Multi-Analytical Assessment of Deterioration in the Qianlong Tripitaka Wooden Scripture Plates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Qianlong Tripitaka
2.1.2. Pear Wood
2.2. Analysis Method
2.2.1. OM
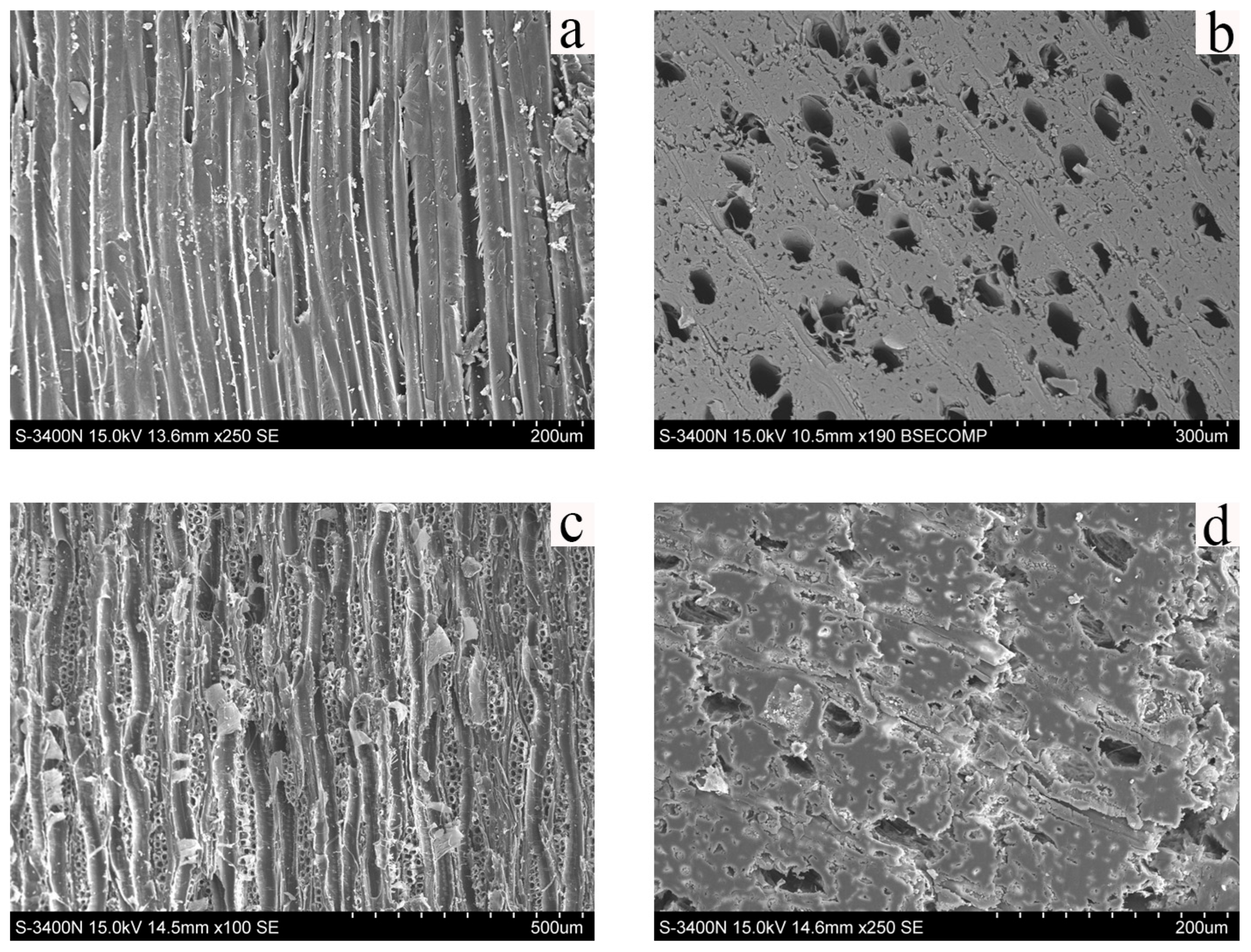
2.2.2. SEM
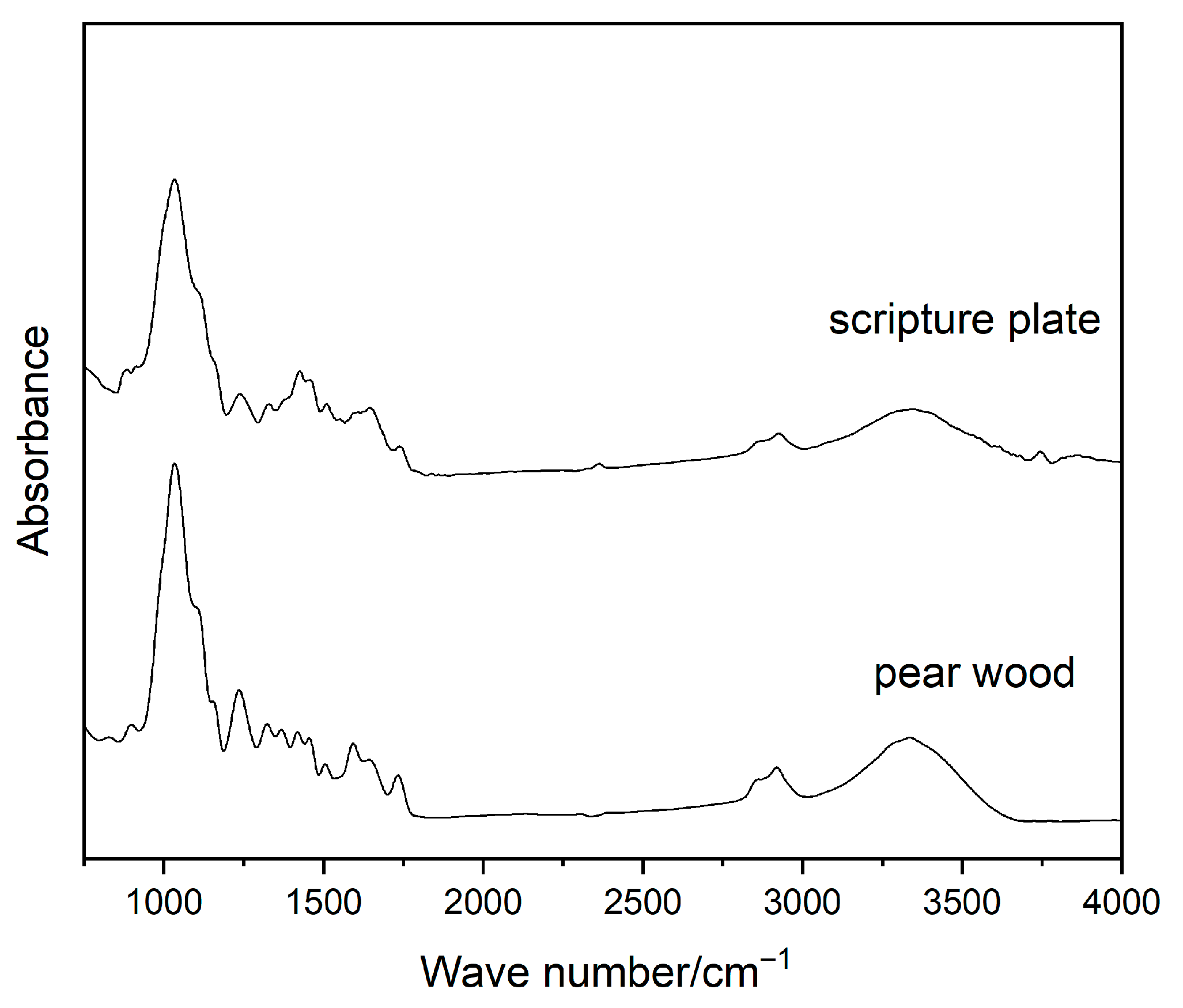
2.2.3. FTIR
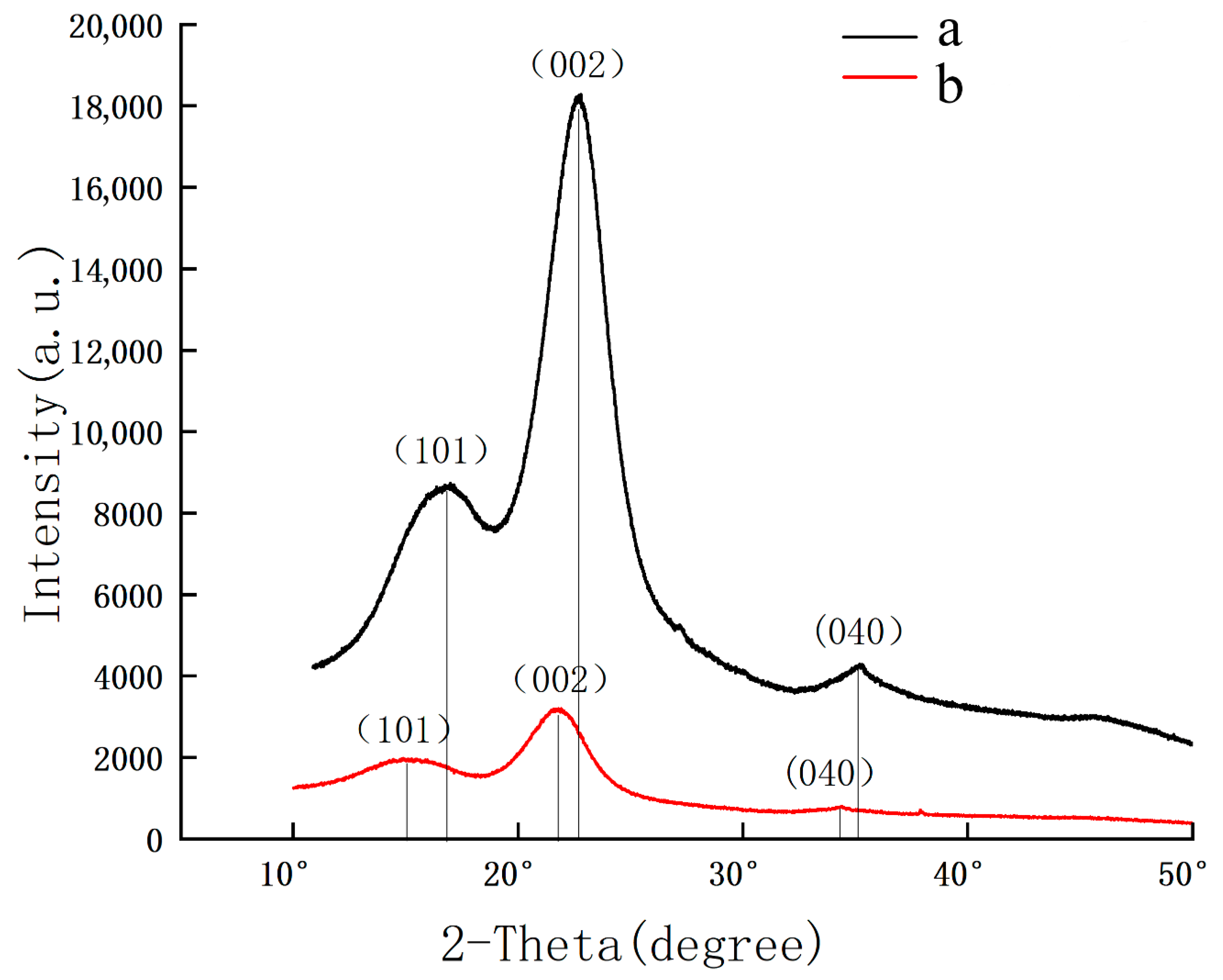
2.2.4. XRD
2.2.5. CT
2.2.6. TGA
2.2.7. BET
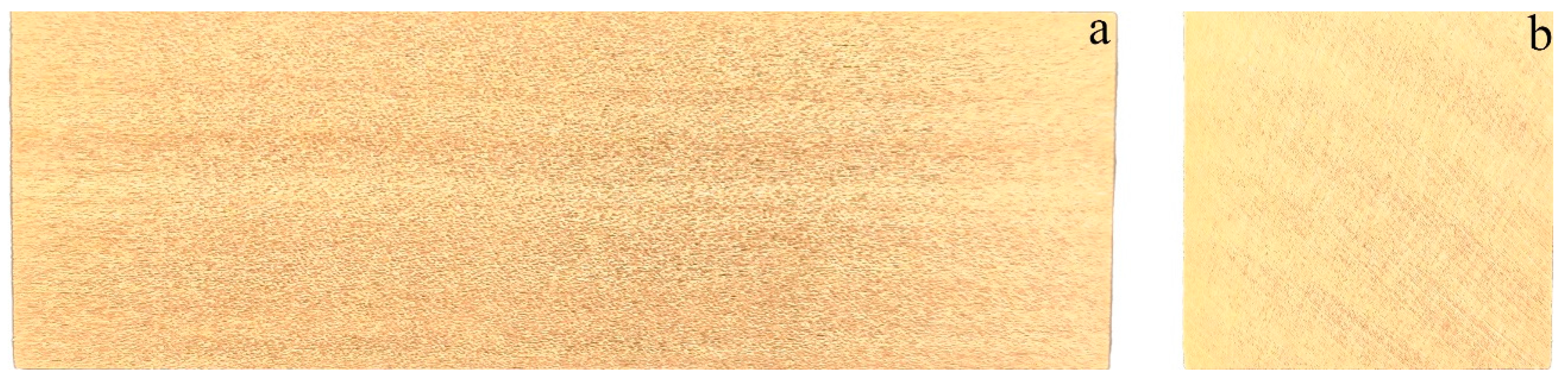
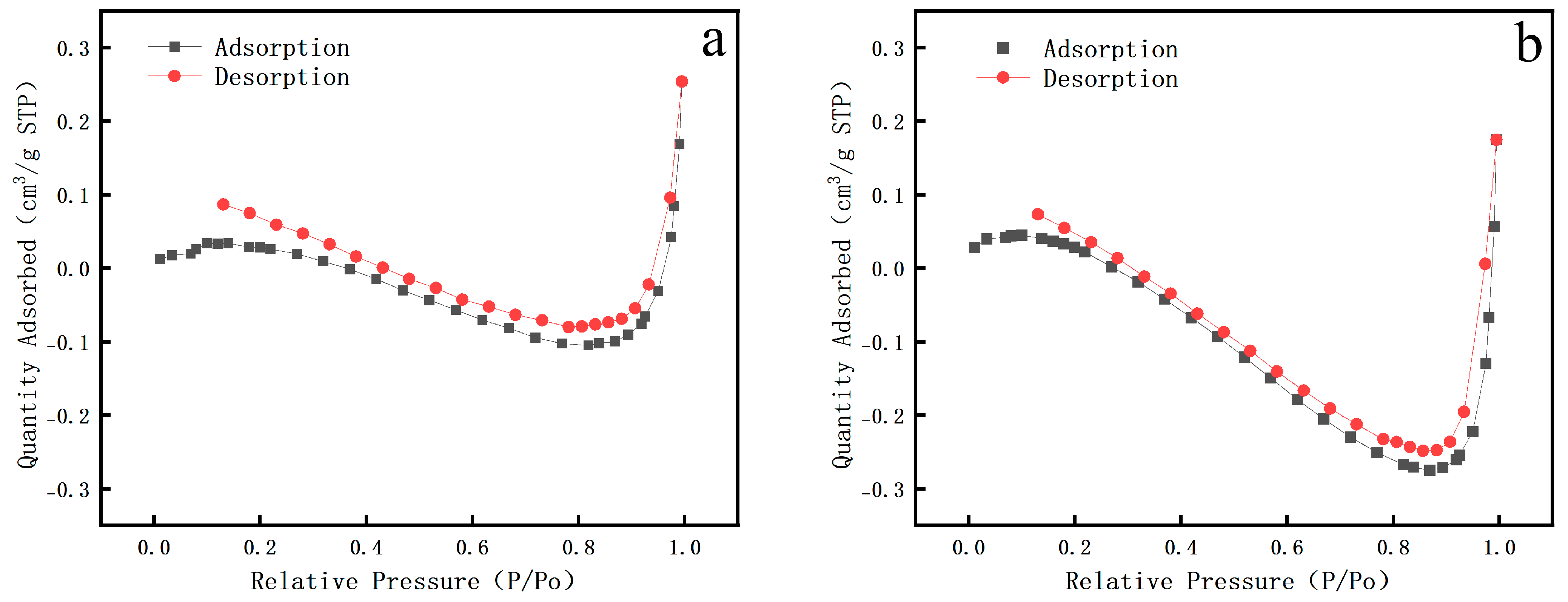
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blanchette, R.A. A review of microbial deterioration found in archaeological wood from different environments. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2000, 46, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, D.; Łucejko, J.J.; Pizzo, B.; Mohammed, M.Y.; Sloggett, R.; Colombini, M.P. A critical evaluation of the degradation state of dry archaeological wood from Egypt by SEM, ATR-FTIR, wet chemical analysis and Py (HMDS)-GC-MS. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 146, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavidel, A.; Hosseinpourpia, R.; Militz, H.; Vasilache, V.; Sandu, I. Characterization of archaeological European white elm (Ulmus laevis P.) and black poplar (Populus nigra L.). Forests 2020, 11, 1329. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.P.; Kim, Y.S.; Chavan, R.R. Advances in understanding microbial deterioration of buried and waterlogged archaeological woods: A review. Forests 2022, 13, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, C.M.; Tibirna, C.M.; Vasile, C. XPS characterization of naturally aged wood. