Evolution of Surface Nanopores in Pressurised Gyrospun Polymeric Microfibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials
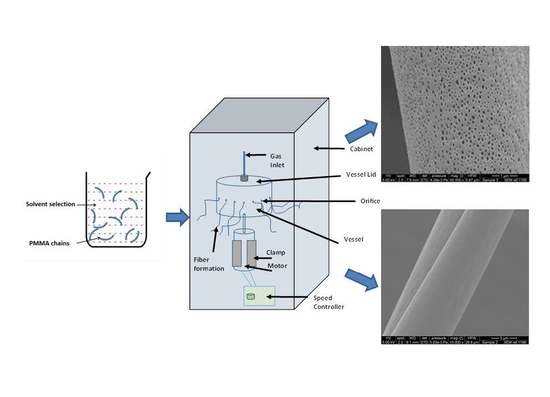
2.2. Preparation of Spinning Solutions
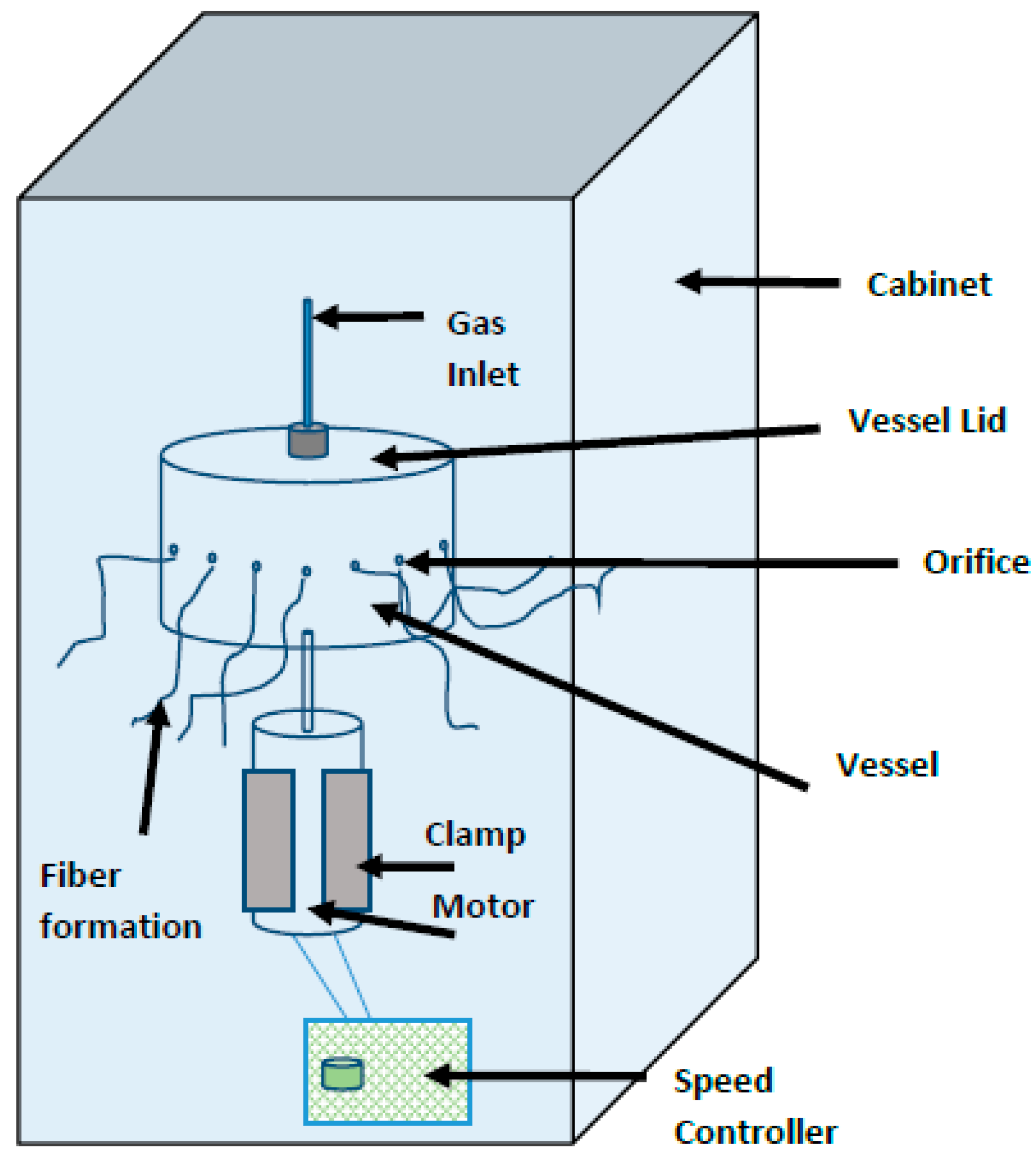
2.3. Pressurised Gyration
2.4. Fiber Characterisation
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
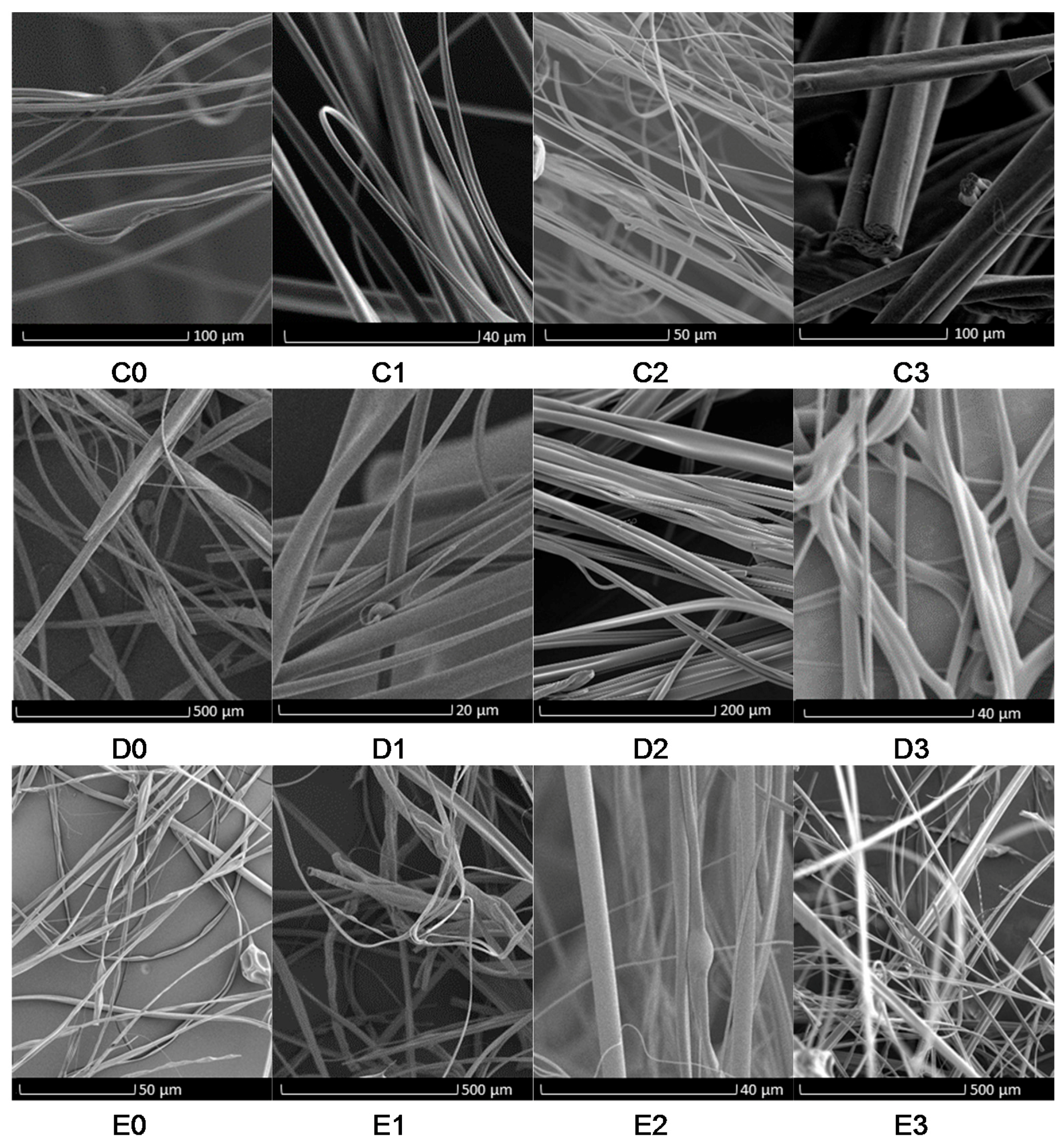
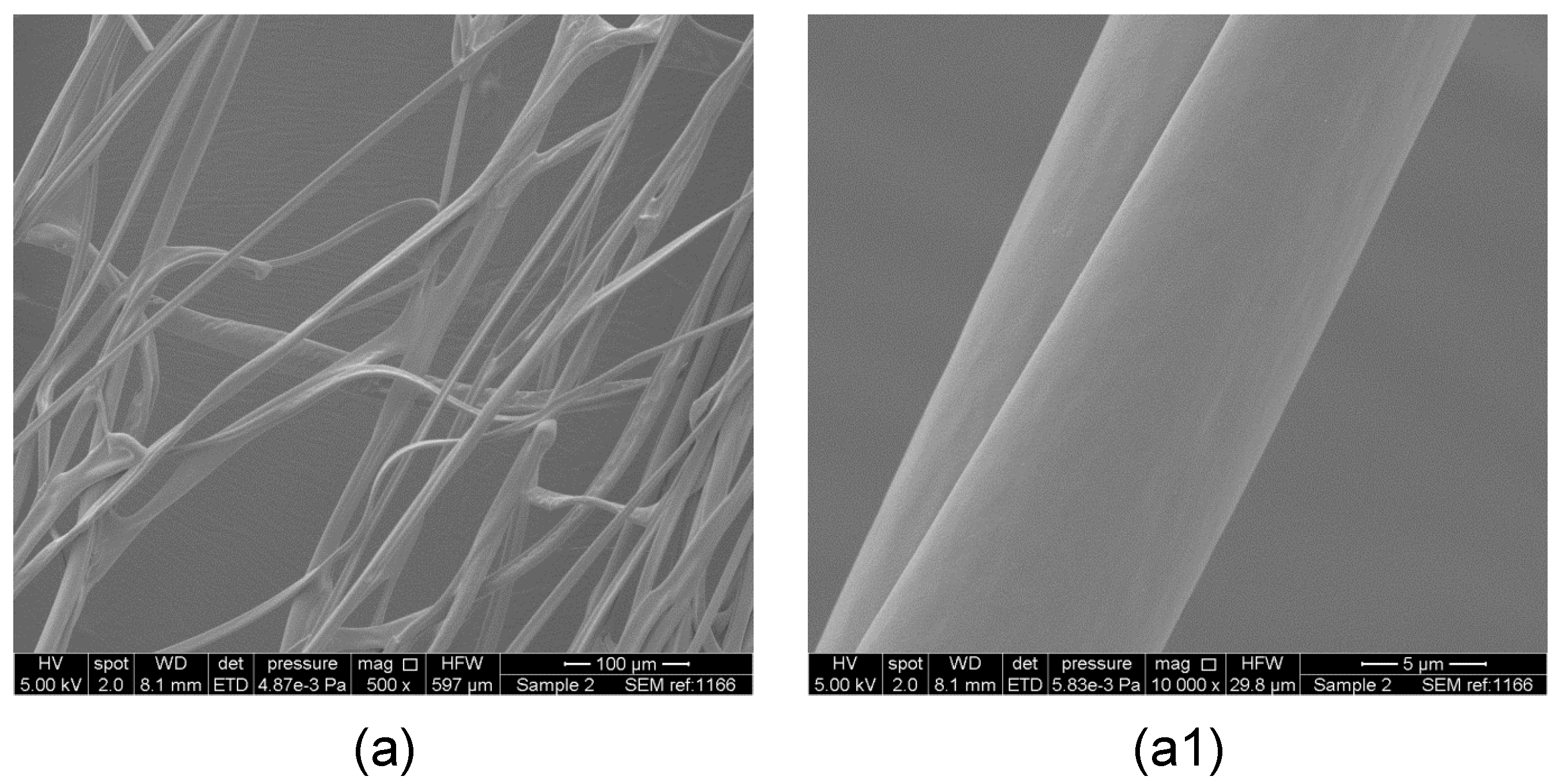
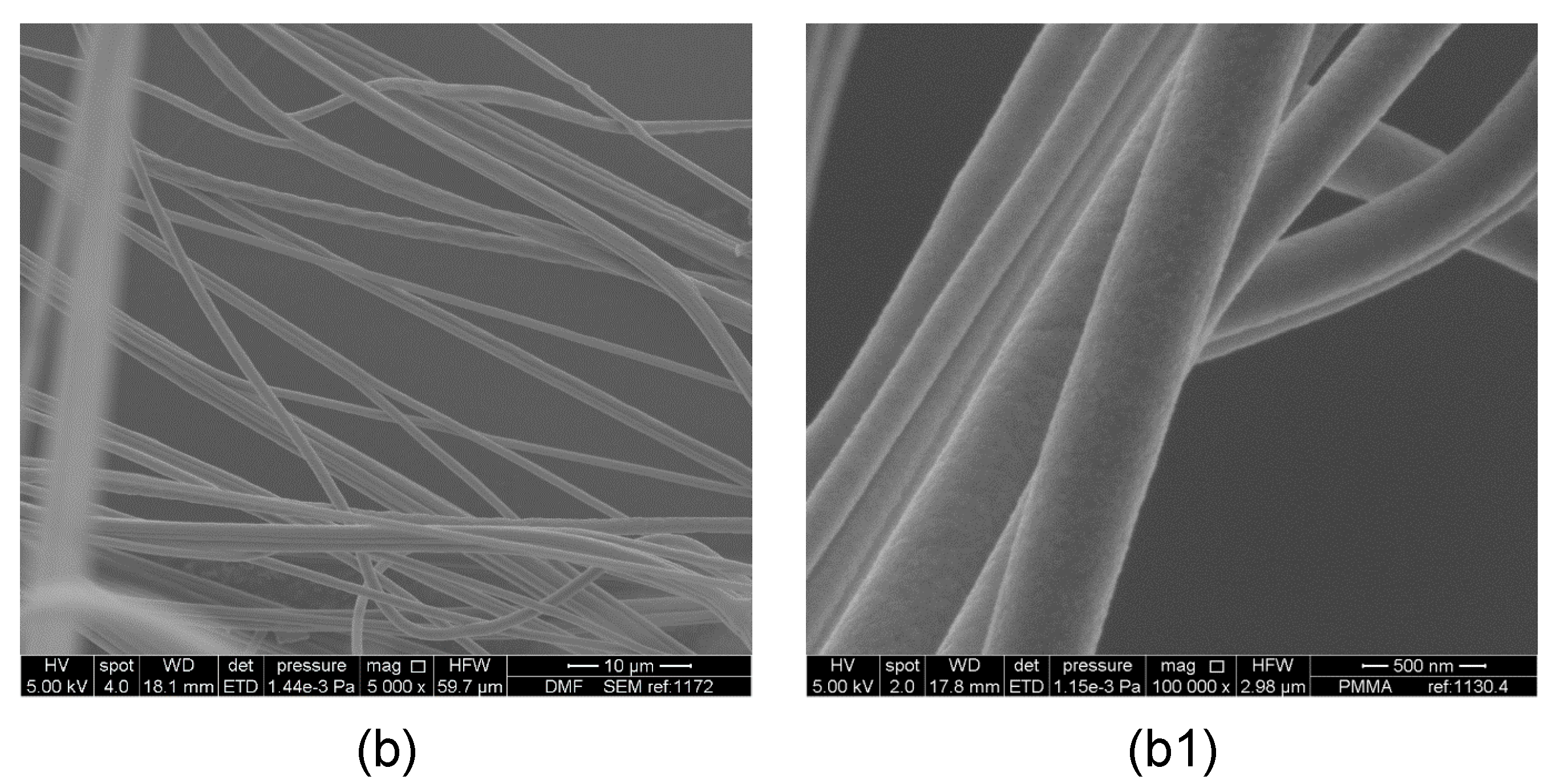
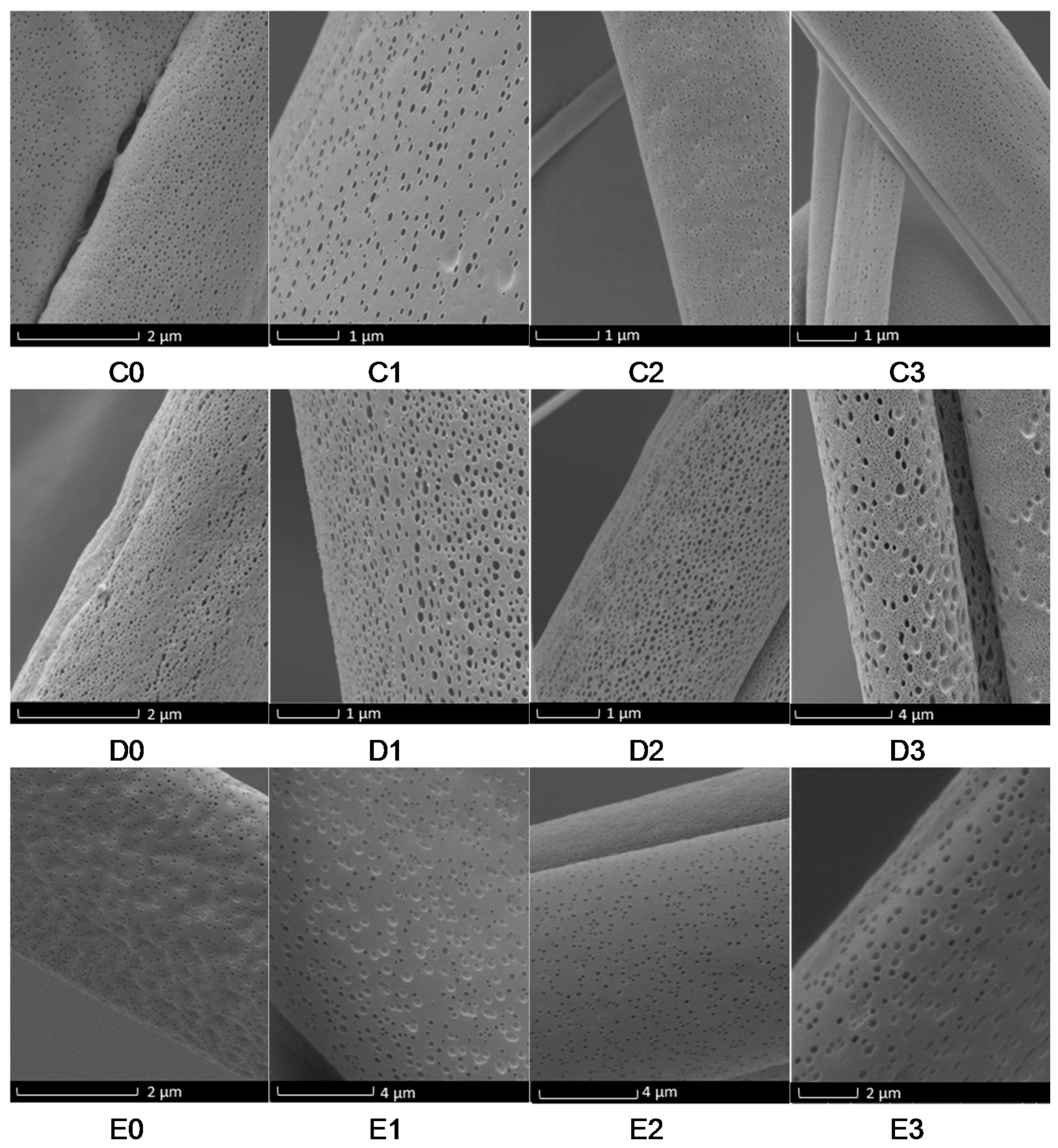
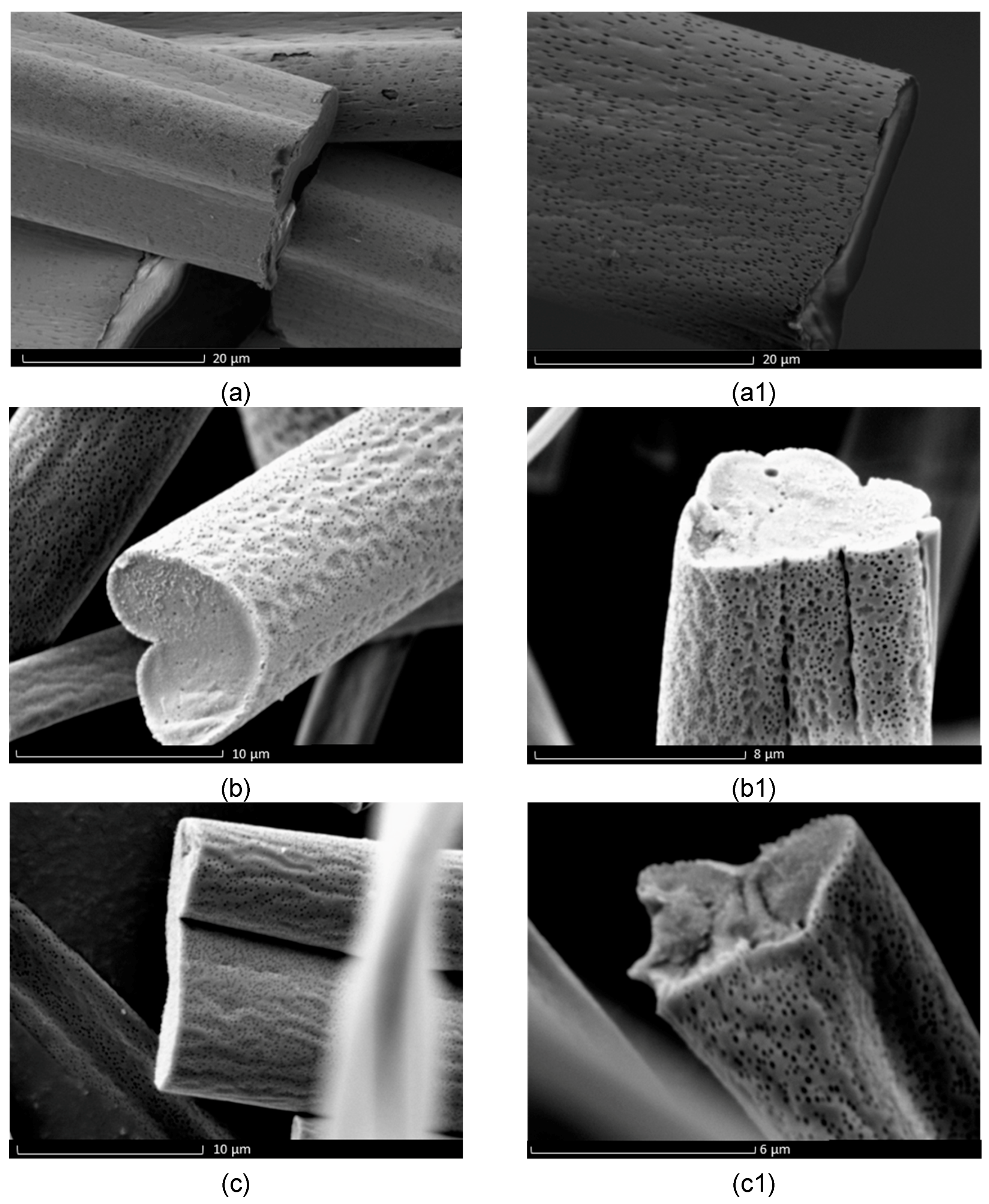
3. Results and Discussion
Evaluation of Microstructure of PMMA Fibers
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Megelski, S.; Stephens, J.S.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Micro- and nanostructured surface morphology on electrospun polymer fibers. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8456–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayi, A.S.; Pashuck, E.T.; Newcomb, C.J.; McClendon, M.T.; Stupp, S.I. Electrospinning bioactive supramolecular polymers from water. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontailler, M.; Illangakoon, E.; Williams, G.R.; Marijon, C.; Bellamy, V.; Balvay, D.; Autret, G.; Vanneaux, V.; Larghero, J.; Planat-Benard, V.; et al. Polymer-based reconstruction of the inferior vena cava in rat: Stem cells or rgd peptide? Tissue Eng. A 2015, 21, 1552–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazgan, G.; Dmitriev, R.I.; Tyagi, V.; Jenkins, J.; Rotaru, G.M.; Rottmar, M.; Rossi, R.M.; Toncelli, C.; Papkovsky, D.B.; Maniura-Weber, K.; et al. Steering surface topographies of electrospun fibers: Understanding the mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalingam, S.; Edirisinghe, M. Forming of polymer nanofibers by a pressurised gyration process. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalingam, S.; Raimi-Abraham, B.T.; Craig, D.Q.M.; Edirisinghe, M. Solubility–spinnability map and model for the preparation of fibres of polyethylene (terephthalate) using gyration and pressure. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illangakoon, U.E.; Mahalingam, S.; Colombo, P.; Edirisinghe, M. Tailoring the surface of polymeric nanofibres generated by pressurised gyration. Surf. Innov. 2016, 4, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illangakoon, U.E.; Mahalingam, S.; Wang, K.; Cheong, Y.K.; Canales, E.; Ren, G.G.; Cloutman-Green, E.; Edirisinghe, M.; Ciric, L. Gyrospun antimicrobial nanoparticle loaded fibrous polymeric filters. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimi-Abraham, B.T.; Mahalingam, S.; Davies, P.J.; Edirisinghe, M.; Craig, D.Q.M. Development and characterization of amorphous nanofiber drug dispersions prepared using pressurized gyration. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 3851–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.W.; Mahalingam, S.; Basnett, P.; Raimi-Abraham, B.; Roy, I.; Craig, D.; Edirisinghe, M. Making nonwoven fibrous poly(epsilon-caprolactone) constructs for antimicrobial and tissue engineering applications by pressurized melt gyration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 301, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, S.; Ren, G.G.; Edirisinghe, M.J. Rheology and pressurised gyration of starch and starch-loaded poly(ethylene oxide). Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 114, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, R.; Li, M.; Rong, Z.; Fang, T. Theoretical selection of solvent for production of electrospun pmma fibers with wrinkled surfaces. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 27914–27921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, D. Polymer chemistry—The basic concepts, p. C. Hiemenz, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1984, 738 pp. No price given. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Lett. Ed. 1984, 22, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Li, R.; Fang, T. Hierarchically structured pmma fibers fabricated by electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 52973–52985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, P.; Liu, J.; Kumar, S.; Kyu, T. Experimental and theoretical investigations of porous structure formation in electrospun fibers. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 7689–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bauer, A.J.P.; Li, B. Solvent vapor annealing: An efficient approach for inscribing secondary nanostructures onto electrospun fibers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2014, 35, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selling, G.W.; Biswas, A.; Patel, A.; Walls, D.J.; Dunlap, C.; Wei, Y. Impact of solvent on electrospinning of zein and analysis of resulting fibers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2007, 208, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattamaprom, C.; Hongrojjanawiwat, W.; Koombhongse, P.; Supaphol, P.; Jarusuwannapoo, T.; Rangkupan, R. The influence of solvent properties and functionality on the electrospinnability of polystyrene nanofibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2006, 291, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, D.; Heinrich, S.; Greil, P. Solvent control of cellulose acetate nanofibre felt structure produced by electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Han, C.C. Construction of hierarchical structures by electrospinning or electrospraying. Polymer 2012, 53, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Electrospun porous cellulose acetate fibers from volatile solvent mixture. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 2291–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, X.-Y.; Lin, F.-W.; Huang, X.-J.; Liang, H.-Q.; Xu, Z.-K. Polymer fibers with hierarchically porous structure: Combination of high temperature electrospinning and thermally induced phase separation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 13851–13858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainudeen, S.S.; Asok, L.B.; Varghese, A.; Nair, A.S.; Krishnan, G. Surfactant-driven direct synthesis of a hierarchical hollow mgo nanofiber-nanoparticle composite by electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35160–35168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Tian, B.; Ke, Q.-F.; Zhu, Z.-A.; Guo, Y.-P. Gentamicin-loaded carbonated hydroxyapatite coatings with hierarchically porous structures: Drug delivery properties, bactericidal properties and biocompatibility. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 41500–41509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Walsh, F.; Gludovatz, B.; Delattre, B.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Tomsia, A.P.; Ritchie, R.O. Bioinspired hydroxyapatite/poly(methyl methacrylate) composite with a nacre-mimetic architecture by a bidirectional freezing method. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, E.; Saralidze, K.; Roth, A.K.; de Jong, J.J.A.; van den Bergh, J.P.W.; Lataster, A.; Brans, B.T.; Knetsch, M.L.W.; Djordjevic, I.; Willems, P.C.