Dielectric Response of Crosslinked Adenanthera pavonina L. Galactomannan in pH-Controlled Medium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Obtaining Galactomannan from Adenanthera pavonina L. Seeds
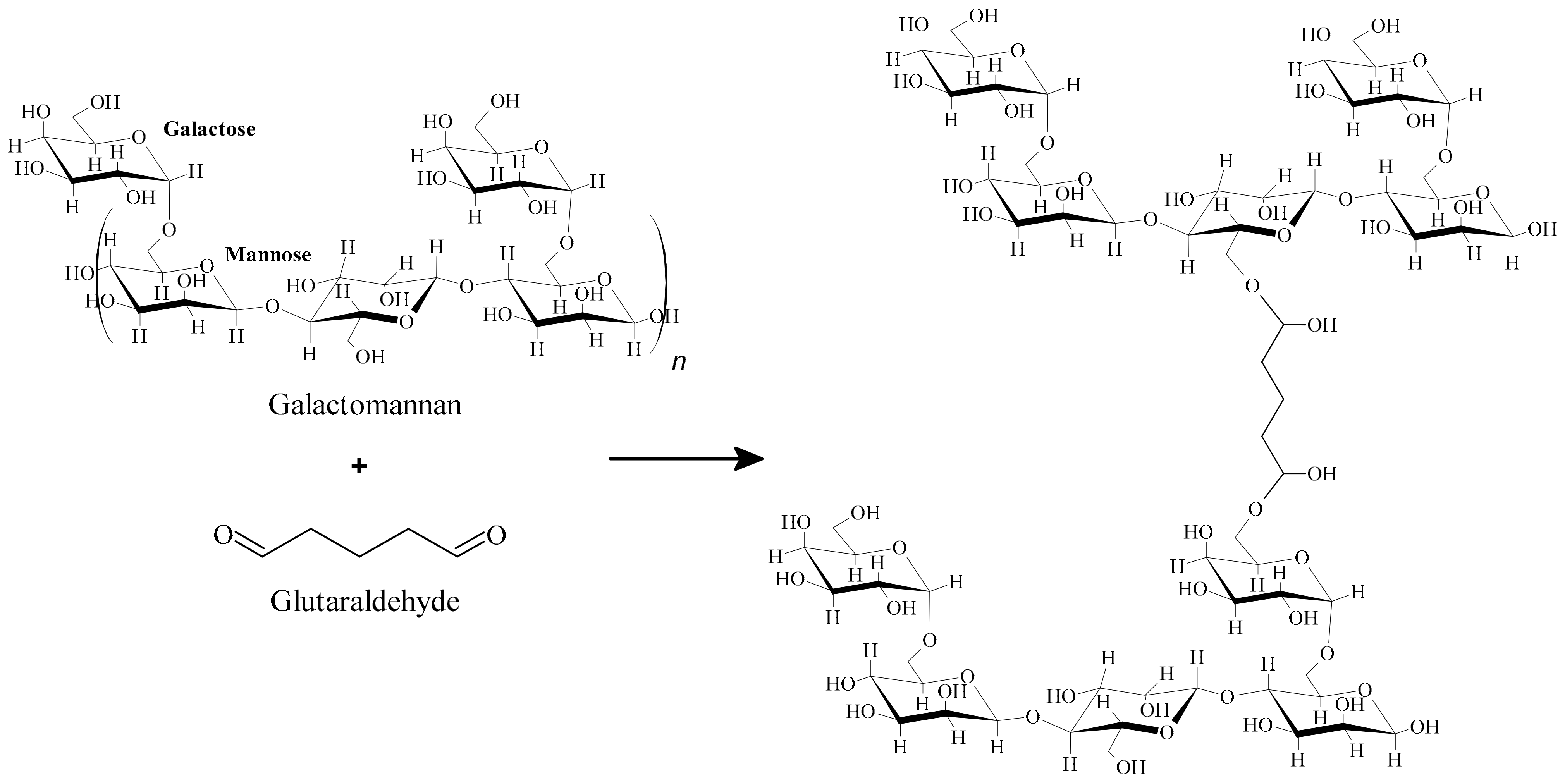
2.3. Galactomannan Crosslinking
2.4. Preparation of Crosslinked Galactomannan Films and Sponges
2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
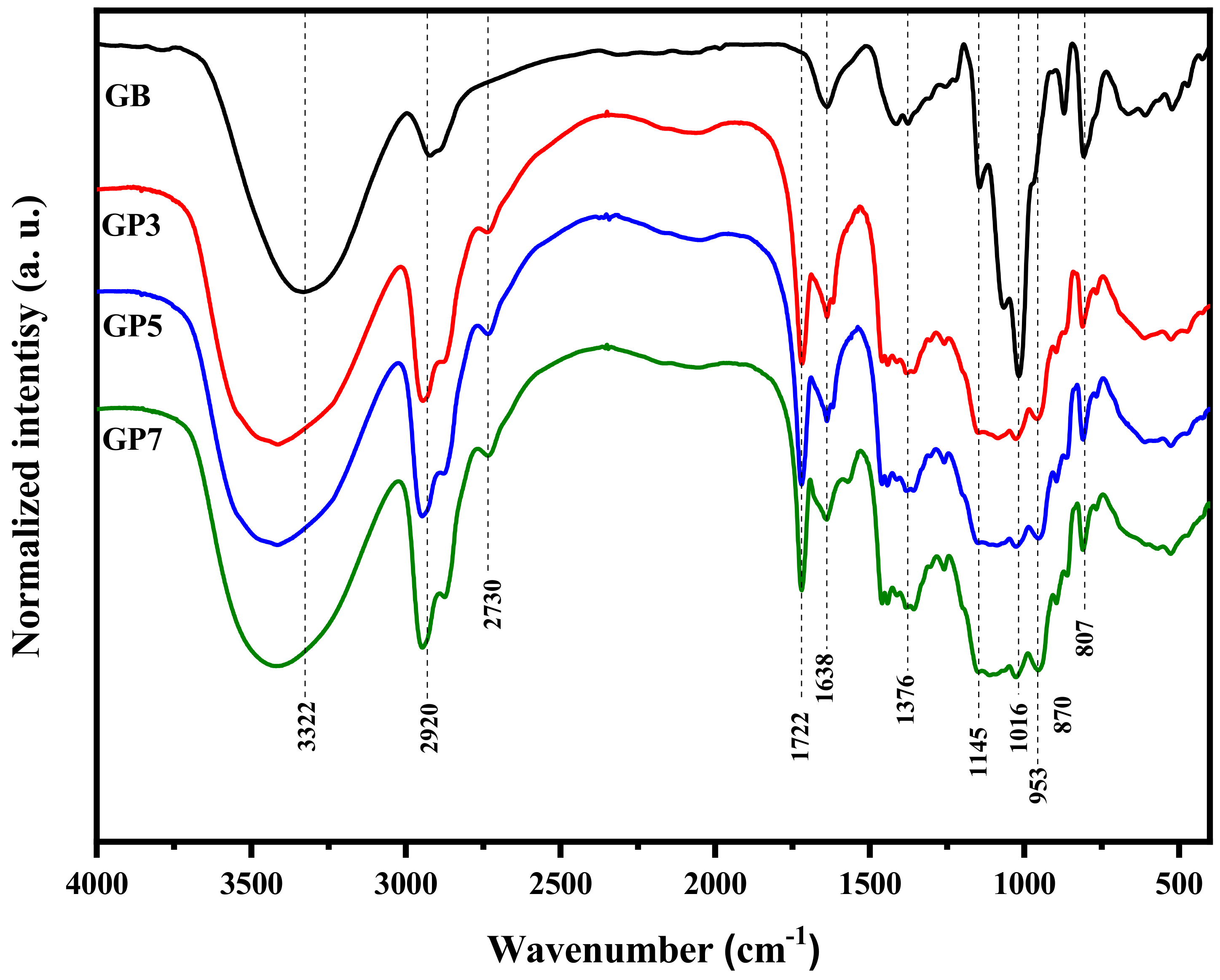
3.1. FTIR Analysis
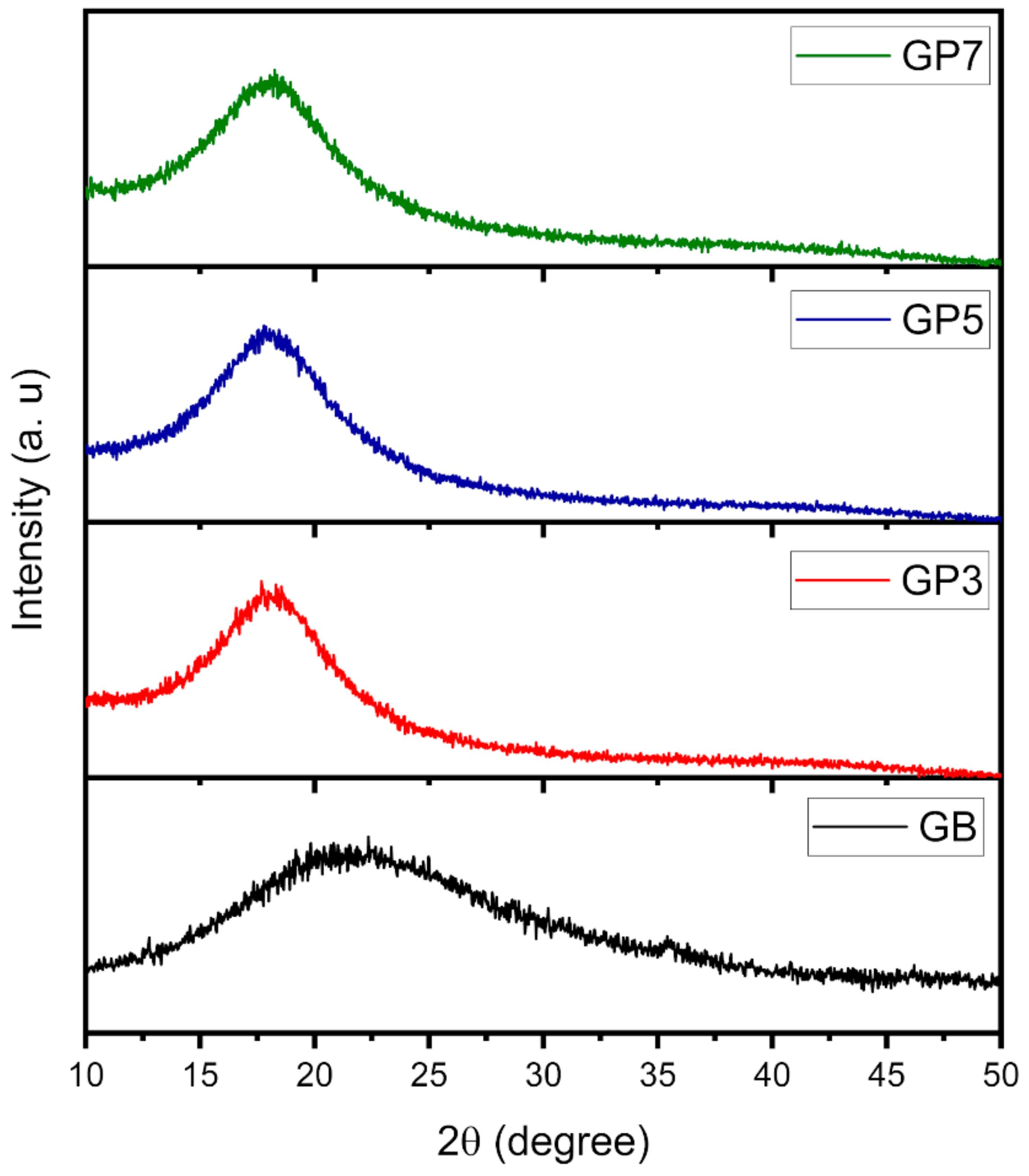
3.2. X-Ray Diffraction
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.4. Swelling Degree
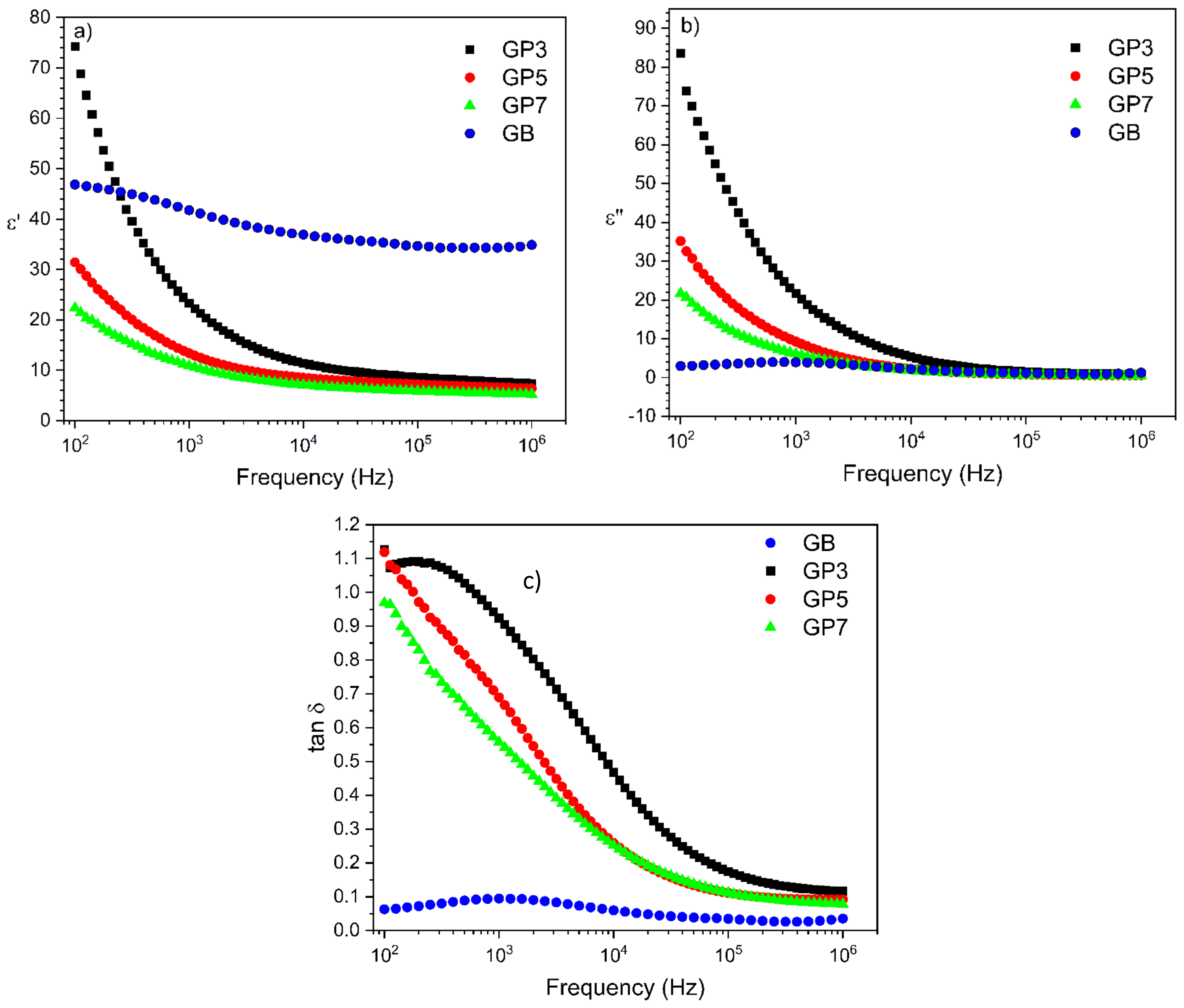
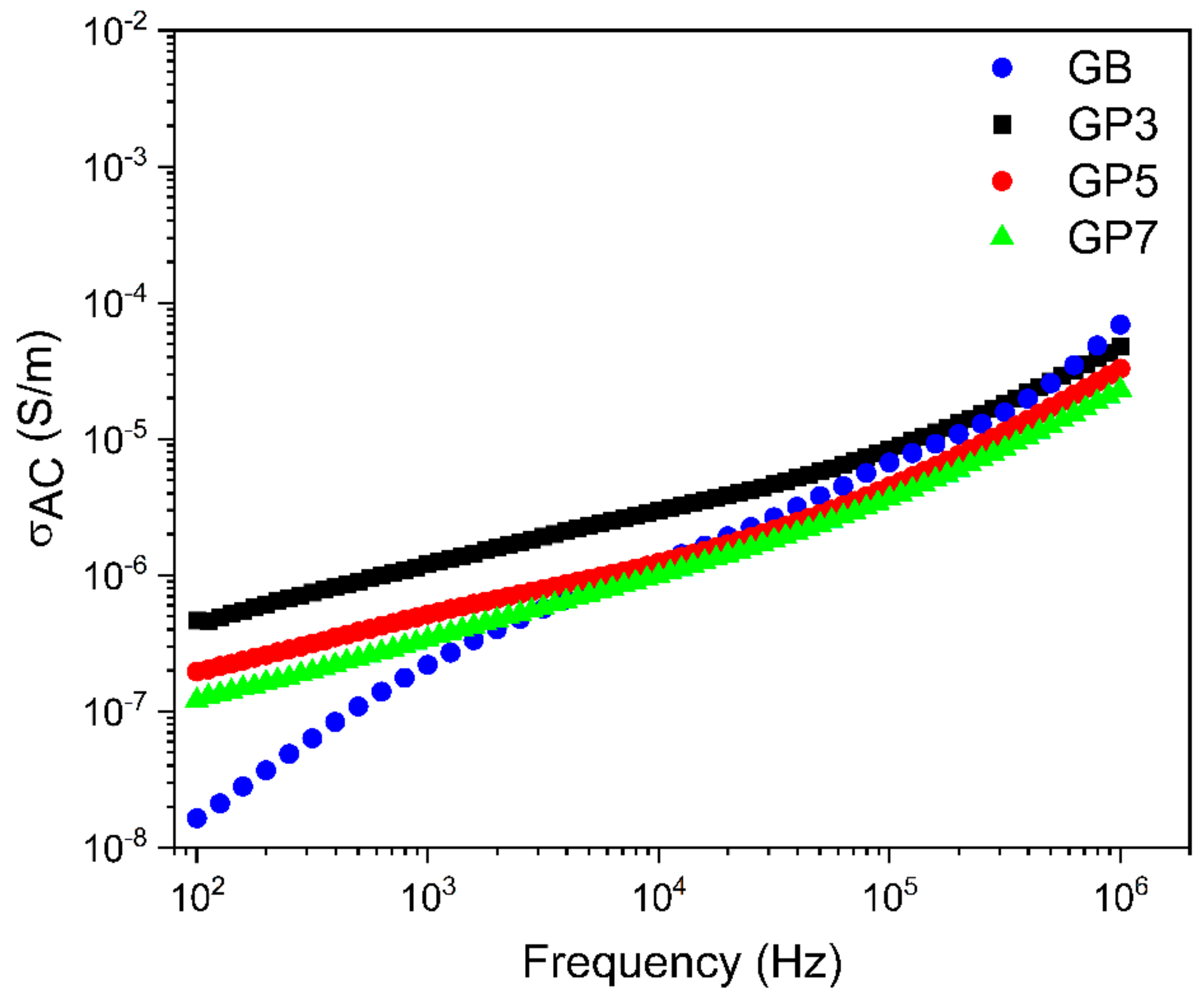
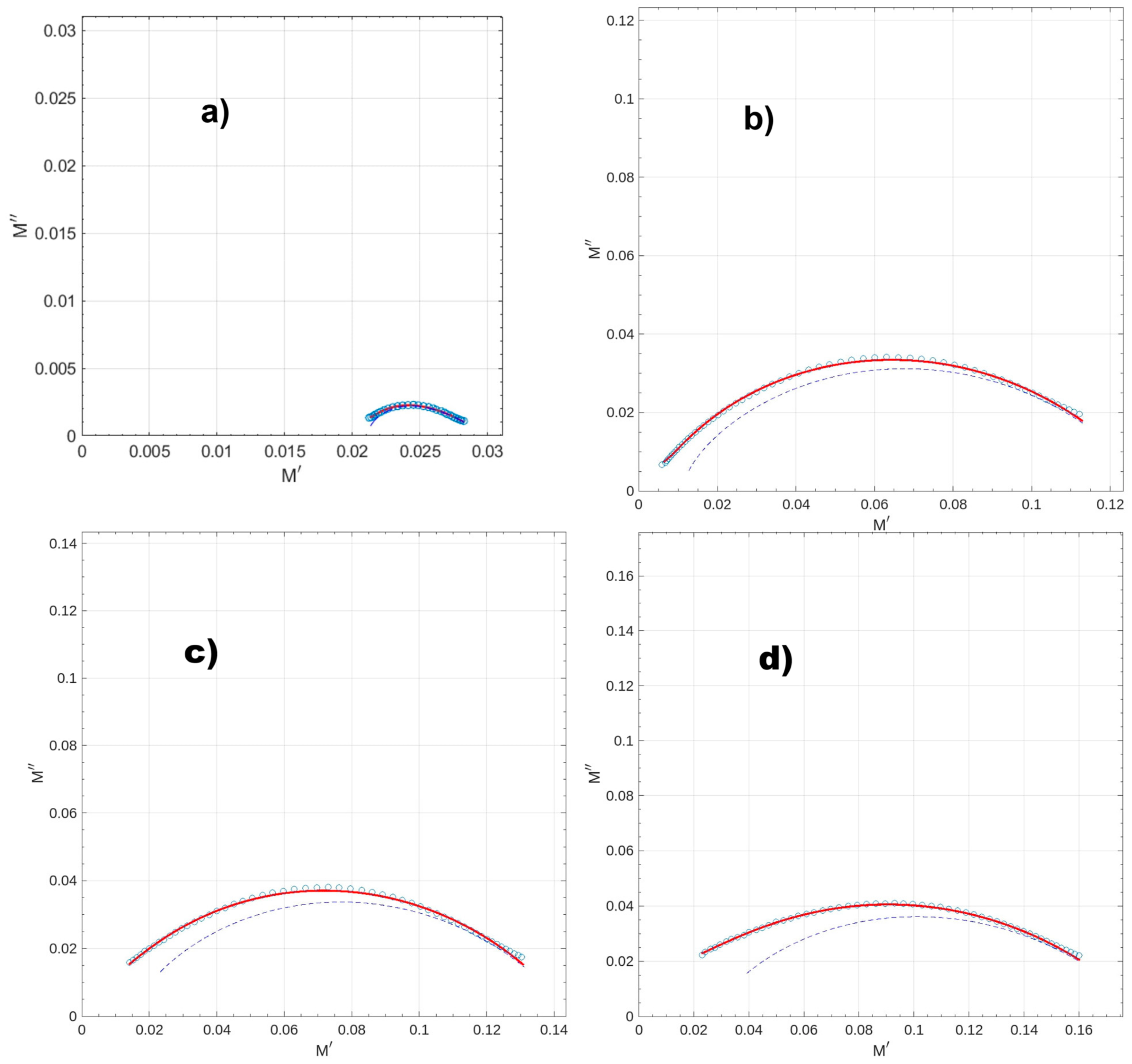
3.5. Impedance Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buriti, F.C.A.; Dos Santos, K.M.; Sombra, V.G.; Maciel, J.S.; Sá, D.M.T.; Salles, H.O.; Oliveira, G.; de Paula, R.C.; Feitosa, J.P.; Moreira, A.C.M.; et al. Characterisation of partially hydrolysed galactomannan from Caesalpinia pulcherrima seeds as a potential dietary fibre. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, S.; Ramakrishna, G.; Srivastava, H.; Gaikwad, K. A comprehensive review on leguminous galactomannans: Structural analysis, functional properties, biosynthesis process and industrial applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 443–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerqueira, M.A.; Souza, B.W.S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A. Effect of glycerol and corn oil on physicochemical properties of polysaccharide films—A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, A.A.C.; Sá, D.M.A.T.; Andrade, P.L.; Barreto, J.J.S.; dos Santos, N.L.; das Chagas, R.M.M.; Alves, T.d.B.; Chaves, M.J.L.; Maciel, J.d.S.; Egito, A.S.D.; et al. Partially hydrolyzed galactomannan from Adenanthera pavonina seeds used as stabilizer, fat substitute, and food fiber source for mousses. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 2951–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Chai, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J.; Yang, H.-Y. Preparation and physical/chemical modification of galactomannan film for food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, E.L.; Vasconcelos, N.F.; Maciel, J.d.S.; Andrade, F.K.; Vieira, R.S.; Feitosa, J.P.A. Injectable hydrogel based on dialdehyde galactomannan and N-succinyl chitosan: A suitable platform for cell culture. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2020, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.; Maiti, S. Research progress in galactomannan-based nanomaterials: Synthesis and application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 2113–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, M.H.; Kauffman, C.A. Aspergillus galactomannan for diagnosing invasive aspergillosis. JAMA 2017, 318, 1175–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.L.M.; Bresolin, T.M.B. Pharmaceutical use of galactomannans. Quimica Nova 2011, 34, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Rizvi, A.; Wahab, S.; Ansari, S.; Hussain, S.; Zareen, I. Antibacterial screening of the bark of Adenanthera pavonina (L.). Int. J. Biomed. Res. 2011, 2, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Das, C.; Sahoo, D.C. Phytochemical and Anthelmintic Screening of Crude Bark Extract of Adenanthera pavonina Linn. Pharm. Glob. Int. J. Comp. Pharm. 2010, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ara, A.; Arifuzzaman, M.; Ghosh, C.K.; Hashem, A.; Ahmad, M.U.; Bachar, S.C.; Nahar, L.; Sarker, S.D. Anti-inflammatory activity of Adenanthera pavonina L., Fabaceae, in experimental animals. Rev. Bras. Farm. 2010, 20, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, R.C.; Geronço, M.S.; Sousa, R.W.R.; Ramos, L.P.S.; Araújo, F.P.; Ribeiro, A.B.; Ferreira, P.M.P.; Osajima, J.A.; Costa, M.P. Biopolymer from Adenanthera pavonina L. Seeds: Characterization, Photostability, Antioxidant Activity, and Biotoxicity Evaluation. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018, 1385830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, S.R.; Vieira, I.G.P.; Mendes, F.N.P.; da Silva, S.C.; Paim, R.T.T.; da Silva, B.B.; Florean, E.O.P.T.; Guedes, M.I.F. Antidiabetic effects of galactomannans from Adenanthera pavonina L. in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2018, 11, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Godoi, A.; Faccin-Galhardi, L.; Lopes, N.; Nozawa, C.; de Almeida, R.; Ricardo, N.; Linhares, R. Characterization and antiherpetic activity of native and chemically sulfated polysaccharide from Adenanthera pavonina. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupama Devi, V.K.; Shyam, R.; Palaniappan, A.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Oh, T.-H.; Nathanael, A.J. Self-healing hydrogels: Preparation, mechanism and advancement in biomedical applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, V.D.; Jani, G.K.; Moradiya, N.G.; Randeria, N.P.; Nagar, B.J.; Naikwadi, N.N.; Variya, B.C. Galactomannan: A versatile biodegradable seed polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 60, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Vermani, K.; Garg, S. Hydrogels: From controlled release to pH-responsive drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2002, 7, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, J.; Shukla, V.K. Cross-linking in hydrogels—A review. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 4, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, J.B.; Ginting, M.; Nainggolan, F.M. Synthesis and properties of new hydrogel from cross-linked galactomannan boric. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1116, 042041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, G.; Kijowska, K.; Witczak, M.; Kuterasiński, Ł.; Łukasiewicz, M. Synthesis and effect of structure on swelling properties of hydrogels based on high methylated pectin and acrylic polymers. Polymers 2019, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalachaveedu, M.; Jenifer, P.; Pandian, R.; Arumugam, G. Fabrication and characterization of herbal drug enriched Guar galactomannan based nanofibrous mats seeded with GMSC’s for wound healing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, T.; He, J.; Jiang, J.; Lei, F. Diffusion of water and protein drug in 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether cross-linked galactomannan hydrogels and its correlation with the physicochemical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1987–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shui, T.; Adhikari, B.B.; Chae, M.; Bressler, D.C. Evaluation of thermally hydrolyzed specified risk materials cross-linked with glutaraldehyde for tackifier applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 140, 105535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.-K.; Cao, H.-L.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Lu, Q.-Q.; Ye, Y.-J.; He, J.; Huang, L.