Investigation of Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Characteristics of Earth-Based Pavements Stabilised with Various Bio-Based Binders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Specimen Preparation
2.2. Experimental Program
3. Results and Discussion
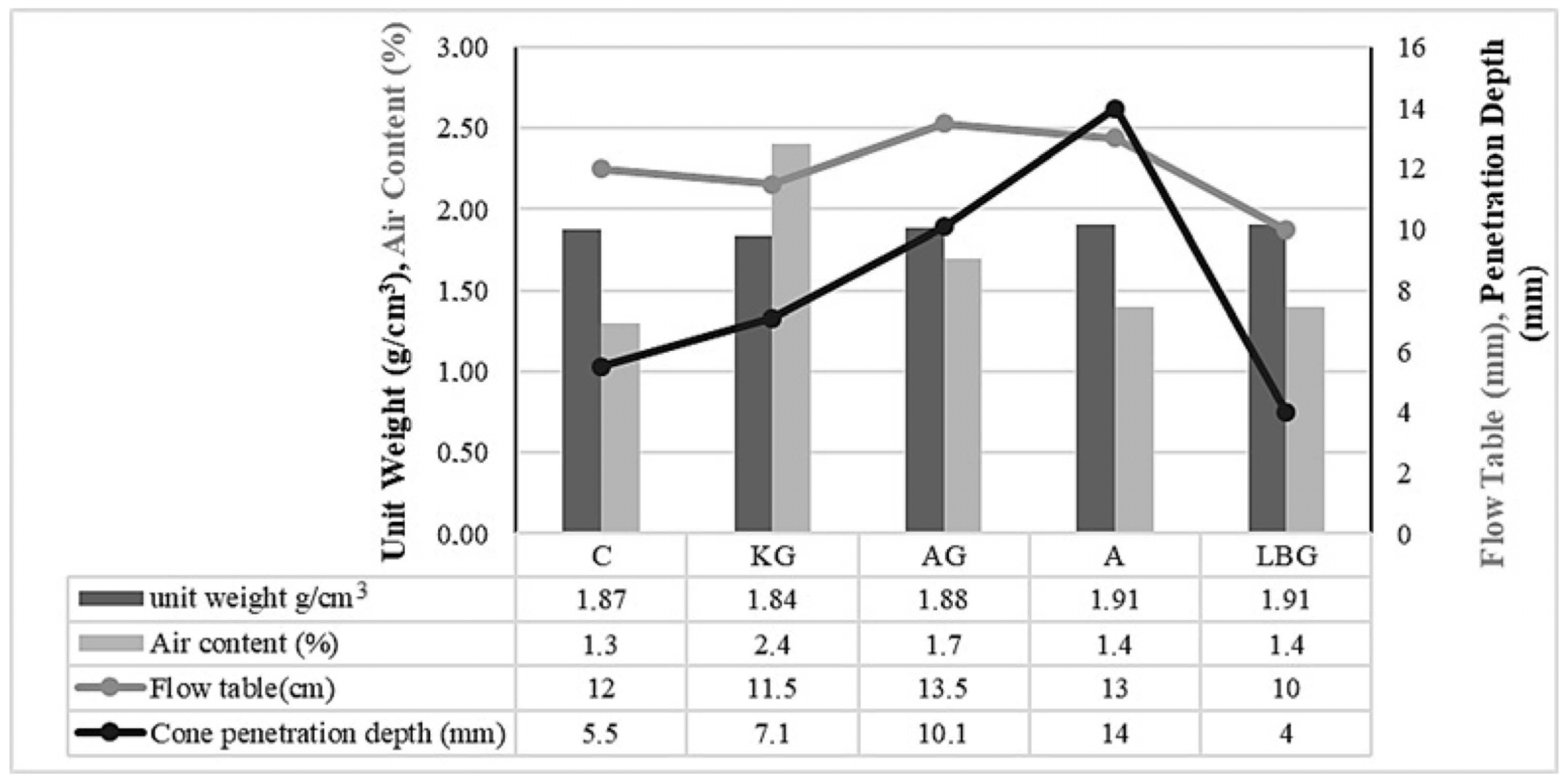
3.1. Fresh State Results
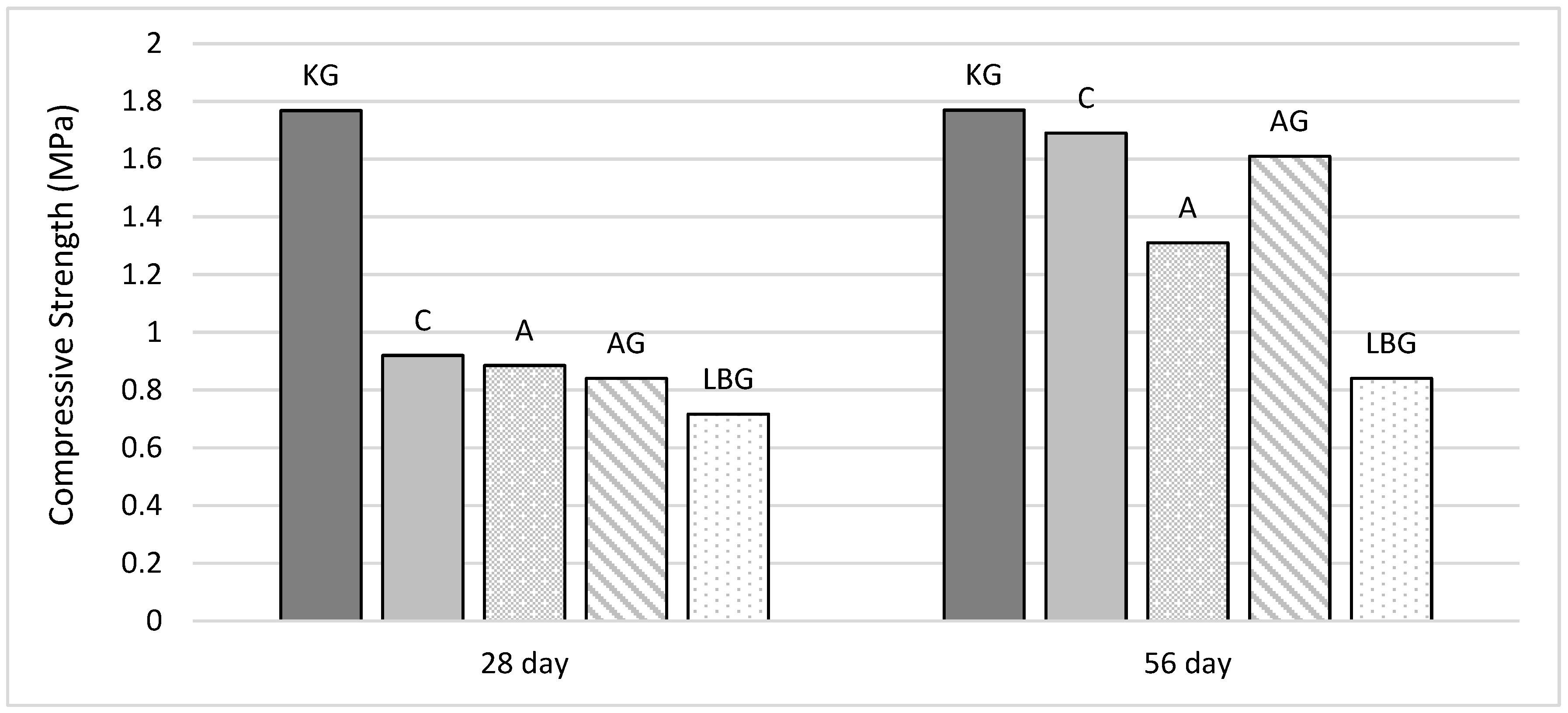
3.2. Hardened State Results
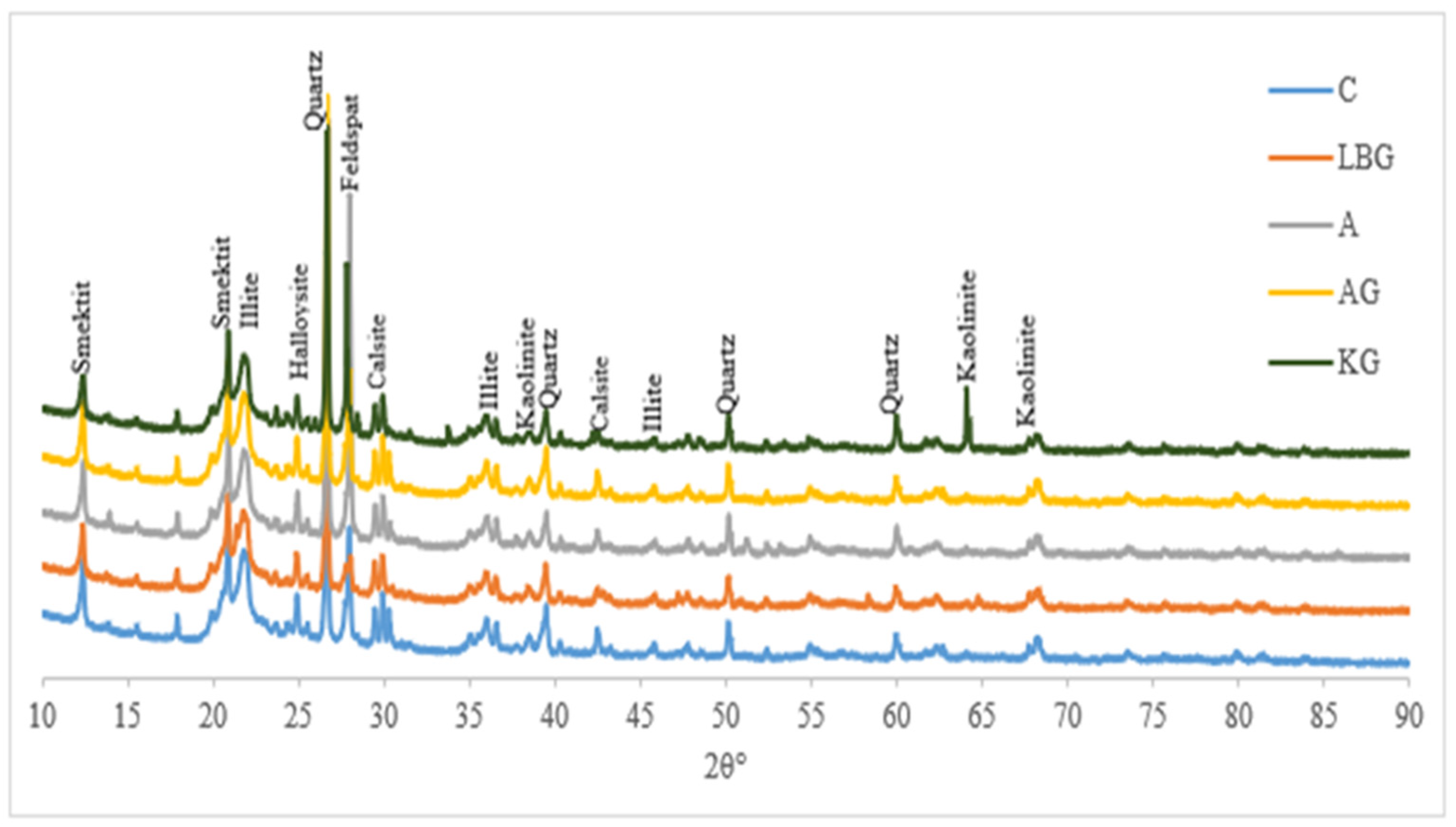
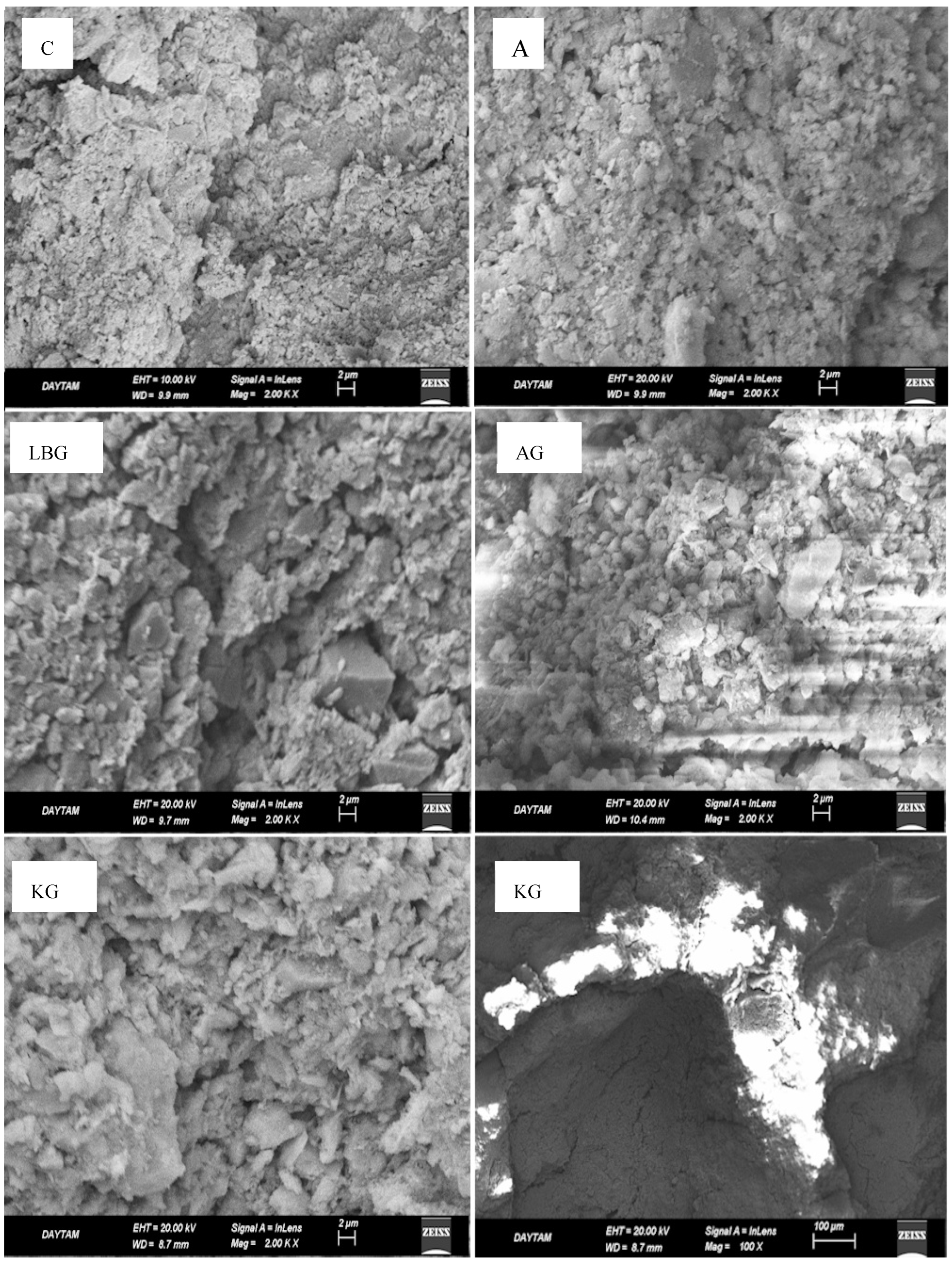
3.3. Micro Structural Analysis Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rael, R. Earth Architecture. Available online: https://books.google.com.tr/books?hl=tr&lr=&id=BsLAeifqe4EC&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&dq=Rael,+R.+(2009).+Earth+Architecture,+Princeton+Architectural+Press,+New+York.+USA.&ots=bMaUeGeTBG&sig=T7hqfxToPaKl4d7FV-mCeMILXTY&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Galan-Marin, C.; Rivera-Gomez, C.; Garcia-Martinez, A. Use of Natural-Fiber Bio-Composites in Construction versus Traditional Solutions: Operational and Embodied Energy Assessment. Materials 2016, 9, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrin, H. A Review on Different Types Soil Stabilization Techniques. Int. J. Transp. Eng. Technol. 2017, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, H.; Houben, H. Earth Concrete. Stabilization Revisited. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, S.Z.S.; Kamarudin, H.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Binhussain, M. Review on Soil Stabilization Techniques. Aust. J. Basic. Appl. Sci. 2013, 7, 258–265. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, M.I.; Faria, P.; Gonçalves, T.D. Earth-Based Mortars for Repair and Protection of Rammed Earth Walls. Stabilization with Mineral Binders and Fibers. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2401–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Antwi-Afari, M.F. Critical Success Factors for Implementing 3D Printing Technology in Construction Projects: Academics and Construction Practitioners’ Perspectives. Constr. Innov. 