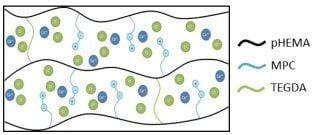
Release of Potassium Ion and Calcium Ion from Phosphorylcholine Group Bearing Hydrogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents
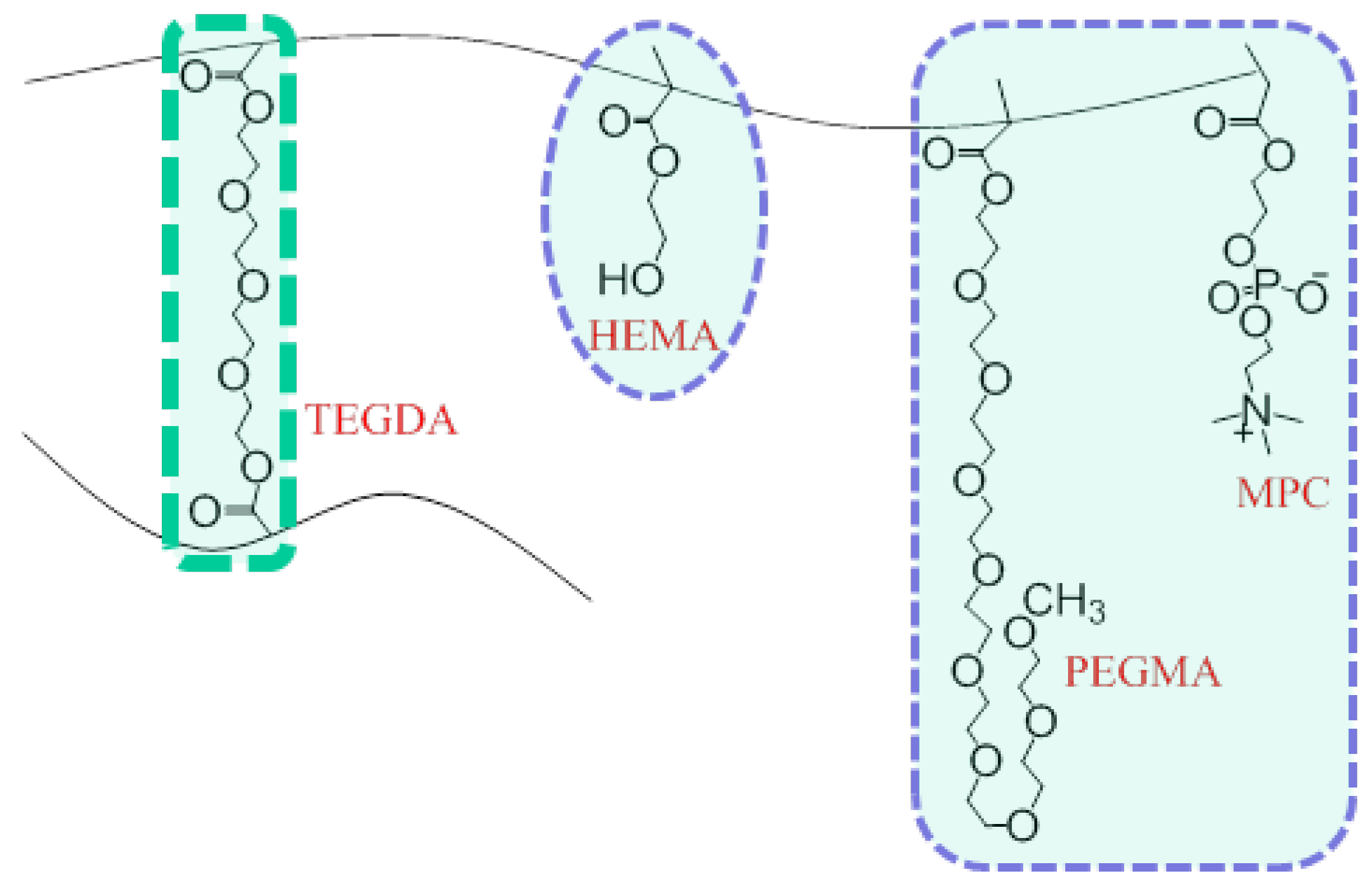
2.2. Preparation of Monomer Cocktail and Synthesis of Hydrogel Discs
| Constituent | Mole fraction (mol %) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEMA | 85.0 | 83.0 | 81.0 | 79.0 | 77.0 | 74.0 |
| TEGDA | 1.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 9.0 | 12.0 |
| OEG(400)MA | 5.00 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| MPC | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
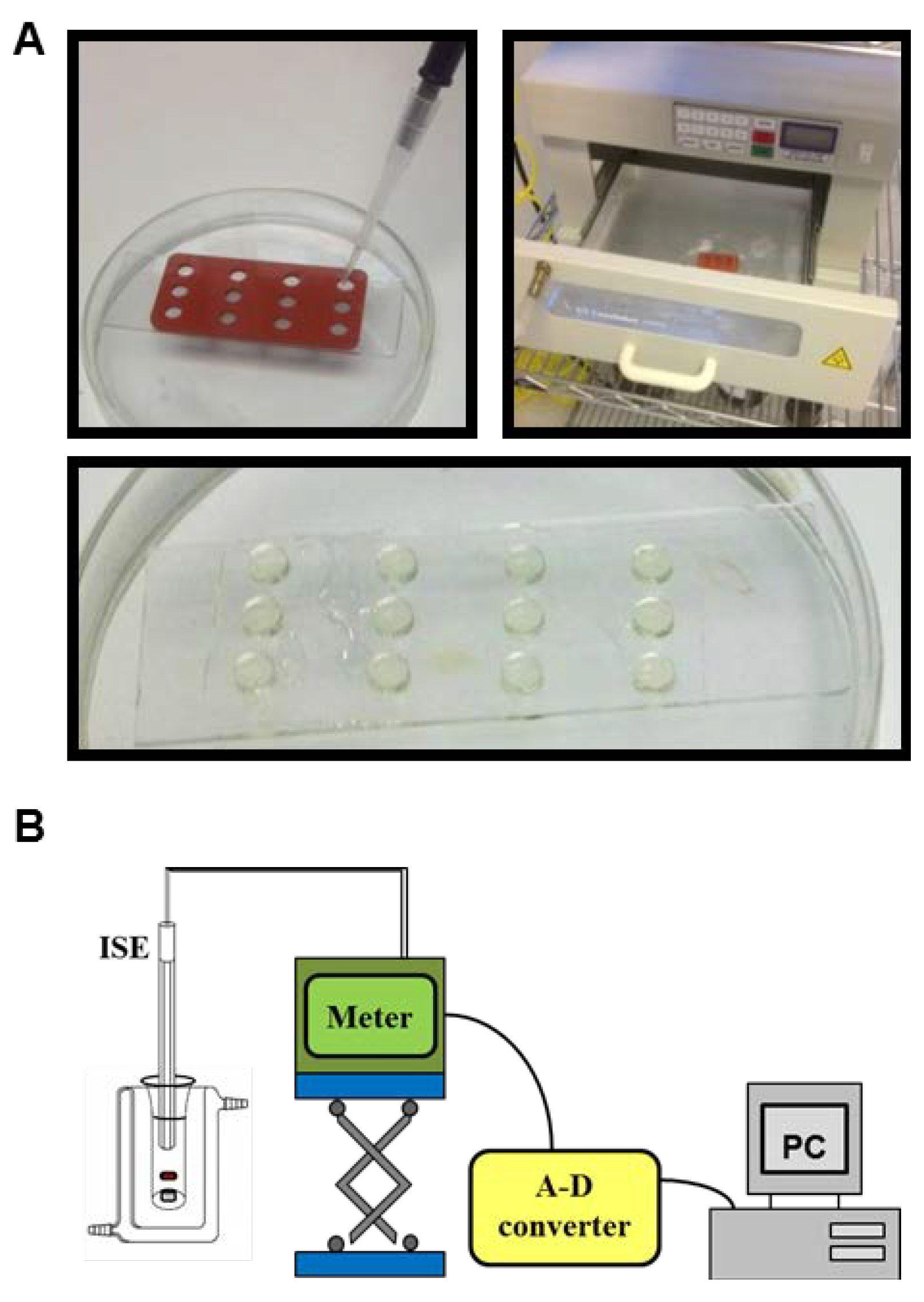
2.3. Release of Charged Species

| Model | Model Equation | Equation No. | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-Order |  | (2) | [25] |
| First-Order | 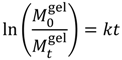 | (3) | [25] |
| Higuchi |  | (4) | [ 27] |
| Hixon-Crowell Cube Root | 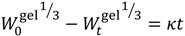 | (5) | [28] |
| Korsmeyer-Peppas | 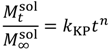 | (6) | [29] |
 is the initial concentration of cation present in the hydrogel,
is the initial concentration of cation present in the hydrogel,  is the concentration of cation present in the hydrogel at time t, k0 is the Zero-Order release constant, k is the First-Order release constant, kH is the Higuchi dissolution constant,
is the concentration of cation present in the hydrogel at time t, k0 is the Zero-Order release constant, k is the First-Order release constant, kH is the Higuchi dissolution constant,  is the mass of the salt initially present within the hydrogel,
is the mass of the salt initially present within the hydrogel,  is the mass of the salt at time t, and κ is a constant incorporating the relationship between the surface area and the volume of the salt molecule,
is the mass of the salt at time t, and κ is a constant incorporating the relationship between the surface area and the volume of the salt molecule,  is the concentration of the salt in the release solution at time t,
is the concentration of the salt in the release solution at time t,  is the equilibrium concentration of the salt in the release solution, kKP is the Korsmeyer-Peppas release rate constant, and is the diffusional exponent.
is the equilibrium concentration of the salt in the release solution, kKP is the Korsmeyer-Peppas release rate constant, and is the diffusional exponent. .
