1. Introduction
Polyethylene (PE) pipes are widely used in urban lifeline infrastructure due to their excellent corrosion resistance, high flexibility, and ease of maintenance. However, with the extensive installation and long-term use of PE pipes, related safety issues have become increasingly prominent [
1], highlighting the need for accurate material models to characterize their properties in simulation and evaluation processes.
PE is a material with high molecular weight and a complex network structure, and its stress–strain relationship is closely related to its molecular structure, elemental composition, and crosslinking density of molecular chains [
2,
3,
4,
5]. Over years of development, two main types of hyperelastic constitutive models have emerged: phenomenological theories based on continuum mechanics and statistical mechanical theories based on molecular structure and conformational entropy changes [
6]. All phenomenological theories lack direct physical connections with deformation mechanisms. In contrast, statistical models, which consider materials at the molecular level, can better describe phase transitions. There are two types of statistical constitutive models: those based on Gaussian chain statistics and those using non-Gaussian statistics [
7]. Kuhn, based on the assumptions of Gaussian chains and affine deformation, proposed the Affine model. Among the widely applied models is the four-chain model proposed by Flory, a Nobel laureate and renowned polymer physical chemist. James developed the Phantom model to study the elastic deformation of polymers, while Ronce and Allegra proposed the Constrained Junction model [
8,
9,
10,
11]. One of the most significant models in the past three decades is the eight-chain model, introduced in 1993 by Professors Arruda and Boyce [
12]. This model assumes that macromolecules (also known as chain molecules) are on average located along the diagonal of the unit cell in the principal stretch space. For phenomenological models, materials are generally treated as isotropic, and the strain energy density function is expressed using three strain invariants. Currently, several models are widely used, including: the Neo-Hookean model, Mooney model, Mooney–Rivlin model, Valanis–Landel (VL) model, Ogden model, Yeoh model, Gent model, and Mansouri–Darijani model [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20]. To date, the development of constitutive models related to polymer elasticity is relatively mature, though the derivational relationships between models remain complex.
In addition to the elastic properties, PE typically exhibits viscoelastic and yield-related behaviors. Regarding viscoelasticity, the modeling has evolved from the early Maxwell model and Kelvin (Kelvin-Voigt) model to three-element and four-element models, and further to the generalized Maxwell and generalized Kelvin models. These models have become well-developed, with many now directly embedded in commercial finite-element software packages. In recent years, to further advance this field, many researchers have introduced mechanical elements involving fractional derivatives to replace traditional dashpots, leading to the development of fractional viscoelastic models [
21,
22]. Among integral-type constitutive models, a representative example is the Schapery nonlinear viscoelastic model [
23], along with a series of specialized models subsequently developed to address specific problems based on it [
24]. For viscoplastic constitutive models, Bergstrom et al. [
25] developed a hybrid model that incorporates features from the Hasan–Boyce model, Arruda–Boyce model, and the Bergstrom–Boyce model within a plasticity framework. Related ratcheting effects have been described by Drozdov and Christiansen [
26], as well as Hassan et al. [
27]. As for viscoelastic–viscoplastic constitutive models, in order to simultaneously account for the viscoelastic and viscoplastic deformation of polymer materials under cyclic loading, researchers such as Schapery [
28], Drozdov [
29], Frank and Brockman [
30], Khan and Zhang [
31], and Kim and Muliana [
32] have developed constitutive models based on experimental studies to describe the creep and relaxation behavior of polymers and polymer-based composites. For elastoviscoplastic models, many studies have adopted phenomenological frameworks to describe the mechanical behavior of semi-crystalline thermoplastics. Le [
33], Nikolov and Doghri [
34,
35], and Dommelen et al. [
36] proposed physical inelastic models under finite strain conditions to investigate the large deformation behavior of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) during monotonic loading and unloading.
The rheological model for semi-crystalline thermoplastics (such as PE) was first proposed by Boyce et al. [
37], who described the deformation mechanism using a network resistance approach, capturing polymer-chain sliding and stretching as deformation modes that act in parallel with intermolecular resistance to account for plasticity. Subsequently, based on micromechanical modeling, researchers such as Ahzi et al. [
38], Makradi et al. [
39], Makki et al. [
40,
41], Ayoub et al. [
42], Liang [
43], Zhu [
44], and PHao [
45] further refined the resistance between molecular chains and the resistance between molecular networks, incorporating the complex micromechanical behavior of the amorphous and crystalline phases. The current rheological model has broken through the limitations of traditional models and can accurately predict the stress–strain behavior of polymer materials. However, research on material aging degradation has long been lacking. From the perspective of aging and degradation, the long-term time-dependent aging characteristics of polymers are difficult to reflect in the aforementioned models. Some researchers have considered the effects of aging on constitutive behavior, but such studies remain limited and relatively superficial. For instance, Belbachir et al. [
46] incorporated the effects of ultraviolet aging into a physical elastic–viscoplastic model to capture the mechanical degradation behavior of PLA. Ayoub et al. [
47] employed a physical viscoelastic–viscoplastic approach to simulate the mechanical and fracture responses of semi-crystalline low-density polyethylene films under accelerated UV aging.
