The Effect of the Fresh Latex Ratio on the Composition and Properties of Bio-Coagulated Natural Rubber
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
2.2. Methods
- (1)
- Microbial coagulant liquid culture
- (2)
- Natural rubber preparation
- (3)
- Preparation of natural rubber compound
- (4)
- Preparation of natural rubber vulcanized rubber
3. Testing and Analysis
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
- The gel content of natural rubber was determined by the GB/T 37498-2019 [24] standard. The molecular weight was measured using gel permeation chromatography under the following conditions: sample concentration of 2 mg/mL, tetrahydrofuran as the mobile phase, and polystyrene as the standard reference material.
- (4)
- The Tg of natural rubber was determined using a DSC 214 Polyma differential scanning calorimeter under the following test conditions: nitrogen atmosphere (flow rate of 0.05 L/min), cooling from room temperature to −90 °C, followed by heating to 25 °C at a rate of 10 °C/min.
- (5)
- The vulcanization characteristics of natural rubber compounds under pure gum formulations were determined using a closed-cup rheometer. The testing conditions were as follows: a test temperature of 143 °C, a test duration of 45 min, an oscillation frequency of 1.7 Hz, and an amplitude of ±0.5°.
- (6)
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Physical and Chemical Indexes of Natural Rubber
4.2. Non-Rubber Components of Natural Rubber
4.2.1. Nitrogen and Acetone Extract Content
4.2.2. Metal Ion Content
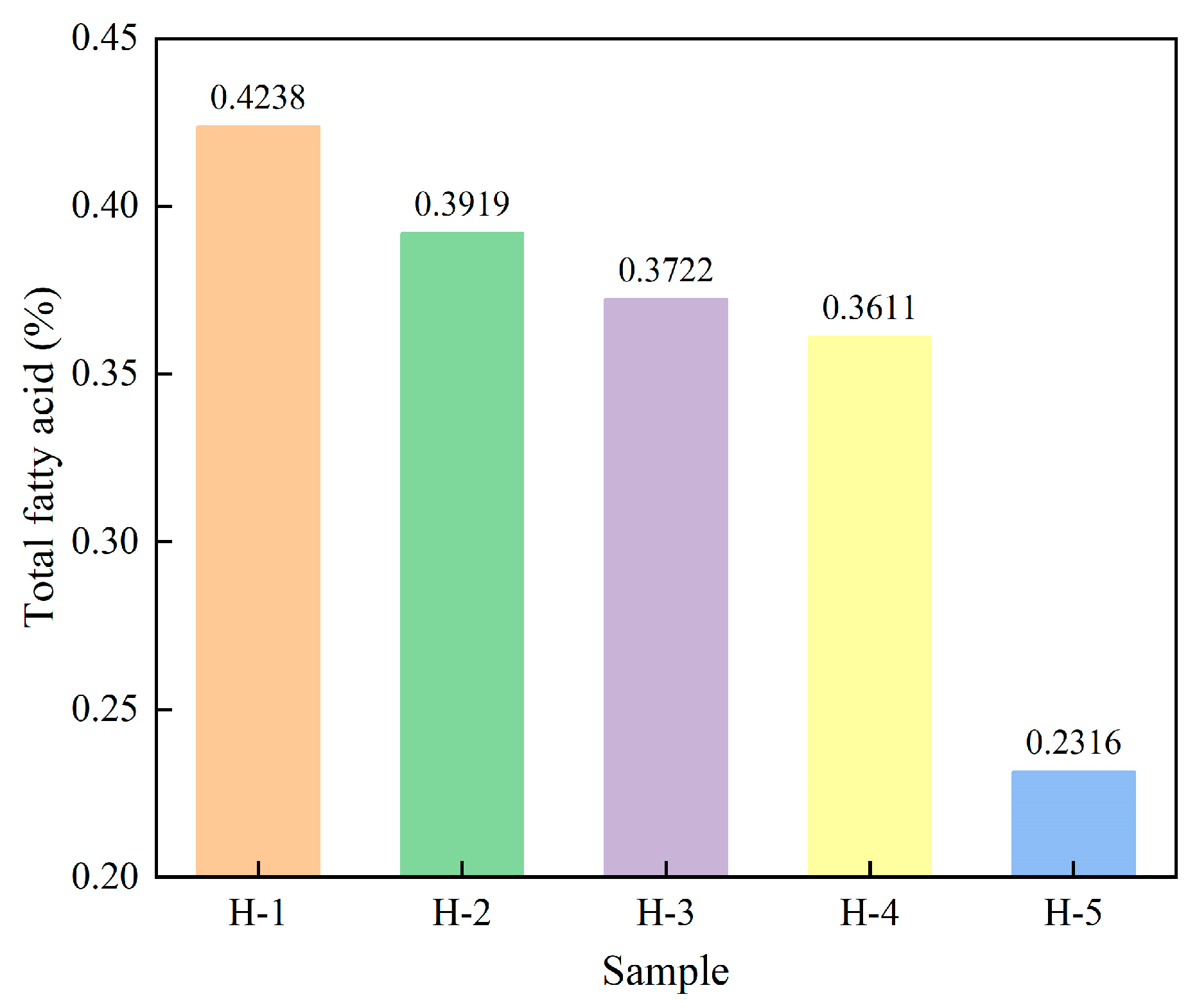
4.2.3. Fatty Acid Content
4.3. Gel Content of Natural Rubber
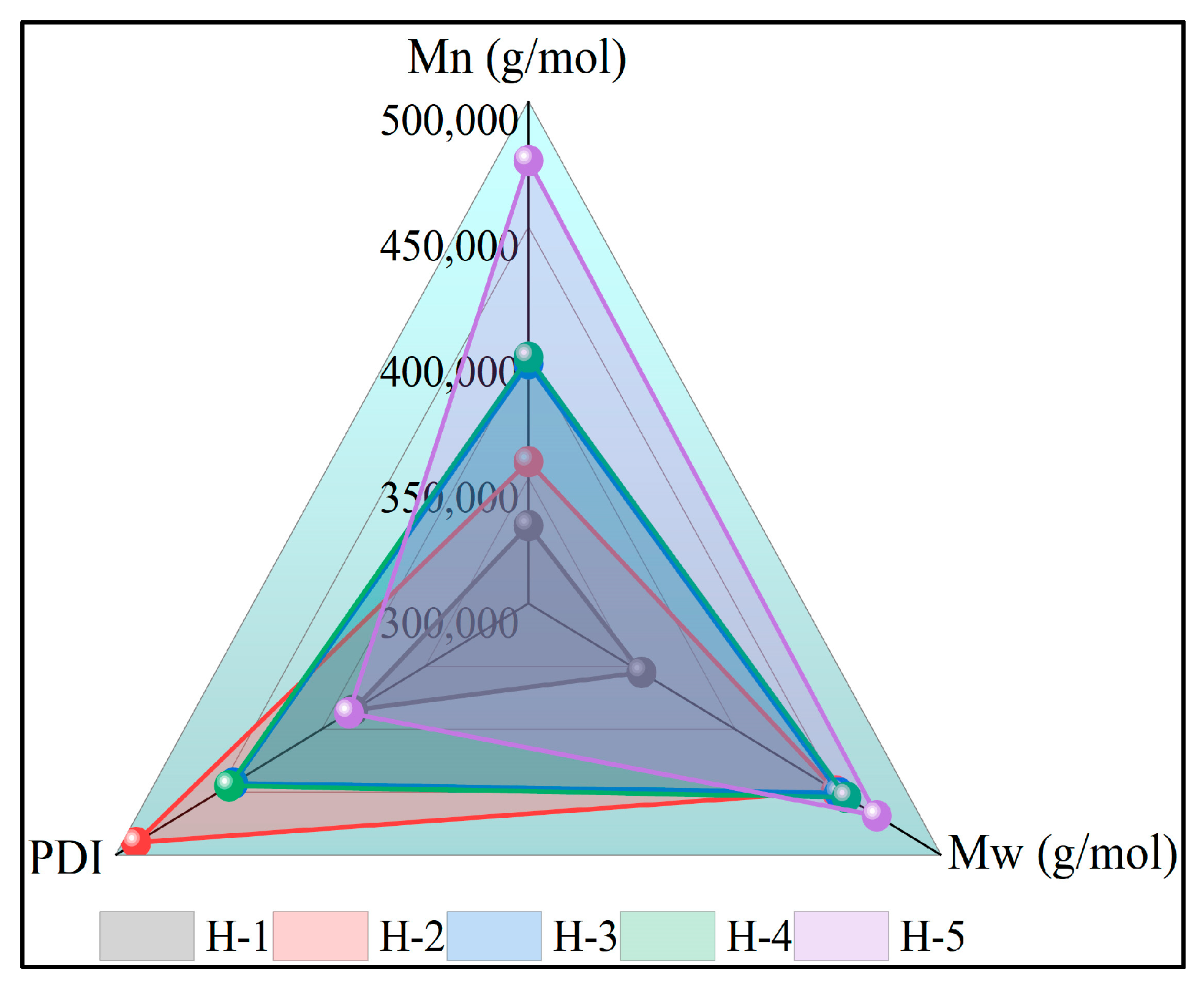
4.4. Molecular Weight Size and Distribution of Natural Rubber
4.5. Glass Transition Temperature of Natural Rubber
4.6. Vulcanization Characteristics of Natural Rubber Compound
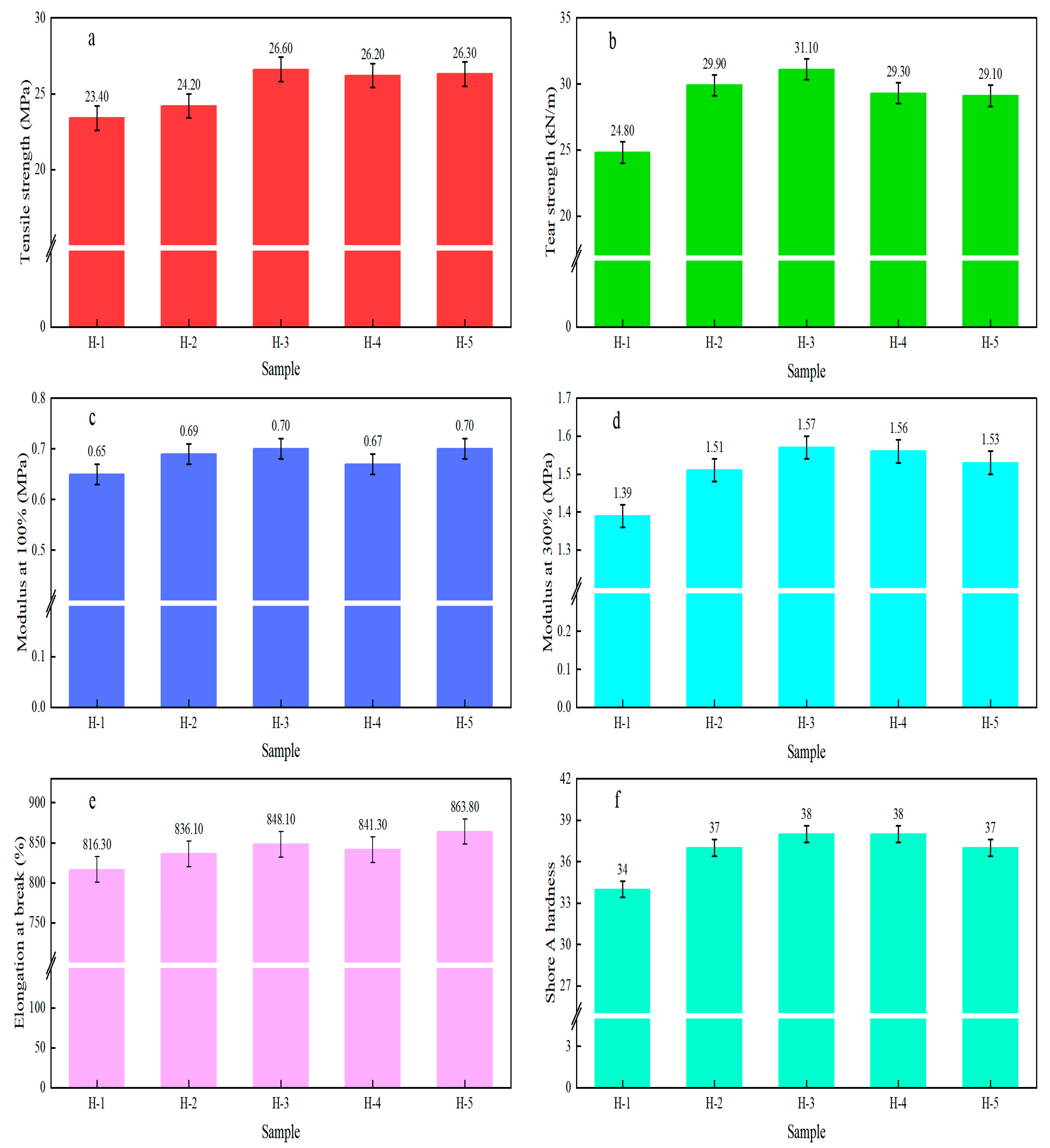
4.7. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Natural Rubber Vulcanized Rubber
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunuwila, P.; Rodrigo, V.H.L.; Goto, N. Sustainability of natural rubber processing can be improved: A case study with crepe rubber manufacturing in Sri Lanka. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 133, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.B.; Luo, Z.R.; Zhang, J.Z.; Kong, N.; Li, J.H.; Zhao, P.F.; Wu, J.Y.; Tan, S.Z.; Tao, J.L. An eco-friendly, high-yield and scalable method for processing concentrated natural rubber latex with superabsorbent polymer beads. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 502, 158013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Zhao, F.C.; Gu, T.T.; Liu, H.; Luo, M.C.; Liao, S.Q. Role of endogenous glucose on natural rubber molecular chains and natural network architecture based on biological action and chelation. Polymer 2020, 202, 122752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongpet, C.; Wisunthorn, S.; Liengprayoon, S.; Vaysse, L.; Bonfils, F.; Nakason, C. Effect of Rubber clone on fatty acid composition and properties of air dried sheet. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 844, 194–197. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; He, Y.T.; Cai, Y.J.; Li, L.; Xing, J.F.; Yang, X.; Ye, D.; Tang, C.R.; Liu, H. Genome-wide identification and functional characterization of phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein family genes in rubber dandelion (Taraxacum kok-saghyz Rodin). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 319, 145448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.M.; Zhang, F.Q.; Gu, F.S.; Zhao, T.Q.; Zhao, Y.F.; Liao, L.S.; Liao, X.X. Influence of Clones on Relationship between Natural Rubber and Size of Rubber Particles in Latex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liengprayoon, S.; Chelbi, K.; Dubascoux, S.; Char, C.; Vaysse, L.; Dubreucq, E.; Beuve, J.S.; Sriroth, K.; Bonfils, F. Mesostructure characterization by asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation of natural rubber samples from different Hevea brasiliensis genotypes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisunthorn, S.; Liengprayoon, S.; Vaysse, L.; Beuve, J.S.; Bonfils, F. SEC-MALS study of dynamic structuring of natural rubber: Comparative study of two Hevea brasiliensis genotypes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.J.; Lu, C.; Li, P.S.; Liu, Z.T. Infrared analysis of different clonal rubber samples. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 1986, 2, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.D.; Yang, C.L.; Lv, M.Z.; Zeng, Z.Q.; Liang, Z.X.; Huang, M.F. Research on properties of natural rubber of different strains. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2013, 41, 5029–5031. [Google Scholar]