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of a new vertebroplasty cement based on gold-containing pmma microspheres. Biomaterials 2016, 82, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caro-Osorio, E.; De la Garza-Ramos, R.; Martínez-Sánchez, S.R.; Olazarán-Salinas, F. Cranioplasty with polymethylmethacrylate prostheses fabricated by hand using original bone flaps: Technical note and surgical outcomes. Surg. Neur. Int. 2013, 4, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canché-Escamilla, G.; Duarte-Aranda, S.; Toledano, M. Synthesis and characterization of hybrid silica/pmma nanoparticles and their use as filler in dental composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 42, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, R.; Tirrell, D.A. Designing materials for biology and medicine. Nature 2004, 428, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. New challenges in biomaterials. Science 1994, 263, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupančič, Š.; Sinha-Ray, S.; Sinha-Ray, S.; Kristl, J.; Yarin, A.L. Long-term sustained ciprofloxacin release from pmma and hydrophilic polymer blended nanofibers. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brint, S.F.; Ostrick, D.M.; Bryan, J.E. Keratometric cylinder and visual performance following phacoemulsification and implantation with silicone small-incision or poly(methyl methacrylate) intraocular lenses. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 1991, 17, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morariu, M.D.; Voicu, N.E.; Schaffer, E.; Lin, Z.; Russell, T.P.; Steiner, U. Hierarchical structure formation and pattern replication induced by an electric field. Nat Mater 2003, 2, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, R.; Liu, S.; Liang, F.; Wang, K.