Overall, this paper proposes a viscoelastic–viscoplastic rheological constitutive model based on thermal-oxidative aging parameters. This model integrates rheological theory and continuum mechanics theory, while accounting for the accelerated degradation process of PE gas pipelines under thermal-oxidative aging. It incorporates crystallinity data obtained from DSC and carbonyl indices measured by FTIR under different aging conditions. This approach provides a novel methodology for constructing constitutive models considering aging degradation.
3. Experiment
Two grades of PE pipes (PE80 and PE100) for thermal-oxidative aging tests were provided by Nansu Plastic Products (Shenzhen, China) Co., Ltd.
Table 1 lists the basic material properties of the two PE pipes under unaged conditions. In this paper, the ratio of pipe diameter to wall thickness, namely the Standard Dimension Ratio (SDR), was selected as 11. Both PE pipe materials were added with 0.1% by weight of Irganox 1010 and 0.1% of Irgafos 168 antioxidants and stabilizers. Additionally, the PE80 material contains 5% by weight of carbon black. For specific FTIR and DSC test results and procedures, please refer to reference [
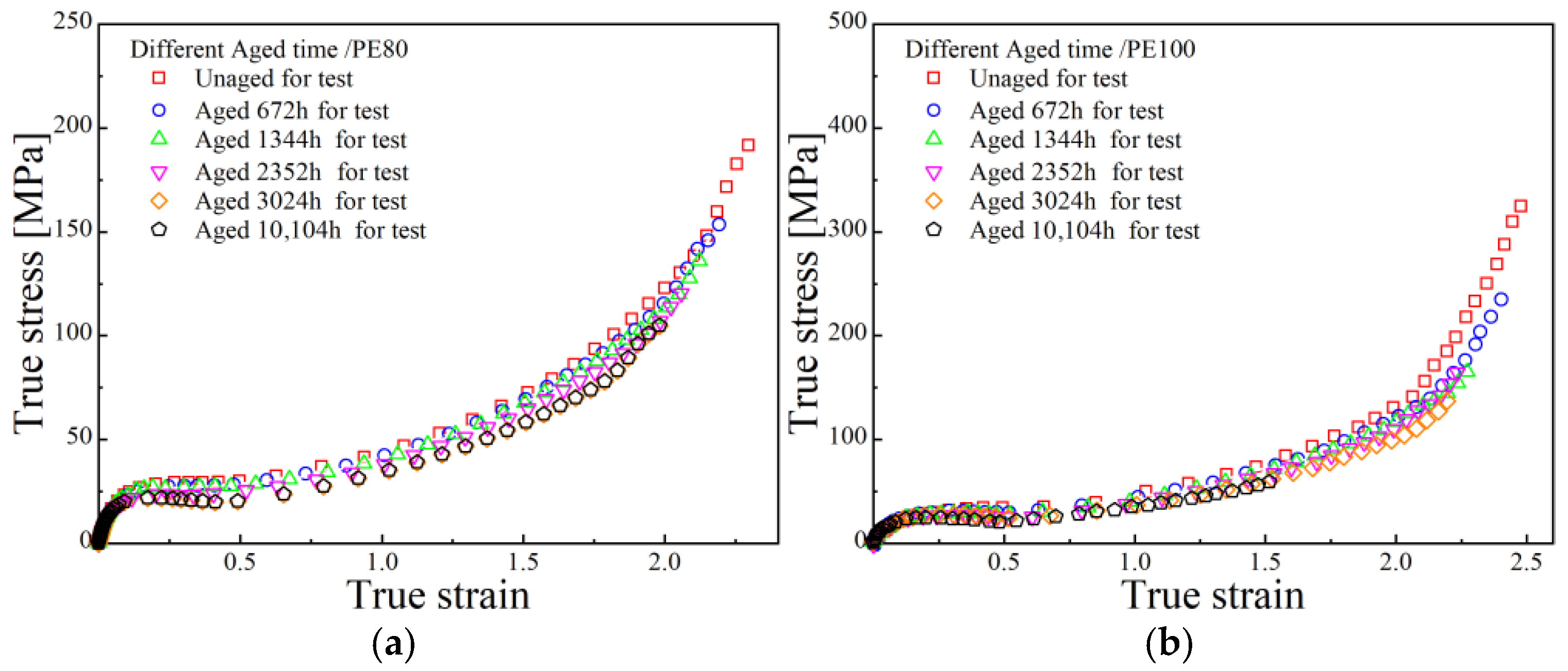
55]; the authors of the paper only carried out tensile tests in this paper and used relevant test data to construct a numerical model.
To investigate the thermo-oxidative aging of PE pipes under accelerated conditions, aging tests were conducted using a specialized aging device [
55]. Notably, both the external and internal surfaces of the PE pipes were exposed to air. The pipes were placed in an oven with adjustable temperature control to 353 K. For precise control of internal pressure in the PE pipes, a custom control program was developed to maintain pressure within 0.01 MPa of the target value (0.4 ± 0.01 MPa). Through coordinated operation of the pressure sensors and solenoid valves, a stable pipe pressure was achieved, with the maximum adjustable pressure range set at 1.0 MPa. Post-aging characterization involved uniaxial tensile tests, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The monotonic tensile tests were conducted using an electronic universal testing machine (MTS CMT4000) at 23 ± 2 °C. Standard dumbbell-shaped pipe specimens were stretched at a rate of 50 mm/min in accordance with ISO 6259-3 [
56]. These dumbbell-shaped samples were machined from intact pipe specimens using a CNC lathe.
