Effect of Repeated Autoclave on Hardness and Tensile Strength of Polypropylene/Natural Rubber Developed for Rubber Dam Clamp
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
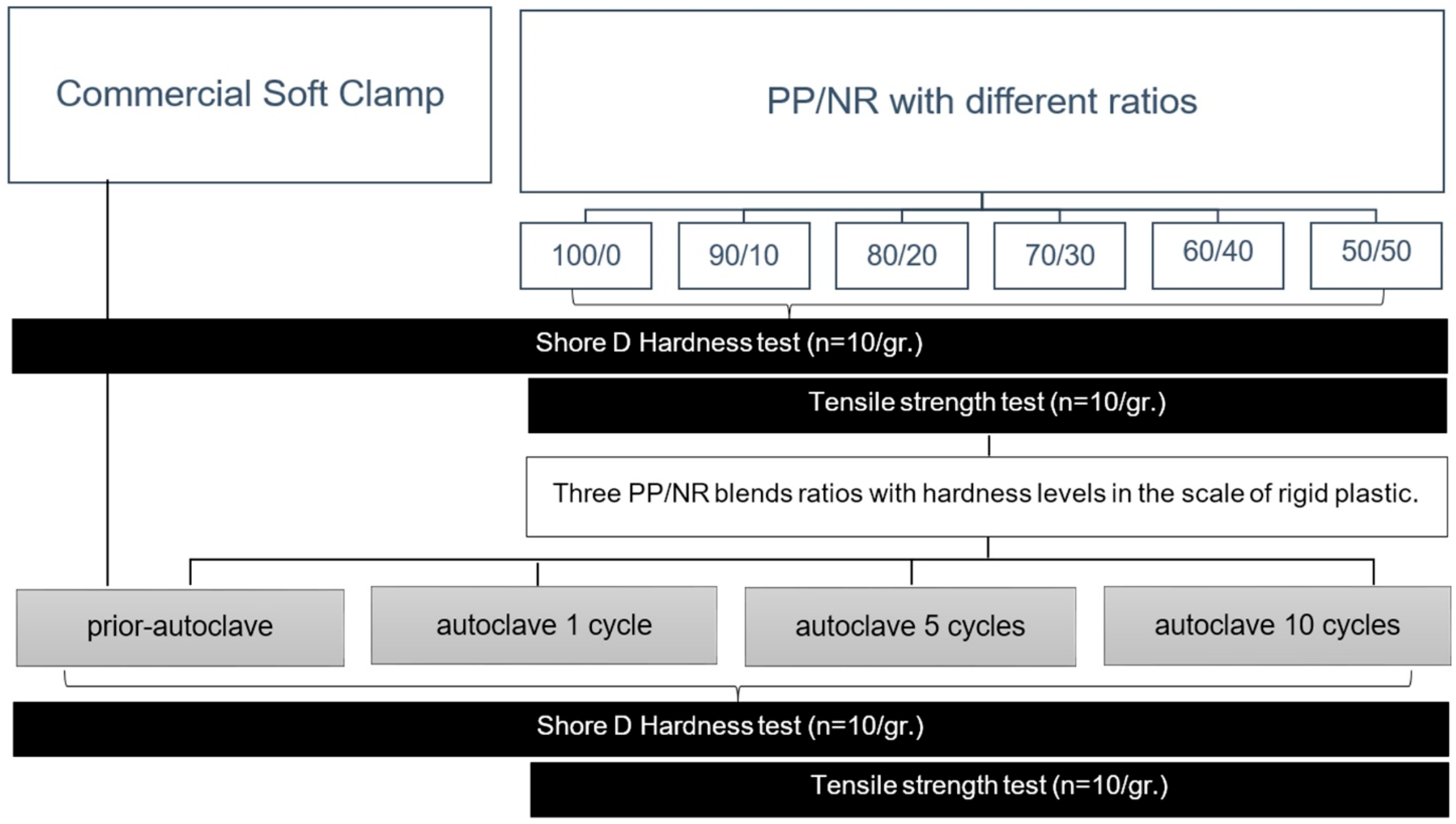
2.1. Experimental Design
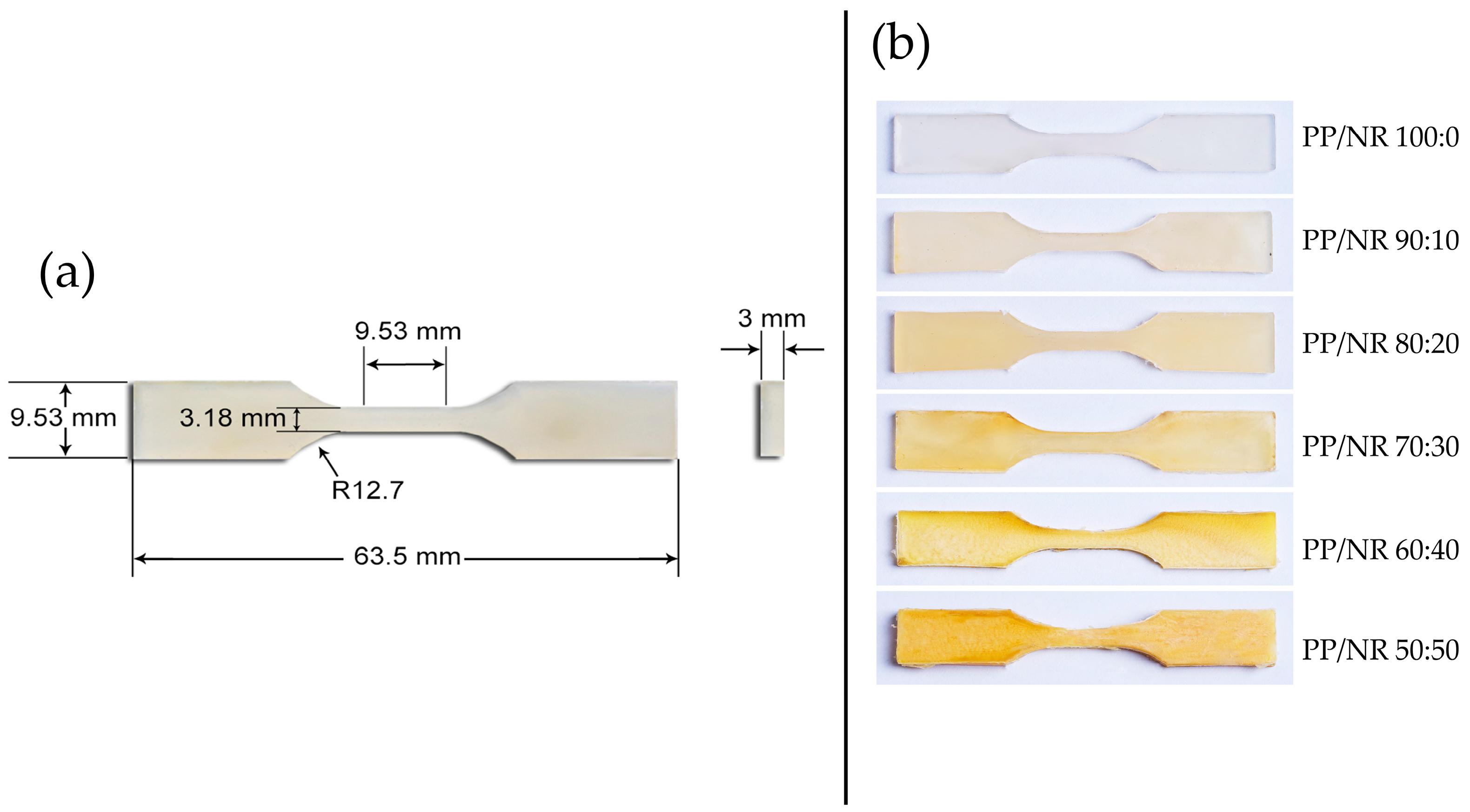
2.2. PP/NR Blended Preparation
2.3. Hardness Test
2.4. Tensile Testing
2.5. Autoclave Steam Sterilization
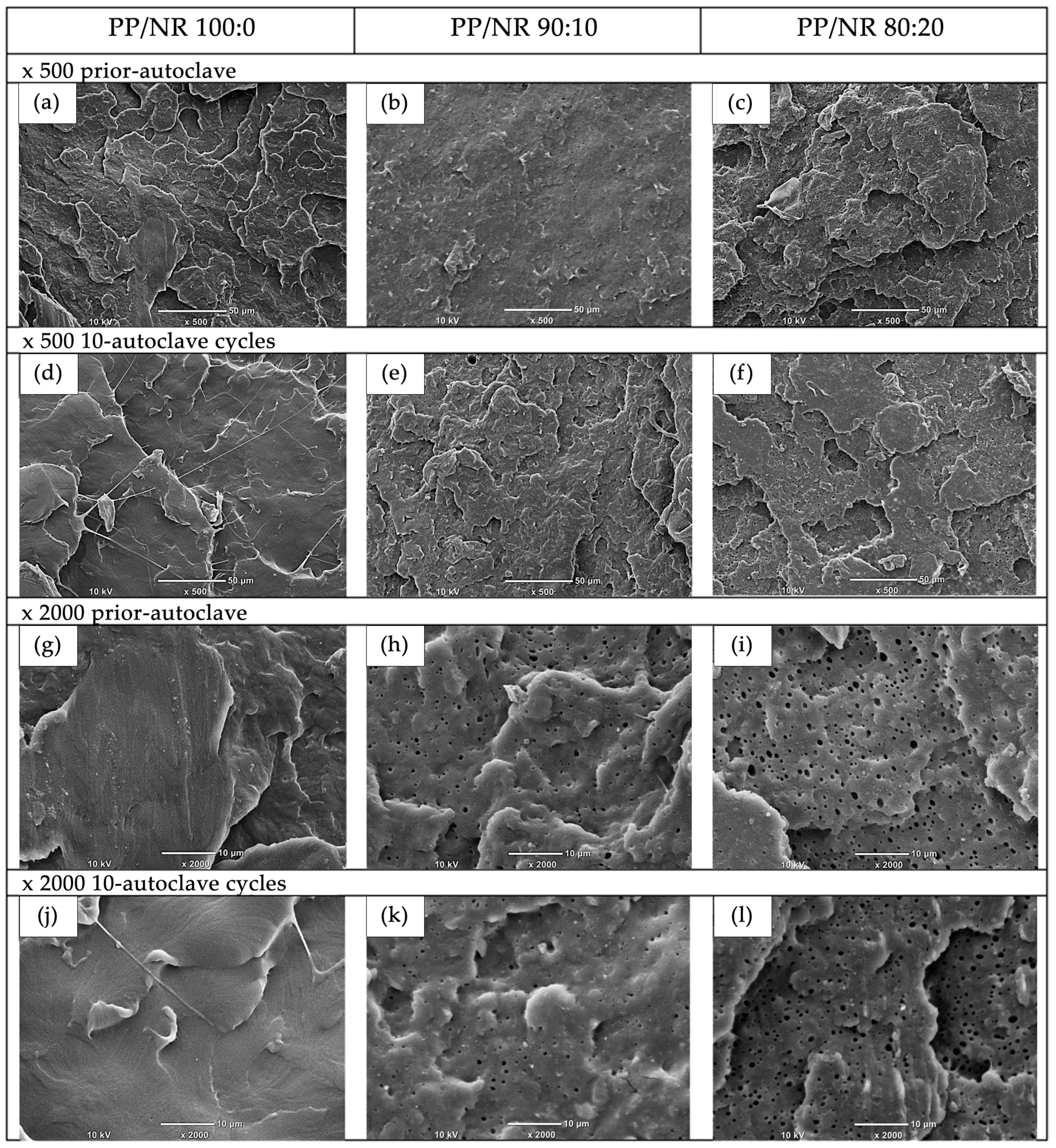
2.6. Morphological Analysis (SEM)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hardness Test
3.2. Tensile Test
3.3. Surface Morphology
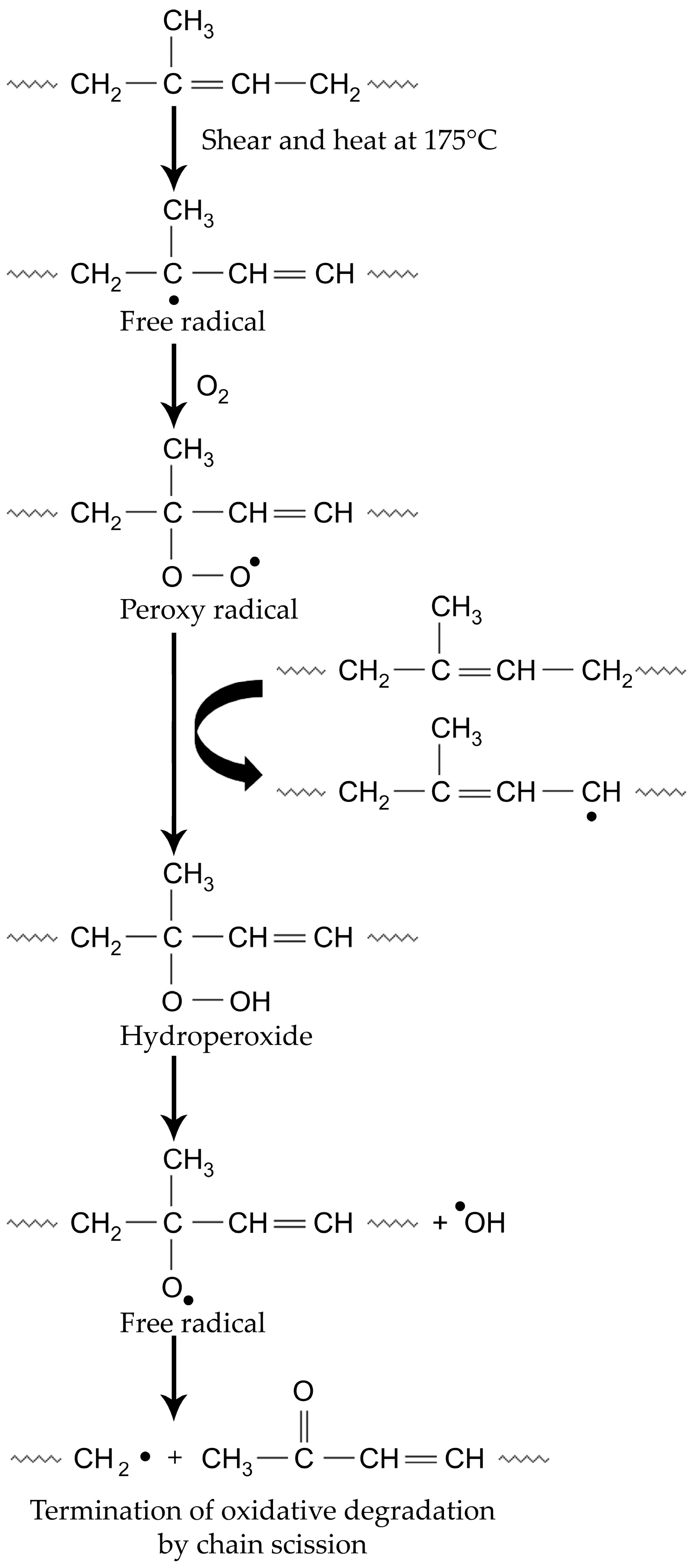
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ballal, V.; Khandelwal, D.; Saraswathi, M.V. Rubber dam in endodontics: An overview of recent advances. Int. J. Clin. Dent. 2013, 6, 319–330. [Google Scholar]
- Cochran, M.A.; Miller, C.H.; Sheldrake, M.A. The efficacy of the rubber dam as a barrier to the spread of microorganisms during dental treatment. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1989, 119, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, J.; Saunders, W.P. Effect of various irrigant and autoclaving regimes on the fracture resistance of rubber dam clamps. Int. Endod. J. 1996, 29, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susini, G.; Pommel, L.; Camps, J. Accidental ingestion and aspiration of root canal instruments and other dental foreign bodies in a French population. Int. Endod. J. 2007, 40, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.; Rahman, A. Rubber dam clamps: Friend or foe? Fac. Dent. J. 2022, 14, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaferani, S.H. Chapter 1—Introduction of polymer-based nanocomposites. In Polymer-Based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications; Jawid, M., Khan, M.