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Z. Polymeric janus particles with hierarchical structures. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 3701–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters: A user’s Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, H.; Bao, Y.; Xu, L.; Yan, D.-X.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Wang, J.-H.; Li, Z.-M. Double-segregated carbon nanotube-polymer conductive composites as candidates for liquid sensing materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 4177–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, J.F.; Lu, J.; Zhang, K.; Kumar, B.; Castro, M.; Gatt, N.; Choi, H.J. Novel architecture of carbon nanotube decorated poly(methyl methacrylate) microbead vapour sensors assembled by spray layer by layer. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 4142–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.-H.; Liu, P.; He, J.-H. Tunable surface morphology of electrospun pmma fiber using binary solvent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 364, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Bai, H.; Li, L. Breath figure: A nature-inspired preparation method for ordered porous films. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9801–9868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.-C.; Kuo, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J.; Chen, W.-C. Highly ordered luminescent microporous films prepared from crystalline conjugated rod-coil diblock copolymers of pf-b-psa and their superhydrophobic characteristics. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9350–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasarao, M.; Collings, D.; Philips, A.; Patel, S. Three-dimensionally ordered array of air bubbles in a polymer film. Science 2001, 292, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.S.; Kim, J.K. Breath figure patterns prepared by spin coating in a dry environment. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5347–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, Y.; Muto, I.; Shimojima, A.; Wada, H.; Kuroda, K. Nanospace-mediated self-organization of nanoparticles in flexible porous polymer templates. Langmuir 2017, 33, 9137–9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Mahalingam, S.; Rohn, J.L.; Ren, G.; Edirisinghe, M. Physio-chemical and antibacterial characteristics of pressure spun nylon nanofibres embedded with functional silver nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 56, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, X.; Edirisinghe, M.; Mahalingam, S. Beads, beaded-fibres and fibres: Tailoring the morphology of poly(caprolactone) using pressurised gyration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 69, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| PMMA | Chloroform | Acetone | DMF | Ethyl Acetate | DCM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Volume (cm3·mol−1) | - | 79.70 | 73.52 | 76.95 | 98.50 | 63.90 |
| Vapour pressure (mm/Hg) | - | 160 | 184 | 2.70 | 73 | 353 |
| Vapour density (vs.·air) | - | 4.1 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 2.9 |
| Boiling point (°C) | - | 61 | 56 | 153 | 77 | 40 |
| δD (J·cm3)1/2 | 17.00 | 17.80 | 15.50 | 17.40 | 15.80 | 18.20 |
| δP (J·cm3)1/2 | 5.80 | 3.10 | 10.40 | 13.70 | 5.30 | 6.30 |
| δh (J·cm3)1/2 | 9.20 | 5.70 | 7.00 | 11.30 | 7.20 | 6.10 |
| δ (J·cm3)1/2 | 22.20 | 18.95 | 19.93 | 24.86 | 18.20 | 20.20 |
