Sustainable and Low Viscous 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium Acetate + PEG Solvent for Cellulose Processing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dissolution of Cellulose in [Amim][CH3COO]/PEG Solvents
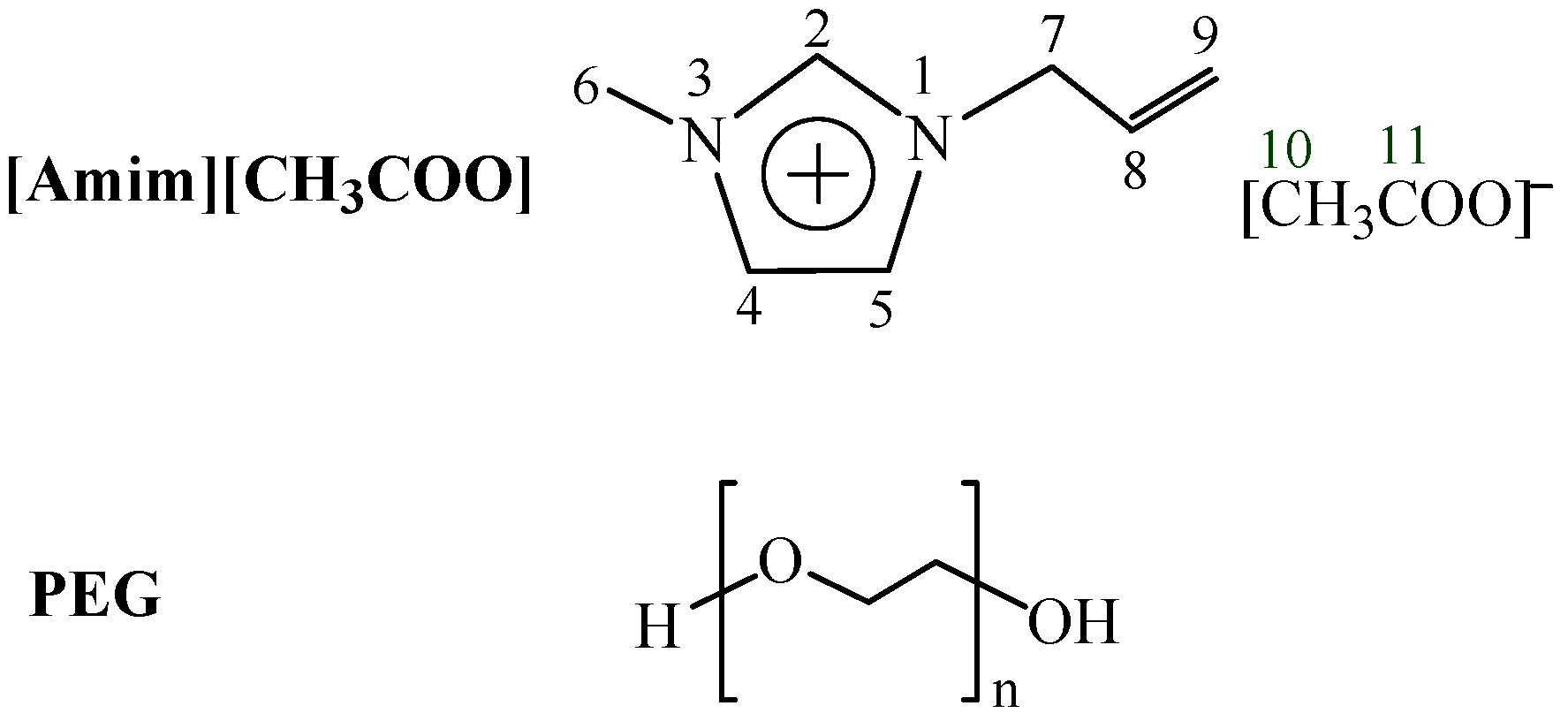
2.3. Measurements 13C NMR Spectra
2.4. Preparation and Characterization of Regenerated Cellulose Film
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dissolution Behavior of Cellulose in [Amim][CH3COO]/PEG Solvent
3.2. Possible Dissolution Mechanism of Cellulose in [Amim][CH3COO]/PEG Solvent
3.3. Recovery of [Amim][CH3COO]/PEG Solvent
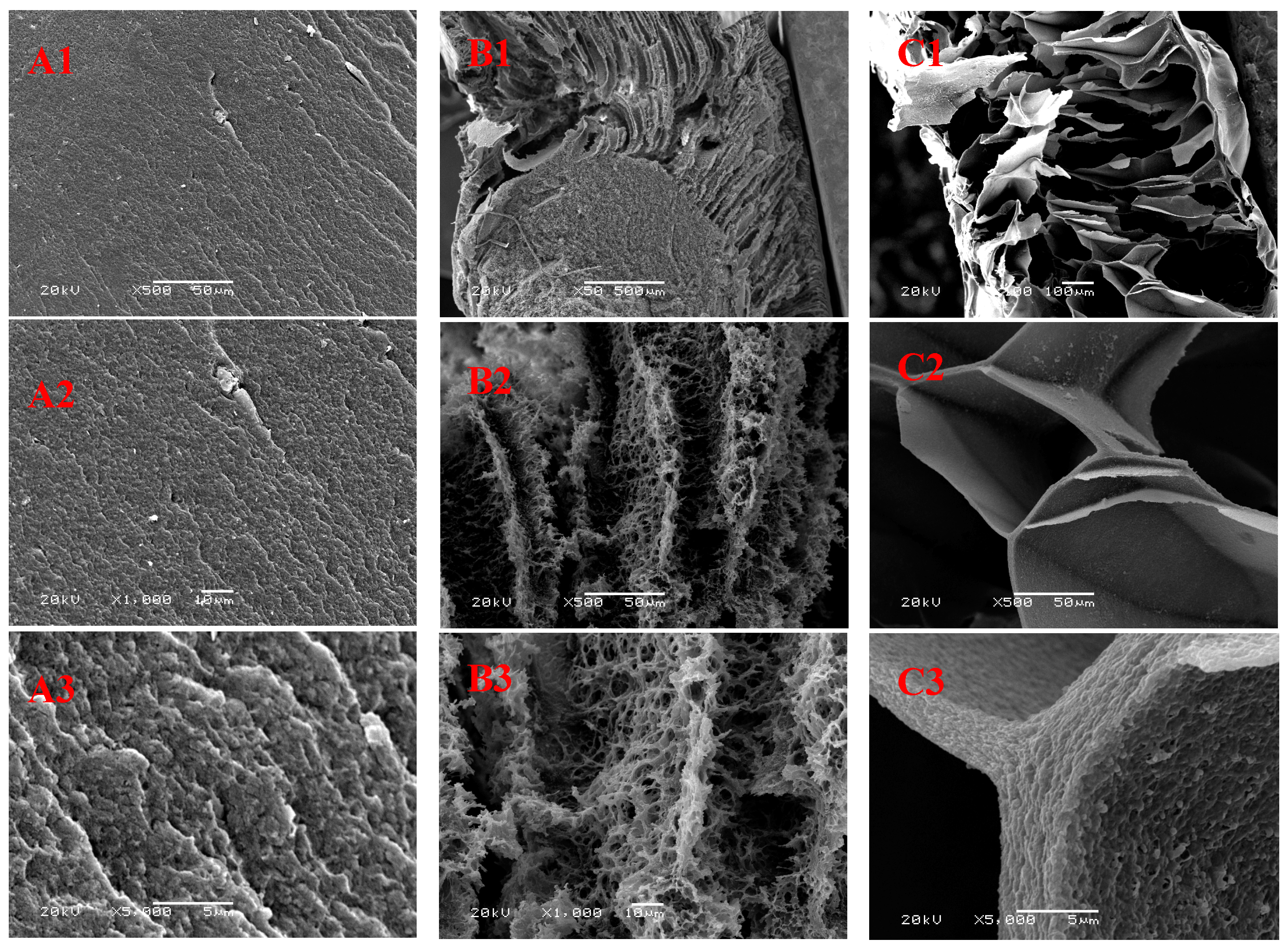
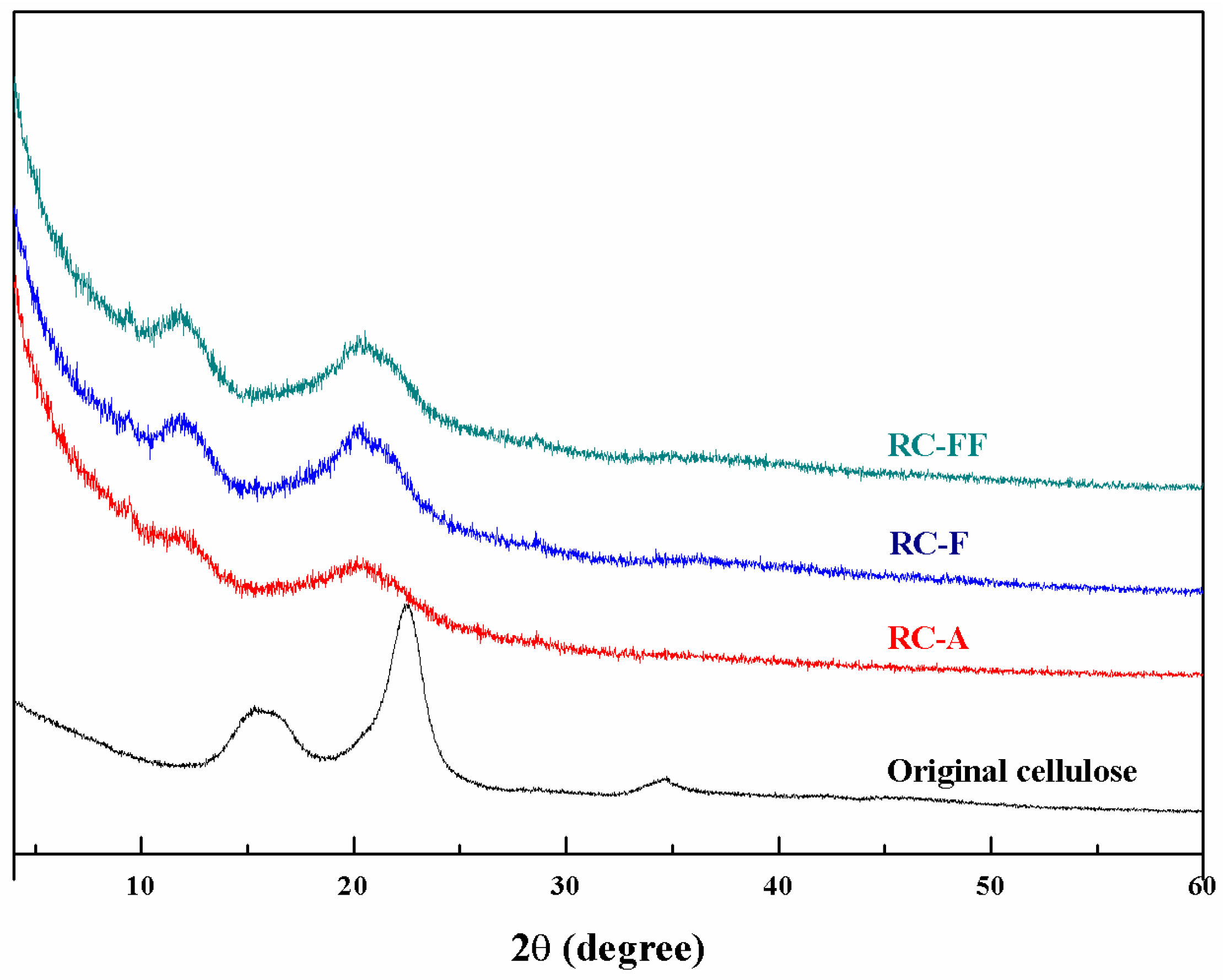
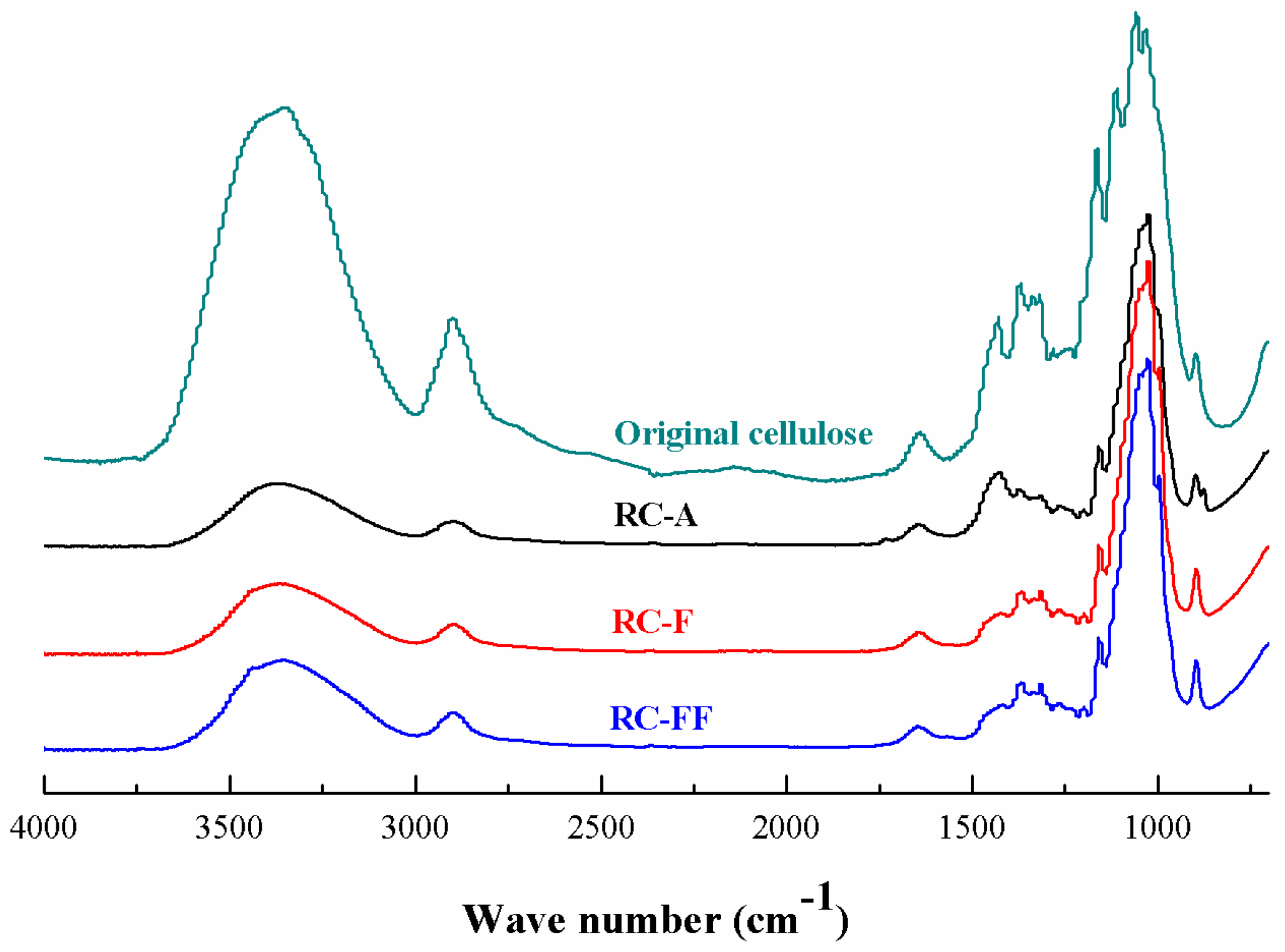
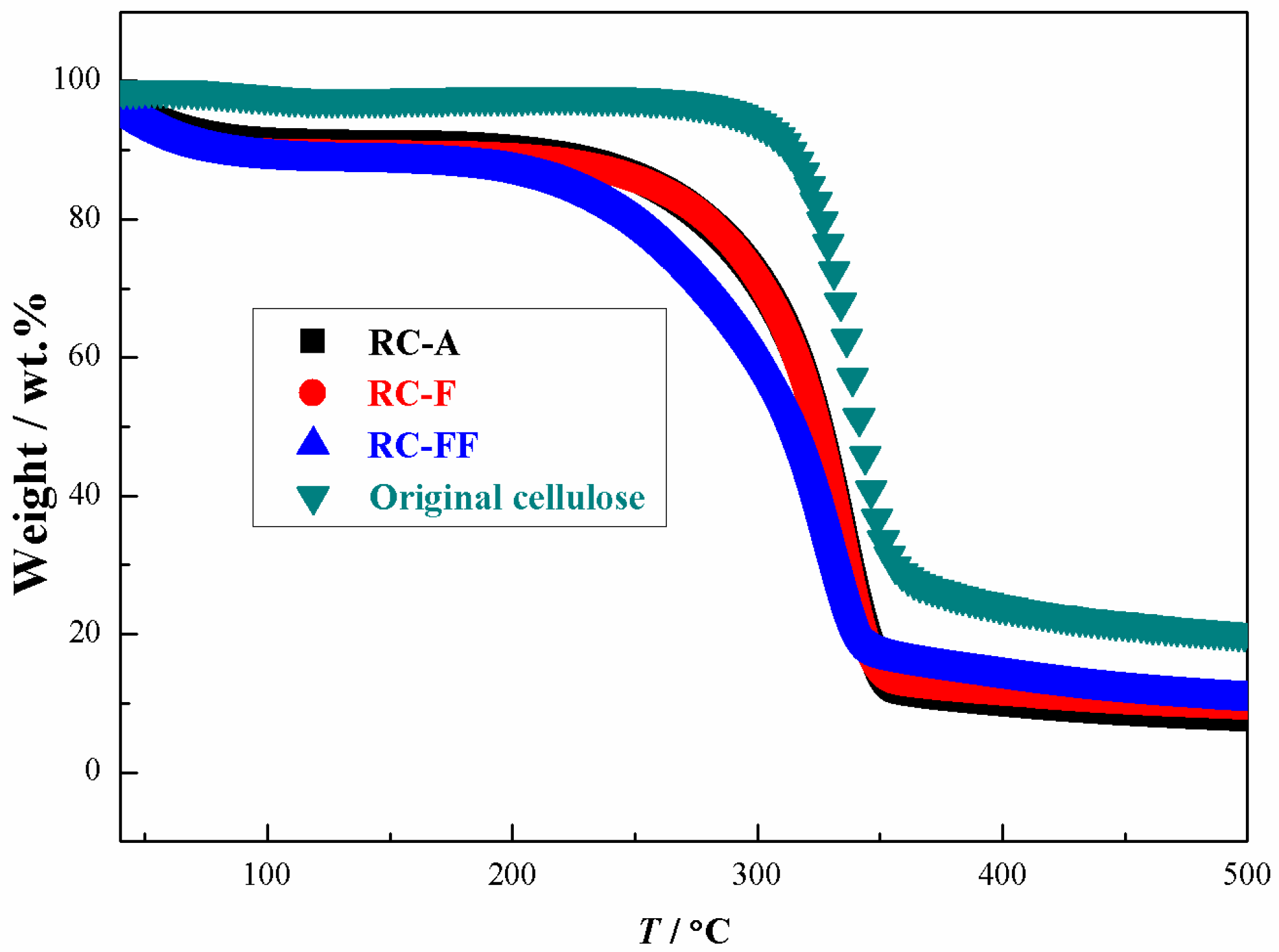
3.4. Properties of the Regenerated Cellulose Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graca, M.P.F.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Faria, F.A.C.; Evtuguin, D.V.; Gomes, M.T.S.R.; Oliveira, J.A.B.P.; Costa, L.C. Electrochemical impedance study of the lignin-derived conducting polymer. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 76, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozite, L.; Varna, J.; Joffe, R.; Pupurs, A. Nonlinear behavior of PLA and lignin-based flax composites subjected to tensile loading. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2013, 26, 476–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanutz, F.; Gähr, F.; Uerdingen, E.; Meister, F.; Kosan, B. New developments in dissolving and processing of cellulose in ionic liquids. Macromol. Symp. 2008, 262, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, C.L.; Dawsey, T.R. Preparation of cellulose derivatives via ring-opening N-dimethylacetamide. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 3606–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, T.; Liebert, T. Unconventional methods in cellulose functionalization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1689–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.N.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, J.P.; Cai, J. Effects of coagulation conditions on the properties of regenerated cellulose films prepared in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gurau, G.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquid processing of cellulose. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1519–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Xu, A.R.; Lu, B.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, J.J. Dissolution of cellulose in 1-allyl-3-methylimizodalium carboxylatesat room temperature: A structure–property relationship study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.F.; Chi, Y.L.; Mu, T.C. Studies on staged precipitation of cellulose from an ionic liquid by compressed carbon dioxide. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2736–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaya, Y.; Sugimoto, A.; Ohno, H. Superior solubility of polysaccharides in low viscosity, polar, and halogen-free 1,3-dialkylimidazolium formats. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3295–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.F.; Feng, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, R.H.; Liu, G.Q.; Cheng, G. Thermogravimetric analysis of lignocellulosic biomass with ionic liquid pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 153, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitz, J.; Erdmenger, T.; Haensch, C.; Schubert, U.S. Extended dissolution studies of cellulose in imidazolium based ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, R. Instantaneous dissolution of cellulose in organic electrolyte solutions. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.R.; Cao, L.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, B.J. Facile cellulose dissolution without heating in [C4mim][CH3COO]/DMF solvent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 125, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.R.; Guo, X.; Xu, R. Understanding the dissolution of cellulose in1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate + DMAc solvent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.R.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.J. Cellulose dissolution at ambient temperature: Role of preferential solvation of cations of ionic liquids by a cosolvent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.B.; Miao, J.J.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, L.P. Dissolution of cellulose with a novel solvent and formation of regenerated cellulose fiber. Appl. Phys. A. 2015, 119, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, D.M.; Khalfin, R.; Szekely, N.; Cohena, Y. True molecular solutions of natural cellulose in the binary ionic liquid-containing solvent mixtures. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.R.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, J.J. Densities and conductivities of seven 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium carboxylate ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.F.; Gao, Z.J. Dissolving of cellulose in PEG/NaOH aqueous solution. Cellulose 2008, 15, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuksanović, J.M.; Radović, I.R.; Šerbanović, S.P.; Kijevčanin, M.L. Experimental investigation of interactions and thermodynamic properties of poly(ethylene glycol) 200/400 + dimethyl adipate/dimethyl phthalate binary mixtures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 1910–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.X.; Xu, Q.; Xiao, J.B.; Wei, X.H. Excess properties and spectroscopic studies for binary system of polyethylene glycol 200 (1) + dimethyl sulfoxide (2) at T = (298.15 to 318.15) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Yoo, D.I.; Shin, Y.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Chung, Y.S.; Parkd, W.H.; Youk, J.H. Crystalline structure analysis of cellulose treated with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide by means of X-ray diffraction and FTIR spectroscopy. Carbohydy. Res. 2005, 340, 2376–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.Q.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.S. Room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs): A new and versatile platform for cellulose processing and derivatization. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 147, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.N.; Ruan, D.; Zhou, J.P. Structure and properties of regenerated cellulose films prepared from cotton linters in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 5923–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, H.G.; Stewart, C.M.; Harrington, K.J. Infrared spectra of cellulose and related polysaccharides. J. Polym. Sci. 1961, 51, 59–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, Y.; Kondo, T. FT-IR microscopic analysis of changing cellulose crystalline structure during wood cell wall formation. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, K.; Hongo, T.; Shirataki, H.; Yamane, C.; Ii, T. Influence of water on structure and mechanical properties of regenerated cellulose studied by an organized combination of infrared spectra, X-ray diffraction, and dynamic viscoelastic data measured as functions of temperature and humidity. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, L.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Chi, D.L. Properties of new natural fibers: Eulaliopsis binata fibers. J. Qingdao Univ. 2008, 23, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
| Solvent | Solubility (gram per 100 g of solvent) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 °C | 40 °C | 50 °C | 60 °C | 70 °C | |
| [Amim][CH3COO] | 14 | 16.0 | 16.5 | 18.0 | 21.0 |
| [Amim][CH3COO]/PEG-10 | 2.9 | 10.2 | 11.2 | 11.4 | 11.8 |
