requirements: proposal for a new dosing regimen. Blood 2005, 106, 2329–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.L.; Horne, B.D.; Stevens, S.M.; Grove, A.S.; Barton, S.; Nicholas, Z.P.; Kahn, S.F.; May, H.T.; Samuelson, K.M.; Muhlestein, J.B.; Carlquist, J.F. Randomized trial of genotype-guided versus standard warfarin dosing in patients initiating oral anticoagulation. Circulation 2007, 116, 2563–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraco, Y.; Blotnick, S.; Muszkat, M. CYP2C9 genotype-guided warfarin prescribing enhances the efficacy and safety of anticoagulation: a prospective randomized controlled study. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillman, M.A.; Wilke, R.A.; Yale, S.H.; Vidaillet, H.J.; Caldwell, M.D.; Glurich, I.; Berg, R.L.; Schmelzer, J.; Burmester, J.K. A prospective, randomized pilot trial of model-based warfarin dose initiation using CYP2C9 genotype and clinical data. Clin. Med. Res. 2005, 3, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B.; Eriksson, N.; Gage, B.F.; Kimmel, S.E.; Lee, M.T.; Limdi, N.A.; Page, D.; Roden, D.M.; Wagner, M.J.; Caldwell, M.D.; Johnson, J.A. Estimation of the warfarin dose with clinical and pharmacogenetic data. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodcock, J.; Lesko, L.J. Pharmacogenetics--tailoring treatment for the outliers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eby, C.S. Counterpoint: pharmacogenetic-based initial dosing of warfarin: not ready for prime time. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flockhart, D.A.; O'Kane, D.; Williams, M.S.; Watson, M.S.; Gage, B.; Gandolfi, R.; King, R.; Lyon, E.; Nussbaum, R.; Schulman, K.; Veenstra, D. Pharmacogenetic testing of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 alleles for warfarin. Genet. Med. 2008, 10, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, P.; Cox, D.G. Study designs for genome-wide association studies. Adv. Genet. 2008, 60, 465–504. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakaoka, H.; Inoue, I. Meta-analysis of genetic association studies: methodologies, between-study heterogeneity and winner's curse. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 54, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raychaudhuri, S.; Plenge, R.M.; Rossin, E.J.; Ng, A.C.; Purcell, S.M.; Sklar, P.; Scolnick, E.M.; Xavier, R.J.; Altshuler, D.; Daly, M.J. Identifying relationships among genomic disease regions: predicting genes at pathogenic SNP associations and rare deletions. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, E.W. Ethical, legal, and social implications of genomic medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an Open Access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Anderson, M.W.; Schrijver, I. Next Generation DNA Sequencing and the Future of Genomic Medicine. Genes 2010, 1, 38-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes1010038
Anderson MW, Schrijver I. Next Generation DNA Sequencing and the Future of Genomic Medicine. Genes. 2010; 1(1):38-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes1010038
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnderson, Matthew W., and Iris Schrijver. 2010. "Next Generation DNA Sequencing and the Future of Genomic Medicine" Genes 1, no. 1: 38-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes1010038
APA StyleAnderson, M. W., & Schrijver, I. (2010). Next Generation DNA Sequencing and the Future of Genomic Medicine. Genes, 1(1), 38-69. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes1010038