Antioxidant capacity testing was performed on samples using a DSC 200F3 differential scanning calorimeter, with measurements including oxidation onset temperature (OOT) and oxidation induction temperature (OIT). To determine the OOT, samples were heated continuously from 25 °C to 300 °C at 20 °C/min in a pure oxygen atmosphere until reaching the oxidation onset temperature [
57]. The OOT value was calculated based on a 0.2 mW baseline shift [
58]. For OIT measurement according to ISO 11357-6 [
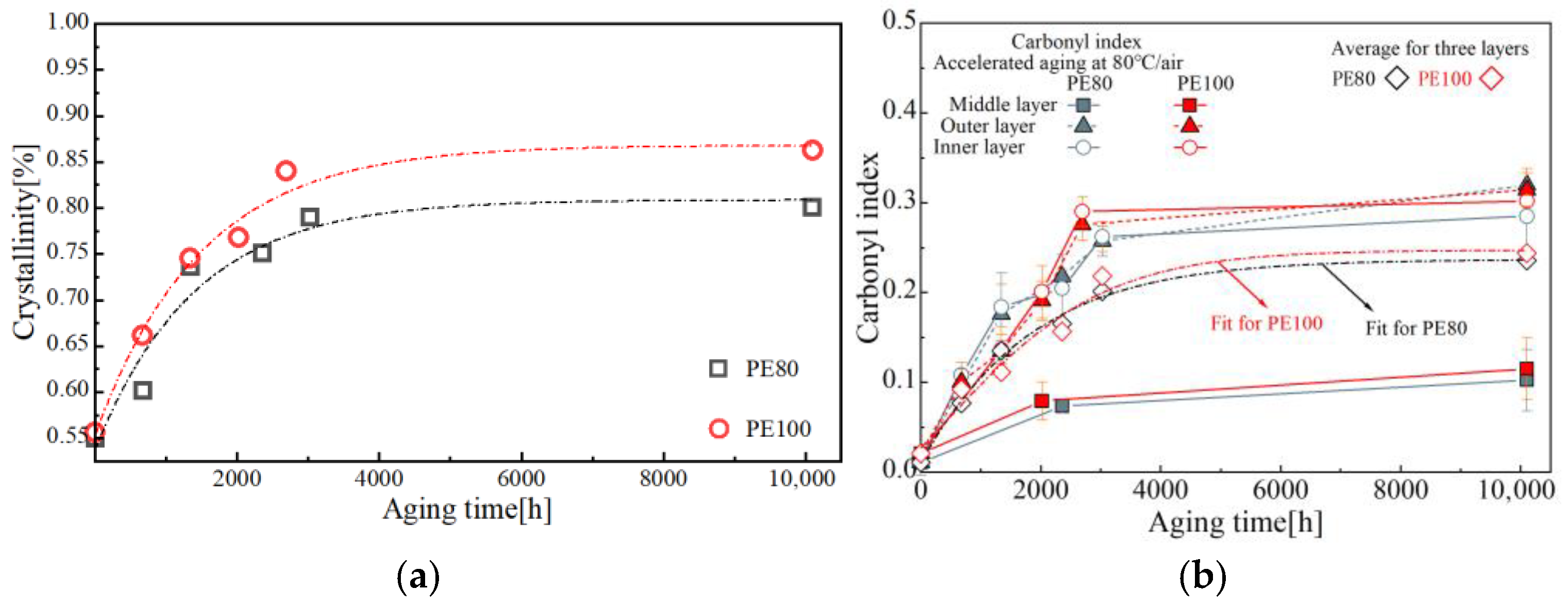
59], samples were first heated to 200 °C under 50 mL/min nitrogen flow, held isothermally for several minutes, then exposed to 50 mL/min pure oxygen while monitoring exothermic behavior. Crystallinity for Equation (15) was obtained through this work.
To characterize the changes in mechanical properties during the aging process through carbonyl index, tests were conducted using a Bruker VERTEX 70 Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer. At each aging interval, degradation of PE pipeline material was assessed through 30 repeated scans at 4 cm
−1 spectral resolution. The 400–4000 cm
−1 spectral range was employed to analyze functional group alterations in pipeline samples resulting from thermo-oxidative aging in heated air [
60]. Finally, the carbonyl index for Equation (15) was calculated by dividing the peak area of the carbonyl peak (C=O) of 1650~1850 cm
−1 by the peak area of the methylene peak (CH
2) of 1330~1500 cm
−1.
Based on the aforementioned experiments, the evolution of crystallinity and carbonyl index with aging time are presented in
Figure 2. Fundamental mechanical parameters were extracted from the engineering and true stress–strain curves shown in
Figure 3.
