Effects of the Mixing Method of Expanded Graphite on Thermal, Electrical, and Water Transport Properties of Thermosetting Nanocomposites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Resin Development
- Ultrasonication: The epoxy precursor and EG, at the defined weight percentage over the total mixture, were mixed using an ultrasonication treatment for 20 min (Hielscher model UP200S-24 kHz high power ultrasonic probe, manufactured by Hielscher Ultrasonics GmbH Oderstr. 53, 14513 Teltow, Germany). The ultrasonic parameters were as follows: 200 W, 100% amplitude, pulse 50%.
- High-Temperature Mixing: The epoxy precursor and EG, at the defined weight percentage over the total mixture, were mixed at high temperature (120 °C for 20 min) under magnetic stirring (300 rpm).
- Centrifugal Planetary Mixing: The epoxy precursor and EG, at the defined weight percentage over the total mixture, were mixed using a centrifugal planetary mixer (THINKY ARE-250, manufactured by THINKY Corporation, Tokyo, Japan), for 1 min at 2000 rpm (mixing) and 2 min at 2000 rpm (defoaming).
2.2. Epoxy Resin Characterization
3. Results
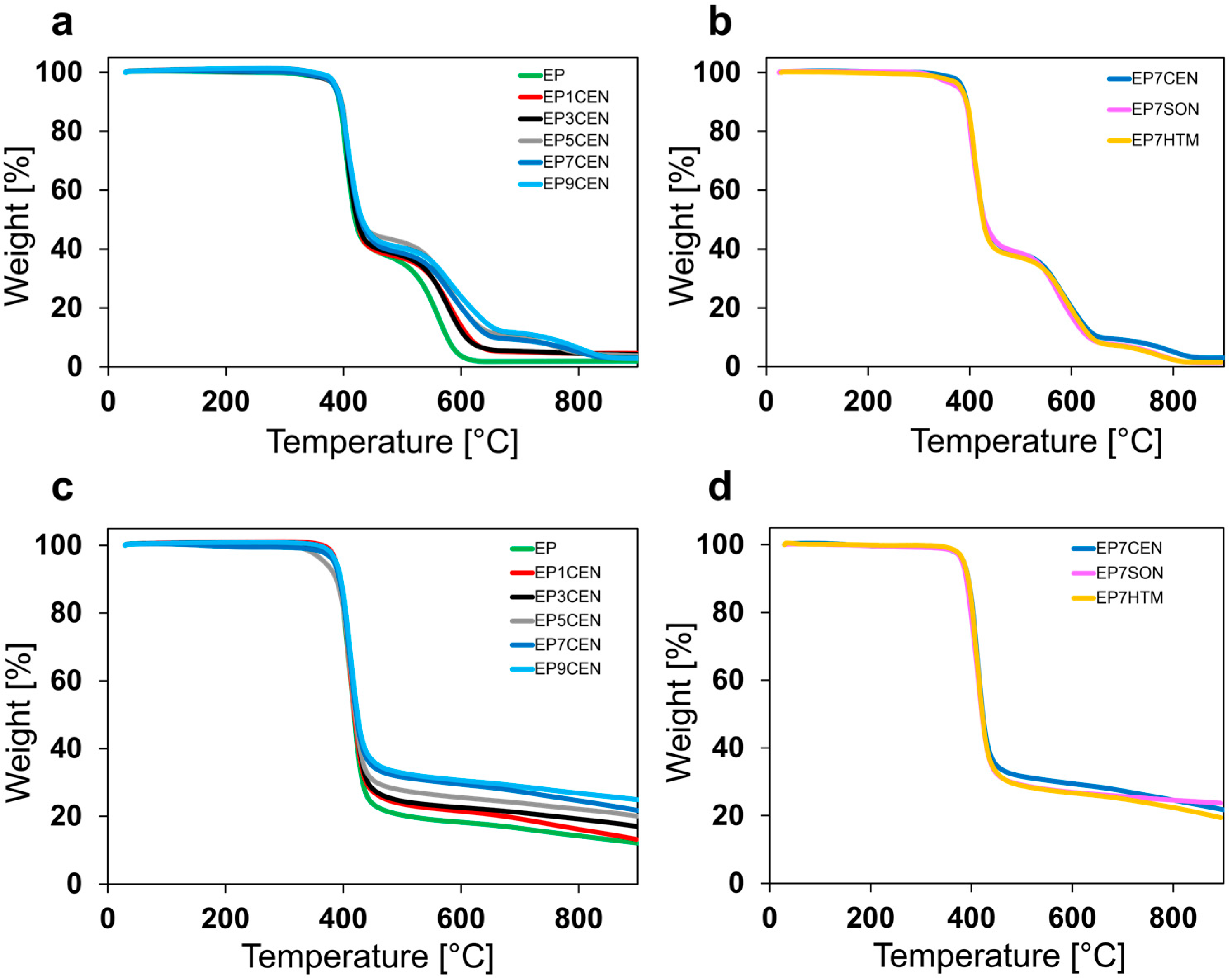
3.1. Thermal Stability
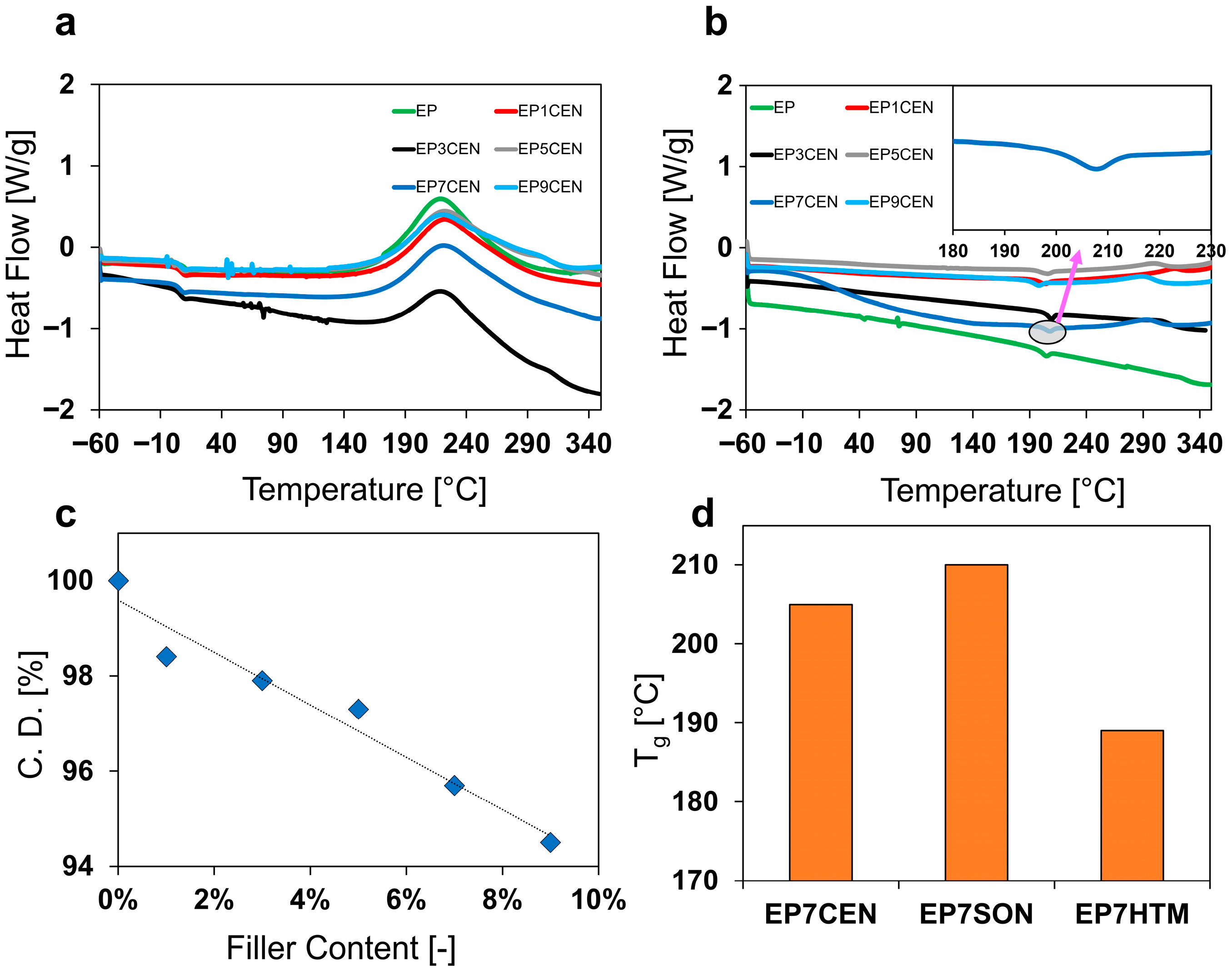
3.2. DSC Analysis
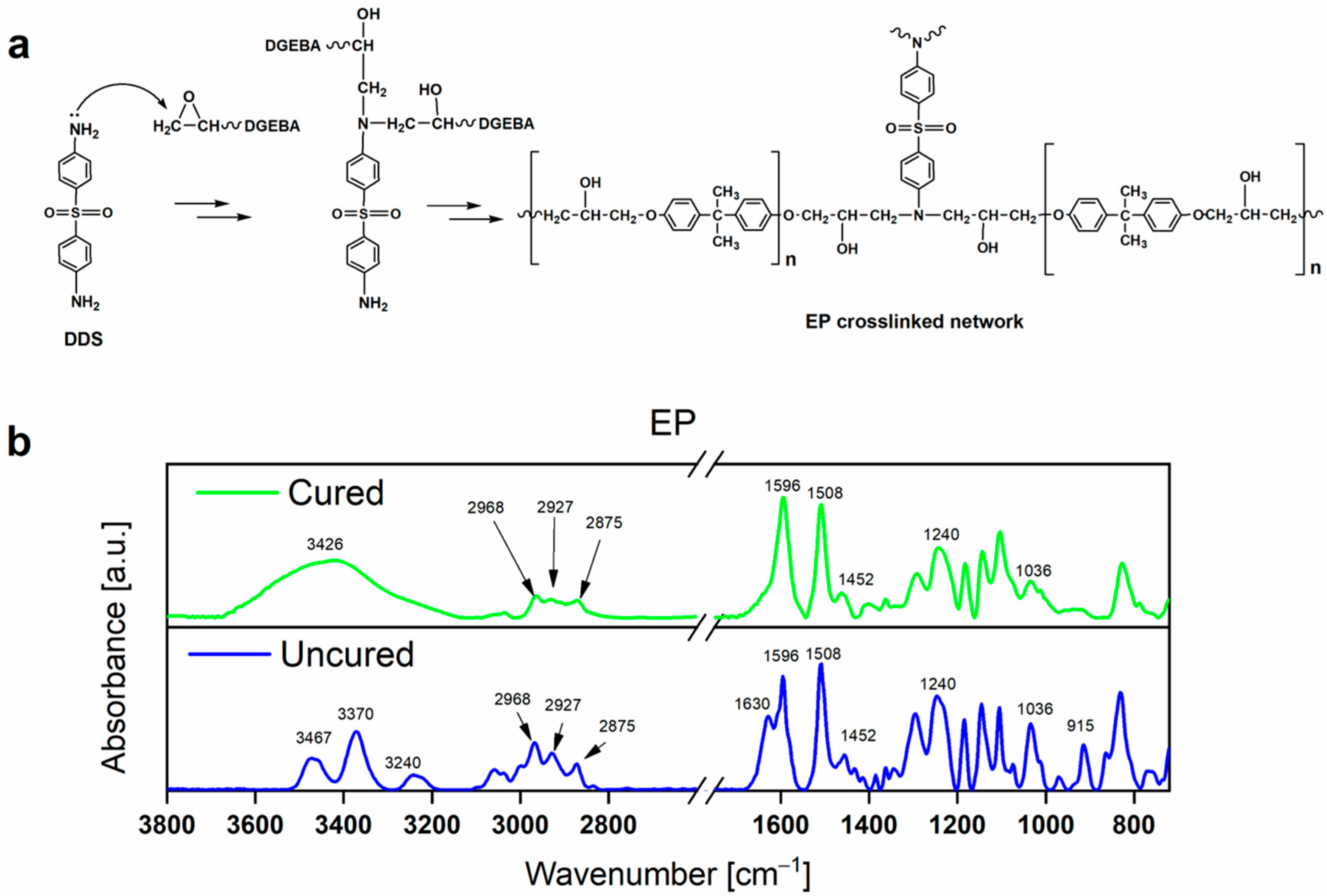
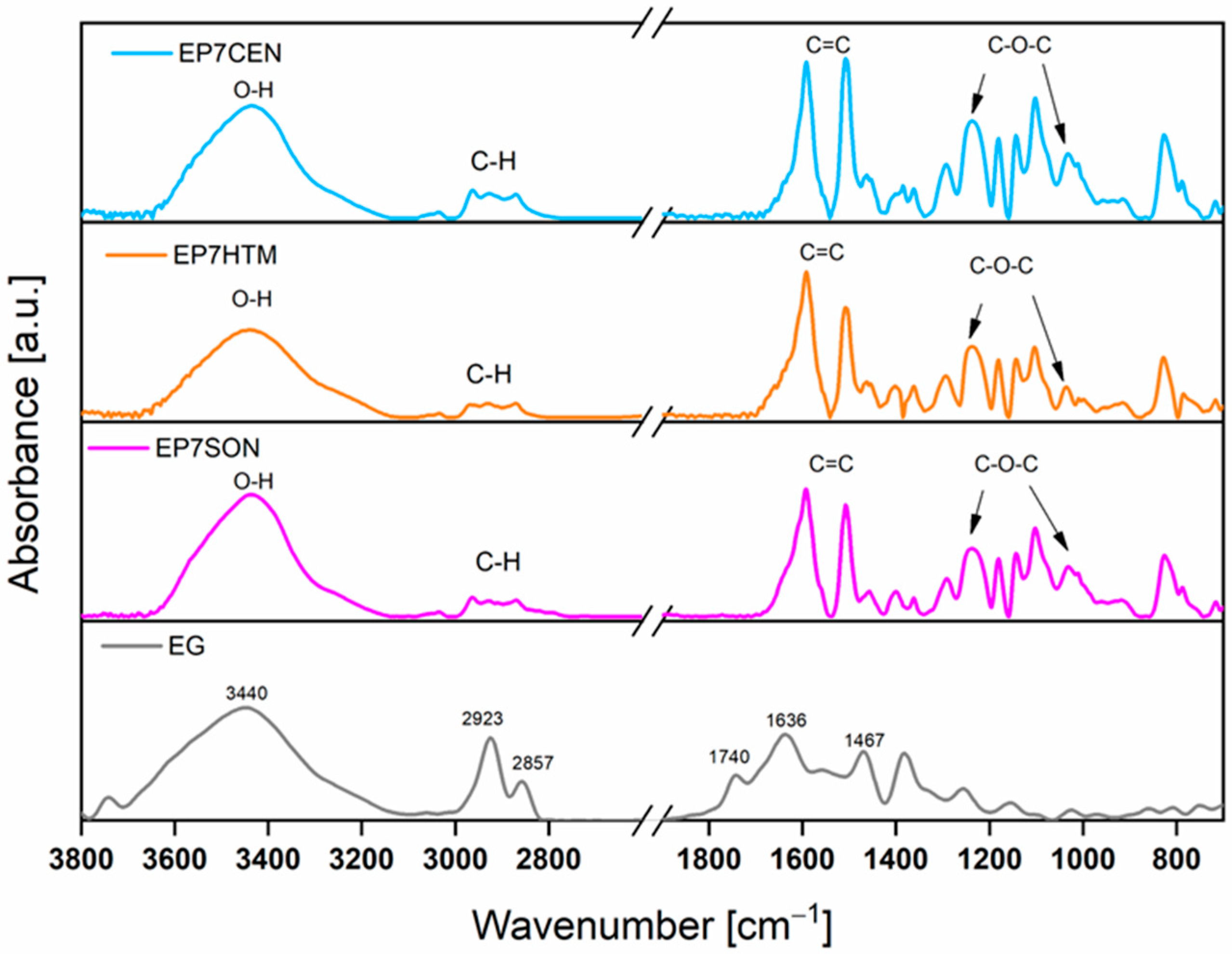
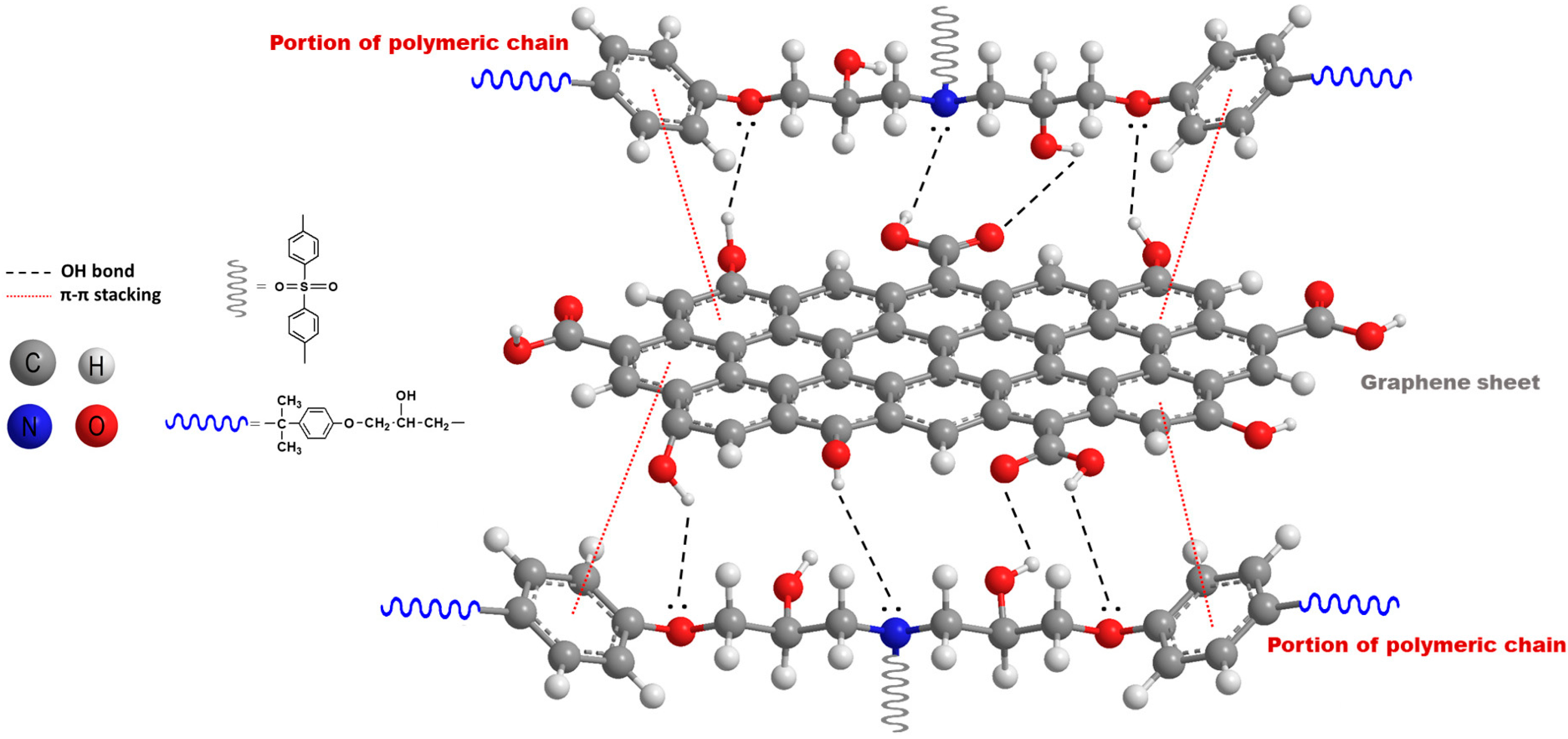
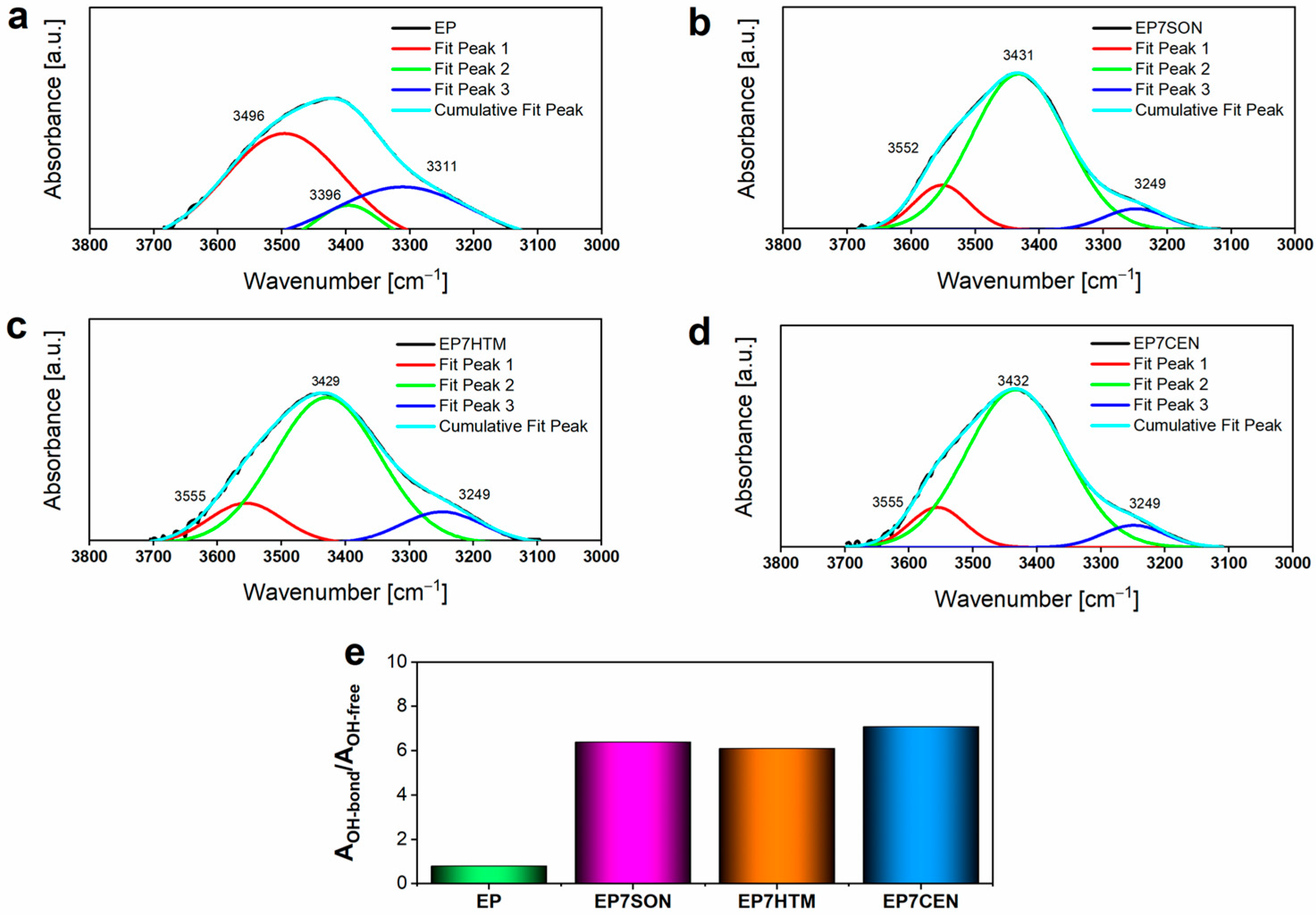
3.3. FT-IR Analyses
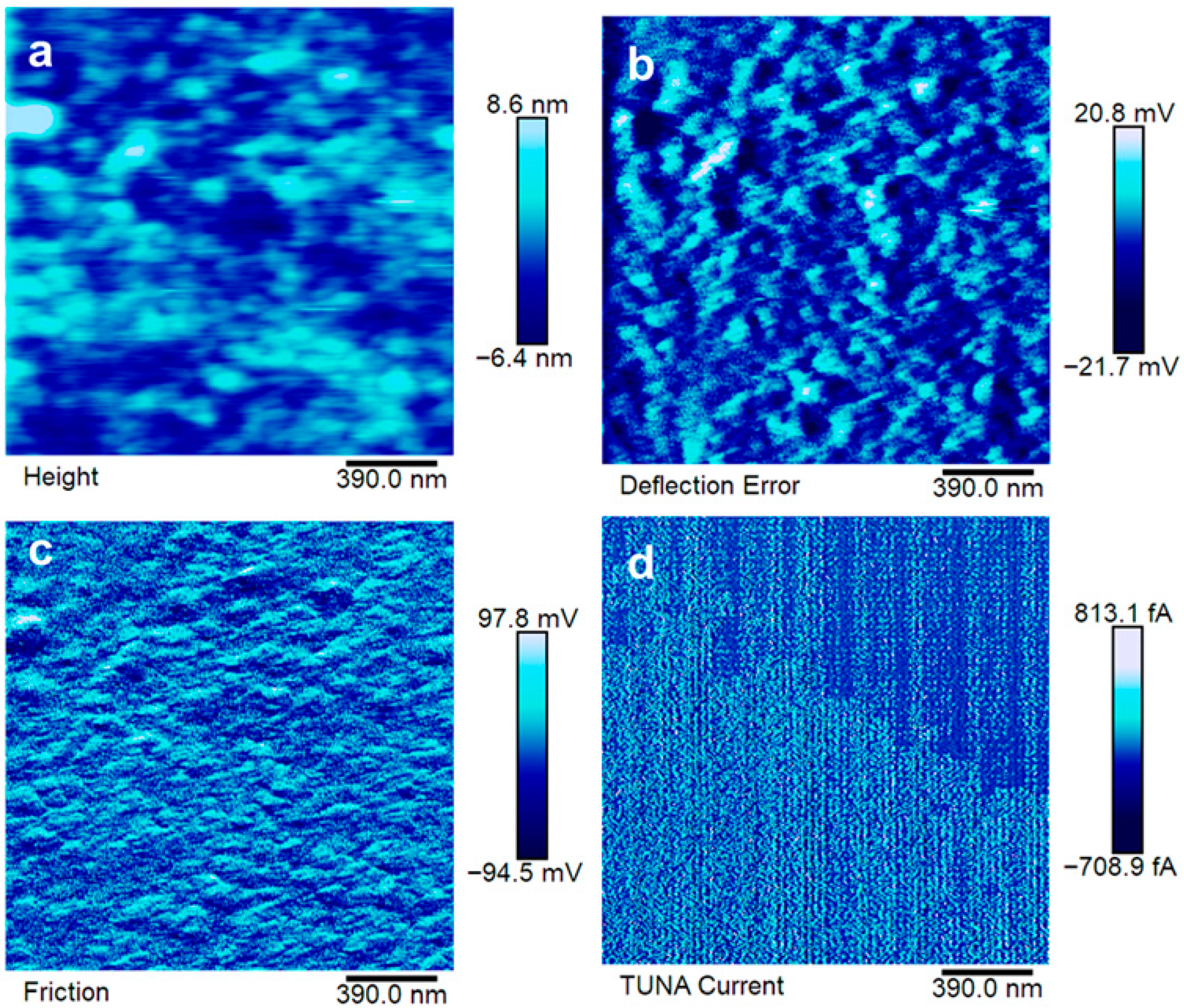
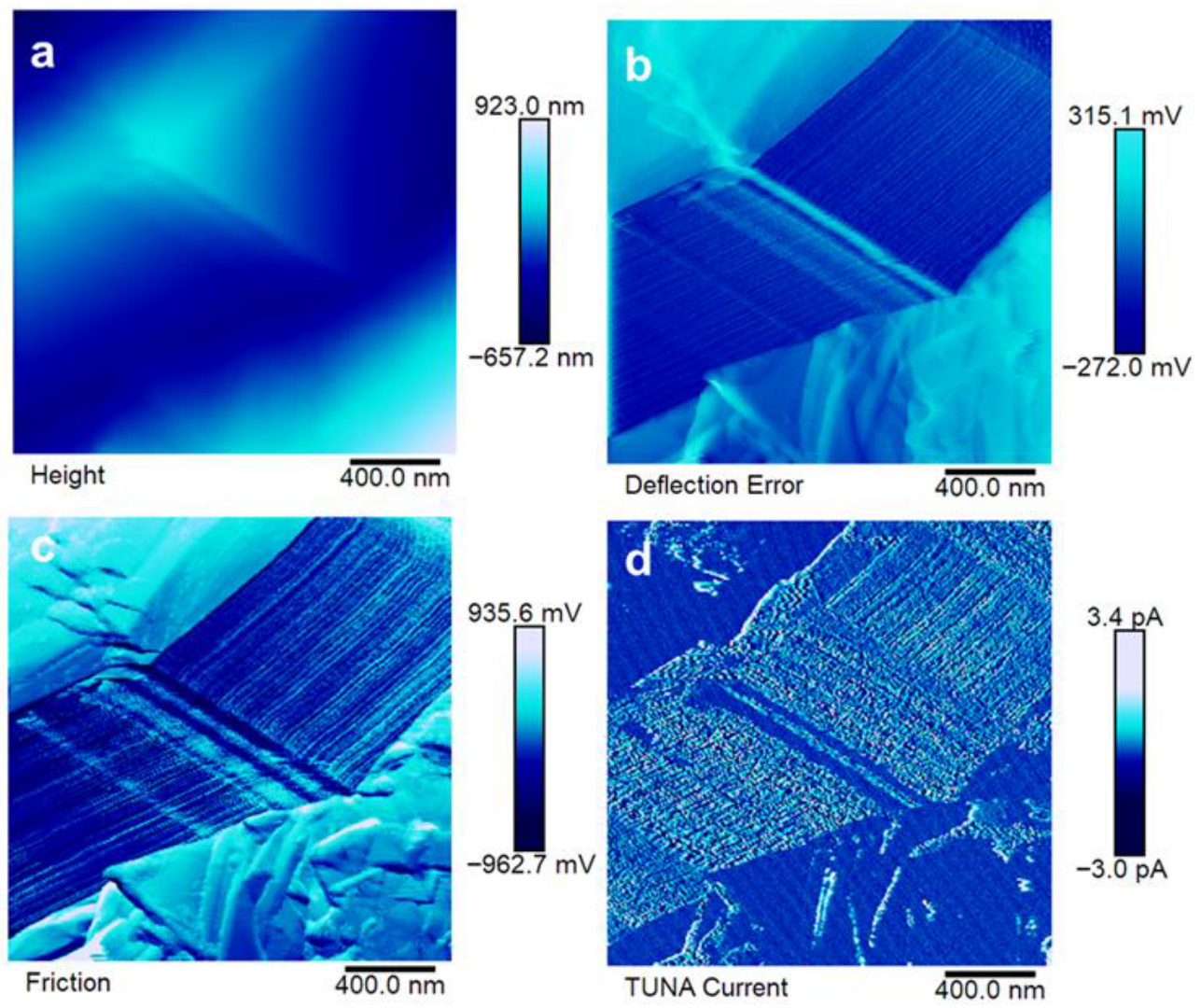
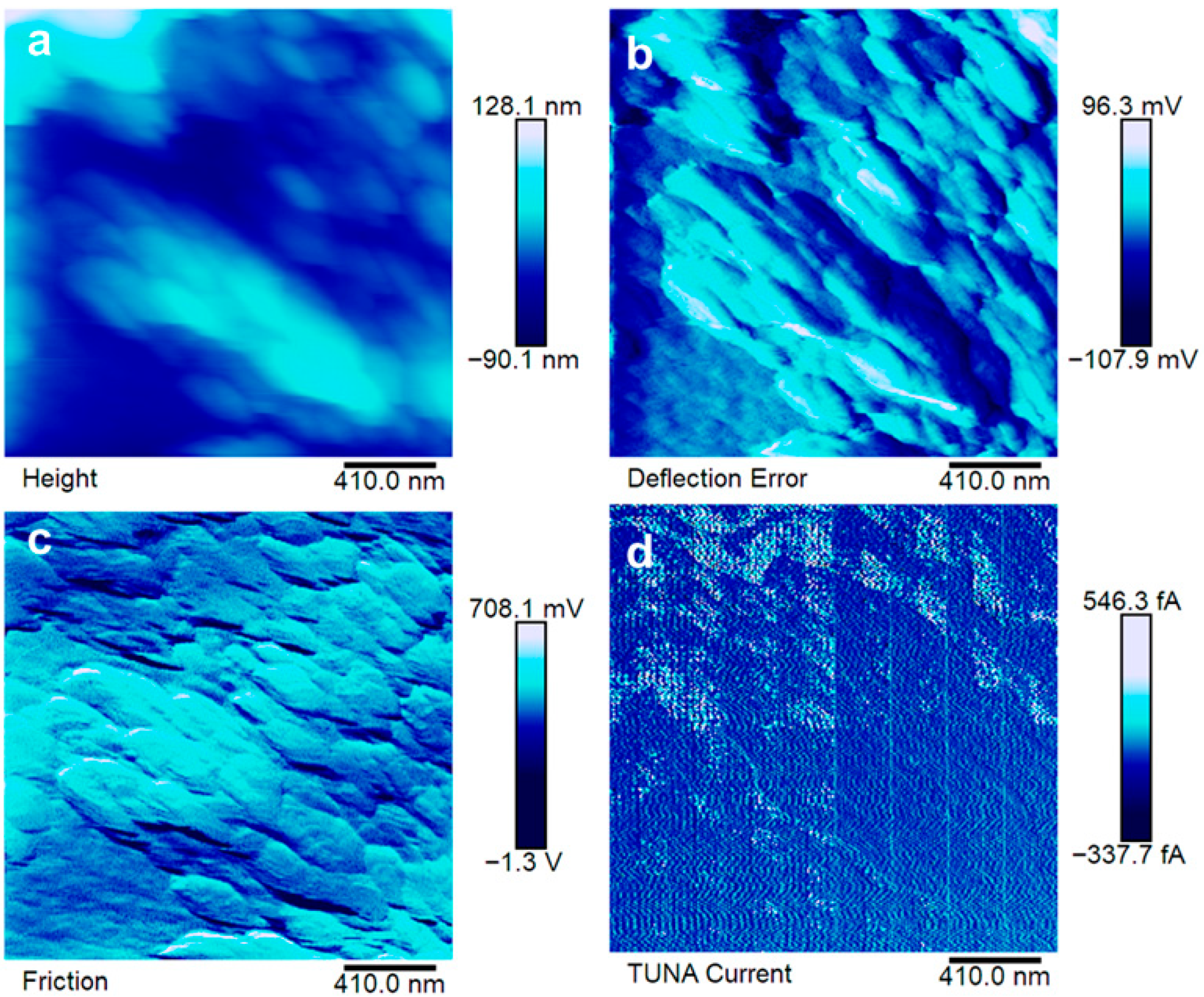
3.4. Morphological Analyses
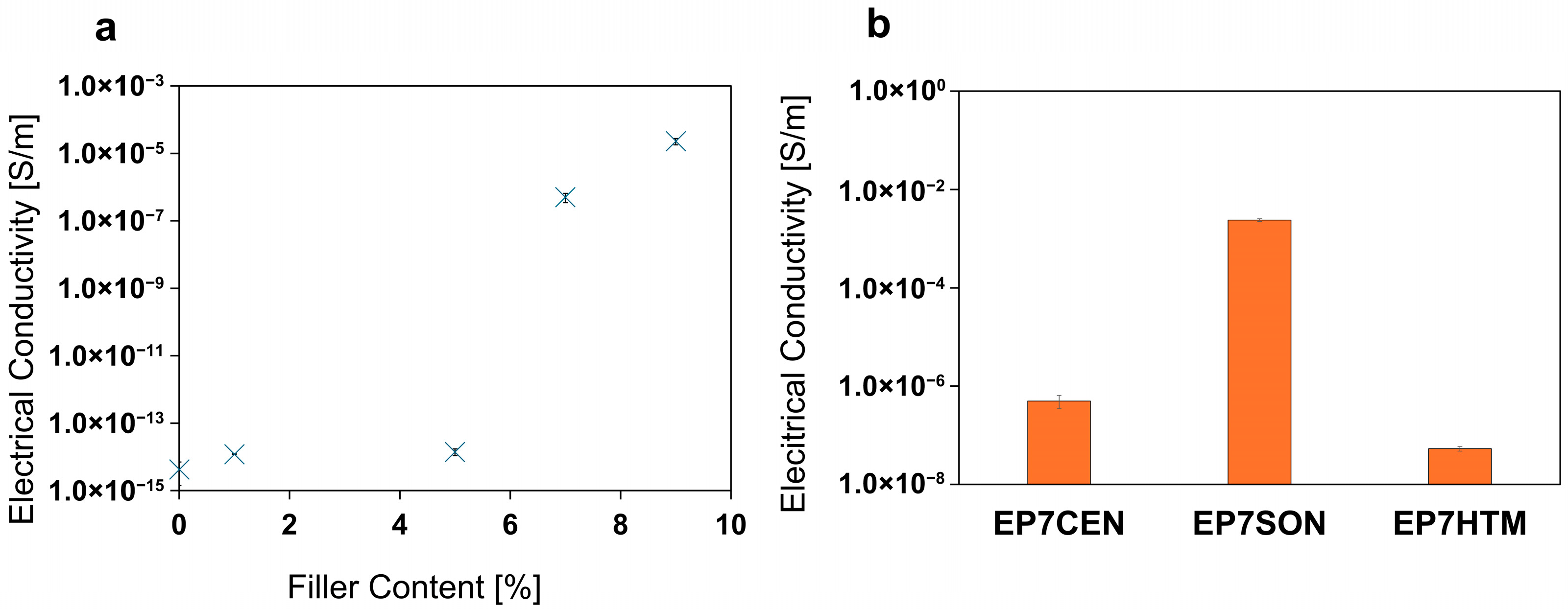
3.5. Electrical Analysis
3.6. Water Sorption Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorokhov, G.; Bychanok, D.; Gayduchenko, I.; Rogov, Y.; Zhukova, E.; Zhukov, S.; Kadyrov, L.; Fedorov, G.; Ivanov, E.; Kotsilkova, R.; et al. THz Spectroscopy as a Versatile Tool for Filler Distribution Diagnostics in Polymer Nanocomposites. Polymers 2020, 12, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Luo, Z.; Liang, J.; Hu, J.; Jiang, N.; He, J.; Li, Q. Polymer Nanocomposite Dielectrics: Understanding the Matrix/Particle Interface. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 13612–13656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balguri, P.K.; Samuel, D.G.H.; Thumu, U. A Review on Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Nanocomposites. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostovoy, A.S.; Yakovlev, A.V.; Lopukhova, M.I. Directional Control of Physico-Chemical and Mechanical Properties of Epoxide Composites by the Addition of Graphite-Graphene Structures. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2020, 59, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shameem, M.M.; Sasikanth, S.M.; Annamalai, R.; Raman, R.G. A Brief Review on Polymer Nanocomposites and Its Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 2536–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branda, F.; Passaro, J.; Pauer, R.; Gaan, S.; Bifulco, A. Solvent-Free One-Pot Synthesis of Epoxy Nanocomposites Containing Mg(OH)2 Nanocrystal–Nanoparticle Formation Mechanism. Langmuir 2022, 38, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bifulco, A.; Imparato, C.; Climaco, I.; Battegazzore, D.; Perrella, M.; Vitiello, G.; Aronne, A.; Malucelli, G. Multifunctional Fire-Resistant and Flame-Triggered Shape Memory Epoxy Nanocomposites Containing Carbon Dots. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, S.; Drigo, N.; Huang, K.; Lehner, S.; Jovic, M.; Bifulco, A.; Gooneie, A.; Aronne, A.; Gaan, S. Developing Flame Retardant Solutions for Partially Aromatic Polyamide with Phosphine Oxides. Mater. Des. 2024, 243, 113080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vivo, B.; Lamberti, P.; Spinelli, G.; Tucci, V.; Guadagno, L.; Raimondo, M.; Vertuccio, L.; Vittoria, V. Improvement of the Electrical Conductivity in Multiphase Epoxy-Based MWCNT Nanocomposites by Means of an Optimized Clay Content. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 89, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, M.O.; Valenzuela-Acosta, E.M.; Prokhorov, E.; Luna-Barcenas, G.; Kumar-Krishnan, S. Percolation Phenomena in Polymer Nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2016, 7, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliberti, F.; Vertuccio, L.; Longo, R.; Sorrentino, A.; Pantani, R.; Guadagno, L.; Raimondo, M. Thermal, Mechanical, Morphological, and Piezoresistive Properties of Poly(Ethylene-Co-Methacrylic Acid) (EMAA) with Carbon Nanotubes and Expanded Graphite. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadagno, L.; Vertuccio, L.; Aliberti, F.; Pantani, R.; Raimondo, M.; Catauro, M.; Longo, R. Development of De-Icing/Self-Sensing Structural Composites via Controlled Joule Heating Curing. Compos. B Eng. 2025, 292, 112079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Thermal, Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Expanded Graphite and Micro-SiC Filled Hybrid Epoxy Composite for Electronic Packaging Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, R.; Vertuccio, L.; Aliberti, F.; Raimondo, M.; Pantani, R.; Russo, S.; Iannuzzo, G.; Guadagno, L. Adaptative Electrothermal Activation of Hybrid Composites for Anti-Icing Function. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2025, 8, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Pal, D.; Poonia, A.K. Exploring Nanofillers: Enhancing Properties in Biopolymer Food Packaging Materials—A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Pollut. Manag. 2025, 2, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jali, S.; Mohan, T.P.; Mwangi, F.M.; Kanny, K. A Review on Barrier Properties of Cellulose/Clay Nanocomposite Polymers for Packaging Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Chavez, S.E.; LaChance, A.M.; Jones, M.D.; French, C.D.; Walsh, A.M.; Shaw, M.T.; Sun, L. Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)/Montmorillonite (MMT) Nanocomposite Coatings via a Rotational Coating Method. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2024, 7, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, M.; Ferrier, E. Effect of Curing Temperature Conditions on Glass Transition Temperature Values of Epoxy Polymer Used for Wet Lay-up Applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 231, 117206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, L.; Jia, M.; Xiong, Y. Nanofillers in Novel Food Packaging Systems and Their Toxicity Issues. Foods 2024, 13, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Hasan, M.B.; Karim, F.E.; Kodrić, M.; Islam, M.R.; Khatun, M.M.; Motaleb, K.Z.M.A. Thermoset and Thermoplastic Polymer Composites Reinforced with Flax Fiber: Properties and Application—A Review. SPE Polym. 2025, 6, e10172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkees, F. Moisture Absorption Behavior and Diffusion Characteristics of Continuous Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites: A Review. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2023, 62, 1789–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, S.; Sakanaka, L.S.; Yamashita, F.; Grossmann, M.V.E. Water Sorption and Mechanical Properties of Cassava Starch Films and Their Relation to Plasticizing Effect. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Naddeo, C.; Raimondo, M.; Barra, G.; Vertuccio, L.; Russo, S.; Lafdi, K.; Tucci, V.; Spinelli, G.; Lamberti, P. Influence of Carbon Nanoparticles/Epoxy Matrix Interaction on Mechanical, Electrical and Transport Properties of Structural Advanced Materials. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 094001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, A.H.A.; Arjmand, M.; Sundararaj, U.; Trifkovic, M. Significance of Interfacial Interaction and Agglomerates on Electrical Properties of Polymer-Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2017, 125, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, L.; Liang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Fei, W.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Liang, L.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Recent Progress in Graphene/Polymer Nanocomposites. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2001105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossiord, N.; Loos, J.; Van Laake, L.; Maugey, M.; Zakri, C.; Koning, C.E.; John Hart, A. High-Conductivity Polymer Nanocomposites Obtained by Tailoring the Characteristics of Carbon Nanotube Fillers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 3226–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauhofer, W.; Kovacs, J.Z. A Review and Analysis of Electrical Percolation in Carbon Nanotube Polymer Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, A.C.; Fischer, M.; Wick, A.; Carosella, S.; Fox, B.L.; Middendorf, P. Mechanical, Thermal and Electrical Properties of Epoxy Nanocomposites with Amine-Functionalized Reduced Graphene Oxide via Plasma Treatment. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Huang, Y.; Chia, L. Effects of Carbon Nanotube (CNT) Geometries on the Dispersion Characterizations and Adhesion Properties of CNT Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Compos. Struct. 2022, 296, 115942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Ma, C.A.; Wu, G.; Sumita, M. Temperature and Time Dependence of Conductive Network Formation: Dynamic Percolation and Percolation Time. Polymer 2006, 47, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiella, G.; Antonucci, V.; Buschhorn, S.T.; Prado, L.A.S.A.; Schulte, K.; Giordano, M. Tailoring the Electrical Properties of MWCNT/Epoxy Composites Controlling Processing Conditions. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jacobs, O.; Wu, W.; Rüdiger, G.; Schädel, B. Effect of Dispersion Method on Tribological Properties of Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Epoxy Resin Composites. Polym. Test. 2007, 26, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prolongo, S.G.; Burón, M.; Gude, M.R.; Chaos-Morán, R.; Campo, M.; Ureña, A. Effects of Dispersion Techniques of Carbon Nanofibers on the Thermo-Physical Properties of Epoxy Nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 2722–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.Y.; Liao, W.Y.; Wang, T.Q.; Lai, W.M. Characteristics and Mechanical Properties of Graphene Nanoplatelets-Reinforced Epoxy Nanocomposites: Comparison of Different Dispersal Mechanisms. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, X.; Shanahan, M.E.R. Thermal and Thermo-Oxidative Ageing of an Epoxy Adhesive. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 68, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Zhong, W.H. Curing Characteristics of an Epoxy Resin in the Presence of Ball-Milled Graphite Particles. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1987–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, Z.S.B.; Araújo do Nascimento, P.L.; Samara, M.; David, É.; Macedo Fechine, G.J.; da Motta Sobrinho, M.A.; Demarquette, N.R. Influence of Graphene Functionalization on the Curing Kinetics, Dynamical Mechanical Properties and Morphology of Epoxy Nanocomposites. Polymer 2025, 320, 128067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhani, F.; Moghari, S.; Jouyandeh, M.; Laoutid, F.; Vahabi, H.; Saeb, M.R.; Dubois, P. Curing Kinetics and Thermal Stability of Epoxy Composites Containing Newly Obtained Nano-Scale Aluminum Hypophosphite (AlPO2). Polymers 2020, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Vertuccio, L.; Aliberti, F.; Calabrese, E.; Raimondo, M.; Pantani, R.; Longo, R. Sustainable Biobased Composites Manufactured via Joule Heating Curing with Recycled Carbon Fibers. Compos. Part C Open Access 2025, 17, 100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdoud-Chihani, A.; Mouzali, M.; Abadie, M.J.M. Study of Crosslinking AMS/DGEBA System by FTIR. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 69, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gouri, M.; El Bachiri, A.; Hegazi, S.E.; Rafik, M.; El Harfi, A. Thermal Degradation of a Reactive Flame Retardant Based on Cyclotriphosphazene and Its Blend with DGEBA Epoxy Resin. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 2101–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerche, E.F.; da Cruz, J.A.; Ornaghi, H.L.; Schrekker, H.S.; Amico, S.C. Viscoelastic Response of Amine Cured Epoxy Composites with Imidazolium Ionic Liquid-Modified Aramid Pulp. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddams, W.F. The Scope and Limitations of Curve Fitting. Appl. Spectrosc. 1980, 34, 245–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Vertuccio, L.; Naddeo, C.; Calabrese, E.; Barra, G.; Raimondo, M.; Sorrentino, A.; Binder, W.H.; Michael, P.; Rana, S. Reversible Self-Healing Carbon-Based Nanocomposites for Structural Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Zheng, S. Influence of Intramolecular Specific Interactions on Phase Behavior of Epoxy Resin and Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Blends Cured with Aromatic Amines. Polymer 2005, 46, 5828–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.F. Thermal Conductivity of Graphene-Polymer Composites: Mechanisms, Properties, and Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Thermally Conducting Polymer/Nanocarbon and Polymer/Inorganic Nanoparticle Nanocomposite: A Review. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2020, 59, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkees, F.; Swart, R.; Barsoum, I. Diffusion Mechanism and Properties of Chemical Liquids and Their Mixtures in 977-2 Epoxy Resin. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xing, P. Moisture Absorption Characterization of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Using Fickian and Non-Fickian Models. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 8935–8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, B.; Marais, S.; Langevin, D.; Médéric, P.; Aubry, T. Nanocomposite-Based Polyamide 12/Montmorillonite: Relationships between Structures and Transport Properties. Desalination 2006, 199, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | EG Content [wt. %] | Mixing Method |
|---|---|---|
| EP | 0 | / |
| EP1CEN | 1 | Centrifugal Planetary Mixing |
| EP3CEN | 3 | Centrifugal Planetary Mixing |
| EP5CEN | 5 | Centrifugal Planetary Mixing |
| EP7CEN | 7 | Centrifugal Planetary Mixing |
| EP7SON | 7 | Ultrasonication |
| EP7HTM | 7 | High Temperature Mixing |
| EP9CEN | 9 | Centrifugal Planetary Mixing |
