Electromagnetic Wave-Absorption Properties of FDM-Printed Acrylonitrile–Styrene–Acrylate/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composite Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of ASA/MWCNT Composite Materials
2.3. Preparation of Coaxial Rings
2.4. Injection Molding of ASA/MWCNT Composites
2.5. Preparation of ASA/MWCNT Filament Materials for 3D Printing
2.6. FDM 3D Printing
2.7. Electromagnetic Simulation Software Calculation
2.8. Testing and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Impact of MWCNT Loading on the Conductive Characteristics of ASA-Based Composites
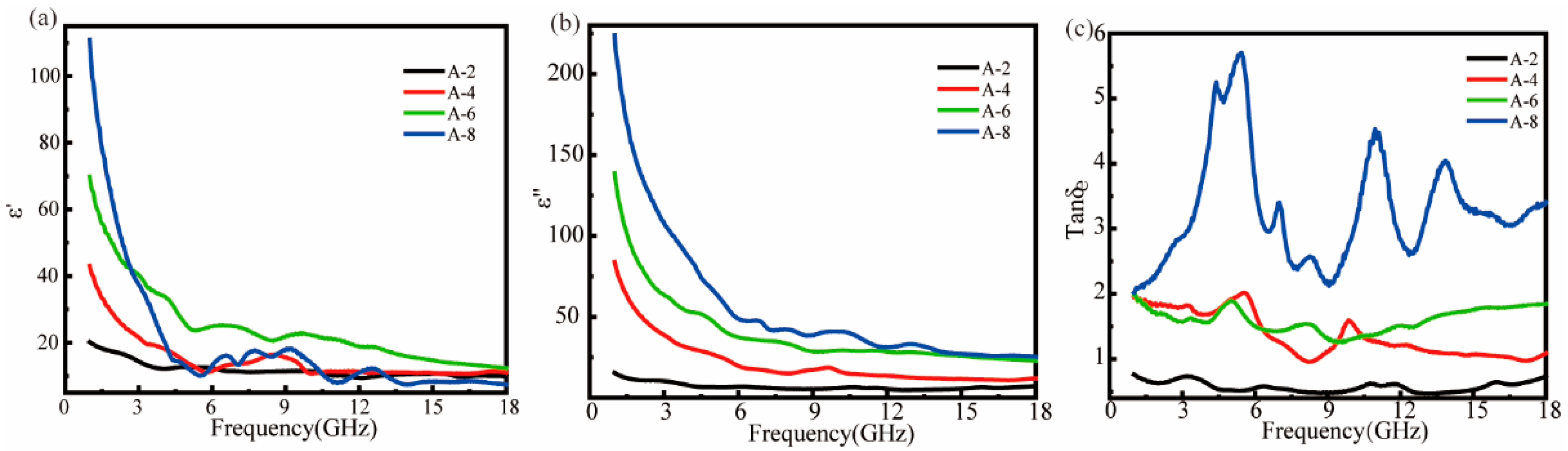
3.2. Influence of MWCNT Loading on Electromagnetic Parameter Characteristics of ASA Composites
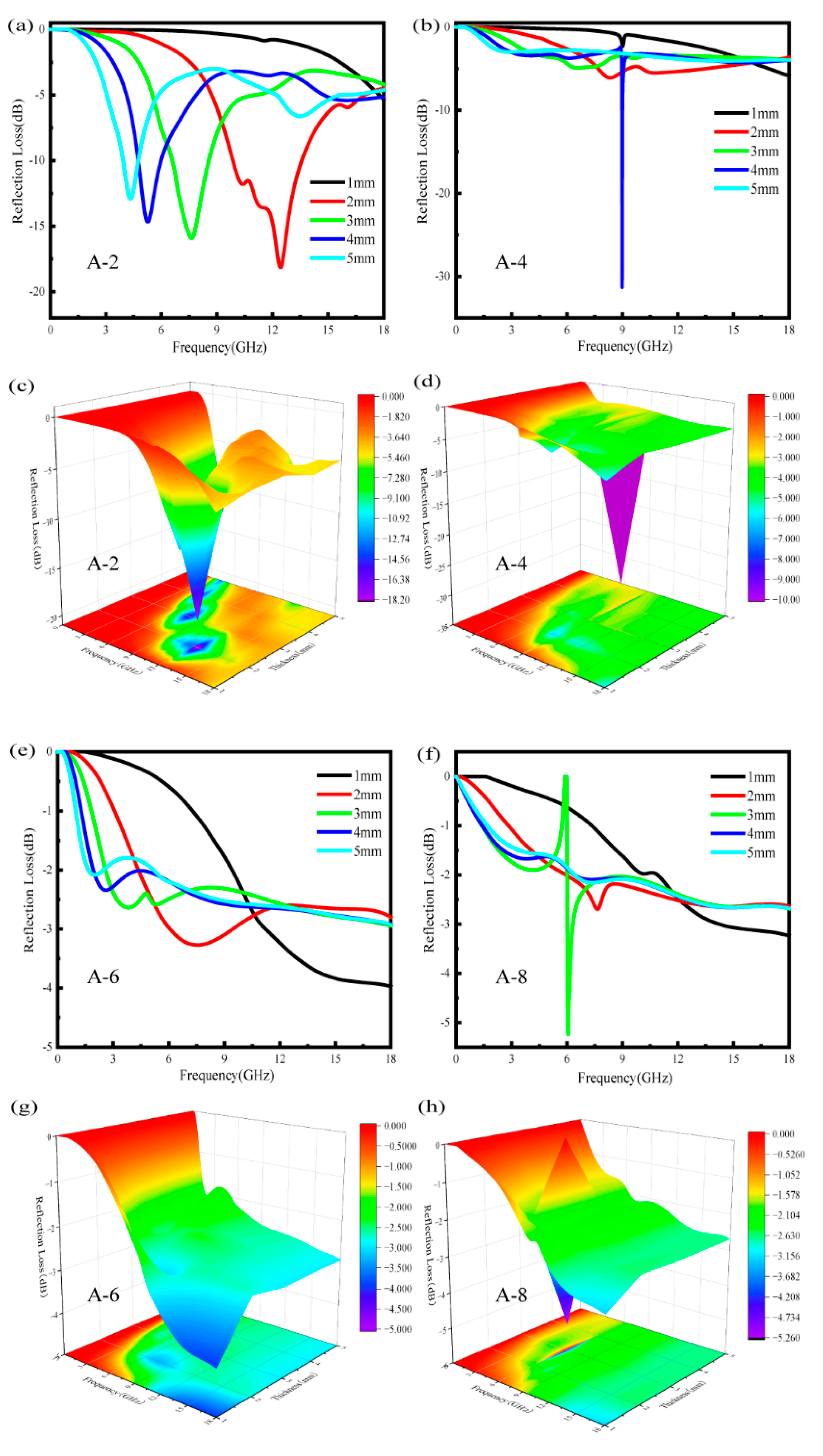
3.3. Simulation of Absorption Properties for ASA/MWCNT Composites
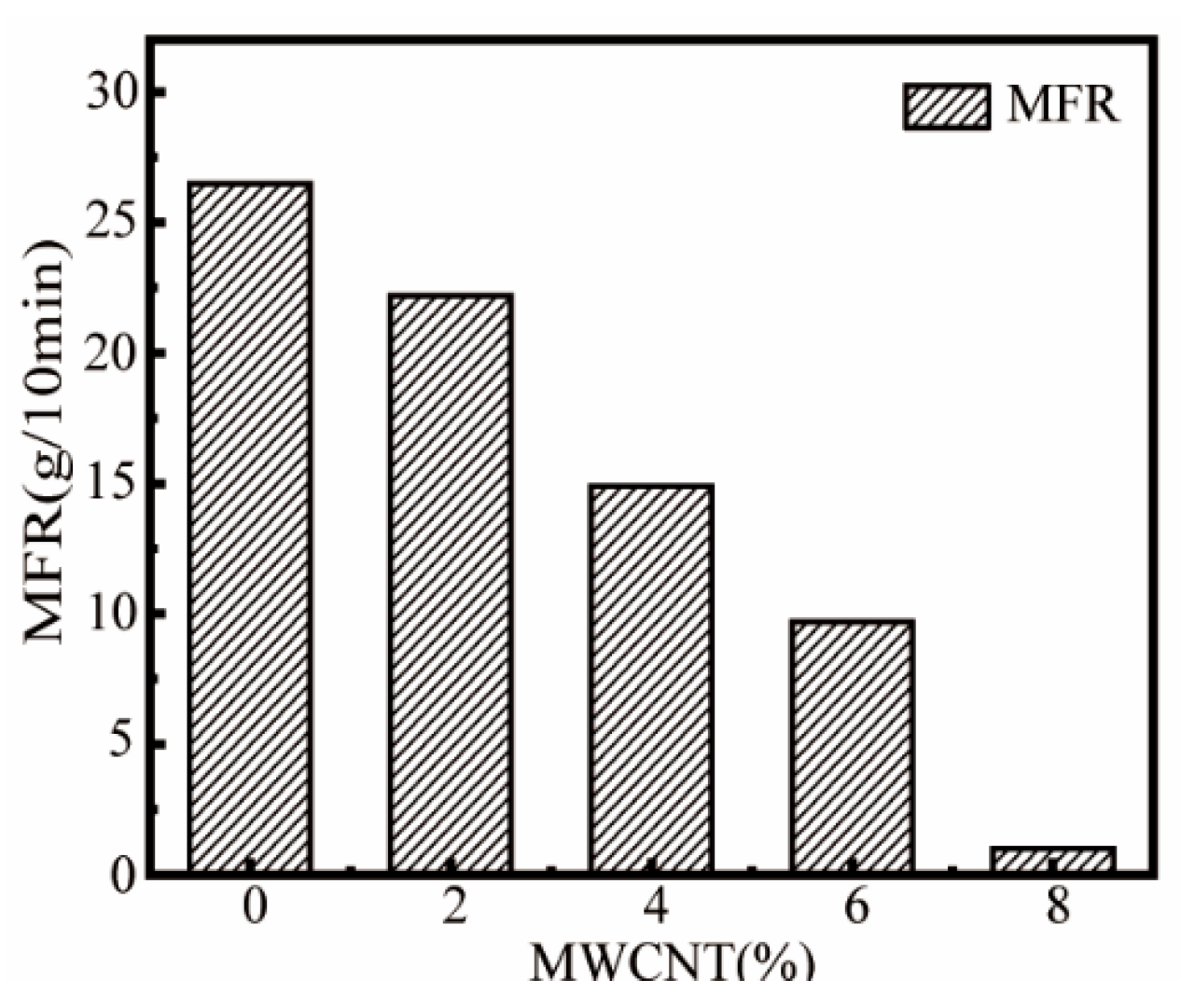
3.4. Effect of MWCNT Content on MFR of ASA/MWCNT Composites
3.5. SEM Observation of MWCNT and ASA/MWCNT Composites
3.6. Electromagnetic Wave-Absorption Properties of 3D-Printed ASA/MWCNTs
3.6.1. Honeycomb Structures
3.6.2. Stacked Wooden Pile Structure
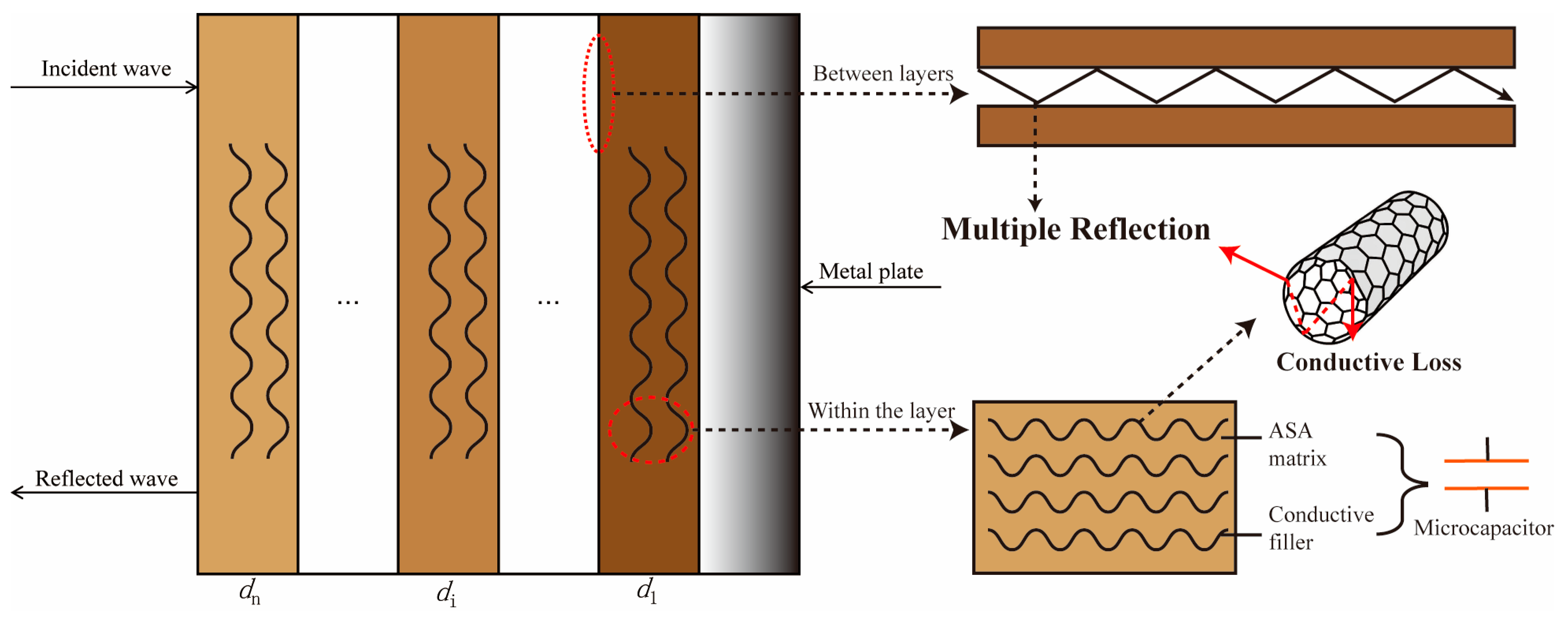
3.7. Analysis of EWA Principles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FDM | Fused deposition modeling |
| ASA | Acrylonitrile-styrene-acrylate |
| MWCNT | Multi-walled carbon nanotube |
| EMR | Escalating electromagnetic radiation |
| EMWs | Electromagnetic waves |
| EWAMs | Electromagnetic wave-absorbing materials |
| EAB | Wide effective absorption bandwidth |
| RL | Reflection loss |
References