-J.; Yin, D.-C. Cross-linked protein crystals by glutaraldehyde and their applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 26163–26174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migneault, I.; Dartiguenave, C.; Bertrand, M.J.; Waldron, K.C. Glutaraldehyde; behavior in aqueous solution, reaction with proteins, and application to enzyme crosslinking. Biotechniques 2004, 37, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospodiuk, M.; Dey, M.; Sosnoski, D.; Ozbolat, I.T. The bioink: A comprehensive review on bioprintable materials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 217–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, L.A.; Batista, B.S.; Fonseca, A.P.G.; Balteiro, A.J.D.; Amaral, F.M.B.; Mendes, F.; Macêdo, A.A.M. Effect of pH on Swelling Profile of Glutaraldehyde Crosslinked Adenanthera pavonina L. Galactomannan. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Architecture, Materials and Construction (ICAMC 2019), Lisbon, Portugal, 2–4 December 2019; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 809, p. 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devesa, S.; Graça, M.P.F.; Pereira, W.O.; Santos, G.L.; Neto, J.F.d.S.; Amaral, F.M.B.; Hammami, I.; Mendes, F.; Macêdo, A.A.M. Dielectric Characterization of Solutions of Galactomannan Extracted from Adenanthera pavonina L.: Effects of Purification and Ethanol Concentration. Polymers 2024, 16, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, S. Bioelectrets: Electrets in Biomaterials and Biopolymers. In Topics in Applied Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.A.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Souza, B.W.; Lima, Á.M.; Ribeiro, C.; Miranda, C.; Teixeira, J.A.; Moreira, R.A.; Coimbra, M.A.; Gonçalves, M.P.; et al. Extraction, purification and characterization of galactomannans from non-traditional sources. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, J.F.; Mazzaro, I.; Silva, L.M.d.A.; Moreira, R.d.A.; Ferreira, M.L.C.; Reicher, F.; Petkowicz, C.L.d.O. Diverse patterns of cell wall mannan/galactomannan occurence in seeds of the Leguminosae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, V.B.; Bentini, R.; Catalani, L.H.; Petri, D.F.S. Synthesis and swelling behavior of xanthan-based hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunanithi, P.; Murali, M.R.; Samuel, S.; Raghavendran, H.R.B.; Abbas, A.A.; Kamarul, T. Three dimensional alginate-fucoidan composite hydrogel augments the chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veríssimo, D.; Leitão, R.; Ribeiro, R.; Figueiró, S.; Sombra, A.; Góes, J.; Brito, G. Polyanionic collagen membranes for guided tissue regeneration: Effect of progressive glutaraldehyde cross-linking on biocompatibility and degradation. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4011–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Somasundaran, P. Study of galactomannose interaction with solids using AFM, IR and allied techniques. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 309, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, V. A galactomannan from the seeds of Delonix regia. Phytochemistry 1972, 11, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiró, S.; Góes, J.C.; Moreira, R.; Sombra, A. On the physico-chemical and dielectric properties of glutaraldehyde cross-linked galactomannan-collagen films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 56, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.G.; Kim, H.C.; Palem, R.R.; Kim, J.; Kang, T.J. Cross-linking of cellulose nanofiber films with glutaraldehyde for improved mechanical properties. Mater. Lett. 2019, 250, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, S.-N.; Choi, S.-M.; Phillips, D.L.; Ma, C.-Y. Raman and FTIR spectroscopic study of carboxymethylated non-starch polysaccharides. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis, E.F.; Campos, F.S.; Lage, A.P.; Leite, R.C.; Heneine, L.G.; Vasconcelos, W.L.; Lobato, Z.I.P.; Mansur, H.S. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Hydrogels and Hybrids for RMPB70 Protein Adsorption. Mater. Res. 2006, 9, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.V.; Cavalcanti, O.A.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Synthesis and characterization of hydrogels formed from a glycidyl methacrylate derivative of galactomannan. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 267, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, I.; Moreno, L.; Dias, S.; Silva, D.; Oliveira, A.C.; Soares, L.; Sousa, R.; Dittz, D.; Rolim, H.; Nunes, L. Acetylated cashew gum nanoparticles for mesalazine delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2023, 5, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, D.; Barak, S.; Khatkar, B. X-ray diffraction, IR spectroscopy and thermal characterization of partially hydrolyzed guar gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallik, H.; Gupta, N.; Sarkar, A. Anisotropic electrical conduction in gum arabica-a biopolymer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2002, 20, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, G.M.M.; Prasad, C.; Murthy, K.R. Evaluation of modified gum karaya as carrier for the dissolution enhancement of poorly water-soluble drug nimodipine. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 234, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamir, K.; Badithi, N.; Venumadhav, K.; Seshagirirao, K. Characterization and comparative studies of galactomannans from Bauhinia vahlii, Delonix elata, and Peltophorum pterocarpum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothara, S.B.; Singh, S. Pharmacognostical studies of seeds on some plants belonging Chhattisgarh. Pharmacogn. J. 2012, 4, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, G.O.; Batista, M.J.; Ávila, A.F.; Franca, A.S.; Oliveira, L.S. Development and characterization of biopolymeric films of galactomannans recovered from spent coffee grounds. J. Food Eng. 2020, 289, 110083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lei, F.; Li, P.; Jiang, J.; Wang, K. Borax cross-linked fenugreek galactomannan hydrogel as potential water-retaining agent in agriculture. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Chiou, B.-S.; Liu, F.; Zhong, F. Modulating physicochemical properties of collagen films by cross-linking with glutaraldehyde at varied pH values. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ning, R.; Lei, F.; Li, P.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J. Study on the structure and physicochemical properties of fenugreek galactomannan modified via octenyl succinic anhydride. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 214, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, Y.; Karel, M. Plasticizing Effect of Water on Thermal Behavior and Crystallization of Amorphous Food Models. J. Food Sci. 1991, 56, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, O.B.; Barminas, J.T.; Nkafamiya, I.I.; Akinterinwa, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Cross-linked Hydrogel of Konkoli (Maesopsis eminii) Grafted Polymethylacrylamide for a Preliminary Study as an Insulin Delivery System. J. Biosci. Med. 2016, 4, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Anbakey, A. Effect of pH on swelling properties of commercial polyacrylic acid hydrogel bead. J. At. Mol. 2014, 4, 656–666. [Google Scholar]
- Clara, I.; Lavanya, R.; Natchimuthu, N. pH and temperature responsive hydrogels of poly(2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid-co-methacrylic acid): Synthesis and swelling characteristics. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2016, 53, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Mahdavinia, G.R. Superabsorbency, pH-sensitivity and swelling kinetics of partially hydrolyzed chitosan-g-poly(acrylamide) hydrogels. Turk. J. Chem. 2006, 30, 595–608. [Google Scholar]
- Dave, P.N.; Gor, A. Natural Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels and Nanomaterials: Recent Trends and Their Applications. In Handbook of Nanomaterials for Industrial Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 36–66. ISBN 9780128133514. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Ranjha, N.M. Effect of Degree of Cross-Linking on Swelling and on Drug Release of Low Viscous Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Hydrogels. Polym. Bull. 2014, 71, 2133–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Du, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, P.; Fu, W. Cross-Linking Behavior and Effect on Delectric Characteristics of Benzocyclobutene-Based Polycarbosiloxanes. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 6482–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomaa, M.; Seveyrat, L.; Lebrun, L.; Masenelli-Varlot, K.; Cavaille, J. Dielectric properties of segmented polyurethanes for electromechanical applications. Polymer 2015, 63, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havriliak, S.; Negami, S. A complex plane representation of dielectric and mechanical relaxation processes in some polymers. Polymer 1967, 8, 161–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Polysaccharide | |
|---|---|
| Composition (% mol) | Mannose (52.8/pm 0.4%); Galactose (39.2/pm 1.1%); Arabinose (4.2/pm 1.0%); Xylose (1.2/pm 0.2%); Rhamnose (1.0/pm 0.3%); Fucose (0.9/pm 0.2%); Glucose (0.8/pm 0.1%). |