2023, ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Colangelo, F.; Farina, I. Sustainable Non-Conventional Concrete 3D Printing—A Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaneldin, E.; Ahmed, W.; Alharbi, N.; Alkaabi, R.; Alnuaimi, M. Potential Construction Applications of Sustainable 3D Printed Elements Made from Plastic Waste. Mater. Sci. Forum 2023, 1082, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinka, M.; Spurina, E.; Korjakins, A.; Bajare, D. Hempcrete—CO2 Neutral Wall Solutions for 3D Printing. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2022, 26, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, A.; Tighe, S. Development and Application of a Sustainable Management System for Unpaved Rural Road Networks. Transp. Res. Rec. 2019, 2673, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdas, V.M.; Mandree, P.; Mgangira, M.; Mukaratirwa, S.; Lalloo, R.; Ramchuran, S. Review of Current and Future Bio-Based Stabilisation Products (Enzymatic and Polymeric) for Road Construction Materials. Transp. Geotech. 2021, 27, 100458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarhan, Y.; Kabakuş, N. Enhancing Sustainable Road Construction: Evaluation of the Mechanical and Durability Properties of Stabilized Earth-Based Pavement Materials. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, V.; Simão, N.; Freire, A.C. A Soil-Cement Formulation for Road Pavement Base and Sub Base Layers: A Case Study. Transp. Infrastruct. Geotechnol. 2017, 4, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muguda, S.; Booth, S.J.; Hughes, P.N.; Augarde, C.E.; Perlot, C.; Bruno, A.W.; Gallipoli, D. Mechanical Properties of Biopolymer-Stabilised Soil-Based Construction Materials. Geotech. Lett. 2017, 7, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; McGregor, J.; Martsinovich, N.; Armistead, S.; Yu, X.; Siripanich, N. Enhancing the Water and Biodegradation Resistance of Biopolymer Stabilised Soils—Design Concepts. RILEM Bookseries 2023, 45, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilham, M.; Baba, K.; Simou, S. Naturally Strengthening Rammed Earth: The Promising Potential of Biopolymers. Google Books. Available online: https://books.google.com.tr/books?hl=tr&lr=&id=vKAAEQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA233&dq=16.%09Masrour,+I.%3B+Baba,+K.%3B+Simou,+S.+Naturally+Strengthening+Rammed+Earth:+The+Promising+Potential+of+Biopolymers.