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 256, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, M.; Kránitz, K.; Bremer, M.; Peters, J.; Fischer, S.; Bues, C.T.; Niemz, P. Effect of natural aging on the chemical composition of Norway spruce, fir, and European oak wood. Pro Ligno 2018, 14, 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Pyzik, A.; Ciuchcinski, K.; Dziurzynski, M.; Dziewit, L. The bad and the good—Microorganisms in cultural heritage environments—An update on biodeterioration and biotreatment approaches. Materials 2021, 14, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, W.; Gu, J.D. Innovative approaches for the processes involved in microbial biodeterioration of cultural heritage materials. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 75, 102716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afifi, H.A.; Mansour, M.M.; Hassan, A.G.; Salem, M.Z. Biodeterioration effects of three Aspergillus species on stucco supported on a wooden panel modeled from Sultan al-Ashraf Qaytbay Mausoleum, Egypt. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geweely, N.; Abu Taleb, A.; Ibrahim, S.; Grenni, P.; Caneva, G.; Galotta, G.; Abdallah, M.; Atwa, D.; Plaisier, J.; Antonelli, F. New data on relevant ancient Egyptian wooden artifacts: Identification of wooden species and study of the state of conservation with multidisciplinary analyses. Archaeometry 2023, 65, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, H.A.M.; Basta, S.A.; Mostafa, A.M. Examination and analysis of a stored stucco window in the conservation lab of Bab Al-azab area, citadel of Salah Al-din Al-Ayyubi, Cairo Egypt. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2024, 218, 111627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łucejko, J.J.; Modugno, F.; Ribechini, E.; Tamburini, D.; Colombini, M.P. Analytical instrumental techniques to study archaeological wood degradation. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2015, 50, 584–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrich, J.; Mai, C.; Militz, H. Evaluation of bacterial wood degradation by Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) measurements. J. Cult. Herit. 2012, 13, S135–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzo, B.; Pecoraro, E.; Alves, A.; Macchioni, N.; Rodrigues, J.C. Quantitative evaluation by attenuated total reflectance infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy of the chemical composition of decayed wood preserved in waterlogged conditions. Talanta 2015, 131, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traoré, M.; Kaal, J.; Cortizas, A.M. Application of FTIR spectroscopy to the characterization of archeological wood. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 153, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukir, A.; Fellak, S.; Doumenq, P. Structural characterization of Argania spinosa Moroccan wooden artifacts during natural degradation progress using infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) and X-Ray diffraction (XRD). Heliyon 2019, 5, e02477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Su, Y.; Shi, J.; Yuan, C.; Zhai, S.; Yong, Q. Revealing the effects of centuries of ageing on the chemical structural features of lignin in archaeological fir woods. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 3520–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High, K.E.; EH, P.K. A review of analytical methods for assessing preservation in waterlogged archaeological wood and their application in practice. Herit. Sci. 2020, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneca, K.; Deforce, K.; Boone, M.N.; VAN Loo, D.; Dierick, M.; VAN Acker, J.; Bulcke, J.V.D. X-ray sub-micron tomography as a tool for the study of archaeological wood preserved through the corrosion of metal objects. Archaeometry 2012, 54, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzner, J.; Million, S. X-ray computed tomography for the anatomical and dendrochronological analysis of archaeological wood. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2015, 55, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.; Streeton, N.L.W. Non-invasive dendrochronology of late-medieval objects in Oslo: Refinement of a technique and discoveries. Appl. Phys. A 2017, 123, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavidel, A.; Scheglov, A.; Karius, V.; Mai, C.; Tarmian, A.; Vioel, W.; Vasilache, V.; Sandu, I. In-depth studies on the modifying effects of natural ageing on the chemical structure of European spruce (Picea abies) and silver fir (Abies alba) woods. J. Wood Sci. 2020, 66, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, S.; Corsaro, C.; Granata, F.; Fazio, E. Clinical CT densitometry for wooden cultural heritage analysis validated by FTIR and Raman spectroscopies. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 199, 110376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwa, D.M.; Ibrahim, S.; Stani, C.; Birarda, G.; Ali, N.; Abdullah, E.; Vaccari, L.; Grenni, P.; Visca, A.; Badr, Y.; et al. Biodeterioration assessment of a unique old pharaonic kingdom wooden statue using advanced diagnostic techniques. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdrabou, A.; Hussein, A.; Sultan, G.M. New insights into a polychrome Middle Kingdom palette applied to a wooden coffin: A multidisciplinary analytical approach. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 54, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čufar, K.; Beeckman, H.; Frelih, M.; Krže, L.; Hubau, W.; Merela, M. Wood identification in objects of Bambuti people from the Congo in the collection of the Slovene ethnographic museum: Identifikacija lesa predmetov ljudstva Bambuti iz Konga v zbirki slovenskega etnografskega muzeja. Les/Wood 2022, 71, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigorelli, L.; Re, A.; Giudorzi, L.; Cavaleri, T.; Buscaglia, P.; Nervo, M.; Del Vesco, P.; Borla, M.; Grassini, S.; Giudice, A.L. Multi-analytical approach for the study of an ancient Egyptian wooden statuette from the collection of Museo Egizio of Torino. Acta Imeko 2022, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBossema, F.G.; Palenstijn, W.J.; Heginbotham, A.; Corona, M.; van Leeuwen, T.; van Liere, R.; Dorscheid, J.; O’fLynn, D.; Dyer, J.; Hermens, E.; et al. Enabling 3D CT-scanning of cultural heritage objects using only in-house 2D X-ray equipment in museums. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierickx, S.; Genbrugge, S.; Beeckman, H.; Hubau, W.; Kibleur, P.; Bulcke, J.V.D. Non-destructive wood identification using X-ray µCT scanning: Which resolution do we need? Plant Methods 2024, 20, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierickx, S.; Beeckman, H.; Josipovic, I.; Charkaoui, C.; Genbrugge, S.; Volper, J.; Alonso, B.V.H.; Boone, M.; Hubau, W.; Bulcke, J.d. Bridging technology and culture: X-ray µCT-based wood identification of Sub-Saharan African heritage. J. Cult. Herit. 