| Average intrinsic viscosity (dL/g) | 9.11 |
| kH | 1.10 |
| Mν (Da) | 1.81 × 106 |
| Sample | Weight Loss (%) | Waste (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔW1 | ΔW2 | ΔW3 | ΔW4 | ||
| GB | 11.45 | 71.95 | - | - | 16.6 |
| GP3 | 32.25 | 14.64 | 29.11 | 6.3 | 17.7 |
| GP5 | 34.14 | 18.86 | 20.85 | 6.69 | 19.46 |
| GP7 | 32.23 | 10.92 | 23.13 | 11.16 | 22.56 |
| Parameter | GB | GP3 | GP5 | GP7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 47.49 | 90.47 | 70.50 | 38.43 | |
| 33.43 | 7.58 | 6.87 | 5.39 | |
| = | 14.06 | 82,89 | 63.63 | 33.04 |
| (s/rad) | 4.16 × 10−4 | 1.47 × 10−3 | 3.97 × 10−3 | 2.89 × 10−3 |
| (Hz) | 973.7 | 8.29 × 103 | 2.33 × 103 | 2.72 × 103 |
| 0.864 | 0.919 | 0.766 | 0.688 | |
| 0.435 | 0.621 | 0.748 | 0.732 | |
| (S/m) | 7.97 × 10−9 | 2.86 × 10−7 | 9.65 × 10−8 | 7.34 × 10−8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lima, A.M.d.O.; Mendes, F.; Cavalcante, L.A.; Araújo, C.C.; Batista, B.d.S.; Morais, J.P.L.; Amaral, F.M.B.; Macêdo, A.A.M. Dielectric Response of Crosslinked Adenanthera pavonina L. Galactomannan in pH-Controlled Medium. Polymers 2025, 17, 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070954
Lima AMdO, Mendes F, Cavalcante LA, Araújo CC, Batista BdS, Morais JPL, Amaral FMB, Macêdo AAM. Dielectric Response of Crosslinked Adenanthera pavonina L. Galactomannan in pH-Controlled Medium. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):954. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070954
Chicago/Turabian StyleLima, Antônia Millena de Oliveira, Fernando Mendes, Lincoln Almeida Cavalcante, Cristiane Carvalho Araújo, Beatriz da Silva Batista, João Pedro Lemos Morais, Filipe Miguel Borges Amaral, and Ana Angélica Mathias Macêdo. 2025. "Dielectric Response of Crosslinked Adenanthera pavonina L. Galactomannan in pH-Controlled Medium" Polymers 17, no. 7: 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070954
APA StyleLima, A. M. d. O., Mendes, F., Cavalcante, L. A., Araújo, C. C., Batista, B. d. S., Morais, J. P. L., Amaral, F. M. B., & Macêdo, A. A. M. (2025). Dielectric Response of Crosslinked Adenanthera pavonina L. Galactomannan in pH-Controlled Medium. Polymers, 17(7), 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070954