4. Results
As discussed in
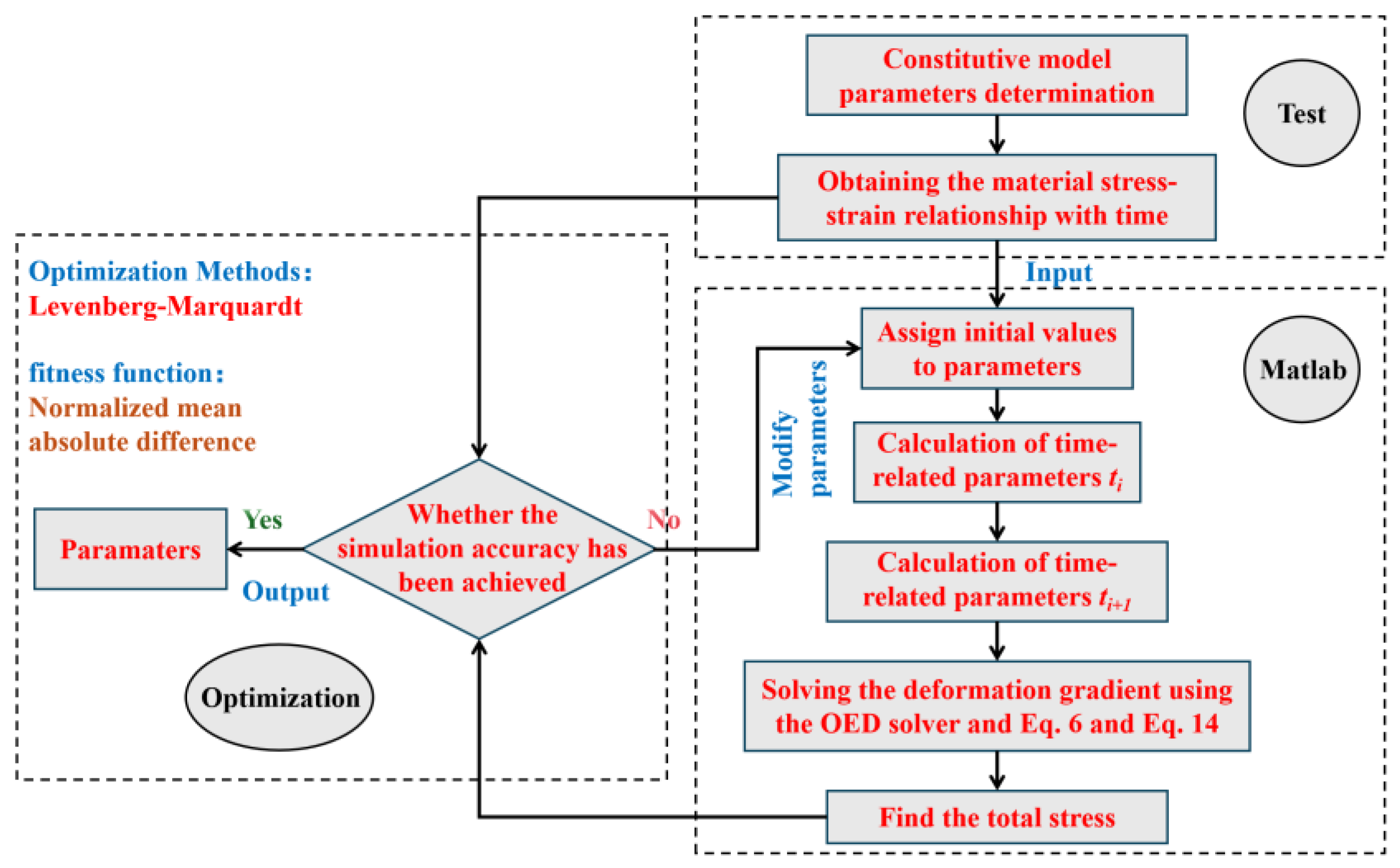
Section 2, the proposed material constitutive model is formulated through a system of differential tensor equations that require solving at each increment. To numerically solve this system of equations, the following iterative method can be employed, with a computational workflow illustrated in
Figure 4. The constitutive model incorporates a total of 21 parameters, with the temperature
set at 293 K. Under the assumption of incompressibility, the Jacobian determinant equals 1 [
61]. Consequently, regardless of the bulk modulus value, stress terms containing the bulk modulus vanish and therefore do not affect the final computational results. The shear modulus
and ultimate elongation
of MDPE and HDPE are generally around 12 MPa and 5 MPa, respectively (assumed values). The strain adjustment coefficient
is typically taken as 0.01. The shear flow index
and strain index
have little impact on the results and are usually set to 3 and −0.5, respectively. The material parameters
,
,
,
, and
are determined by fitting the tensile test data at quasi-static. The remaining parameters are obtained through the calculated theories and methods above. The proposed material constitutive model is defined by a system of differential equations requiring solution at each increment. To solve this system, the iterative method presented in the flowchart of
Figure 4 is employed, Levenberg–Marquardt (LM) methods and normalized mean absolute difference error (NMAD) methods are used for this optimization [
62]. The assumed parameters are listed in
Table 1; the parameters after fitting are listed in
Table 2,
Appendix A.4. shows the details for LM with NMAD method.
- 1.
Solve for the relevant parameter values at time , including:
Deformation gradient:
State variables: , , ,
- 2.
Solve for the relevant parameter values at time :
Deformation gradient:
- 3.
Use an ODE45 solver and Equation (6) to solve for and at time .
- 4.
Use an ODE45 solver and Equation (14) to solve for at time .
- 5.
Calculate the total stress at time using Equation (1).
- 6.
Enter the strain value , experimentally measured stress value (in uniaxial test) , and initial parameter guesses, set the initial damping factor to 0.01, the maximum number of iterations to 30,000, and the convergence threshold to 1 .
- 7.
Calculate the sum of squared residuals between the experimental stress and the computed stress.
- 8.
Calculate the LM update step and update all material parameters.
