Repeated Thermomechanical Recycling of Polypropylene-Organosheets to Injection-Moulded Glass-Fibre-Reinforced Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
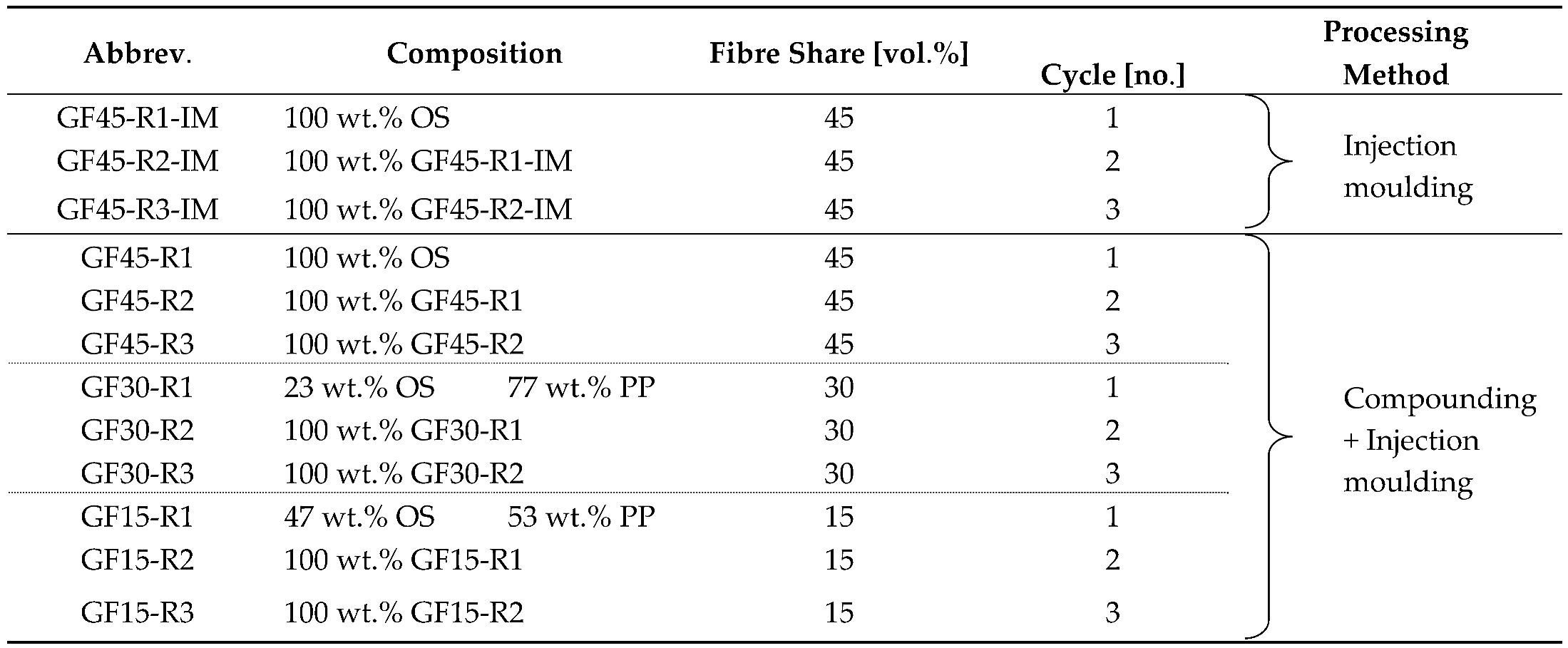
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Preprocessing
2.2. Recycling Processing Methods