+Materials+Research+&ots=f4fj_iYSF5&sig=tKDmfs6eT4i8c9sBf6ewJ29dEkE&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Losini, A.E.; Grillet, A.C.; Bellotto, M.; Woloszyn, M.; Dotelli, G. Natural Additives and Biopolymers for Raw Earth Construction Stabilization—A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 304, 124507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Sanjay, M.R.; Srisuk, R.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. A Comprehensive Review on Chemical Properties and Applications of Biopolymers and Their Composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehi, H.; Abtahi, S.M.; Hashemolhosseini, H.; Hejazi, S.M. A Novel Study on Using Protein Based Biopolymers in Soil Strengthening. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 167, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D. Assessment of the Potential for Salt Damage to Asphalt Surfacings When Chloride-Treated Unpaved Roads Are Upgraded to a Sealed Standard. Transp. Res. Rec. 2019, 2673, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabalar, A.F.; Akbulut, N.; Demir, S.; Yildiz, O. Use of a Biopolymer for Road Pavement Subgrade. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berninger, T.; Dietz, N.; González López, Ó. Water-Soluble Polymers in Agriculture: Xanthan Gum as Eco-Friendly Alternative to Synthetics. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1881–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatehi, H.; Ong, D.E.L.; Yu, J.; Chang, I. Biopolymers as Green Binders for Soil Improvement in Geotechnical Applications: A Review. Geosciences 2021, 11, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabani, M.; Shalchian, M.M.; Baghbani, A. A State-of-the-Art Review on Interactive Mechanisms and Multi-Scale Application of Biopolymers (BPs) in Geo-Improvement and Vegetation Growth. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 358, 120905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muguda, S.; Hughes, P.N.; Augarde, C.E.; Perlot, C.; Walter Bruno, A.; Gallipoli, D. Cross-Linking of Biopolymers for Stabilizing Earthen Construction Materials. Build. Res. Inf. 2022, 50, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ana Sayfa. Ata