- 9.
Adaptive adjustment of damping factor and NMAD parameter evaluation.
- 10.
Output the optimal parameters.
Equations (16)–(18) and (24) establish a Boltzmann-based empirical relationship between thermo-oxidative aging parameters and mechanical properties, highlighting the impact of thermo-oxidative aging on the elastic modulus
, initial shear strength
and activation energy
of PE pipes [
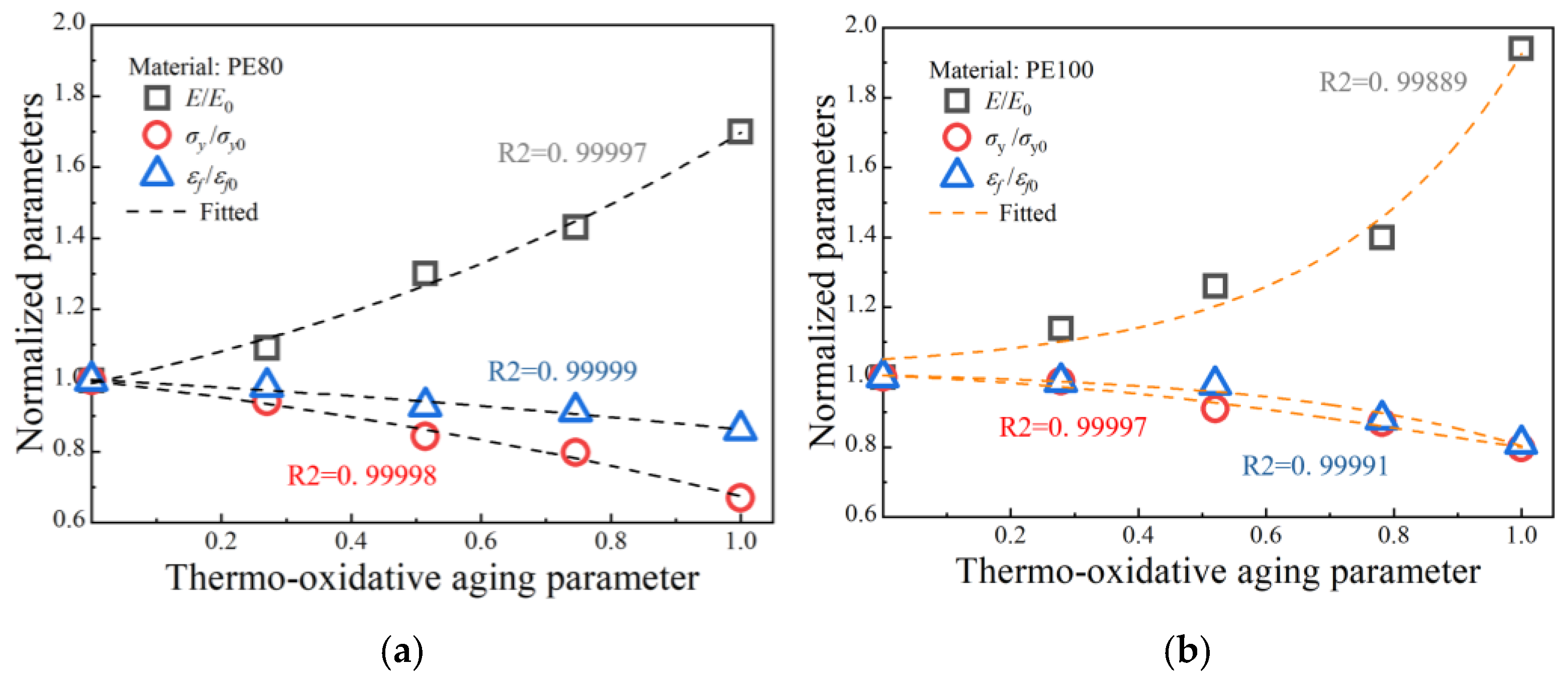
47]. The mechanical property parameters, crystallinity, and carbonyl index obtained in previous sections were extracted and plotted as parameter evolution diagrams in
Figure 5 and
Figure 6. By fitting these data with the Boltzmann function, quantitative relationships between the main mechanical property parameters and thermo-oxidative aging parameters were established. Once these parameters are known, the parameters related to thermo-oxidative aging can then be identified.
Figure 5 shows the relationship between thermo-oxidative aging parameters and normalized parameters and
Table 3 and
Table 4 show the fitting parameters for PE80 and PE100.
Figure 6 shows the relationship between initial shear strength, activation energy, and thermo-oxidative aging parameters and
Table 5 and
Table 6 show the fitting parameters for PE80 and PE100.
