Laser Polishing of Vertically Oriented FDM-PLA Components: Influence of Laser Power and Polishing Speed on Surface Topography and Mechanical Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
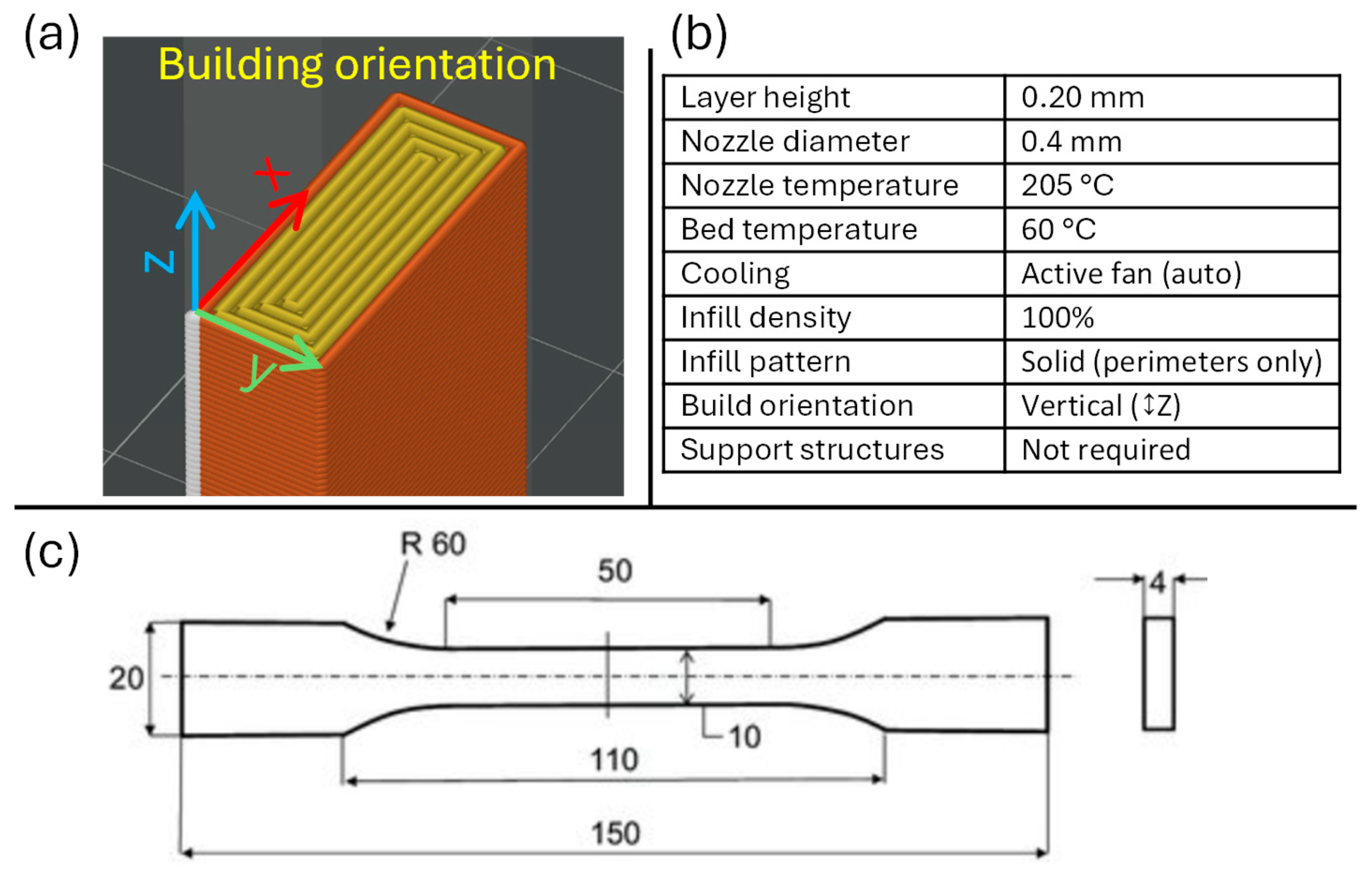
2.1. Material and 3D Printing Method
