Investigation of Blade Printing Technique for Nano-Structuring Piezoelectric Polymer Ink in a Porous Anodic Aluminum Oxide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
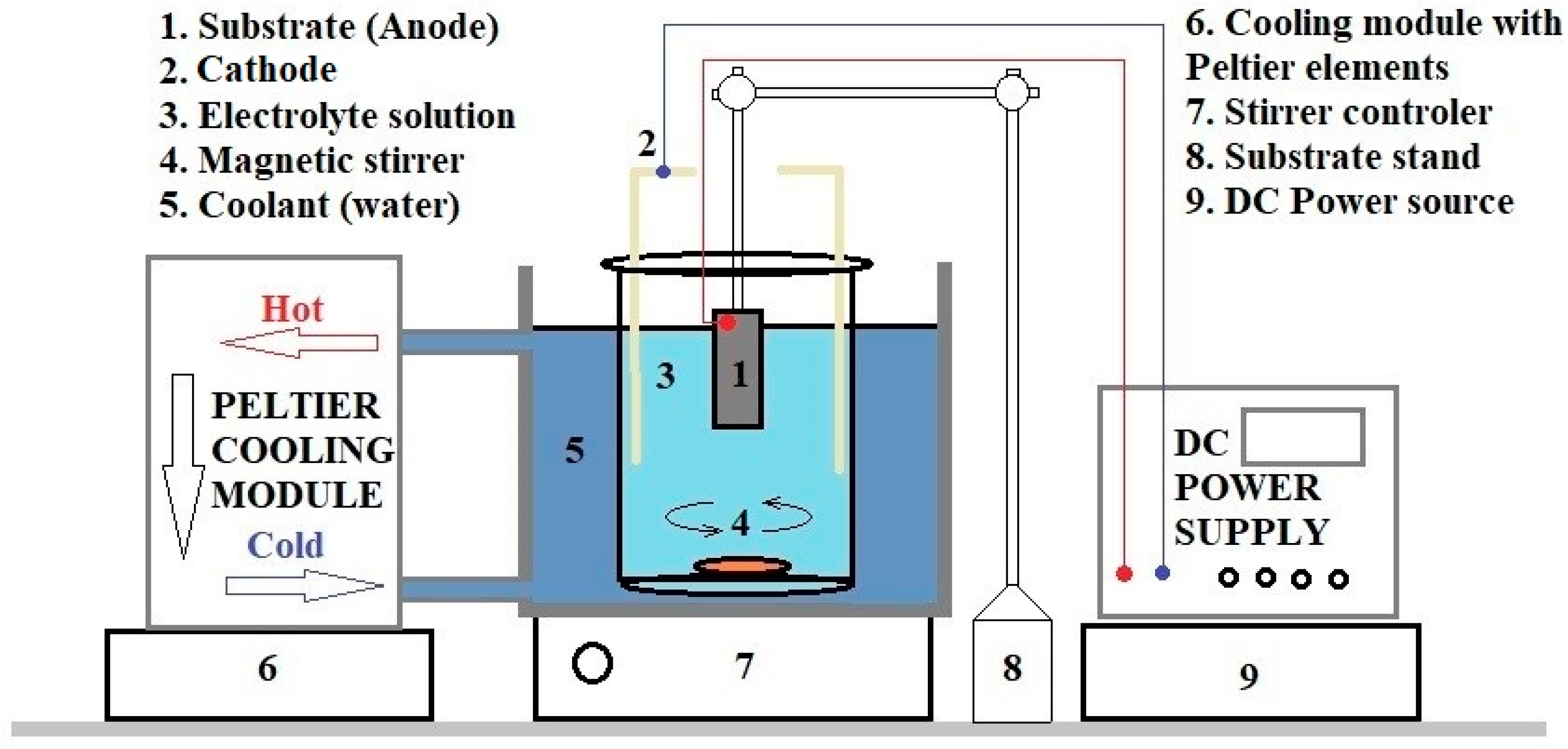
2.1. AAO Deposition Method
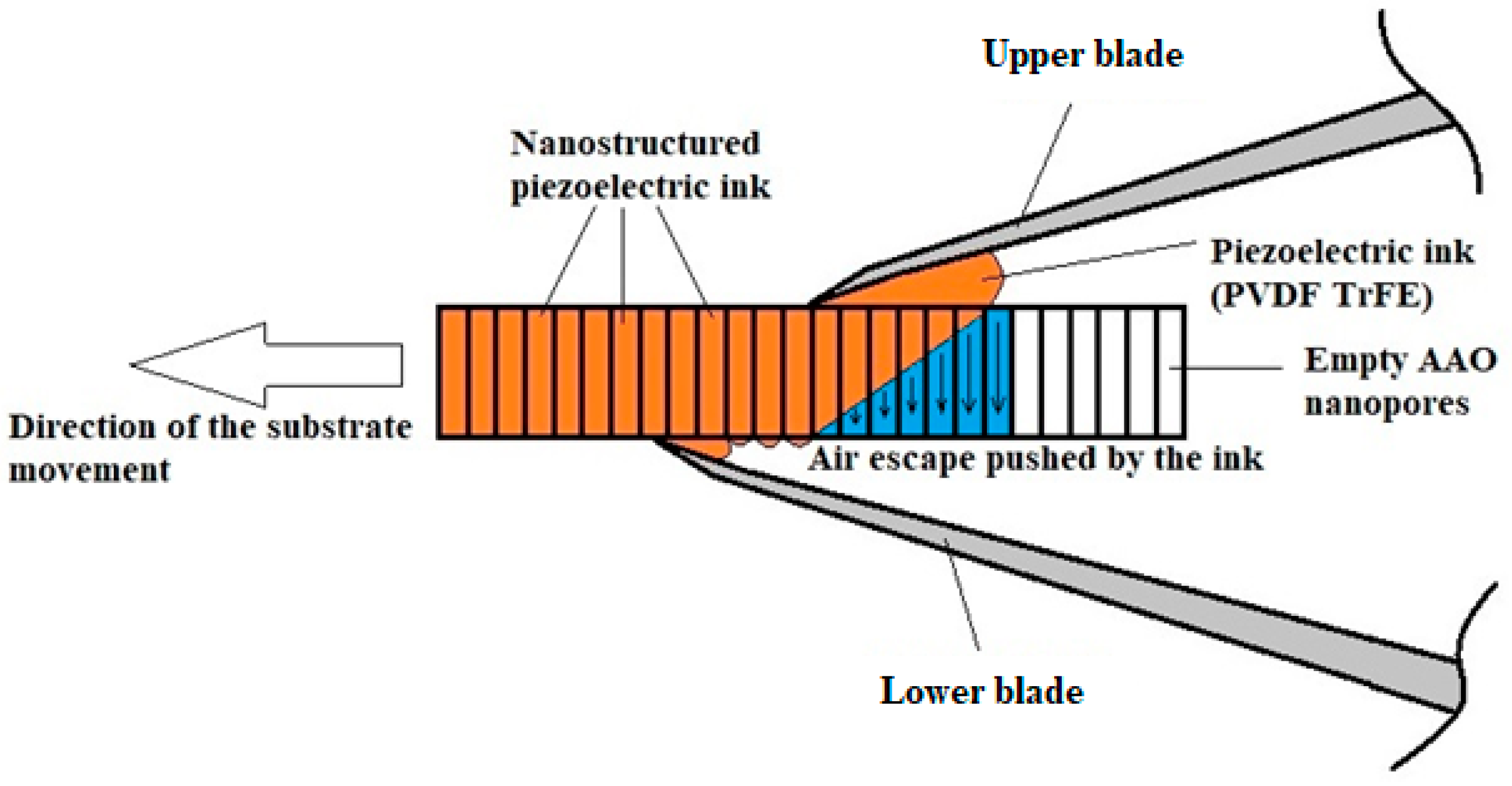
2.2. Blade Printing of PEI in AAO
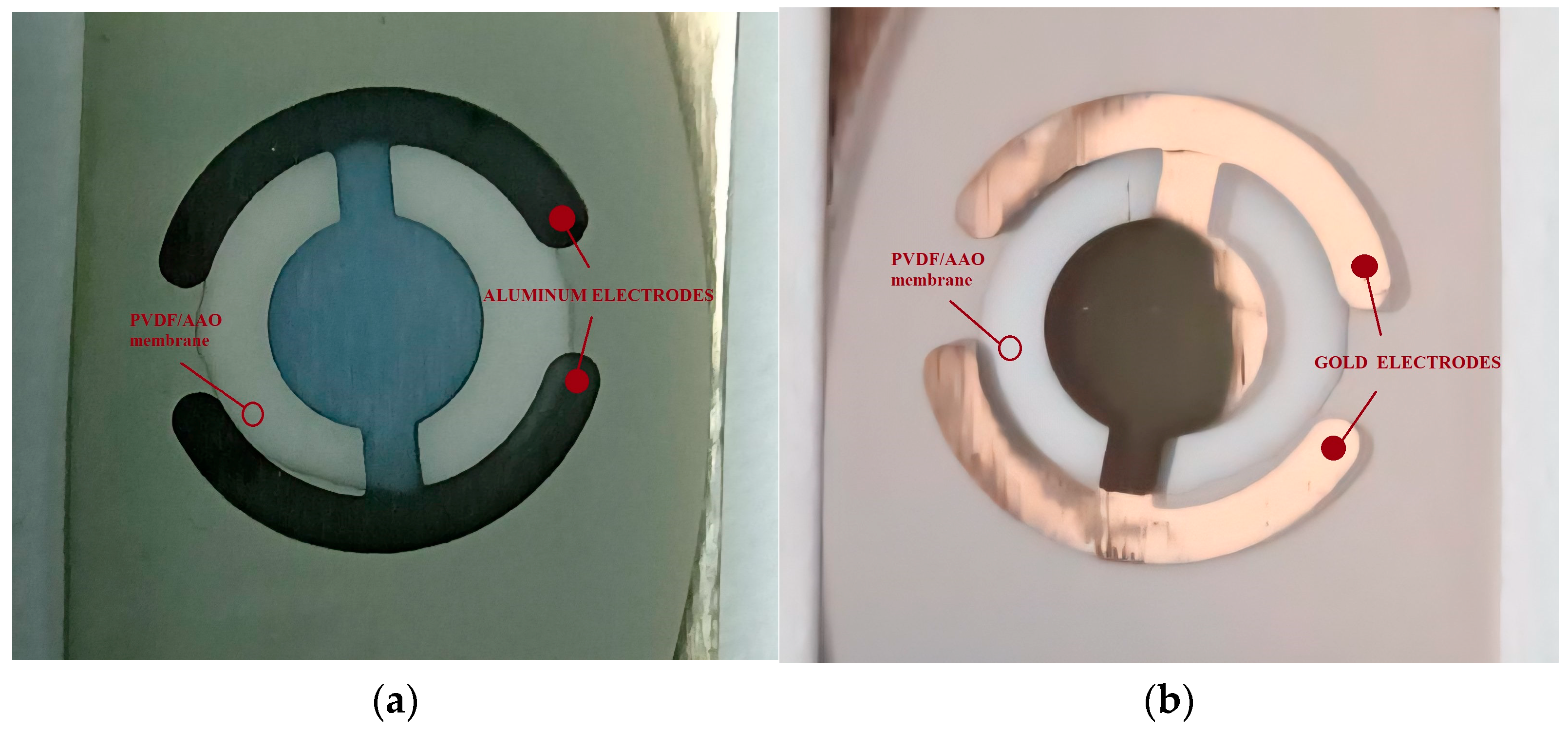
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of Energy-Harvesting Element
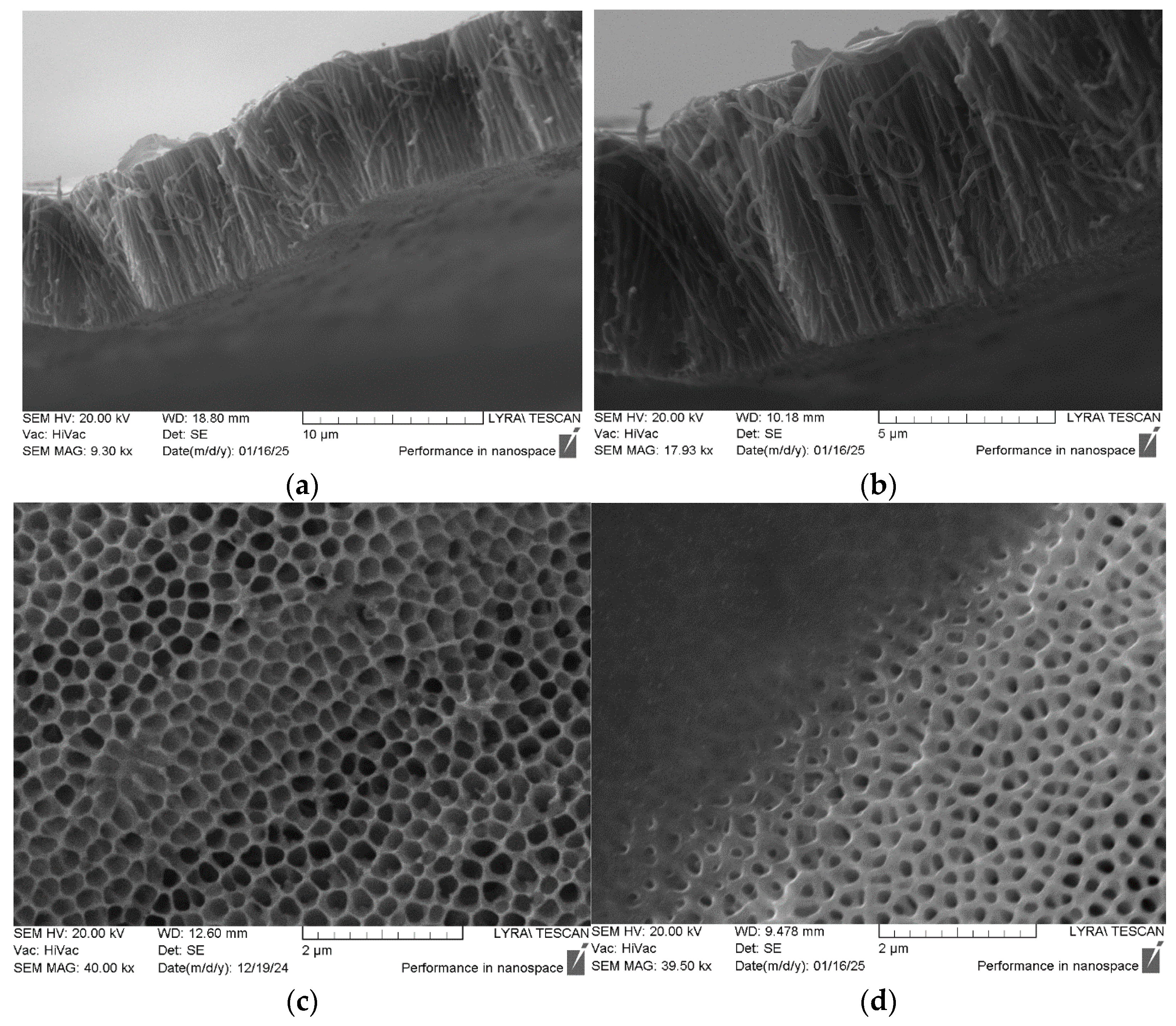
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kroener, M. Energy harvesting technologies: Energy sources, generators and management for wireless autonomous applications. In Proceedings of the International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices, Chemnitz, Germany, 20–23 March 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, K. Chapter 1—The Development of Piezoelectric Materials and the New Perspective. In Advanced Piezoelectric Materials, 2nd ed.; Uchino, K., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 1–92. ISBN 9780081021354. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Kang, L.; Yu, Y.; Long, Y.; Jeffery, J.; Cai, W.; Wang, X. Study of long-term biocompatibility and bio-safety of implantable nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 51, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Kim, S.B.; Yan, Y.; Hur, S.; Hyun, C.S. Brief Review of Lead-Free Piezoelectric Ceramics for High-Power Applications. J. Sens. Sci. Technol. 2025, 34, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.S.; Bhatt, U.M.; Gautam, P.; Thote, S.; Joglekar, M.M.; Manhas, S.K. Fabrication and modeling of β-phase PVDF-TrFE based flexible piezoelectric energy harvester. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 304, 111879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, K.L.; Laurila, M.-M.; Mäntysalo, M. Effect of Electrode Structure on the Performance of Fully Printed Piezoelectric Energy Harvesters. IEEE J. Flex. Electron. 2022, 1, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, M.; Tsanev, T.; Gupta, A.; Singh, A.K.; Dobrikov, G.; Videkov, V. Sensing Ability of Ferroelectric Oxide Nanowires Grown in Templates of Nanopores. Materials 2020, 13, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.J.; Chen, Y.; Wong, C.M.; Qiu, W.B.; Chan, H.L.W.; Dai, J.Y.; Li, Q.; Yan, Q.F. Anodic aluminum oxide–epoxy composite acoustic matching layers for ultrasonic transducer