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Tomić, N.Z.; Marinković, A.D. Chapter 4—Compatibilization of polymer blends by the addition of graft copolymers. In Compatibilization of Polymer Blends; Ajitha, A.R., Thomas, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 103–144. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, A.B.; Chatterjee, T.; Naskar, K. Automotive applications of thermoplastic vulcanizates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Shahid, M.A.; Mahmud, N.; Habib, A.; Rana, M.; Khan, S.; Hossain, M. Research and application of polypropylene: A review. Discov. Nano 2024, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brehler, R.; Kütting, B. Natural rubber latex allergy: A problem of interdisciplinary concern in medicine. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangsantham, P.; Nonthiphalang, T.; Wongwitthayakool, P.; Sirisinha, C.; Krajangta, N.; Phumpatrakom, P. The Flexural Strength and the Effect of the Autoclave Sterilization of Polypropylene/Natural Rubber Blended Materials. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranquillo, J.; Goldberg, J.; Allen, R. Chapter 8—Detailed Design. In Biomedical Engineering Design; Tranquillo, J., Goldberg, J., Allen, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 235–285. [Google Scholar]
- Panta, G.; Richardson, A.K.; Shaw, I.C. Effectiveness of autoclaving in sterilizing reusable medical devices in healthcare facilities. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2019, 13, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadmehri, F.; Cai, X.; Hojjati, M.; Chen, J.; Hoa, S.V. Effect of autoclave process on the quality of thermoplastic composite truncated cones manufactured using automated fiber placement technique. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2015, 22, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendjaouhdou, C.; Bensaad, S. Aging studies of a polypropylene and natural rubber blend. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2018, 9, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.M.; Howell, A.P. Reusability of autoclaved 3D printed polypropylene compared to a glass filled polypropylene composite. 3D Print. Med. 2021, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broitman, E. Indentation hardness measurements at macro-, micro-, and nanoscale: A critical overview. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vîlcea, E.-J.; Rodica-Mariana, I. Determination of hardness polypropylene flame retardants reogard 2000® using shore D methode. Sci. Bull. Valahia Univ. Mater. Mech. 2014, 12, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Farhat, H. (Ed.) Chapter 3—Materials and coating technologies. In Operation, Maintenance, and Repair of Land-Based Gas Turbines; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 63–87. [Google Scholar]
- D2240-15´1; Standard Test Method for Rubber Property—Durometer Hardness. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. [CrossRef]