- Sun, H.; Che, R.C.; You, X.; Jiang, Y.S.; Yang, Z.B.; Deng, J.; Qiu, L.B.; Peng, H.S. Cross-Stacking Aligned Carbon-Nanotube Films to Tune Microwave Absorption Frequencies and Increase Absorption Intensities. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 8120–8125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Zhang, X.Z.; Guo, Y.; Mu, C.H.; Zhou, P.H.; Yin, L.J.; Zhang, L.B.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.P.; Jian, X.; et al. Hybrid silica-carbon bilayers anchoring on FeSiAl surface with bifunctions of enhanced anti-corrosion and microwave absorption. Carbon 2021, 173, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.S.; Yuan, J.; Liu, T.T.; Wang, Q.Q.; Cao, W.Q.; Cao, M.S. Clipping electron transport and polarization relaxation of Ti3C2Tx based nanocomposites towards multifunction. Carbon 2023, 201, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.P.; Gao, H.; Guo, R.H.; Li, W.J.; Wu, F.; Tao, S.F.; Zhu, X.F.; Xie, A.M. MnO2 Intercalation-Guided impedance tuning of Carbon/Polypyrrole double conductive layers for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Jiang, J.; Wu, D.; He, Q.; Wang, Y. Three-dimensional conductive network constructed by in-situ preparation of sea urchin-like NiFe2O4 in expanded graphite for efficient microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 650, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Quan, B.; Ai, B.; Sheng, M.; Liu, S.; Huang, X.; Wu, H.; Lu, X.; Qu, J. Engineering asymmetric multifunctional phase change composites for improved electromagnetic interference shielding and wireless personal thermal therapy. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 16138–16152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhi, D.