Development of Molecularly Imprinted Photonic Crystals Sensor for High-Sensitivity, Rapid Detection of Sulfamethazine in Food Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Preparation of SiO2 Microspheres
2.4. Preparation of MIPC Sensor for SMZ
2.5. Reflection Spectrum Measurement
2.6. Detection of SMZ in Real Samples
2.6.1. Milk Samples
2.6.2. Chicken Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Preparation Conditions for MIPC
3.2. Characterization of the MIPC Sensor
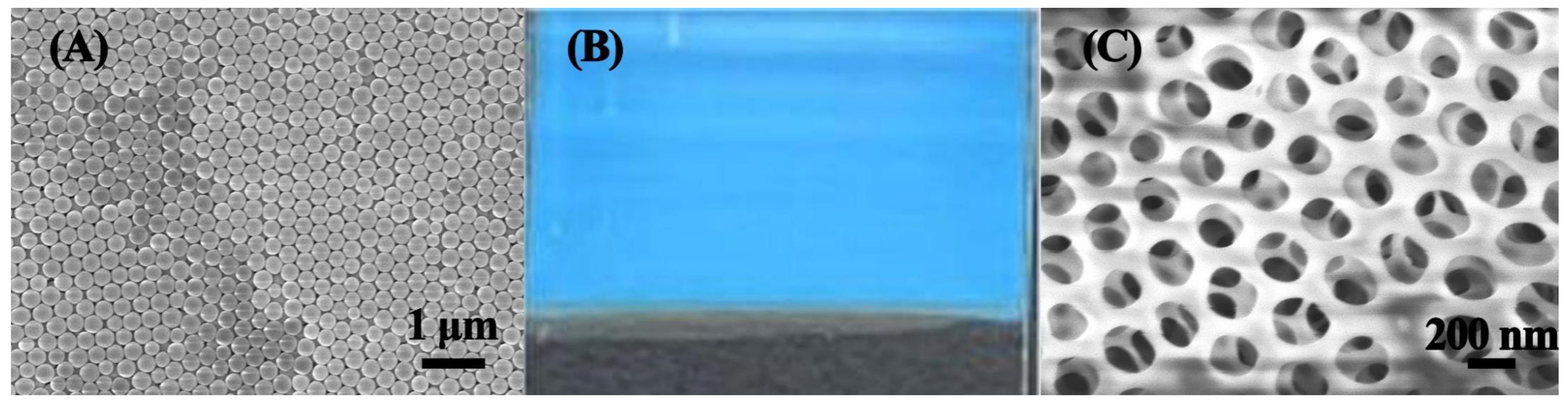
3.2.1. Morphology Characterization of SiO2 Microspheres and the MIPC Sensor
3.2.2. Reflection Spectra Characterization
3.3. Optimization of Adsorption Conditions for MIPC
3.3.1. Effect of Adsorption Solvent
3.3.2. Effect of Solvent pH
3.4. Performance Analysis of MIPC Sensor
3.4.1. Optimum Detection Time
3.4.2. Selectivity of the MIPC Sensor
3.4.3. Reusability of the MIPC Sensor
3.4.4. Application to Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basak, S.; Venkatram, R.; Singhal, R.S. Recent advances in the application of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) in food analysis. J. Food Sci. 2022, 139, 109074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, H.; He, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Shen, J. Adsorption and convenient ELISA detection of sulfamethazine in milk based on MOFs pretreatment. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Deng, X.; Qu, X.; Chen, Q.; Niu, B. Risk Assessment of Veterinary Drug Residues in Pork on the Market in the People’s Republic of China. J. Food Prot. 2022, 85, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errayess, S.A.; Lahcen, A.A.; Idrissi, L.; Marcoaldi, C.; Chiavarini, S.; Amine, A. A sensitive method for the determination of Sulfonamides in seawater samples by Solid Phase Extraction and UV–Visible spectrophotometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2017, 181, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tian, D.; Phan, A.; Seididamyeh, M.; Alanazi, M.; Ping Xu, Z.; Sultanbawa, Y.; Zhang, R. Luminescent sensors for residual antibiotics detection in food: Recent advances and perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 498, 215455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wei, J.; Pan, F.; Yuan, T.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Q. Advances in Photonic Crystal Research for Structural Color. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2400865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.P.; McComb, D.W.; Richel, A.; Treble, B.M.; De La Rue, R.M. Synthesis and optical properties of opal and inverse opal photonic crystals. Synth. Met. 2001, 116, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, F.; Hannaneh, M.; Farideh, R.; Kazem, N.-K. Inverse opal photonic crystals: Recent advances in fabrication methods and biological applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 72, 103377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Ye, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, T.; Jiang, L.; Song, Y. Facile Fabrication of Tough SiC Inverse Opal Photonic Crystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 22303–22308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamie, A.; Echresh, A.; Zargar, B.; Nur, O.; Willander, M. Fabrication and characterization of highly-ordered Zinc Oxide nanorods on gold/glass electrode, and its application as a voltammetric sensor. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 174, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Tian, Y.; Xu, P.; Du, X.; Weng, J.; He, J.; Li, H. Application of surface-imprinted polymers in pretreatment for detection of sulfamonomethoxine in water samples. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.; Yan, S.; Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Song, Z. Recent Advances in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Antibiotic Analysis. Molecules 2023, 28, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, S.; Frasco, M.F.; Sales, M.G.F. A biomimetic photonic crystal sensor for label-free detection of urinary venous thromboembolism biomarker. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 312, 127947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shao, K.; Hong, C.; Chen, S.; Lin, Z.; Huang, Z.; Lai, Z. Fluorimetric identification of sulfonamides by carbon dots embedded photonic crystal molecularly imprinted sensor array. Food Chem. 2022, 407, 135045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, H.; He, J.; Cui, A.; Wu, X.; Lai, J.; Sun, H. Rapid Screening of Butyl Paraben Additive in Toner Sample by Molecularly Imprinted Photonic Crystal. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Pan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H. Narrowly Dispersed Hydrophilic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Efficient Molecular Recognition in Real Aqueous Samples Including River Water, Milk, and Bovine Serum. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 52, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lin, Z.; Huang, Z.; Peng, A. Rapid detection of sulfaguanidine in fish by using a photonic crystal molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Chem. 2018, 281, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Bai, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Z.; Ning, B.; Li, M.; Pu, Y.; Ying, Y.; Su, F.; et al. Au-doped photonic crystal allows naked-eye determination of small organic molecules. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Ma, J.; Huang, G.; Xing, F.; Gao, J. Molecularly imprinted photonic crystals for the direct label-free distinguishing of l-proline and d-proline. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 40, 17250–17256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z. Recent advances of polymeric photonic crystals in molecular recognition. Dyes Pigments 2022, 205, 110544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukadida, M.; Anene, A.; Jaoued-Grayaa, N.; Chevalier, Y.; Hbaieb, S. Choice of the functional monomer of molecularly imprinted polymers: Does it rely on strong acid-base or hydrogen bonding interactions? Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2022, 50, 100669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yuan, L.; Ding, M.; Wang, S.; Ren, F.; Zhang, J.; Du, S.; Li, F.; Zhou, X. The study of core–shell molecularly imprinted polymers of 17β-estradiol on the surface of silica nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 2791–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mu, Z.; Liu, R.; Pu, Y.; Yin, L. Molecular imprinted photonic crystal hydrogels for the rapid and label-free detection of imidacloprid. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3947–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Qiu, L.; Qiao, Y.; Xue, M.; Dong, X.; Meng, Z. Recent advances in sensing applications of molecularly imprinted photonic crystals. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 665119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazhir, N.; Kiani, F.; Tahermansouri, H.; Azade, S.G.-H.; Koohyar, F. Prediction of Thermodynamic and Structural Properties of Sulfamerazine and Sulfamethazine in Water Using DFT and ab Initio Methods. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2018, 62, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, F.; Li, C.; Ahmad, N.; Yuan, Z.; Tan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, C. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on Carboxymethylcellulose/Graphene Oxide Composites for Selective Adsorption of Hydroxycamptothecin. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 9294–9304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Development of water-compatible molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the detection of six sulfonamides in animal-derived foods. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1574, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Chen, W.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H. Highly Sensitive α-Amanitin Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Photonic Crystals. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1093, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, N.; Shi, B.; Hu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zou, X.; Shi, J. A ternary heterostructure aptasensor based on metal-organic framework and polydopamine nanoparticles for fluorescent detection of sulfamethazine. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Syritski, V. Sulfamethizole-imprinted polymer on screen-printed electrode: Towards the design of a portable environmental sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xing, K.; Ding, N.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Lai, W. Lateral flow immunoassay based on dual spectral-overlapped fluorescence quenching of polydopamine nanospheres for sensitive detection of sulfamethazine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 423, 127204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wen, Y.; Hu, W.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, L.; Zeng, Q.; Tang, H.; Hong, Y.; Tang, K. A signal-amplified electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of sulfadimidine in crayfish using COOH-MWCNTs-Fe3O4-GO nanohybrids modified working electrode. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 134, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wang, S.; Tong, W.; Peng, J. Quantum Dot Nanobeads Based Fluorescence Immunoassay for the Quantitative Detection of Sulfamethazine in Chicken and Milk. Sensors 2021, 21, 6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ni, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wen, K.; Ke, Y.; Yang, H.; Shi, W.; Zhang, S.; Shen, J.; et al. Development of a highly specific chemiluminescence aptasensor for sulfamethazine detection in milk based on in vitro selected aptamers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 281, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán-Vázquez de Prada, A.; Reviejo, A.J.; Pingarrón, J.M. A method for the quantification of low concentration sulfamethazine residues in milk based on molecularly imprinted clean-up and surface preconcentration at a Nafion-modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Bai, J.; Peng, Y.; Qie, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ning, B.; Xiao, D.; Gao, Z. A core–shell-structured molecularly imprinted polymer on upconverting nanoparticles for selective and sensitive fluorescence sensing of sulfamethazine. Analyst 2015, 140, 5301–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

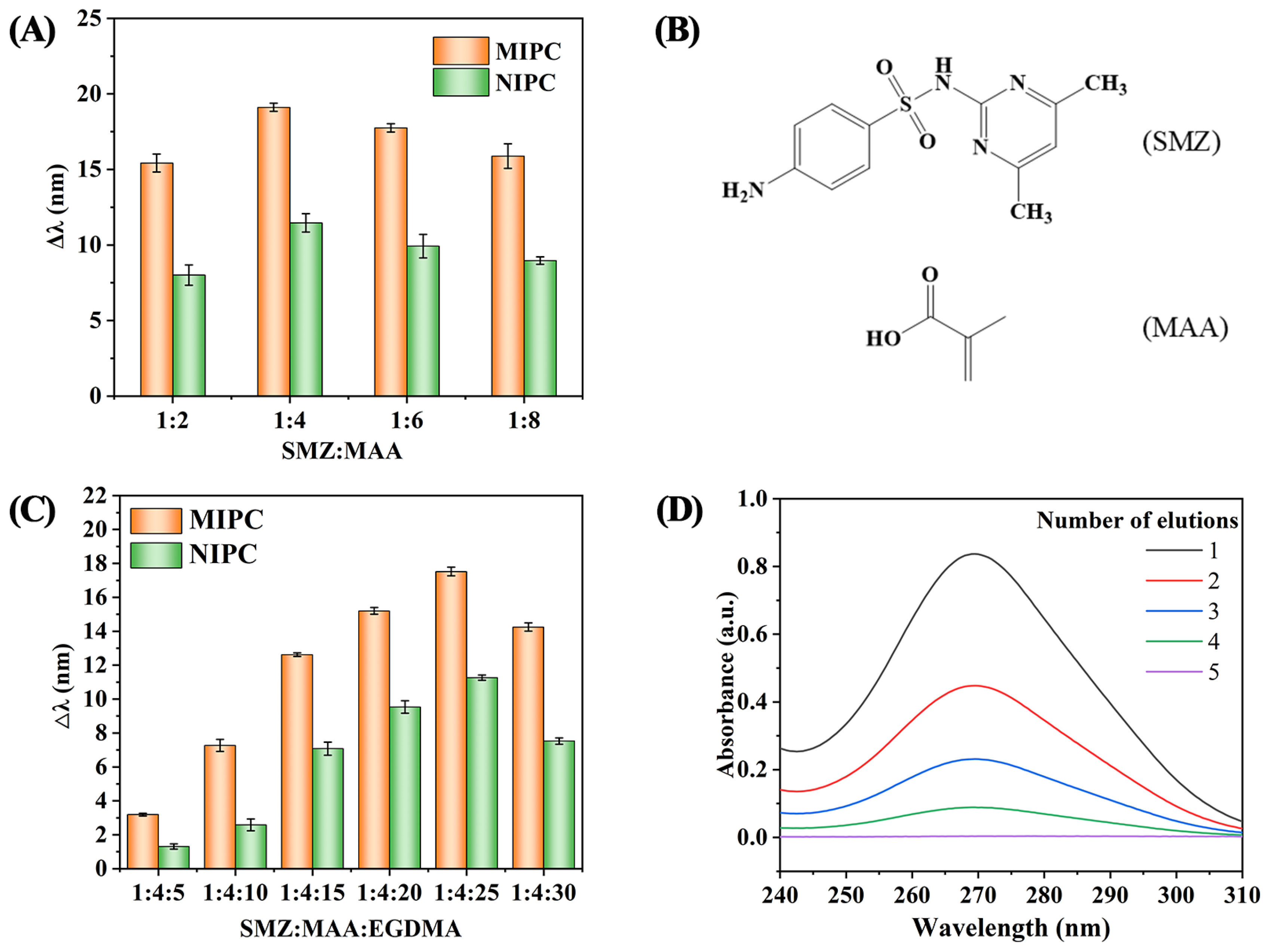

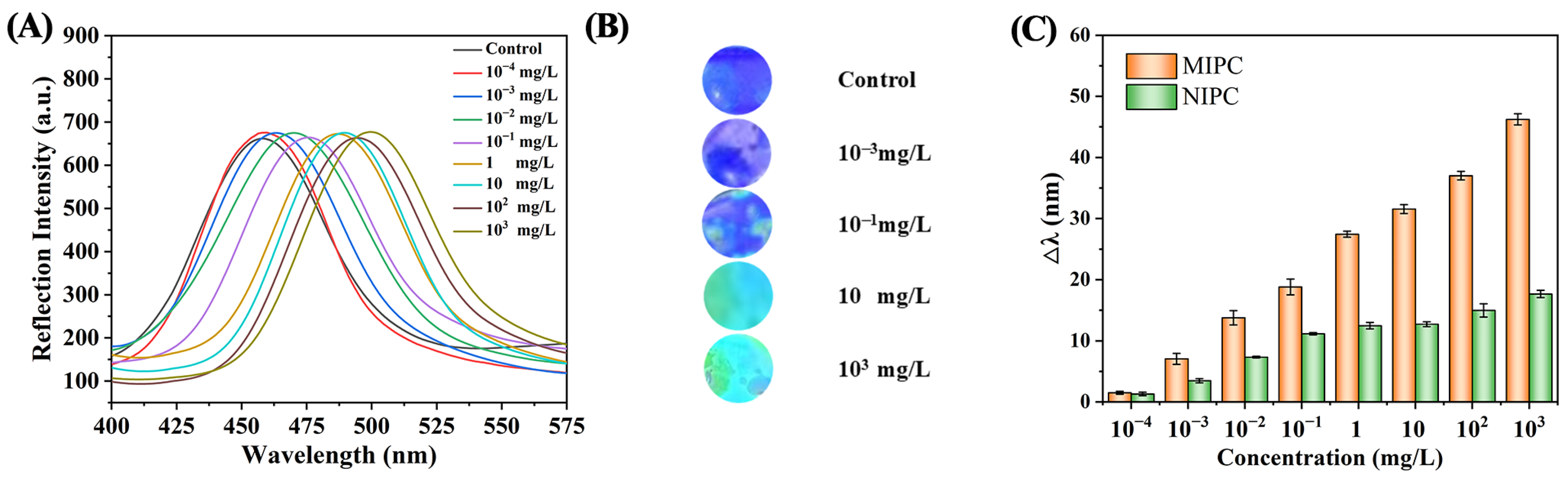
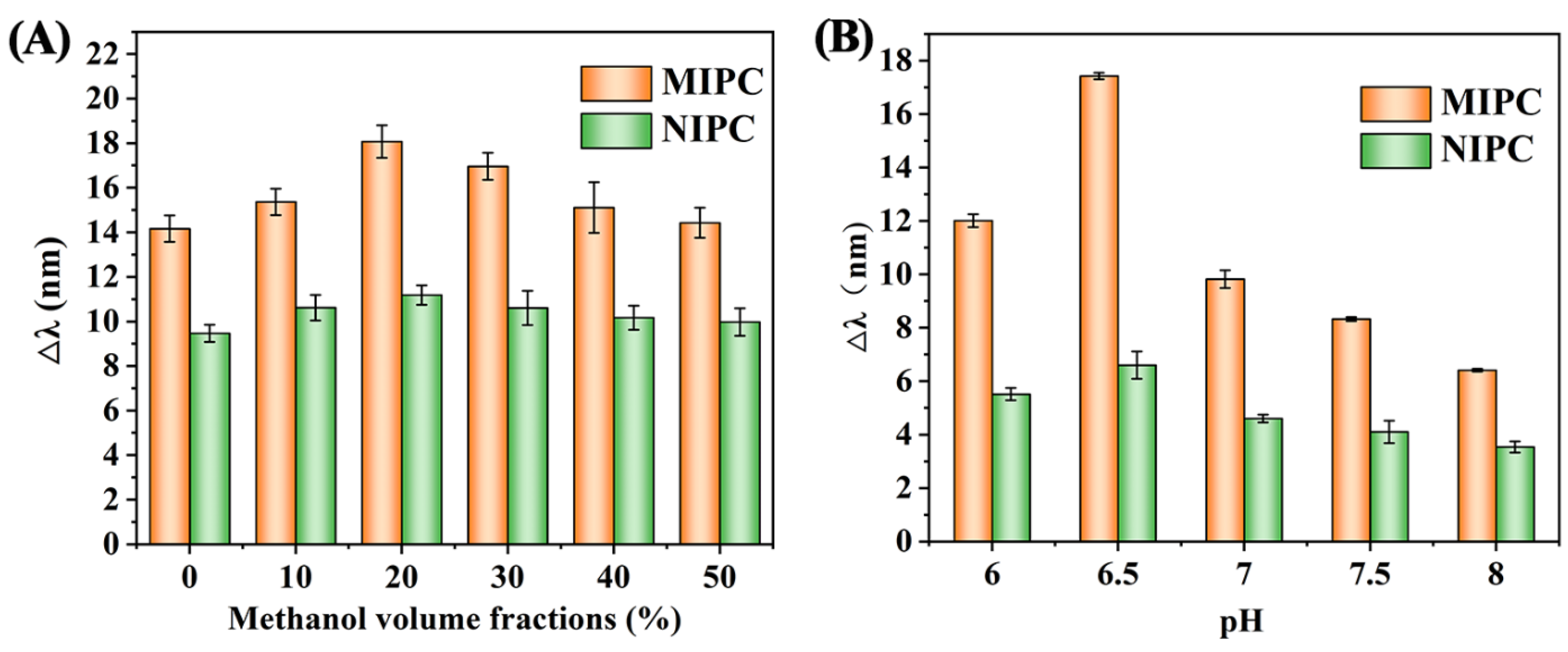
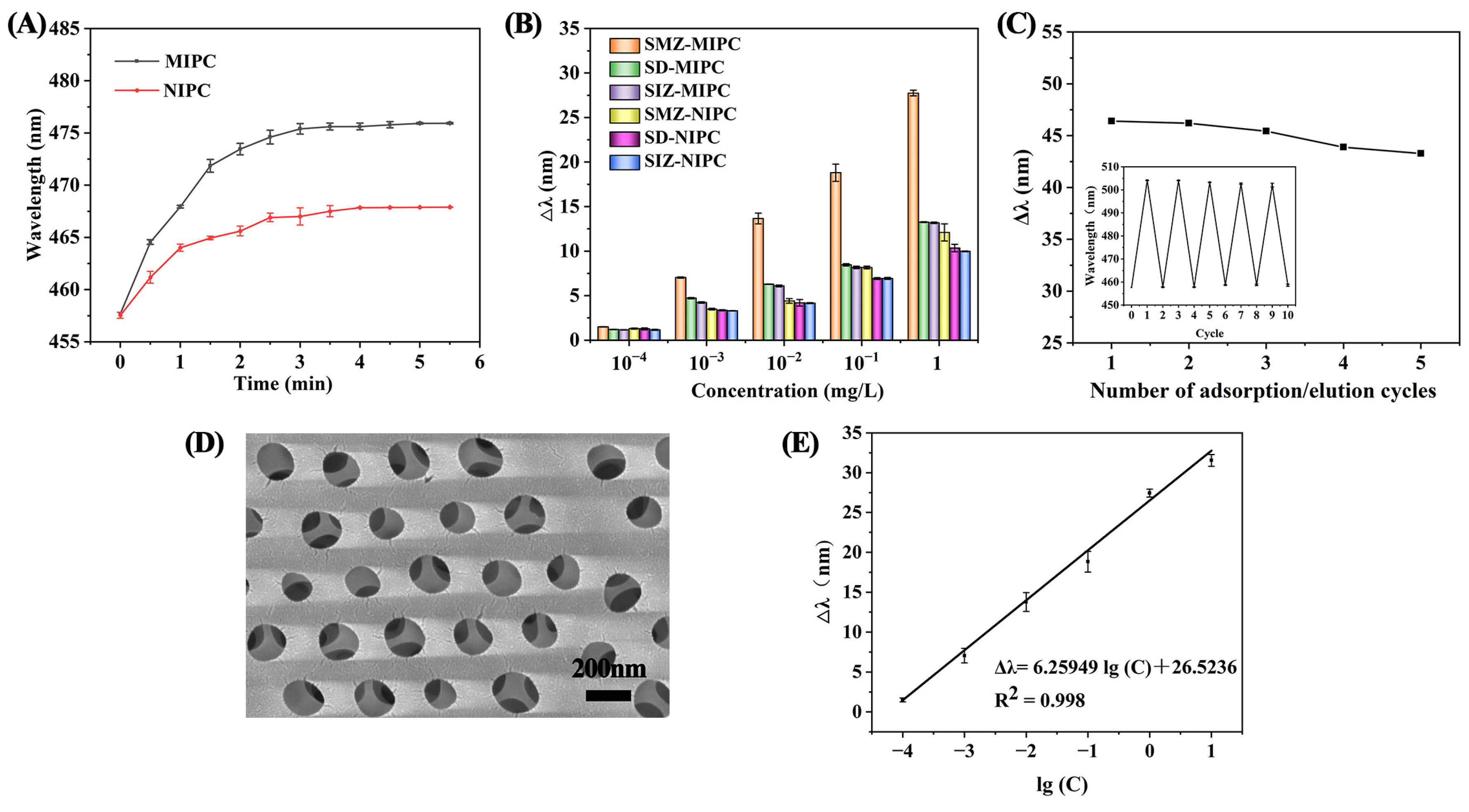
| Sample | Spiked Concentration (μg/L) | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Found Concentration (μg/L) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | Found Concentration (μg/L) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Milk | 1 | 0.90 | 89.80 | 3.50 | 0.93 | 93.28 | 1.49 |
| 10 | 9.61 | 96.13 | 4.45 | 8.80 | 87.86 | 2.73 | |
| 1 × 102 | 88.00 | 88.00 | 4.84 | 80.56 | 80.56 | 4.78 | |
| 1 × 103 | 1035.90 | 103.59 | 4.92 | 1016.90 | 101.69 | 4.86 | |
| Chicken | 1 | 0.89 | 89.01 | 1.47 | 0.82 | 81.61 | 4.90 |
| 10 | 10.25 | 102.48 | 6.41 | 8.08 | 80.77 | 5.55 | |
| 1 × 102 | 91.71 | 91.71 | 4.35 | 88.14 | 88.14 | 3.30 | |
| 1 × 103 | 922.00 | 92.20 | 3.77 | 1016.90 | 101.69 | 4.28 | |