| Assignment | Wavenumber (cm−1) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uncured | Cured | ||
| ν O-H | - | 3426 | [39] |
| ν N-H | 3467, 3370 | - | [23,39] |
| δ N-H | 3240, 1630 | - | [23,39] |
| ν aliphatic C-H | 2968, 2927, 2875 | 2968, 2927, 2875 | [40] |
| ν C=C | 1596, 1508, 1452 | 1596, 1508, 1452 | [40] |
| ν alkyl-aryl ethers C-O-C | 1240, 1036 | 1240, 1036 | [40,41] |
 | 915 | - | [39,40] |
| EP | EP7CEN | EP7SON | EP7HTM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D [mm2/s] | 9.83 × 10−6 | 3.42 × 10−6 | 5.39 × 10−6 | 5.90 × 10−6 |
| R2 | 0.9978 | 0.9992 | 0.9994 | 0.9985 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Longo, R.; Calabrese, E.; Aliberti, F.; Vertuccio, L.; De Piano, G.; Pantani, R.; Raimondo, M.; Guadagno, L. Effects of the Mixing Method of Expanded Graphite on Thermal, Electrical, and Water Transport Properties of Thermosetting Nanocomposites. Polymers 2025, 17, 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17202759
Longo R, Calabrese E, Aliberti F, Vertuccio L, De Piano G, Pantani R, Raimondo M, Guadagno L. Effects of the Mixing Method of Expanded Graphite on Thermal, Electrical, and Water Transport Properties of Thermosetting Nanocomposites. Polymers. 2025; 17(20):2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17202759
Chicago/Turabian StyleLongo, Raffaele, Elisa Calabrese, Francesca Aliberti, Luigi Vertuccio, Giorgia De Piano, Roberto Pantani, Marialuigia Raimondo, and Liberata Guadagno. 2025. "Effects of the Mixing Method of Expanded Graphite on Thermal, Electrical, and Water Transport Properties of Thermosetting Nanocomposites" Polymers 17, no. 20: 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17202759
APA StyleLongo, R., Calabrese, E., Aliberti, F., Vertuccio, L., De Piano, G., Pantani, R., Raimondo, M., & Guadagno, L. (2025). Effects of the Mixing Method of Expanded Graphite on Thermal, Electrical, and Water Transport Properties of Thermosetting Nanocomposites. Polymers, 17(20), 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17202759