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Kang, W.; Meng, F. Graphene-based aerogel microspheres with annual ring-like structures for broadband electromagnetic attenuation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Cheng, R.; Wang, N.; Li, Y. Construction of multi-dimensional NiCo/C/CNT/rGO aerogel by MOF derivative for efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 2023, 205, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Brosseau, C. A review and analysis of microwave absorption in polymer composites filled with carbonaceous particles. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 061301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Wang, H.; Huang, F.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hui, D.; Zhou, Z. Graphene-based microwave absorbing composites: A review and prospective. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2018, 137, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullen, A.; Zhao, G.L.; Bagayoko, D.; Yang, L. Structural, elastic, and electronic properties of deformed carbon nanotubes under uniaxial strain. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 205410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.N.; Khan, U.; Blau, W.J.; Gun’ko, Y.K. Small but strong: A review of the mechanical properties of carbon nanotube–polymer composites. Carbon 2006, 44, 1624–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, G.-L. Electromagnetic wave absorption of multi-walled carbon nanotube-epoxy composites in the R band. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 9406–9411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buswell, R.A.; de Silva, W.R.L.; Jones, S.Z.; Dirrenberger, J. 3D printing using concrete extrusion: A roadmap for research. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 112, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhou, D.; Huang, T.; Huang, H.; Jiao, D.; Shi, C. A feasible method for measuring the buildability of fresh 3D printing mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Gu, J.; Wang, D.