.| Diffusional exponent, n | Drug release mechanism | Rate as a function of time |
|---|---|---|
| ≥0.45 | Fickian diffusion | t−0.5 |
| 0.45 < n < 0.89 | Anomalous transport | tn−1 |
| 0.89 | Case-II transport | Zero-Order release |
| n > 0.89 | Super case-II transport | tn−1 |


3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Release Profiles of Ions
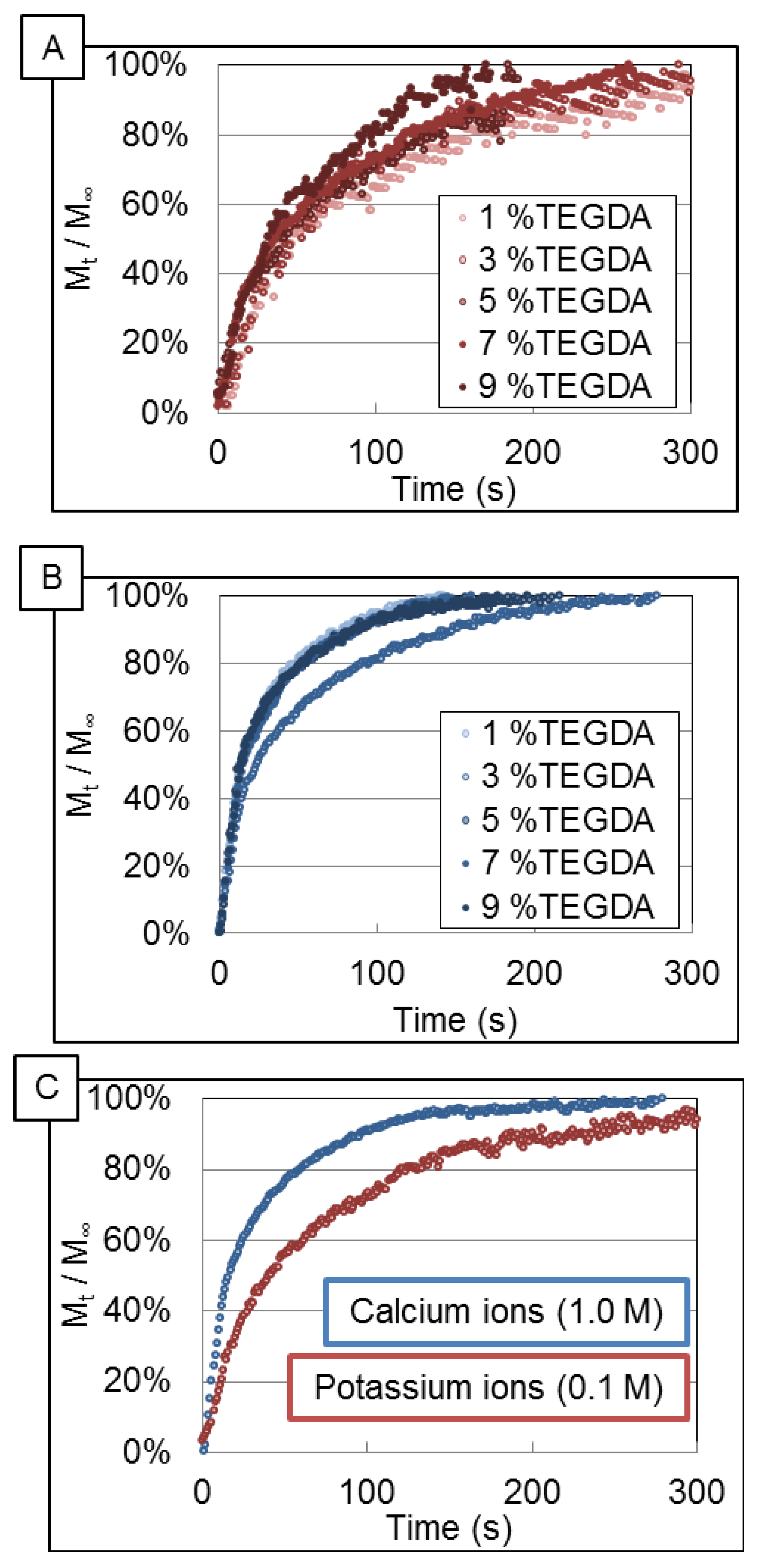
3.2. Data Analysis
| mol % Crosslinker | Zero-Order | First-Order | Higuchi | Hixson-Crowell | Korsmeyer-Peppas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium ion | |||||
| 1% TEGDA | −0.63 | 0.89 | 0.65 | −0.60 | 0.87 |
| 3% TEGDA | −0.34 | 0.91 | 0.75 | −0.32 | 0.88 |
| 5% TEGDA | −0.07 | 0.83 | 0.76 | −0.05 | 0.89 |
| 7% TEGDA | −0.10 | 0.91 | 0.87 | −0.04 | 0.96 |
| 9% TEGDA | 0.02 | 0.93 | 0.86 | 0.05 | 0.94 |
| Calcium ion | |||||
| 1% TEGDA | −2.01 | 0.94 | 0.28 | −1.99 | 0.90 |
| 3% TEGDA | −1.95 | 0.91 | 0.34 | −1.93 | 0.92 |
| 5% TEGDA | −2.32 | 0.91 | 0.17 | −2.29 | 0.88 |
| 7% TEGDA | −1.21 | 0.93 | 0.56 | −1.19 | 0.92 |
| 9% TEGDA | −1.35 | 0.90 | 0.50 | −1.33 | 0.91 |
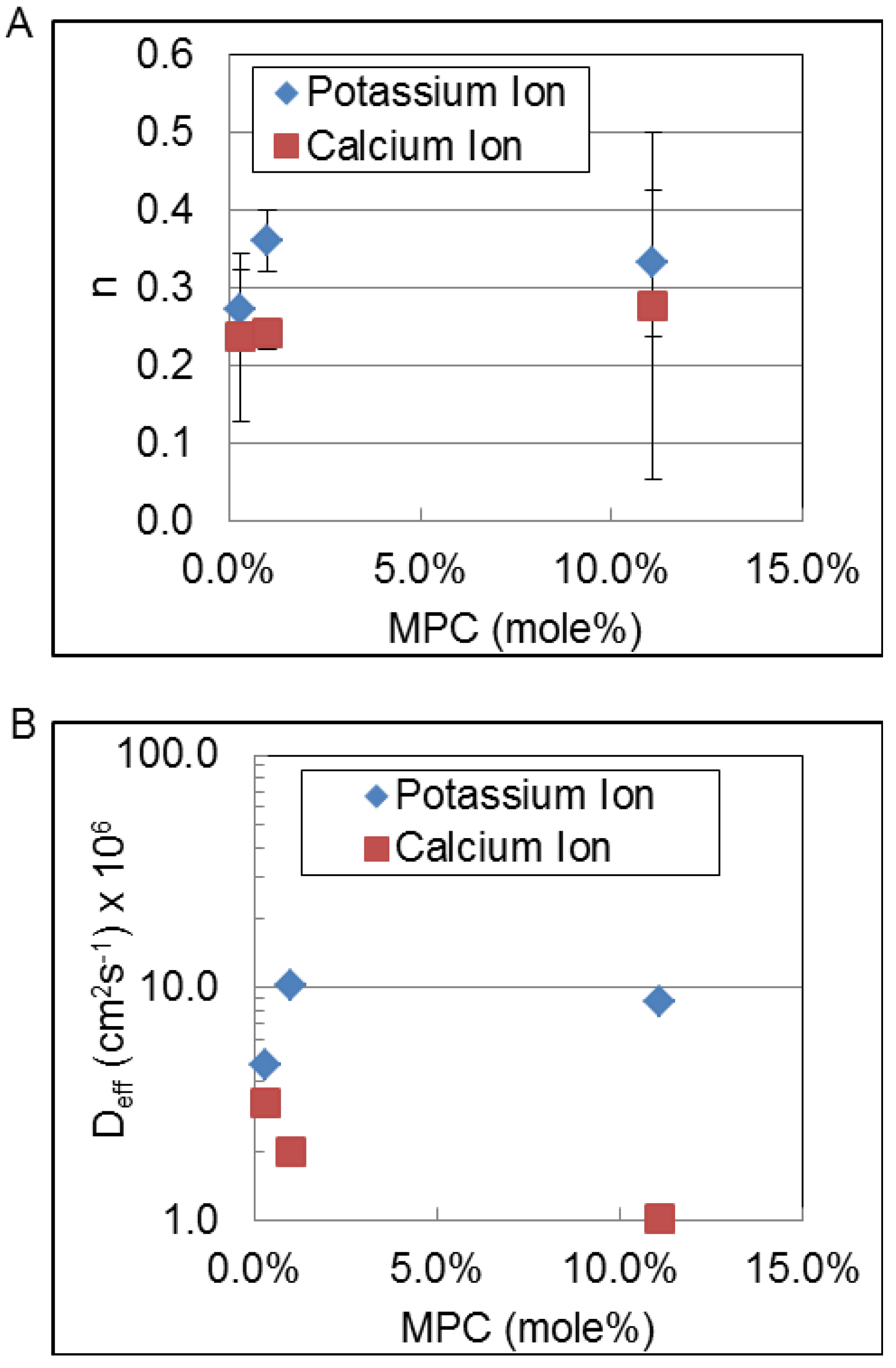
3.3. Korsmeyer-Peppas Fit Parameters
| Model parameter | Ion Type | % TEGDA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 7.0 | 9.0 | ||
| KKP | Calcium ion | 0.30 ± 0.09 | 0.25 ± 0.13 | 0.31 ± 0.08 | 0.24 ± 0.09 | 0.26 ± 0.12 |
| Potassium ion | 0.15 ± 0.84 † | 0.14 ± 0.11 † | 0.30 ± 0.32 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.12 ± 0.08 | |
| n | Calcium ion | 0.24 ± 0.11 | 0.25 ± 0.12 | 0.24 ± 0.07 | 0.27 ± 0.04 | 0.26 ± 0.05 |
| Potassium ion | 0.32 ± 0.90 † | 0.33 ± 0.16 † | 0.39 ± 0.36 | 0.35 ± 0.03 | 0.38 ± 0.18 | |
| Deff | Calcium ion | 3.2 ± 10 × 10−6 | 2.2 ± 5.9 × 10−6 | 1.4 ± 2.7 × 10−6 | 3.4 ± 4.4 × 10−6 | 3.0 ± 2.0 × 10−6 |