- Lehman, N.; Tuljittraporn, A.; Songtipya, L.; Uthaipan, N.; Sengloyluan, K.; Johns, J.; Nakaramontri, Y.; Kalkornsurapranee, E. Influence of Non-Rubber Components on the Properties of Unvulcanized Natural Rubber from Different Clones. Polymers 2022, 14, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 6038-2006; Rubber Test Mixes―Preparation, Mixing and Vulcanization―Equipment and Procedures. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- NY/T 1403-2007; Evaluation Methods for Natural Rubber. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- GB/T 3510-2006; Rubber, Unvulcanized-Determination of Plasticity-Rapid Plastimeter Method. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- GB/T 3517-2014; Rubber, Raw Natural. Determination of Plasticity Retention Index (PRI). National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- GB/T 1232.1-2016; Rubber, Unvulcanized—Determinations Using a Shearing-Disc Viscometer—Part 1: Determination of Mooney Viscosity. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 4498.1-2013; Rubber—Determination of Ash—Part 1: Muffle Furnace Method. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- GB/T 8086-2019; Rubber, Raw Natural—Determination of Dirt Content. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- GB/T 24131-2009; Rubber, Raw—Determination of Volatile Matter Content. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 8088-2008; Rubber, Raw Natural and Rubber Latex, Natural—Determination of Nitrogen Content. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB/T 3516-2006; Rubber—Determination of Solvent Extract. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Q/440803 JGS003-2020; Raw Natural Rubber—Determination of the Content of Fatty Acids—Gas Chromatography. Enterprise Standard of the Agricultural Products Processing Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences: Zhanjiang, China, 2020.
- GB/T 39486-2020; Chemical Reagent—General Rules for Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- GB/T 37498-2019; Rubber, Raw Natural—Determination of the Gel Content of Technically Specified Rubber (TSR). National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- GB/T 528-2009; Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic-Determination of Tensile Stress-Strain Properties. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 529-2008; Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic-Determination of Tear Strength (Trouser, Angle and Crescent Test Pieces). National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Li, J.W.; Yang, R.R.; Ding, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.H.; Dai, T.; Wu, F.; Gui, H.X. Effect of dilution concentration of fresh latex on composition and properties of natural rubber coagulated by enzymes. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2024, 53, 814–817. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, T.