Refining Biodegradability Assessments of Polymers Through Microbial Biomolecule Quantification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Biodegradation Assay Setup and Conditions
2.3. Biodegradation Experiments for PBG
2.4. Biomolecular Quantification
2.5. Protein Quantification
2.6. Lipid Quantification
2.7. Carbohydrate Quantification
2.8. Statistical Analysis
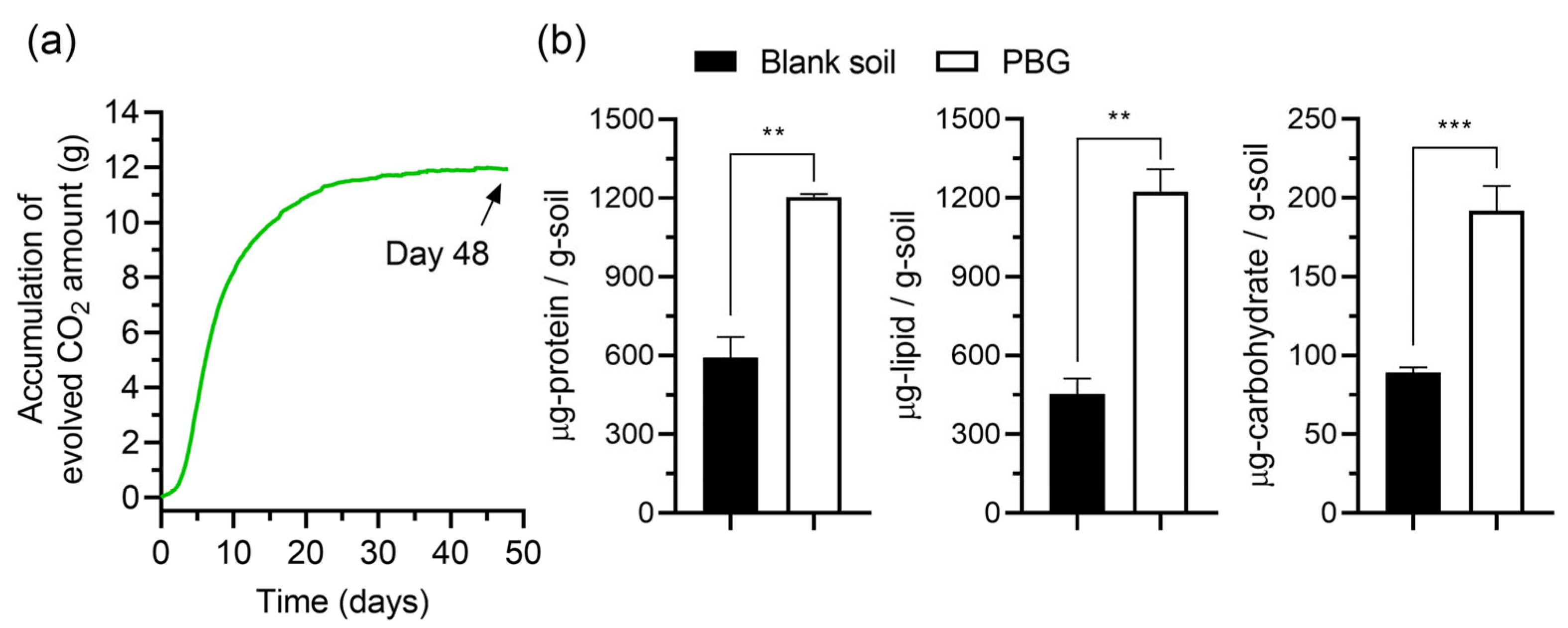
3. Results
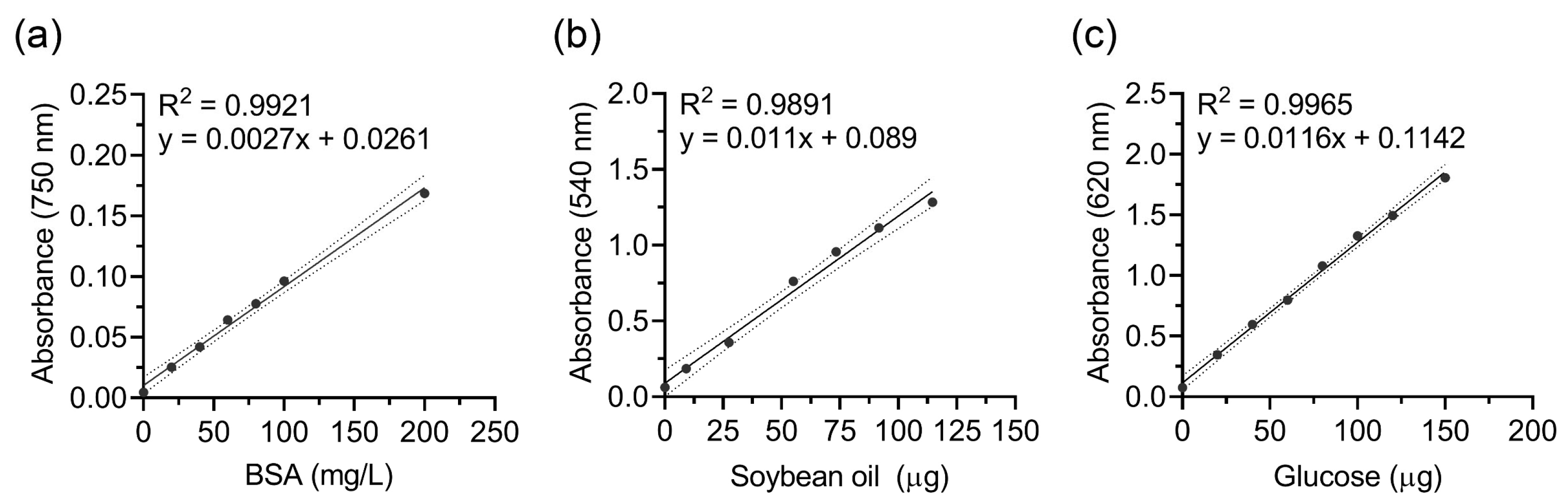
3.1. Optimization of Biochemical Assays for Biomolecules in Soil
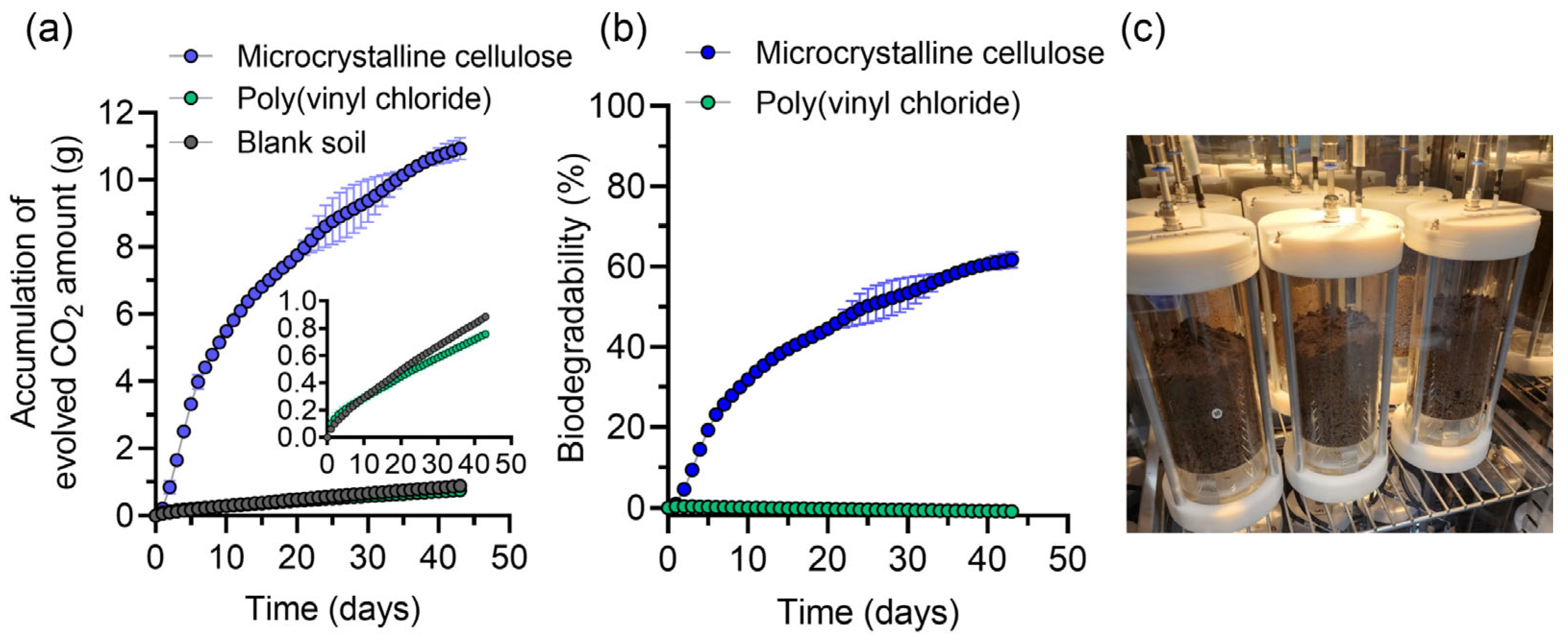
3.2. Biodegradation Experiments
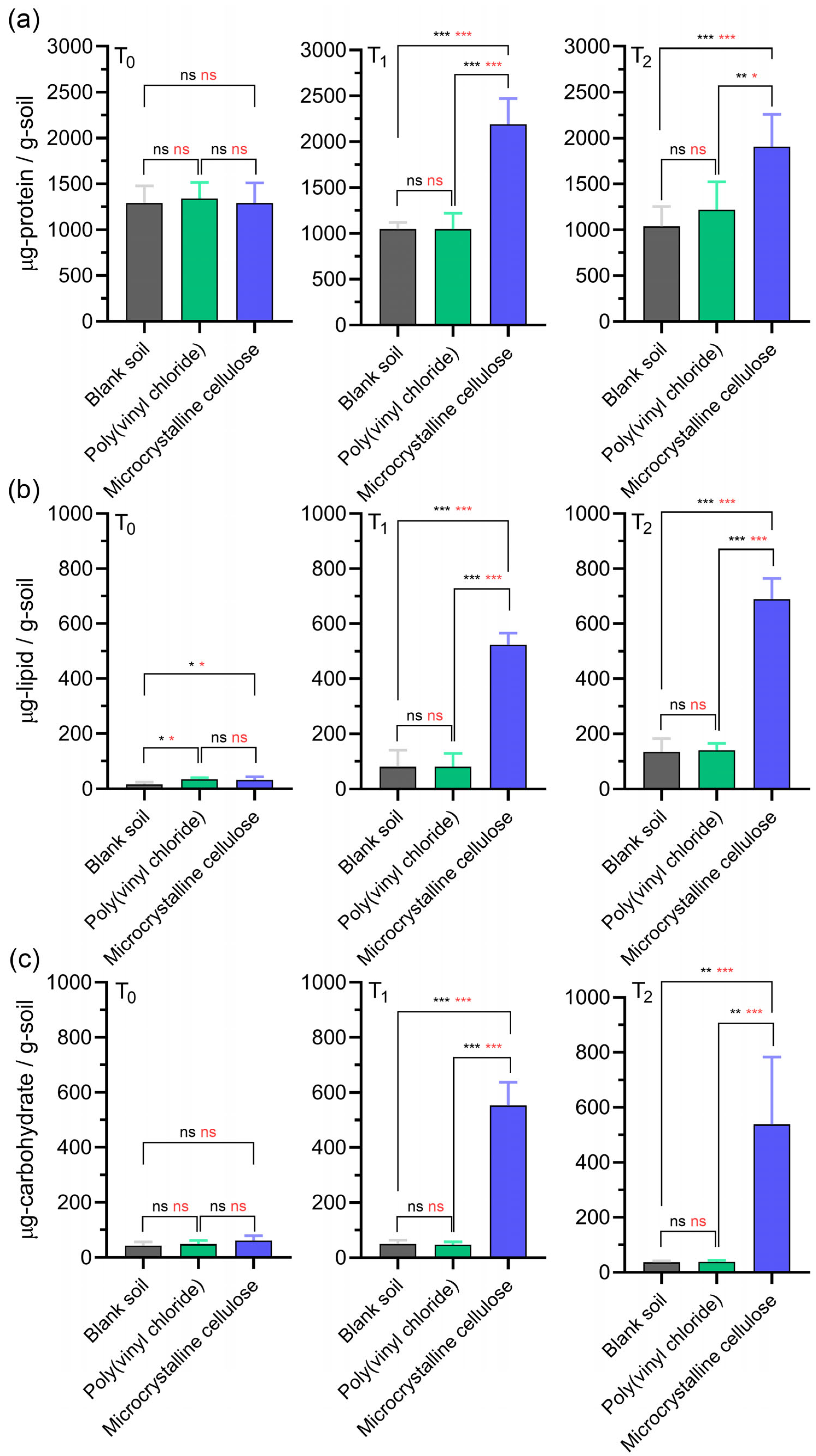
3.3. Quantitative Analysis of Biomolecules in Soil
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lau, W.W.Y.; Shiran, Y.; Bailey, R.M.; Cook, E.; Stuchtey, M.R.; Koskella, J.; Velis, C.A.; Godfrey, L.; Boucher, J.; Murphy, M.B.; et al. Evaluating Scenarios toward Zero Plastic Pollution. Science 2020, 369, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Adyel, T.M.; Iqbal, S.S.; Wu, J.; Miao, L.; Hou, J. Characterization of the dynamic aging and leached dissolved organic carbon from biodegradable and conventional plastics under photooxidation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Global Plastics Outlook: Economic Drivers, Environmental Impacts and Policy Options; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Plastic Pollution Is Growing Relentlessly as Waste Management and Recycling Fall Short. Press Release. 2022. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/environment/plastic-pollution-is-growing-relentlessly-as-waste-management-and-recycling-fall-short.htm (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- OECD. Why Is the OECD Monitoring the Trade of Plastic Waste? 2025. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/environment/plastics/why-is-the-oecd-monitoring-the-trade-of-plastic-waste/ (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Shen, M.; Song, B.