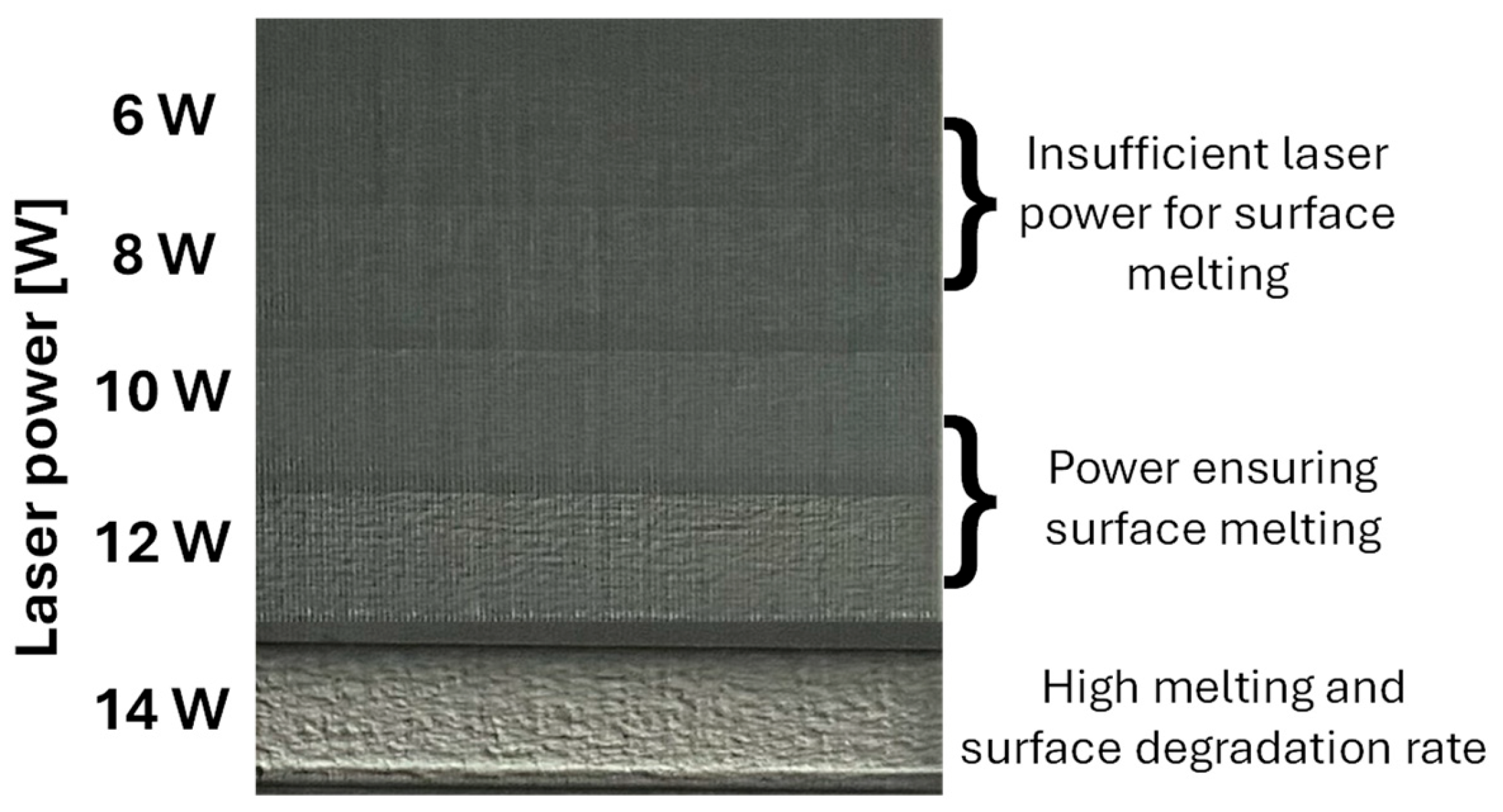
2.2. Laser Polishing
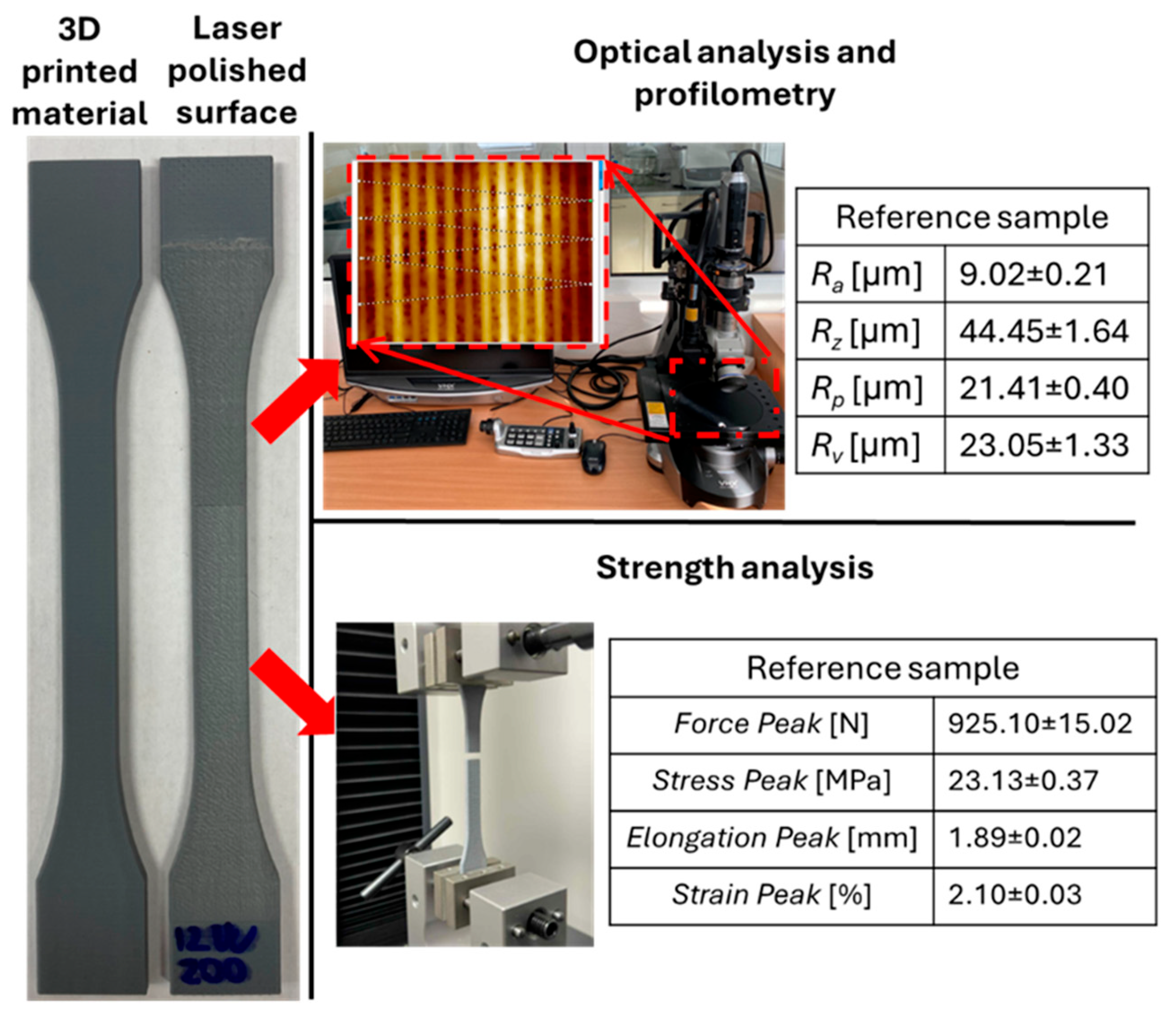
2.3. Measurement Methods
3. Results and Discussion
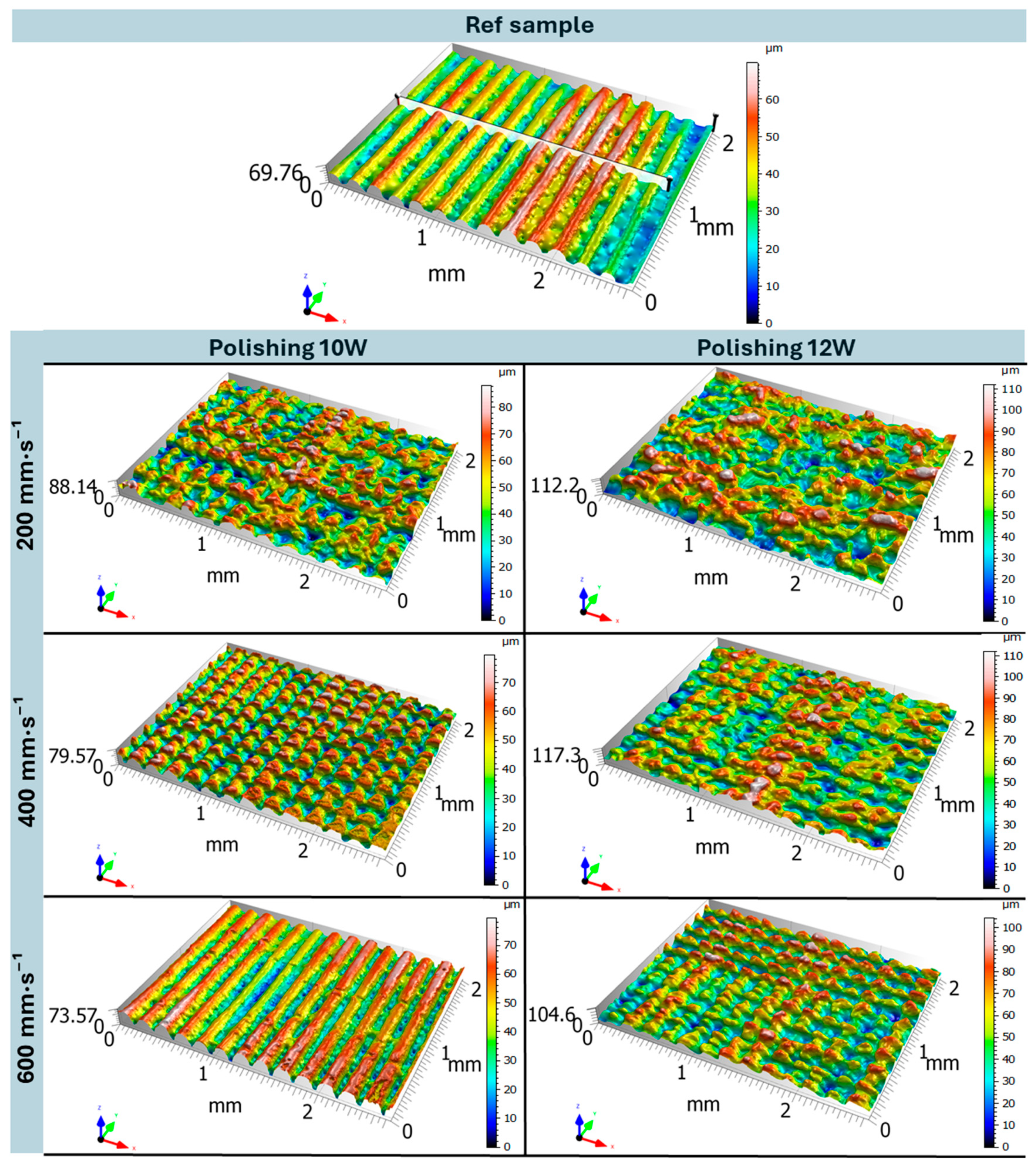
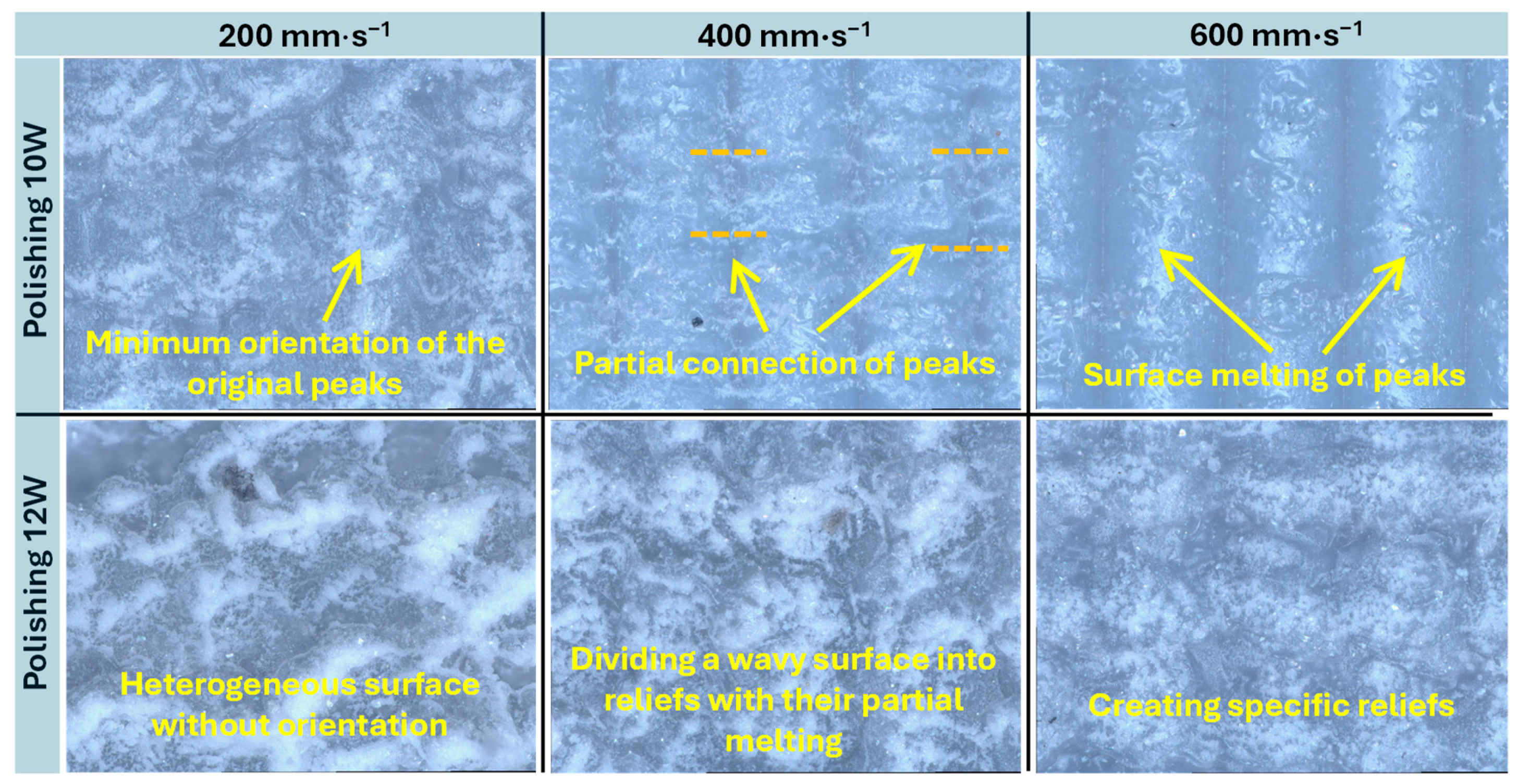