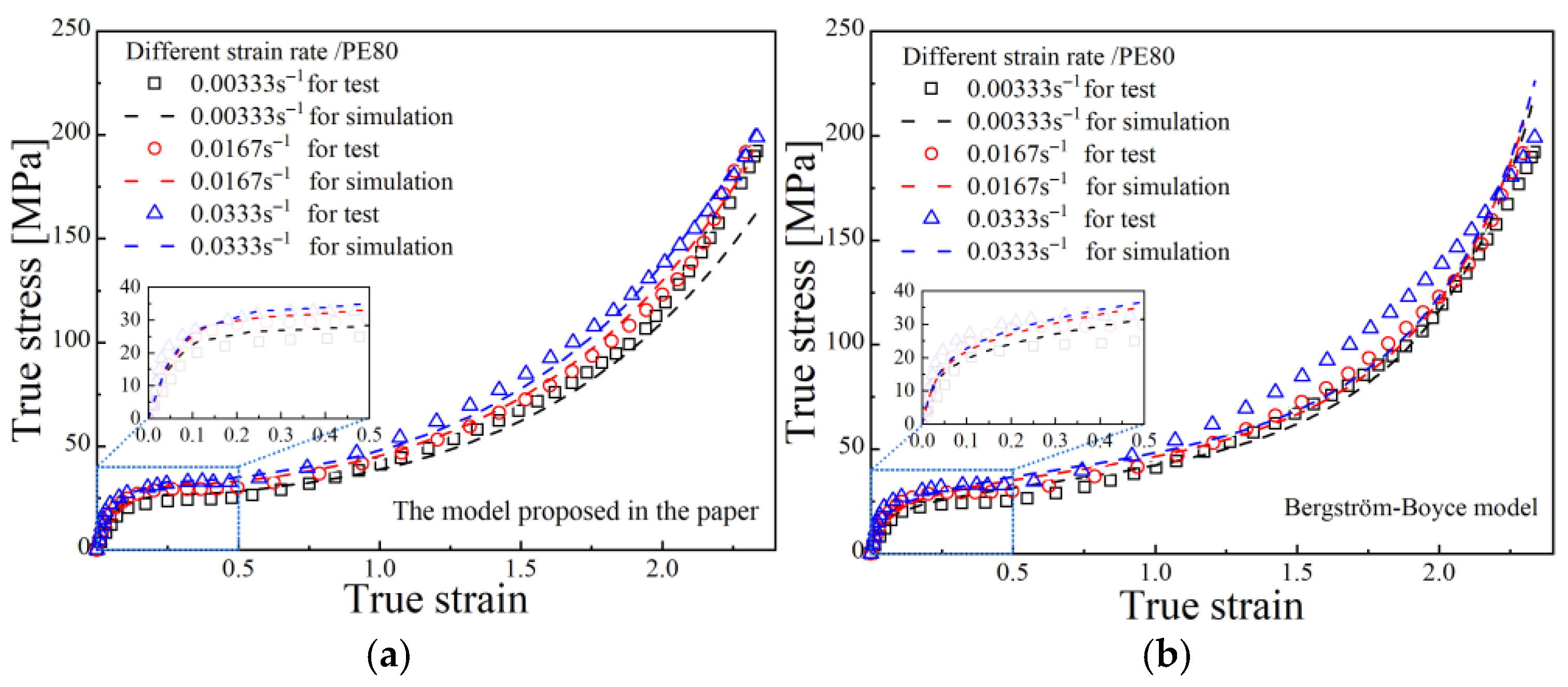
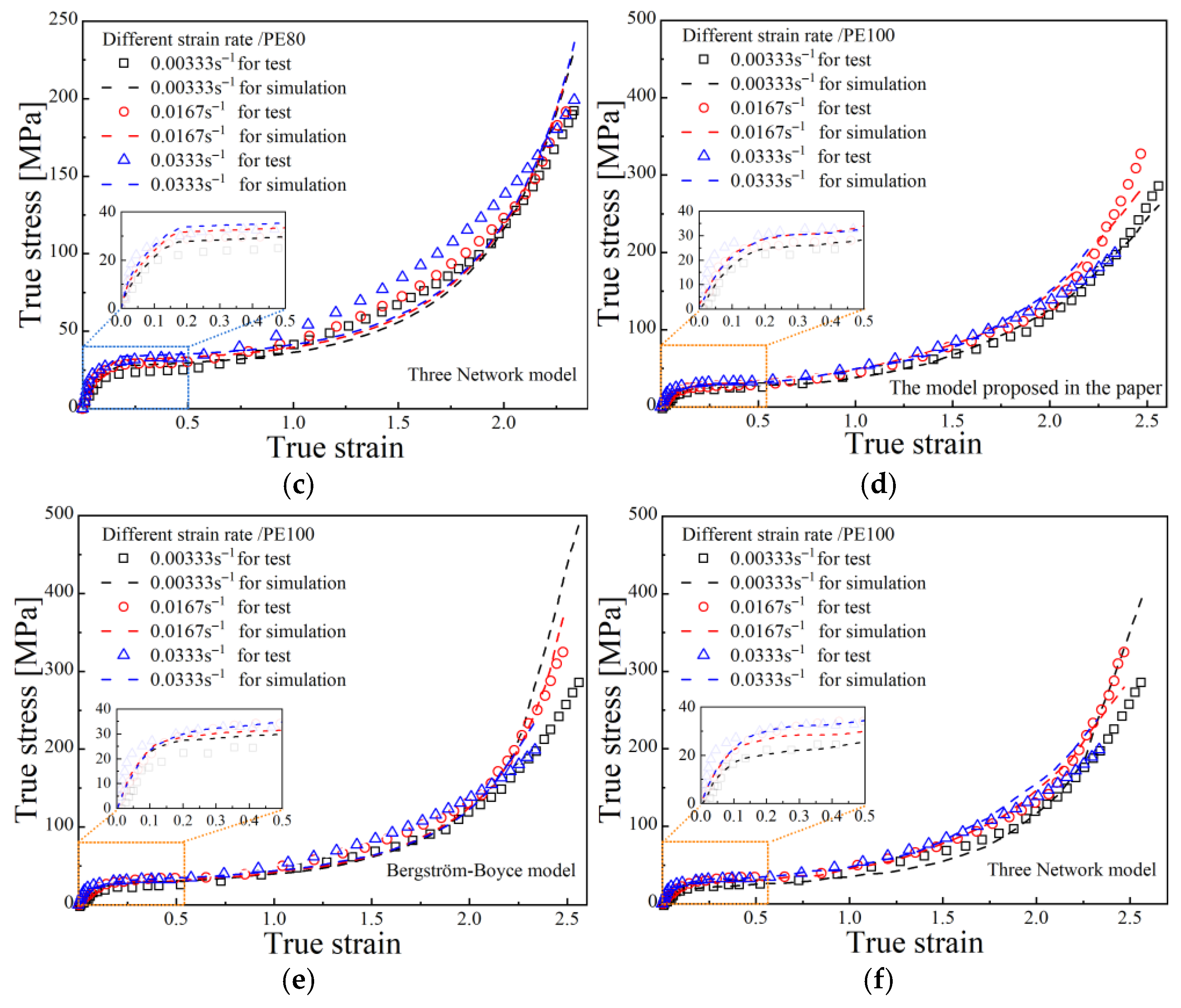
Figure 7 first presents the fitting performance of true stress–strain curves for PE80 under different strain rates, comparing the proposed model in this study with the BB model and the TNM.