Kimya. Yapı Kimyasalları ve Boya Sanayisine Hammadde Tedariği. Available online: http://www.atakimya.com.tr/ (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Artuk, F. Lif ve uçucu kül katkili polimer içi boş kaziklarin yumuşak kil zeminlerdeki davranişinin deneysel olarak araştirilmasi. Master’s Thesis, Atatürk University, Erzurum, Türkiye, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- TS EN 12350-7/AC TS EN 12350-7/AC; Beton—Taze Beton Deneyleri—Bölüm 7: Hava Içeriğinin Tayini—Basınç Yöntemleri (Testing Fresh Concrete—Part 7: Air Content—Pressure Methods). TSE: Ankara, Turkey, 2022. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/Standard/Standard/Standard.aspx?081118051115108051104119110104055047105102120088111043113104073086065089087052072056121054068120 (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- TS EN 12350-5 TS EN 12350-5; Beton—Taze Beton Deneyleri—Bölüm 5: Yayılma Tablası Deneyi (Testing Fresh Concrete—Part 5: Flow Table Test). TSE: Ankara, Turkey, 2010. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/standard/standard/Standard.aspx?081118051115108051104119110104055047105102120088111043113104073082112065070113087101115117109052 (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- CEN ISO 17892-6 ISO 17892-6:2017; Geotechnical Investigation and Testing—Laboratory Testing of Soil—Part 6: Fall Cone Test. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/55248.html (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- TS EN 13057 TS EN 13057; Beton Yapılar—Koruma ve Tamir Için Mamul ve Sistemler—Deney Metotları—Kılcal Su Emmeye Direncin Tayini (Products and Systems for the Protection and Repair of Concrete Structures—Test Methods—Determination of Resistance of Capillary Absorption). TSE: Ankara, Turkey, 2002. Available online: https://intweb.tse.org.tr/standard/standard/Standard.aspx?081118051115108051104119110104055047105102120088111043113104073081068111056079084053120078107114 (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Giroud, J.P.; Bonaparte, R.; Beech, J.F.; Gross, B.A. Design of Soil Layer-Geosynthetic Systems Overlying Voids. Geotext. Geomembr. 1990, 9, 11–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabani, M.; Shalchian, M.M. A Review of the Use of Bio-Based Substances in Soil Stabilization. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 13685–13737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olarte, J.; Dashti, S.; Liel, A.B. Can Ground Densification Improve Seismic Performance of the Soil-Foundation-Structure System on Liquefiable Soils? Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 47, 1193–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.S.A.; Turrakheil, K.S.; Naveed, M. Impact of Wetting and Drying Cycles on the Hydromechanical Properties of Soil and Implications on Slope Stability. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatmadari, N.; Reza, M.; Tasuji, A.; Ghadir, P.; Javadi, A.A. Experimental Study on the Effect of Chitosan Biopolymer on Sandy Soil Stabilization. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 195, 06007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri Tasuji, M.R.; Ghadir, P.; Hosseini, A.; Javadi, A.A.; Habibnejad Korayem, A.; Ranjbar, N. Experimental Investigation of Sandy Soil Stabilization Using Chitosan Biopolymer. Transp. Geotech. 2024, 46, 101266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Ouyang, F.; Xiao, H.; Wang, L.; Tao, G. Experimental Study on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Modified Clay Using Xanthan Gum and Guar Gum Composite Materials. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Deng, S.; Liang, B.; Zhuang, J.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Z. Mechanical Behavior and Strengthening Mechanism of Loess Stabilized with Xanthan Gum and Guar Gum Biopolymers. Mater. Res. Express 2024, 11, 105305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, L.; Harbottle, M. Exploring the Effect of Biopolymers in Near-Surface Soils Using Xanthan Gum–Modified Sand under Shear. Can. Geotech. J. 2019, 57, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chang, I.; Chung, M.K.; Kim, Y.; Kee, J. Geotechnical Shear Behavior of Xanthan Gum Biopolymer Treated Sand from Direct Shear Testing. Geomech. Eng. 2017, 12, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.; Kwon, Y.M.; Im, J.; Cho, G.C. Soil Consistency and Interparticle Characteristics of Xanthan Gum Biopolymer–Containing Soils with Pore-Fluid Variation. Can. Geotech. J. 2019, 56, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Geng, X. Investigation of Unconfined Compressive Strength for Biopolymer Treated Clay. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 385, 131458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzyski, P. The Influence of Gum Arabic Admixture on the Mechanical Properties of Lime-Metakaolin Paste Used as Binder in Hemp Concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagherinia, M. Mechanical, Durability, and Microstructure of Soft Clay Stabilised with Anionic Biopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 417, 135343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitikie, B.B.; Geleta, D.G. Enhancement of Concrete Performance with Xanthan Gum: Potential of Natural Biopolymer. Discov. Civil Eng. 2025, 2, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos, P.R.; Andrade Neto, J.S.; Jansen, D.; De la Torre, A.G.; Kirchheim, A.P.; Campos, C.E.M. In-Situ Laboratory X-Ray Diffraction Applied to Assess Cement Hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022, 162, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Huerta, A.M.; Palma-Ramírez, D.; Domínguez-Crespo, M.A.; Del Angel-López, D.; De La Fuente, D. Comparative Assessment of Miscibility and Degradability on PET/PLA and PET/Chitosan Blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 61, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Chemical Properties | Value (%) | Geotechnical Properties | Value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 69.10 | Grain size < 0.002 mm, % | 28 |
| Al2O3 | 15.20 | Grain size < 0.075 mm, % | 100 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.20 | Specific gravity | 2.63 |
| CaO | 0.10 | Liquid limit, % | 49 |
| SO3 | 4.29 | Plastic limit, % | 26 |
| Na2O | 0.03 | Plasticity index, % | 23 |
| K2O | 11.07 | Optimum moisture content, % | 25 |
| CR2O3 | 0.01 | Maximum dry unit weight, kN/m3 | 13.2 |
| Unconfined compressive strength, kPa | 307 |
| Product Properties | LBG | A | AG | KG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS number | 9000-40-2 | 14984-39-5 | 9000-01-5 | 11138-66-2 |
| Appearance/ texture/smell | Pale white, no smell | White, powder, no smell | White, powder, slightly smelly | White, solid, no smell |