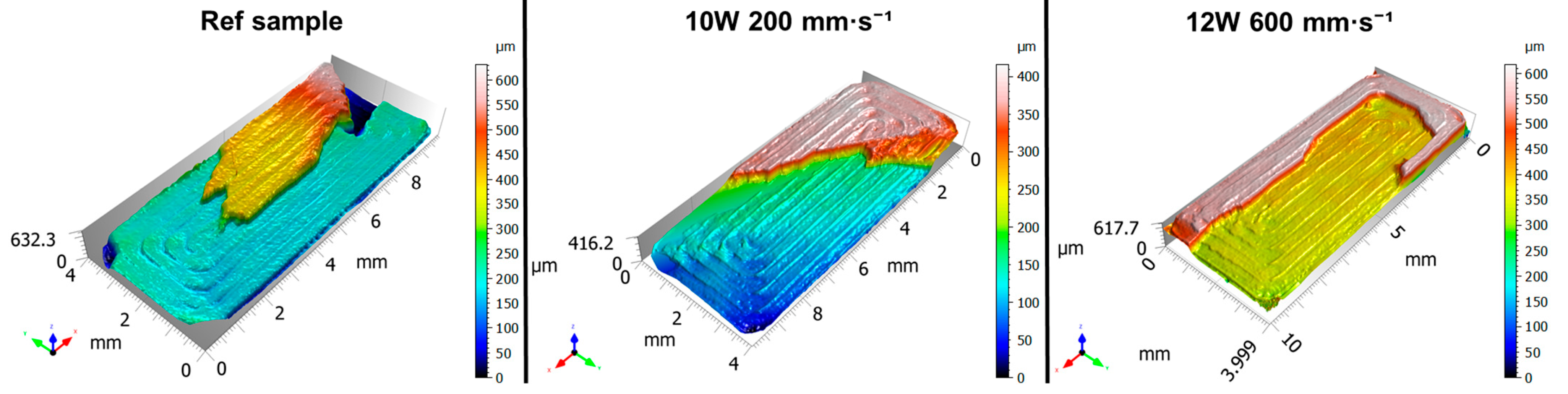
3.1. Optical Analysis and 3D Reproduction of Surfaces
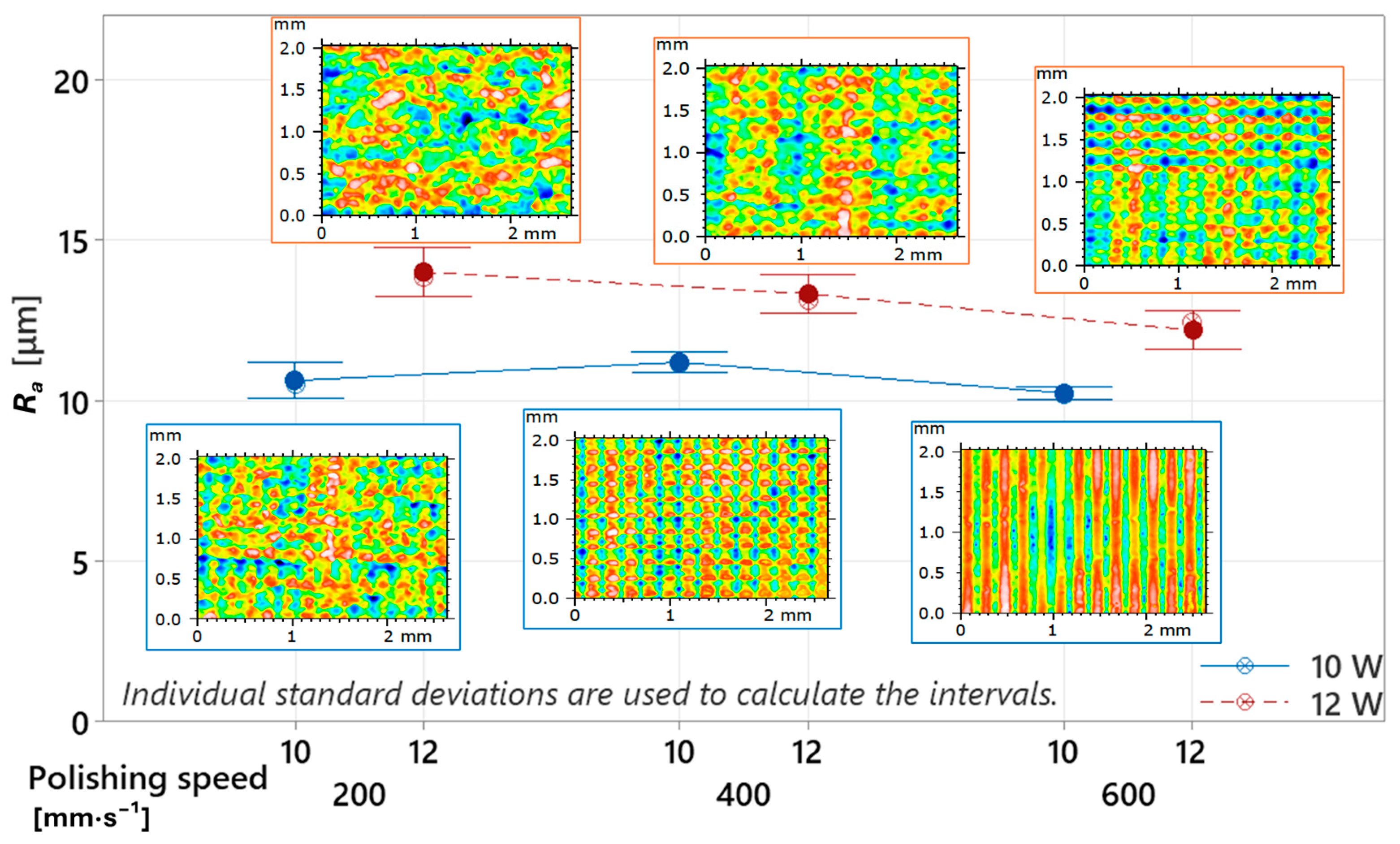
3.2. Surface Roughness
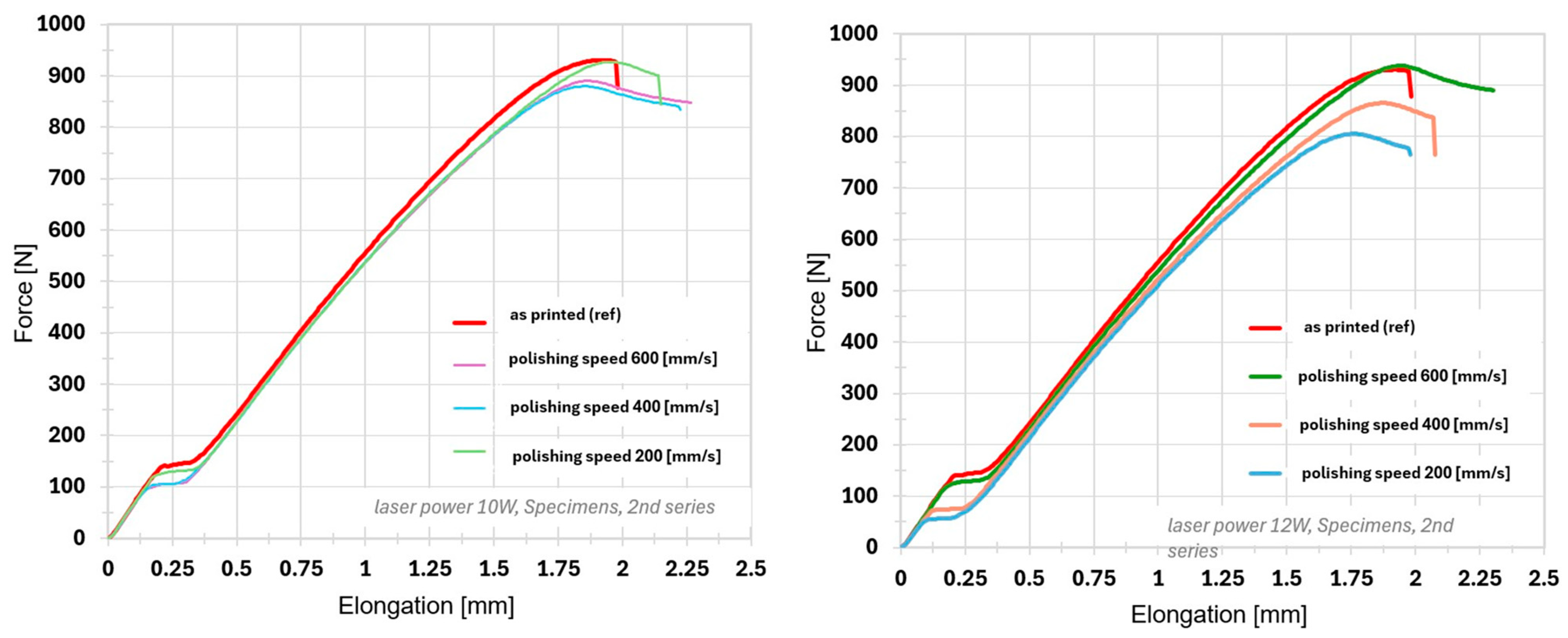
3.3. Mechanical Properties
3.4. Failure and Facture Characteristics
- -
- The printhead extrudes an excessive amount of material at the starting point due to a temporary delay in XY motion. This can cause over-deposition and local material buildup, which may lead to defects in the subsequent infill process. The excess material prematurely solidifies, and during the following infill passes, the printhead may collide with the hardened material, inducing micro-vibrations or slight displacement of the part, resulting in the accumulation of defects in that region.