2025, 73, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Grenni, P.; Mancini, L.; Voltolini, M.; Abdel-Fatah, H.M.K.; Refaat, A.; Atwa, D.M. Multifactorial Analysis of Wood Deterioration in Ancient Egypt: A Case Study of Khufu’s Second Solar Boat. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 15777-2017; Method for Determination of the Modulus of Elasticity in Compression Parallel to Grain of wood. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Kabekkodu, S.; Dosen, A.; Blanton, T. PDF-5+: A comprehensive Powder Diffraction File™ for materials characterization. Powder Diffr. 2024, 39, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 19587-2017; Determination of the Specific Surface Area of Solids by Gas Adsorption Using the BET Method. Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Bouramdane, Y.; Haddad, M.; Mazar, A.; Aît Lyazidi, S.; Oudghiri Hassani, H.; Boukir, A. Aged Lignocellulose Fibers of Cedar Wood (9th and 12th Century): Structural Investigation Using FTIR-Deconvolution Spectroscopy, X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Crystallinity Indices, and Morphological SEM Analyses. Polymers 2024, 16, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apaydın Varol, E.; Mutlu, Ü. TGA-FTIR analysis of biomass samples based on the thermal decomposition behavior of hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin. Energies 2023, 16, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Baker, J.O.; Himmel, M.E.; Parilla, P.A.; Johnson, D.K. Cellulose crystallinity index: Measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulase performance. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2010, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broda, M.; Popescu, C.M.; Timpu, D.I.; Rowiński, D.; Roszyk, E. Factors That Affect the Mechanical Strength of Archaeological Wood—A Case Study of 18th-Century Wooden Water Pipes from Bóżnicza Street in Poznań, Poland. Materials 2021, 14, 7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Liang, Y.; Li, N. Physical and chemical degradation characteristics of waterlogged archaeological wood from the wenzhou no. 1 shipwreck. npj Herit. Sci. 2025, 13, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellaportas, P.; Papageorgiou, E.; Panagiaris, G. Museum factors affecting the ageing process of organic materials: Review on experimental designs and the INVENVORG project as a pilot study. Herit. Sci. 2014, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.L.; Sadek, H.; Chemello, C.G.; Smith, G.D.; Hatchfield, P.B.; Blanchette, R.A.; Abdel-Azeem, A.; Richards, J. Conservation of Severely Deteriorated, Dry Painted Wood: A Case Study From Abydos, Egypt. J. Am. Inst. Conserv. 2022, 61, 254–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zha, J. Preparation and Application of Humidity-Adaptive Wooden Artifact Crack Consolidants Based on Lignin–Epoxy Acrylate. Polymers 2025, 17, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




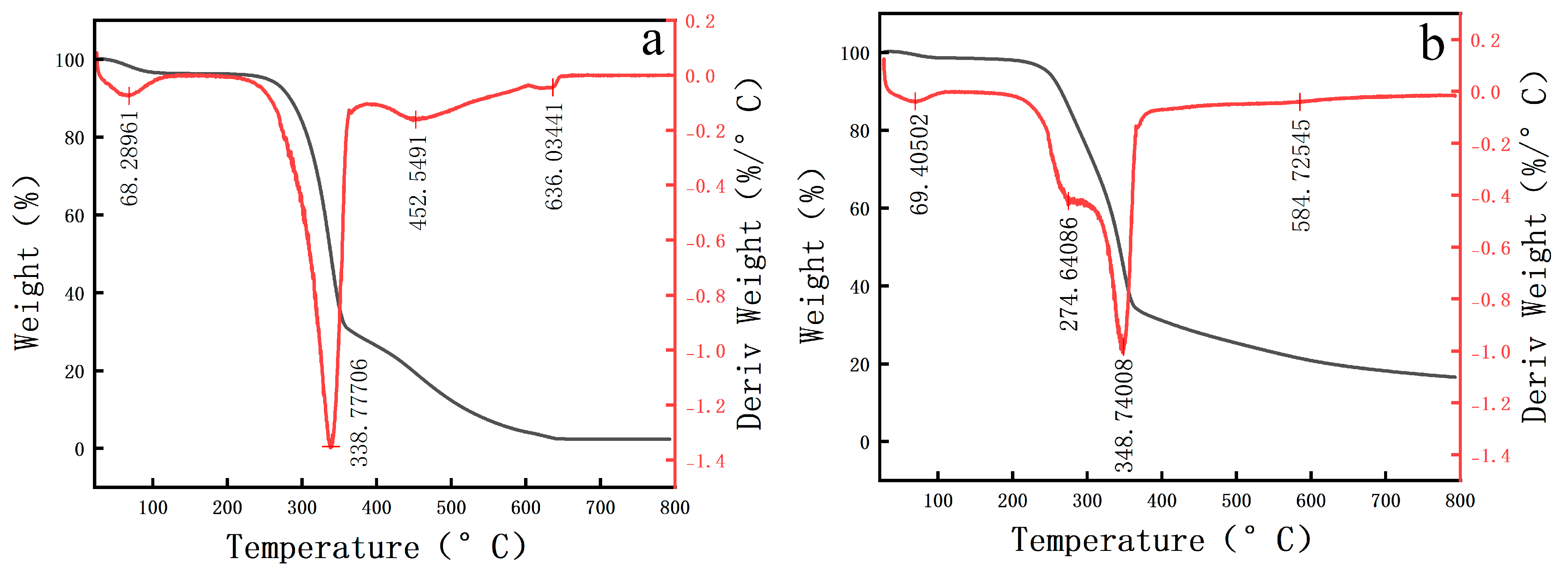