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.H.; Ding, L.; Li, J.W.; Geng, H.R.; Song, Y.Z.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, L.G.; Gui, H.X. A study on the preparation of environmentally friendly high-performance natural rubber using the interaction mechanism of alkaline protease and calcium ions. Polymers 2025, 17, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Huang, H.H.; Wang, Y.K.; Li, J.W.; Gui, H.X.; Chen, Y.P. The Influence of Fresh Latex Coagulation on the Parameter Characteristics of the Yeoh Hyperelastic Constitutive Model for Natural Rubber. Polymers 2024, 16, 3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.P. Natural Rubber Processing; Hainan Publishing House: Haikou, China, 2007; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, S.D.; Yang, L.; Zhong, J.P.; Li, L.F.; Wang, Z.F. Contrastive Study on Properties of Acid and Microorganisms Coagulated Natural Rubber during Accelerated Storage. J. Rubber Res. 2018, 21, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payungwong, N.; Liu, H.N.; Wu, J.R.; Nakajima, K.; Ho, C.C.; Sakdapipanich, J. Nanomechanical mapping of green and vulcanized natural rubber latex film by AFM PeakForce QNM: Impact of proteins and lipids contents on film quality. Polymer 2025, 317, 127944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Bharadwaj, Y.K.; Sabharwal, S.; Bhowmick, A.K. Effect of electron beam-cross-linked gels on the rheological properties of raw natural rubber. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2008, 77, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nun-anan, P.; Wisunthorn, S.; Pichaiyut, S.; Vennemann, N.; Nakason, C. Novel approach to determine non-rubber content in Hevea brasiliensis: Influence of clone variation on properties of un-vulcanized natural rubber. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 118, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, K.X.; Fu, R.Z.; Han, D.L.; Li, R.Y.; Wu, Y.F.; Dong, Y.Y.; Liu, J.H.; Zhang, J.C. Effect of none rubber components on relationship between structure and performance of natural rubber. Polym. Bull. 2022, 35, 42–57. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.Y.; Zhu, Y.B.; Ni, H.; Cai, H.N.; Li, L.J.; Xiao, A.F. Isolation, identification of a k-carrageenase-producing bacterium and k-carrageenase characterization. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2015, 55, 140–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.C.; Guan, J.; Bai, W.N.; Gu, T.T.; Liu, H.; Liao, S.Q. Role of Divalent Metal Ions on the Basic Properties and Molecular Chains of Natural Rubber. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 452, 022057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. Different Strains and Different Years Rubber Latex and Raw Rubber Performance from the Research; Hainan University: Haikou, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, D.B.; Wang, B.B.; Lin, H.T.; Zhang, F.Q.; Li, G.R.; Liao, J.H.; Liao, L.S. Effect of coagulation method on fatty acid content and properties of natural rubber. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 40, 108–117. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Q.L.; Wang, X.N.; Liu, S.; Cui, J.Y.; Xin, Z.X.; Wang, H.Z.; Ding, S.Q. Effect of alkaline protease content on the structure and properties of natural rubber. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimpaiboon, A.; Amnuaypornsri, S.; Sakdapipanich, J. Influence of gel content on the physical properties of unfilled and carbon black filled natural rubber vulcanizates. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Huang, G.S.; Li, S.Q.; Luo, M.C.; Liu, H.; Fu, X.; Qu, W.; Xie, Z.T.; Wu, J.R. Research on architecture and composition of natural network in natural rubber. Polymer 2018, 154, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiani, D.; Malmonge, A.; Soares, G.; Mattoso, H.C. Studies on thermal–oxidative degradation behaviours of raw natural rubber: PRI and thermogravimetry analysis. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2013, 42, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Guo, T.Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, J.H.; Dong, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.C. Rational Rubber Extraction and Simultaneous Determination of Rubber Content and Molecular Weight Distribution in Taraxacum kok-saghyz Rodin by Size-Exclusion Chromatography. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, H.T.; Kawahara, S. Critical Condition of Nanostructured Magnesium Oxide for Accelerated Sulfur Vulcanization of Natural Rubber. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 3279–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovuttikulrangsie, S.; Sakdapipanich, T.J. The molecular weight (MW) and molecular weight distribution (MWD) of NR from different age and clone Hevea trees. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2005, 27, 337. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.N.; Liu, H.C.; Wang, Q.F.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.P. Studies on vulcanization characterizations and mechanical properties of natural rubber coagulated by enzymes. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2016, 16, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.J. Analysis and Testing of Natural Rubber; China Agricultural University Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.J.; Cen, Y.W.; Liang, X.M.; Chen, W.B.; Liu, H.C.; Li, Y.Z.; Gui, H.X.; Gao, T.M. Effect of enzymolytic product on the curing characteristics and physicomechanical properties of natural rubber. China Synth. Rubber Ind. 2023, 46, 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.D.; Chen, J.; Li, L.F.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhong, J.P.; Yang, L. Investigation Of The Vulcanization Characteristics Of Natural Rubber Coagulated By Microorganisms. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2017, 90, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Huang, M.F.; Liao, J.H.; Li, P.W.; Gao, T.M. The effects of Hanging Microbe Coagulation Natural Rubber on Molecular Structures and Mechanical Properties. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 581, 715–718. [Google Scholar]
- Junkong, P.; Morimoto, R.; Miyaji, K.; Tohsan, A.; Sakaki, Y.; Ikeda, Y. Effect of fatty acids on the accelerated sulfur vulcanization of rubber by active zinc/carboxylate complexes. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farida, E.; Bukit, N.; Ginting, E.; Buki, B. The effect of carbon black composition in natural rubber compound. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2019, 16, 100566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Wang, L.; Huang, J.N.; Liu, C.W.; Peng, W.L.; Xiao, H.T.; Li, S.L. Mechanical Properties and Mullins Effect in Natural Rubber Reinforced by Grafted Carbon Black. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2019, 2019, 4523696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Variety | Ratio | Coagulation Method | Enzyme Amount (%, w/w) | Microbial Amount (%, w/w) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-1 | 73397 | 0 | Acid coagulation | 0 | 0 |
| H-2 | 73397 | 0 | Enzyme-assisted microbial coagulation | 0.05 | 10 |
| H-3 | 107:72059:73397 | 1:1:3 | Enzyme-assisted microbial coagulation | 0.05 | 10 |
| H-4 | 107:72059:73397 | 1:1:2 | Enzyme-assisted microbial coagulation | 0.05 | 10 |
| H-5 | 107:72059:73397 | 1:1:1 | Enzyme-assisted microbial coagulation | 0.05 | 10 |
| Formulation | Raw Rubber | Stearic Acid | Zinc Oxide | Accelerator M | Sulphur |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass, g | 100 | 0.5 | 6.0 | 0.5 | 3.5 |