application. Ultrasonics 2016, 70, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briscoe, J.; Dunn, S. Piezoelectric nanogenerators—A review of nanostructured piezoelectric energy harvesters. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.J.; Lee, M.K.; Park, J.J.; Hyeon, D.Y.; Jeong, C.K.; Park, K.I. Piezoelectric energy harvesting from two-dimensional boron nitride nanoflakes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 37920–37926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscow, J.I.; Zhang, Y.; Kraśny, M.J.; Lewis, R.W.C.; Taylor, J.; Bowen, C.R. Freeze cast porous barium titanate for enhanced piezoelectric energy harvesting. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 225301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwuozor, K.O.; Jimoh, T.A.; Ojo, H.T.; Emenike, E.C.; Emeghai, J.; Adeniyi, A.G. Polymer-based piezoelectric materials: Structure, mechanism, applications, and future trends. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 70, 106855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, M.; Tsanev, T.; Kadikoff, B.; Alexandrov, D.; Nedelchev, K.; Kralov, I. Piezoelectric Elements with PVDF–TrFE/MWCNT-Aligned Composite Nanowires for Energy Harvesting Applications. Crystals 2023, 13, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, G.; Seo, H.; Hwangbo, J.; Kim, T.; Choi, Y. Nano-structured piezoelectric polymers for biomedical application. APL Electron. Devices 2025, 1, 021504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, L.; Liang, F.; Li, M.; Yabuta, Y.; Iqbal, M.A.; Mayakrishnan, G.; Shi, J.; Kim, I.S. Flexible Piezoelectric Sensor Based on Two-Dimensional Topological Network of PVDF/DA Composite Nanofiber Membrane. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 6, 1212–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Hesse, D.; Gösele, U. Nanostructure Patterns of Piezoelectric and Ferroelectric Complex Oxides with Various Shapes, Obtained by Natural Lithography and Pulsed Laser Deposition. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molarius, J.; Kaitila, J.; Pensala, T.; Ylilammi, M. Piezoelectric ZnO Films by R.F. Sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2003, 14, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, M.; Chandraiahgari, C.R.; De Bellis, G.; Ballirano, P.; Soltani, P.; Kaciulis, S.; Caneve, L.; Sarto, F.; Sarto, M.S. Piezoelectric Thin Films of ZnO-Nanorods/Nanowalls Grown by Chemical Bath Deposition. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2018, 17, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammel, R.S.; Sabry, R.S. Effects of the Aspect Ratio of ZnO Nanorods on the Performance of Piezoelectric Nanogenerators. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadigadapa, S. Piezoelectric Microelectromechanical Systems—Challenges and Opportunities. Procedia Eng. 2010, 5, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiter, R.A.; Narayan, V.; Narayan, S.K. A Scalable Nanogenerator Based on Self-Poled Piezoelectric Polymer Nanowires with High Energy Conversion Efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1400519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanopaint-tech.com. Available online: https://nanopaint-tech.com/piezoelectric-inks (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- Nanopaint-tech.com. Available online: https://nanopaint-tech.com/wp-content/uploads/PEInk01NP.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- Aleksandrova, M.; Mateev, V.; Iliev, I. Behavior of Polymer Electrode PEDOT:PSS/Graphene on Flexible Substrate for Wearable Biosensor at Different Loading Modes. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Lu, J. Zinc Oxide Nanostructures: Synthesis and Properties. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ren, W.; Liao, X. On the Relationship between Contact Resistance and Load Force for Electrode Materials with Rough Surfaces. Materials 2022, 15, 5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liang, C.; Prorok, B.C. A Comparison of Testing Methods in Assessing the Elastic Properties of Sputter Deposited Gold Films. Thin Solid Film. 2007, 515, 7911–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, D.T.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Keller, R.R.; McColskey, J.D. Tensile Properties of Free-Standing Aluminum Thin Films. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X.-D.; Guo, X.; Liu, T.; Su, X. Synchronization of Broadband Energy Harvesting and Vibration Mitigation via 1:2 Internal Resonance. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2025, 301, 110503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, R.; Yu, K.; Lee, H.P.; Liao, B. A quasi-zero-stiffness device capable of vibration isolation and energy harvesting using piezoelectric buckled beams. Energy 2021, 233, 121146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