| Potassium ion | 3.5 ± 31 × 10−6† | 5.1 ± 14 × 10−6† | 17 ± 34 × 10−6 | 8.6 ± 4.2 × 10−6 | 17 ± 37 × 10−6 | |
4. Discussion

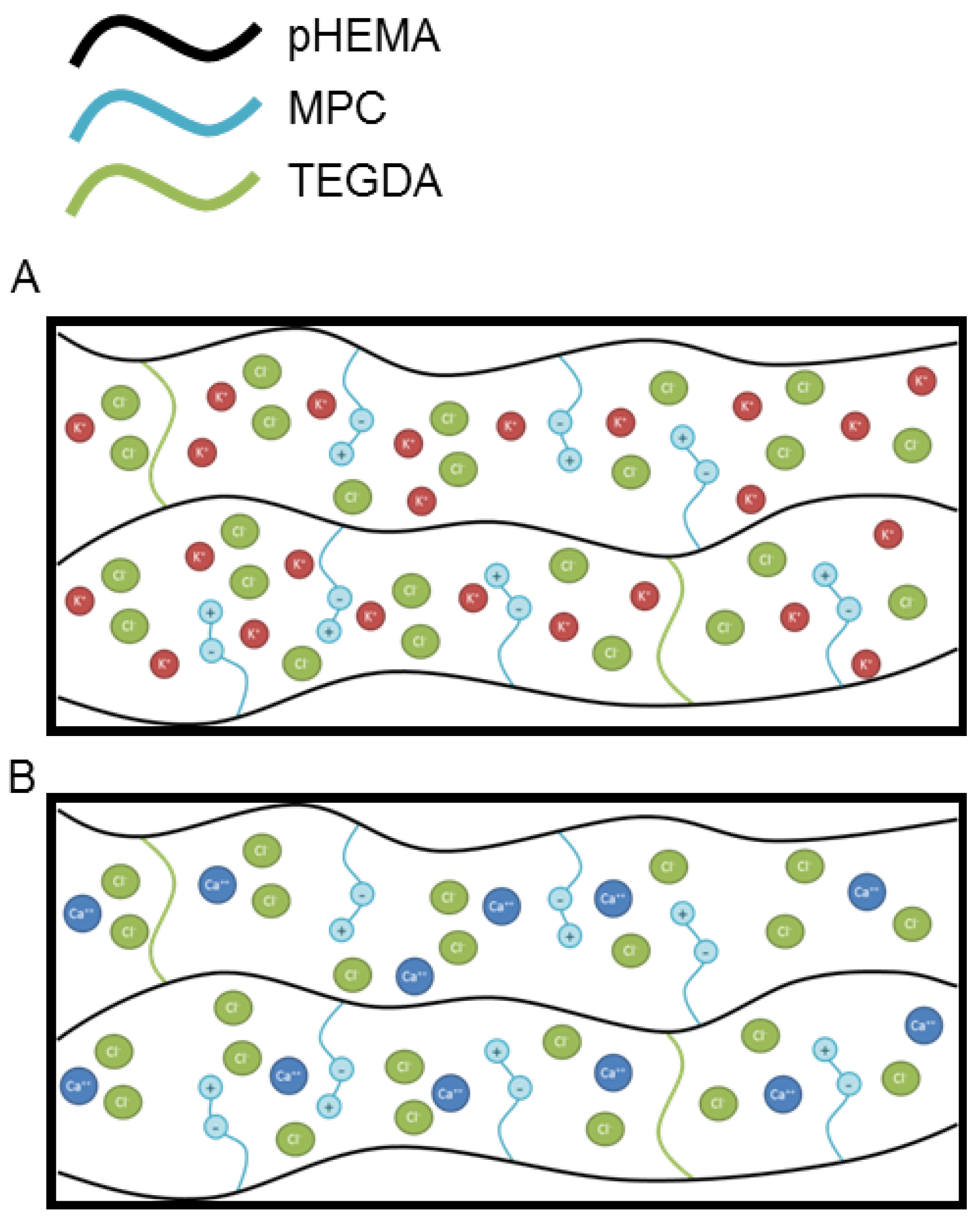
| Parameter | Deff | n |
|---|---|---|
| TEGDA mol % | 0.40 | 0.25 |
| Ion charge density | 0.68 | 0.92 |
| Charge per unit volume | −0.68 | −0.92 |
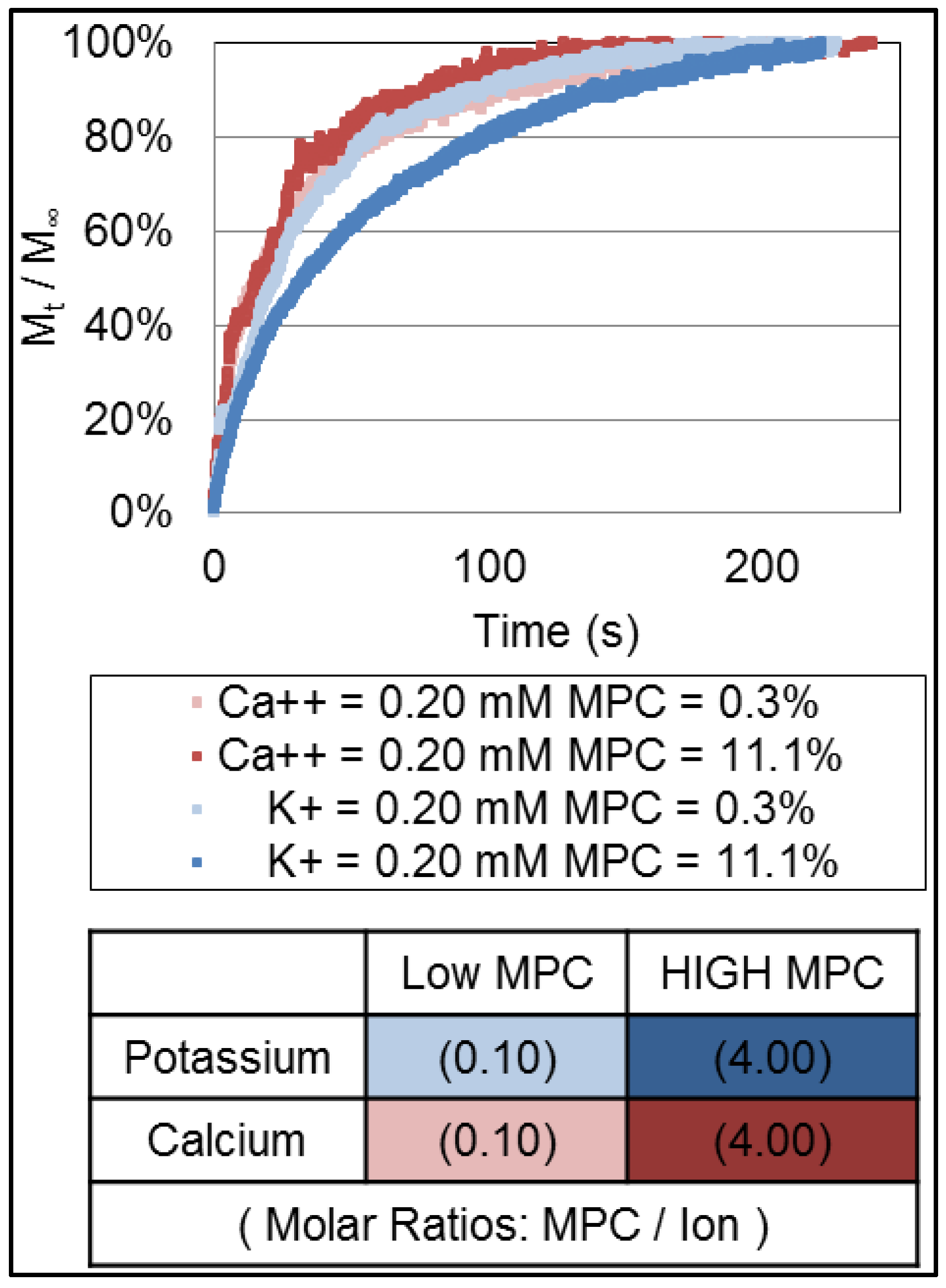
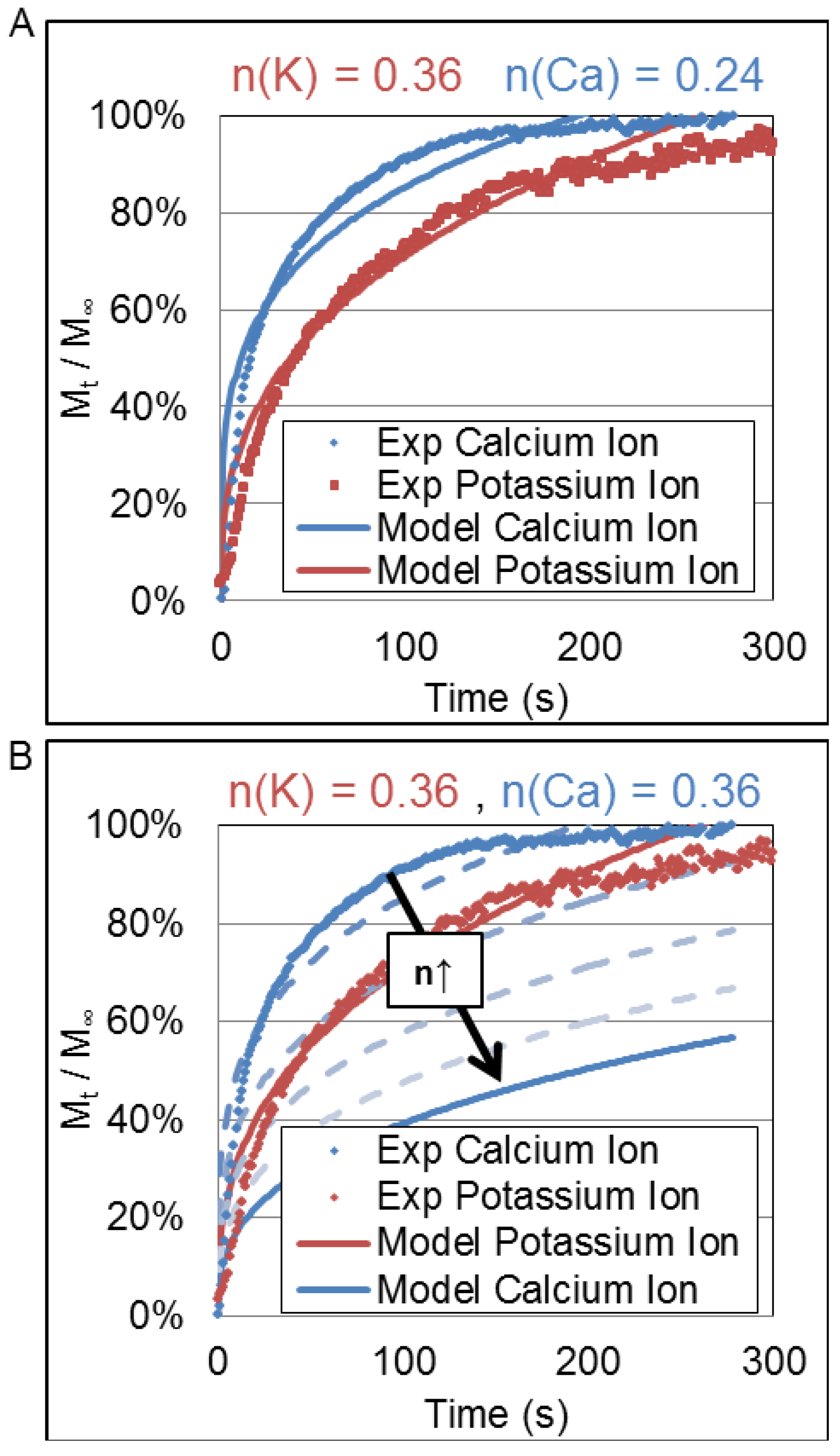
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karunwi, O.; Wilson, A.N.; Kotanen, C.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Engineering the abio-bio interface to enable more than moore in functional bioelectronics. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, B60–B65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.; Bures, P.; Leobandung, W.; Ichikawa, H. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.N.; Salas, R.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Bioactive hydrogels demonstrate mediated release of a chromophore by chymotrypsin. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaughter, B.V.; Khurshid, S.S.; Fisher, O.Z.; Khademhosseini, A.; Peppas, N.A. Hydrogels in regenerative medicine. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3307–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiseppi-Elie, A.; Dong, C.; Dinu, C.Z. Crosslink density of a biomimetic poly(HEMA)-based hydrogel influences growth and proliferation of attachment dependent RMS 13 cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 19529–19539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Bae, Y.H. Hydrogels based on poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(tetramethylene oxide) or poly(dimethyl siloxane): Synthesis, characterization, in vitro protein adsorption and platelet adhesion. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.N.