| pH | 5.4–7 | 6.0–8.0 | 4.1–4.8 | 6–8 |
| Density | 1.2 ± 0.1 g/cm3 | 1.6 g/cm3 | 1.15 g/cm3 | 1.5 g/cm3 |
| Molecular weight | 226.66 g/mol | 216.121 g/mol | 180.41 g/mol | 1016.8 g/mol |
| Molecular formula | C10H11CIN202 | C6H7O6Na | C12H36 | (C35H49O29)n |
| E-code | E410 | E401 | E414 | E415 |
| Sample Code | Material Amounts (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earth | Sand | Clay | Water | A | AG | KG | LBG | |
| C | 40 | 30 | 30 | 20 | - | - | - | - |
| A | 40 | 30 | 29.9 | 20 | 0.1 | - | - | - |
| AG | 40 | 30 | 29.9 | 20 | - | 0.1 | - | - |
| KG | 40 | 30 | 29.9 | 20 | - | - | 0.1 | - |
| LBG | 40 | 30 | 29.9 | 20 | - | - | - | 0.1 |
| Sample | Beginning | 2 min Later Weight (g) | 6 min Later Weight (g) | 30 min. Later Weight (g) | Mass Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 204.19 | 206.63 | 206.39 | 195.39 | (−) 4.31 |
| A | 188.11 | 188.76 | 190.43 | 170.61 | (−) 9.3 |
| LBG | 190.62 | 203.04 | 206.06 | 219.12 ** | (+) 14.95 |
| AG | 198.48 | 185.44 | 178.36 | * | (−) 10.14 |
| KG | 195.60 | 201.98 | 203.79 | 215.33 | (+) 10.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabakuş, N.; Tarhan, Y. Investigation of Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Characteristics of Earth-Based Pavements Stabilised with Various Bio-Based Binders. Polymers 2025, 17, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070864
Kabakuş N, Tarhan Y. Investigation of Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Characteristics of Earth-Based Pavements Stabilised with Various Bio-Based Binders. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070864
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabakuş, Nuriye, and Yeşim Tarhan. 2025. "Investigation of Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Characteristics of Earth-Based Pavements Stabilised with Various Bio-Based Binders" Polymers 17, no. 7: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070864
APA StyleKabakuş, N., & Tarhan, Y. (2025). Investigation of Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Characteristics of Earth-Based Pavements Stabilised with Various Bio-Based Binders. Polymers, 17(7), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070864