2.3. Characterisation Methods
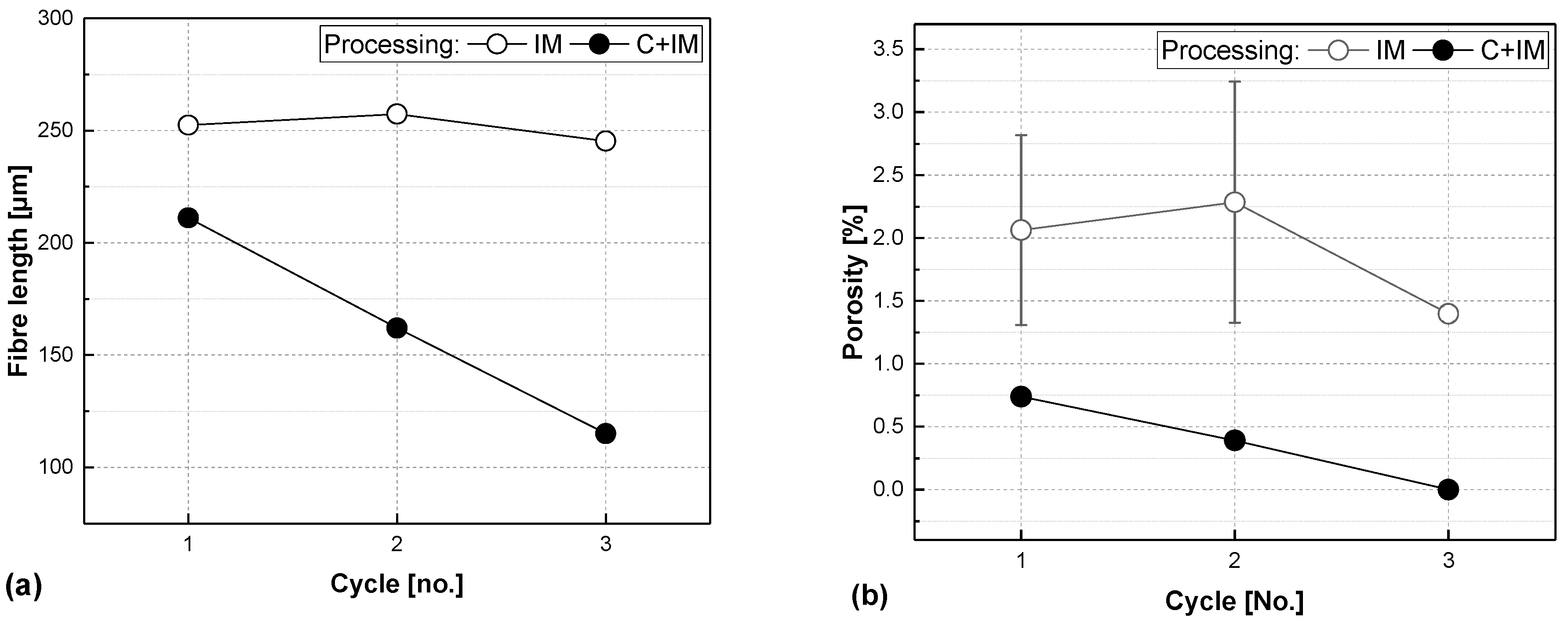
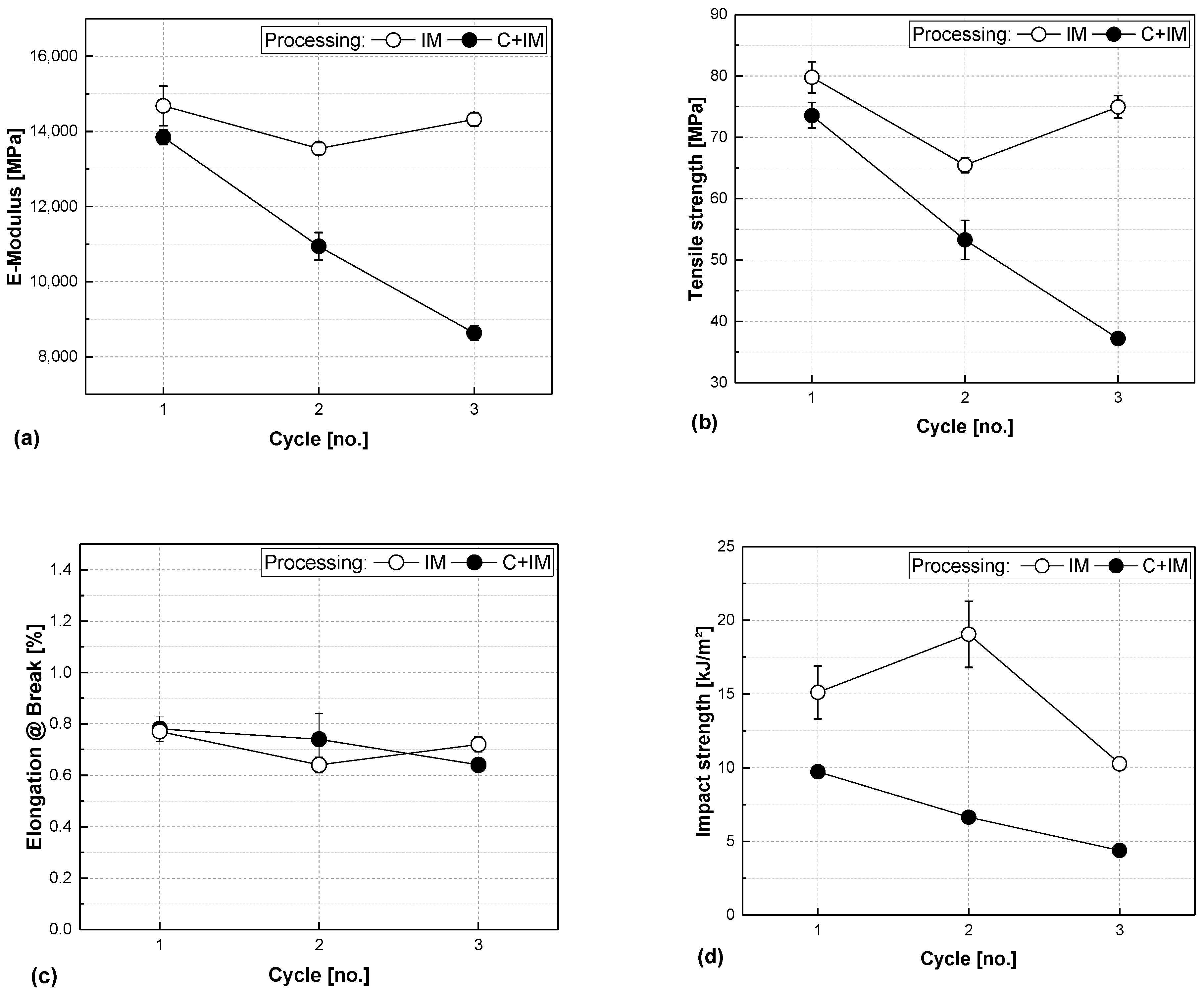
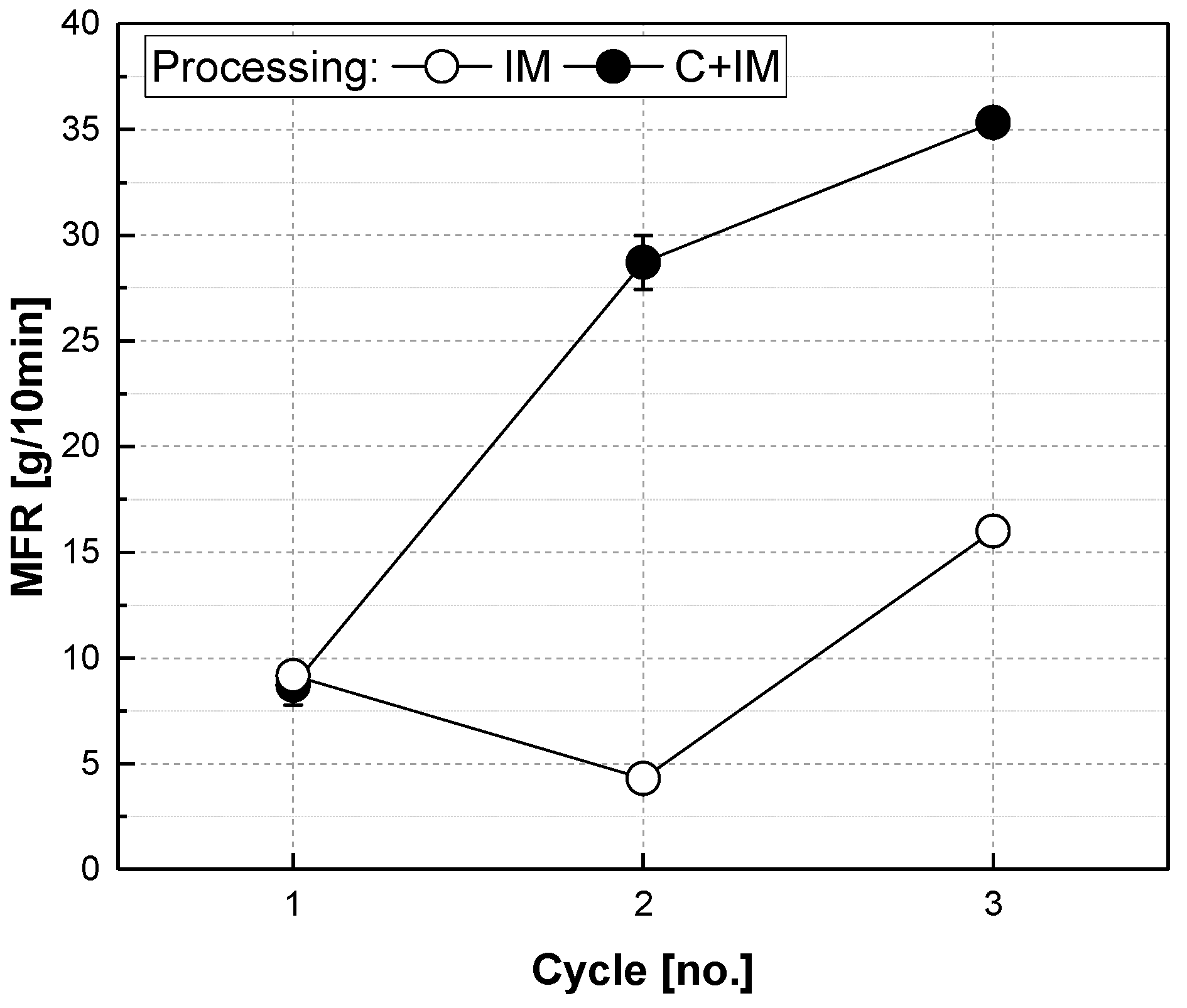
3. Results and Discussion
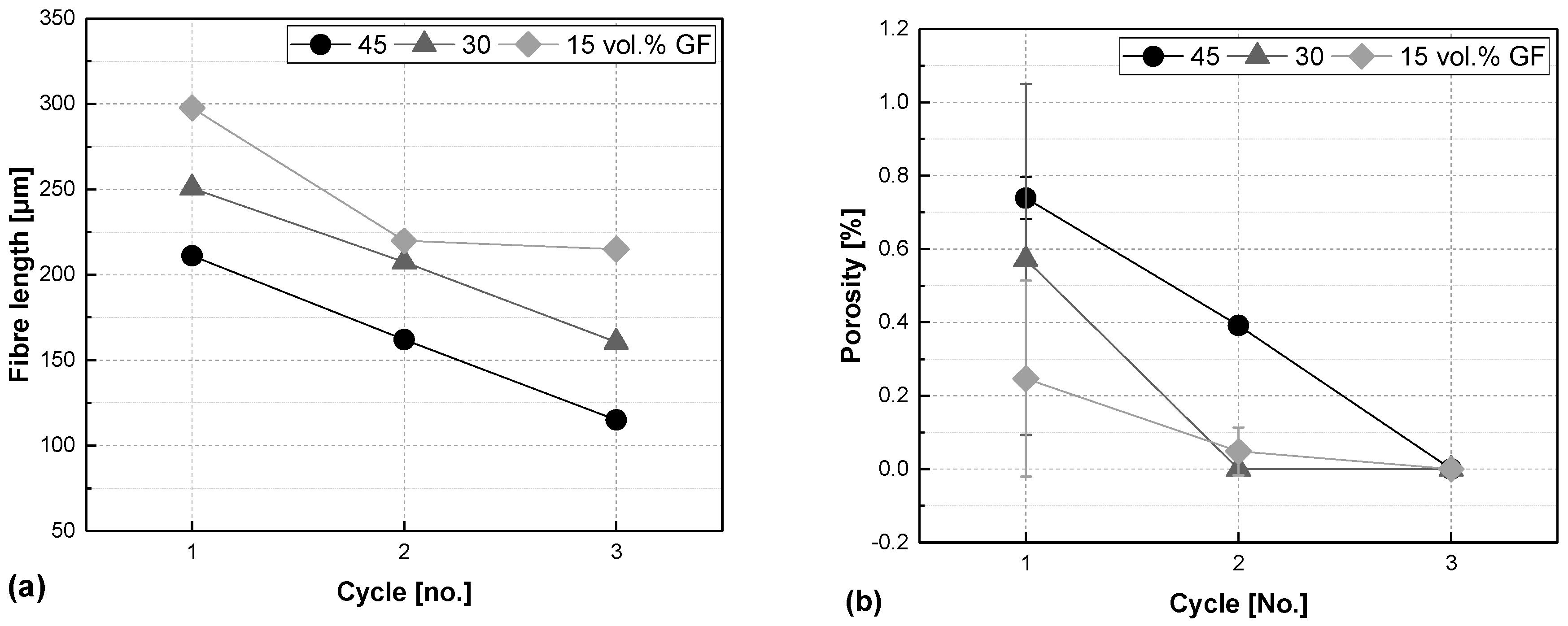
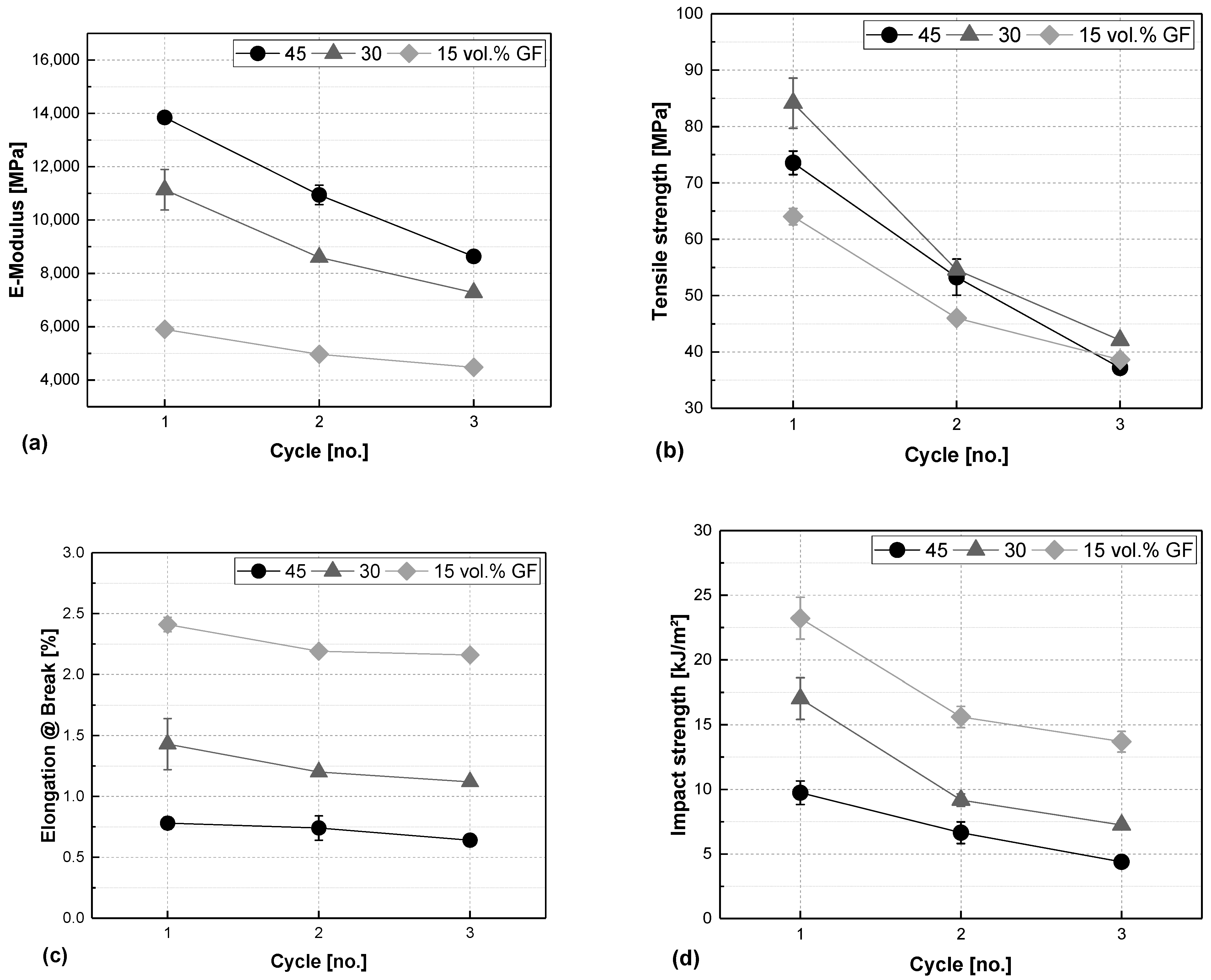
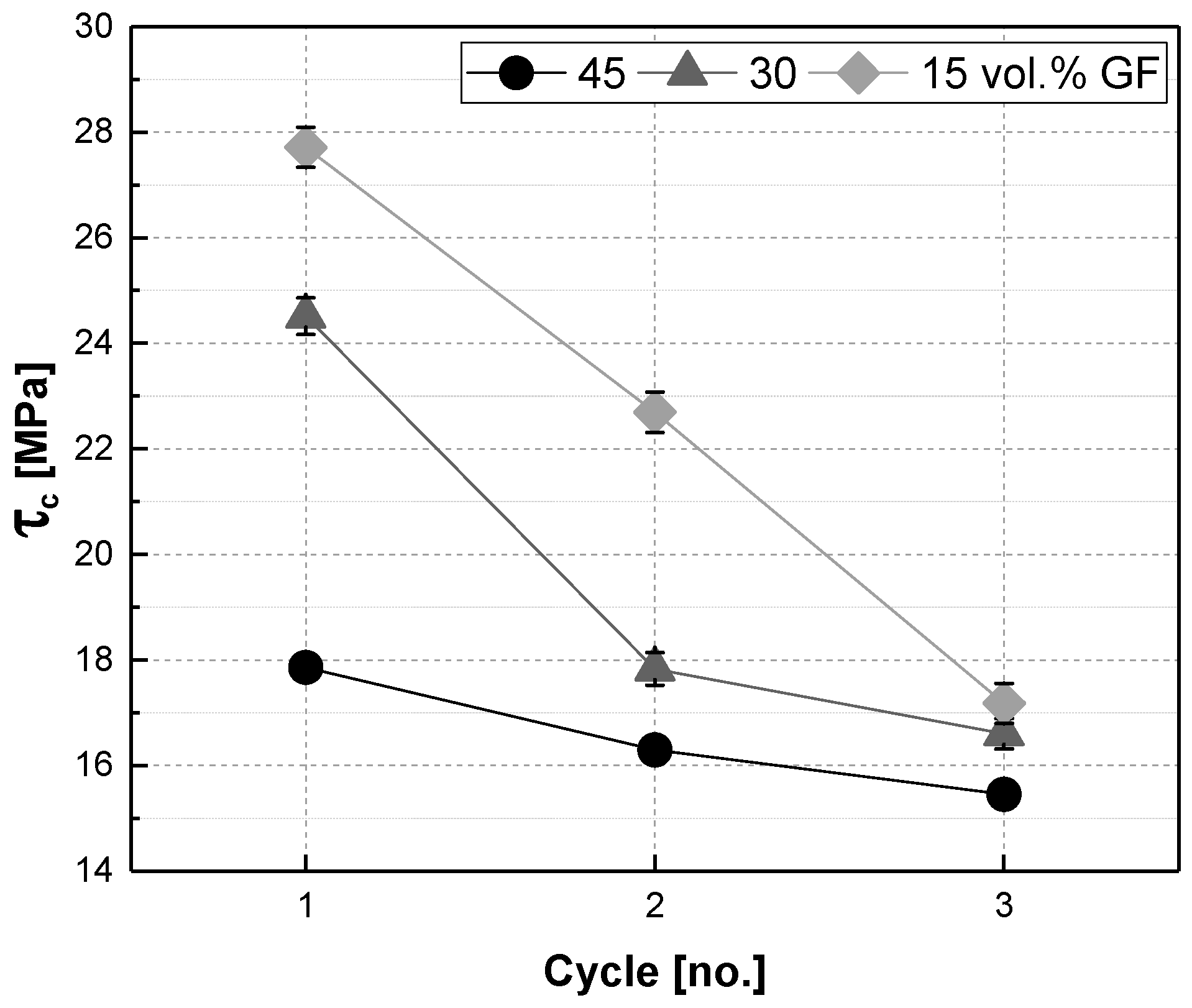
