Plastic Degradation and Its Environmental Implications with Special Reference to Poly(ethylene terephthalate)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Plastics in the Environment
2.1. Environmental Impacts of Plastic Pollution
2.2. Levels of Plastic in the Marine Environment
2.3. Degradation
3. Poly(ethylene terephthalate)
3.1. Properties and Applications
| Manufacturer | Commercial name |
|---|---|
| DSM Engineering Plastics | Arnitel® |
| Du Pont De Nemours & Co., Inc. | Mylar® |
| Du Pont De Nemours & Co., Inc. | Rynite® |
| Eastman Chemical Company | Eastapac® |
| ENKA-Glazstoff | Diolen® |
| Farbwerke Hoescht AG | Hostadur® |
| Imperial Chemical Industries Ltd. | Melinex® |
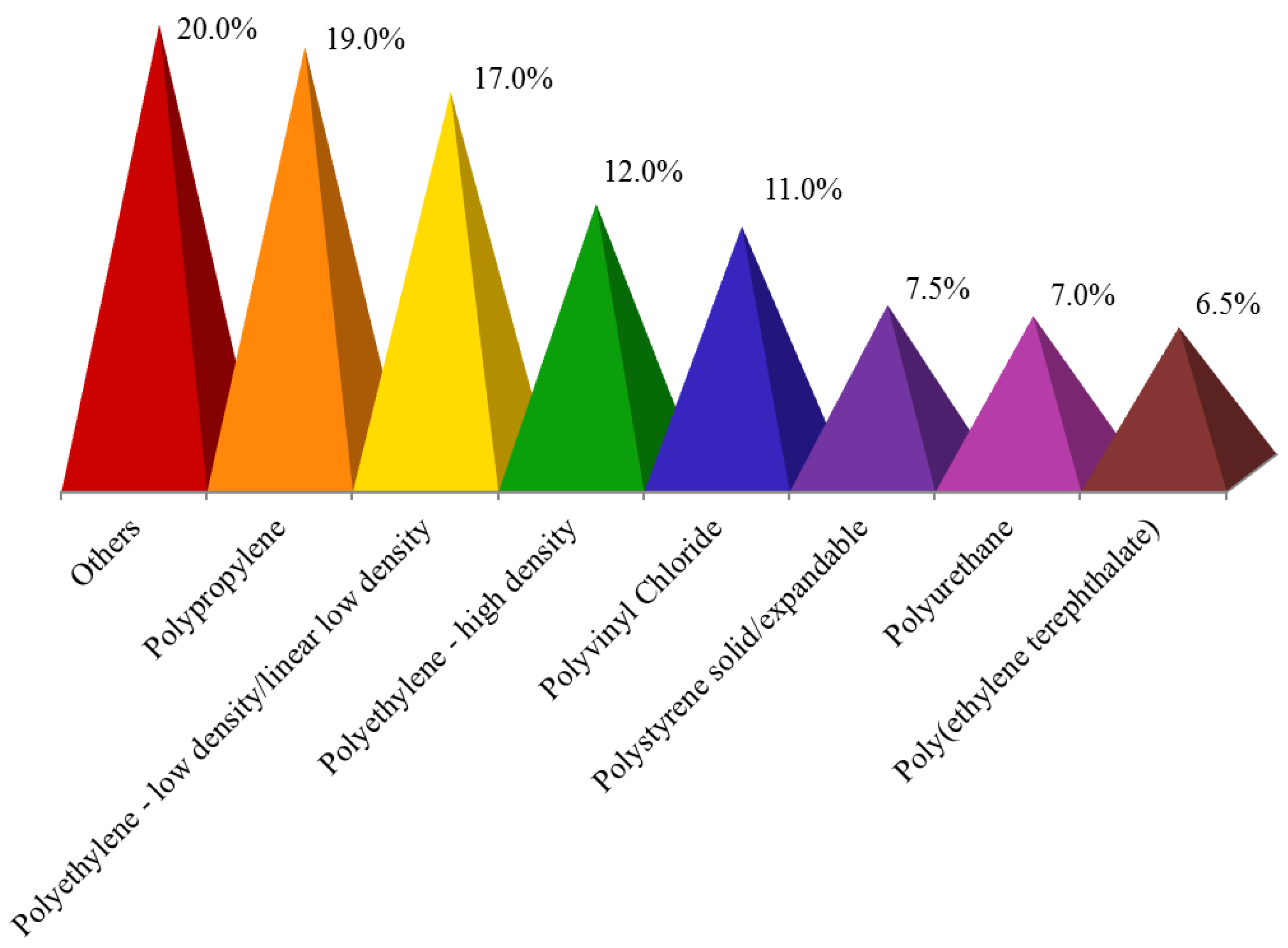
| Property | Value * |
|---|---|
| Average molecular weight | 30,000–80,000 g mol−1 |
| Density | 1.41 g cm−3 |
| Melting temperature | 255–265 °C |
| Glass transition temperature | 69–115 °C |
| Young’s modulus | 1700 MPa |
| Water absorption (24 h) | 0.5% |
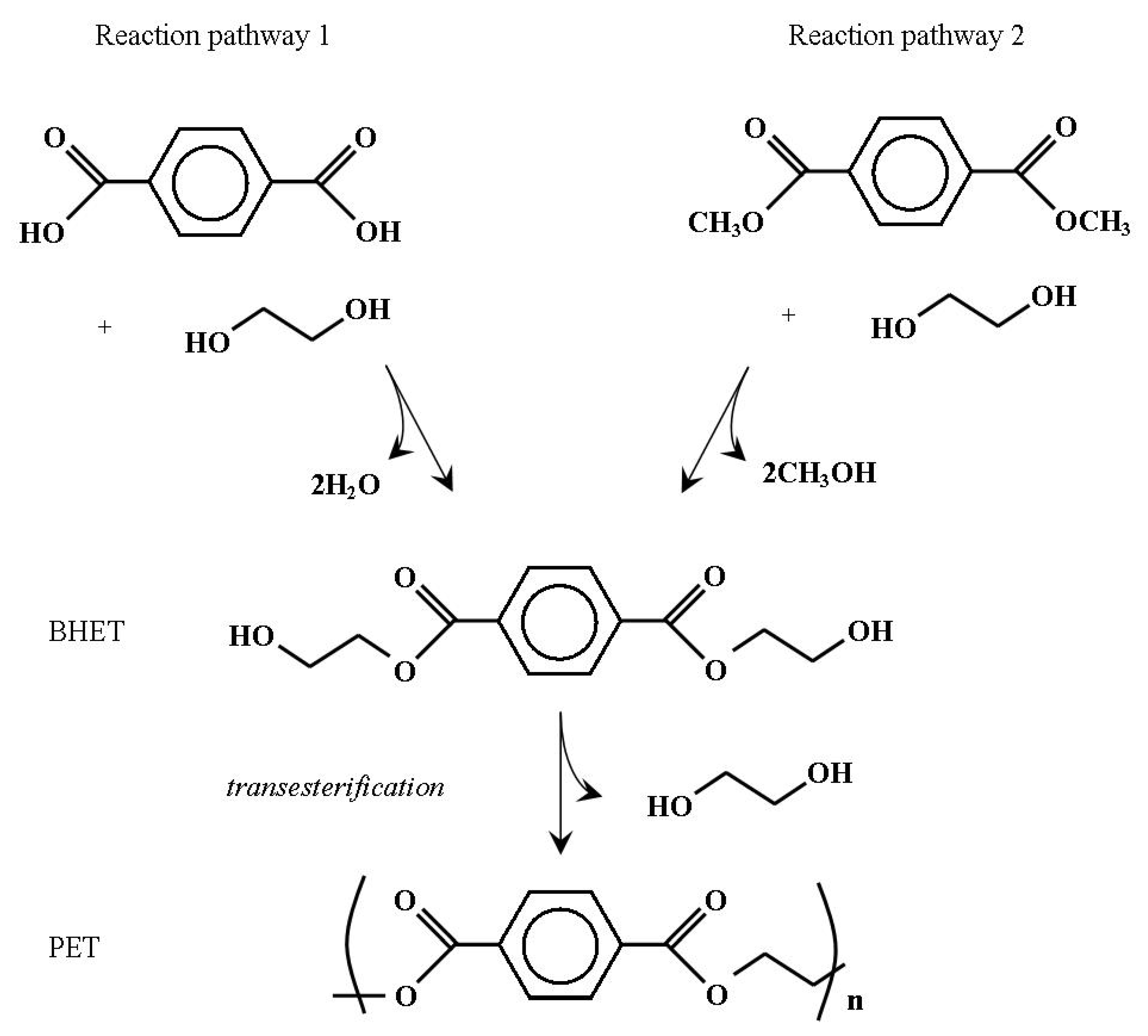
3.2. Chemistry, Synthesis and Manufacture
4. Plastic Disposal Methods
4.1. Landfill
4.2. Incineration
4.3. Recycling
| Property | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Flake size | 0.4–8 mm |
| Melting temperature | >240 °C |
| Viscosity (η) | >0.7 dL g−1 |
| Water content | <0.02% |
| Dye content | <10 ppm |
| PVC content | <50 ppm |
| Polyolefin content | <10 ppm |
| Metal content | <3 ppm |
| Yellowing index * | <20 |
4.4. Biodegradation
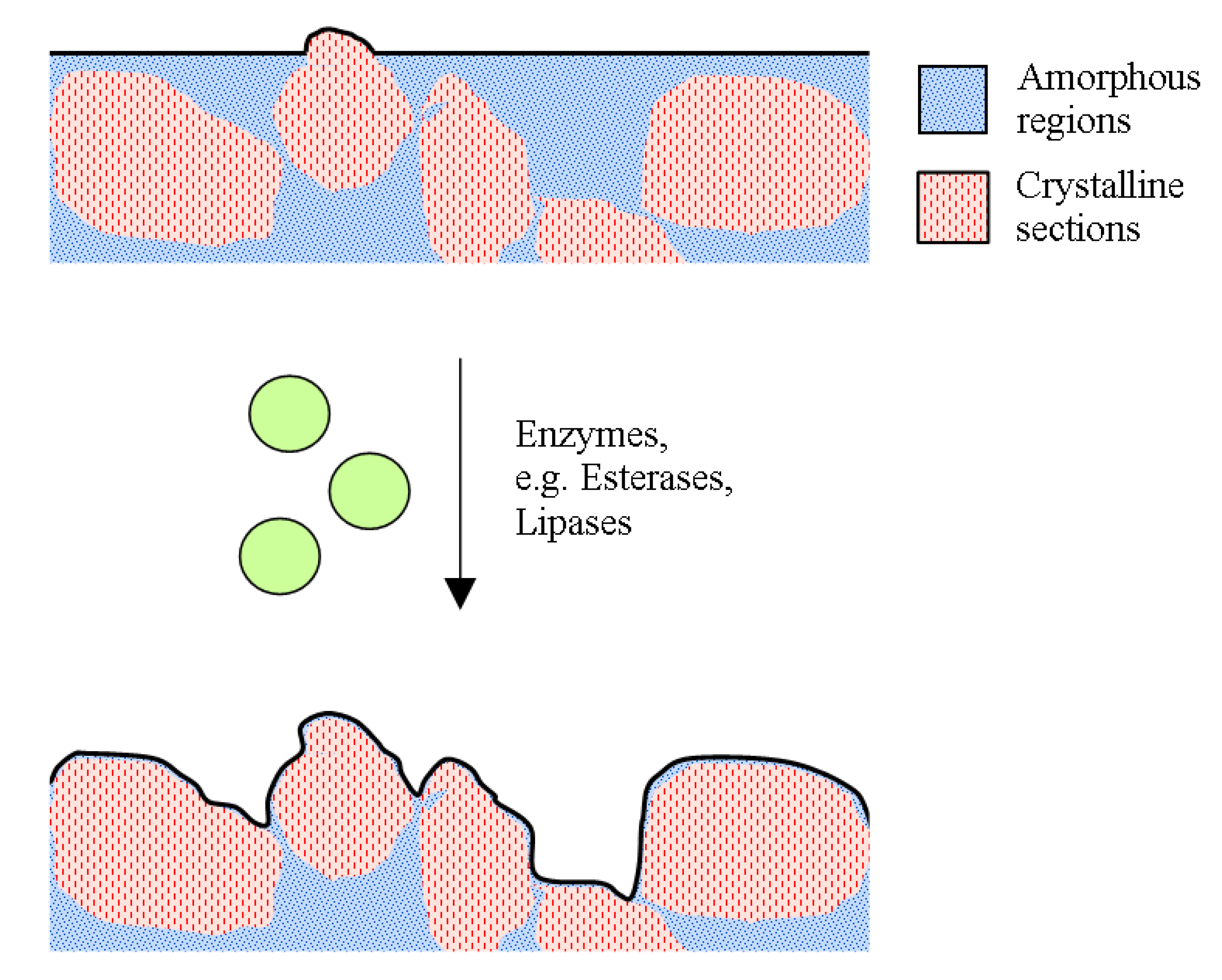
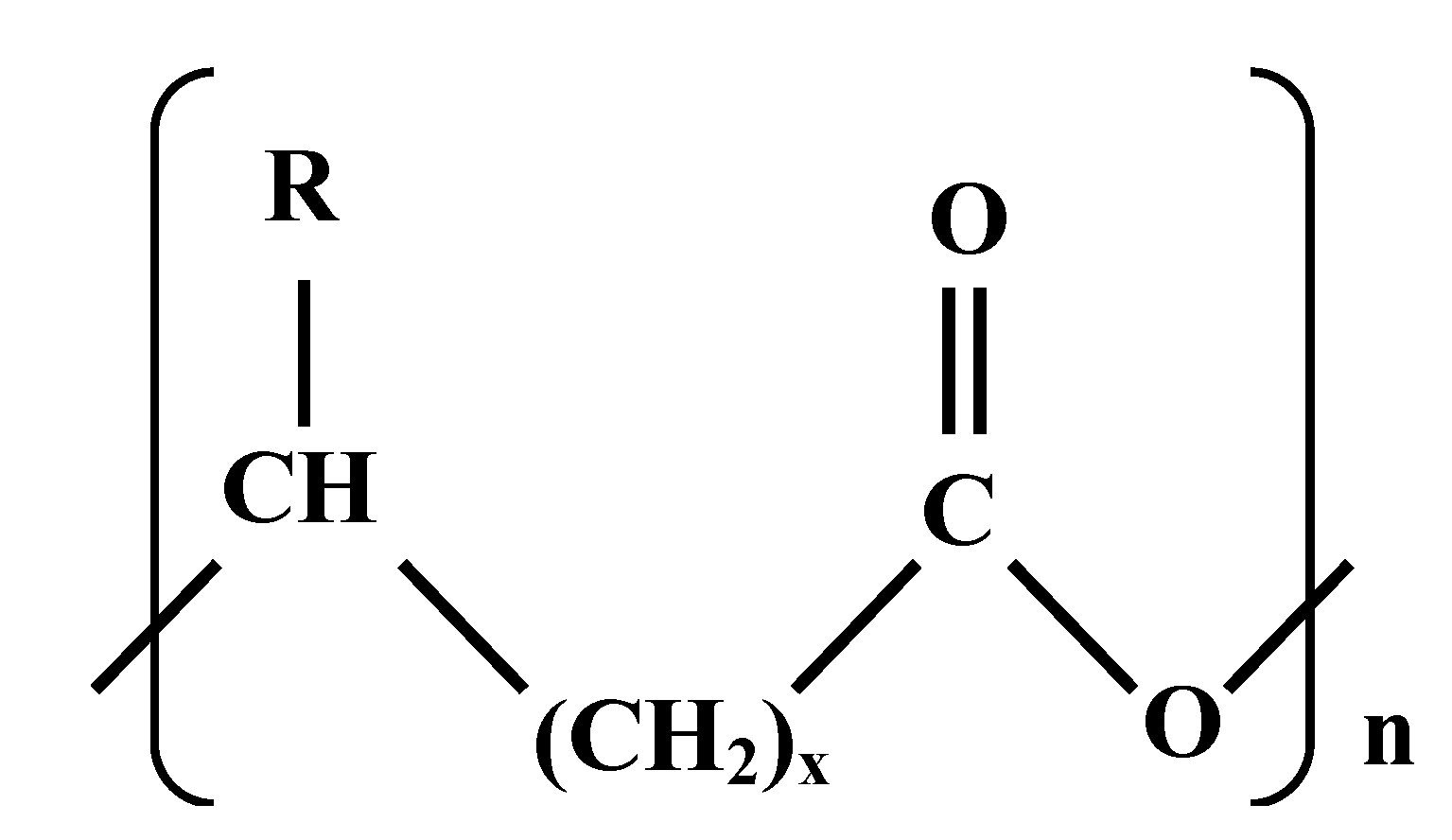
4.5. Biodegradable Polymers
| Polymer | Biodegradation rate (%) a | EdK b |
|---|---|---|
| starch | 78.34 ± 1.74 | 100.00 ± 0.00 |
| pullulan | 73.77 ± 1.35 | 94.22 ± 3.74 |
| curdlan | 64.60 ± 1.79 | 82.50 ± 3.13 |
| Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate), PHBHHx | 62.12 ± 0.88 | 79.36 ± 1.28 |
| Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate), PHBV | 53.47 ± 0.67 | 68.29 ± 2.28 |
| Poly(ester amide), PEA | 36.29 ± 1.84 | 46.34 ± 2.58 |
| Poly(e-caprolactone), PCL | 25.68 ± 0.7 | 32.77 ± 0.21 |
| cellulose | 25.00 ± 0.6 | 31.93 ± 1.36 |
| chitosan | 14.86 ± 0.42 | 18.98 ± 0.71 |
| Poly(ethylene glycol), PEG | 11.97 ± 0.39 | 15.28 ± 0.42 |
| Poly(vinyl alcohol), PVA | 5.02 ± 0.44 | 6.41 ± 0.53 |
| Poly(ethylene oxide), PEO | 3.76 ± 0.26 | 4.81 ± 0.43 |
| Poly(propylene carbonate), PPC | 3.38 ± 0.26 | 4.31 ± 0.27 |
| Poly(butylenes succinate-co-adipate), PBSA | 2.90 ± 0.26 | 3.70 ± 0.32 |
| Poly(butylenes succinate), PBS | 1.93 ± 0.10 | 2.47 ± 0.16 |
| Poly(lactic acid), PLA | 0.97 ± 0.26 | 1.23 ± 0.32 |
| Polyethylene, PE | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
5. Conclusions and Summary
References
- Derraik, J.G.B. The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemberton, D.; Brothers, N.P.; Kirkwood, R. Entanglement of Australian fur seals in man-made debris in Tasmanian waters. Wildl. Res. 1992, 19, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazima, I.; Gadig, O.B.F.; Namora, R.C.; Motta, F.S. Plastic debris collars on juvenile carcharhinid sharks (Rhizoprionodon lalandii) in southwest Atlantic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, M.R. Environmental implications of plastic debris in marine settings—Entanglement, ingestion, smothering, hangers-on, hitch-hiking and alien invasions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2009, 364, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzarello, M.Y.; van Vleet, E.S. Marine birds and plastic pollution. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1987, 37, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blight, L.K.; Burger, A.E. Occurrence of plastic particles in sea-birds from the eastern north pacific. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1997, 34, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiros, J.P.; Barcelos, J. Plastic ingestion by a leatherback turtle Dermochelys coriacea from the Azores (NE Atlantic). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 1196–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, R.W.; Hooker, S.K. Ingestion of plastic and unusual prey by a juvenile harbour porpoise. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 719–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J.; Moore, S.L.; Leecaster, M.K.; Weisberg, S.B. A comparison of plastic and plankton in the north Pacific central gyre. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, Y.; Isobe, T.; Takada, H.; Kanehiro, H.; Ohtake, C.; Kaminuma, T. Plastic resin pellets as a transport medium for toxic chemicals in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, L.M.; Moore, C.; Jones, P.R. Persistent organic pollutants carried by synthetic polymers in the ocean environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H.; Takada, H.; Ogata, Y.; Yamashita, R.; Mizukawa, K.; Saha, M.; Kwan, C.; Moore, C.; Gray, H.; Laursen, D.; Zettler, E.R.; Farrington, J.W.; Reddy, C.M.; Peacock, E.E.; Ward, M.W. Organic micropollutants in marine plastic debris from the open ocean and remote and urban beaches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Schecter, A.; Colacino, J.; Haffner, D.; Patel, K.; Opel, M.; Päpke, O.; Birnbaum, L. Perfluorinated compounds, polychlorinated biphenyls, and organochlorine pesticide contamination in composite food samples from Dallas, Texas, USA. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 796–802. [Google Scholar]
- Trudel, D.; Scheringer, M.; von Goetz, N.; Hungerbühler, K. Total consumer exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers in North America and Europe. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2391–2397. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.Y.; Yettella, R.R.; Kim, J.S.; Kwon, K.; Kim, M.C.; Min, D.B. Effects of grilling and roasting on the levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in beef and pork. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Gao, Y.; Xie, G. Determination of bisphenol A, 4-n-nonylphenol, and 4-tert-octylphenol by temperature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid-phase microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detector. Talanta 2011, 85, 1598–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masó, M.; Garcés, E.; Pagès, F.; Camp, J. Drifting plastic debris as a potential vector for harmful algal bloom (HAB) species. Sci. Mar. 2003, 67, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, W.M. Ants carried in a floating log from the brazilian mainland to San Sebastian Island. Psyche 1916, 23, 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Censky, E.J.; Hodge, K.; Dudley, J. Over-water dispersal of lizards due to hurricanes. Nature 1998, 395, 556. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Milner, P. Drifting plastic and its consequences for sessile organism dispersal in the Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Biol. 2005, 146, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, A.; Cullen, M. Marine debris on northern New South Wales beaches (Australia): Sources and the role of beach usage. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1997, 34, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.R.; Reid, K.; Arnould, J.P.Y.; Croxall, J.P. Marine debris surveys at Bird Island, South Georgia 1990–1995. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1997, 34, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Ribes, L.; Basterretxea, G.; Palmer, M.; Tintoré, J. Origin and abundance of beach debris in the Balearic Islands. Sci. Mar. 2007, 71, 305–314. [Google Scholar]
- Morishige, C.; Donohue, M.J.; Flint, E.; Swenson, C.; Woolaway, C. Factors affecting marine debris deposition at French Frigate Shoals, northwestern Hawaiian islands marine national monument, 1990–2006. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.R.; Friedrich, A.C.; Ivar do Sul, J.A. Marine debris contamination along undeveloped tropical beaches from northeast Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 148, 455–462. [Google Scholar]
- Ivar do Sul, J.A.; Costa, M.F. Marine debris review for Latin America and the wider Caribbean region: From the 1970s until now, and where do we go from here? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1087–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.L.; Morét-Ferguson, S.; Maximenko, N.A.; Proskurowski, G.; Peacock, E.E.; Hafner, J.; Reddy, C.M. Plastic accumulation in the North Atlantic subtropical gyre. Science 2010, 329, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, P.G.; Moore, C.J.; van Franeker, J.A.; Moloney, C.L. Monitroing the abundance of plastic debris in the marine environment. Philos. T. Roy. Soc. B 2009, 364, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada-Onodera, K.; Mukumoto, H.; Katsuyaya, Y.; Saiganji, A.; Tani, Y. Degradation of polyethylene by a fungus, Penicillium simplicissimum YK. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2001, 72, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yanful, E.K.; Bassi, A.S. A review of plastic waste biodegradation. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2005, 25, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marqués-Calvo, M.S.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Kint, D.P.R.; Bou, J.J.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Enzymatic and microbial biodegradability of poly(ethylene terephthalate) copolymers containing nitrated units. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2006, 91, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhomme, S.; Cuer, A.; Delort, A.-M.; Lemaire, J.; Sancelme, M.; Scott, G. Environmental degradation of polyethylene. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2003, 81, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar]