-A.; Bi, S.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. Applications of 3D printing in aging. Int. J. Bioprinting 2023, 9, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Zeng, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Droplet interface in additive manufacturing: From process to application. Droplet 2023, 2, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Bi, S.; Gu, J.; Che, Q.; Liu, R.; Li, W.; Dai, T.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Achieving personalized nutrition for patients with diabetic complications via 3D food printing. Int. J. Bioprinting 2024, 10, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Gu, J.; Ma, M.; Liu, R.; Bi, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Unique benefits and challenges of 3D-printed microneedles. Int. J. Bioprinting 2024, 10, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, O.A.; Masood, S.H.; Bhowmik, J.L. Optimization of fused deposition modeling process parameters: A review of current research and future prospects. Adv. Manuf. 2015, 3, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yan, L.; Ma, H.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, M.; Qu, S. Electromagnetic wave absorption and compressive behavior of a three-dimensional metamaterial absorber based on 3D printed honeycomb. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, K.; Samykano, M.; Kadirgama, K.; Harun, W.S.W.; Rahman, M.M. Fused deposition modeling: Process, materials, parameters, properties, and applications. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 1531–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.W.; Wang, Y.; He, J.K. Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of Structural Conductive ABS Fabricated by Fused Deposition Modeling. Polymers 2020, 12, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y. Electromagnetic-Wave Absorption Properties of 3D-Printed Thermoplastic Polyurethane/Carbonyl Iron Powder Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Study of poly(vinyl chloride)/acrylonitrile–styrene–acrylate blends for compatibility, toughness, thermal stability and UV irradiation resistance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Effect of core–shell structures of acrylonitrile–styrene–acrylate (ASA) terpolymer on the properties of poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC)/ASA blends: Miscibility, toughness, and heat resistance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.W.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.R.; Wang, X.Z.; Deng, Y.H. Incorporation of graphitic nano-filler and poly(lactic acid) in fused deposition modeling. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimdusit, S.; Damrongsakkul, S.; Wongmanit, P.; Saramas, D.; Tiptipakorn, S. Characterization of coconut fiber-filled polyvinyl chloride/acrylonitrile styrene acrylate blends. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2011, 30, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazey, S.D. Formulation strategy to achieve highly colorable and weatherable ASA. Plast. Eng. 2015, 71, 4–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; He, C.; Jin, Q.J.B. Effect of acrylate-styrene-acrylonitrile on the aging properties of eucalyptus/PVC wood-plastic composites. BioResources 2019, 14, 9159–9168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.B.; Yang, W.B.; Liu, X.S.; Zhang, W.B.; Zhang, Y.H. ASA/graphite/carbon black composites with improved EMI SE, conductivity and heat resistance properties. Iran. Polym. J. 2016, 25, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camposeco-Negrete, C. Optimization of printing parameters in fused deposition modeling for improving part quality and process sustainability. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 2131–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liang, Q.; Duan, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Cao, Y. A 3D-printed lightweight broadband electromagnetic absorbing metastructure with preserved high-temperature mechanical property. Compos. Struct. 2021, 274, 114330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobha, A.P.; Sreekala, P.S.; Narayanankutty, S.K. Electrical, thermal, mechanical and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of PANI/FMWCNT/TPU composites. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 113, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, J.D. Helical Beam Antennas for Wide-Band Applications. Proc. IRE 1948, 36, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, T.; Wang, W.; Zhai, P.; Guan, J. Broadband patterned magnetic microwave absorber. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 044110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Guo, S. High-performance electromagnetic wave absorption by designing the multilayer graphene/thermoplastic polyurethane porous composites with gradient foam ratio structure. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 125, 105522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

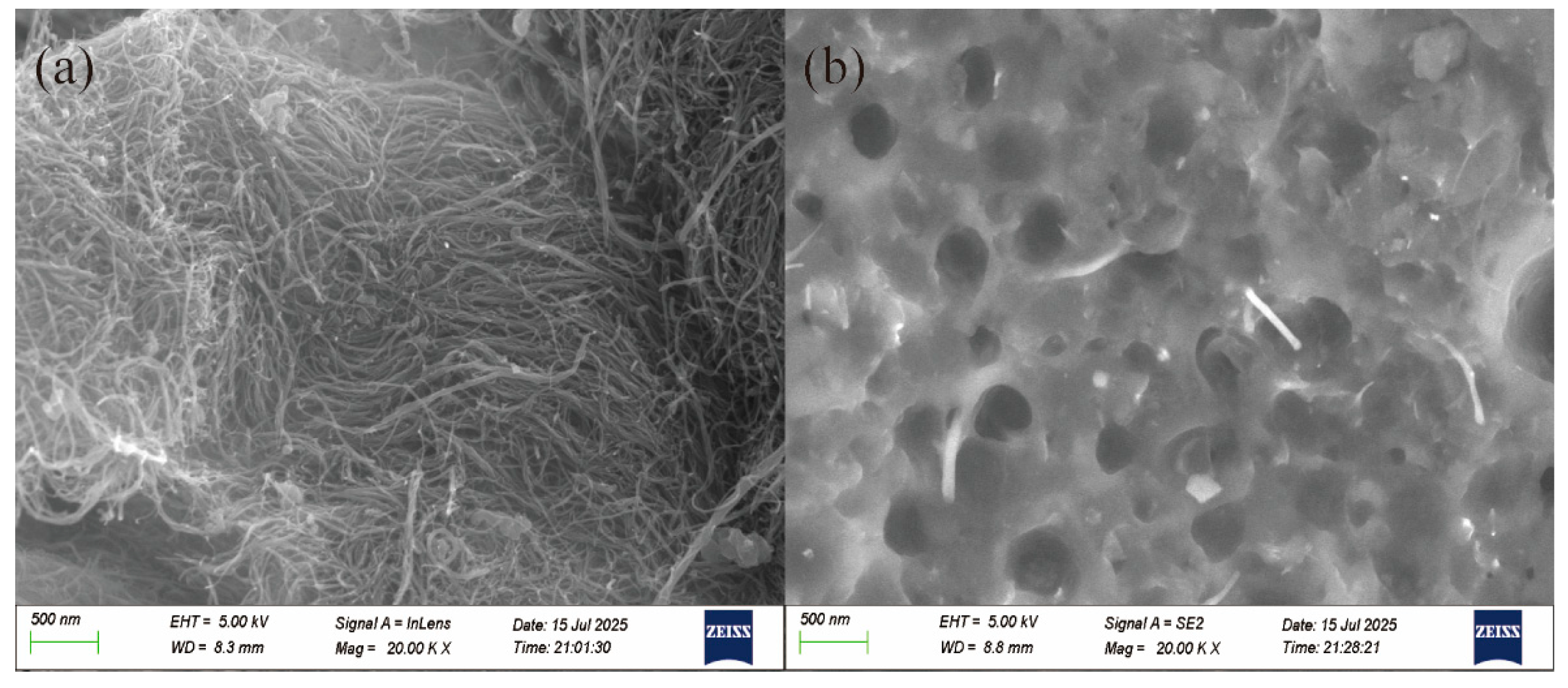


| Sample | ASA (wt.%) | MWCNTs (wt.%) | PETS (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-2 | 96 | 2 | 2 |
| A-4 | 94 | 4 | 2 |
| A-6 | 92 | 6 | 2 |
| A-8 | 90 | 8 | 2 |
| Sample | MWCNTs (wt.%) | ρ (Ω·cm) | σ (S/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-2 | 2 | 3.08 × 108 | 3.25 × 10−9 |