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Bioresponsive hydrogels. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawel, K.; Barriet, D.; Sletmoen, M.; Stokke, B.T. Responsive hydrogels for label-free signal transduction within biosensors. Sensors 2010, 10, 4381–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganji, F.; Vasheghani-Farahani, S.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E. Theoretical description of hydrogel swelling: A review. Iran. Polym. J. 2010, 19, 375–398. [Google Scholar]
- Kotanen, C.N.; Wilson, A.N.; Dong, C.; Dinu, C.-Z.; Justin, G.A.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. The effect of the physicochemical properties of bioactive electroconductive hydrogels on the growth and proliferation of attachment dependent cells. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 6318–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Sasaki, J.-I.; Egusa, H.; Lee, K.Y.; Nakano, T.; Sohmura, T.; Nakahira, A. Effect of calcium ion concentrations on osteogenic differentiation and hematopoietic stem cell niche-related protein expression in osteoblasts. Tissue Eng. A 2010, 16, 2467–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiseppi-Elie, A. Electroconductive hydrogels: Synthesis, characterization and biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2701–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-C.; Chauhan, A. Ion transport in silicone hydrogel contact lenses. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 399, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotanen, C.N.; Wilson, A.N.; Wilson, A.M.; Ishihara, K.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Biomimetic hydrogels gate transport of calcium ions across cell culture inserts. Biomed. Microdevices 2012, 14, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boztas, A.O.