- -
- Alternatively, premature XY motion relative to the extrusion rate may occur. In this case, the filament is under-deposited at the starting point, which again leads to poor interlayer bonding and the formation of structurally critical defects.
4. Conclusions
- -
- The unpolished reference surface exhibited a distinct periodic wavy morphology introduced by the FDM process—characterized by smooth peak regions and porous valleys—confirming the natural anisotropy and interlayer heterogeneity that critically influence mechanical performance.
- -
- 3D surface reconstructions revealed, at both 10 W and 12 W, the formation of periodic relief structures caused by the perpendicular laser polishing direction combined with insufficient hatch overlap. At 10 W, the relief was mildly periodic and partially ordered, whereas at 12 W and lower polishing speeds (vf = 200–400 mm·s−1), the surface became stochastically melted. At vf = 600 mm·s−1, the surface partially stabilized, yet persistent relief features remained due to insufficient overlap of laser passes.
- -
- This insufficient track overlap resulted in increased surface roughness at both energy levels—Ra = 10.24 ± 0.14 µm (10 W) and Ra = 12.20 ± 0.43 µm (12 W) at vf = 600 mm·s−1—in comparison with the reference sample (Ra = 9.02 ± 0.21 µm), confirming the necessity of further optimization of this parameter.
- -
- Rp and Rv analysis showed that at 10 W, valley depth dominated (Rv > Rp), indicating surface-level melting without altering the fundamental FDM topography, whereas at 12 W, Rp exceeded Rv (Rp > Rv) due to intensified subsurface melting and material flow into the valleys.
- -
- The mechanical analysis revealed that the current polishing settings led to a degradation of mechanical performance, attributed to the formation of relief features acting as stress concentrators.
- -
- The fracture analysis confirmed a change in failure mechanism—at 10 W, a more stable layered fracture occurred with improved bonding of the outer shell, while at 12 W, deeper melted zones resulted in fracture initiation within the infill region.
- -
- The transverse displacement between laser passes was identified as a critical parameter, as insufficient overlap segmented the original wavy surface into isolated reliefs, increasing roughness and degrading mechanical properties due to stress concentration effects. A systematic optimization of this parameter is essential to enhance both surface quality and mechanical stability.
- -
- A second research opportunity concerns the laser polishing trajectory. In this study, a perpendicular polishing strategy was used relative to the surface waviness from printing. However, a parallel polishing orientation may potentially suppress relief formation, leading to a more compact and uniform surface structure—and should be considered in future studies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, R.; Xia, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, P.; Hou, W.; Hu, Q.; Shan, C. Isotropic and Anisotropic Elasticity and Yielding of 3D Printed Material. Compos. B Eng. 2016, 99, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćwikła, G.; Grabowik, C.; Kalinowski, K.; Paprocka, I.; Ociepka, P. The Influence of Printing Parameters on Selected Mechanical Properties of FDM/FFF 3D-Printed Parts. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; Institute of Physics Publishing: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; Volume 227. [Google Scholar]
- Casavola, C.; Cazzato, A.; Moramarco, V.; Pappalettere, C. Orthotropic Mechanical Properties of Fused Deposition Modelling Parts Described by Classical Laminate Theory. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z.; Song, L.; Li, Z. Short Fiber Reinforced Composites for Fused Deposition Modeling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 301, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropovik, R.; Peti, D.; Hatala, M. Strength Analyses of Fdm Products from Additively Strengthened Pla Materials. MM Sci. J. 2025, 2025, 8512–8519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Eagle, I.N.R.; Yodo, N. A Review on Filament Materials for Fused Filament Fabrication. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arockiam, A.J.; Subramanian, K.; Padmanabhan, R.G.; Selvaraj, R.; Bagal, D.K.; Rajesh, S. A Review on PLA with Different Fillers Used as a Filament in 3D Printing. In Proceedings of the Materials Today: Proceedings; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 50, pp. 2057–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Rankouhi, B.; Javadpour, S.; Delfanian, F.; Letcher, T. Failure Analysis and Mechanical Characterization of 3D Printed ABS With Respect to Layer Thickness and Orientation. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2016, 16, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojković, J.R.; Turudija, R.; Vitković, N.; Górski, F.; Păcurar, A.; Pleşa, A.; Ianoşi-Andreeva-Dimitrova, A.; Păcurar, R. An Experimental Study on the Impact of Layer Height and Annealing Parameters on the Tensile Strength and Dimensional Accuracy of FDM 3D Printed Parts. Materials 2023, 16, 4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalihan, R.; Aggari, J.; Alon, A.; Latayan, R.; Montalbo, F.; Javier, A. On the Optimized Fused Filament Fabrication of Polylactic Acid Using Multiresponse Central Composite Design and Desirability Function Algorithm. J. Process Mech. Eng. 2024, 09544089241247454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kačergis, L.; Mitkus, R.; Sinapius, M. Influence of Fused Deposition Modeling Process Parameters on the Transformation of 4D Printed Morphing Structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 105042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Osswald, T.A. Laser Polishing of Cu/PLA Composite Parts Fabricated by Fused Deposition Modeling: Analysis of Surface Finish and Mechanical Properties. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 1356–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Yuan, Q. Experimental Investigations for Optimizing the Extrusion Parameters on FDM PLA Printed Parts. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.A.; Kamil, M. Effect of Print Speed and Extrusion Temperature on Properties of 3D Printed PLA Using Fused Deposition Modeling Process. In Proceedings of the Materials Today: Proceedings; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 45, pp. 5462–5468. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Mulholland, T.; Osswald, T.A. Effects of Raster Angle on the Mechanical Properties of PLA and Al/PLA Composite Part Produced by Fused Deposition Modeling. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 2122–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgun, I.; Ertan, R. Experimental Investigation of FDM Process for Improvement of Mechanical Properties and Production Cost. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2014, 20, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón, J.M.; Caminero, M.A.; García-Plaza, E.; Núñez, P.J. Additive Manufacturing of PLA Structures Using Fused Deposition Modelling: Effect of Process Parameters on Mechanical Properties and Their Optimal Selection. Mater. Des. 2017, 124, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es-Said, O.S.; Foyos, J.; Noorani, R.; Mendelson, M.; Marloth, R.; Pregger, B.A. Effect of Layer Orientation on Mechanical Properties of Rapid Prototyped Samples. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2000, 15, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambali, R.H.; Celik, H.K.; Rennie, A.; Hambali, R.H.; Celik, H.K.; Smith, P.C.; Rennie, A.E.W.; Ucar, M. Effect of Build Orientation on FDM Parts: A Case Study for Validation of Deformation Behaviour by FEA. In Proceedings of the iDECON 2010—International Conference on Design and Concurrent Engineering, Malacca, Malaysia, 20–21 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tymrak, B.M.; Kreiger, M.; Pearce, J.M. Mechanical Properties of Components Fabricated with Open-Source 3-D Printers under Realistic Environmental Conditions. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Espin, M.; Puigoriol-Forcada, J.M.; Garcia-Granada, A.A.; Llumà, J.; Borros, S.; Reyes, G. Mechanical Property Characterization and Simulation of Fused Deposition Modeling Polycarbonate Parts. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, D.A.; Shinde, B.M.; Raykar, S.J. Post Processing Techniques Used to Improve the Quality of 3D Printed Parts Using FDM: State of Art Review and Experimental Work. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Taufik, M.; Jain, P.K. Laser Assisted Finishing Process for Improved Surface Finish of Fused Deposition Modelled Parts. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 30, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, R.T.; Iqbal, A.; Wang, Y.; Khan, A.M.; Petra, M.I. Advancing PLA 3D Printing with Laser Polishing: Improving Mechanical Strength, Sustainability, and Surface Quality. Crystals 2023, 13, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, P.D.; Bialas, O.; Wozniak, A.; Adamiak, M.; Appiah, A.; Tampu, C.; Mazurchevici, S.N.; Kyratsis, P.; Tzotzis, A.; Nedelcu, A.; et al. Characterization of Laser-Textured Surfaces of Parts of a Biodegradable Polymer. Coatings 2025, 15, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Wang, W.; Fan, D.; He, P. Effects of Femtosecond Laser Micromachining on the Surface and Substrate Properties of Poly-Lactic Acid (PLA). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 538, 148117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Mingareev, I. Utilizing Ultrafast Lasers for Postprocessing to Improve Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printed Parts. J. Laser Appl. 2023, 31, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Gan, S. Effects of Laser Polishing on Surface Quality and Mechanical Properties of PLA Parts Built by Fused Deposition Modeling. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, X. Modification the Surface Quality and Mechanical Properties by Laser Polishing of Al/PLA Part Manufactured by Fused Deposition Modeling. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 492, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, M.P.; Ulutan, D. Development of Laser Polishing as an Auxiliary Post-Process to Improve Surface Quality in Fused Deposition Modeling Parts. In Proceedings of the International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 4–8 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Arthanari, S.; Park, J.E.; Heo, J.S.; Cho, D.H.; Yang, M.; Hwang, J.S.; Lee, H. Laser Surface Polishing of 3D Printed Polylactic Acid (PLA) with Different Levels of Absorption. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 98, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L. Effects of Laser Scanning Speed on Surface Roughness and Mechanical Properties of Aluminum/Polylactic Acid (Al/PLA) Composites Parts Fabricated by Fused Deposition Modeling. Polym. Test. 2020, 91, 106785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 527-2:2012; Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties–Part 2: Test Conditions for Moulding and Extrusion Plastics. British, European and International Standard: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 26.