| Formulation | Raw Rubber | Zinc Oxide | Sulfur | Stearic Acid | Carbon Black | TBBS 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass, g | 100 | 5.0 | 2.25 | 2.0 | 35.00 | 0.70 |
| Sample | Ash Content, % | Volatile Matter Content, % | Dirt Content, % | P0 | PRI, % | ML(1+4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-1 | 0.41 ± 0.02 | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 0.026 ± 0.004 | 39.73 ± 0.61 | 83.70 ± 0.75 | 81.67 ± 0.58 |
| H-2 | 0.45 ± 0.03 | 0.35 ± 0.03 | 0.025 ± 0.003 | 45.43 ± 0.65 | 77.20 ± 0.82 | 95.00 ± 1.00 |
| H-3 | 0.43 ± 0.02 | 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.025 ± 0.005 | 44.97 ± 0.31 | 77.37 ± 0.4 | 92.00 ± 0.00 |
| H-4 | 0.42 ± 0.04 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 0.027 ± 0.005 | 46.40 ± 0.53 | 78.50 ± 0.89 | 93.67 ± 0.58 |
| H-5 | 0.40 ± 0.03 | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.027 ± 0.006 | 46.30 ± 0.36 | 82.10 ± 0.46 | 92.67 ± 1.53 |
| Sample | ML/dN·m | MH/dN·m | ΔM/dN·m | t10/min | t90/min | CRI/s−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-1 | 0.68 | 5.61 | 4.93 | 1.72 | 19.13 | 0.17 |
| H-2 | 0.75 | 6.52 | 5.77 | 1.35 | 12.82 | 0.11 |
| H-3 | 0.73 | 6.94 | 6.21 | 1.28 | 12.53 | 0.11 |
| H-4 | 0.7 | 6.63 | 5.93 | 1.27 | 12.7 | 0.11 |
| H-5 | 0.56 | 6.61 | 6.05 | 1.4 | 13.18 | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Huang, H.; Ding, L.; Dai, T.; Geng, H.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, L.; Wu, F.; Gui, H. The Effect of the Fresh Latex Ratio on the Composition and Properties of Bio-Coagulated Natural Rubber. Polymers 2025, 17, 2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162211
Li J, Huang H, Ding L, Dai T, Geng H, Zhao T, Zhao L, Wu F, Gui H. The Effect of the Fresh Latex Ratio on the Composition and Properties of Bio-Coagulated Natural Rubber. Polymers. 2025; 17(16):2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162211
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jianwei, Honghai Huang, Li Ding, Tuo Dai, Haoran Geng, Tao Zhao, Liguang Zhao, Fan Wu, and Hongxing Gui. 2025. "The Effect of the Fresh Latex Ratio on the Composition and Properties of Bio-Coagulated Natural Rubber" Polymers 17, no. 16: 2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162211
APA StyleLi, J., Huang, H., Ding, L., Dai, T., Geng, H., Zhao, T., Zhao, L., Wu, F., & Gui, H. (2025). The Effect of the Fresh Latex Ratio on the Composition and Properties of Bio-Coagulated Natural Rubber. Polymers, 17(16), 2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162211