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Immobilization and release of the redox mediator ferrocene monocarboxylic acid from within cross-linked p(HEMA-co-PEGMA-co-HMMA) hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Anderson, J.L. Partitioning and diffusion of proteins and linear polymers in polyacrylamide gels. Biophys. J. 1996, 70, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, G.M.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R. Sodium chloride diffusion in sulfonated polymers for membrane applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidian, H.; Park, K. Introduction to Hydrogels. In Biomedical Applications of Hydrogels Handbook; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Flory, P.J.; Rehner, J., Jr. Statistical mechanics of cross-linked polymer networks II. Swelling. J. Chem. Phys. 1943, 11, 521–526. [Google Scholar]
- Peppas, N.A.; Merrill, E.W. Crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels as swollen elastic networks. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1977, 21, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.K.; Aluru, N.; Johnson, B.; Crone, W.; Beebe, D.J.; Moore, J. Equilibrium swelling and kineticsof pH-responsive hydrogels: Models, experiments, and simulations. Microelectromech. Syst. J. 2002, 11, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafe, S.; Manzanares, J.A.; Reiss, H. Donnan phenomena in membranes with charge due to ion adsorption. Effects of the interaction between adsorbed charged groups. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 2325–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.; Brahim, S.; Ishihara, K.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Molecularly engineered p(HEMA)-based hydrogels for implant biochip biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4767–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-F.; Lin, Y.-H. Swelling behavior and drug release of NIPAAm/PEGMEA copolymeric hydrogels with different crosslinkers. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 7333–7340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Murthy, P.N.; Nath, L.; Chowdhury, P. Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Poloniae Pharm. 2010, 67, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, K.; Ueda, T.; Nakabayashi, N. Preparation of phospholipid polymers and their properties as polymer hydrogel membranes. Polym. J. 1990, 22, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T. Mechanism of sustained-action medication. Theoretical analysis of rate of release of solid drugs dispersed in solid matrices. J. Pharm. Sci. 1963, 52, 1145–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hixson, A.; Crowell, J. Dependence of reaction velocity upon surface and agitation. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1931, 23, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, L.R.; Xue, H.; Jiang, S. Functionalizable and nonfouling zwitterionic carboxybetaine hydrogels with a carboxybetaine dimethacrylate crosslinker. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, C.J.; Murphy, S.M.; Atherton, N.D.; Tighe, B.J. Synthetic hydrogels: 4. The permeability of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) to cations—An overview of solute-Water interactions and transport processes. Polymer 1988, 29, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, M.; Terayama, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Hoshino, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Ogawa, H.; Masunaga, H.; Koike, J.