3.1. Comparing Fibre Content
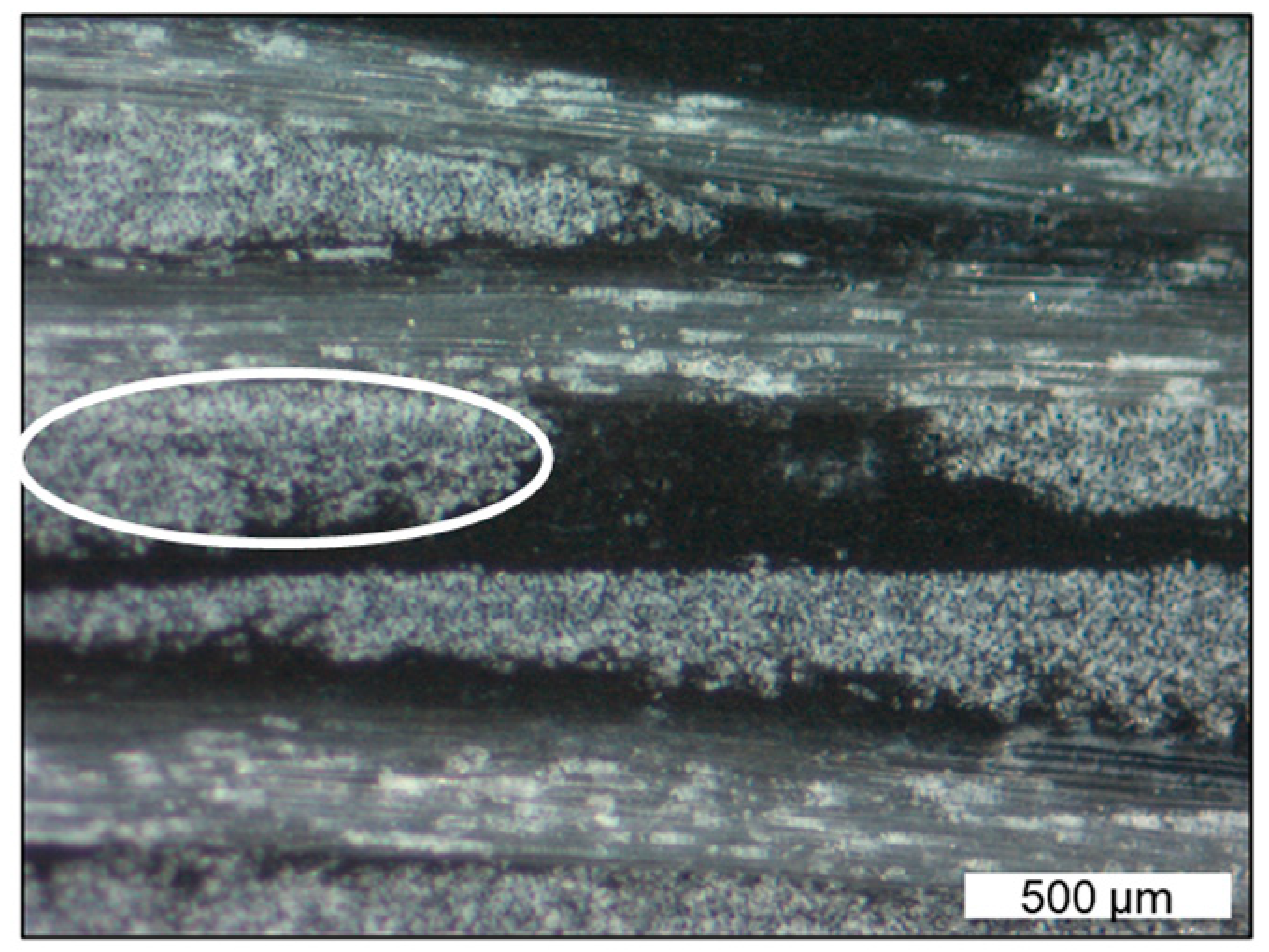
3.2. Comparing Processing Routes
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FRC | Fibre-reinforced composites |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| GF | Glass fibre |
| MFR | Melt flow rate |
| IM | Injection moulding |
| C | Compounding |
| IFSS | Interfacial shear strength |
References
- Scaffaro, R.; Di Bartolo, A.; Dintcheva, N.T. Matrix and Filler Recycling of Carbon and Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatas, R.; Dagreou, S.; Despax-Ferreres, A.; Barasinski, A. Recycling of Fiber Reinforced Composites with a Focus on Thermoplastic Composites. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 5, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.; Jenkins, P.; Yang, L. Glass Fibre Strength—A Review with Relation to Composite Recycling. Fibers 2016, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthos, M. Functional Fillers for Plastics; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; ISBN 978-3-527-31054-8. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/book/10.1002/3527605096 (accessed on 2 September 2025).