- Raquez, J.-M.; Bourgeois, A.; Jacobs, H.; Degée, P.; Alexandre, M.; Dubois, P. Oxidative degradations of oxodegradable LDPE enhanced with thermoplastic pea starch: thermo-mechanical properties, morphology, and UV-ageing studies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.-J.; Kleeberg, I.; Deckwer, W.-D. Biodegradation of polyesters containing aromatic constituents. J. Biotechnol. 2001, 86, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Levchik, S.V.; Weil, E.D. A review on thermal decomposition and combustion of thermoplastic polyesters. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2004, 15, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeret, A.; Ferry, L.; Ienny, P. Influence of the fibre/matrix interface on ageing mechanisms of glass fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites (PA-6,6, PET, PBT) in a hygrothermal environment. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2009, 94, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaja, F.; Pavel, D. Recycling of PET. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 1453–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kint, D.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. A review on the potential biodegradability of poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polym. Int. 1999, 48, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PlasticsEurope. Plastics—The Facts 2012. Available online: http://www.plasticseurope.org/Document/plastics-the-facts-2012.aspx?FolID=2 (accessed on 24 December 2012).
- Sinha, V.; Patel, M.R.; Patel, J.V. PET waste management by chemical recycling: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, T.; Ozaki, Y. Real-time monitoring of the initial oligomerization of bis(hydroxyethyl) terephthalate by attenuated total reflection/infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 7459–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin Associates, Cradle-to-Gate Life Cycle Inventory of Nine Plastic Resins and Four Polyurethane Precursors; The Plastics Division of the American Chemistry Council: Prairie Village, KS, USA, 2011.
- Williams, C.L.; Chang, C.C.; Do, P.; Nikbin, N.; Caratzoulas, S.; Vlachos, D.G.; Lobo, R.F.; Fan, W.; Dauenhauer, P.J. Cycloaddition of biomass-derived furans for catalytic production of renewable p-xylene. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Gong, J.; Gu, Z. A study on the biodegradability of polyethylene terephthalate fiber and diethylene glycol terephthalate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansel, B.; Yildiz, B.S. Goal-based waste management strategy to reduce persistence of contaminants in leachate at municipal solid waste landfills. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2011, 13, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massardier-Nageotte, V.; Pestre, C.; Cruard-Pardet, T.; Bayard, R. Aerobic and anerobic biodegradability of polymer films and phsyico-chemical characterization. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2006, 91, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollner, E.W.; Annis, P.A.; Das, K.C. Evaluation of strength properties of polypropylene-based polymers in simulated landfill and oven conditions. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 137, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Urase, T.; Okumura, H.; Panyosaranya, S.; Inamura, A. Emission of volatile organic compounds from solid waste disposal sites and importance of heat management. Waste Manag. Res. 2008, 26, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-Y.; Zhang, H.; He, P.-J.; Shao, L.-M. Leaching behaviour of bisphenol A from municipal solid waste under landfill environment. Environ. Technol. 2011, 32, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenson, A.; Sjöholm, S.; Allard, A.-S.; Kaj, L. Antiestrogenicity and estrogenicity in leachates from solid waste deposits. Environ. Toxicol. 2009, 26, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida, D.; Kajihara, Y.; Shimidzu, N.; Hamamura, K.; Nagase, M. Hydrogen sulfide production by sulfate-reducing bacteria utilizing additives eluted from plastic resins. Waste Manag. Res. 2011, 29, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, T.; Møller, J.; Fruergaard, T. Incineration and co-combustion of waste: Accounting of greenhouse gases and global warming contributions. Waste Manag. Res. 2009, 27, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.H.; Tan, R.B.H. Environmental impacts of conventional plastic and bio-based carrier bags: Part 2:End-of-life options. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010, 15, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Tang, X.; Yao, J.; Shi, D.; Fang, J.; Khan, M.I.; Cheema, S.A.; Chen, Y. Levels and patterns of polycyclic aromatic hydrocabons and polychlorinated biphenyls in municipal waste incinerator bottom ash in Zhejiang province, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneit, B.R.T.; Medeiros, P.M.; Didyk, B.M. Combustion products of plastics as indicators for refuse burning in the atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6961–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanidis, A.; Iliopoulos, N.; Gotsis, G.; Fiotakis, K. Persistent free-radicals, heavy metals and PAHs generated in particulate soot emissions and residue ash from controlled combustion of common types of plastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paci, M.; La Mantia, F.P. Influence of small amounts of polyvinylchloride on the recycling of polyethyleneterephthalate. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 1999, 63, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Cardi, N.; Po, R.; Giannotta, G.; Occhiello, E.; Garbassi, F.; Messina, G. Chain extension of recycled poly(ethylene terephthalate) with 2,2'-Bis(2-oxazoline). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1993, 50, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paci, M.; La Mantia, F.P. Competition between degradation and chain extension during processing of reclaimed poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 1998, 61, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villain, F.; Coudane, J.; Vert, M. Thermal degradation of polyethylene terephthalate: Study of polymer stabilization. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 1995, 49, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demertzis, P.G.; Johansson, F.; Lievens, C.; Franz, R. Studies on the development of a quick inertness test procedure for multi-use PET containers—Sorption behaviour of bottle wall strips. Packag. Technol. Sci. 1997, 10, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranzo, M.; Sainz-Pardo, I.; Boluda, R.; Sánchez, J.; Mormeneo, S. The use of microorgansims in environmental remediation. Ann. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Head, I.M.; Swannell, R.P.J. Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants in marine habitats. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1999, 10, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.P.; Triguis, J.A. Bioremediation process on Brazil shoreline. Laboratory experiments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2007, 14, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedad Díaz, M.; Boyd, K.G.; Grigson, S.J.W.; Burgess, J.G. Biodegradation of crude oil across a wide range of salinities by an extremely halotolerant bacterial consortium MPD-M, immobilized onto polypropylene fibers. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002, 79, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, T.C.; Dubinsky, E.A.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Piceno, Y.M.; Singh, N.; Jansson, J.K.; Probst, A.; Borglin, S.E.; Fortney, J.L.; Stringfellow, W.T.; Bill, M.; Conrad, M.E.; Tom, L.M.; Chavarria, K.L.; Alusi, T.R.; Lamendella, R.; Joyner, D.C.; Spier, C.; Baelum, J.; Auer, M.; Zemla, M.L.; Chakraborty, R.; Sonnenthal, E.L.; D'haeseleer, P.; Holman, H.-Y.N.; Osman, S.; Lu, Z.; van Nostrand, J.D.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Mason, O.U. Deep-sea oil plume enriches indigenous oil-degrading bacteria. Science 2010, 330, 204–208. [Google Scholar]
- Luigi, M.; Gaetano, D.M.; Vivia, B.; Angelina, L.G. Biodegradative potential and characterization of psychrotolerant polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading marine bacteria isolated from a coastal station in the Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, J.; Ramaiah, N.; Vardanyan, L. Detoxification of toxic heavy metals by marine bacteria highly resistant to mercury. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, M.; Kawahata, H.; Gupta, L.P.; Kita, N.; Morishita, Y.; Ono, Y.; Komai, T. Arsenic resistance and removal by marine and non-marine bacteria. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 127, 434–442. [Google Scholar]
- Pieper, D.H.; Reineke, W. Engineering bacteria for bioremediation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2000, 11, 262–270. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.-J.; Schrader, H.; Profe, J.; Dresler, K.; Deckwer, W.-D. Enzymatic degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate): rapid hydrolyse using a hydrolase from T. fusca. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 2005, 26, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, K.; Müller, R.-J.; Deckwer, W.-D. Mechanism and kinetics of the enzymatic hydrolysis of polyester nanoparticles by lipases. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2006, 91, 2486–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artham, T.; Doble, M. Biodegradation of physicochemically treated polycarbonate by fungi. Biomacromolecules 2009, 11, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratowicz, F.L.; Ukielski, R. Synthesis and hydrolytic degradation of poly(ethylene succinate) and poly(ethylene terephthalate) copolymers. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2009, 94, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marten, E.; Müller, R.-J.; Deckwer, W.-D. Studies on the enzymatic hydrolysis of polyesters I. Low molecular mass model esters and aliphatic polyesters. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2003, 80, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakuma, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Maeda, K.; Fukui, K. Theoretical study of the transesterification reaction of polethylene terephthalate under basic conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2009, 94, 240–245. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, R.-J. Biological degradation of synthetic polyesters-enzymes as potential catalysts for polyester recycling. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 2124–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mantia, F.P.; Botta, L.; Morreale, M.; Scaffaro, R. Effects of small amounts of poly(lactic acid) on the recycling of poly(ethylene terephthalate) bottles. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2012, 97, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rwei, S.-P.; Lin, W.-P.; Wang, J.-F. Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable and weather-durable PET/PEG/NDC copolymers. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Amass, W.; Amass, A.; Tighe, B. A review of biodegradable polymers: Uses, current developments in the synthesis and characterization of biodegradable polyesters, blends of biodegradable polymers and recent advances in biodegradation studies. Polym. Int. 1998, 47, 89–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Tao, J.; Yang, C.; Song, C.; Geng, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Kong, M.; Wang, S. Introduction of environmentally degradable parameters to evaluate the biodegradability of biodegradable polymers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, M.A.L.; O'Sullivan, C.; Rounsefell, B.; Halley, P.J.; Truss, R.; Clarke, W.P. The anaerobic degradability of thermoplastic starch: Polyvinyl alcohol blends: Potential biodegradable food packaging materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandelero, R.P.H.; Grossmann, M.V.E.; Yamashita, F. Effect of the method of production of the blends on mechanical and structural properties of biodegradable starch films produced by blown extrusion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Tan, J.P.K.; Fukushima, K.; Nederberg, F.; Yang, Y.Y.; Waymouth, R.M.; Hedrick, J.L. Thermoresponsive nanostructured polycarbonate block copolymers as biodegradable therapeutic delivery carriers. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5505–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canché-Escamilla, G.; Canché-Canché, M.; Duarte-Aranda, S.; Cáceres-Farfán, M.; Borges-Argáez, R. Mechanical properties and biodegradation of thermoplastic starches obtained from grafted starches with acrylics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nampoothiri, K.M.; Nair, N.R.; John, R.P. An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (PLA) research. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8493–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.-R.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Wang, Q.-F.; Yang, K.; Luo, S.-H. Synthesis of biodegradable material poly(lactic acid-co-aspartic acid) via direct melt polycondensation and its characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 121, 3662–3668. [Google Scholar]
- Neppalli, R.; Causin, V.; Marega, C.; Saini, R.; Mba, M.; Marigo, A. Structure, morphology and biodegradability of poly(ε-caprolactone)-based nanocomposites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Verbeek, C.; van den Berg, L.E. Extrusion processing and properties of protein-based thermoplastics. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, J.; Wilson, S.A.; Hölter, D. Degradation of cellulose acetate-based materials: A review. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemlou, M.; Khodaiyan, F.; Oromiehie, A.; Yarmand, M.S. Development and characterisation of a new biodegradable edible film made from kefiran, an exopolysaccharide obtained from kefir grains. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitschke, M.; Costa, S.G.V.A.O.; Contiero, J. Rhamnolipids and PHAs: Recent reports on Pseudomonas-derived molecules of increasing industrial interest. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-Q. A microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) based bio- and materials industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2434–2446. [Google Scholar]
- Akaraonye, E.; Keshavarz, T.; Roy, I. Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates: The future green materials of choice. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunasundari, B.; Sudesh, K. Isolation and recovery of microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Express Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Webb, H.K.; Arnott, J.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Plastic Degradation and Its Environmental Implications with Special Reference to Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polymers 2013, 5, 1-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5010001
Webb HK, Arnott J, Crawford RJ, Ivanova EP. Plastic Degradation and Its Environmental Implications with Special Reference to Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polymers. 2013; 5(1):1-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleWebb, Hayden K., Jaimys Arnott, Russell J. Crawford, and Elena P. Ivanova. 2013. "Plastic Degradation and Its Environmental Implications with Special Reference to Poly(ethylene terephthalate)" Polymers 5, no. 1: 1-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5010001
APA StyleWebb, H. K., Arnott, J., Crawford, R. J., & Ivanova, E. P. (2013). Plastic Degradation and Its Environmental Implications with Special Reference to Poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polymers, 5(1), 1-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5010001