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Wen, X.; Tang, W. Are biodegradable plastics a promising solution to solve the global plastic pollution? Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrha, H.; Cabrera, J.; Dai, Y.; Irfan, M.; Toma, A.; Jiao, S.; Liu, X. Bio-based plastics production, impact and end of life: A literature review and content analysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 17556:2019; Plastics—Determination of the Biodegradation of Plastic Materials in Soil under Aerobic Conditions—Method by Analysis of Released Carbon Dioxide. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Microbial and Enzymatic Degradation of Synthetic Plastics. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 580709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, F. The biochemistry and molecular biology of xenobiotic polymer degradation by microorganisms. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 1743–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardisson, G.B.; Tosin, M.; Barbale, M.; Degli-Innocenti, F. Biodegradation of plastics in soil and effects on nitrification activity. A laboratory approach. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briassoulis, D.; Mistriotis, A.; Mortier, N.; Tosin, M. A horizontal test method for biodegradation in soil of bio-based and conventional plastics and lubricants. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E.; Burkowska-But, A.; Tarach, I.; Walczak, M.; Jakubowska, E. Biodegradation of polylactide-based composites with an addition of a compatibilizing agent in different environments. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2020, 147, 104840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richert, A.; Dąbrowska, G.B. Enzymatic degradation and biofilm formation during biodegradation of polylactide and polycaprolactone polymers in various environments. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 176, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.S.; Yan, Z.F.; Chen, X.Q.; Du, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.Z.; Xia, W.; Chen, S.; Wu, J. Accelerated biodegradation of polyethylene terephthalate by Thermobifida fusca cutinase mediated by Stenotrophomonas pavanii. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogovina, S.; Zhorina, L.; Yakhina, A.; Shapagin, A.; Iordanskii, A.; Berlin, A. Hydrolysis, biodegradation and ion sorption in binary biocomposites of chitosan with polyesters: Polylactide and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Polymers 2023, 15, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosin, M.; Barbale, M.; Chinaglia, S.; Degli-Innocenti, F. Disintegration and mineralization of mulch films and leaf litter in soil. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 179, 109309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amobonye, A.; Bhagwat, P.; Singh, S.; Pillai, S. Plastic biodegradation: Frontline microbes and their enzymes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanlioglu, M.; Preziosi, R.; Robson, G.D. Abiotic and biotic environmental degradation of the bioplastic polymer poly(lactic acid): A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 137, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, T.P.; Völker, C.; Kramm, J.; Landfester, K.; Wurm, F.R. Plastics of the future? The impact of biodegradable polymers on the environment and on society. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidurah, S. Methods of analyses for biodegradable polymers: A review. Polymers 2022, 14, 4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumstein, M.T.; Schintlmeister, A.; Nelson, T.F.; Baumgartner, R.; Woebken, D.; Wagner, M.; Kohler, H.E.; McNeill, K.; Sander, M. Biodegradation of synthetic polymers in soils: Tracking carbon into CO2 and microbial biomass. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaas9024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, T.F.; Baumgartner, R.; Jaggi, M.