- D638-14; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Eskibağlar, M.; Erdem, S.; Kaman, M.O. Evaluation of the effect of different rubber dam clamps on the mandibular first molar with Finite element analysis. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 27, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Ukey, P.D.; Francis, V.; Singh, R.P.; Sahu, S. Chapter 16—Plastic pellets. In Polymers for 3D Printing; Izdebska-Podsiadły, J., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 307–323. [Google Scholar]
- Yahya, S.; Azura, A. Effect of Curing Systems on Thermal Degradation Behavior of Natural Rubber (SMR CV 60); Penerbit Universiti Sains Malaysia: Nibong Tebal, Malaysia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Danielle Galiani, P.; Antonio Malmonge, J.; Guenther Soares, B.; Henrique Capparelli Mattoso, L. Studies on thermal–oxidative degradation behaviours of raw natural rubber: PRI and thermogravimetry analysis. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2013, 42, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, T.; Bierögel, C.; Seidler, S. Conventional Hardness Values—Introduction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 423–427. [Google Scholar]
- Bergström, J. (Ed.) 2—Experimental Characterization Techniques. In Mechanics of Solid Polymers; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 19–114. [Google Scholar]
- Pottammal, N.; Rao, A.; Natarajan, S.; Karuna, Y.M.; Nayak, A.P.; Rao, S. Evaluation of pain response in children to the SoftClamp™ as an alternative to the metal rubber dam clamp: A randomized clinical trial. Dent. Res. J. 2023, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, M.; Greenwell, A.L. Effect of Repeated Sterilization on the Tensile Strength of Rubber Dam Clamps. Pediatr. Dent. 2018, 40, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giebink, D.L.; Mathieu, G.P.; Hondrum, S.O. Effect of sterilization on stiffness and dimensional stability of rubber-dam clamps. Gen. Dent. 1996, 44, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Material | Mean (SD) of Hardness (Shore D) | p-Value of Two-Way ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Autoclave Cycles | |||||
| Prior | 1 Cycle | 5 Cycles | 10 Cycles | ||
| PP/NR 100:0 | 70.4 (0.50) aA | 70.0 (0.25) aA | 70.0 (0.47) aA | 69.75 (0.28) aA | Diff among PP/NR ratios < 0.001 Diff among cycles = 0.52 |
| PP/NR 90:10 | 68.45 (0.29) bA | 65.85 (0.25) bA | 66.60 (0.27) bA | 67.20 (0.25) bA | |
| PP/NR 80:20 | 63.95 (0.34) cA | 64.30 (0.34) cA | 63.20 (0.36) cA | 63.80 (0.23) cA | |
| PP/NR 70:30 | 57.10 (0.48) d | N/A | |||
| PP/NR 60:40 | 54.00 (0.30) e | ||||
| PP/NR 50:50 | 45.00 (0.21) f | ||||
| SoftClampTM | 85.70 (0.42) g | ||||
| p-value of one-way ANOVA | <0.001 | ||||
| Material | Mean (SD) of Tensile Strength (MPa) | p-Value of Two-Way ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Autoclave Cycles | |||||
| Prior | 1 Cycle | 5 Cycles | 10 Cycles | ||
| PP/NR 100:0 | 36.78 (0.52) aA | 46.85 (0.84) aA | 35.29 (0.23) aA | 35.72 (0.31) aA | Diff among PP/NR ratios < 0.001 Diff among cycles = 0.058 |
| PP/NR 90:10 | 29.79 (0.62) bA | 29.34 (0.62) bA | 27.62 (0.18) bA | 28.79 (0.23) bA | |