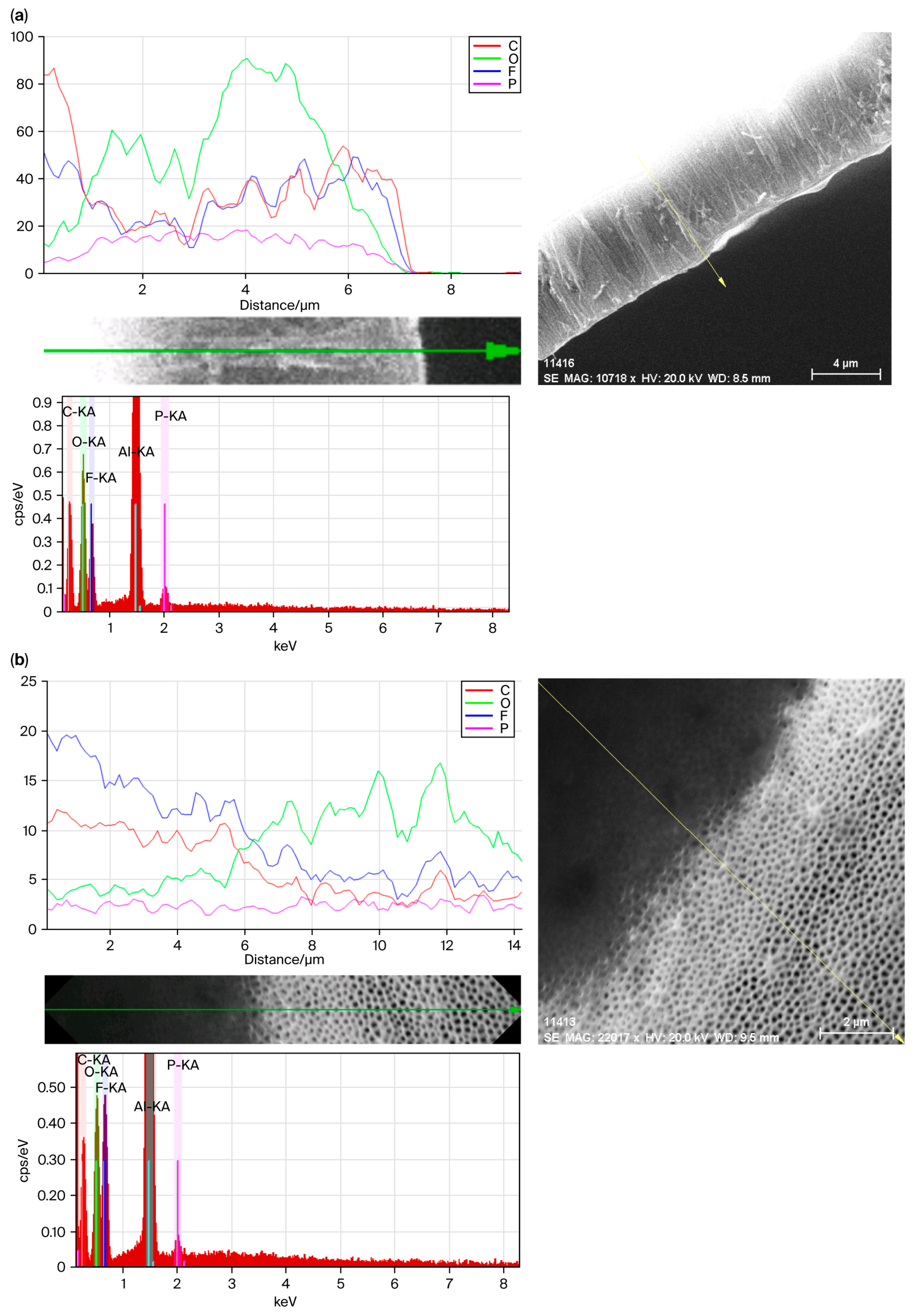

| Applied Voltage DC [V] | Electrolyte Temperature [°C] | Anodization Time [min] | Current [mA] | Layer Thickness [μm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 135 | From 7 to 9 | 20 | 8 | 2 |
| 135 | From 7 to 9 | 40 | 15 | 4 |
| 135 | From 7 to 9 | 60 | 17 | 6 |
| 135 | From 7 to 9 | 80 | 20 | 8 |
| 135 | From 7 to 9 | 120 | 30 | 12 |
| Appearance | Clear/transparent |
| Cure processing | Thermal cure |
| Solid content (%) | 25% |
| Viscosity | 4000–8000 cP |
| Piezoelectric coefficient d33 (pC/N) | 18–23 |
| Pyroelectric coefficient ρ (μC/m2.K) | −23 |
| Remnant polarization Pr (mC/m2) | 80 |
| Curie temperature | 135 °C |
| Sample Thickness [μm] | d33 [pC/N] |
|---|---|
| 2 | 18.5 |
| 4 | 18.7 |
| 6 | 18.6 |
| 8 | 19.2 |
| 12 | 20.4 |
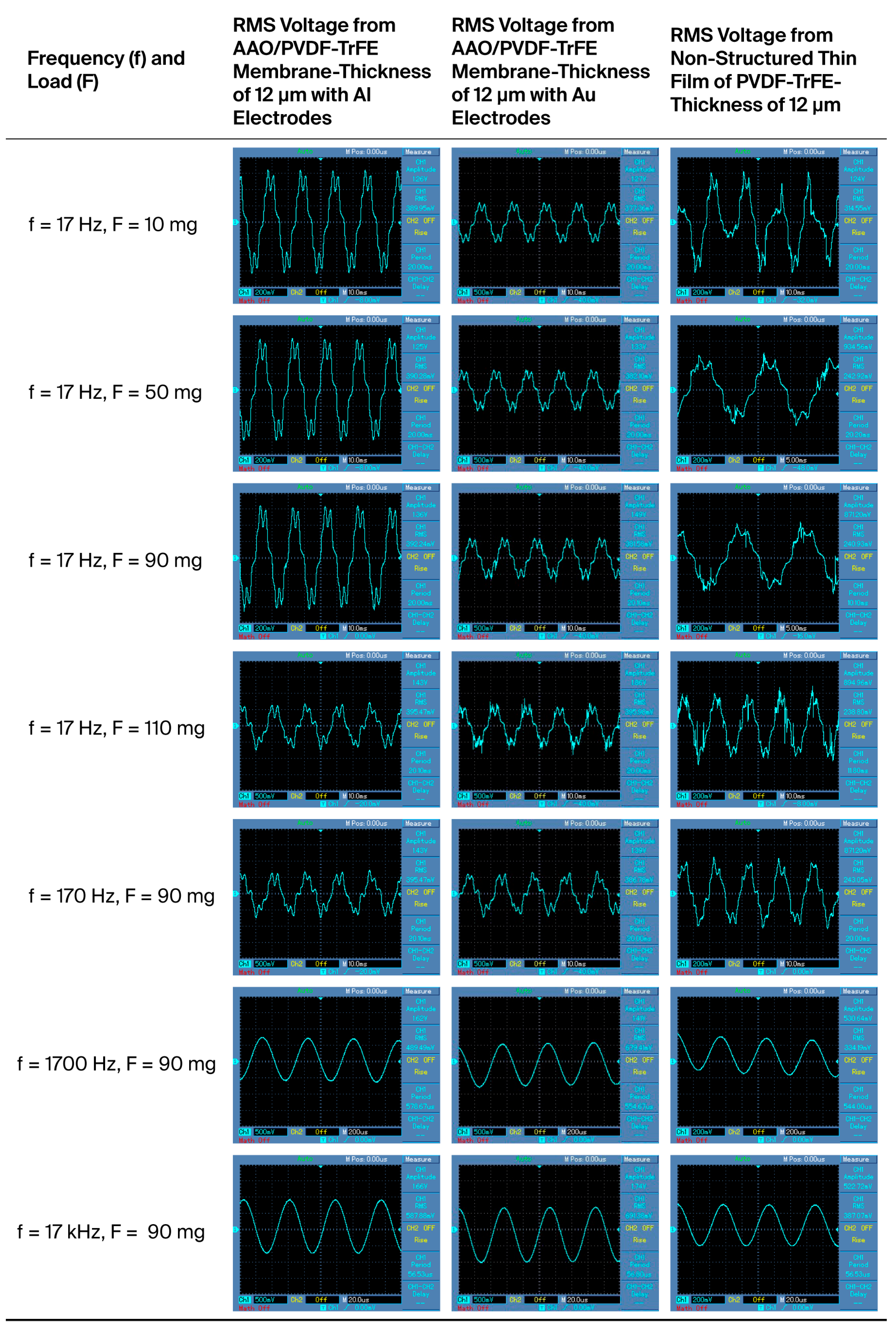
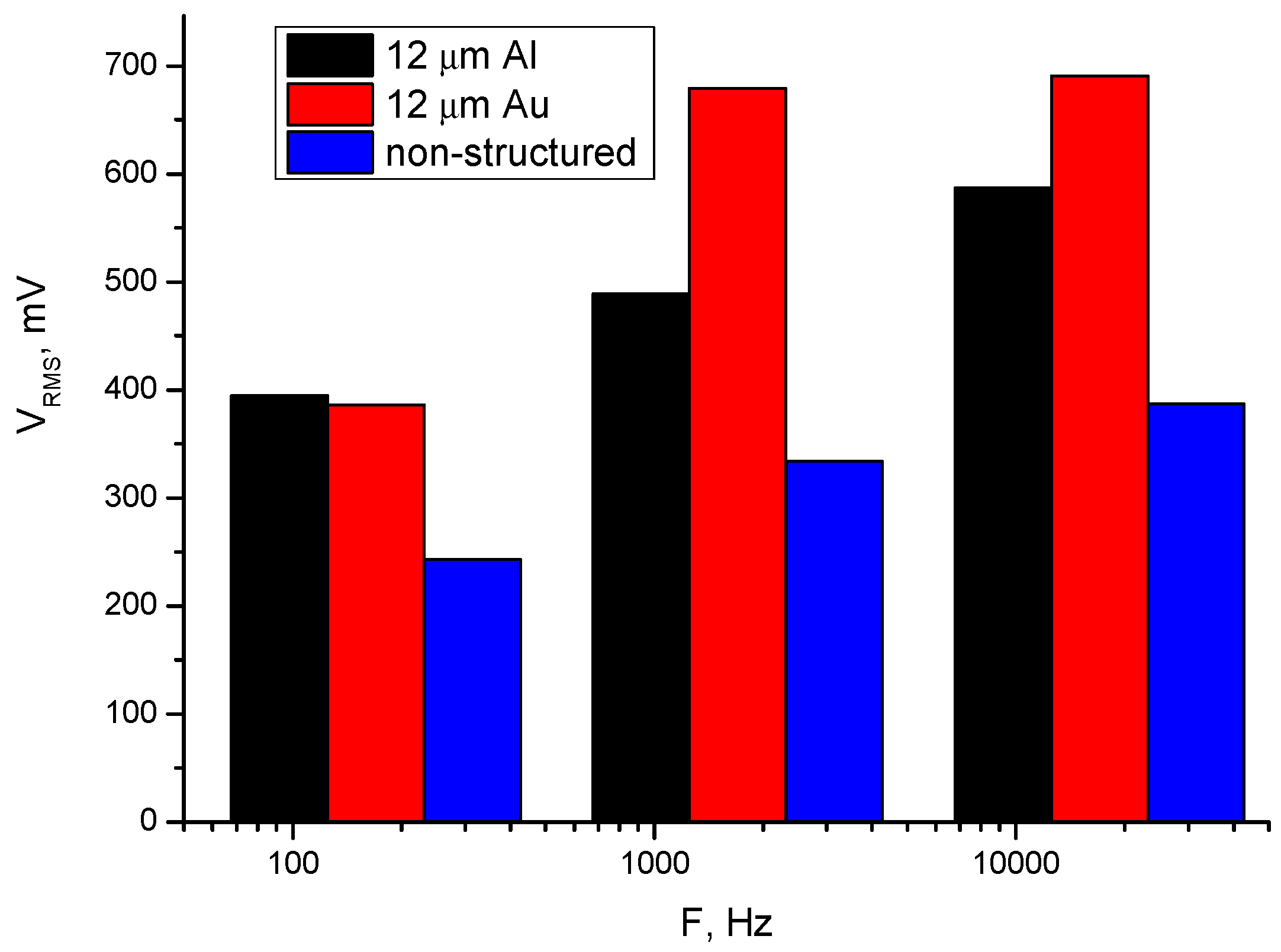
| F [mg] | 12 μm Al Electrode [mV] | 12 μm Au Electrode [mV] | 12 μm Non-Structured [mV] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 389 | 377 | 314 |
| 50 | 390 | 382 | 242 |
| 90 | 392 | 381 | 240 |
| 110 | 395 | 395 | 238 |
| f [Hz] | 12 μm Al Electrode [mV] | 12 μm Au Electrode [mV] | 12 μm Non-Structured [mV] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 170 | 395 | 386 | 243 |
| 1700 | 489 | 679 | 334 |
| 17000 | 587 | 691 | 387 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsanev, T.; Aleksandrova, M. Investigation of Blade Printing Technique for Nano-Structuring Piezoelectric Polymer Ink in a Porous Anodic Aluminum Oxide. Polymers 2025, 17, 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17212839
Tsanev T, Aleksandrova M. Investigation of Blade Printing Technique for Nano-Structuring Piezoelectric Polymer Ink in a Porous Anodic Aluminum Oxide. Polymers. 2025; 17(21):2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17212839
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsanev, Tsvetozar, and Mariya Aleksandrova. 2025. "Investigation of Blade Printing Technique for Nano-Structuring Piezoelectric Polymer Ink in a Porous Anodic Aluminum Oxide" Polymers 17, no. 21: 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17212839
APA StyleTsanev, T., & Aleksandrova, M. (2025). Investigation of Blade Printing Technique for Nano-Structuring Piezoelectric Polymer Ink in a Porous Anodic Aluminum Oxide. Polymers, 17(21), 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17212839