| Methods | Linear Range (ng/mL) | Detection Time (min) | LOD (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorescent sensor | 0.50–100 | 55 | 0.025 | 92.69–108.48 | [29] |
| Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors | 0.28–2.30 | 10 | 0.250 | - | [30] |
| Lateral flow immunoassay | 0.05–10 | 35 | 0.043 | 99.70–106.60 | [31] |
| Electrochemical immunosensors | 0.01–100 | 30 | 0.003 | 99.40–109 | [32] |
| Fluorescence immunoassay | 0.20–12.50 | 25 | 0.110 | 80.90–109.40 | [33] |
| Chemiluminescence | 1.85–21.57 | 65 | 0.920 | 88–91.10 | [34] |
| Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors | 2.5–250 | 5 | 1.900 | 100 ± 3 | [35] |
| Molecularly imprinted fluorescent sensors | 50–700 | 60 | 34 | 96.01–98.90 | [36] |
| Molecularly imprinted photonic crystal sensor | 10−1–104 | 3 | 1.160 | 80.56–103.59 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X. Development of Molecularly Imprinted Photonic Crystals Sensor for High-Sensitivity, Rapid Detection of Sulfamethazine in Food Samples. Polymers 2025, 17, 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020160
He J, Wu M, Wang X, Xu R, Zhang S, Zhao X. Development of Molecularly Imprinted Photonic Crystals Sensor for High-Sensitivity, Rapid Detection of Sulfamethazine in Food Samples. Polymers. 2025; 17(2):160. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020160
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jinxing, Mengke Wu, Xin Wang, Ruoxuan Xu, Shuting Zhang, and Xiaolei Zhao. 2025. "Development of Molecularly Imprinted Photonic Crystals Sensor for High-Sensitivity, Rapid Detection of Sulfamethazine in Food Samples" Polymers 17, no. 2: 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020160
APA StyleHe, J., Wu, M., Wang, X., Xu, R., Zhang, S., & Zhao, X. (2025). Development of Molecularly Imprinted Photonic Crystals Sensor for High-Sensitivity, Rapid Detection of Sulfamethazine in Food Samples. Polymers, 17(2), 160. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020160