- Boria, S.; Scattina, A.; Belingardi, G. Experimental Evaluation of a Fully Recyclable Thermoplastic Composite. Compos. Struct. 2016, 140, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, U.K.; Chawla, K.K. Processing of Fibre Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites. Int. Mater. Rev. 2008, 53, 185–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höftberger, T.; Dietrich, F.; Zitzenbacher, G.; Burgstaller, C. Influence of Fiber Content and Dosing Position on the the Mechanical Properties of Short-Carbon-Fiber Polypropylene Compounds. Polymers 2022, 14, 4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morici, E.; Dintcheva, N.T. Recycling of Thermoset Materials and Thermoset-Based Composites: Challenge and Opportunity. Polymers 2022, 14, 4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feih, S.; Mouritz, A.P.; Case, S.W. Determining the Mechanism Controlling Glass Fibre Strength Loss during Thermal Recycling of Waste Composites. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 76, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigore, M. Methods of Recycling, Properties and Applications of Recycled Thermoplastic Polymers. Recycling 2017, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-W.; Peng, H.-S. Number of Times Recycled and Its Effect on the Recyclability, Fluidity and Tensile Properties of Polypropylene Injection Molded Parts. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikrishnan, S.; Jubinville, D.; Tzoganakis, C.; Mekonnen, T.H. Thermo-Mechanical Degradation of Polypropylene (PP) and Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) Blends Exposed to Simulated Recycling. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 182, 109390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evens, T.; Bex, G.-J.; Yigit, M.; De Keyzer, J.; Desplentere, F.; Van Bael, A. The Influence of Mechanical Recycling on Properties in Injection Molding of Fiber-Reinforced Polypropylene. Int. Polym. Process. 2019, 34, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, E.; Brinkmann, S.; Osswald, T.A.; Rudolph, N. Saechtling Kunststoff Taschenbuch; 31., Ed.; Carl-Hanser-Verlag: München, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pukánszky, B. Particulate Filled Polypropylene Composites. In Polypropylene; Karger-Kocsis, J., Ed.; Polymer Science and Technology Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 2, pp. 574–580. [Google Scholar]
- Etcheverry, M.; Barbosa, S.E. Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Mechanical Properties Enhancement by Adhesion Improvement. Materials 2012, 5, 1084–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durin, A.; De Micheli, P.; Ville, J.; Inceoglu, F.; Valette, R.; Vergnes, B. A Matricial Approach of Fibre Breakage in Twin-Screw Extrusion of Glass Fibres Reinforced Thermoplastics. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2013, 48, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgacs, O.L.; Mason, S.G. Particle Motions in Sheared Suspensions: IX. Spin and Deformation of Threadlike Particles. J. Colloid Sci. 1959, 14, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, J.H.; Abd El-Rahman, A.I.; Kunc, V.; Tucker, C.L. A Model for Fiber Length Attrition in Injection-Molded Long-Fiber Composites. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2013, 51, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Regan, D.; Akay, M. The Distribution of Fibre Lengths in Injection Moulded Polyamide Composite Components. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1996, 56, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inceoglu, F.; Ville, J.; Ghamri, N.; Pradel, J.L.; Durin, A.; Valette, R.; Vergnes, B. Correlation between Processing Conditions and Fiber Breakage during Compounding of Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polyamide. Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L.; Vlug, M.A. Influence of Fibre Length and Concentration on the Properties of Glass Fibre-Reinforced Polypropylene: 1. Tensile and Flexural Modulus. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1996, 27, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douiri, L.; Jdidi, H.; Kordoghli, S.; El Hajj Sleiman, G.; Béreaux, Y. Degradation Indicators in Multiple Recycling Processing Loops of Impact Polypropylene and High Density Polyethylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 219, 110617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam-Daliri, O.; Ghabezi, P.; Steinbach, J.; Flanagan, T.; Finnegan, W.; Mitchell, S.; Harrison, N. Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Material Extrusion Additive Manufactured Parts from Recycled Glass Fibre-Reinforced Polypropylene Composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 241, 110125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtane, M.; Meraghni, F.; Chatzigeorgiou, G.; Harper, L.T.; Pelascini, F. Multiscale Viscoplastic Modeling of Recycled Glass Fiber-Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites: Experimental and Numerical Investigations. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 242, 110087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, P.; Stadlbauer, W.; Burgstaller, C.; Stadler, H.; Fehringer, S.; Haeuserer, F.; Archodoulaki, V.-M. In-House Recycling of Carbon- and Glass Fibre-Reinforced Thermoplastic Composite Laminate Waste into High-Performance Sheet Materials. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 139, 106110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, G.; Simon, H.; Roncato, D.; Martorana, B.; Badini, C. Effect of Recycling on Polypropylene Composites Reinforced with Glass Fibres. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2017, 30, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, A.; Davoli, P.; Rossin, D.; Armanni, C. Effect of Reprocessing on the Fatigue Strength of a Fibreglass Reinforced Polyamide. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedl, B.; Höftberger, T.; Burgstaller, C. Properties of Multiple-Processed Natural Short Fiber Polypropylene and Polylactic Acid Composites: A Comparison. Macromol 2024, 4, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourmaud, A.; Baley, C. Investigations on the Recycling of Hemp and Sisal Fibre Reinforced Polypropylene Composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Long Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene. In Polypropylene; Karger-Kocsis, J., Ed.; Polymer Science and Technology Series; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 2, pp. 407–414. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 3451; Plastics—Determination of Ash. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- ISO 1183; Plastics—Methods for Determining the Density of Non-Cellular Plastics. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- ISO 291; Plastics—Standard Atmospheres for Conditioning and Testing. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Pegoretti, A.; Fabbri, E.; Migliaresi, C.; Pilati, F. Intraply and Interply Hybrid Composites Based on E-glass and Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Woven Fabrics: Tensile and Impact Properties. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulmajeed, A.A.; Närhi, T.O.; Vallittu, P.K.; Lassila, L.V. The Effect of High Fiber Fraction on Some Mechanical Properties of Unidirectional Glass Fiber-Reinforced Composite. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 1133; Plastics—Determination of the Melt Mass-Flow Rate (MFR) and Melt Volume-Flow Rate (MVR) of Thermoplastics. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- ISO 527; Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- ISO 179; Plastics—Determination of Charpy Impact Properties. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Fu, S.-Y.; Lauke, B.; Mäder, E.; Yue, C.-Y.; Hu, X. Tensile Properties of Short-Glass-Fiber- and Short-Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Polypropylene Composites. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2000, 31, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.; Tyson, W.R. Tensile Properties of Fibre-Reinforced Metals: Copper/Tungsten and Copper/Molybdenum. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1965, 13, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekube, B.M.; Purgleitner, B.; Renner, K.; Burgstaller, C. Influence of Screw Configuration and Processing Temperature on the Properties of Short Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgstaller, C. Comparison of Interfacial Shear Strength from Fibre Pull out and Mechanical Testing in Polypropylene Sisal Composites. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 2009, 36, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, B.; Babarinde, V.O.; Abaimov, S.G.; Lomov, S.V.; Akhatov, I. Interface Strength of Glass Fibers in Polypropylene: Dependence on the Cooling Rate and the Degree of Crystallinity. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 1310–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannerfeldt, G.; Törnqvist, R.; Rambert, N.; Boogh, L.; Månson, J.-A.E. Matrix Modification for Improved Reinforcement Effectiveness in Polypropylene/Glass Fibre Composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2001, 8, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Sugahara, A.; Hagihara, H.; Mizukado, J.; Shinzawa, H. Insight into Interfacial Compatibilization of Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Polypropylene (PP) Using Maleic-Anhydride Modified PP Employing Infrared Spectroscopic Imaging. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 199, 108379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikiaris, D.; Matzinos, P.; Larena, A.; Flaris, V.; Panayiotou, C. Use of Silane Agents and Poly (Propylene-g-maleic Anhydride) Copolymer as Adhesion Promoters in Glass Fiber/Polypropylene Composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 81, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, S.; Obermeier, K.; Zier, K.; Krommes, S.; Schemme, M.; Karlinger, P. Analysis of mechanical properties related to fiber length of closed-loop-recycled offcuts of a thermoplastic fiber composites (organo sheets). Materials 2022, 15, 3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achukwu, E.O.; Owen, M.M.; Danladi, A.; Dauda, B.M.; Romli, A.Z.; Ishiaku, U.S.; Akil, H.M. Effect of glass fiber loading and reprocessing cycles on the mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties of isotactic polypropylene composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 |
| Extruder Zones | Intake | Zone 2 | Zone 3 | Zone 4 | Zone 5 | Zone 6 |
| Temperature [°C] | 40 | 190 | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Screw elements | c | c | 5 × 30° | c | c | c |
| 7 × 60° | ||||||
| 4 × 90° | ||||||
| Zone 7 | Zone 8 | Zone 9 | Zone 10 | Die | ||
| 200 | 200 | 190 | 190 | 190 | ||
| 7 × 60° | c | 4 × 60° | c | - | ||
| 6 × 90° | 4 × 90° |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liedl, B.; Höftberger, T.; Zitzenbacher, G.; Burgstaller, C. Repeated Thermomechanical Recycling of Polypropylene-Organosheets to Injection-Moulded Glass-Fibre-Reinforced Composites. Polymers 2025, 17, 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182528
Liedl B, Höftberger T, Zitzenbacher G, Burgstaller C. Repeated Thermomechanical Recycling of Polypropylene-Organosheets to Injection-Moulded Glass-Fibre-Reinforced Composites. Polymers. 2025; 17(18):2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182528
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiedl, Barbara, Thomas Höftberger, Gernot Zitzenbacher, and Christoph Burgstaller. 2025. "Repeated Thermomechanical Recycling of Polypropylene-Organosheets to Injection-Moulded Glass-Fibre-Reinforced Composites" Polymers 17, no. 18: 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182528
APA StyleLiedl, B., Höftberger, T., Zitzenbacher, G., & Burgstaller, C. (2025). Repeated Thermomechanical Recycling of Polypropylene-Organosheets to Injection-Moulded Glass-Fibre-Reinforced Composites. Polymers, 17(18), 2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17182528