| PP/NR 80:20 | 26.13 (0.38) cA | 24.28 (0.37) cA | 24.75 (0.39) cA | 25.09 (0.22) cA | |
| PP/NR 70:30 | 20.69 (0.33) d | N/A | |||
| PP/NR 60:40 | 19.45 (0.43) d | ||||
| PP/NR 50:50 | 15.00 (0.37) e | ||||
| p-value of one-way ANOVA | <0.001 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nonthiphalang, T.; Phumpatrakom, P.; Rangsantham, P.; Wongwitthayakool, P.; Sirisinha, C.; Krajangta, N. Effect of Repeated Autoclave on Hardness and Tensile Strength of Polypropylene/Natural Rubber Developed for Rubber Dam Clamp. Polymers 2025, 17, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020143
Nonthiphalang T, Phumpatrakom P, Rangsantham P, Wongwitthayakool P, Sirisinha C, Krajangta N. Effect of Repeated Autoclave on Hardness and Tensile Strength of Polypropylene/Natural Rubber Developed for Rubber Dam Clamp. Polymers. 2025; 17(2):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020143
Chicago/Turabian StyleNonthiphalang, Thitaporn, Panupat Phumpatrakom, Paphavarin Rangsantham, Panjaporn Wongwitthayakool, Chakrit Sirisinha, and Nantawan Krajangta. 2025. "Effect of Repeated Autoclave on Hardness and Tensile Strength of Polypropylene/Natural Rubber Developed for Rubber Dam Clamp" Polymers 17, no. 2: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020143
APA StyleNonthiphalang, T., Phumpatrakom, P., Rangsantham, P., Wongwitthayakool, P., Sirisinha, C., & Krajangta, N. (2025). Effect of Repeated Autoclave on Hardness and Tensile Strength of Polypropylene/Natural Rubber Developed for Rubber Dam Clamp. Polymers, 17(2), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17020143