-I.; Horigome, M.; Ishihara, K.; et al. Chain dimension of polyampholytes in solution and immobilized brush states. Polym. J. 2012, 44, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Annaka, M.; Ishihara, K.; Takahara, A. Dimension of poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) in aqueous solutions with various ionic strength. Chem. Lett. 2006, 35, 1310–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, A.; O’Donnell, M.J. Analysis of Na+, Cl−, K+, H+ and NH4+ concentration gradients adjacent to the surface of anal papillae of the mosquito Aedes aegypti: Application of self-referencing ion-selective microelectrodes. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Aucoin, H.R.; Wilson, A.N.; Wilson, A.M.; Ishihara, K.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Release of Potassium Ion and Calcium Ion from Phosphorylcholine Group Bearing Hydrogels. Polymers 2013, 5, 1241-1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5041241
Aucoin HR, Wilson AN, Wilson AM, Ishihara K, Guiseppi-Elie A. Release of Potassium Ion and Calcium Ion from Phosphorylcholine Group Bearing Hydrogels. Polymers. 2013; 5(4):1241-1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5041241
Chicago/Turabian StyleAucoin, Hanna R., A. Nolan Wilson, Ann M. Wilson, Kazuhiko Ishihara, and Anthony Guiseppi-Elie. 2013. "Release of Potassium Ion and Calcium Ion from Phosphorylcholine Group Bearing Hydrogels" Polymers 5, no. 4: 1241-1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5041241
APA StyleAucoin, H. R., Wilson, A. N., Wilson, A. M., Ishihara, K., & Guiseppi-Elie, A. (2013). Release of Potassium Ion and Calcium Ion from Phosphorylcholine Group Bearing Hydrogels. Polymers, 5(4), 1241-1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5041241