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Battagliarin, G.; Sinkel, C.; Künkel, A.; Kohler, H.-P.E.; McNeill, K.; Sander, M. Biodegradation of poly(butylene succinate) in soil laboratory incubations assessed by stable carbon isotope labelling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Elsner, M.; Leung, A.E.; Wacklin-Knecht, H.; Allgaier, J.; Heiling, M.; Ivleva, N.P. Raman microspectroscopy to trace the incorporation of deuterium from labeled (micro)plastics into microbial cells. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 4440–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, M.; Simpson, M.J. Dissolved organic matter molecular composition controls potential biodegradability. Org. Geochem. 2025, 200, 104924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.N.; Kallem, P.; Mounika, K.V.S.S.N.; Muqeet, A.; Raj, J.C.J.; Aishwarya, C.V.S.; Gupta, R.K.; Polisetti, V.; Mishra, B.; Yadavalli, R.; et al. Review of Microplastic Degradation: Understanding Metagenomic Approaches for Microplastic Degrading Organisms. Polym. Test. 2023, 128, 108223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmile-Gordon, M.A.; Armenise, E.; White, R.P.; Hirsch, P.R.; Goulding, K.W.T. A comparison of two colorimetric assays, based upon Lowry and Bradford techniques, to estimate total protein in soil extracts. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 67, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.F.; Upadhyaya, A. A survey of soils for aggregate stability and glomalin, a glycoprotein produced by hyphae of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Plant Soil 1998, 198, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anschau, A.; Caruso, C.S.; Kuhn, R.C.; Franco, T.T. Validation of the sulfo-phosphovanillin (SPV) method for the determination of lipid content in oleaginous microorganisms. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.S.; Zheng, Y.; VanderGheynst, J.S. Rapid quantitative analysis of lipids using a colorimetric method in a microplate format. Lipids 2011, 46, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandy, A.S.; Erich, M.S.; Porter, G.A. Suitability of the anthrone–sulfuric acid reagent for determining water soluble carbohydrates in soil water extracts. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Ascher, J.; Ceccherini, M.; Landi, L.; Pietramellara, G.; Renella, G. Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnuk, E.; Waśko, A.; Walkiewicz, A.; Bartmiński, P.; Bejger, R.; Mielnik, L.; Bieganowski, A. The effects of humic substances on DNA isolation from soils. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, R. Enzymatic degradation of cellulose in soil: A review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Leyva, M.F.; Beltrán-Arredondo, L.I.; Cervantes-Gámez, R.; Cervantes-Chávez, J.; López-Meyer, M.; Castro-Ochoa, D.; Calderón-Vázquez, C.L.; Castro-Martínez, C. Effect of CMC and MCC as sole carbon sources on cellulase activity and eglS gene expression in three Bacillus subtilis strains isolated from corn stover. BioResources 2017, 12, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Canarini, A.; Fuchslueger, L.; Schnecker, J.; Metze, D.; Nelson, D.B.; Kahmen, A.; Watzka, M.; Pötsch, E.M.; Schaumberger, A.; Bahn, M.; et al. Soil fungi remain active and invest in storage compounds during drought independent of future climate conditions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances in soil: Interfacial behaviour to ecological multifunctionality. Geo-Bio Interfaces 2024, 1, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, O.Y.A.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Kuramae, E.E. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: Ecological function and impact on soil aggregation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.J.; Zhang, C.; Nilsson, A.; Lahtvee, P.-J.; Kerkhoven, E.J.; Nielsen, J. Improving the phenotype predictions of a yeast genome-scale metabolic model by incorporating enzymatic constraints. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picker, K.M.; Hoag, S.W. Characterization of the Thermal Properties of Microcrystalline Cellulose by Modulated Temperature Differential Scanning Calorimetry. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepnov, A.A.; Lopez-Tavera, E.; Klauer, R.; Lincoln, C.L.; Chowreddy, R.R.; Beckham, G.T.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Solomon, K.; Blenner, M.; Vaaje-Kolstad, G. Revisiting the Activity of Two Poly(Vinyl Chloride)- and Polyethylene-Degrading Enzymes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
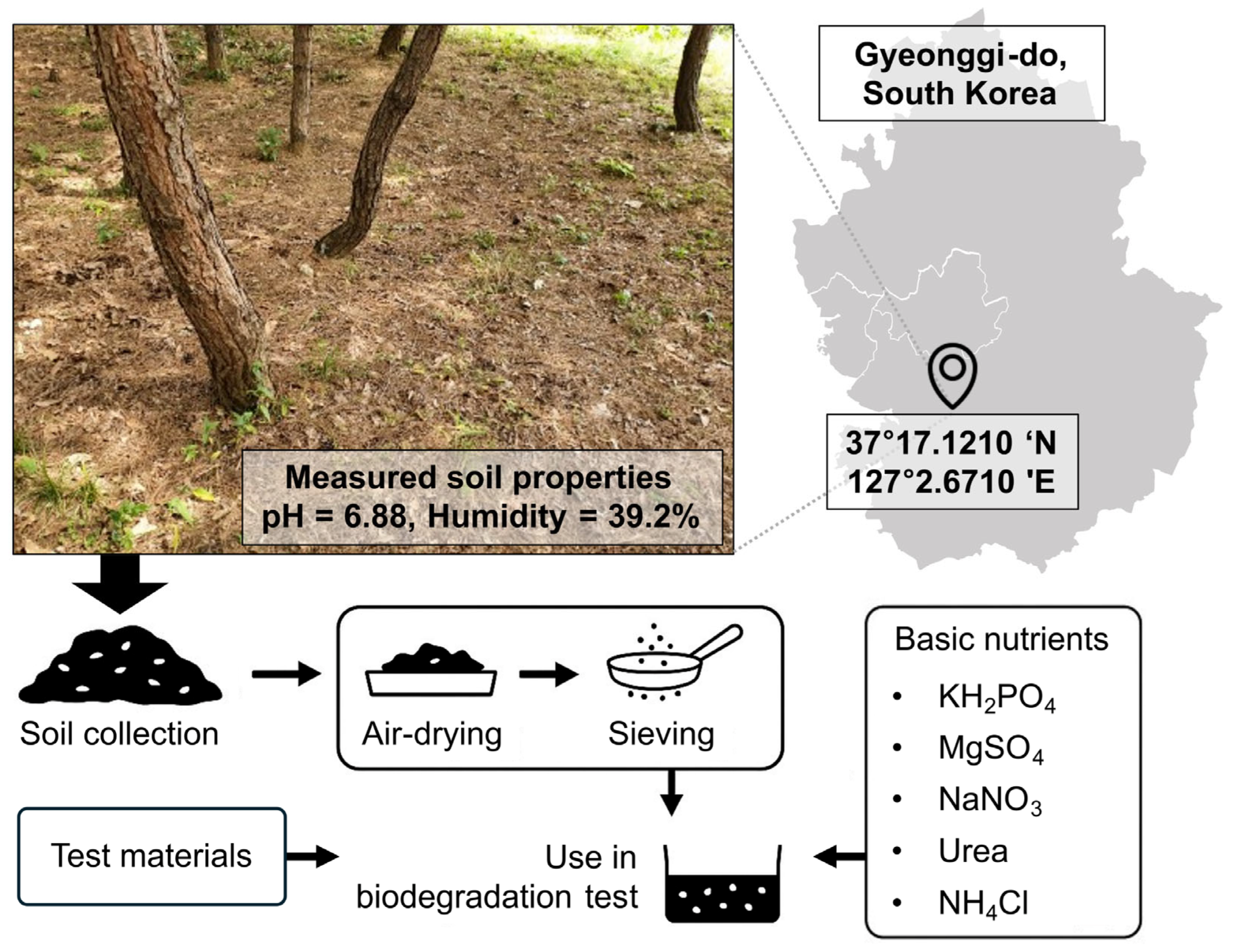
| Constituent | Quantity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Soil | 500 g | Base medium for biodegradation experiments |
| KH2PO4 | 0.1 g | Essential minerals for microbial growth |
| MgSO4 | 0.05 g | Essential minerals for microbial growth |
| NaNO3 | 0.2 g | Nitrogen source for microbial growth |
| Urea | 0.1 g | Additional nitrogen source |
| NH4Cl | 0.2 g | Additional nitrogen source |
| Deionized H2O | 60 mL | Added to achieve 55% soil water content |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, W.Y.; Lee, P.C. Refining Biodegradability Assessments of Polymers Through Microbial Biomolecule Quantification. Polymers 2025, 17, 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172376
Cho WY, Lee PC. Refining Biodegradability Assessments of Polymers Through Microbial Biomolecule Quantification. Polymers. 2025; 17(17):2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172376
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Woo Yeon, and Pyung Cheon Lee. 2025. "Refining Biodegradability Assessments of Polymers Through Microbial Biomolecule Quantification" Polymers 17, no. 17: 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172376
APA StyleCho, W. Y., & Lee, P. C. (2025). Refining Biodegradability Assessments of Polymers Through Microbial Biomolecule Quantification. Polymers, 17(17), 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17172376