| [Amim][CH3COO]/PEG-20 | 0.9 | 2.0 | 5.0 | 5.5 | 5.8 |
| [Amim][CH3COO]/PEG-30 | Insoluble | Insoluble | Insoluble | Insoluble | Insoluble |
| Cellulose concentration (%) | C2 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | C11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 137.94 | 122.54 | 123.91 | 35.34 | 50.45 | 132.24 | 119.43 | 25.17 | 175.16 |
| 8 | 137.28 | 122.31 | 123.79 | 35.46 | 50.56 | 131.82 | 119.79 | 24.70 | 175.94 |
| ∆δ | –0.66 | –0.23 | –0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 | –0.42 | 0.36 | –0.47 | 0.78 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, A.; Li, Q. Sustainable and Low Viscous 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium Acetate + PEG Solvent for Cellulose Processing. Polymers 2017, 9, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9020054
Xu A, Li Q. Sustainable and Low Viscous 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium Acetate + PEG Solvent for Cellulose Processing. Polymers. 2017; 9(2):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9020054
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Airong, and Quan Li. 2017. "Sustainable and Low Viscous 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium Acetate + PEG Solvent for Cellulose Processing" Polymers 9, no. 2: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9020054
APA StyleXu, A., & Li, Q. (2017). Sustainable and Low Viscous 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium Acetate + PEG Solvent for Cellulose Processing. Polymers, 9(2), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9020054