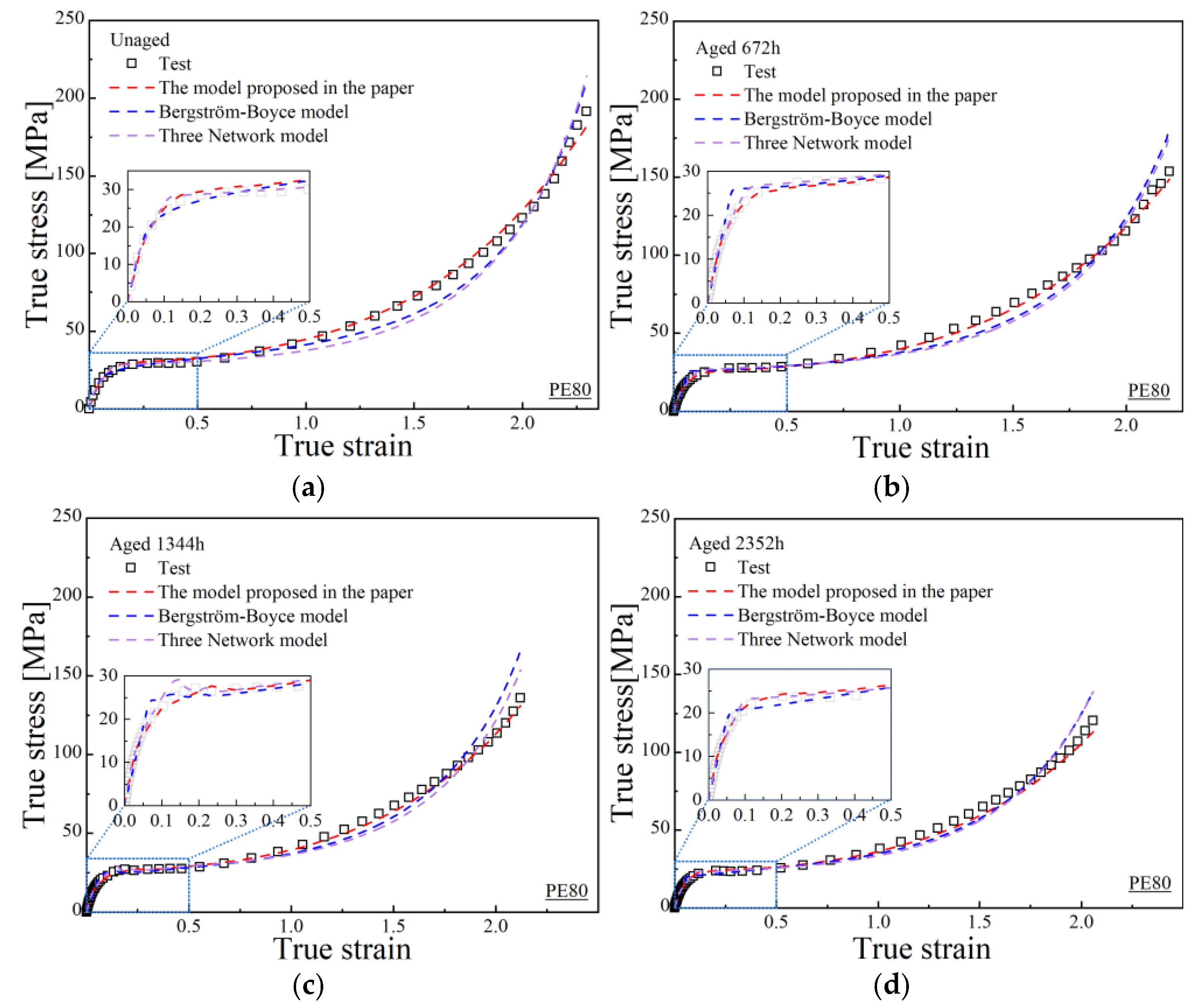
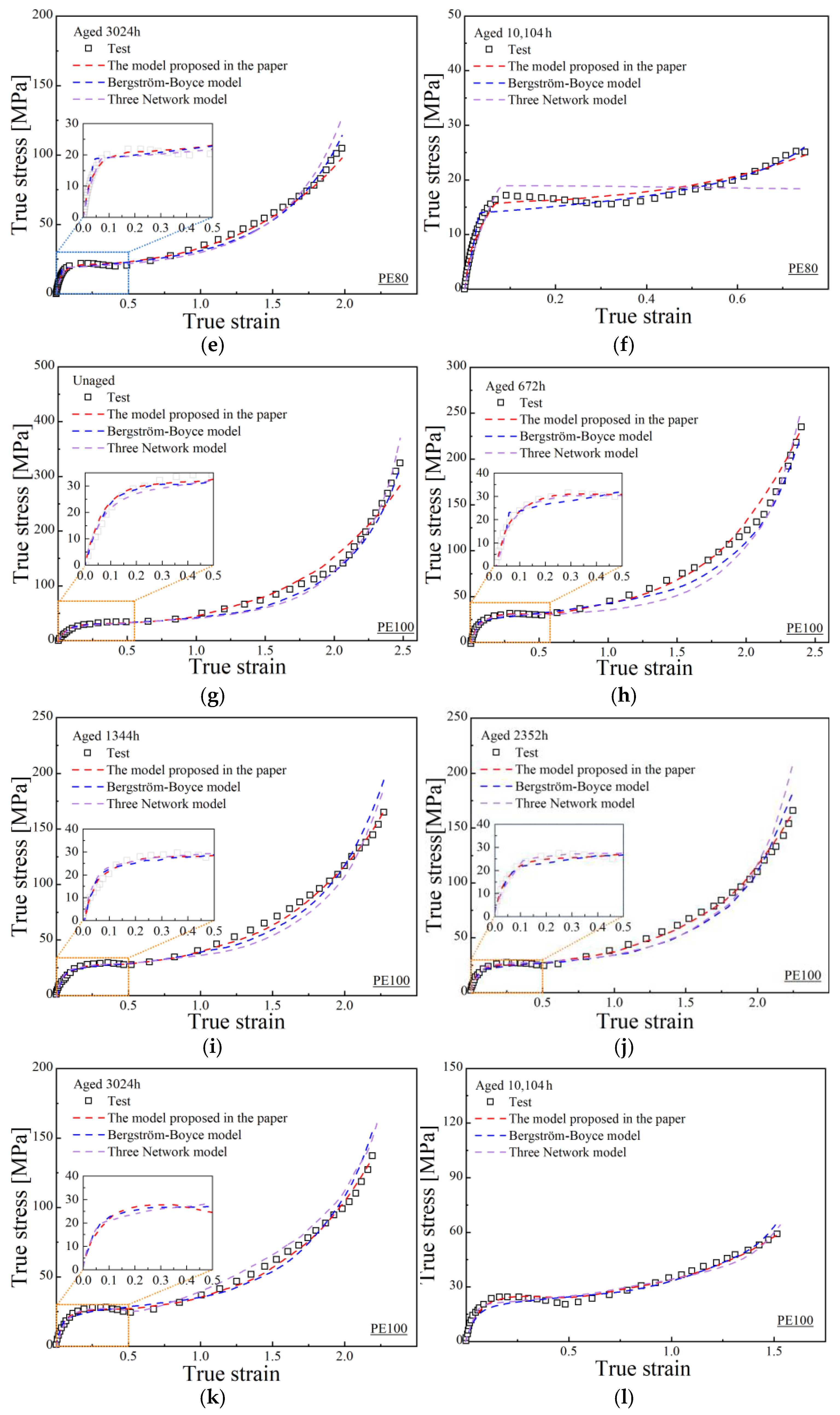
Figure 8 illustrates the fitting results for quasi-static true stress–strain curves at different aging times, also comparing the proposed model with the BB model and the TNM.
Table 7 and
Table 8 shows the relevant goodness of fit for PE80 and PE100 pipes.
5. Conclusions
1. Based on uniaxial tensile test results of two types of PE air pipe dumbbell-shaped specimens under thermo-oxidative aging, and considering the carbonyl index and crystallinity as thermo-oxidative aging parameters, an elastic–viscoplastic constitutive model incorporating both thermo-oxidative aging effects and yield behavior was developed within a finite deformation framework.
2. The model defines carbonyl index and crystallinity as normalized aging parameters for the first time, and demonstrates the temporal evolution of partial constitutive model parameters by fitting the Boltzmann equation
3. Compared to the B-B model and TNM model, this model not only achieves higher prediction accuracy across various test results, the overall goodness-of-fit exceeds 0.982, but more importantly, incorporates variations in material parameters during thermo-oxidative aging thereby significantly enhancing the model’s microscopic interpretability.
4. It should be noted that, like the B-B and TNM models, the current model, which is based on finite deformation theory, calculates stress from strain. Future work will develop a finite-element (FE) simulation model by referencing the methods of Tømmernes and Liang [
63,
64], and incorporating aging effects into simulation models, such as by developing a UEL (User Element) in ABAQUS, presents a viable approach [
65].