| χ12 | - | 0.34 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.64 | 0.10 |
| Ra | - | 8.25 | 3.72 | 3.99 | 5.98 | 5.67 |
| Pressure (MPa) | Fiber Diameter (µm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroform | Dichloromethane | Ethyl Acetate | DMF | Acetone | |
| 0 | 2.9 ± 2.5 | 5.5 ± 2.2 | 4.5 ± 2.3 | - | - |
| 0.1 | 3.3 ± 1.2 | 4.3 ± 2.1 | 5.1 ± 1.1 | 1 ± 0.4 | 11 ± 3 |
| 0.2 | 2.9 ± 1.5 | 3.9 ± 1.6 | 4.8 ± 2.3 | - | - |
| 0.3 | 2.8 ± 1.8 | 3.7 ± 1.9 | 4.7 ± 2.8 | - | - |
| Pressure (MPa) | Pore Size (nm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroform | Dichloromethane | Ethyl Acetate | |
| 0 | 54 ± 12 | 42 ± 12 | 121 ± 23 |
| 0.1 | 126 ± 18 | 126 ± 33 | 199 ± 54 |
| 0.2 | 109 ± 20 | 104 ± 43 | 400 ± 80 |
| 0.3 | 44 ± 10 | 220 ± 180 | 124 ± 23 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Illangakoon, U.E.; Mahalingam, S.; Matharu, R.K.; Edirisinghe, M. Evolution of Surface Nanopores in Pressurised Gyrospun Polymeric Microfibers. Polymers 2017, 9, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100508
Illangakoon UE, Mahalingam S, Matharu RK, Edirisinghe M. Evolution of Surface Nanopores in Pressurised Gyrospun Polymeric Microfibers. Polymers. 2017; 9(10):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100508
Chicago/Turabian StyleIllangakoon, U. Eranka, Suntharavathanan Mahalingam, Rupy K. Matharu, and Mohan Edirisinghe. 2017. "Evolution of Surface Nanopores in Pressurised Gyrospun Polymeric Microfibers" Polymers 9, no. 10: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100508
APA StyleIllangakoon, U. E., Mahalingam, S., Matharu, R. K., & Edirisinghe, M. (2017). Evolution of Surface Nanopores in Pressurised Gyrospun Polymeric Microfibers. Polymers, 9(10), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9100508