| A-4 | 4 | 6.29 × 103 | 1.59 × 10−4 |
| A-6 | 6 | 8.40 × 101 | 1.19 × 10−2 |
| A-8 | 8 | 2.70 × 101 | 3.68 × 10−2 |
| Sample | RLmin (dB) | EABmax (GHz) (RL < −10 dB) |
|---|---|---|
| A-2 | −18.15 | 3.74 |
| A-4 | −31.31 | 0.04 |
| A-6 | −3.98 | 0 |
| A-8 | −5.22 | 0 |
| Sample | RLmin (dB) | EABmax (GHz) (RL < −10 dB) |
|---|---|---|
| Honeycomb structure | −12.50 | 1.00 |
| Gradient-based honeycomb structure | −15.49 | 1.32 |
| Larger-sized gradient honeycomb structure | −32.60 | 6.56 |
| Stacked wooden pile structure | −22.82 | 10.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, A.; Wang, Y. Electromagnetic Wave-Absorption Properties of FDM-Printed Acrylonitrile–Styrene–Acrylate/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composite Structures. Polymers 2025, 17, 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152010
Zhou A, Wang Y. Electromagnetic Wave-Absorption Properties of FDM-Printed Acrylonitrile–Styrene–Acrylate/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composite Structures. Polymers. 2025; 17(15):2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152010
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Aobo, and Yan Wang. 2025. "Electromagnetic Wave-Absorption Properties of FDM-Printed Acrylonitrile–Styrene–Acrylate/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composite Structures" Polymers 17, no. 15: 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152010
APA StyleZhou, A., & Wang, Y. (2025). Electromagnetic Wave-Absorption Properties of FDM-Printed Acrylonitrile–Styrene–Acrylate/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Composite Structures. Polymers, 17(15), 2010. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17152010