| Decomposition Stage | Initial Weight Loss Water Evaporation | Main Decomposition Stage Cellulose/Hemicellulose Decomposition | Secondary Decomposition Stage Lignin Decomposition | High-Temperature Stable Stage Inorganic Residues | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pear wood | Temperature (°C) | 68.28 | 338.77 | 452.54 | 636.03 |
| Weight Loss Rate (%) | 3.767 | 69.015 | 23.207 | 1.720 | |
| Scripture Plate Wood | Temperature (°C) | 69.40 | 274.64 | 348.74 | 584.72 |
| Weight Loss Rate (%) | 1.71 | 13.886 | 55.459 | 16.547 | |
| Type | Specific Surface Area | Average Pore Size |
|---|---|---|
| Pear wood | 415–420 m2/g | 4.1–4.2 nm |
| Scripture Plate Wood | 365–380 m2/g | 6.0–6.3 nm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.; Peng, Y.; Zha, J.; Zhang, G.; Lv, M.; Wang, Y. Multi-Analytical Assessment of Deterioration in the Qianlong Tripitaka Wooden Scripture Plates. Polymers 2025, 17, 2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17212855
Wu W, Peng Y, Zha J, Zhang G, Lv M, Wang Y. Multi-Analytical Assessment of Deterioration in the Qianlong Tripitaka Wooden Scripture Plates. Polymers. 2025; 17(21):2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17212855
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wangting, Yuhan Peng, Jianrui Zha, Ge Zhang, Mengdie Lv, and Yingzhu Wang. 2025. "Multi-Analytical Assessment of Deterioration in the Qianlong Tripitaka Wooden Scripture Plates" Polymers 17, no. 21: 2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17212855
APA StyleWu, W., Peng, Y., Zha, J., Zhang, G., Lv, M., & Wang, Y. (2025). Multi-Analytical Assessment of Deterioration in the Qianlong Tripitaka Wooden Scripture Plates. Polymers, 17(21), 2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17212855