- Chai, Y.; Li, R.W.; Perriman, D.M.; Chen, S.; Qin, Q.H.; Smith, P.N. Laser Polishing of Thermoplastics Fabricated Using Fused Deposition Modelling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 4295–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 21920-2:2021; Specifications, Geometrical Product. Surface Texture: Profile—Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Alhuzaim, A. Investigating the Mechanical Properties of PLA Polymer Tensile Test Samples Produced Via 3D Printing in Various Orientations: Flat, Vertical, and 45 Degrees. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. (IJMET) 2024, 15, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, J.; Bhaskar, R.; Mohaghegh, V. Investigating the Effects of Extrusion Temperatures and Material Extrusion Rates on FFF-Printed Thermoplastics. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 117, 2679–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axinte, M.; Chicet, D.L.; Chelariu, R.; Comăneci, R.I. The Role of Overflow on The Mechanical Properties of 3d Printed Pla. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2024, 69, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorleo, L.; Ravelli, M. Laser Polishing of Polymer Parts Produced with Material Jetting Technology: Effect of Laser Scan Speed, Overlapping and Loop Cycles. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. C 2023, 104, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, R.T.; Wang, Y.; Khan, A.M.; Rehman, M.; Li, X.; Sharma, S. A Post-Processing Laser Polishing Method to Improve Process Performance of 3D Printed New Industrial Nylon-6 Polymer. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 101, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamimoghadam, M.; Dezaki, M.L.; Zolfagharian, A.; Bodaghi, M. Influence of Post-Processing CO2 Laser Cutting and FFF 3D Printing Parameters on the Surface Morphology of PLAs: Statistical Modelling and RSM Optimisation. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2023, 6, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharatish, A.; Murthy, H.N.N.; Harish, D.V.N.; Kumar, S.M.; Solaiachari, S. Investigating the Impact of Laser Polishing Parameters on Surface Roughness, Mass Ablation Rate, and Optical Transmittance of 3D-Printed PLA Substrates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuschi, F.; Rungi, S.; Hellmianni, R. Influence of Polishing Orientation on the Generation of LIPSS on Stainless Steel. Laser 2018, 14, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Chen, X.B.; Zhang, D.; Lynch, J.; Birbilis, N.; Qin, Q.H.; Smith, P.N.; Li, R.W. Laser Polished Fused Deposition Poly-Lactic Acid Objects for Personalized Orthopaedic Application. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Captan Prabakaran, A.; Senthil, P.; Sathies, T. Effect of Laser Surface Polishing on the Surface Characteristics, Tribological, and Mechanical Behavior of 3D-Printed Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate Parts. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 5042–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, R.T.; Wang, Y.; Bao, C.; Chen, X.; Anwar, S.; Sharma, S.; Khan, A.M.; Sharma, K.; Bisht, Y.S.; Abbas, M.; et al. Multi-Objective Optimization of Laser Polishing Parameters for Enhanced Mechanical Properties, Sustainability, and Surface Finish of 3D-Printed Industrial ABS Polymers Using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 3168–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, D.; Ward, C.; Herrmann, G.; Etches, J. Filament Temperature Dynamics in Fused Deposition Modelling and Outlook for Control. In Proceedings of the Procedia Manufacturing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 11, pp. 536–544. [Google Scholar]
- Gisario, A.; Barletta, M.; Veniali, F. Laser Polishing: A Review of a Constantly Growing Technology in the Surface Finishing of Components Made by Additive Manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 1433–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, P.; Zhao, J.; Wu, W.; Ye, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S. Effects of Extrusion Speed and Printing Speed on the 3D Printing Stability of Extruded PEEK Filament. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 37, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Roughness Parameter | Laser Power P [W] | Reference Sample | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10W | 12W | ||||||
| Laser Polishing Speed vf [mm·s−1] | |||||||
| 200 | 400 | 600 | 200 | 400 | 600 | ||
| Ra D ± σD [µm] | 10.63 ± 0.40 | 11.20 ± 0.22 | 10.24 ± 0.14 | 14.01 ± 0.55 | 13.34 ± 0.43 | 12.20 ± 0.43 | 9.02 ± 0.21 |
| Rz D ± σD [µm] | 57.87 ± 2.92 | 54.89 ± 2.05 | 46.99 ± 1.22 | 70.46 ± 2.12 | 70.40 ± 2.26 | 63.03 ± 2.45 | 44.45 ± 1.64 |
| Rp D ± σD [µm] | 28.95 ± 2.09 | 24.82 ± 1.66 | 20.20 ± 0.67 | 36.13 ± 1.86 | 35.91 ± 1.64 | 32.84 ± 1.40 | 21.41 ± 0.40 |
| Rv D ± σD [µm] | 28.93 ± 1.60 | 30.07 ± 0.93 | 26.79 ± 0.65 | 34.33 ± 0.55 | 34.50 ± 0.78 | 30.19 ± 1.46 | 23.05 ± 1.33 |
| Specimen Group | Force Peak [N] | Stress Peak [MPa] | Elongation Peak [mm] | Strain Peak [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. | 925.10 ± 15.02 | 23.13 ± 0.37 | 1.89 ± 0.02 | 2.10 ± 0.03 |
| 10 W 200 mm·s−1 | 896.80 ± 41.28 | 22.42 ± 1.03 | 1.92 ± 0.03 | 2.13 ± 0.03 |
| 10 W 400 mm·s−1 | 879.37 ± 13.39 | 21.98 ± 0.34 | 1.86 ± 0.01 | 2.06 ± 0.01 |
| 10 W 600 mm·s−1 | 880.26 ± 12.74 | 22.01 ± 0.31 | 1.88 ± 0.05 | 2.09 ± 0.05 |
| 12 W 200 mm·s−1 | 838.83 ± 30.49 | 20.97 ± 0.76 | 1.81 ± 0.05 | 2.01 ± 0.05 |
| 12 W 400 mm·s−1 | 875.73 ± 13.34 | 21.89 ± 0.33 | 1.87 ± 0.01 | 2.08 ± 0.01 |
| 12 W 600 mm·s−1 | 922.79 ± 13.59 | 23.07 ± 0.34 | 1.93 ± 0.06 | 2.14 ± 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stolárik, G.; Vandžura, R.; Ropovík, R.; Peti, D.; Geľatko, M. Laser Polishing of Vertically Oriented FDM-PLA Components: Influence of Laser Power and Polishing Speed on Surface Topography and Mechanical Response. Polymers 2025, 17, 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233096
Stolárik G, Vandžura R, Ropovík R, Peti D, Geľatko M. Laser Polishing of Vertically Oriented FDM-PLA Components: Influence of Laser Power and Polishing Speed on Surface Topography and Mechanical Response. Polymers. 2025; 17(23):3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233096
Chicago/Turabian StyleStolárik, Gabriel, Radoslav Vandžura, Róbert Ropovík, Damián Peti, and Matúš Geľatko. 2025. "Laser Polishing of Vertically Oriented FDM-PLA Components: Influence of Laser Power and Polishing Speed on Surface Topography and Mechanical Response" Polymers 17, no. 23: 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233096
APA StyleStolárik, G., Vandžura, R., Ropovík, R., Peti, D., & Geľatko, M. (2025). Laser Polishing of Vertically Oriented FDM-PLA Components: Influence of Laser Power and Polishing Speed on Surface Topography and Mechanical Response. Polymers, 17(23), 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233096







